Submitted:
02 April 2025
Posted:
02 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
Soft Agar Motility Assays
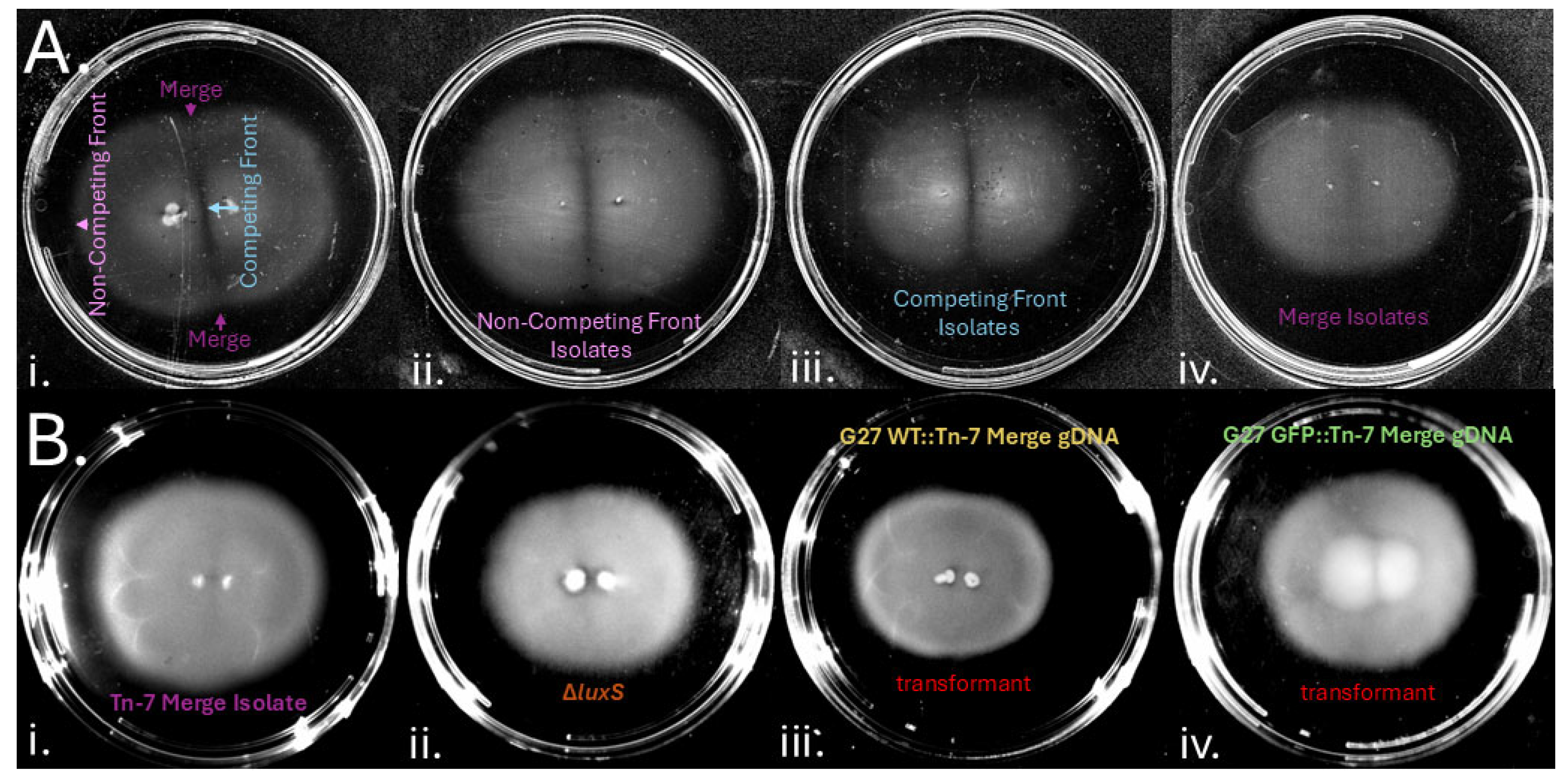
