Submitted:
02 May 2024
Posted:
06 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
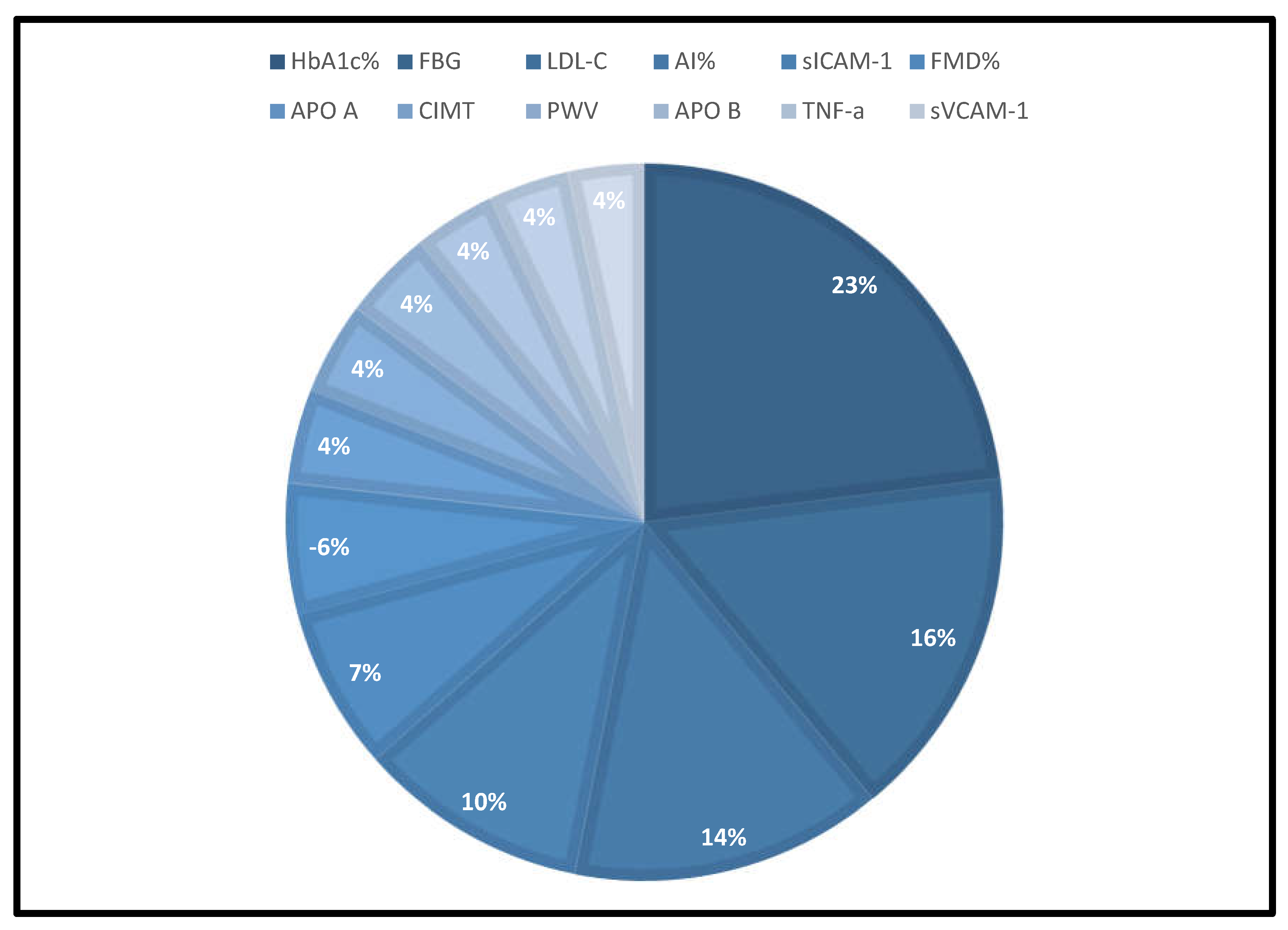
- Six major biomarkers have been identified as potential diagnostic surrogates that could indicate the onset of diabetes-induced ED in persons under the age of 40 years.
- They consist of HbA1c%, FBG, LDL-c, AI%, sICAM-1, and FMD% which could be measured with a simple blood test or non-invasive techniques.
