Submitted:
20 March 2025
Posted:
21 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. MSC Preparation and Characterization
2.3. MSC Administration Protocol
2.4. Follow-Up and Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
-
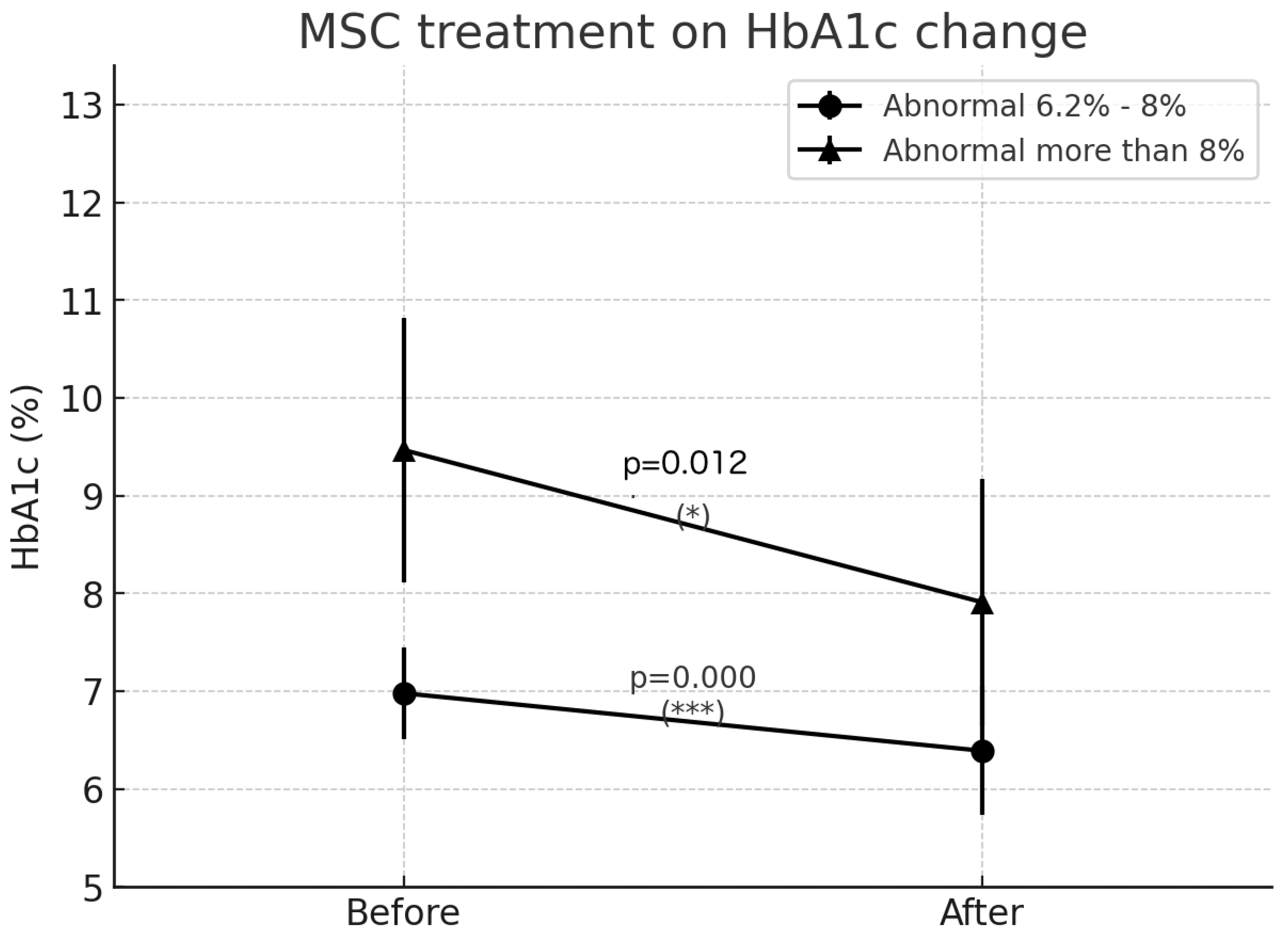
Moderate Diabetes Group (HbA1c 6.2-8%):
- o
- Mean HbA1c reduction: 0.58%
- o
- Statistical significance: p < 0.0000002 (highly significant)
-
Severe Diabetes Group (HbA1c >8%):
- o
- Mean HbA1c reduction: 1.55%
- o
- Statistical significance: p = 0.0122 (significant)
-
Sustained Effect Duration:
- o
- Median follow-up duration: 35.5 months
- o
- Interquartile range: 15.25 - 45.75 months
- o
- Correlation between duration and HbA1c reduction: 0.041 (no significant correlation)
| Sex | Age | Stem cell Dose x million cells |
HbA1c Before treatment | HbA1c After Treatment | Observed Month |
| M | 66 | 1000 | 7.5 | 6.4 | 27 |
| M | 66 | 2000 | 7.2 | 4.6 | 51 |
| M | 71 | 100 | 7.6 | 6.7 | 45 |
| M | 61 | 2000 | 7.1 | 6.5 | 18 |
| M | 76 | 2000 | 6.8 | 7.7 | 68 |
| M | 66 | 2000 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 13 |
| M | 79 | 1000 | 7.1 | 5.7 | 64 |
| M | 55 | 1000 | 6.8 | 5.9 | 18 |
| M | 72 | 1000 | 6.3 | 5.9 | 64 |
| M | 89 | 400 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 18 |
| F | 42 | 1000 | 7.2 | 8 | 62 |
| F | 60 | 1000 | 6.3 | 5.9 | 7 |
| M | 66 | 500 | 9.3 | 8.5 | 16 |
| M | 61 | 1000 | 7.2 | 6.9 | 53 |
| M | 52 | 2000 | 6.9 | 5.7 | 54 |
| M | 59 | 1000 | 6.4 | 5.1 | 53 |
| M | 63 | 2000 | 6.3 | 5.7 | 45 |
| F | 52 | 2000 | 6.4 | 5.7 | 47 |
| M | 69 | 2000 | 12.4 | 6.5 | 51 |
| M | 61 | 2000 | 7 | 6.9 | 46 |
| F | 53 | 2000 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 37 |
| M | 63 | 2000 | 7.9 | 7.2 | 45 |
