Submitted:
01 April 2025
Posted:
01 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- firstly, a tilt-rotor aircraft with a quad-rotor airframe layout is introduced and dynamically modeled with respect to the requirements of the flight characteristics of a tilt-rotor vertical take-off and landing UAV.
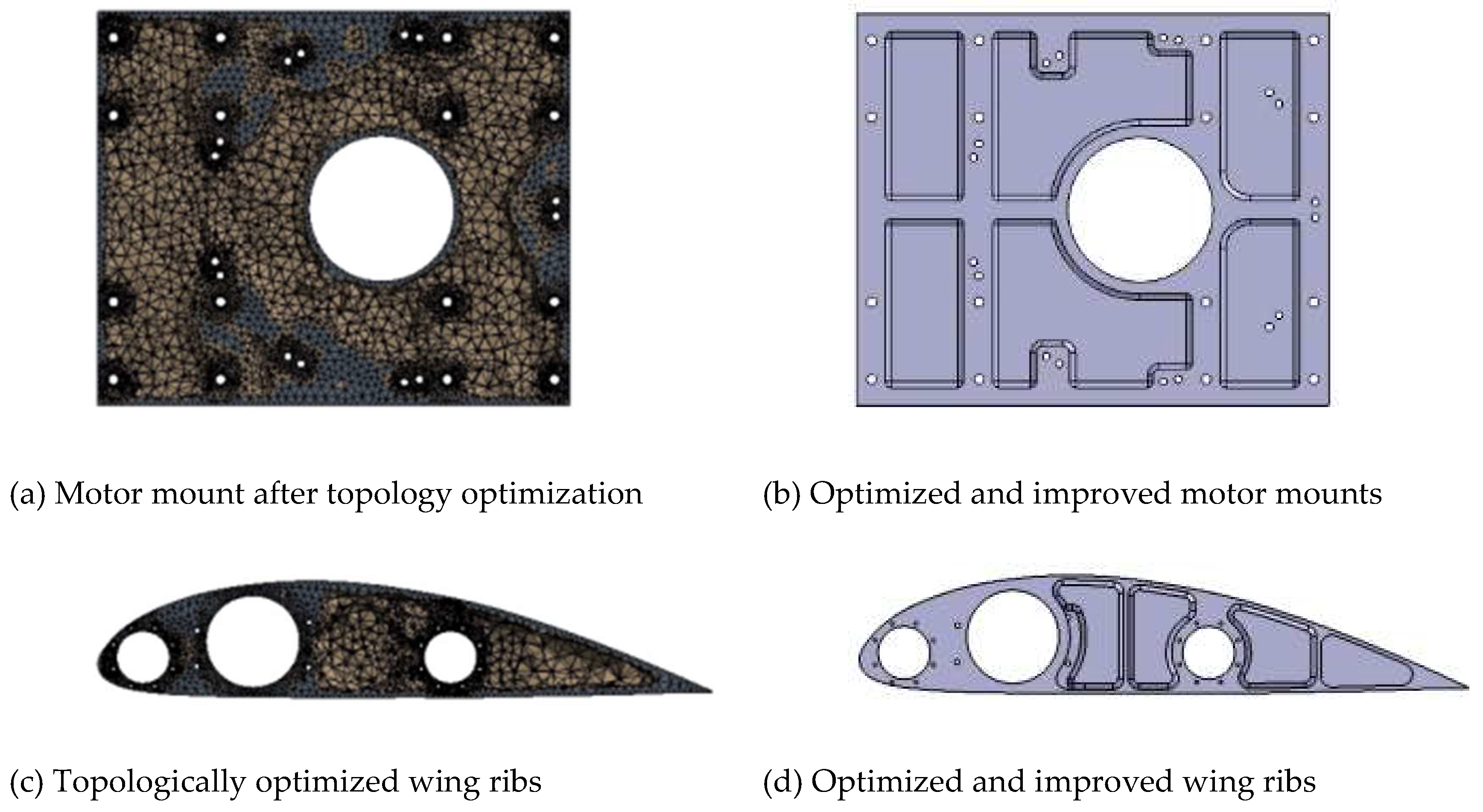
- In addition, the dynamic characteristics of the landing gear are analyzed for the landing characteristics of vertical take-off and landing UAVs and lightweight requirements, and it is proposed to optimize the landing gear structure by adopting the unified objective method, and to optimize the main motor seat and wing ribs of the UAV by means of the topology optimization module in workbench.
- The vibration characteristics of the test aircraft body are analyzed, and it is propose d to introduce the harmonic response analysis method to determine the hazardous excitation frequency point of the final tilt-rotor vertical take-off and landing UAV flight.
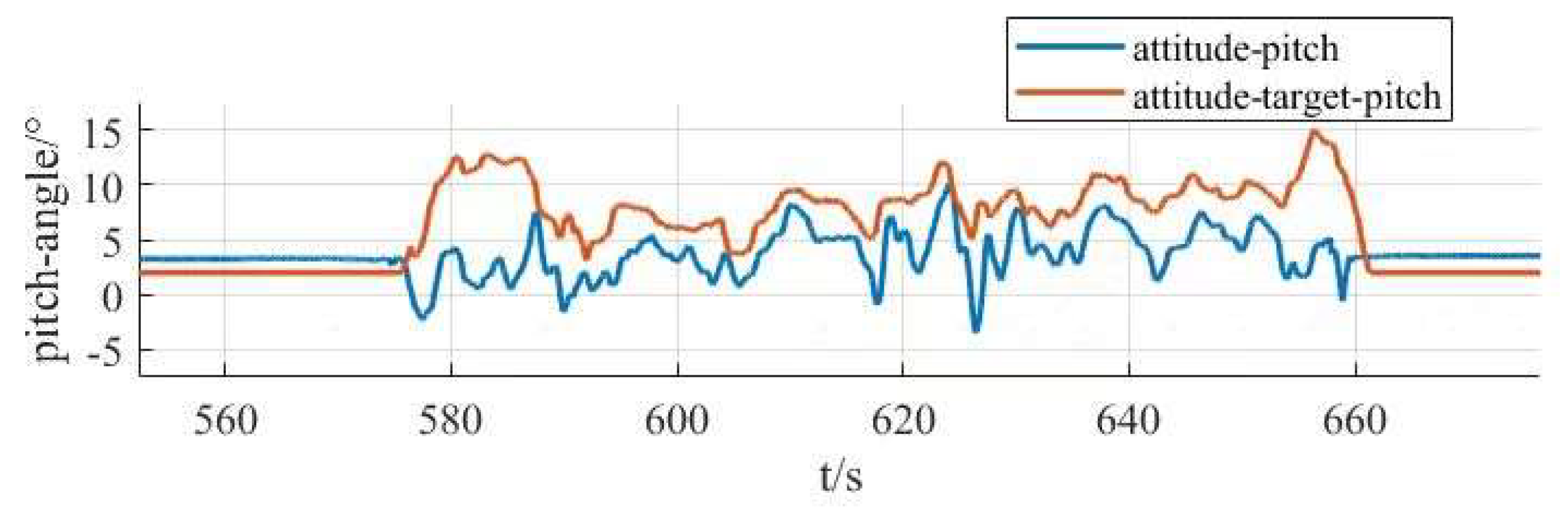
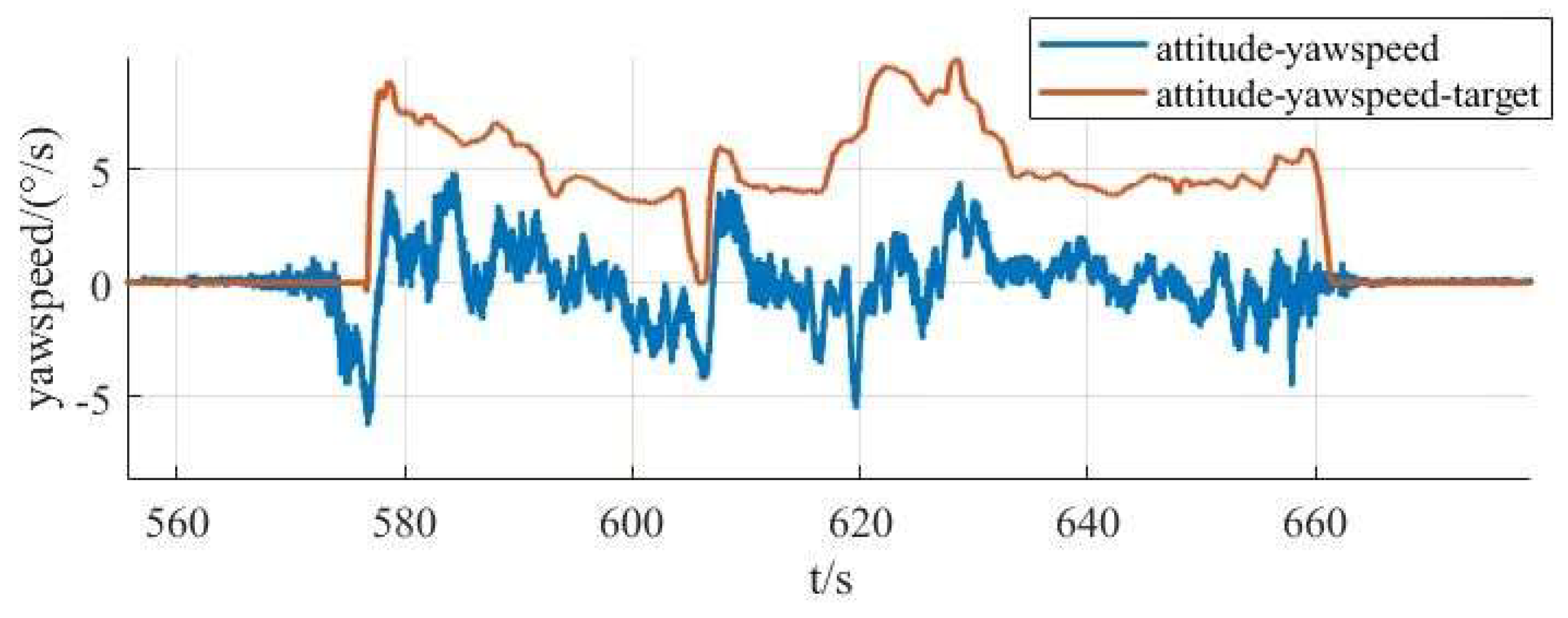
- Finally, for the phenomenon that the tilt-rotor vertical take-off and landing UAV is subjected to a lot of interference during its operation, the series PID control method is proposed to collect simulation data and experimental data on the flight attitudes of the experimental aircraft, such as roll, pitch and yaw, to select and optimize the control scheme, and then carry out experiments on the basis of the optimized control scheme to obtain experimental data and draw conclusions for the research of the tilt-rotor vertical take-off and landing UAV. Provide experimental data with reference and guidance.