- These markers are particularly important for the children, adolescents, young adults, and clinicians who find managing diabetes a very challenging and arduous task.
- These markers should be regularly tested in the clinic as routine investigative metabolic checkpoints that will reveal the health status of the younger population which is vitally important for their wellbeing.
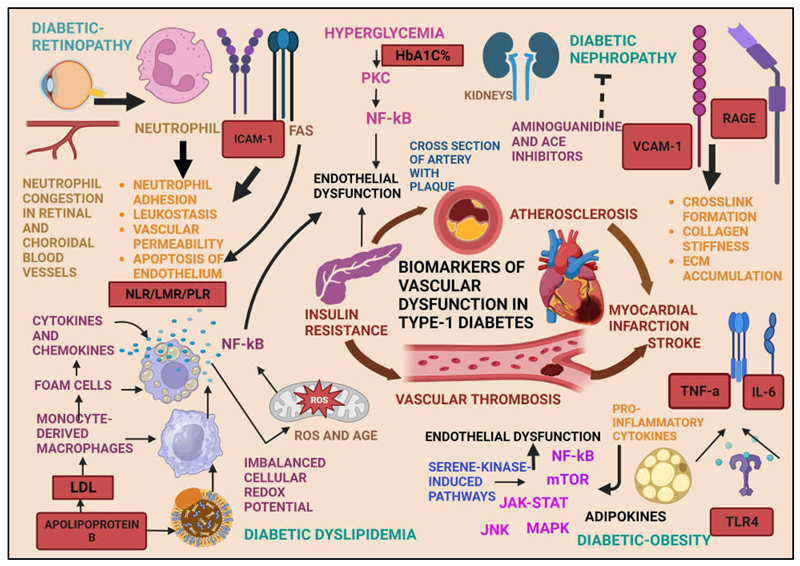
1. Introduction
1.1. Diabetes
1.2. T1D

1.3. CVD
1.4. Risk Factors
1.5. Research Question
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria for Considering Studies for This Meta-Analysis
2.2. Types of Outcome Measures
2.3. Search Methods for Identification of Studies
2.4. Data Collection and Analysis
2.5. Data Extraction and Management
2.6. Assessment of Risk of Bias