| M | 66 | 2000 | 6.4 | 5.8 | 51 |
| F | 59 | 2000 | 10.3 | 7.4 | 44 |
| M | 69 | 2000 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 60 |
| F | 60 | 2000 | 7.3 | 6.3 | 40 |
| M | 64 | 2000 | 6.7 | 6.3 | 40 |
| M | 63 | 2000 | 6.8 | 6.3 | 40 |
| M | 64 | 2000 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 60 |
| F | 71 | 2000 | 8.7 | 7.4 | 39 |
| M | 65 | 2000 | 7.8 | 7.9 | 44 |
| M | 62 | 2000 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 45 |
| M | 47 | 2000 | 6.4 | 6.2 | 35 |
| F | 61 | 2000 | 7.5 | 6.7 | 42 |
| F | 57 | 100 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 14 |
| F | 58 | 2000 | 11.9 | 8.4 | 16 |
| F | 77 | 2000 | 7.5 | 6.4 | 19 |
| M | 59 | 2000 | 6.7 | 6.4 | 27 |
| F | 71 | 2000 | 6.9 | 7.4 | 17 |
| M | 48 | 2000 | 7.2 | 6.6 | 15 |
| F | 70 | 2000 | 6.4 | 5.9 | 17 |
| F | 60 | 2000 | 9.3 | 10.9 | 22 |
| M | 62 | 2000 | 8 | 6.6 | 25 |
| M | 66 | 2000 | 7.1 | 6.4 | 6 |
| M | 59 | 2000 | 6.9 | 6.4 | 11 |
| M | 67 | 400 | 8.2 | 8.2 | 9 |
| M | 45 | 2000 | 7.8 | 6.1 | 12 |
| M | 72 | 1000 | 7.7 | 7.2 | 14 |
| M | 68 | 2000 | 6.9 | 7 | 14 |
| M | 80 | 2000 | 6.5 | 5.8 | 14 |
| M | 76 | 2000 | 6.4 | 5.5 | 15 |
| M | 56 | 1000 | 9.8 | 8.4 | 16 |
| F | 74 | 700 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 7 |
| M | 46 | 2000 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 41 |
| M | 67 | 2000 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 48 |
| M | 64 | 2000 | 8.3 | 5.4 | 36 |
| F | 43 | 500 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 9 |
| M | 72 | 500 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 15 |
4. Discussion
- D’Addio et al. (2014) reported that 59% of patients achieved insulin independence within 6 months, with 32% remaining insulin-free at the last follow-up.