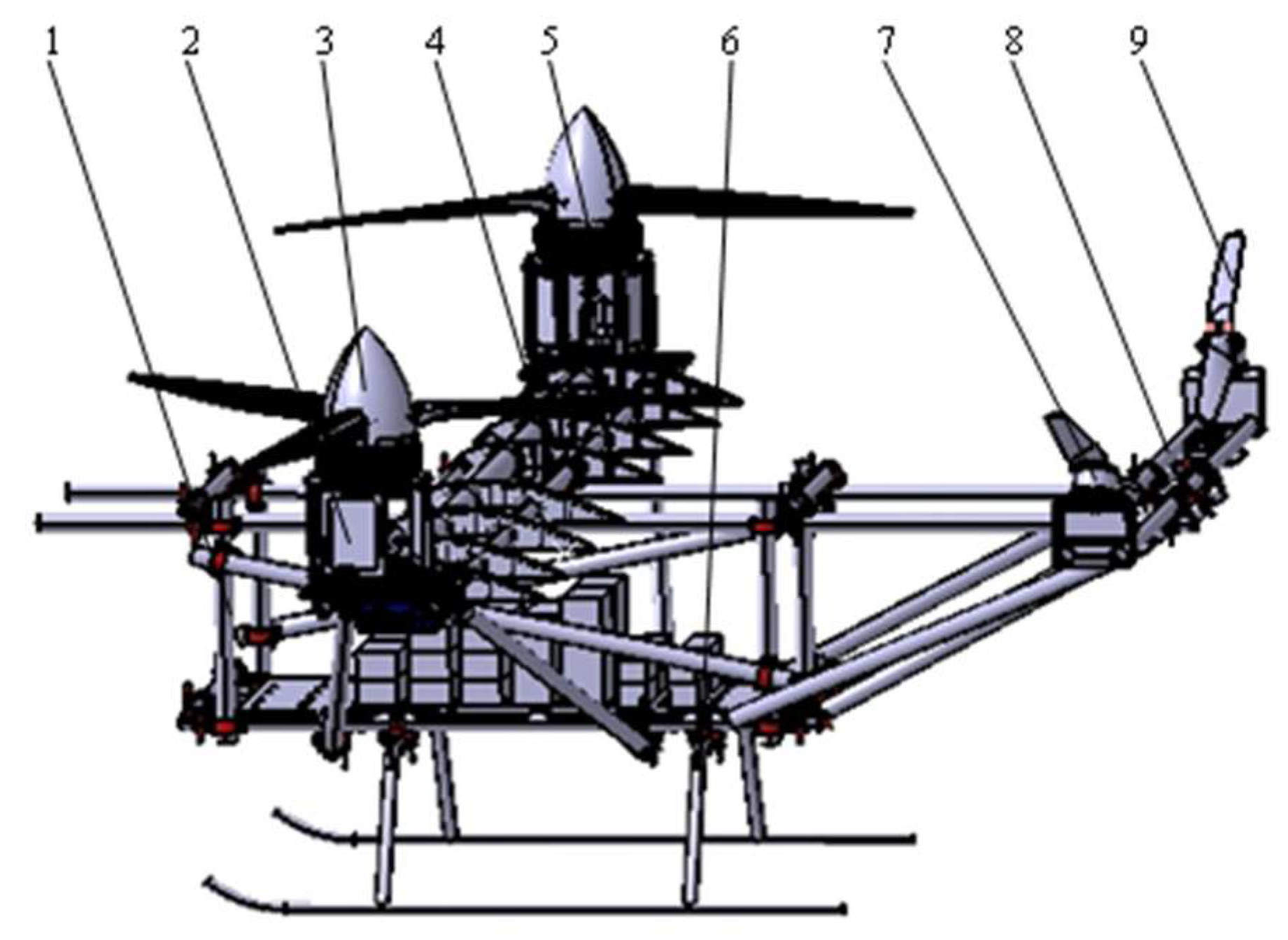
2. Complete UAV Design
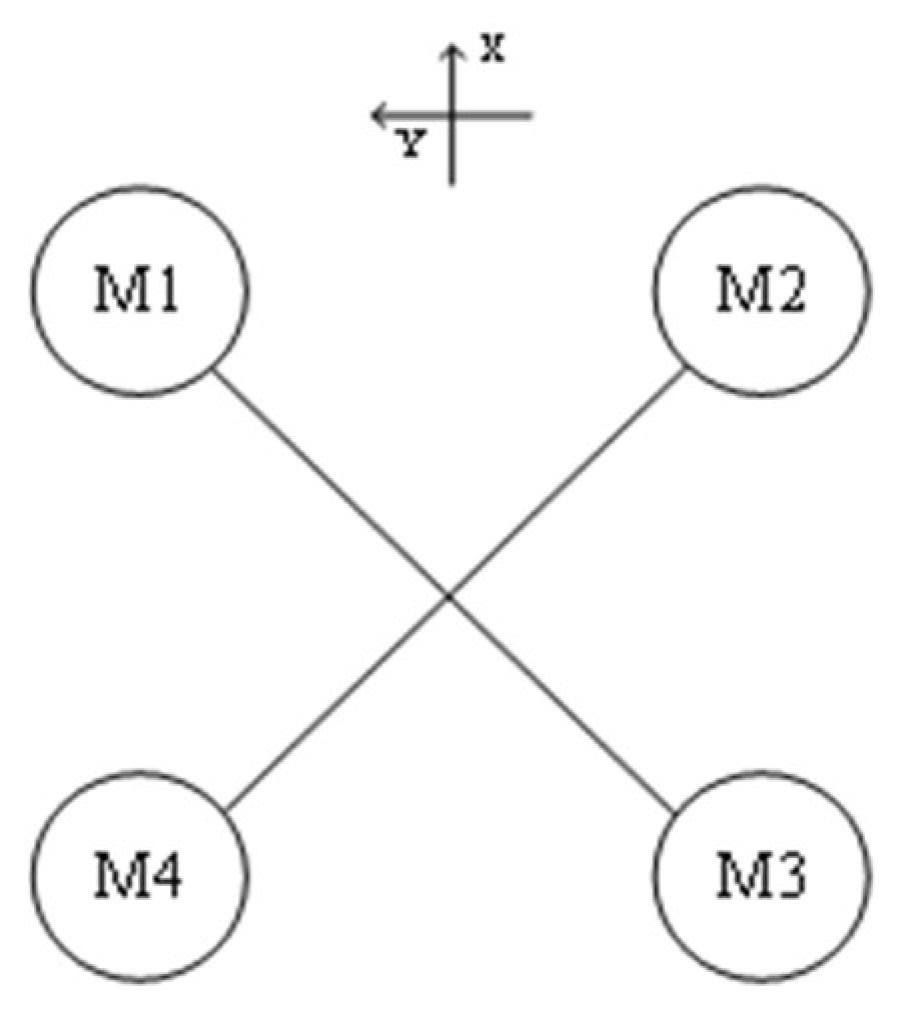
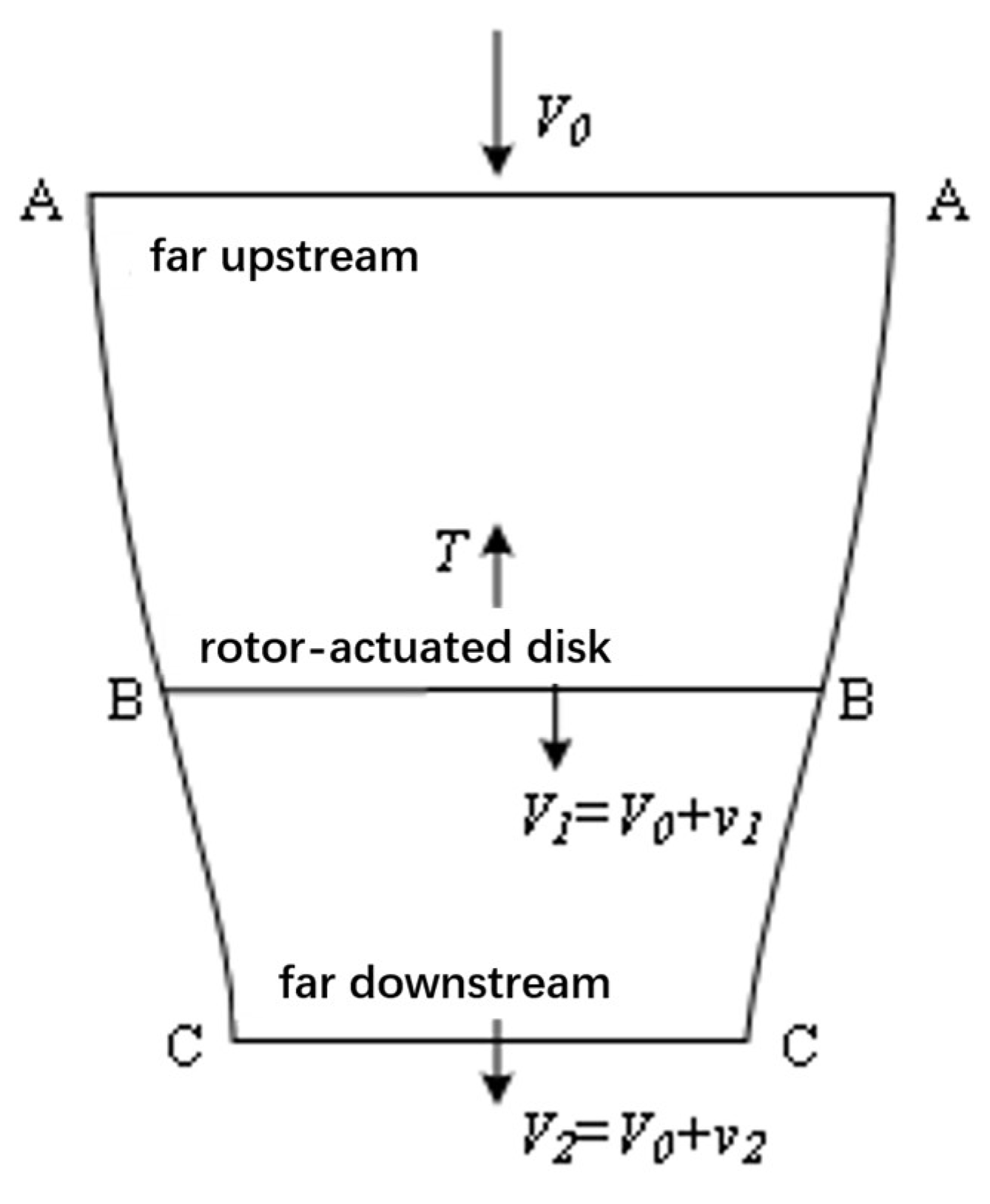
2.1. Dynamic Modeling
2.2. Fuselage Design
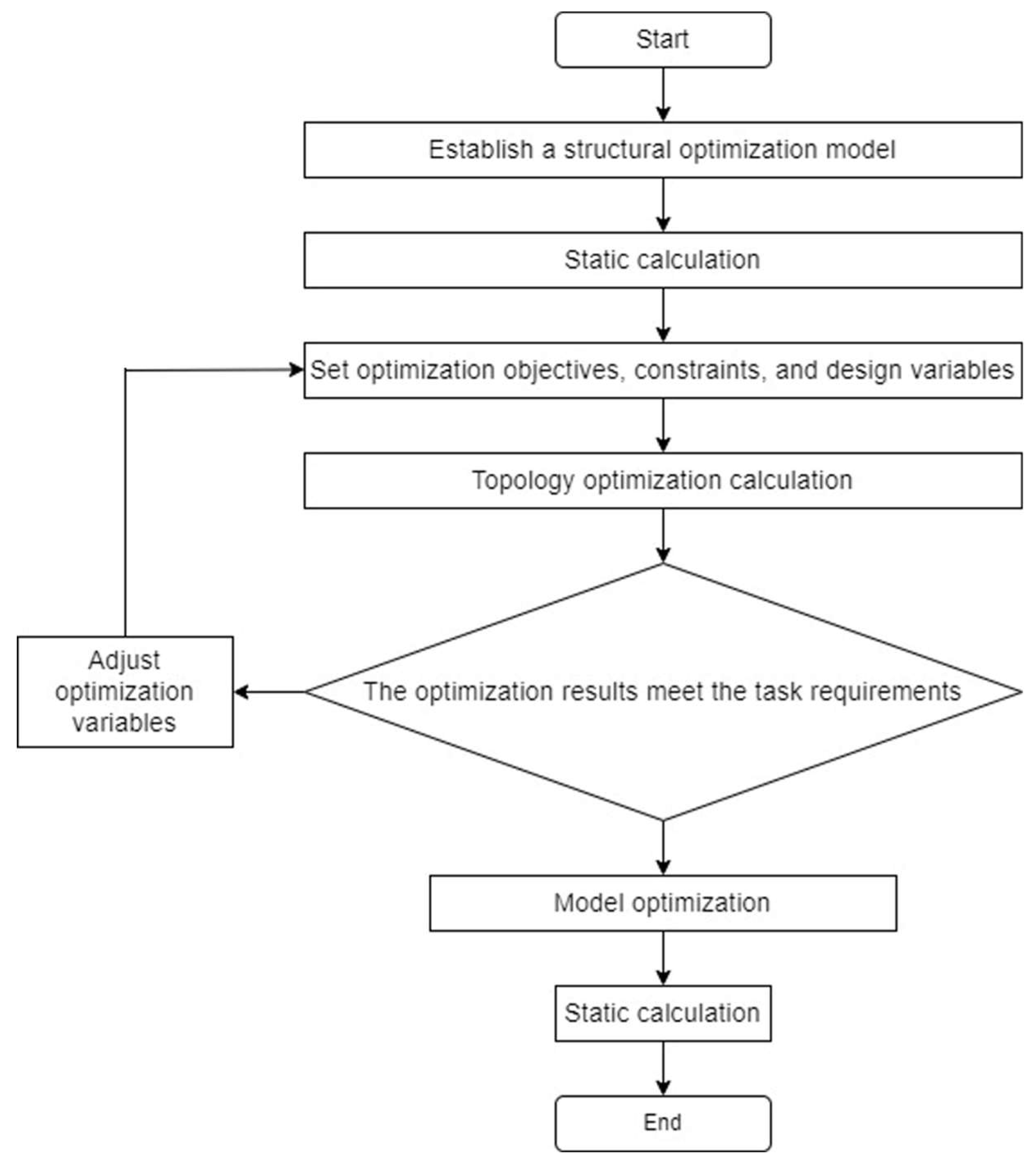
3. Prototype Structure Optimization
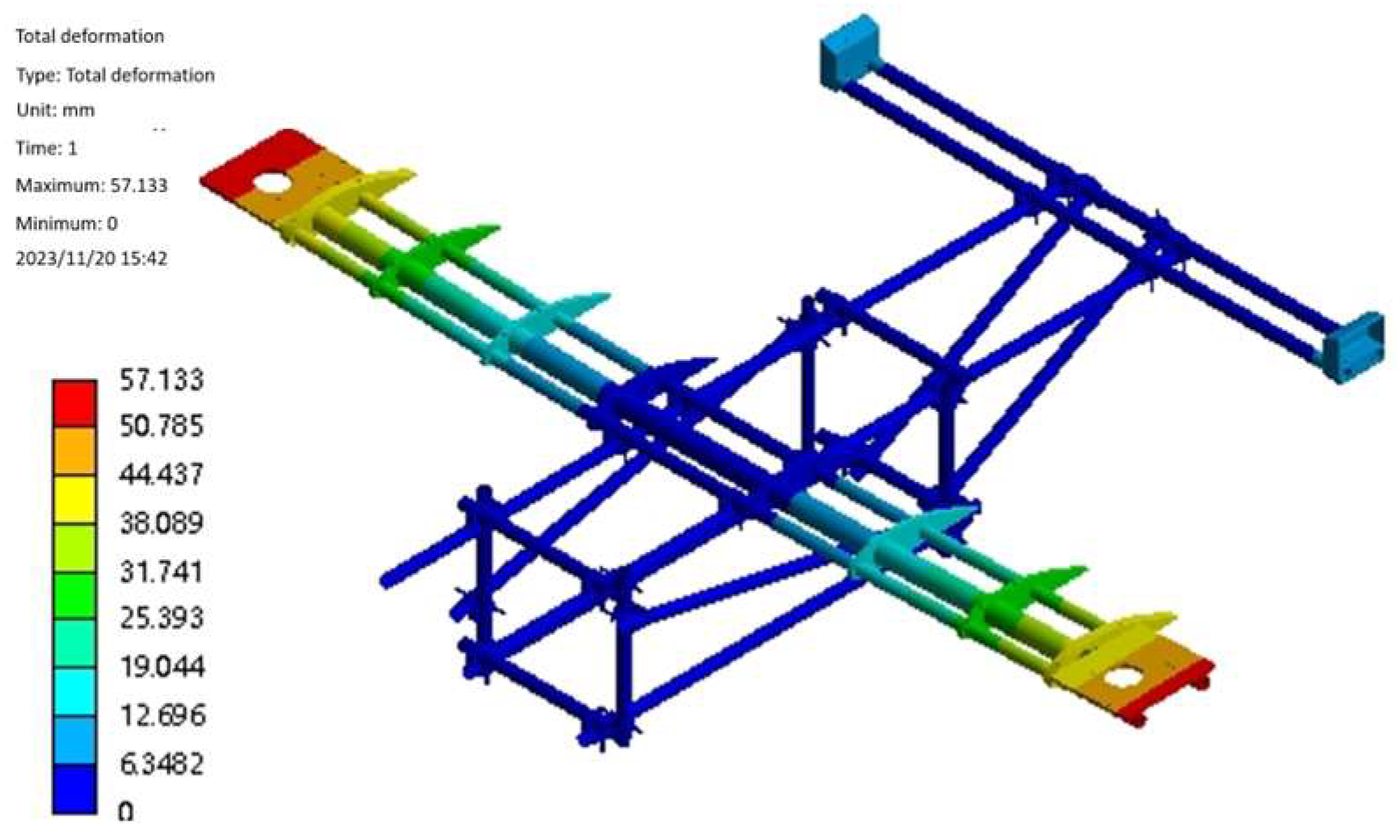
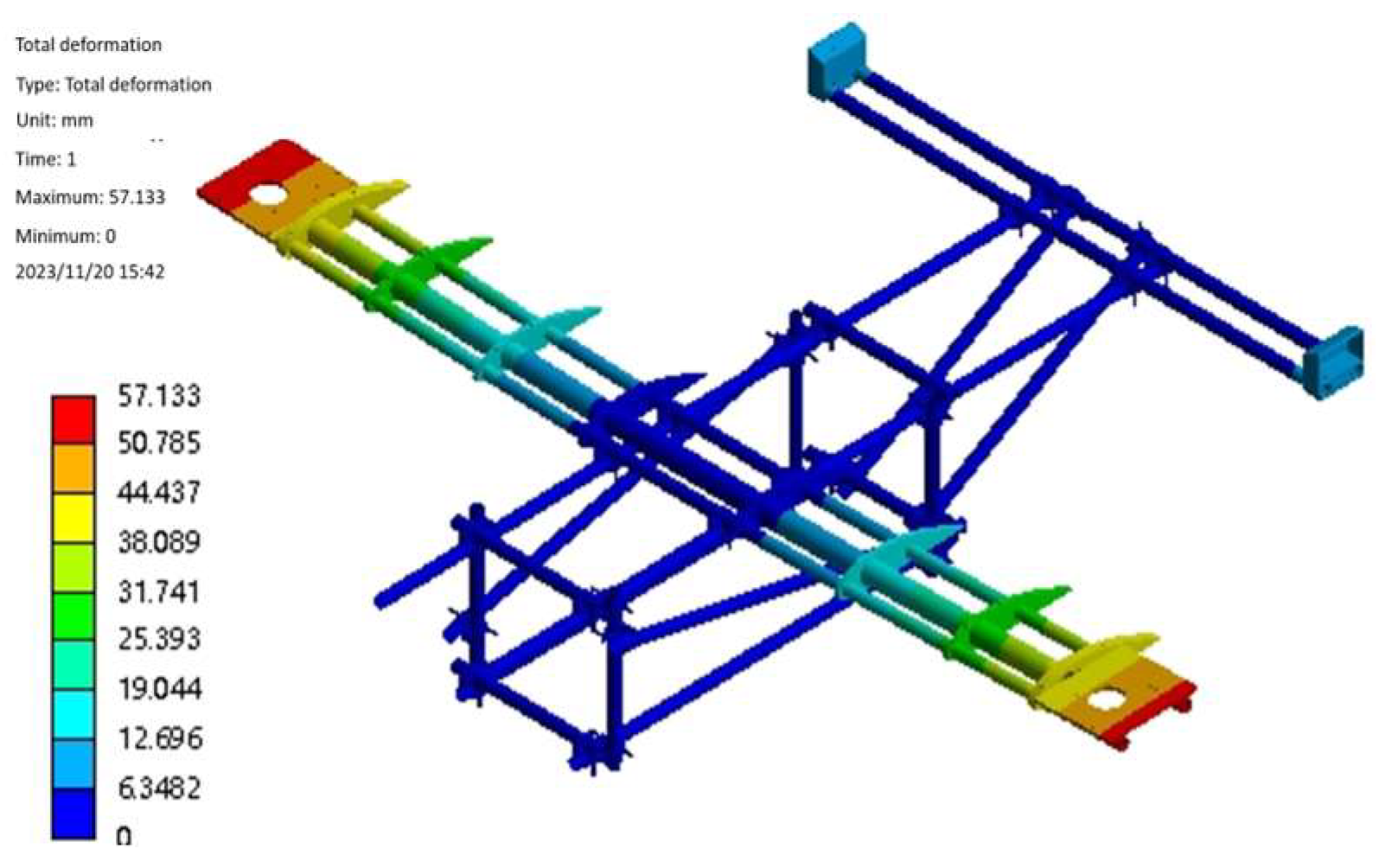
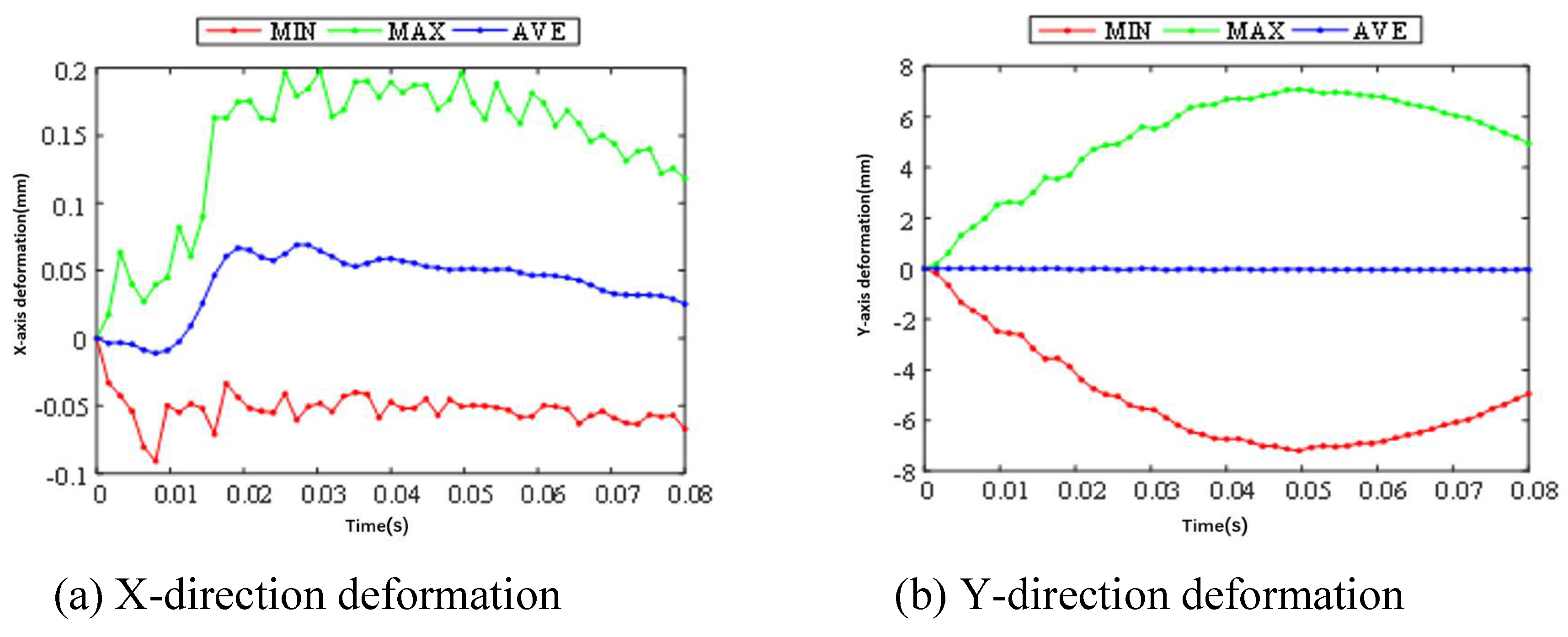
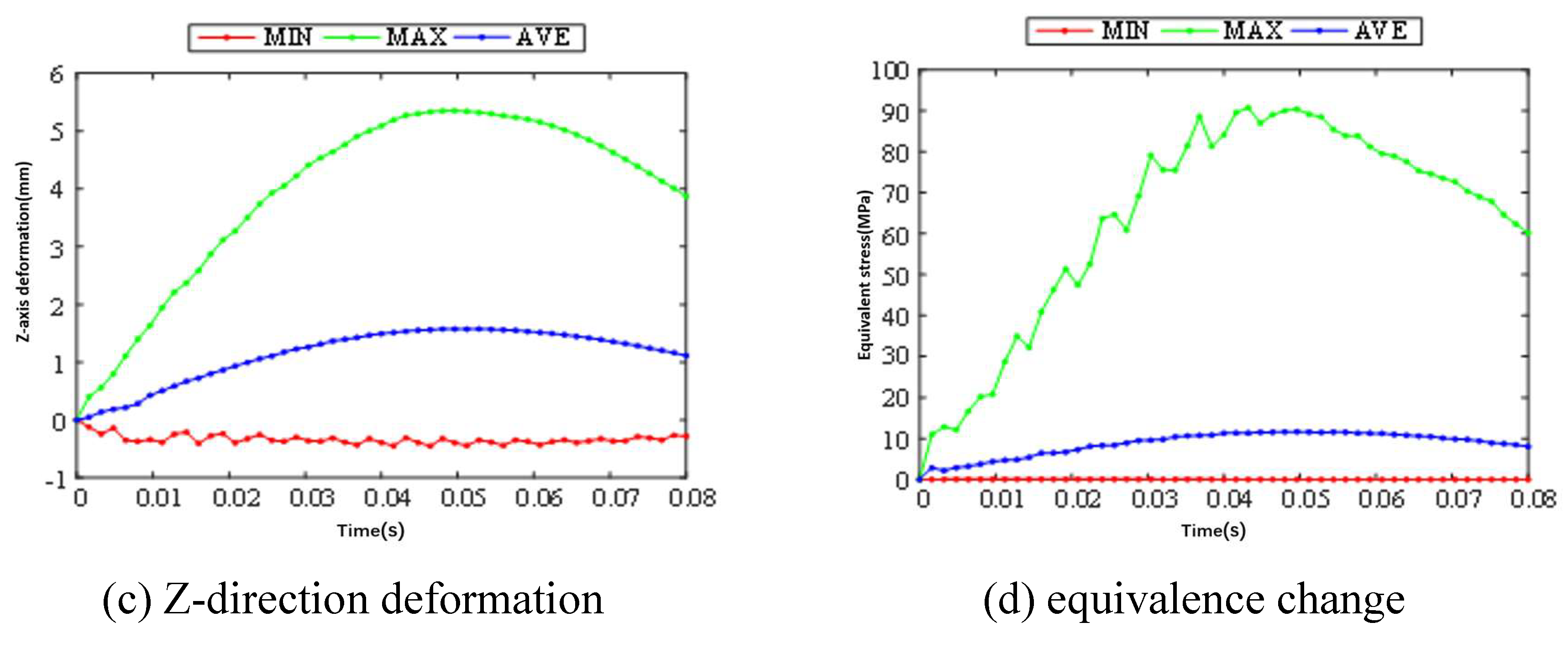
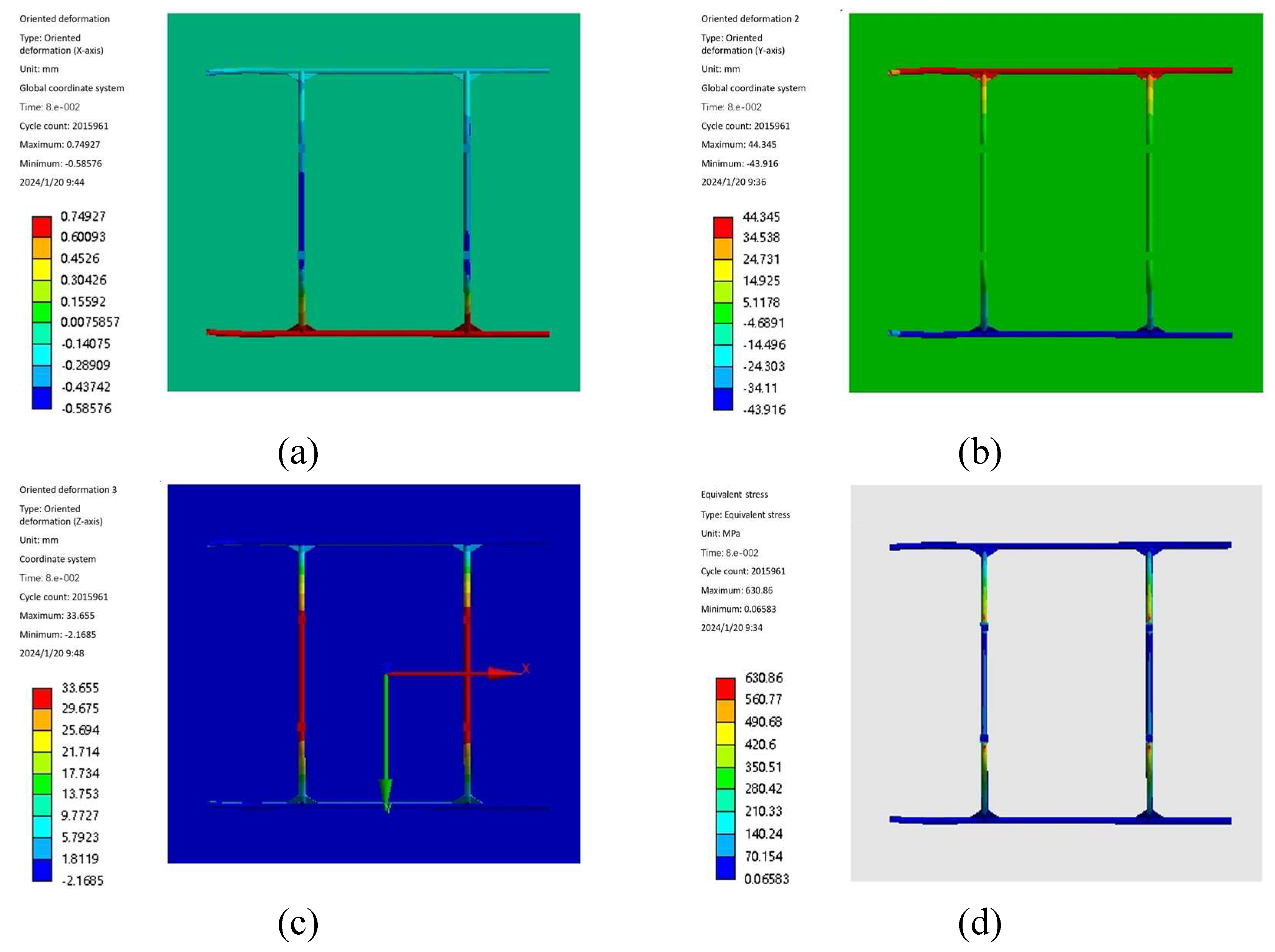
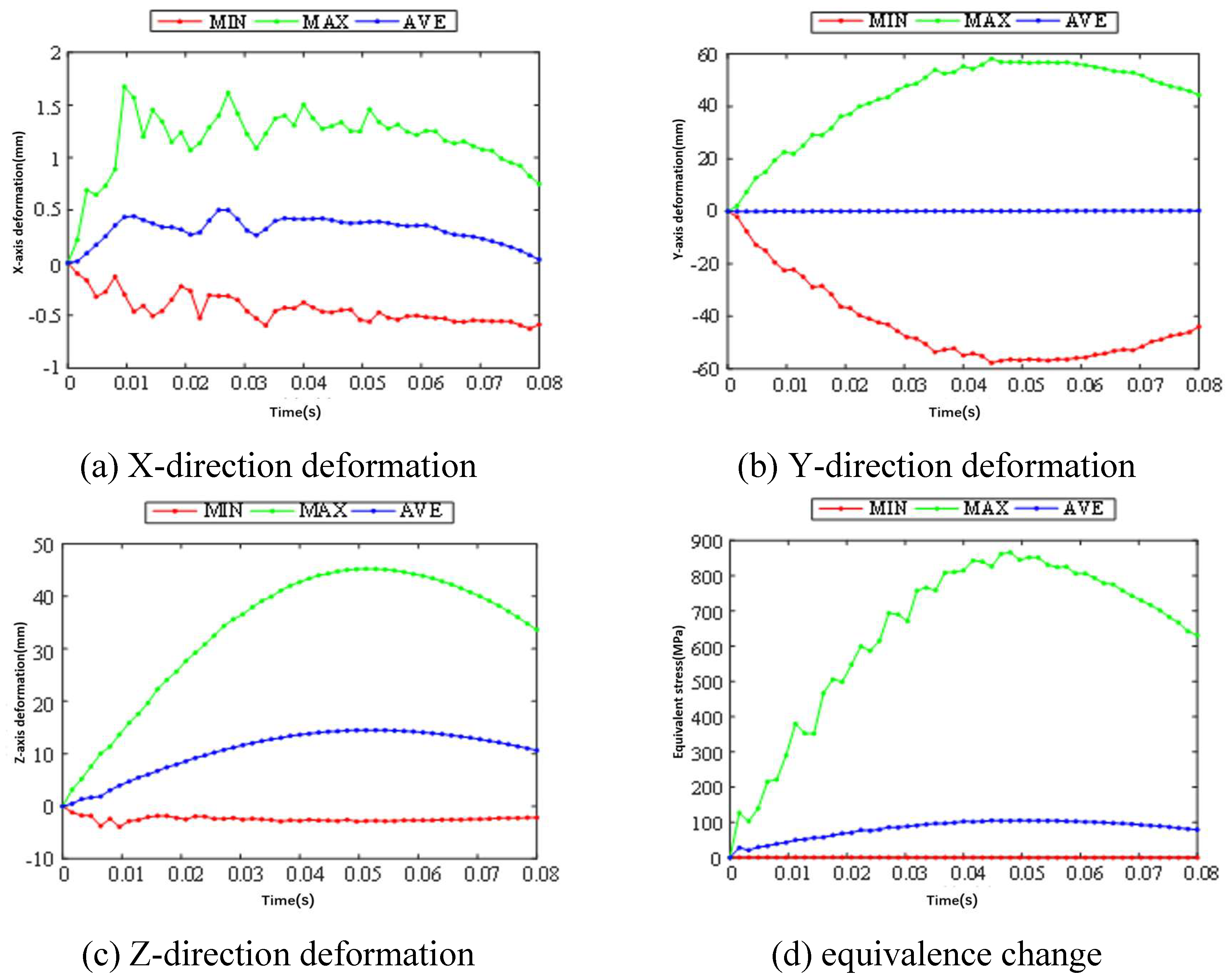
3.1. Static Analysis
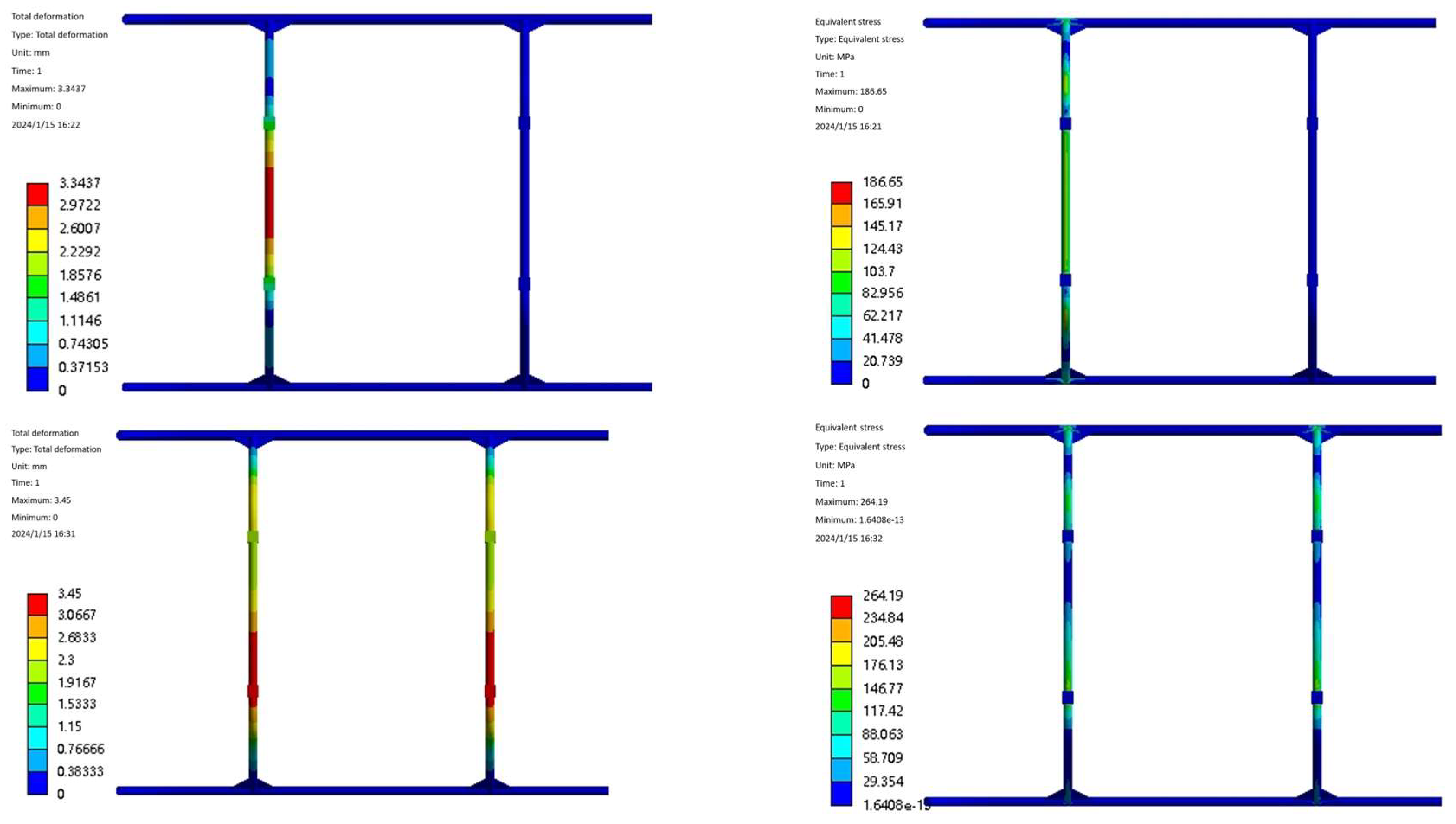
3.2. Optimization of Landing Gear, Wing Ribs and Main Motor Seat
3.2.1. Optimization of Landing Gear Structural Parameters
3.2.2. Wing Ribs and Main Motor Mount Optimization
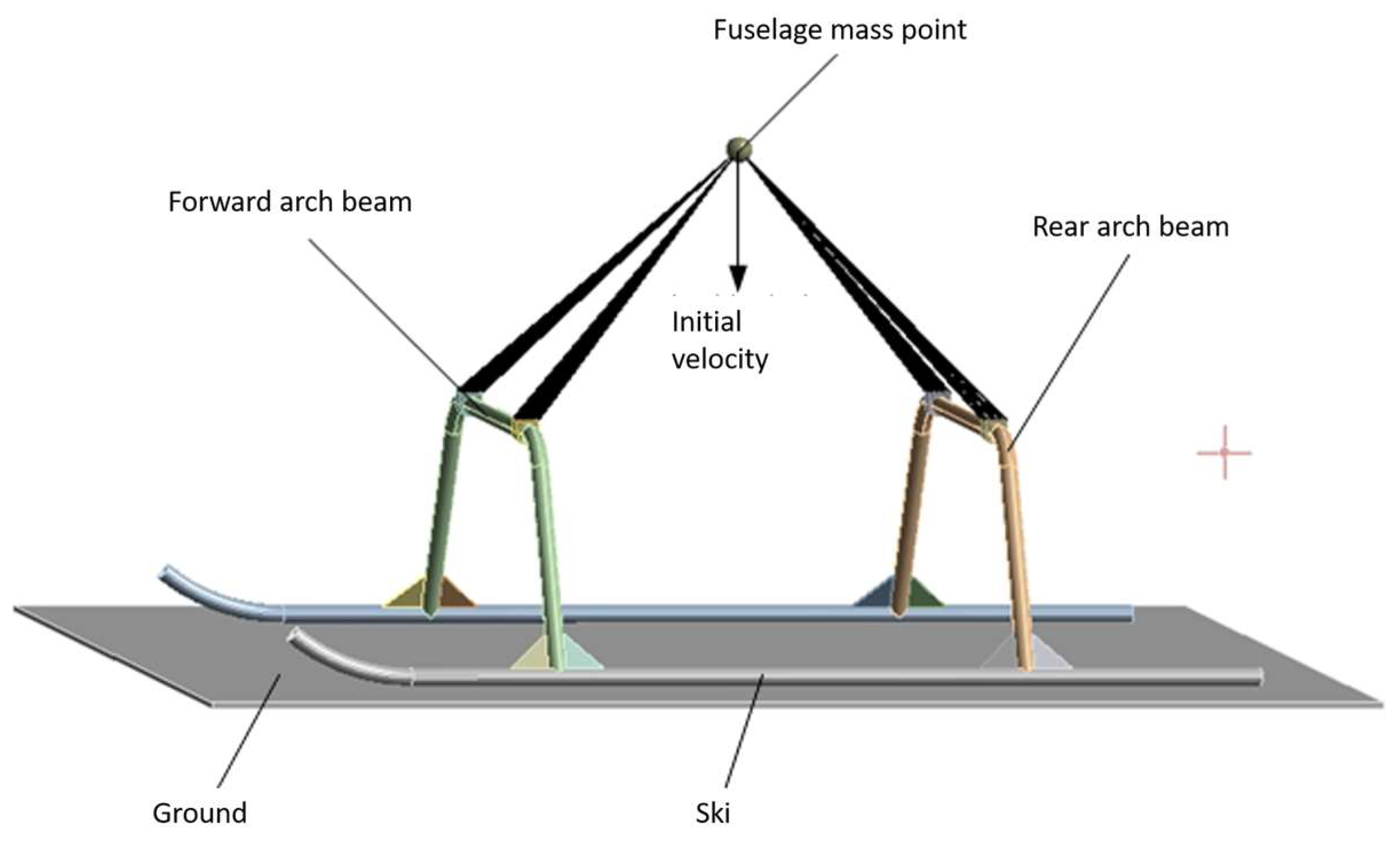
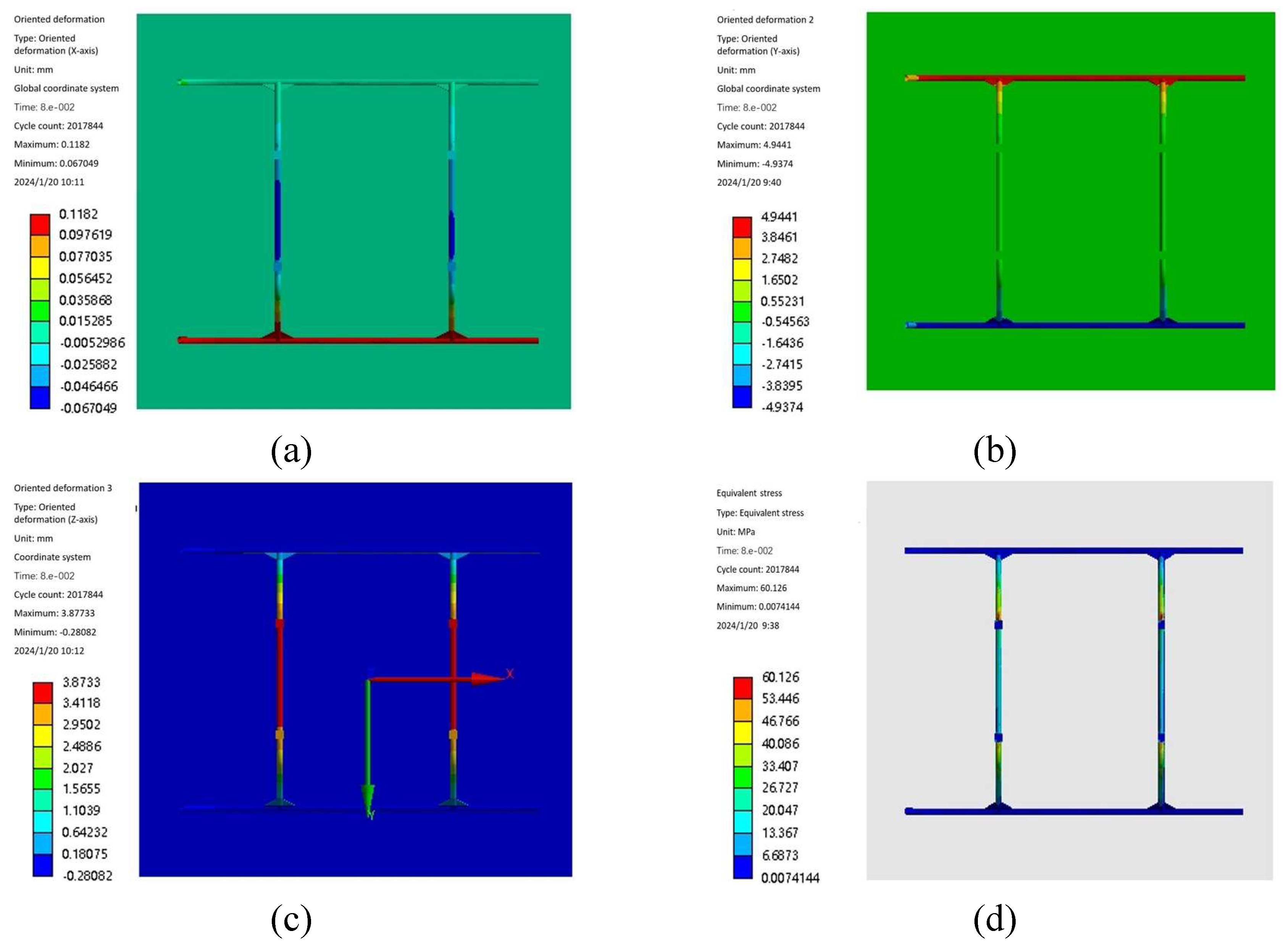