2.6.1. Assessment of Reporting Biases
2.7. Data Synthesis and Measures of Treatment Effect Size
2.8. Assessment of Heterogeneity
2.8.1. Subgroup Analysis and Investigation of Heterogeneity
2.8.2. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
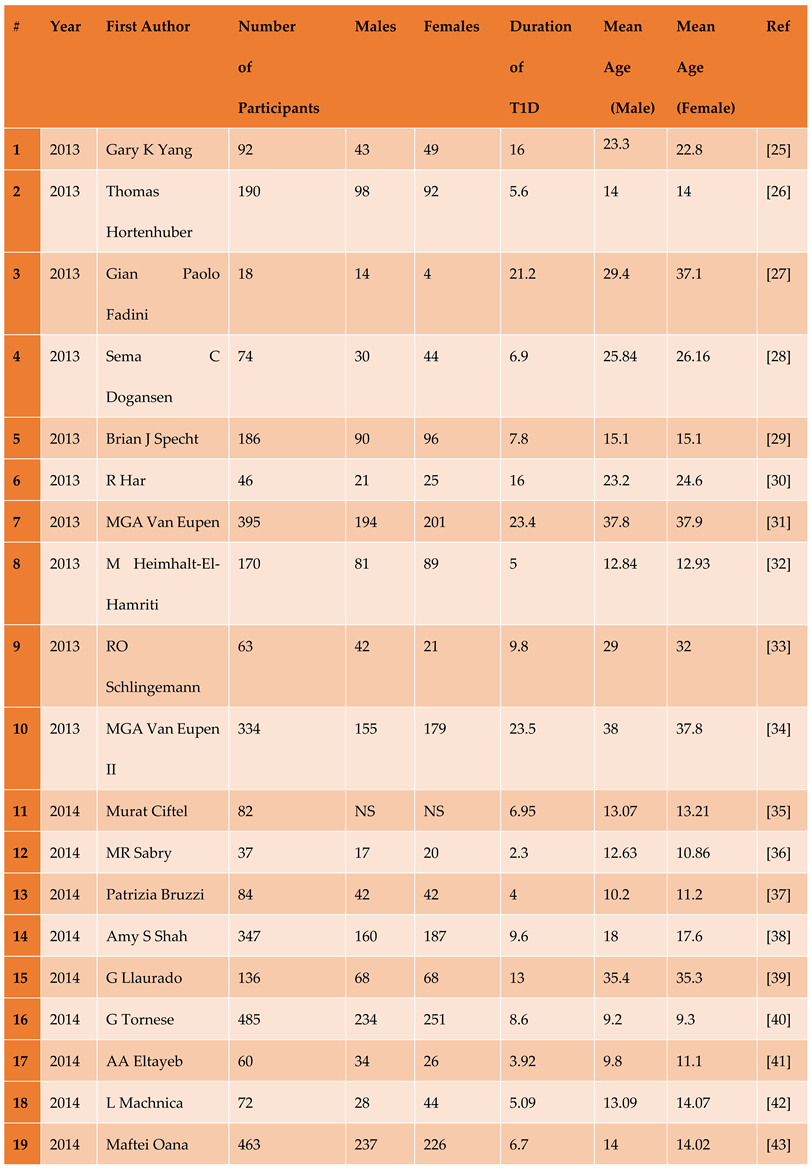
3.1. Description of Included Studies
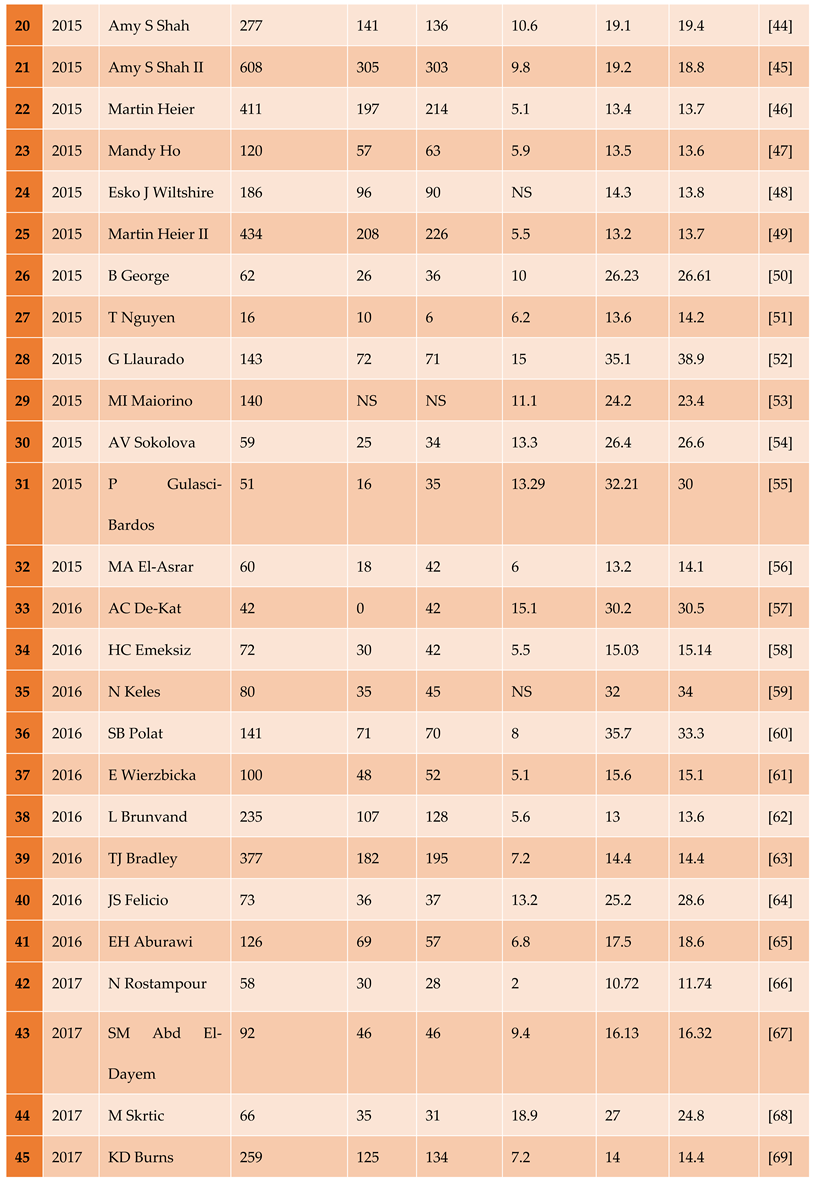
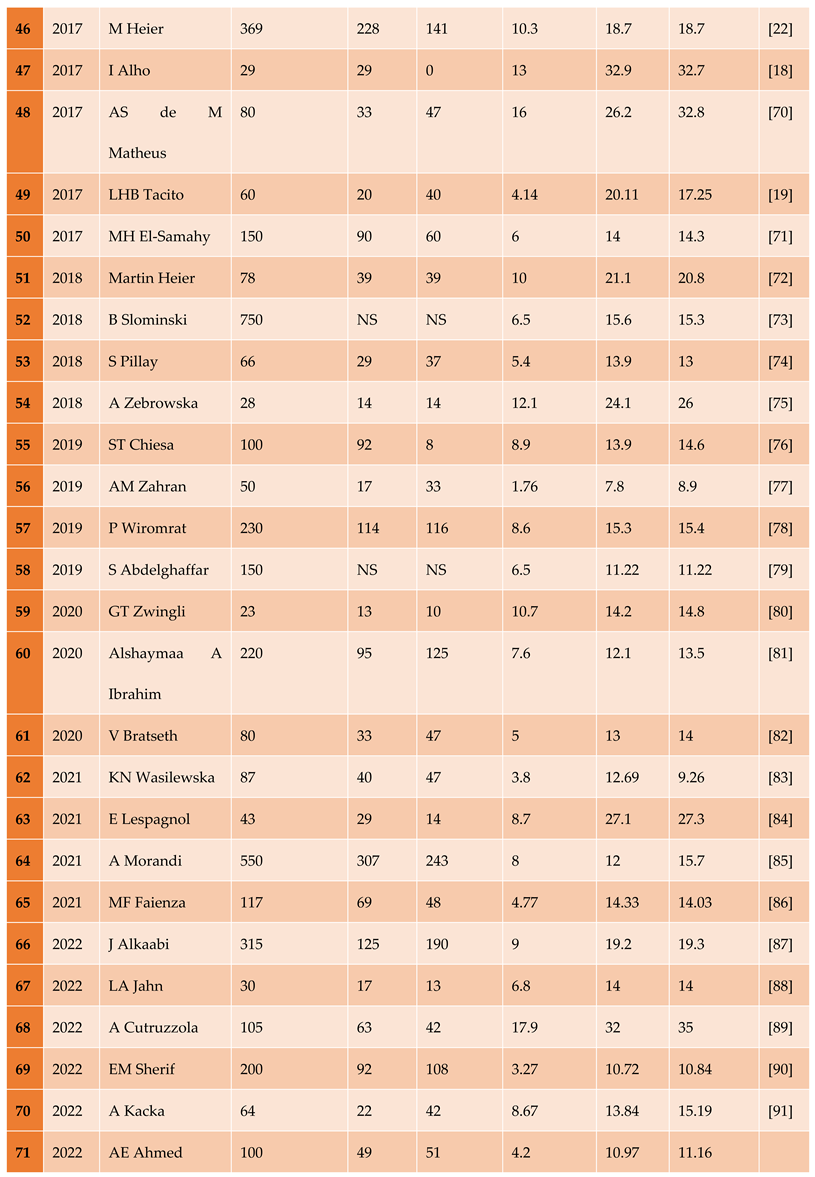