Isolation of Tn-7 mutants without clear gap formation phenotype
Identification of transposon insertion sites
Genomic Transformations
Microscopy
Growth Curves
Clear Gap Materials Assessment
3. Results
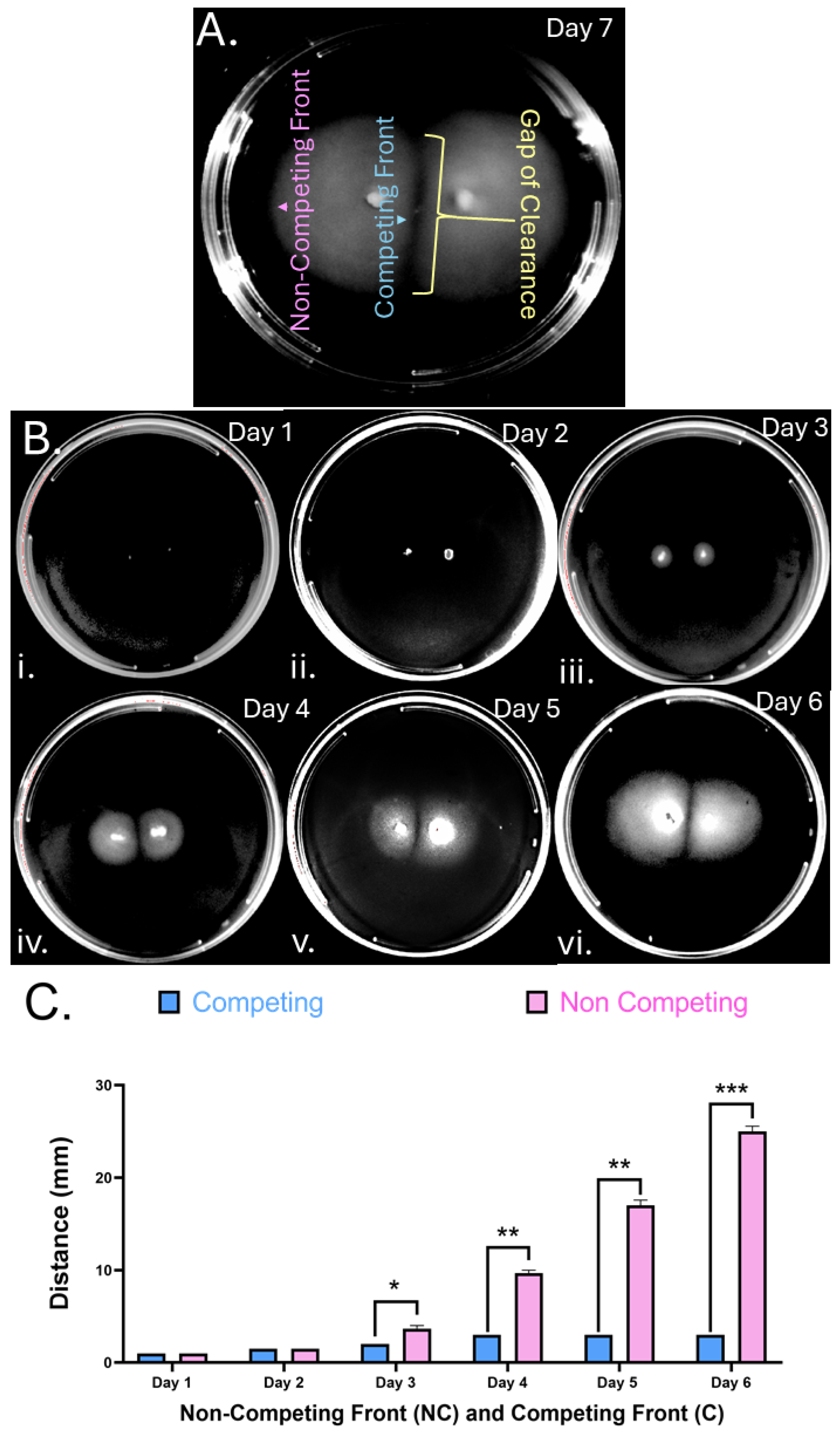
H. pylori ceases soft agar migration and forms a gap when two colonies meet
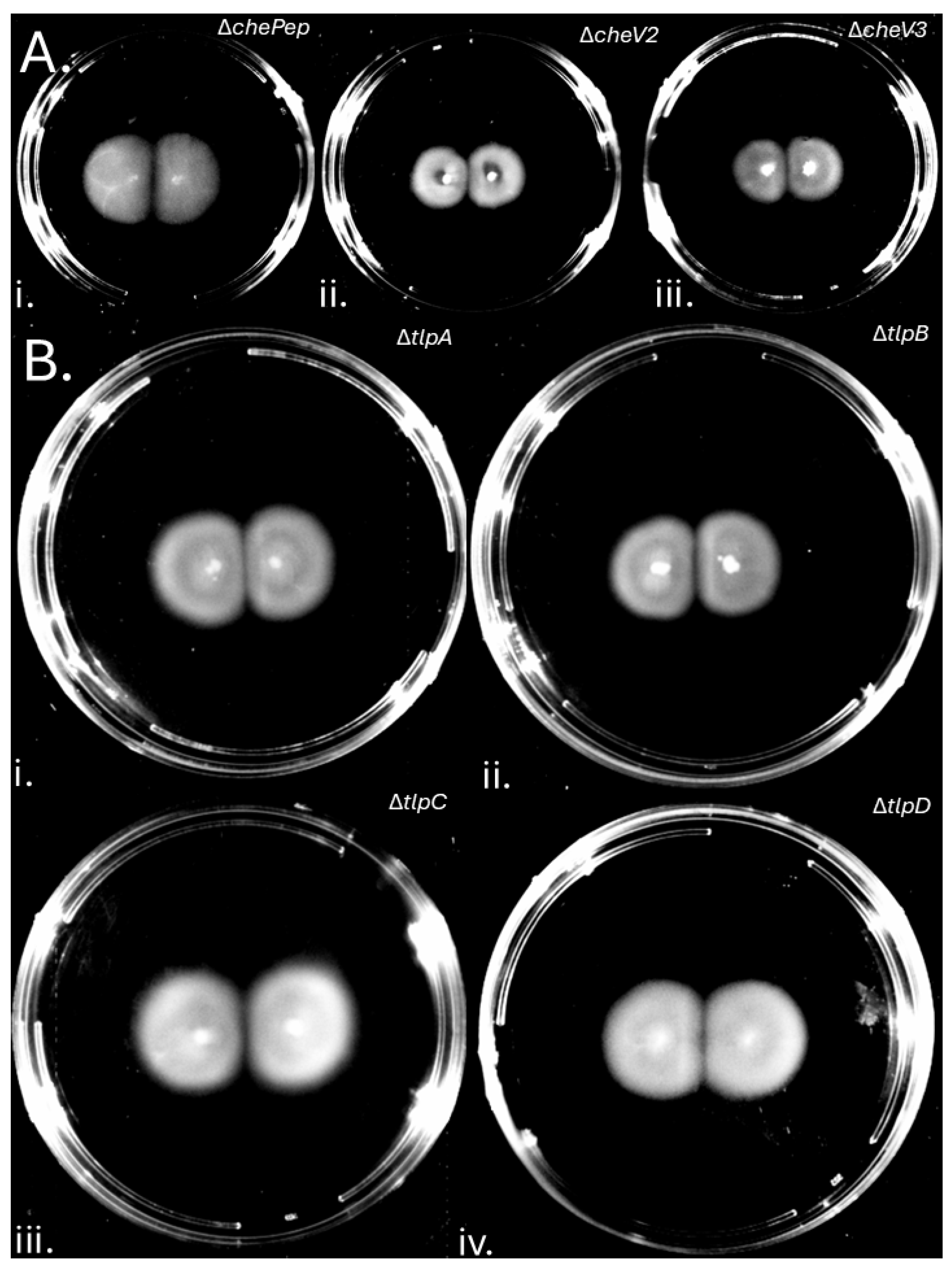