- Hu et al. (2016) observed a significant reduction in insulin requirements, with 32.3% of patients achieving insulin withdrawal.
- Voltarelli et al. (2009) found that 14 out of 15 patients became insulin-free for varying durations.
- Zang et al. (2022) reported a significant reduction in insulin requirements, with a higher percentage of insulin reduction in the UC-MSCs group compared to placebo.
- Snarski et al. (2011) observed that all patients became independent of exogenous insulin after treat- ment, although one patient resumed low-dose insulin after 7 months.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuoka T, Itohara T, Hara Y, Kobayashi N. Systematic Intravenous Administration of Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Is Safe. J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 7;13(23):7460. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu J, Wang Y, Gong H, Yu C, Guo C, Wang F, Yan S, Xu H. Long term effect and safety of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on type 2 diabetes. Exp Ther Med. 2016 Sep;12(3):1857-1866. Epub 2016 Jul 26. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bhansali, Premkumar Asokumar, R. Walia, S. Bhansali, Vivek Gupta, Ashish Jain, N. Sachdeva, R. Sharma, N. Marwaha, and N. Khandelwal.. Efficacy and Safety of Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. Bhansali, Premkumar Asokumar, R. Walia, S. Bhansali, Vivek Gupta, Ashish Jain, N. Sachdeva, R. Sharma, N. Marwaha, and N. Khandelwal. “Efficacy and Safety of Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study.” Cell Transplantation. 2014.
- E. Snarski, A. Milczarczyk, T. Torosian, M. Paluszewska, E. Urbanowska, M. Król, P. Boguradzki, et al.. Independence of Exogenous Insulin Following Immunoablation and Stem Cell Reconstitution in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Type I. Snarski, A. Milczarczyk, T. Torosian, M. Paluszewska, E. Urbanowska, M. Król, P. Boguradzki, et al. “Independence of Exogenous Insulin Following Immunoablation and Stem Cell Reconstitution in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Type I.” Bone Marrow Transplantation. 2011.
- F. D’Addio, Alessandro Valderrama Vasquez, M. Ben Nasr, Edward Franek, Dalong Zhu, Lirong Li, G. Ning, E. Snarski, and P. Fiorina.. Autologous Nonmyeloablative Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicenter Analysis. D’Addio, Alessandro Valderrama Vasquez, M. Ben Nasr, Edward Franek, Dalong Zhu, Lirong Li, G. Ning, E. Snarski, and P. Fiorina. “Autologous Nonmyeloablative Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicenter Analysis.” Diabetes. 2014.
- J. G. Penaforte-Saboia, R. Montenegro, C. Couri, L. Batista, A. P. Montenegro, V. Fernandes, H. Akhtar, et al.. Microvascular Complications in Type 1 Diabetes: A Comparative Analysis of Patients Treated with Autologous Nonmyeloablative Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation and Conventional Medical Therapy. G. Penaforte-Saboia, R. Montenegro, C. Couri, L. Batista, A. P. Montenegro, V. Fernandes, H. Akhtar, et al. “Microvascular Complications in Type 1 Diabetes: A Comparative Analysis of Patients Treated with Autologous Nonmyeloablative Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation and Conventional Medical Therapy.” Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2017.
- J. Gan, Yingjin Wang, and Xiaodong Zhou.. Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Gan, Yingjin Wang, and Xiaodong Zhou. “Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis.” Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2018.
- J. Markmann, A. Naji, M. Rickels, Maria Alba, G. Marigowda, Leorah Ross, Chenkun Wang, et al.. 259-OR: Stem Cell–Derived, Fully Differentiated Islet Cells for Type 1 Diabetes. Markmann, A. Naji, M. Rickels, Maria Alba, G. Marigowda, Leorah Ross, Chenkun Wang, et al. “259-OR: Stem Cell–Derived, Fully Differentiated Islet Cells for Type 1 Diabetes.” Diabetes. 2022.