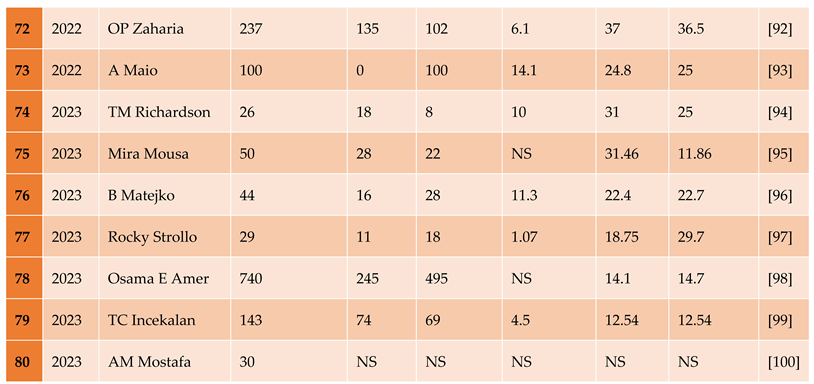
3.1.1. The Included Studies Comprised of 80 Relevant Research Articles
3.2. Results of the Search
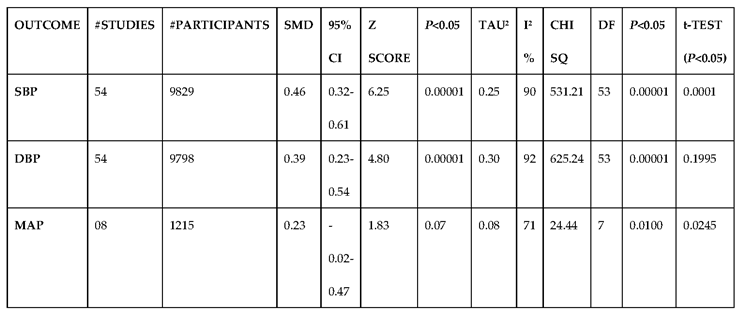
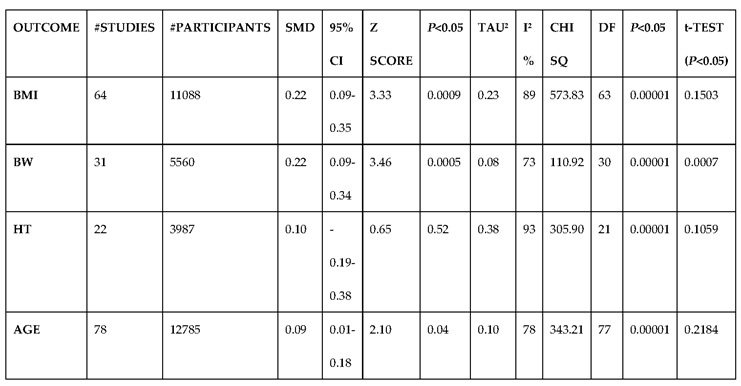
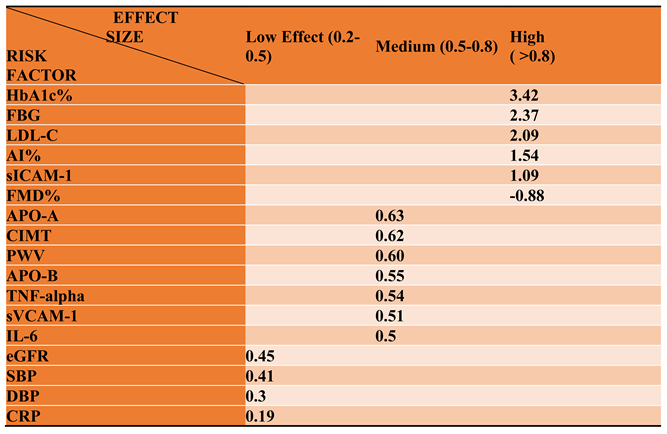
3.2.1. The Blood Pressure Makes a Moderate Impact on the T1D-Induced ED
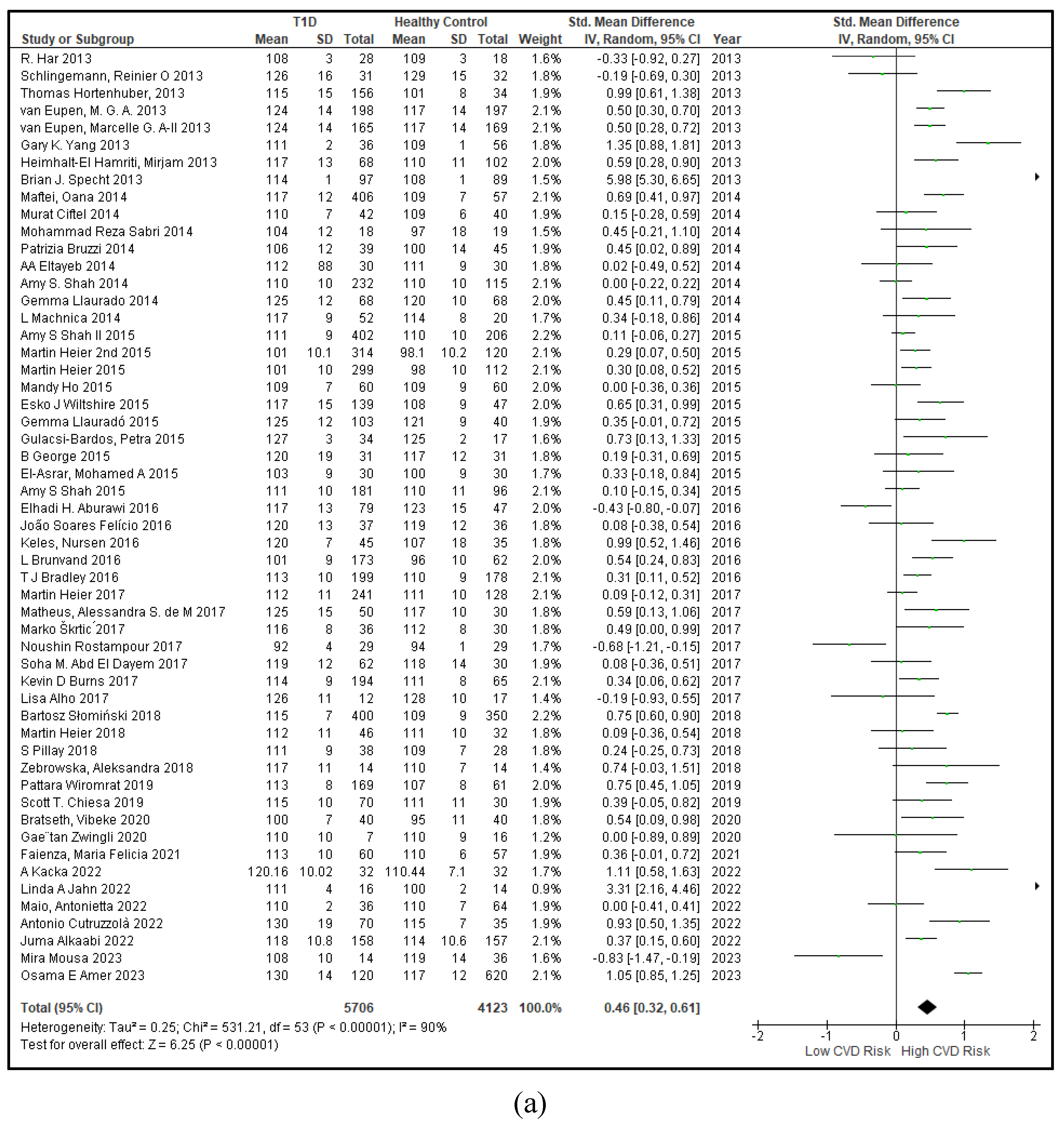
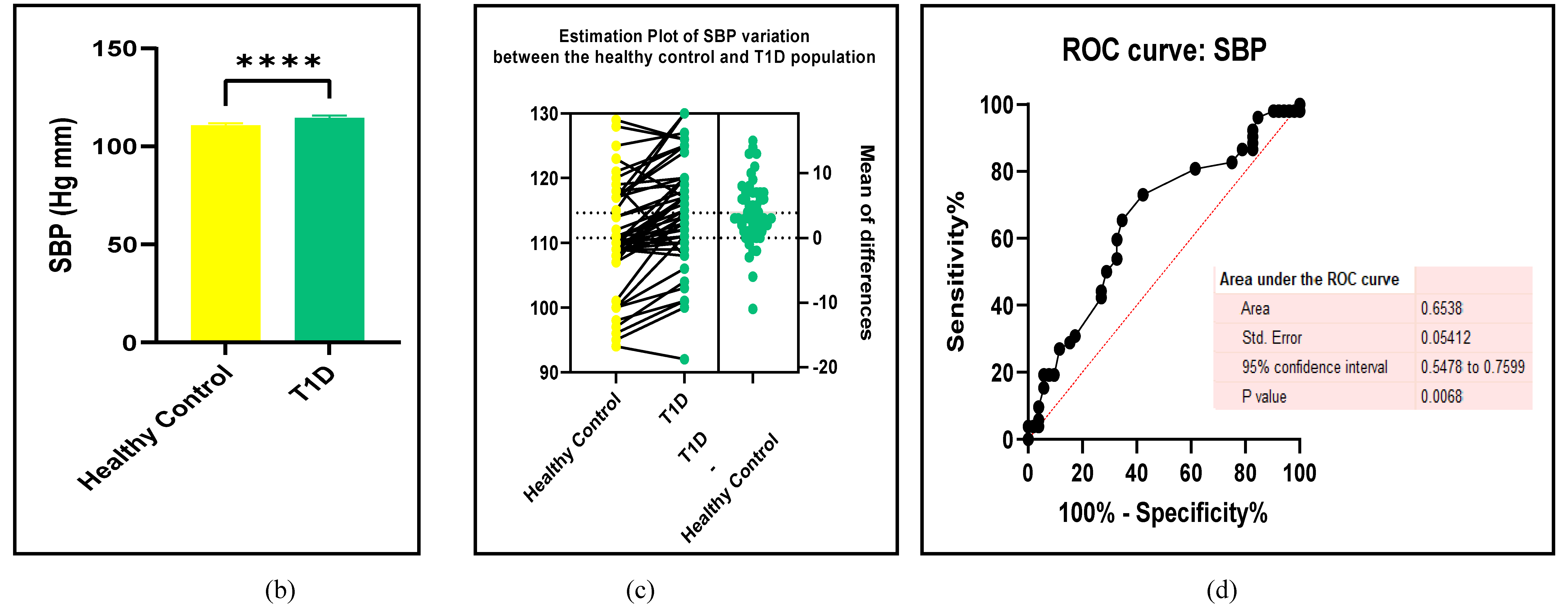