Formation of colony gaps is chemotaxis independent
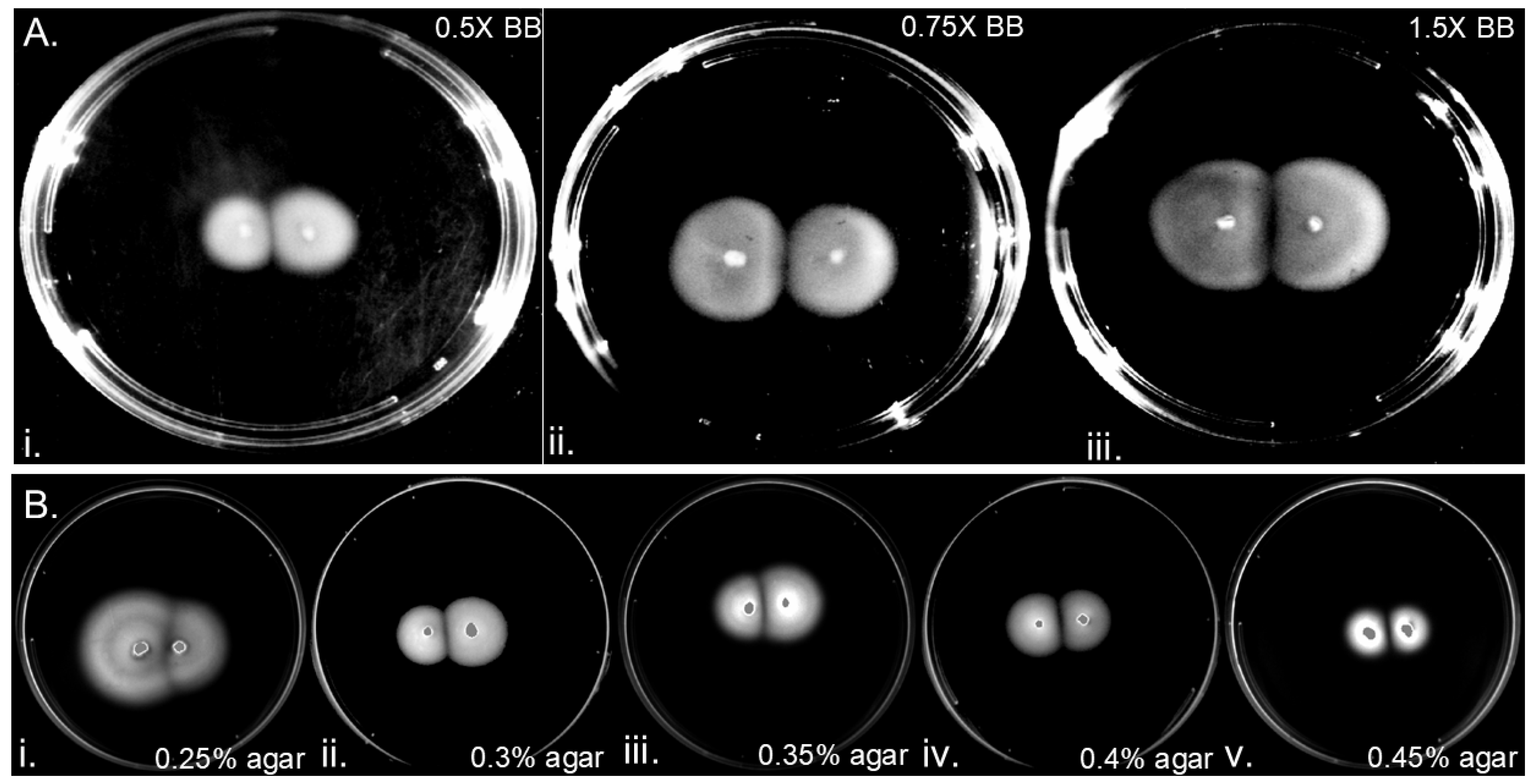
H. pylori colony gap formation is independent of nutrient level and agar percentages