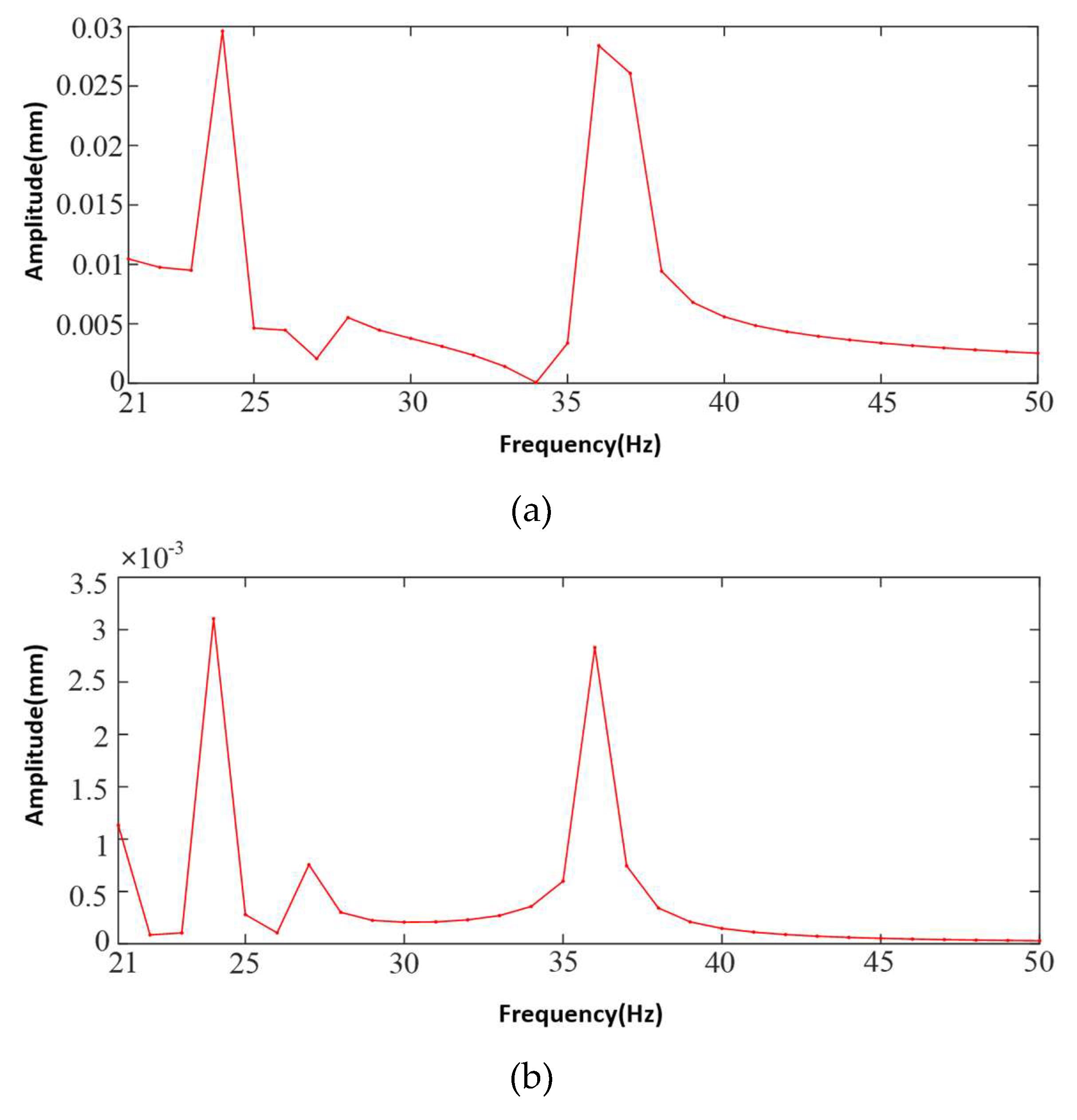
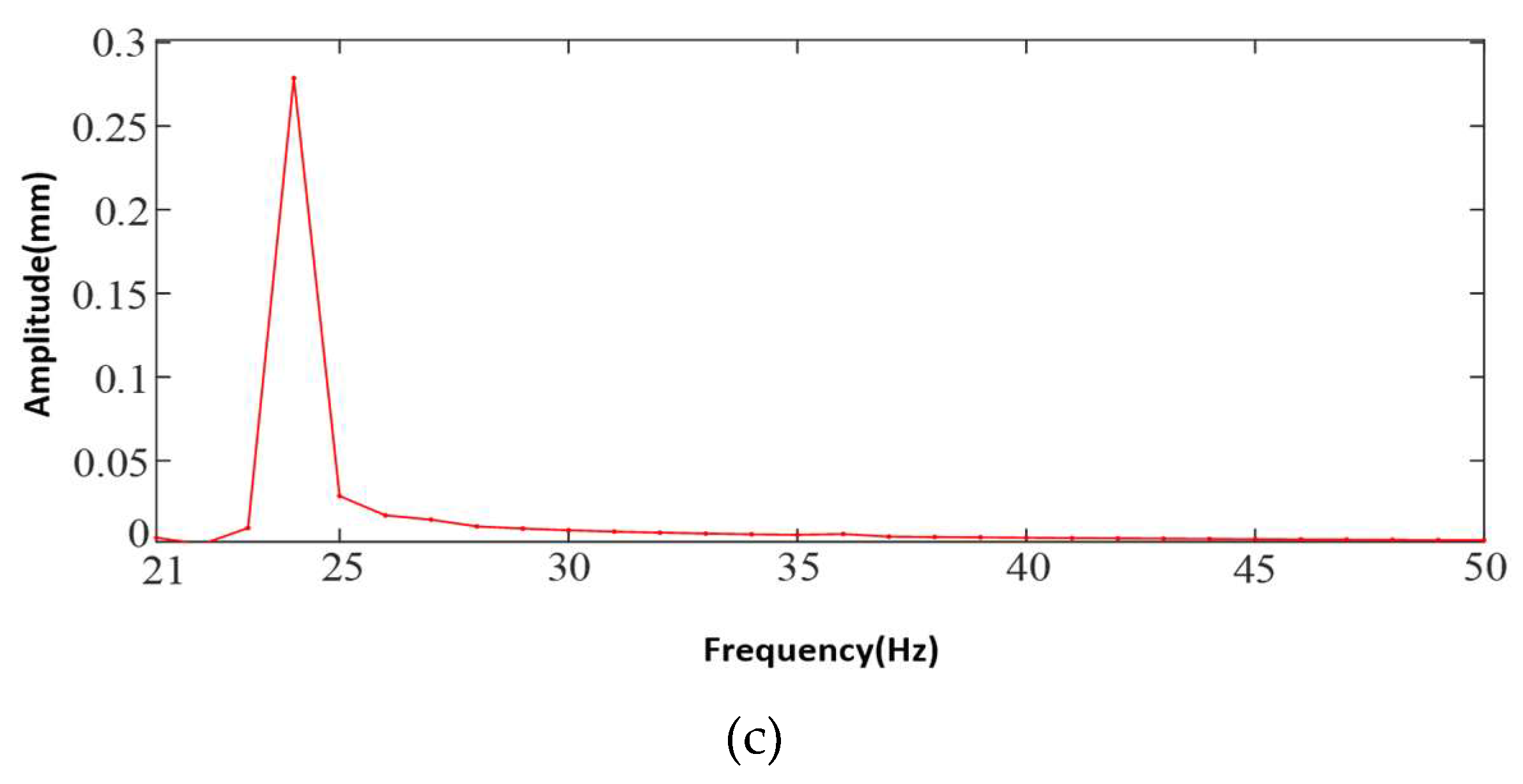
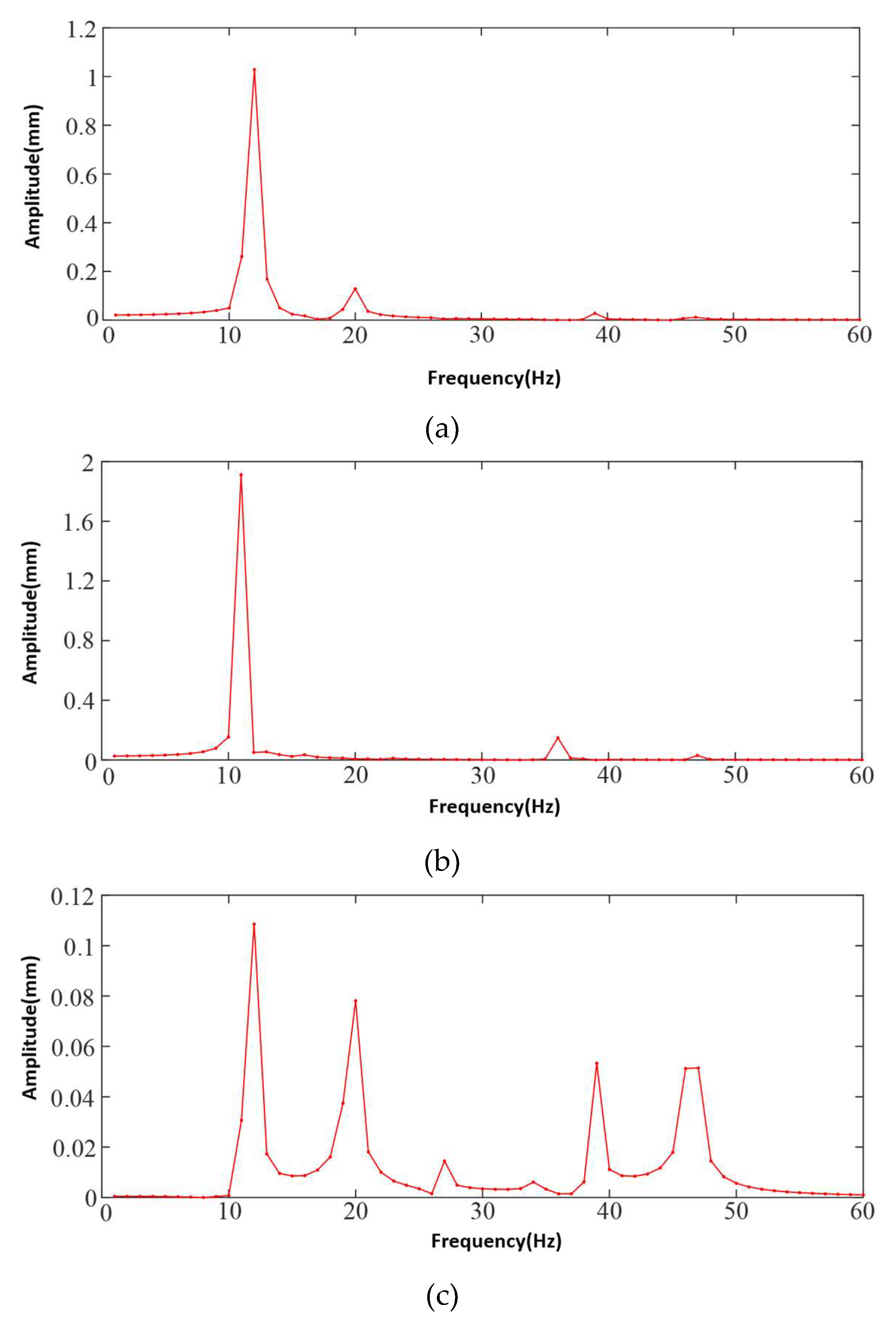
4. Vibration Characterization of the Prototype
5. Prototype System Integration and Control Scheme Optimization
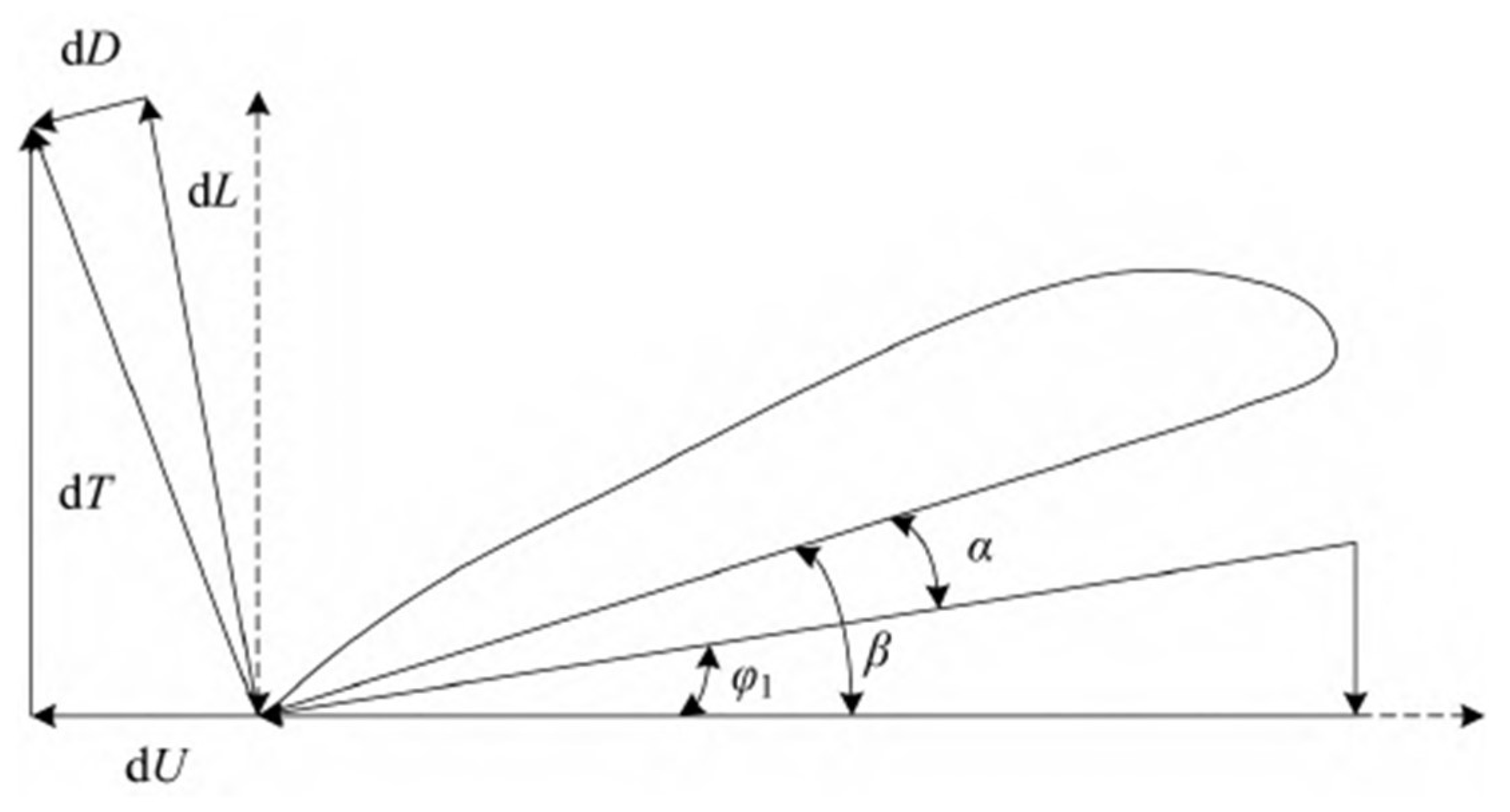
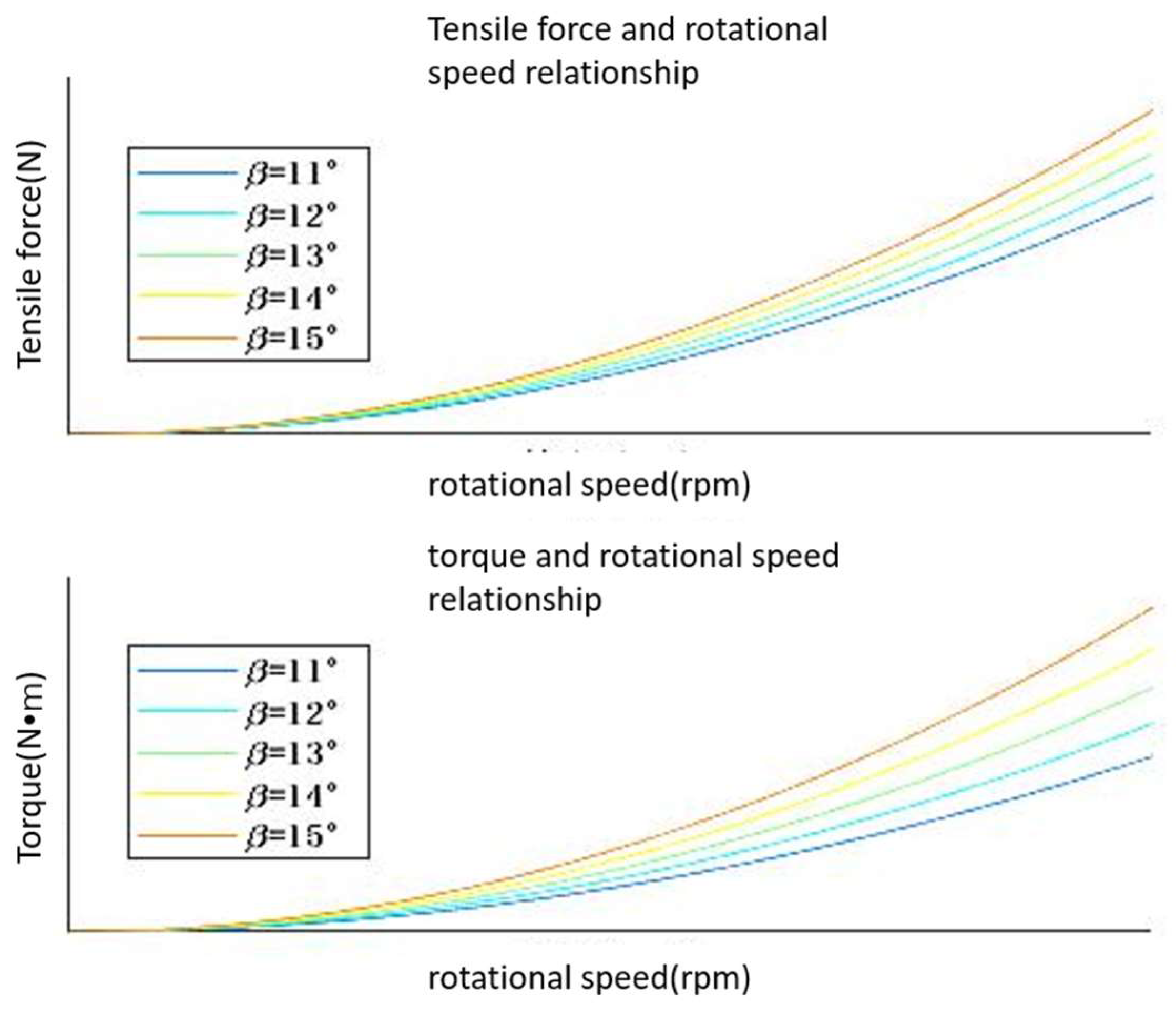
5.1. Power System Design
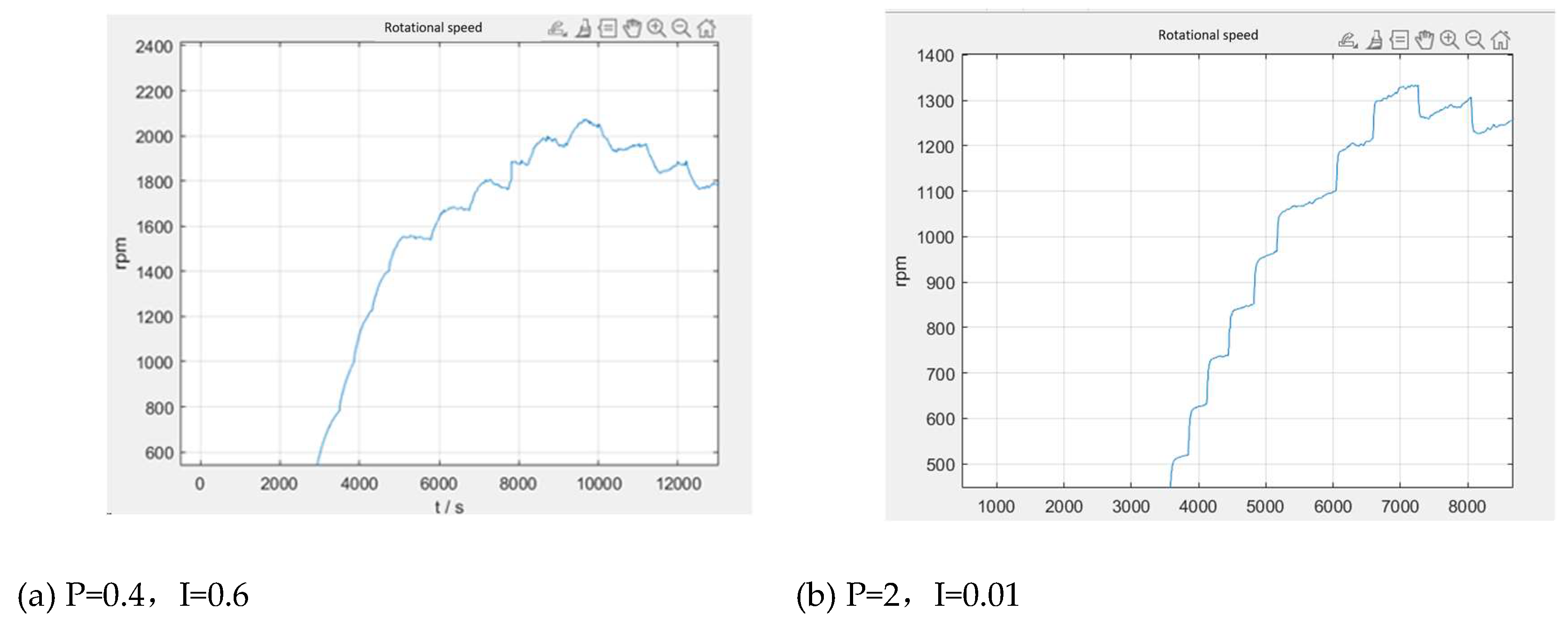
5.2. Control System Design
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, K.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Chen, R. Flight Dynamics Modeling and Dynamic Stability Analysis of TiltRotor Aircraft. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering. 2019, 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Park, B.J.; Cho, A.; Yoo, C.S.; Koo, S.O.; Tahk, M.J. Development of Flight Control System and Troubleshooting on Flight Test of a