- J. Skyler, V. Fonseca, K. Segal, and J. Rosenstock.. Allogeneic Mesenchymal Precursor Cells in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Escalation Safety and Tolerability Pilot Study. Skyler, V. Fonseca, K. Segal, and J. Rosenstock. “Allogeneic Mesenchymal Precursor Cells in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Escalation Safety and Tolerability Pilot Study.” Diabetes Care. 2015.
- J. Voltarelli, C. Couri, A. Stracieri, M. Oliveira, D. Moraes, F. Pieroni, M. Coutinho, et al.. Autologous Non- myeloablative Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Voltarelli, C. Couri, A. Stracieri, M. Oliveira, D. Moraes, F. Pieroni, M. Coutinho, et al. “Autologous Non- myeloablative Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.” Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). 2009.
- Jianxia Hu, Yangang Wang, Huimin Gong, Chundong Yu, Caihong Guo, F. Wang, Shengli Yan, and Hongmei Xu.. Long Term Effect and Safety of Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Type 2 Diabetes. Wang, Shengli Yan, and Hongmei Xu. “Long Term Effect and Safety of Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Type 2 Diabetes.” Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2016.
- Jing Lu, S. Shen, Qing Ling, Bin Wang, Li-rong Li, Wei Zhang, Duo-duo Qu, Y. Bi, and Dalong Zhu.. One Repeated Transplantation of Allogeneic Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Type 1 Diabetes: An Open Parallel Controlled Clinical Study. Shen, Qing Ling, Bin Wang, Li-rong Li, Wei Zhang, Duo-duo Qu, Y. Bi, and Dalong Zhu. “One Repeated Transplantation of Allogeneic Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Type 1 Diabetes: An Open Parallel Controlled Clinical Study.” Stem Cell Research & Therapeutics. 2020.
- L. Nguyen, Duc M. Hoang, Kien T. Nguyen, D. Bui, Hieu T Nguyen, Hong T A Le, Van T. Hoang, et al.. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Duration and Obesity Alter the Efficacy of Autologously Transplanted Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells. Nguyen, Duc M. Hoang, Kien T. Nguyen, D. Bui, Hieu T Nguyen, Hong T A Le, Van T. Hoang, et al. “Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Duration and Obesity Alter the Efficacy of Autologously Transplanted Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells.” Stem Cells Translational Medicine. 2021.
- L. Zang, Yijun Li, Hao-jie Hao, Jiejie Liu, Qian Zhang, Fei Gao, Haibin Wang, et al.. Efficacy of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Assessed by Retrospective Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Zang, Yijun Li, Hao-jie Hao, Jiejie Liu, Qian Zhang, Fei Gao, Haibin Wang, et al. “Efficacy of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Assessed by Retrospective Continuous Glucose Monitoring.” Stem Cells Translational Medicine. 2023.
- L. Zang, Yijun Li, Hao-jie Hao, Jiejie Liu, Yu Cheng, Bing Li, Y. Yin, et al.. Efficacy and Safety of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Chinese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Single-Center, Double- Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial. Zang, Yijun Li, Hao-jie Hao, Jiejie Liu, Yu Cheng, Bing Li, Y. Yin, et al. “Efficacy and Safety of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Chinese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Single-Center, Double- Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial.” Stem Cell Research & Therapeutics. 2022.
- Lirong Li, S. Shen, J. Ouyang, Yun Hu, Limin Hu, Weijuan Cui, Ning Zhang, et al.. Autologous Hematopoi- etic Stem Cell Transplantation Modulates Immunocompetent Cells and Improves -Cell Function in Chi- nese Patients with New Onset of Type 1 Diabetes. Shen, J. Ouyang, Yun Hu, Limin Hu, Weijuan Cui, Ning Zhang, et al. “Autologous Hematopoi- etic Stem Cell Transplantation Modulates Immunocompetent Cells and Improves -Cell Function in Chi- nese Patients with New Onset of Type 1 Diabetes.” Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2012.
