Submitted:
23 March 2025
Posted:
24 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Problem
1.2. Objectives
1.3. Summary of Method
1.4. Summary of Main Results
2. Methods
2.1. General Dark Energy Ratio Equation
2.2. Cartesian Solution to Dark Energy Ratio Equation
2.3. Polar Solution to Dark Energy Ratio Equation
2.3.1. Theorem Polar Dark Energy Equation
2.3.2. Proof Polar Dark Energy Equation
3. Dark Energy Percentage (%) Results
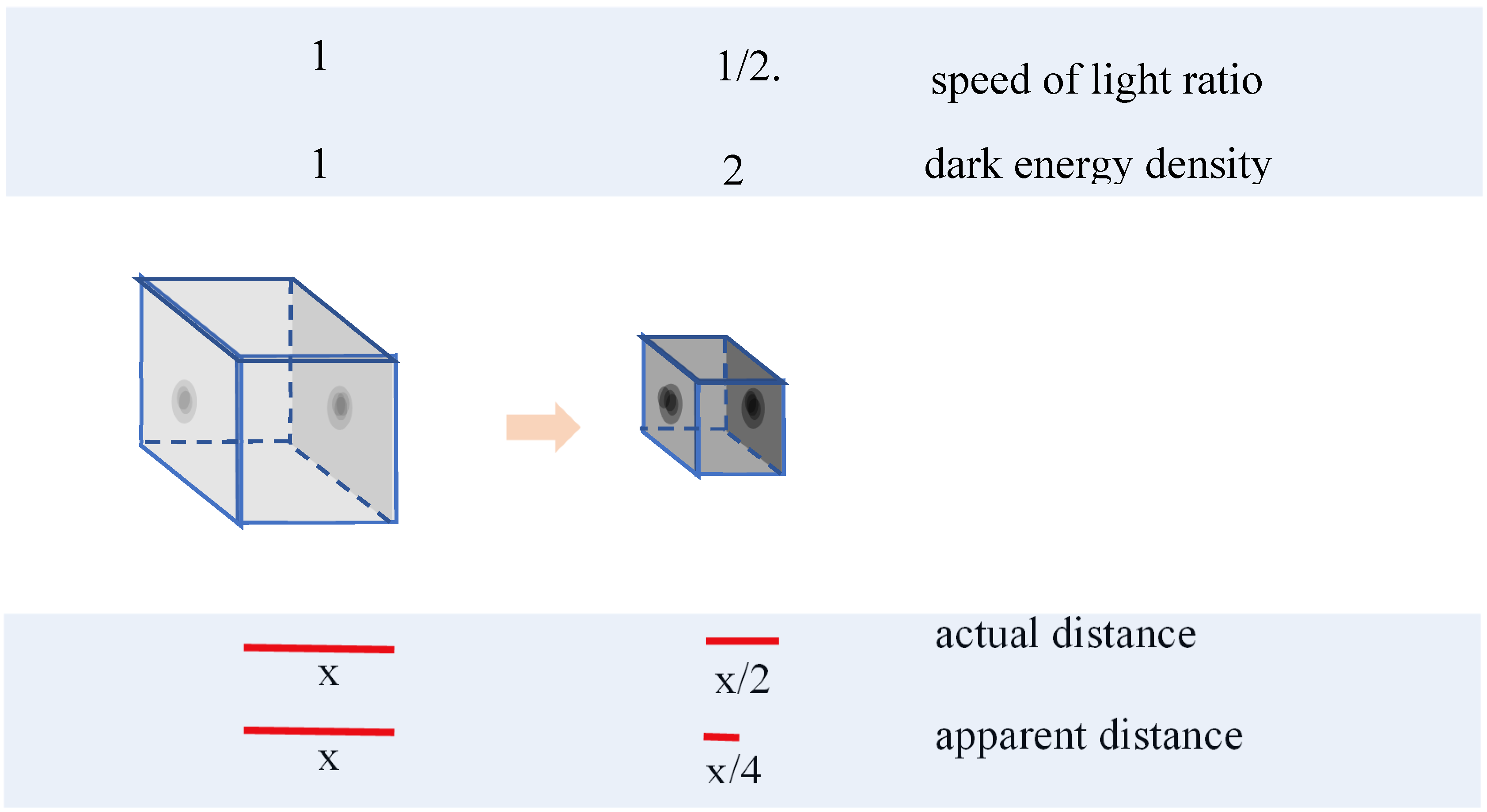
4. Discussion
4.1. Dark Energy Equation
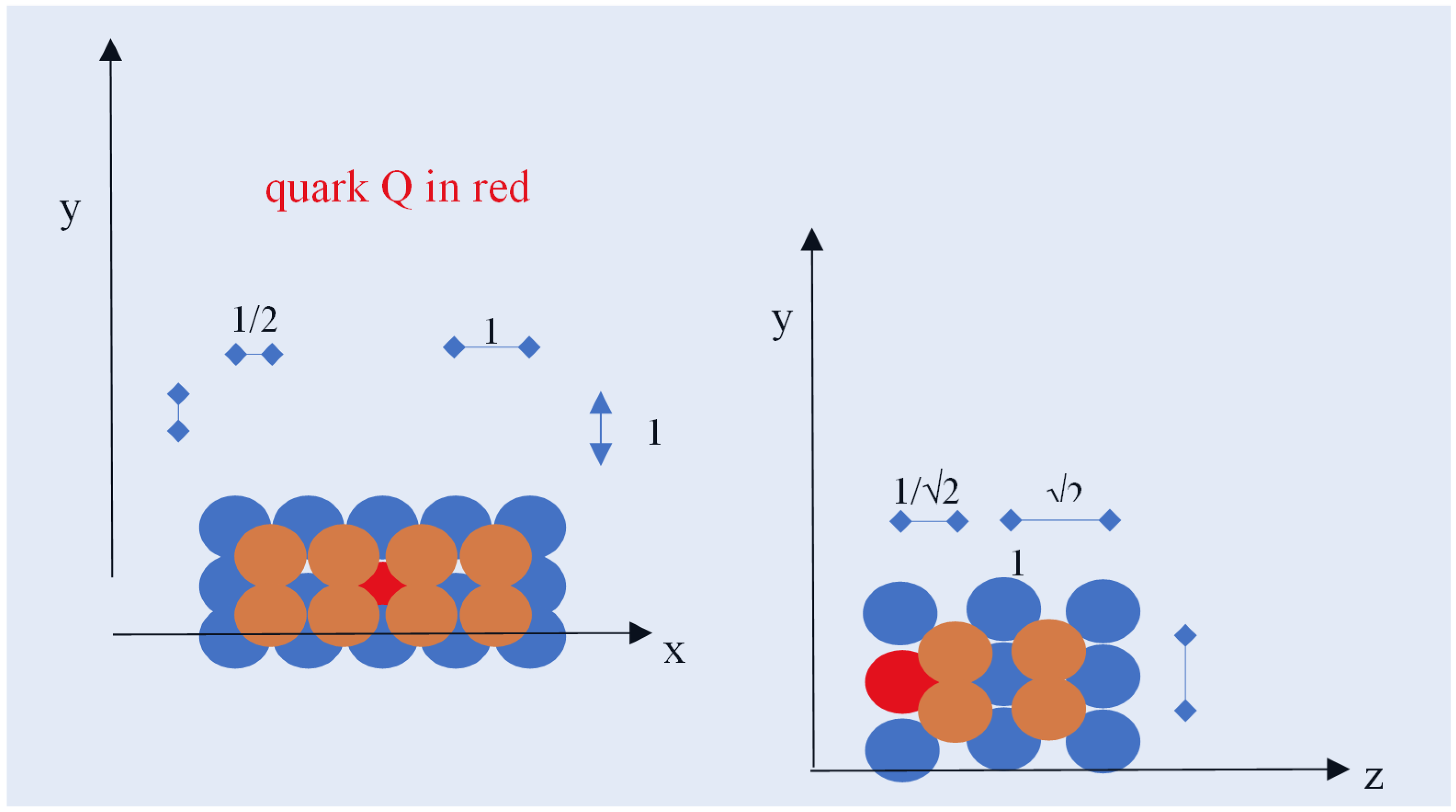
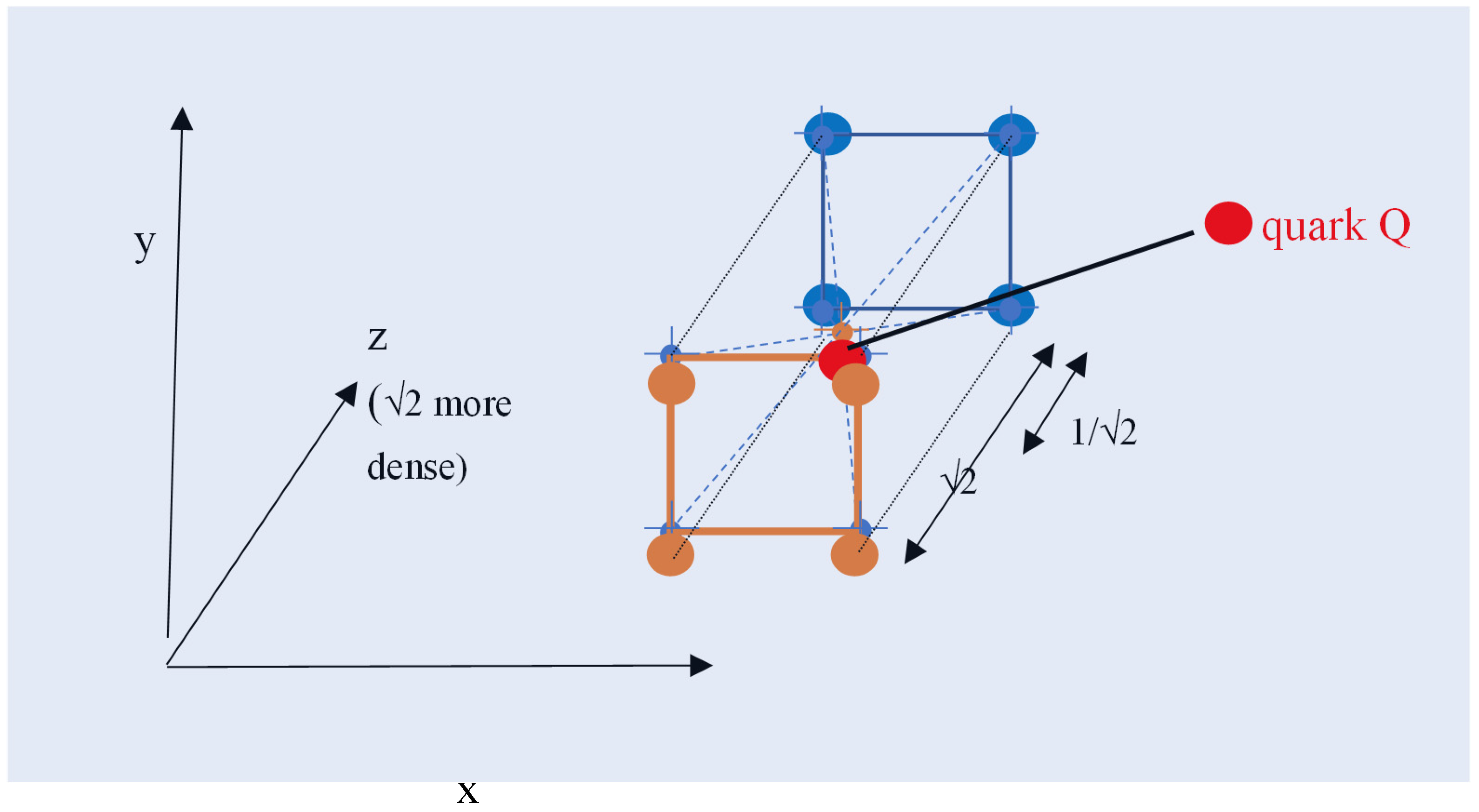
4.2. Radius of a Quark
4.3. Curvature of Space
4.4. Rate of Expansion of Dark Energy
4.5. Black Holes
5. Conclusion
6. Statements and Declarations
7. Appendices
8. Average Mass of a Quark
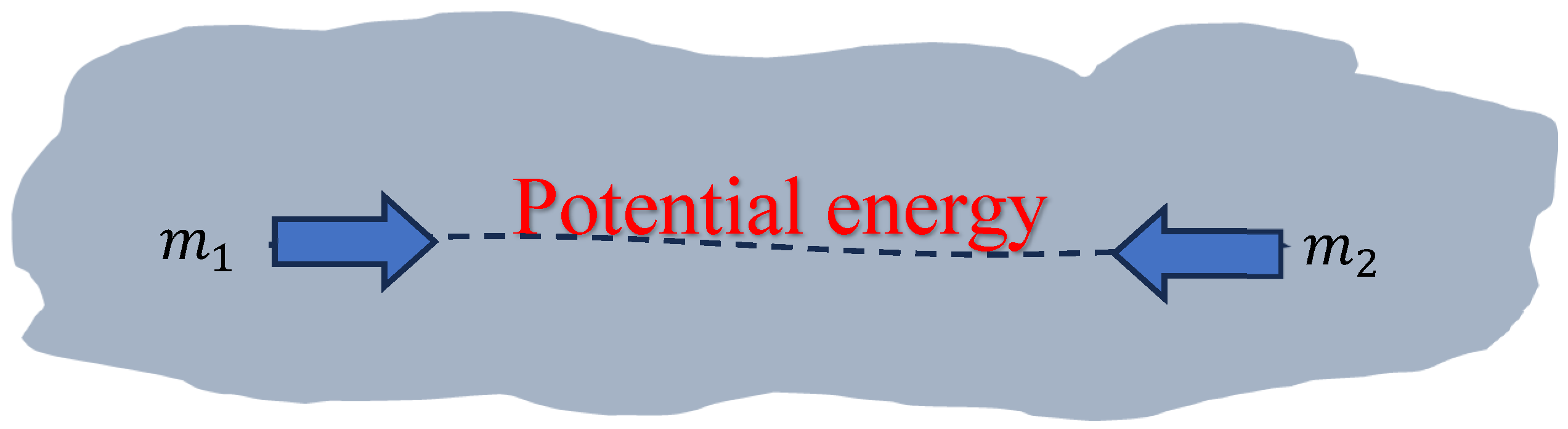
9. Two-Mass Theorems
9.1. Theorem: Marginal Energy Two Masses