Tilt-Rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Int J Aeronaut Space 2016, 17, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Xu, Y.F.; Yu, Z.L. Wind Field Disturbance Analysis and Flight Control System Design for a Novel Tilt-Rotor UAV. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 211401–211410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducard, G.J.J.; Allenspach, M. Review of designs and flight control techniques of hybrid and convertible VTOL UAVs. Aerosp Sci Technol 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Su, C.; Xu, S.; Yang, X. A multi-body model of tilt-rotor aircraft based on Kane’s method. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering. 2019, 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Park, B.; Cho, A.; Yoo, C.; Choi, S. Envelop expansion flight test of flight control systems for TR-60 tilt-rotor UAV. 2013 13th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 2013). 2013, 13, 1866-1871. 2013; 13, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Barkai, S.M.; Rand, O.; Peyran, R.J.; Carlson, R.M. Modeling and analysis of tilt-rotor aeromechanical phenomena. Mathematical and Computer Modelling. 1998, 27, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristos, C.; Alexis, K.; Tzes, A. Design and experimental attitude control of an unmanned Tilt-Rotor aerial vehicle. 2011 15th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR).2011, 11, 465-471. 2011; 11, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.B.; Kulhare, A.; Raina, G. Back-stepping control strategy for stabilization of a Tilt-rotor UAV. 2012 24th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). 2012, 12, 3475-3480. 