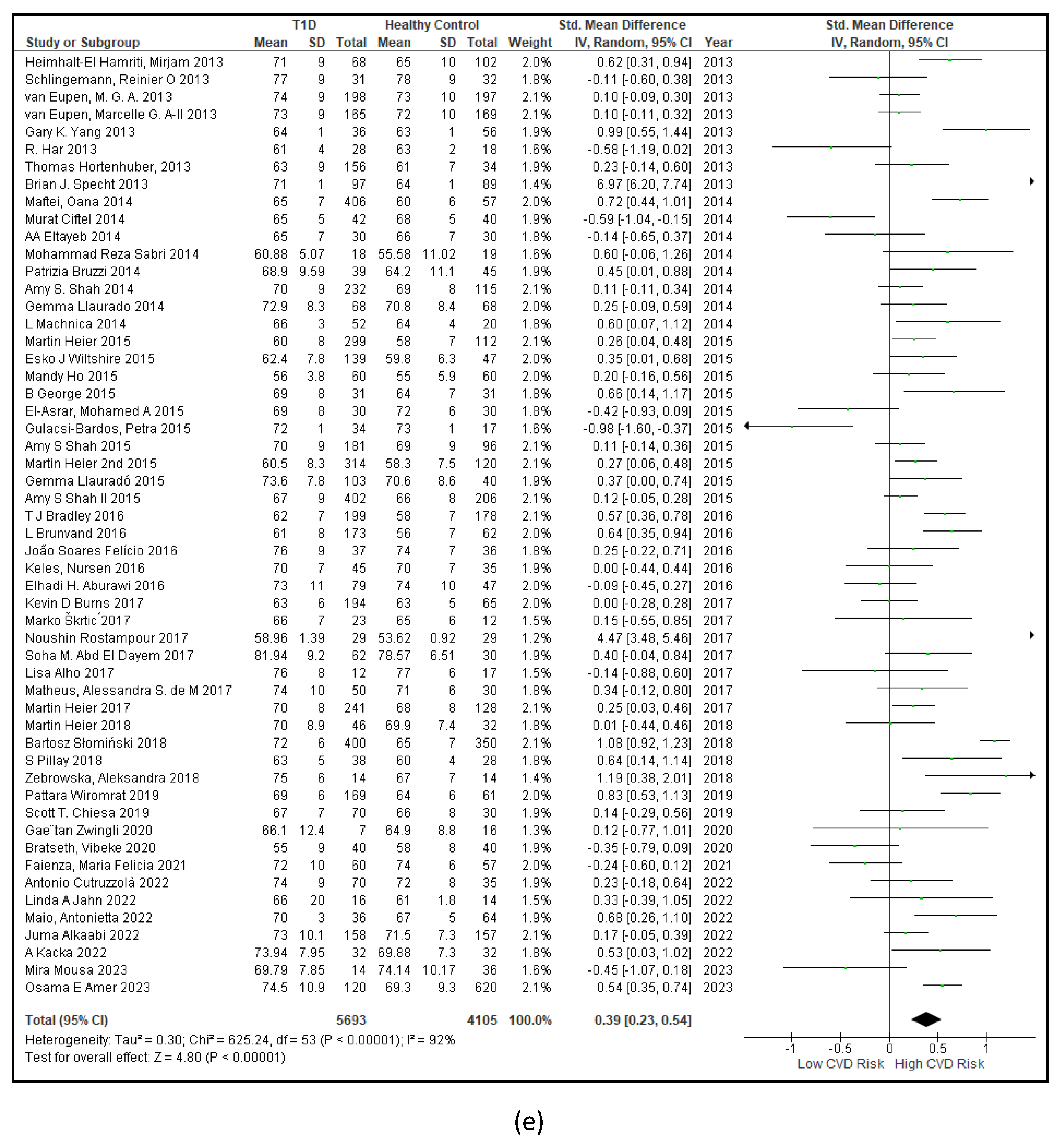
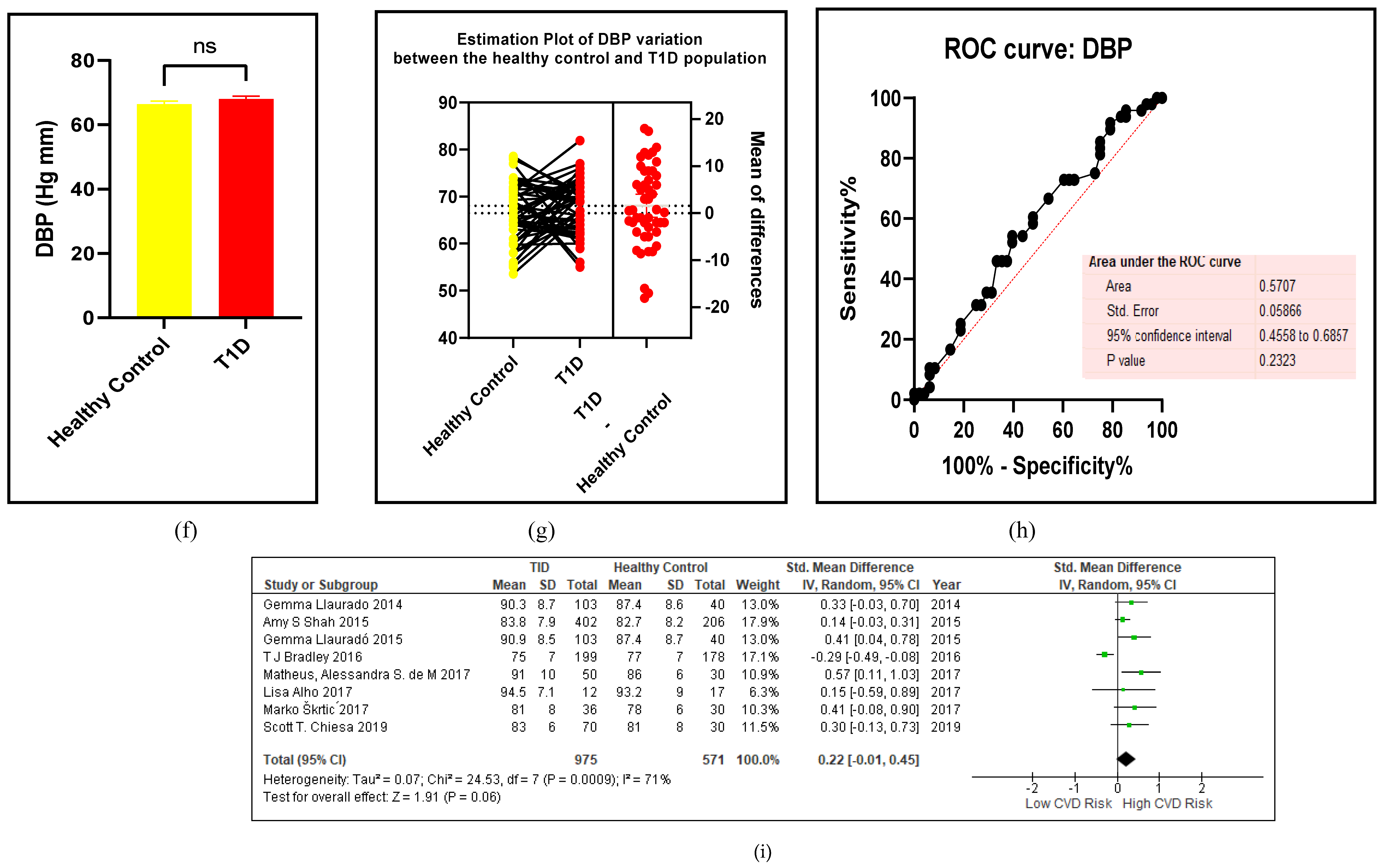
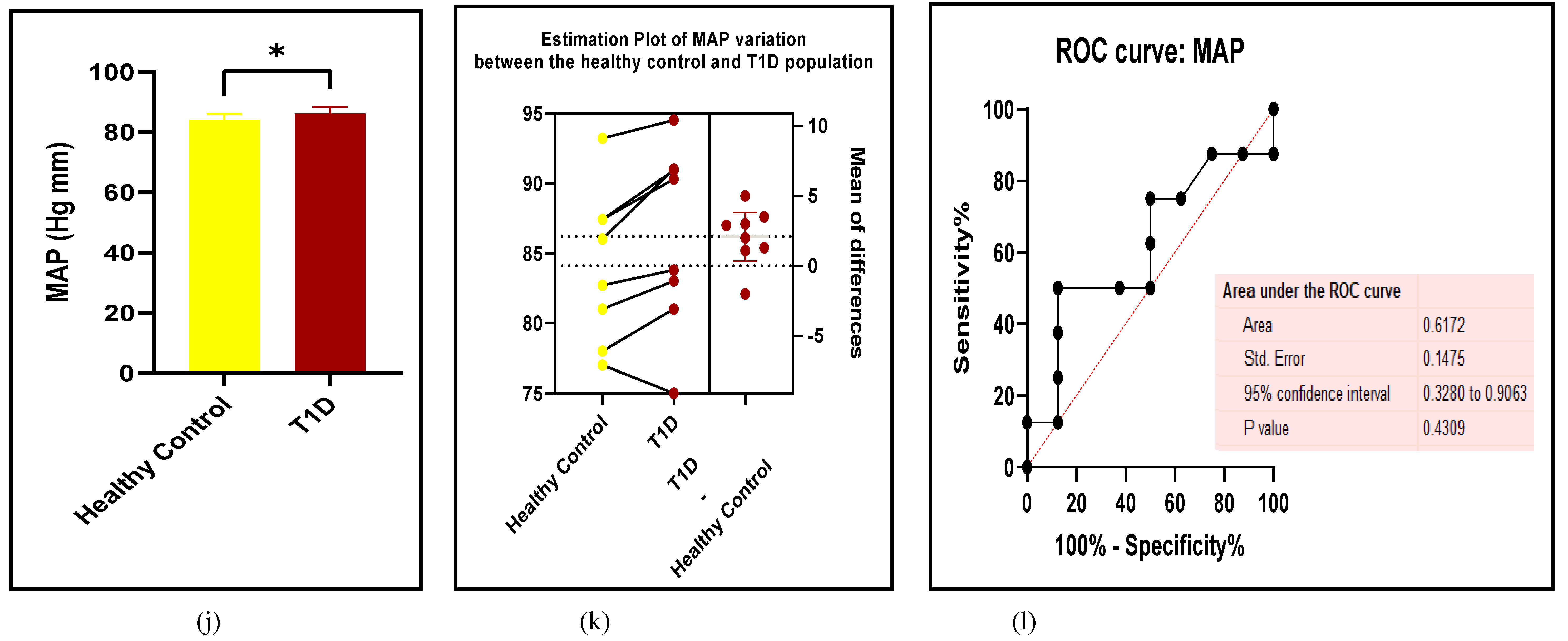
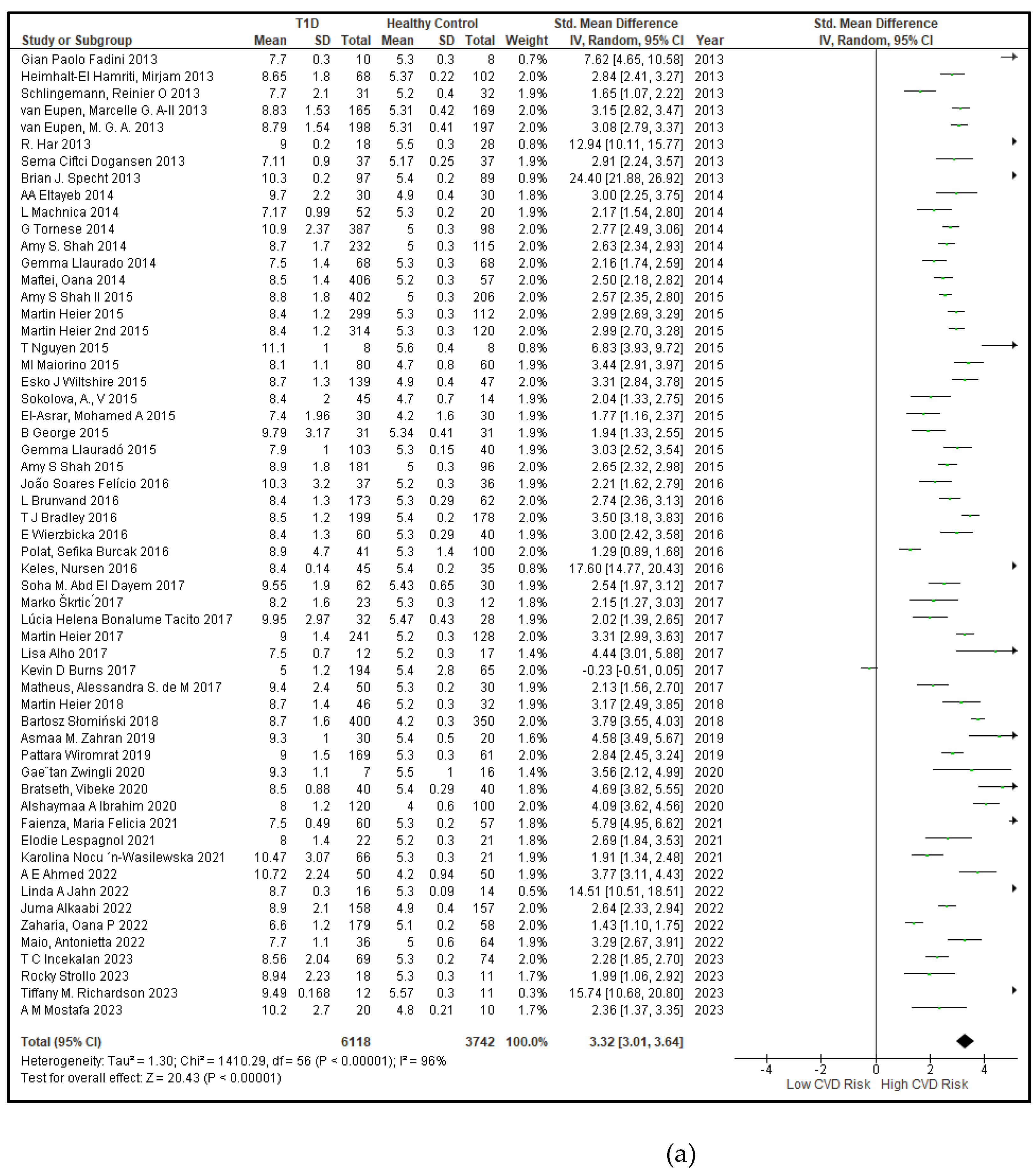
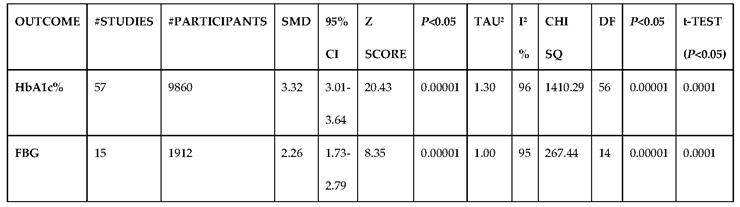
3.2.2. Glucose Metabolism Is the Best Diagnostic Biomarker for Confirming T1D-Induced ED
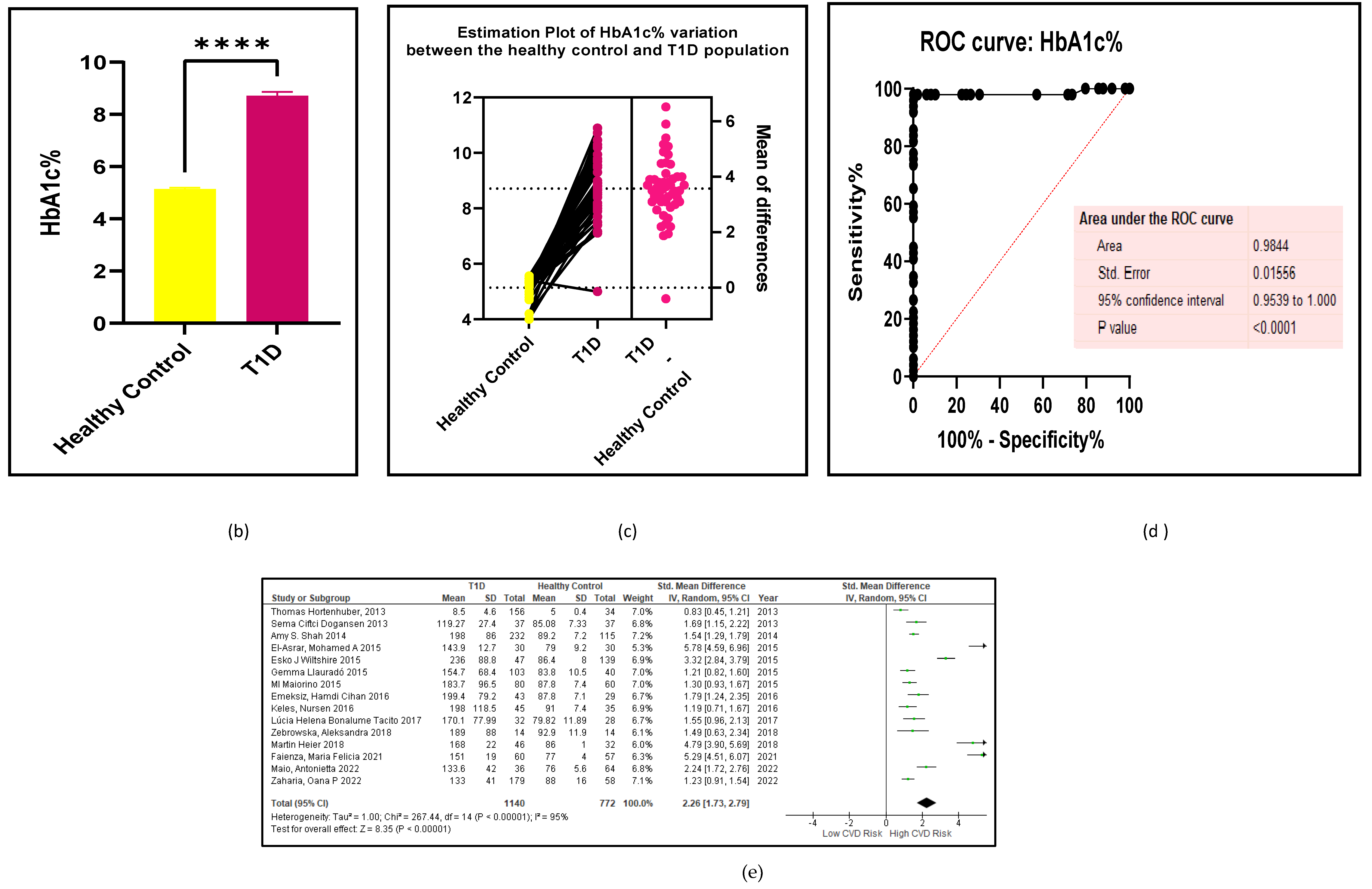
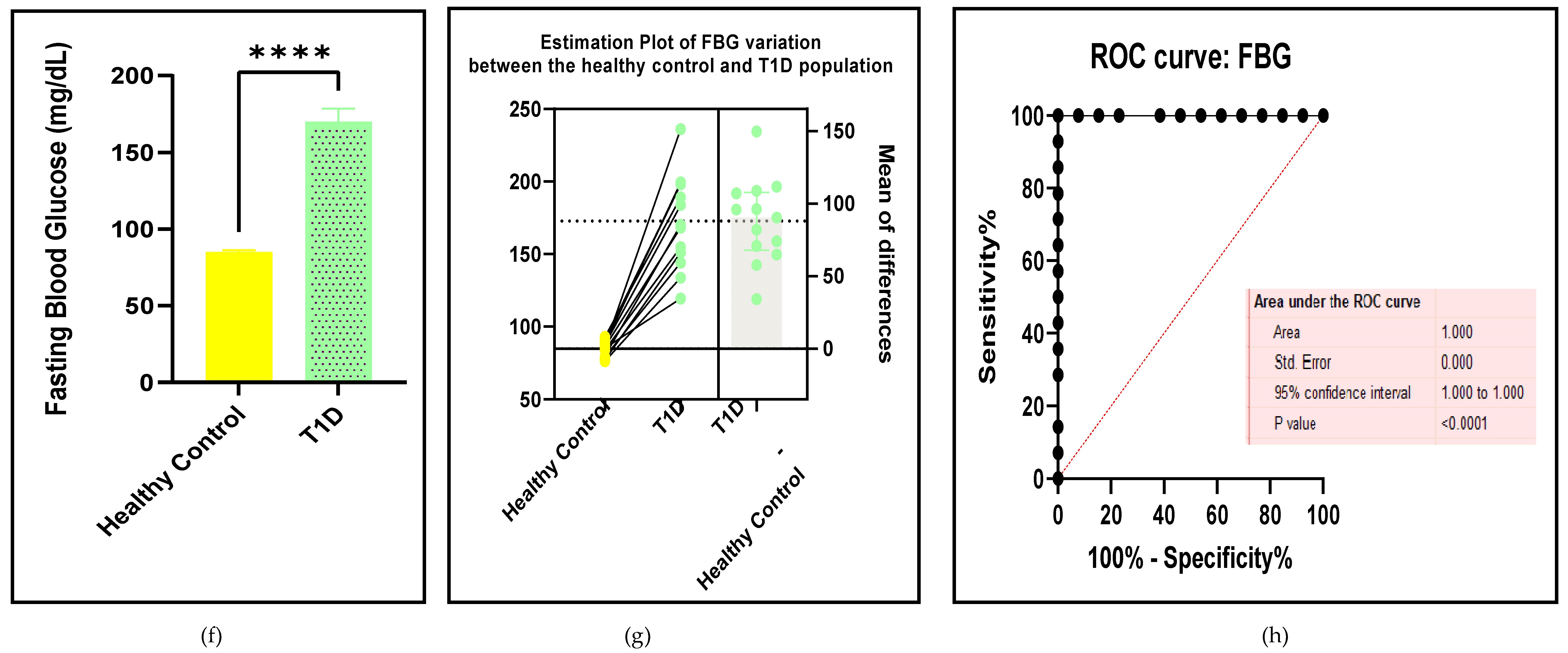
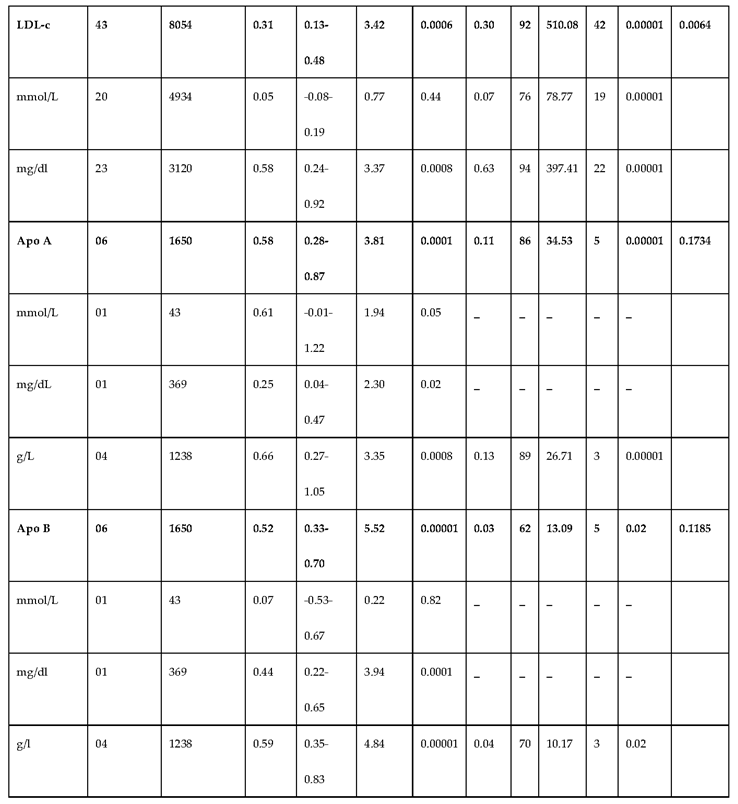