- M. Izadi, Anavasadat Sadr Hashemi Nejad, M. Moazenchi, S. Masoumi, A. Rabbani, Farzad Kompani, Amir Abbas Hedayati Asl, et al.. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Newly Diagnosed Type-1 Diabetes Patients: A Phase I/II Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Izadi, Anavasadat Sadr Hashemi Nejad, M. Moazenchi, S. Masoumi, A. Rabbani, Farzad Kompani, Amir Abbas Hedayati Asl, et al. “Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Newly Diagnosed Type-1 Diabetes Patients: A Phase I/II Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.” Stem Cell Research & Therapeutics. 2021.
- P. Carlsson, D. Espes, L. Davies, and M. Svahn. “Dose-Dependent Preservation of Beta-Cell Function in Type i Diabetes by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells,” 2020.
- Pin Chen, Qin Huang, Xiangjin Xu, Z. Shao, Huang Lh, Yang Xz, W. Guo, Li Cm, and C. Chen.. [The Effect of Liraglutide in Combination with Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Treatment on Glucose Metabolism and Cell Function in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus]. Shao, Huang Lh, Yang Xz, W. Guo, Li Cm, and C. Chen. “[The Effect of Liraglutide in Combination with Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Treatment on Glucose Metabolism and Cell Function in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus].” Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2016.
- U. Thakkar, H. Trivedi, A. Vanikar, and S. Dave.. Insulin-Secreting Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells with Bone Marrow-Derived Hematopoietic Stem Cells from Autologous and Allogenic Sources for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Thakkar, H. Trivedi, A. Vanikar, and S. Dave. “Insulin-Secreting Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells with Bone Marrow-Derived Hematopoietic Stem Cells from Autologous and Allogenic Sources for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.” Cytotherapy. 2015.
- V. Sood, A. Bhansali, B. Mittal, Baljinder Singh, N. Marwaha, Ashish Jain, and N. Khandelwal.. Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cell Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Defining Adequate Administration Methods. Sood, A. Bhansali, B. Mittal, Baljinder Singh, N. Marwaha, Ashish Jain, and N. Khandelwal. “Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cell Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Defining Adequate Administration Methods.” World Journal of Diabetes. 2017.
- Wenwen Li, X. Jiao, Jing-yun Song, B. Sui, Zhili Guo, Yingji Zhao, Jun Li, S. Shi, and Qin Huang.. Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Infusion into Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Depends on Basal Lipid Levels and Islet Function. Jiao, Jing-yun Song, B. Sui, Zhili Guo, Yingji Zhao, Jun Li, S. Shi, and Qin Huang. “Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Infusion into Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Depends on Basal Lipid Levels and Islet Function.” Stem Cells Translational Medicine. 2021.
- Xianliang Gu, Xi Yu, Chen Zhao, P. Duan, Tongtao Zhao, Yong Liu, Shiying Li, et al.. Efficacy and Safety of Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. Duan, Tongtao Zhao, Yong Liu, Shiying Li, et al. “Efficacy and Safety of Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy.” Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2018.
- Xiaoyu Lian, Dong-Hui Lu, Hong-Li Liu, Yanjun Liu, Xiu-Qun Han, Yang Yang, Yuan Lin, et al.. Effectiveness and Safety of Human Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. “Effectiveness and Safety of Human Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.” World Journal of Diabetes. 2022.
- Yong Zhao, Zhaoshun Jiang, Tingbao Zhao, Mingliang Ye, Chengjin Hu, Hui-min Zhou, Zhaohui Yin, et al.. Targeting Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes via Immune Modulation of Cord Blood-Derived Multipotent Stem Cells (CB-SCs) in Stem Cell Educator Therapy: Phase I/II Clinical Trial. “Targeting Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes via Immune Modulation of Cord Blood-Derived Multipotent Stem Cells (CB-SCs) in Stem Cell Educator Therapy: Phase I/II Clinical Trial.” BMC Medicine. 2013.
- Yong Zhao, Zhaoshun Jiang, Tingbao Zhao, Mingliang Ye, Chengjin Hu, Zhaohui Yin, Heng Li, et al.. Reversal of Type 1 Diabetes via Islet Cell Regeneration Following Immune Modulation by Cord Blood- Derived Multipotent Stem Cells. “Reversal of Type 1 Diabetes via Islet Cell Regeneration Following Immune Modulation by Cord Blood- Derived Multipotent Stem Cells.” BMC Medicine. 2012.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