9.2. Proof: Marginal Energy Two Masses
9.3. Theorem: Total Energy Released by Two Masses
9.4. Proof: Total Energy Released by Two Masses
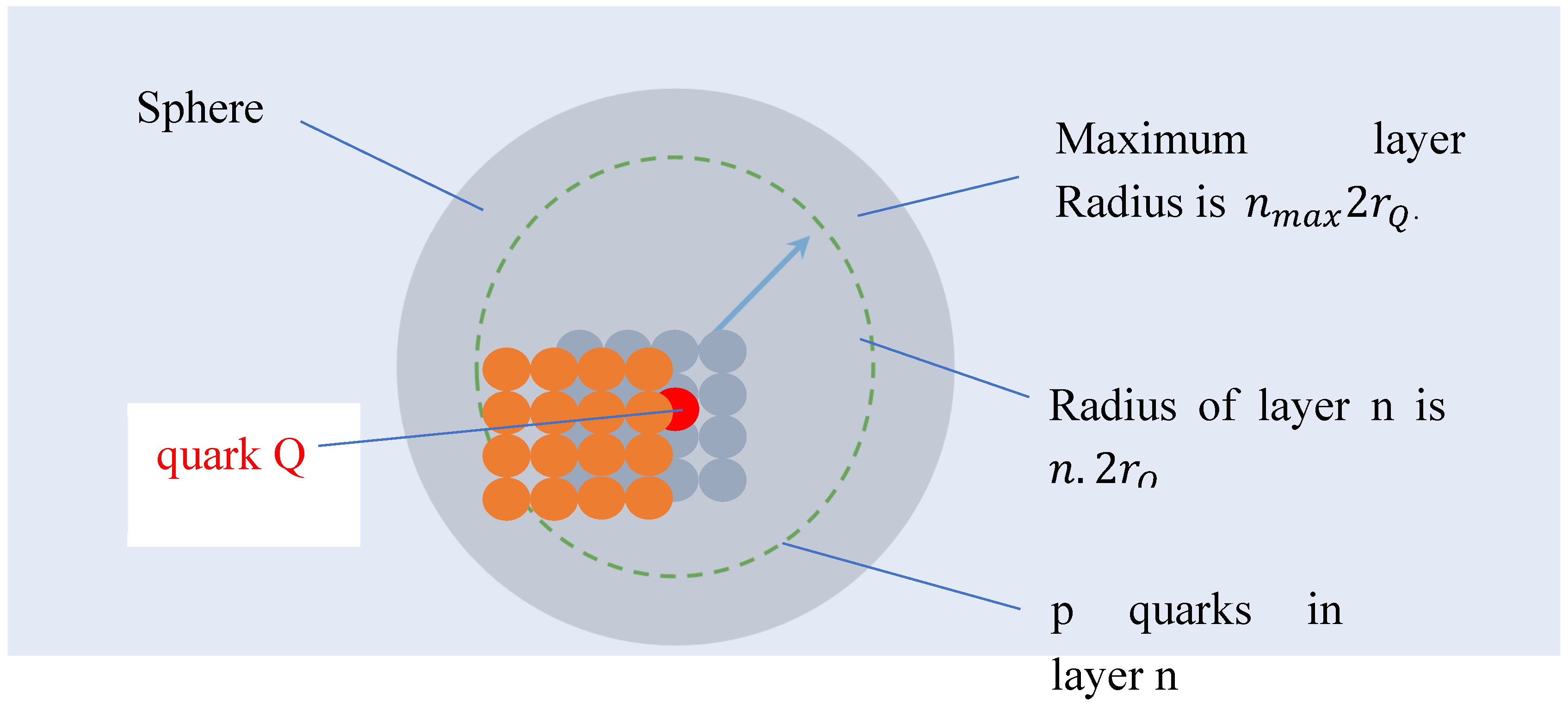
10. Theorem Dark Energy for n Masses
10.1. Theorem
10.2. Proof
References
- Bennett, C.L.; Larson, D.; Weiland, J.L.; Jarosik, N.; Hinshaw, G.; Odegard, N.; Smith, K.; Hill, R.; Gold, B.; Halpern, M.; et al. Nine-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: Final maps and results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 208, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark Energy: Theory and Observations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-521-51600-6. [Google Scholar]
- Misner, C.W.; Thorne, K.S.; Wheeler, J.A. Gravitation; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-691-17779-3. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan, T. Dark energy and gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2008, 40, 529–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnes, J. A unifying theory of dark energy and dark matter: Negative masses and matter creation within a modified CDM framework. Astrophys. J. 2018, 620, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.-P. Relativity, Gravitation and Cosmology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-19-9573646. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A. Relativity: The Special and General Theory; Martino Publishing: Eastford, CT, USA, 2010; ISBN 1-891396-30-7. [Google Scholar]
- Katti, A.N. The Mathematical Theory of Special and General Relativity; CreateSpace Publishing: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2017; ISBN 1-5305-0199-7. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A. The Principle of Relativity; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1952; ISBN 978-0-486-60081-3. [Google Scholar]
- Penrose, R. The Road to Reality: A Complete Guide to the Laws of the Universe; Vintage: London, UK, 2005; ISBN 0-099-44068-7. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, J.H.; Sloane, N.J.A.; Bannai, E. Sphere Packings, Lattices, and Groups; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-387-98585-5. [Google Scholar]
- ZEUS Collaboration. Limits on the effective quark radius from inclusive ep scattering at HERA. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 757, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A. Mass of the common quark finally nailed down. Science 2010, 328, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Gaztañaga, E. The mass of our observable universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2023, 521, L59–L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babb, E. New theory of general relativity giving the percentage of dark energy and solving the black hole time stop problem. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/127738030.
- Babb, E. A Modification to general relativity which calculates the expansion of dark energy, the Hubble constant, at an almost exact 71km/sec/megaparsec. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/42186366.
- Babb, E. A correction to general relativity that removes time and singularity problems with black holes and even gives the radius of a Quark. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/99161234.
- Berkeley Labs. Proportion of hydrogen and helium in the universe. Available online: https:w2.lbl.gov/abc/wallchart/chapters/10/0.html (accessed on 18 March 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