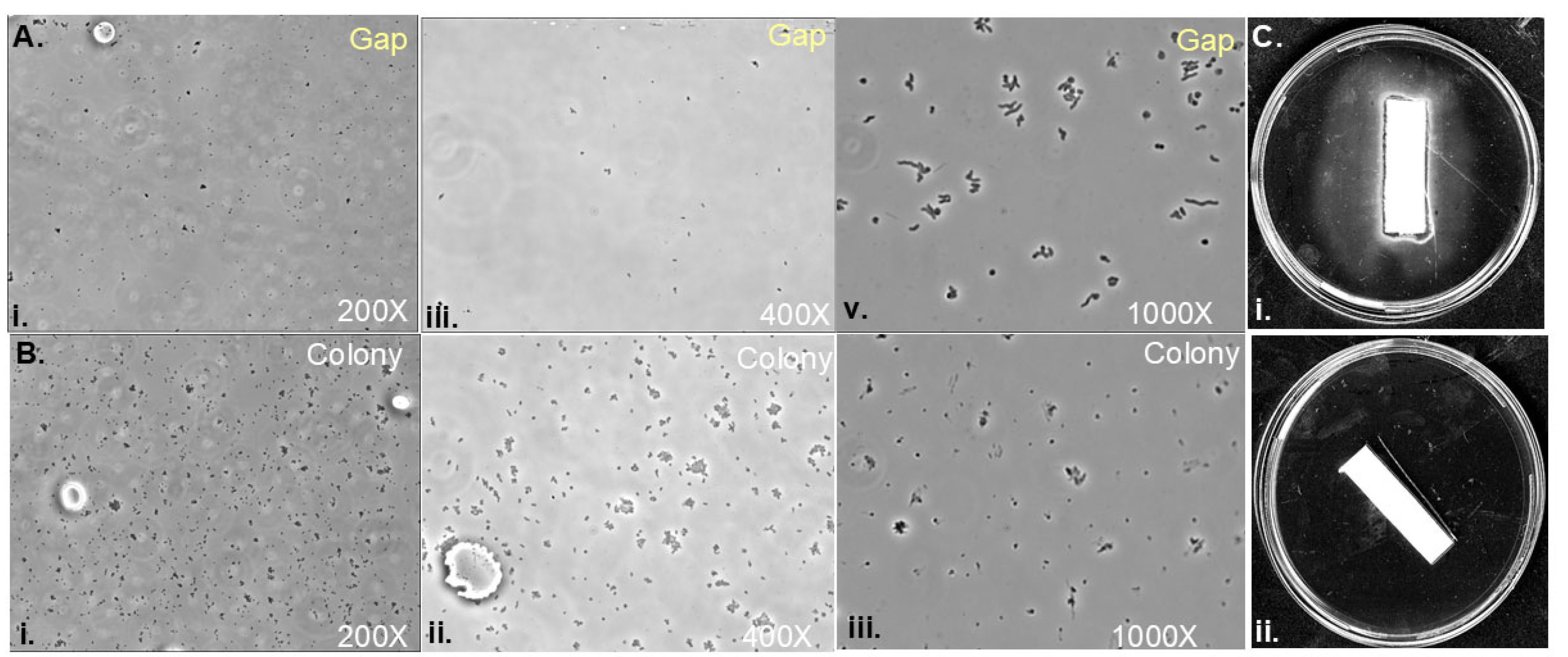
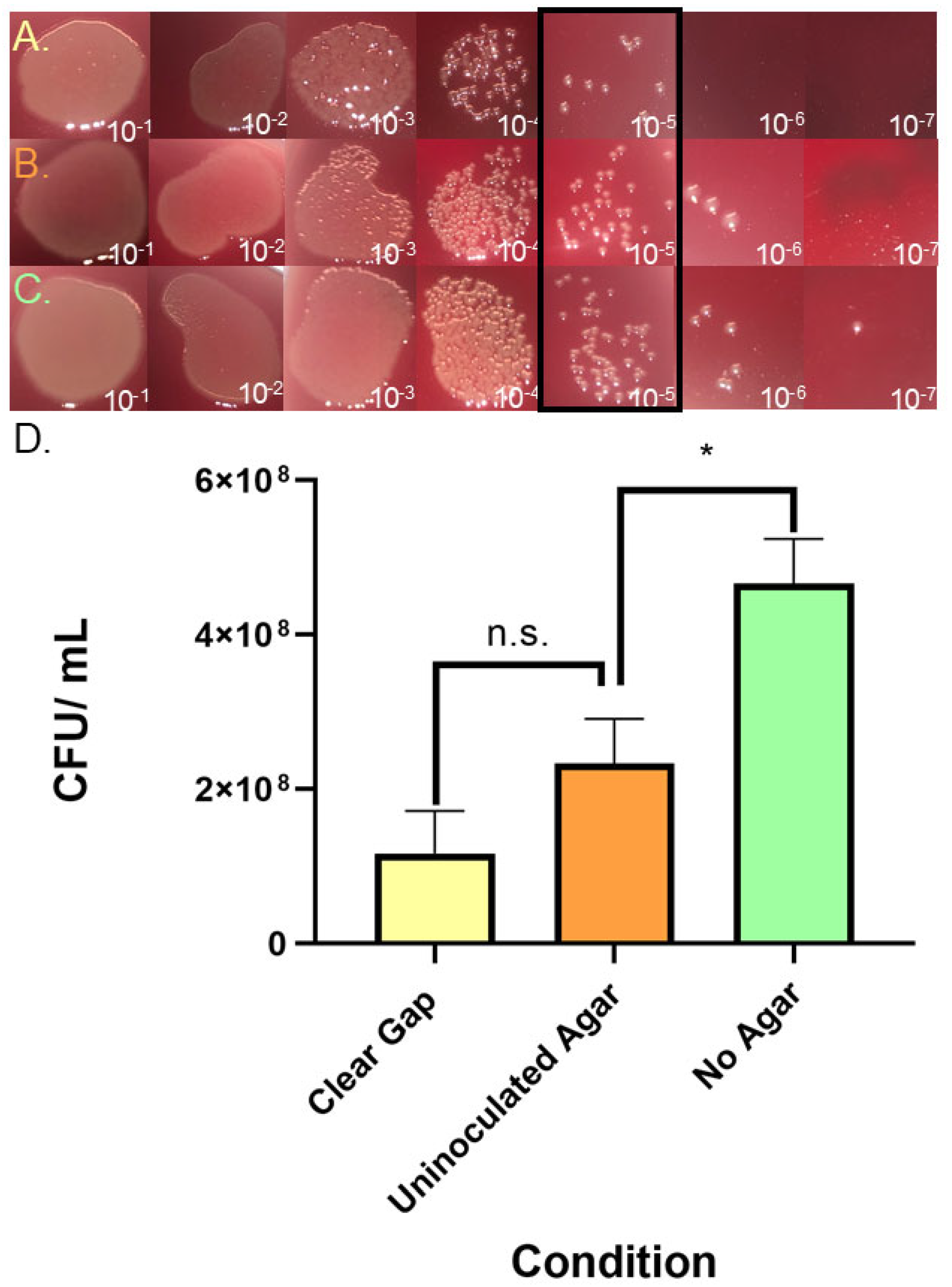
Soft agar colony gaps contain low densities of H. pylori cells with spiral morphology.