2012; 12, 3475–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, D.N.; Esteban, S.; Raffo, G. A new robust adaptive mixing control for trajectory tracking with improved forward flight of a tilt-rotor UAV. Isa T 2021, 110, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Agarwal, S.R.; Kumar, M. Modeling and Control of a Tethered Tilt-Rotor Quadcopter with Atmospheric Wind Model. IFAC PapersOnLine. 2021, 54–20, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Radaideh, A.; Sun, L. Self-localization of a tethered quadcopter using inertial sensors in a GPS-denied environment. 2017 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS).2017, 17, 271-277. 2017; 17, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Muraoka, K. Flight Controller Design and Demonstration of Quad-Tilt-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. J Guid Control Dynam 2015, 38, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, S.; Lovera, M.; Sato, M.; Muraoka, K. Structured μ-Synthesis of Robust Attitude Control Laws for Quad-Tilt-Wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. J Guid Control Dynam 2020, 43, 2258–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksek, B.; Vuruskan, A.; Ozdemir, U.; Yukselen, M.A.; Inalhan, G. Transition flight modeling of a fixed-wing VTOLUAV. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2016, 84, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Xu, S.; Su, C.Y.; Feng, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Z.; Lian, J. An adaptive recursive sliding mode attitude control for tiltrotor UAV in flight mode transition based on super-twisting extended state observer. arXiv arXiv:2111.02046, 2021.