3.2.3. The Lipid Profile Remains as Traditional Biomarkers of T1D-Induced ED
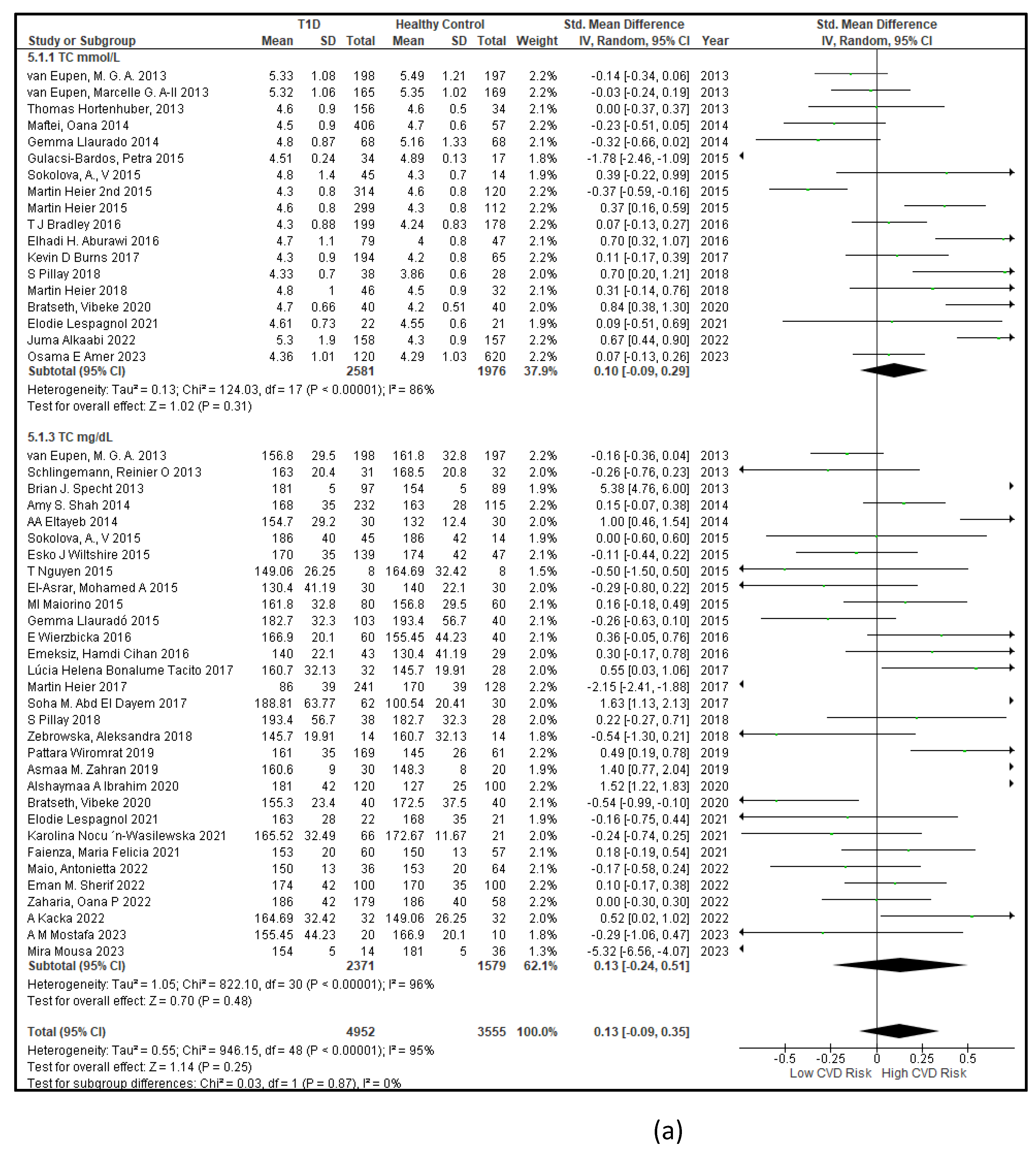
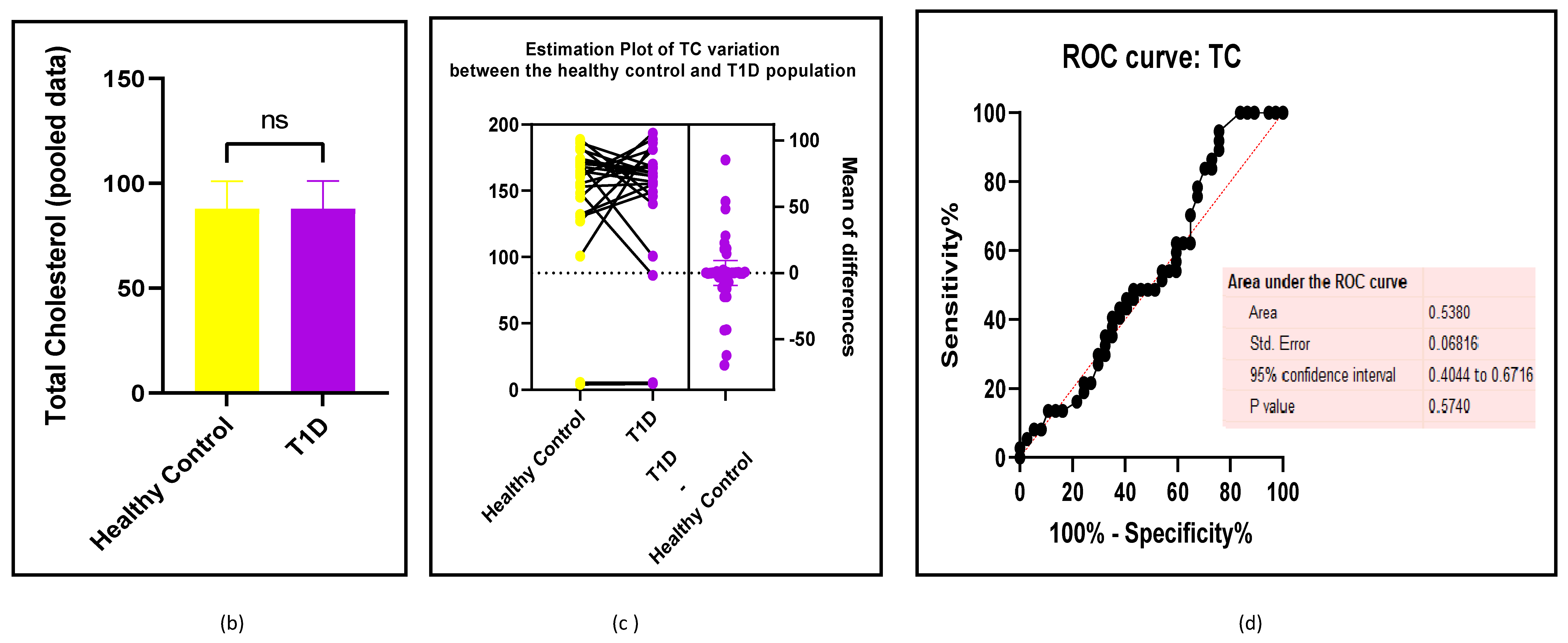
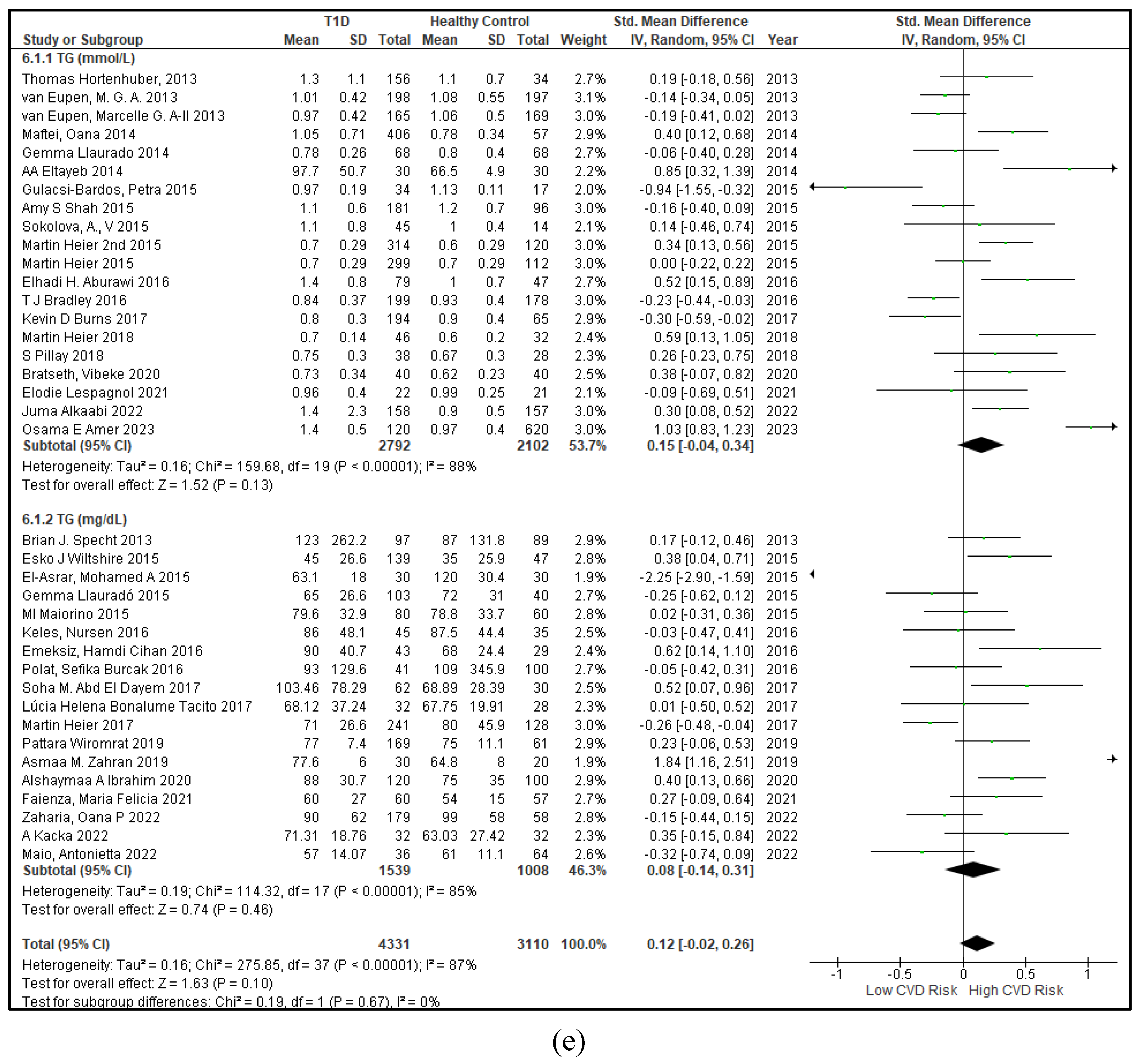
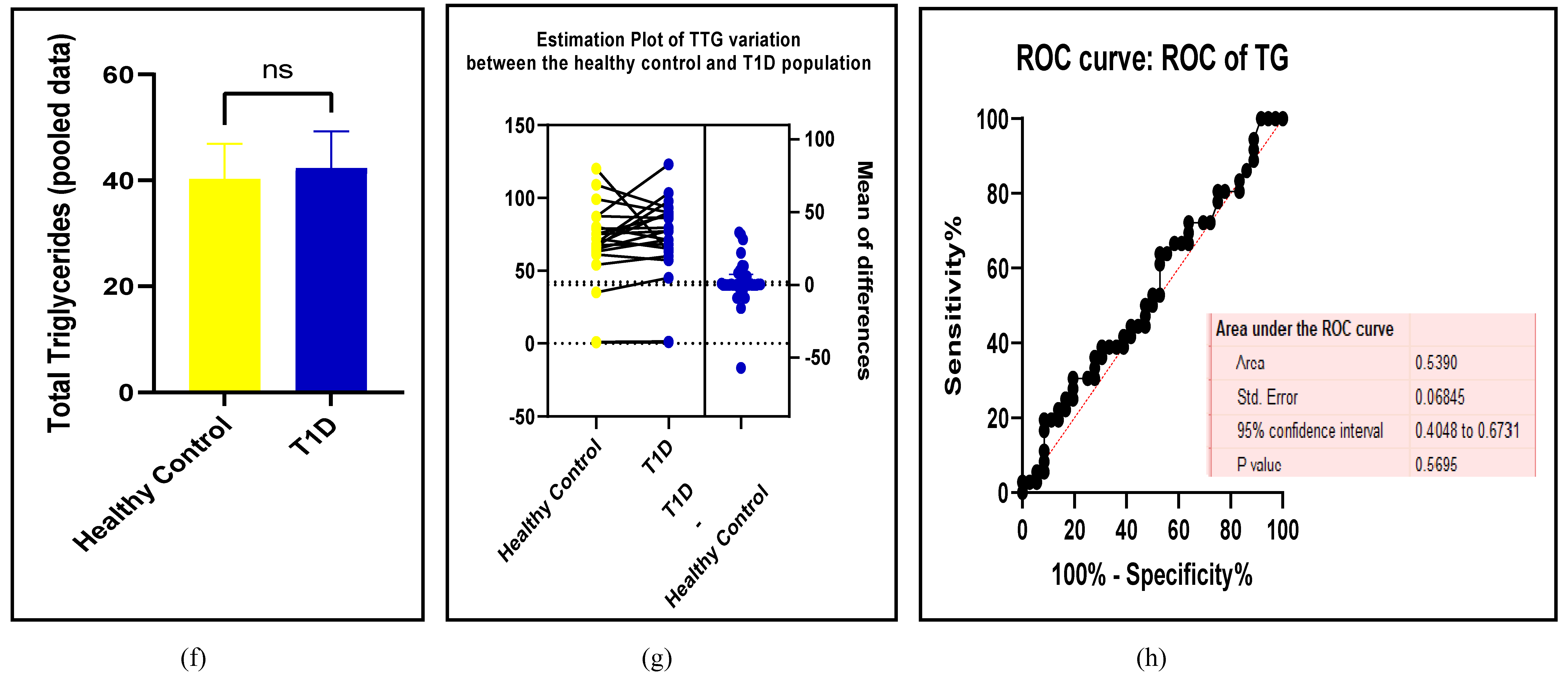
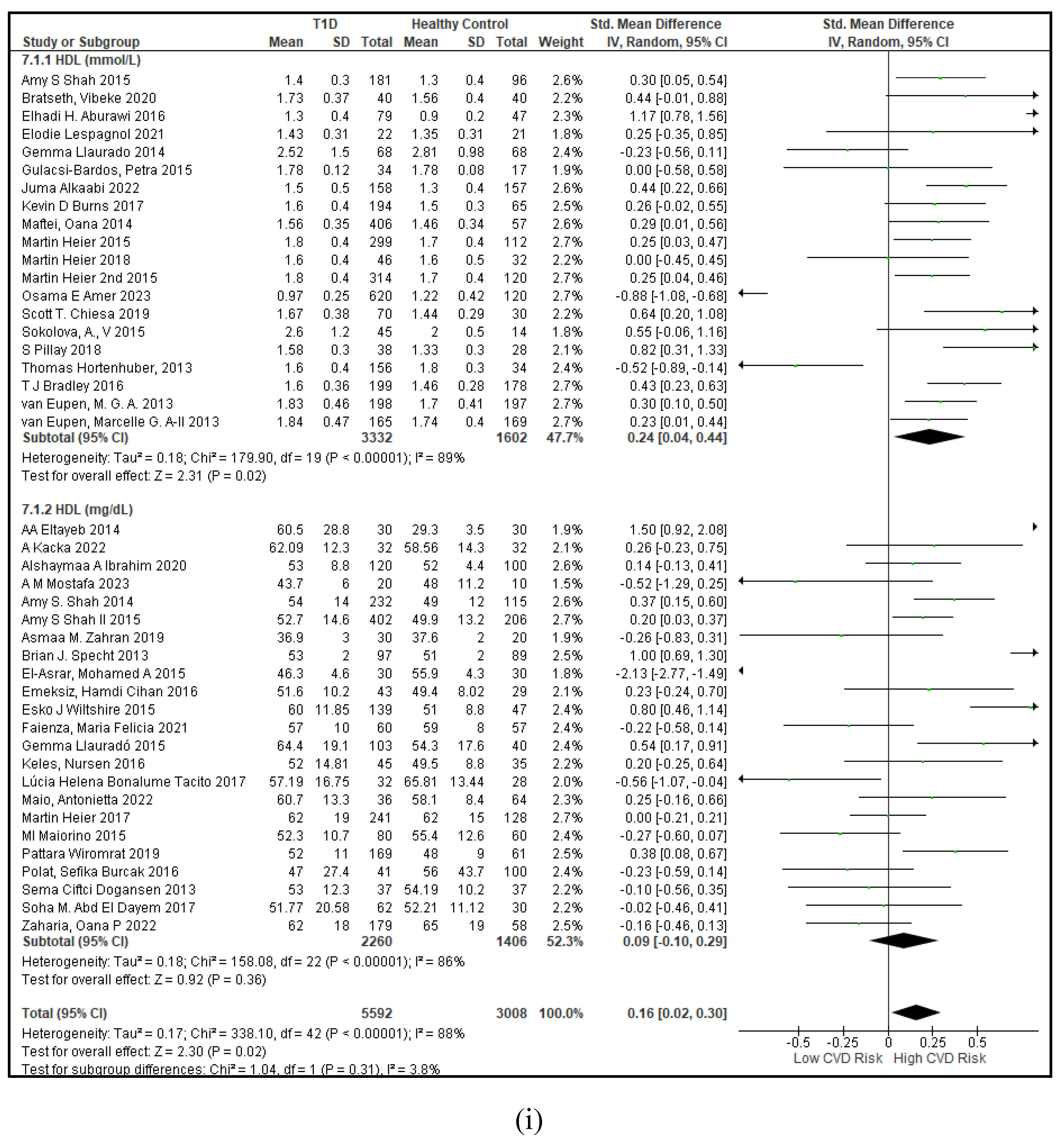
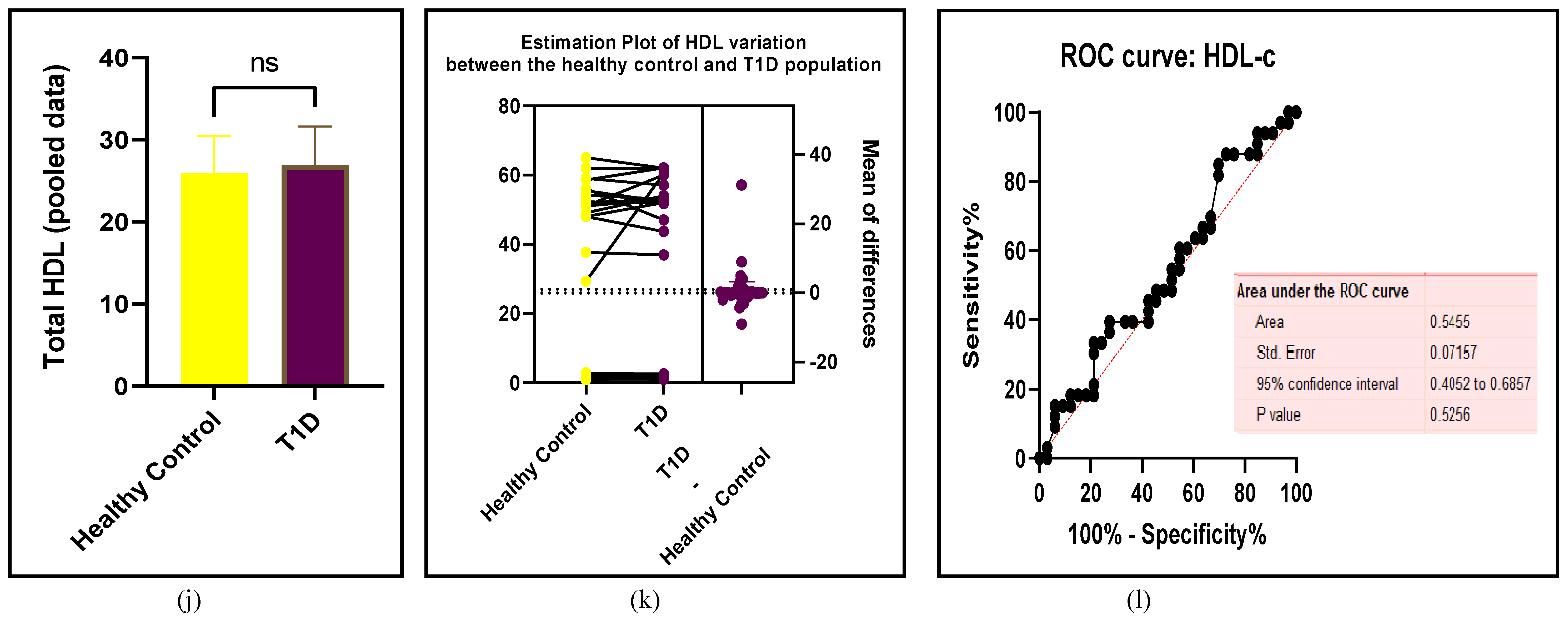
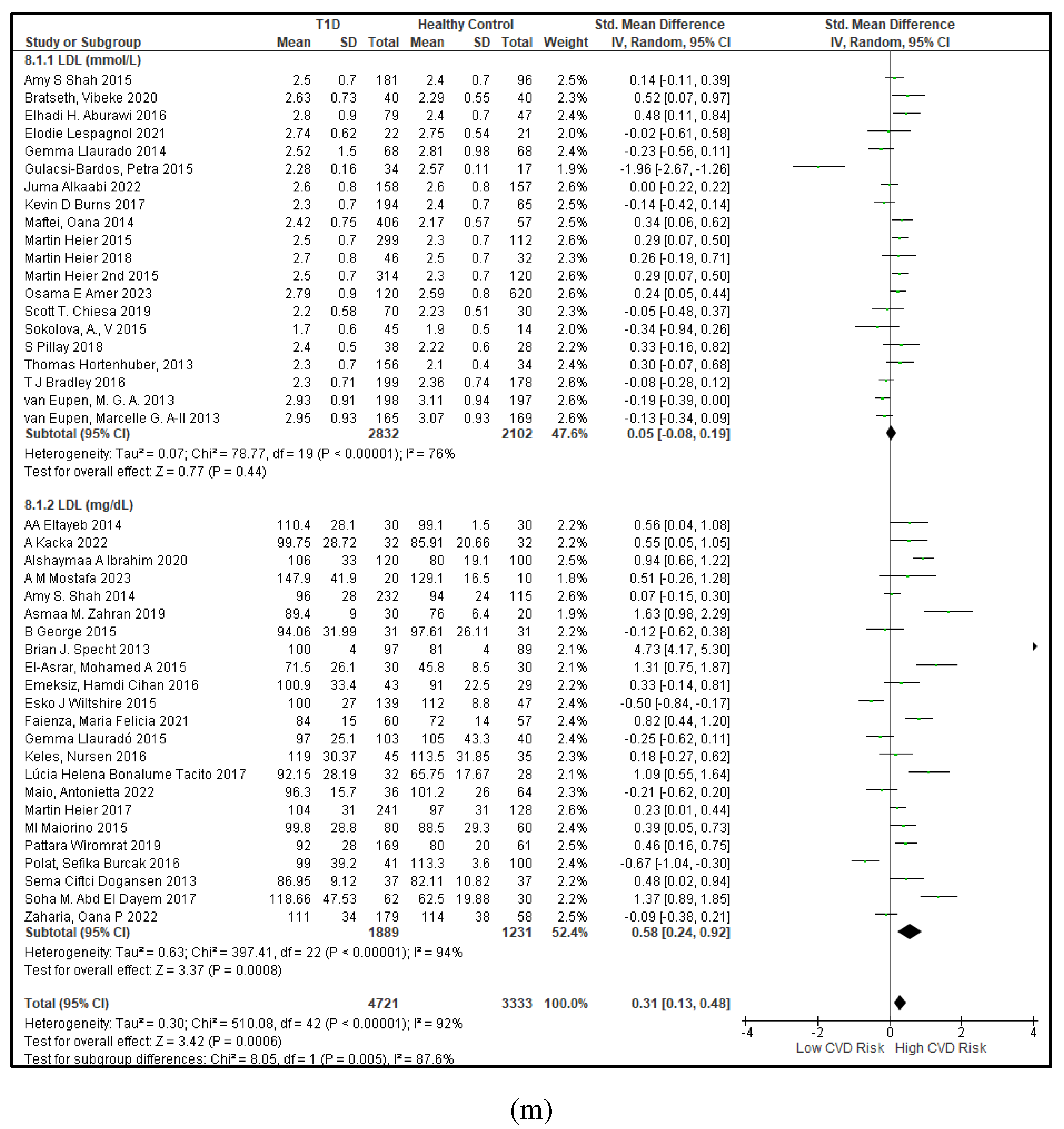
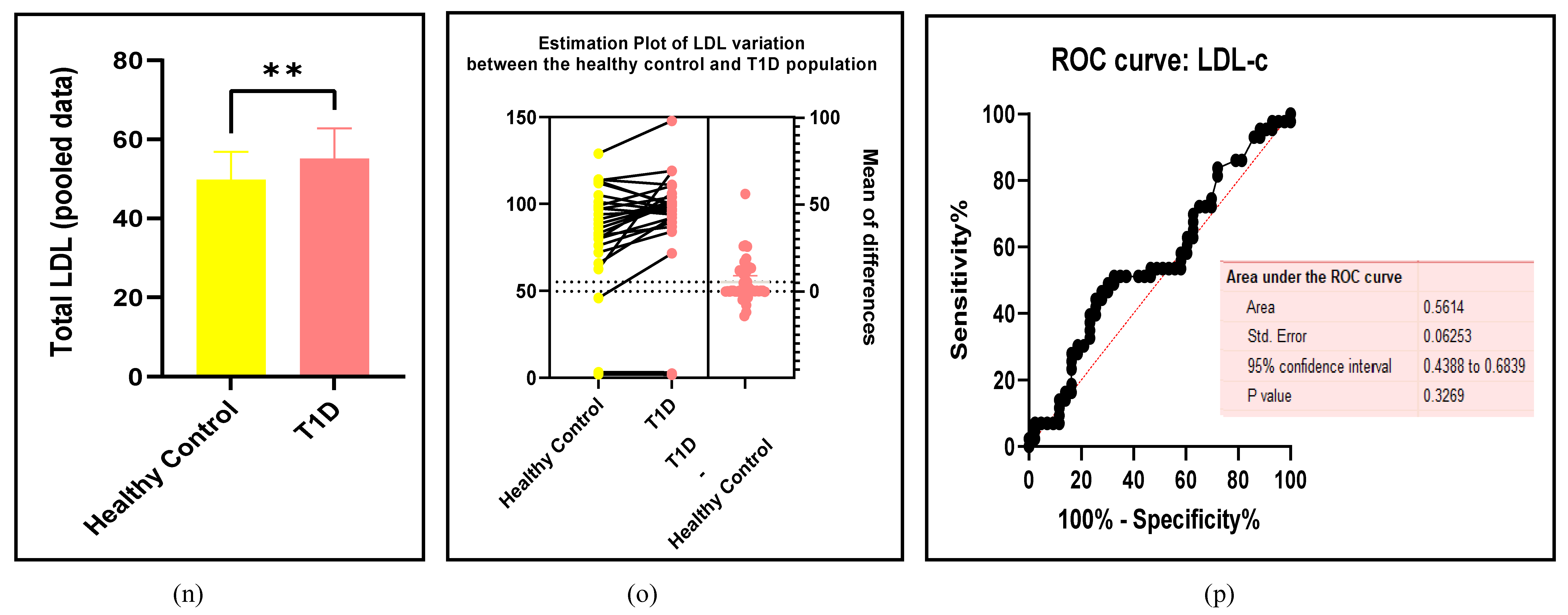