Assessing inhibitory compounds in gap regions.
H. pylori gap formation has a genetic basis.
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Wuichet, K.; Zhulin, I.B. Origins and Diversification of a Complex Signal Transduction System in Prokaryotes. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, A.J.; Berg, H.C. Migration of Bacteria in Semisolid Agar. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1989, 86, 6973–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croze, O.A.; Ferguson, G.P.; Cates, M.E.; Poon, W.C.K. Migration of Chemotactic Bacteria in Soft Agar: Role of Gel Concentration. Biophysical Journal 2011, 101, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, L.; Andermann, T.M.; Ottemann, K.M. A Supplemented Soft Agar Chemotaxis Assay Demonstrates the Helicobacter pylori Chemotactic Response to Zinc and Nickel. Microbiology 2013, 159, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekowska, A.; Masson, J.-B.; Celani, A.; Danchin, A.; Vergassola, M. Repulsion and Metabolic Switches in the Collective Behavior of Bacterial Colonies. Biophysical Journal 2009, 97, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espeso, D.R.; Martínez-García, E.; De Lorenzo, V.; Goñi-Moreno, Á. Physical Forces Shape Group Identity of Swimming Pseudomonas putida Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassmann, J.E.; Gilbert, O.M.; Queller, D.C. Kin Discrimination and Cooperation in Microbes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M.J.; Gibbs, K.A. Peer Pressure from a Proteus mirabilis Self-Recognition System Controls Participation in Cooperative Swarm Motility. PLoS Pathog 2019, 15, e1007885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budding, A.E.; Ingham, C.J.; Bitter, W.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Schneeberger, P.M. The Dienes Phenomenon: Competition and Territoriality in Swarming Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol 2009, 191, 3892–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadell, C.D.; Drescher, K.; Wingreen, N.S.; Bassler, B.L. Extracellular Matrix Structure Governs Invasion Resistance in Bacterial Biofilms. The ISME Journal 2015, 9, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.; Tan, S.; Nakajima, M.; Skoog, E.C.; Camarillo-Guerrero, L.F.; Klein, J.A.; Lawley, T.D.; Solnick, J.V.; Fukami, T.; Amieva, M.R. High-Resolution Mapping Reveals That Microniches in the Gastric Glands Control Helicobacter pylori Colonization of the Stomach. PLoS Biol 2019, 17, e3000231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foynes, S.; Dorrell, N.; Ward, S.J.; Stabler, R.A.; McColm, A.A.; Rycroft, A.N.; Wren, B.W. Helicobacter pylori Possesses Two CheY Response Regulators and a Histidine Kinase Sensor, CheA, Which Are Essential for Chemotaxis and Colonization of the Gastric Mucosa. Infect Immun 2000, 68, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagoo, J.; Abedrabbo, S.; Liu, X.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori cheV1 Mutants Recover Semisolid Agar Migration Due to Loss of a Previously Uncharacterized Type IV Filament Membrane Alignment Complex Homolog. J Bacteriol 2024, 206, e00406–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.-M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Schlemper, R.J. Helicobacter pylori Infection and the Development of Gastric Cancer. The New England Journal of Medicine 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polk, D.B.; Peek, R.M. Helicobacter pylori: Gastric Cancer and Beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 2010, 10, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, K. Gastric Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma and Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Review of Current Diagnosis and Management. Biomark Res 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottemann, K.M.; Lowenthal, A.C. Helicobacter pylori Uses Motility for Initial Colonization and To Attain Robust Infection. Infect Immun 2002, 70, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, K.; Williams, S.M.; Connolly, L.; Ottemann, K.M. Chemotaxis Plays Multiple Roles during Helicobacter pylori Animal Infection. Infect Immun 2005, 73, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.S.; Ottemann, K.M. Colonization, Localization, and Inflammation: The Roles of H. pylori Chemotaxis in Vivo. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2018, 41, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keilberg, D.; Zavros, Y.; Shepherd, B.; Salama, N.R.; Ottemann, K.M. Spatial and Temporal Shifts in Bacterial Biogeography and Gland Occupation during the Development of a Chronic Infection. mBio 2016, 7, e01705–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Roujeinikova, A.; Ottemann, K.M. FliL Functions in Diverse Microbes to Negatively Modulate Motor Output via Its N-Terminal Region. mBio 2023, 14, e00283–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censini, S.; Lange, C.; Xiang, Z.; Crabtree, J.E.; Ghiara, P.; Borodovsky, M.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. Cag, a Pathogenicity Island of Helicobacter pylori, Encodes Type I-Specific and Disease-Associated Virulence Factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1996, 93, 14648–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomb, J.-F.; White, O.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Clayton, R.A.; Sutton, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Ketchum, K.A.; Klenk, H.P.; Gill, S.; Dougherty, B.A.; et al. The Complete Genome Sequence of the Gastric Pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 1997, 388, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, I.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Amieva, M.R.; Roers, A.; Flavell, R.A.; Sparwasser, T.; Müller, A. Tolerance Rather Than Immunity Protects From Helicobacter pylori–Induced Gastric Preneoplasia. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 199–209.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; O’Rourke, J.; De Ungria, M.; Robertson, B.; Daskalopoulos, G.; Dixon, M. A Standardized Mouse Model of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Introducing the Sydney Strain. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, M.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Lertsethtakarn, P.; Vogelmann, R.; Joubert, L.-M.; Ottemann, K.M.; Amieva, M.R. ChePep Controls Helicobacter pylori Infection of the Gastric Glands and Chemotaxis in the Epsilonproteobacteria. mBio 2011, 2, e00098–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, M.S.; Goodwin, M.; Kelly, D.J. Chemotaxis in the Human Gastric Pathogen Helicobacter pylori: Different Roles for CheW and the Three CheV Paralogues, and Evidence for CheV2 Phosphorylation. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenthal, A.C.; Simon, C.; Fair, A.S.; Mehmood, K.; Terry, K.; Anastasia, S.; Ottemann, K.M. A Fixed-Time Diffusion Analysis Method Determines That the Three Chev Genes of Helicobacter pylori Differentially Affect Motility. Microbiology 2009, 155, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andermann, T.M.; Chen, Y.-T.; Ottemann, K.M. Two Predicted Chemoreceptors of Helicobacter pylori Promote Stomach Infection. Infect Immun 2002, 70, 5877–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, D.J.; Langford, M.L.; Watson, E.L.; Carter, J.E.; Chen, Y.-T.; Ottemann, K.M. Colonization and Inflammation Deficiencies in Mongolian Gerbils Infected by Helicobacter pylori Chemotaxis Mutants. Infect Immun 2005, 73, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, K.D.; Andermann, T.M.; Draper, J.; Sanders, L.; Williams, S.M.; Araghi, C.; Ottemann, K.M. The Helicobacter pylori CZB Cytoplasmic Chemoreceptor TlpD Forms an Autonomous Polar Chemotaxis Signaling Complex That Mediates a Tactic Response to Oxidative Stress. J Bacteriol 2016, 198, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, N.R.; Shepherd, B.; Falkow, S. Global Transposon Mutagenesis and Essential Gene Analysis of Helicobacter pylori. J Bacteriol 2004, 186, 7926–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoney-Marino, C.R.; Wolfe, A.J.; Visick, K.L. Chemoattraction of Vibrio fischeri to Serine, Nucleosides, and N -Acetylneuraminic Acid, a Component of Squid Light-Organ Mucus. Appl Environ Microbiol 2003, 69, 7527–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lees, J.A.; Bee, G.C.W.; Brown, S.P.; Weiser, J.N. Pneumococcal Quorum Sensing Drives an Asymmetric Owner–Intruder Competitive Strategy during Carriage via the Competence Regulon. Nat Microbiol 2018, 4, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Faller, G.; Haas, R. Role of the AlpAB Proteins and Lipopolysaccharide in Adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to Human Gastric Tissue. International Journal of Medical Microbiology 2002, 292, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Swoboda, K.; Barwig, I.; Ruhl, S.; Borén, T.; Koletzko, S.; Haas, R. Outer Membrane Protein Expression Profile in Helicobacter pylori Clinical Isolates. Infect Immun 2009, 77, 3782–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkovich, O.A.; Yin, J.; Ekshyyan, V.; Conant, C.; Traylor, J.; Adegboyega, P.; McGee, D.J.; Rhoads, R.E.; Slepenkov, S.; Testerman, T.L. Helicobacter pylori AlpA and AlpB Bind Host Laminin and Influence Gastric Inflammation in Gerbils. Infect Immun 2011, 79, 3106–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Woo, T.; Kurata, S.; Zaman, C.; Hojo, F.; Hanawa, T.; Kato, S.; Kamiya, S. Analysis of Outer Membrane Vesicle Protein Involved in Biofilm Formation of Helicobacter pylori. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Fukutomi, T.; Hanawa, T.; Kurata, S.; Zaman, C.; Hojo, F.; Kamiya, S. Diversification of the AlpB Outer Membrane Protein of Helicobacter pylori Affects Biofilm Formation and Cellular Adhesion. J Bacteriol 2017, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, R.; Durrani, Z.; Rijpkema, S.G.; Kuipers, E.J.; Van Vliet, A.H.M.; Kusters, J.G. Role of the Helicobacter pylori Outer-Membrane Proteins AlpA and AlpB in Colonization of the Guinea Pig Stomach. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2004, 53, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenbreit, S.; Till, M.; Hofreuter, D.; Faller, G.; Haas, R. Genetic and Functional Characterization of the alpAB Gene Locus Essential for the Adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to Human Gastric Tissue. Molecular Microbiology 1999, 31, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Wu, J.Y.; Beswick, E.J.; Ohno, T.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Reyes, V.E.; Kita, M.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Functional and Intracellular Signaling Differences Associated with the Helicobacter pylori AlpAB Adhesin from Western and East Asian Strains. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2007, 282, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathroubi, S.; Hu, S.; Ottemann, K.M. Genetic Requirements and Transcriptomics of Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Formation on Abiotic and Biotic Surfaces. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, B.J.; Loh, J.T.; Hill, S.; Rose, K.L.; McDonald, W.H.; Cover, T.L. Alteration of the Helicobacter pylori Membrane Proteome in Response to Changes in Environmental Salt Concentration. Proteomics Clinical Apps 2015, 9, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caston, R.R.; Loh, J.T.; Voss, B.J.; McDonald, W.H.; Scholz, M.B.; McClain, M.S.; Cover, T.L. Effect of Environmental Salt Concentration on the Helicobacter pylori Exoproteome. Journal of Proteomics 2019, 202, 103374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, E.A.; Bassler, B.L.; Wright, A. Evidence for a Signaling System in Helicobacter pylori : Detection of a luxS -Encoded Autoinducer. J Bacteriol 2000, 182, 3638–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, B.A.; Campagna, S.R.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L.; Guillemin, K. The Quorum-Sensing Molecule Autoinducer 2 Regulates Motility and Flagellar Morphogenesis in Helicobacter pylori. J Bacteriol 2007, 189, 6109–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, B.A.; Wreden, C.; Hicks, K.G.; Sweeney, E.G.; Ottemann, K.M.; Guillemin, K. Helicobacter pylori Perceives the Quorum-Sensing Molecule AI-2 as a Chemorepellent via the Chemoreceptor TlpB. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; She, F.; Wen, Y. AI-2 Induces Urease Expression Through Downregulation of Orphan Response Regulator HP1021 in Helicobacter pylori. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 790994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.K.; Huang, J.Y.; Wreden, C.; Sweeney, E.G.; Goers, J.; Remington, S.J.; Guillemin, K. Chemorepulsion from the Quorum Signal Autoinducer-2 Promotes Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Dispersal. mBio 2015, 6, e00379–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helicobacter - 2021 - Wen - AI-2 Represses CagA Expression and Bacterial Adhesion Attenuating the Helicobacter.Pdf.
- Czechowska, K.; McKeithen-Mead, S.; Al Moussawi, K.; Kazmierczak, B.I. Cheating by Type 3 Secretion System-Negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa during Pulmonary Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2014, 111, 7801–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Disrupted by Tn-7 | Gene Function | Number of Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| HPG27_843 Intergenic HPG27_843&844 HPG27_147 |
Outer membrane protein HopC/AlpA | 3 |
| Outer membrane protein HopCB/AlpAB locus | 2 | |
| cysteine-rich protein D | 1 | |
|
HPG27_412 HPG27_413 |
phosphatidyl glycerophosphate synthase | 1 |
| Hypothetical protein | 1 | |
|
HPG27_462 HPG27_1061 HPG27_1062 HPG27_1299 |
Hypothetical protein | 1 |
| Cysteine-rich protein X | 1 | |
| Hypothetical Protein | 1 | |
| Type II Endorestriction Nuclease HpyAIV | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