- Liu, N.J.; Cai, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.X. Predictor-based model reference adaptive roll and yaw control of a quad-tiltrotor UAV. Chinese J Aeronaut 2020, 33, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristos, C.; Alexis, K.; Tzes, A. Dual-Authority Thrust-Vectoring of a Tri-TiltRotor employing Model Predictive Control. J Intell Robot Syst 2016, 81, 471–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmawan, E.; Harjoko, A.; Dharmawan, A. Model, Control, and Realistic Visual 3D Simulation of VTOL Fixed-Wing Transition Flight Considering Ground Effect. Drones 2023, 7, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.L.; Yang, Z.S.; Su, H.Z.; Wang, L.J. Online Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Optimal Self-Learning Control of VTOL Aircraft Systems With Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng 2024, 21, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dalatony, A.M.; Attia, T.; Ragheb, H.; Sharaf, A.M. Cascaded PID Trajectory Tracking Control for Quadruped Robotic Leg. Int J Mech Eng Robot 2023, 12, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
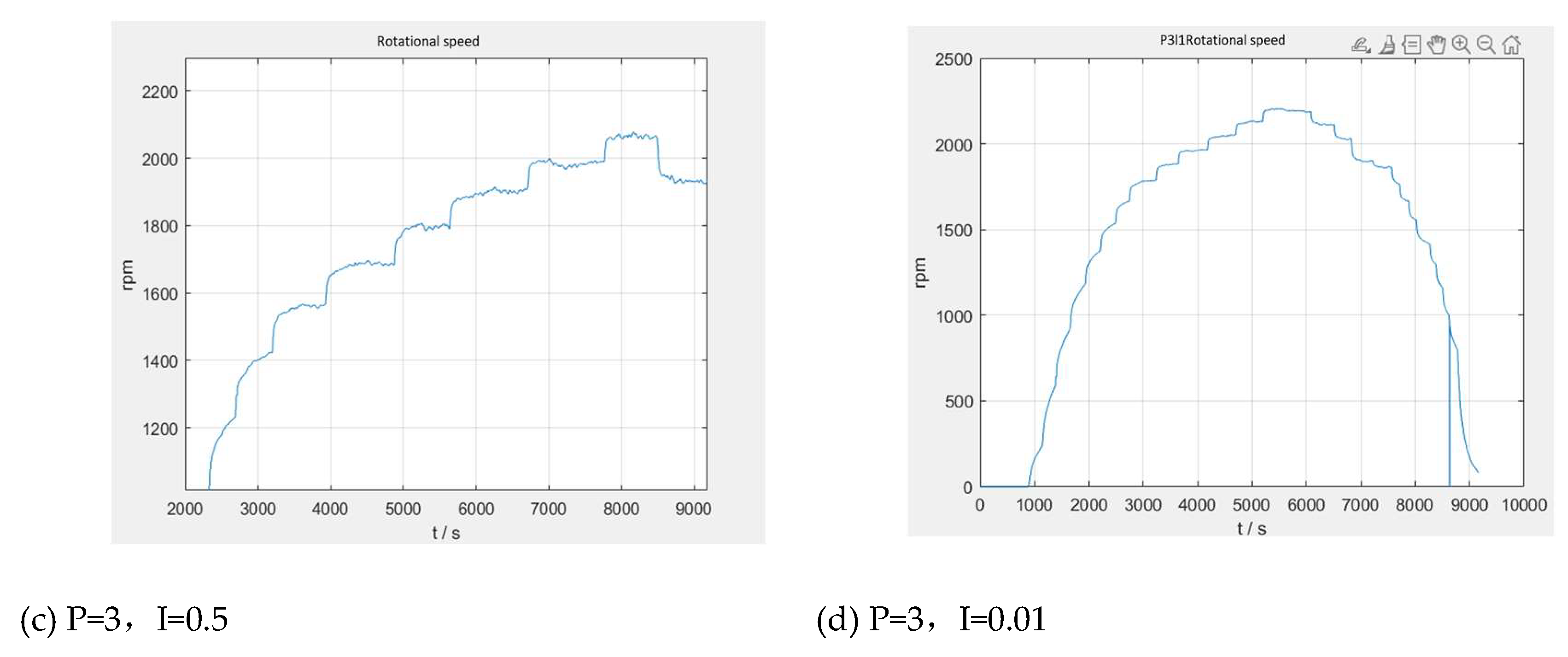
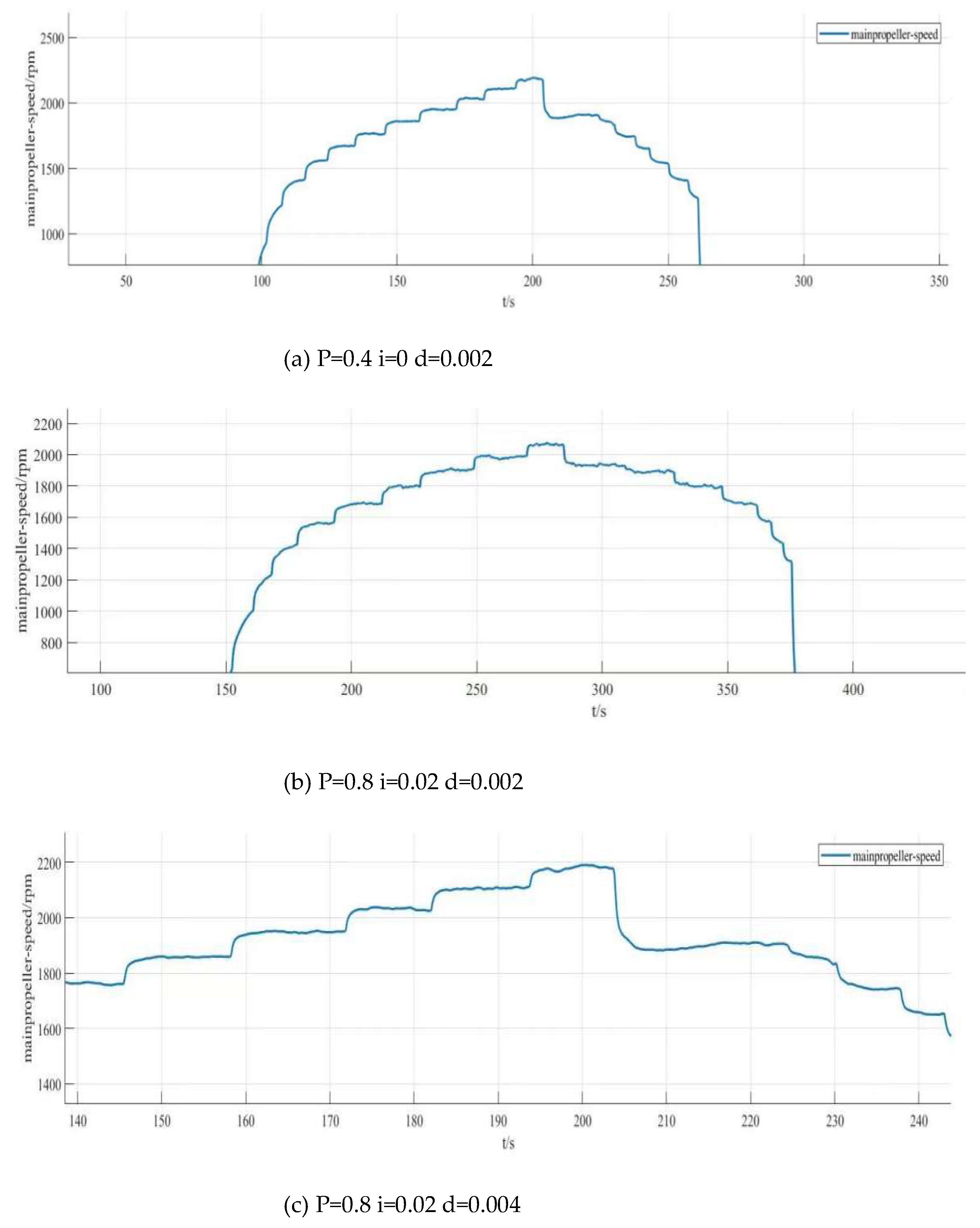
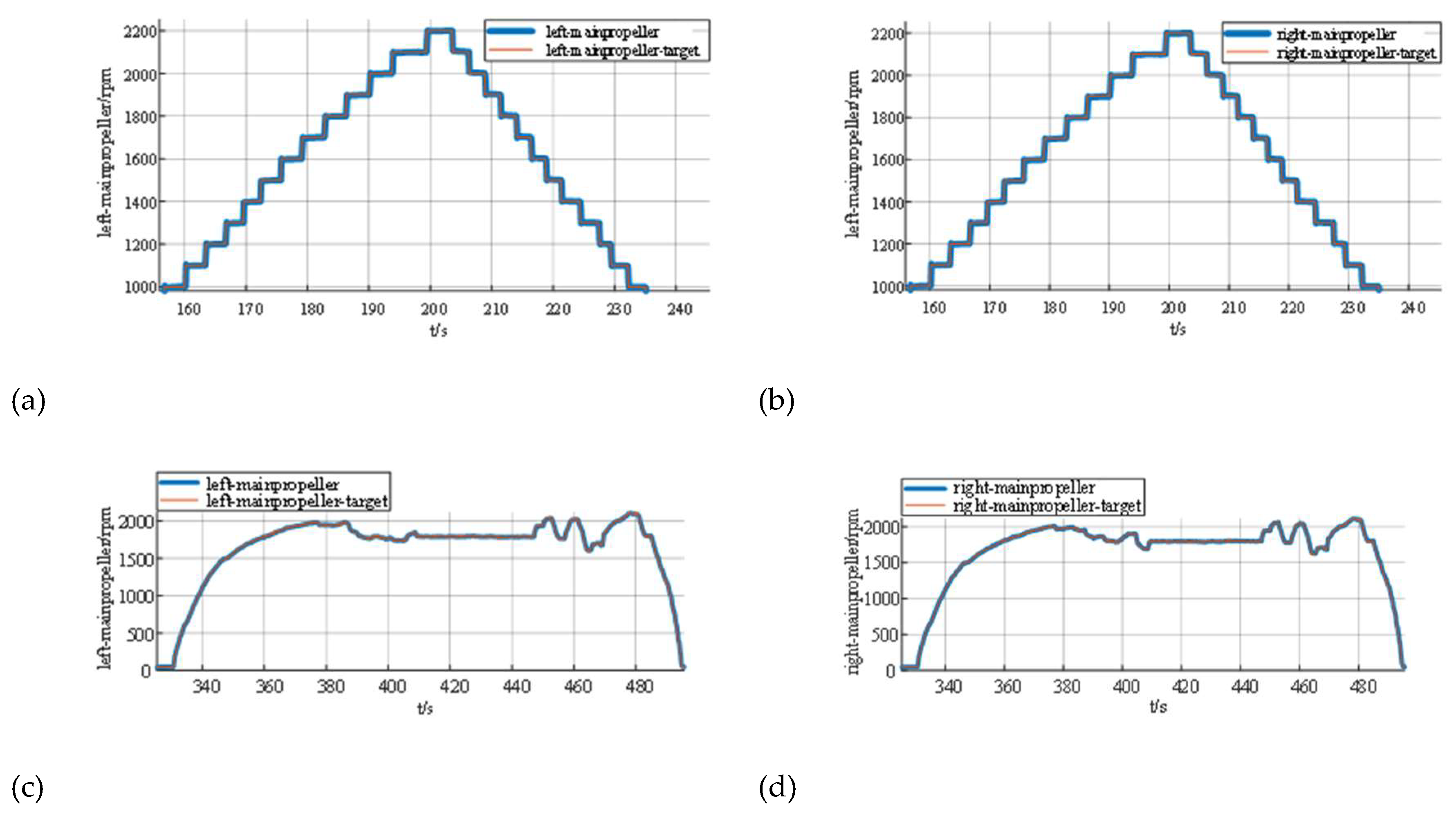
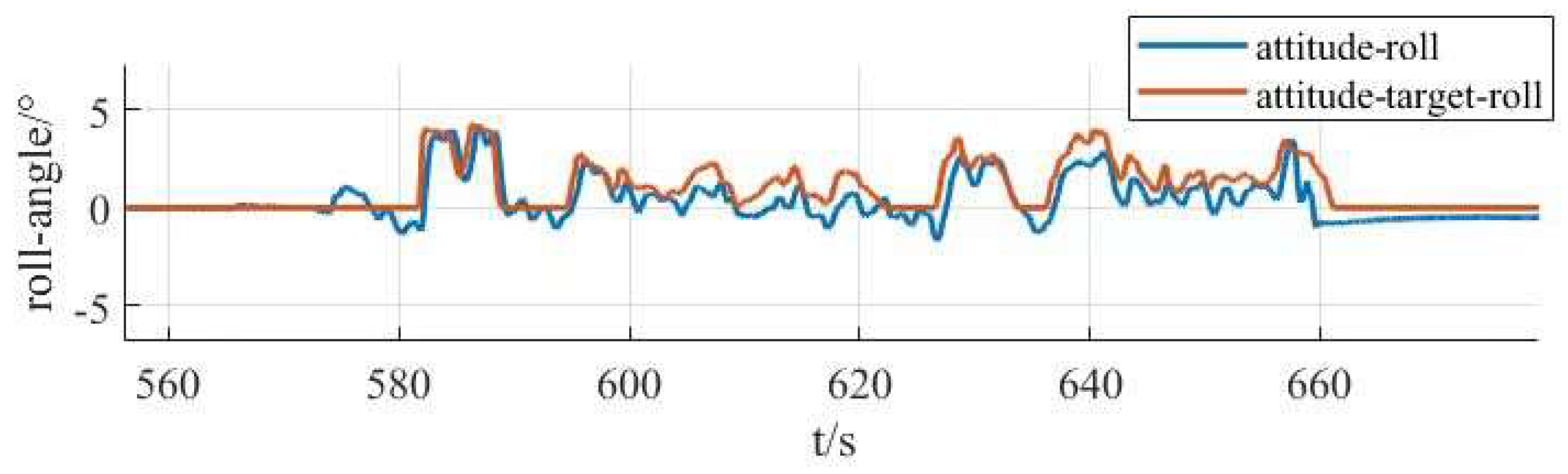
| parameters | numerical value | parameters | numerical value |
| fuselage length | 3000mm | tail rotor wheelbase | 2190mm |
| fuselage width | 548mm | Main tail rotor X-direction wheelbase | 1763.7mm |
| Fuselage height | 645mm | Maximum weight of the drone | 350 kg |
| wingspan | 4045mm | Maximum main rotor power | 160kw |
| tail spread | 2260mm | Tail rotor power | 18kw |
| main rotor wheelbase | 3695.4mm | thrust ratio | 1.3 |
| Optimization Variables | Bow-beam pole length L (mm) | Bow-beam angle α(°) | Mass m(kg) | maximum equivalent force (physics) σ(MPa) |
| pre-optimization | 600 | 120 | 5.795 | 616.54 |
| post-optimization | 579.15 | 123.9 | 5.758 | 412.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