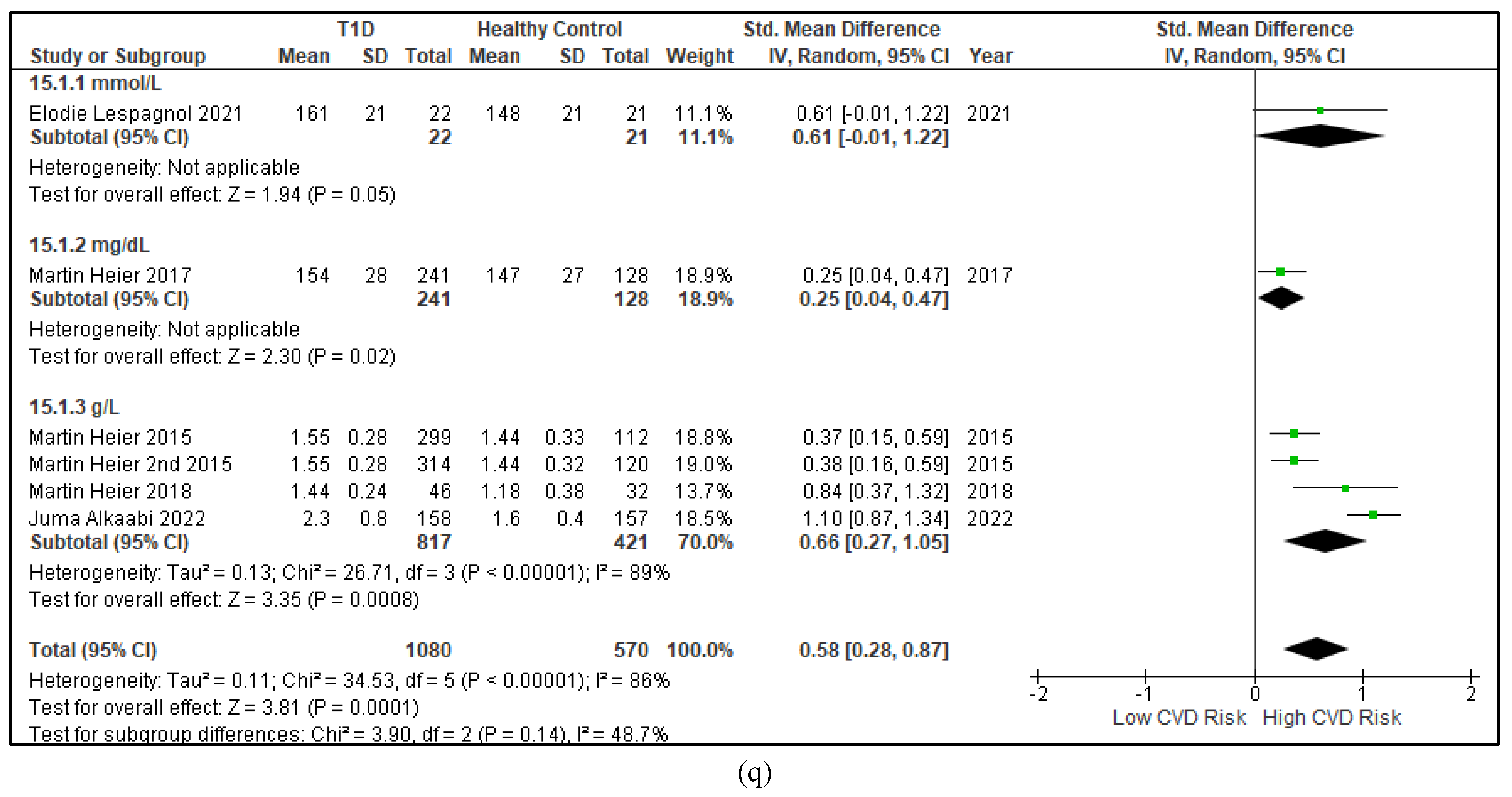
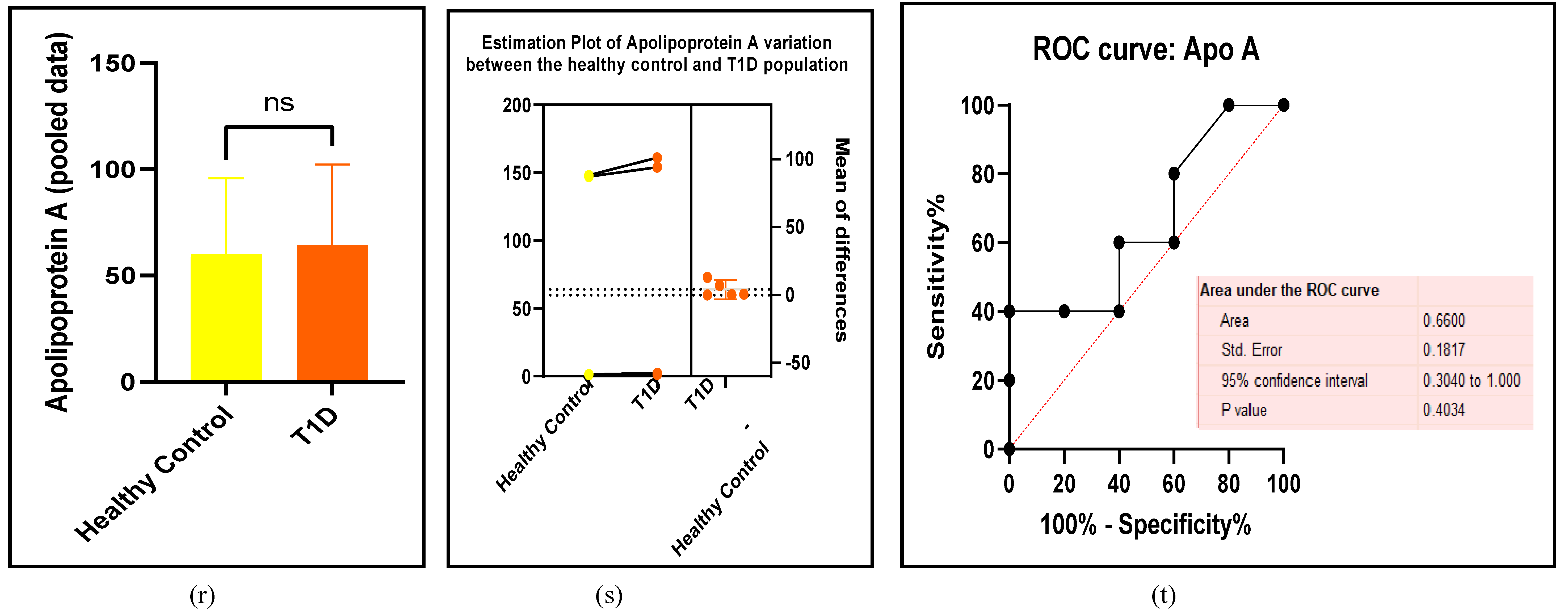
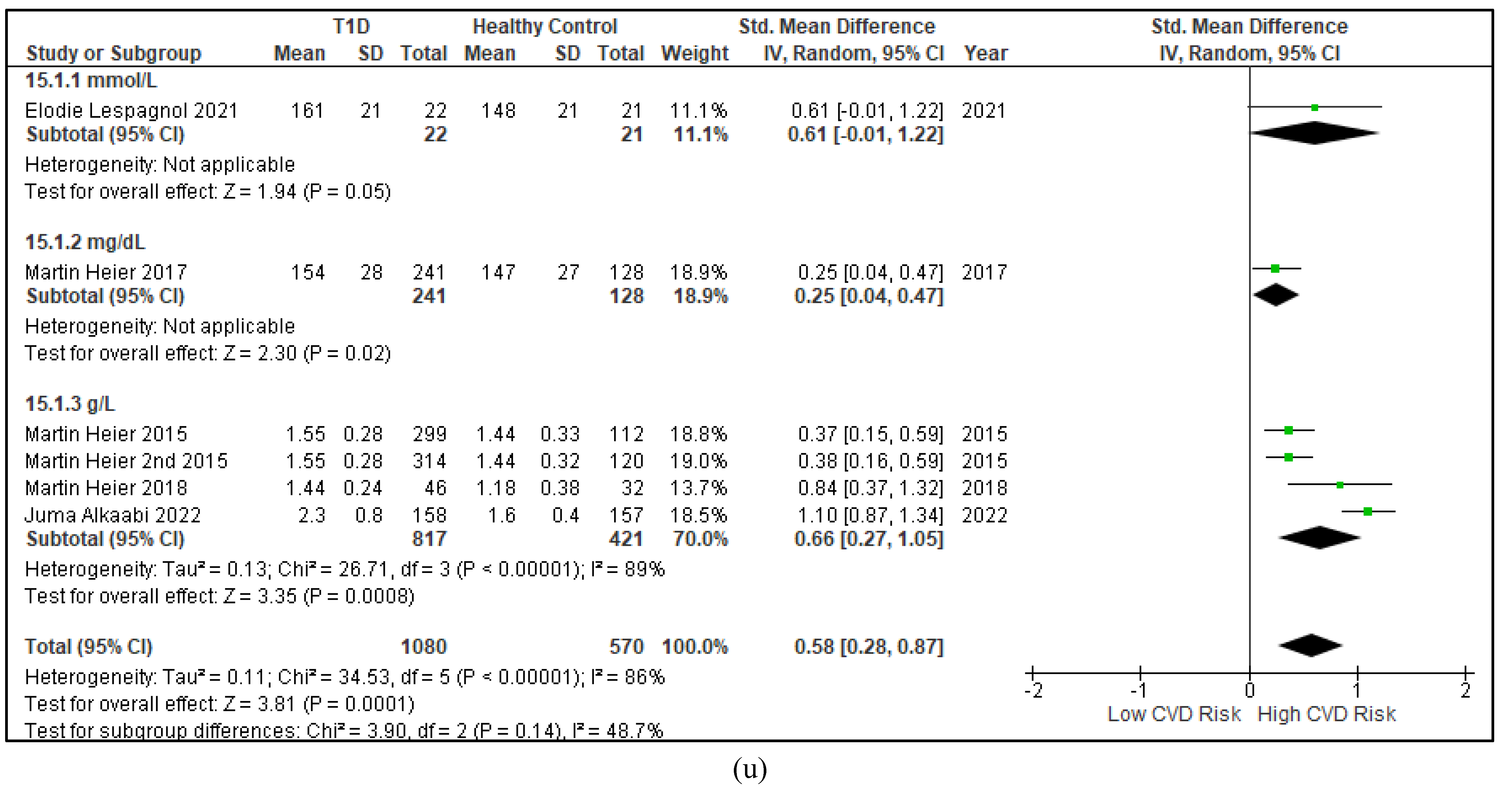
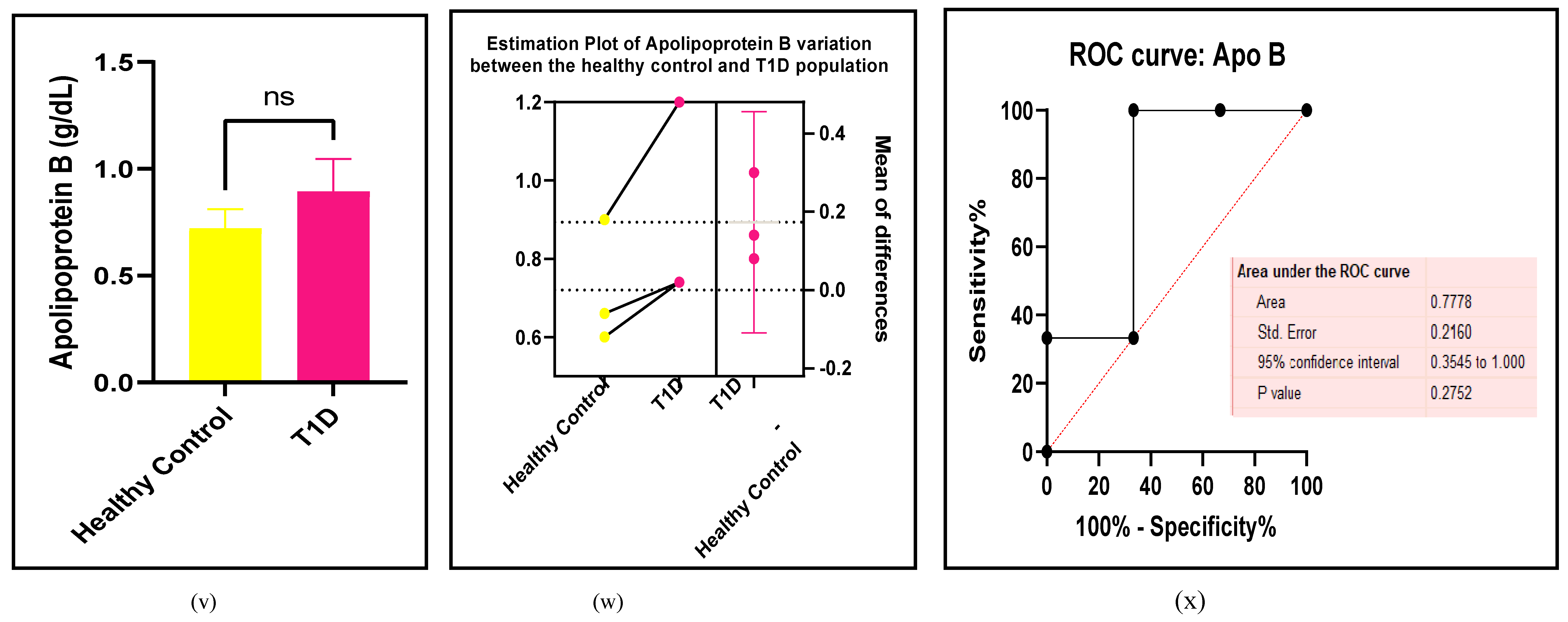
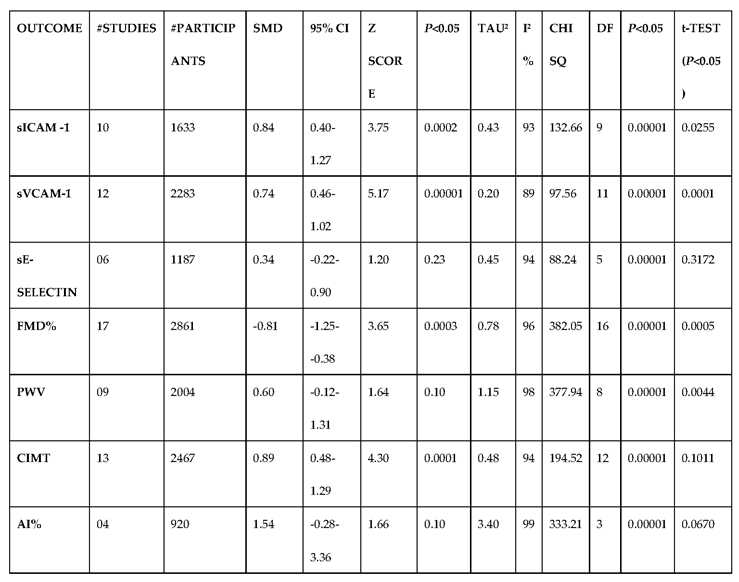
3.2.4. The Biomarkers of Vascular Function Are the Second-Best Indicators of T1D-Induced ED
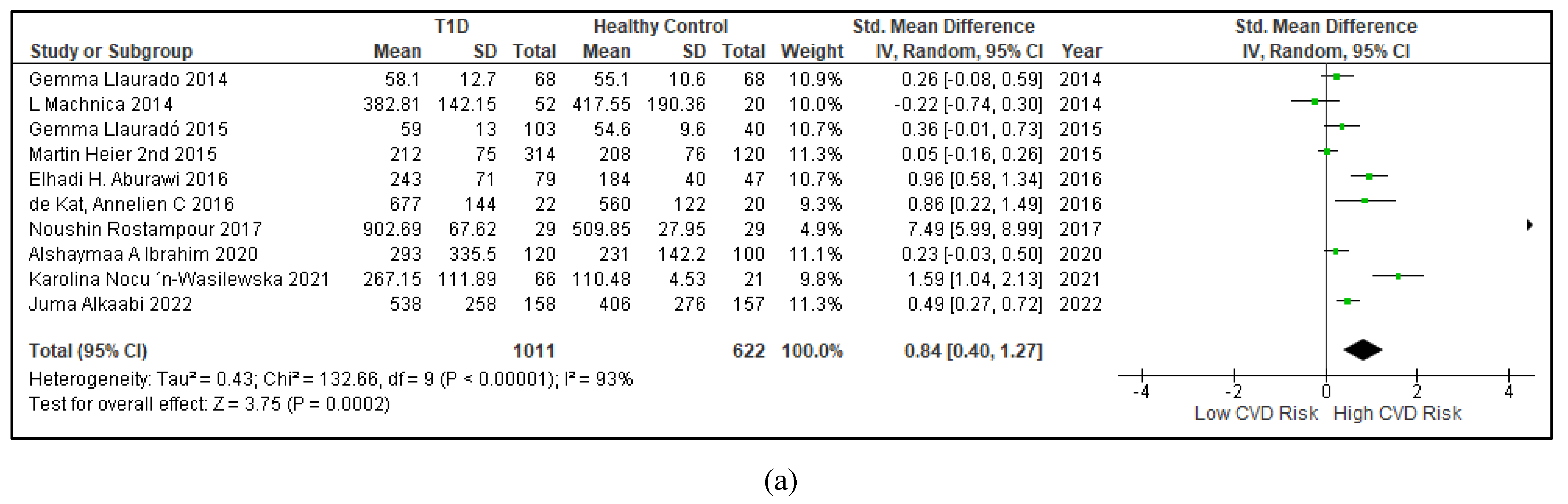
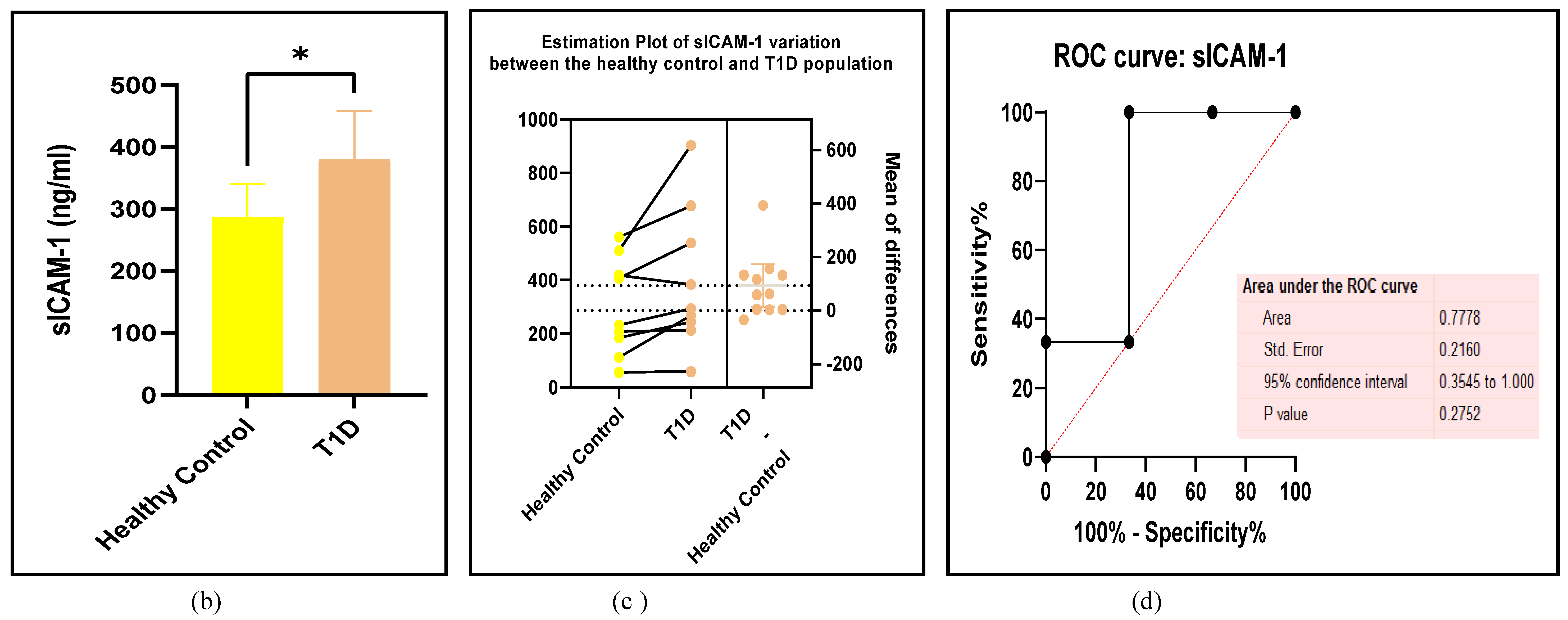
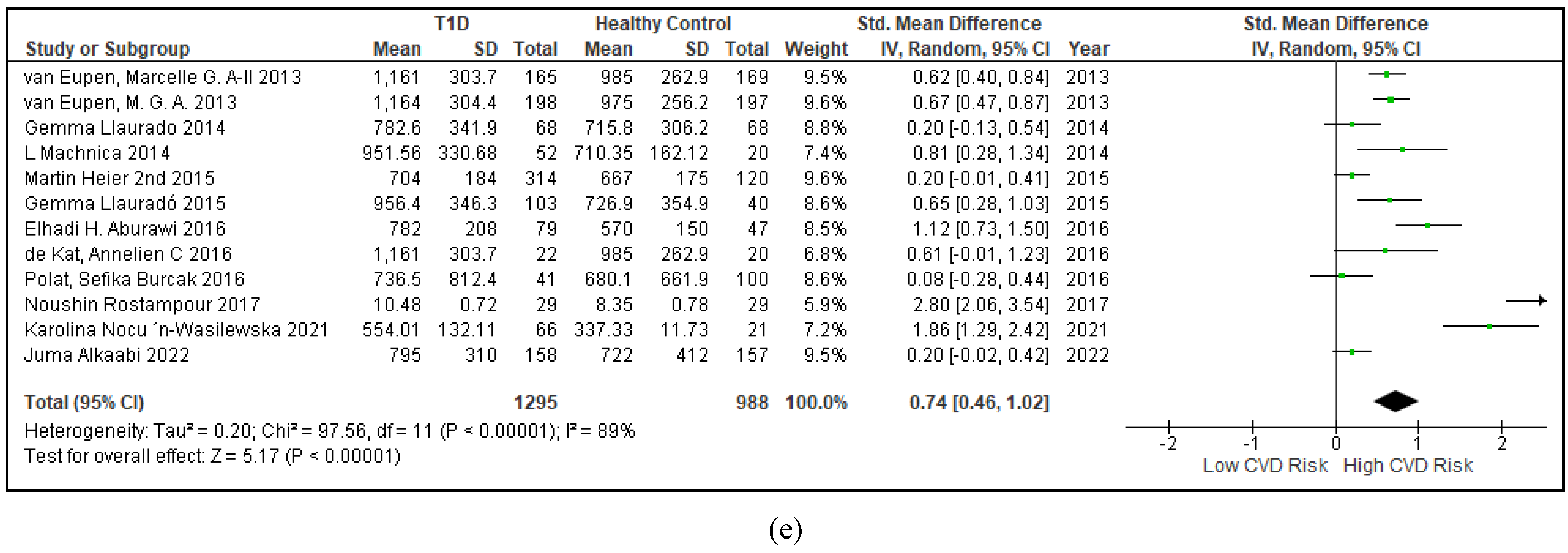
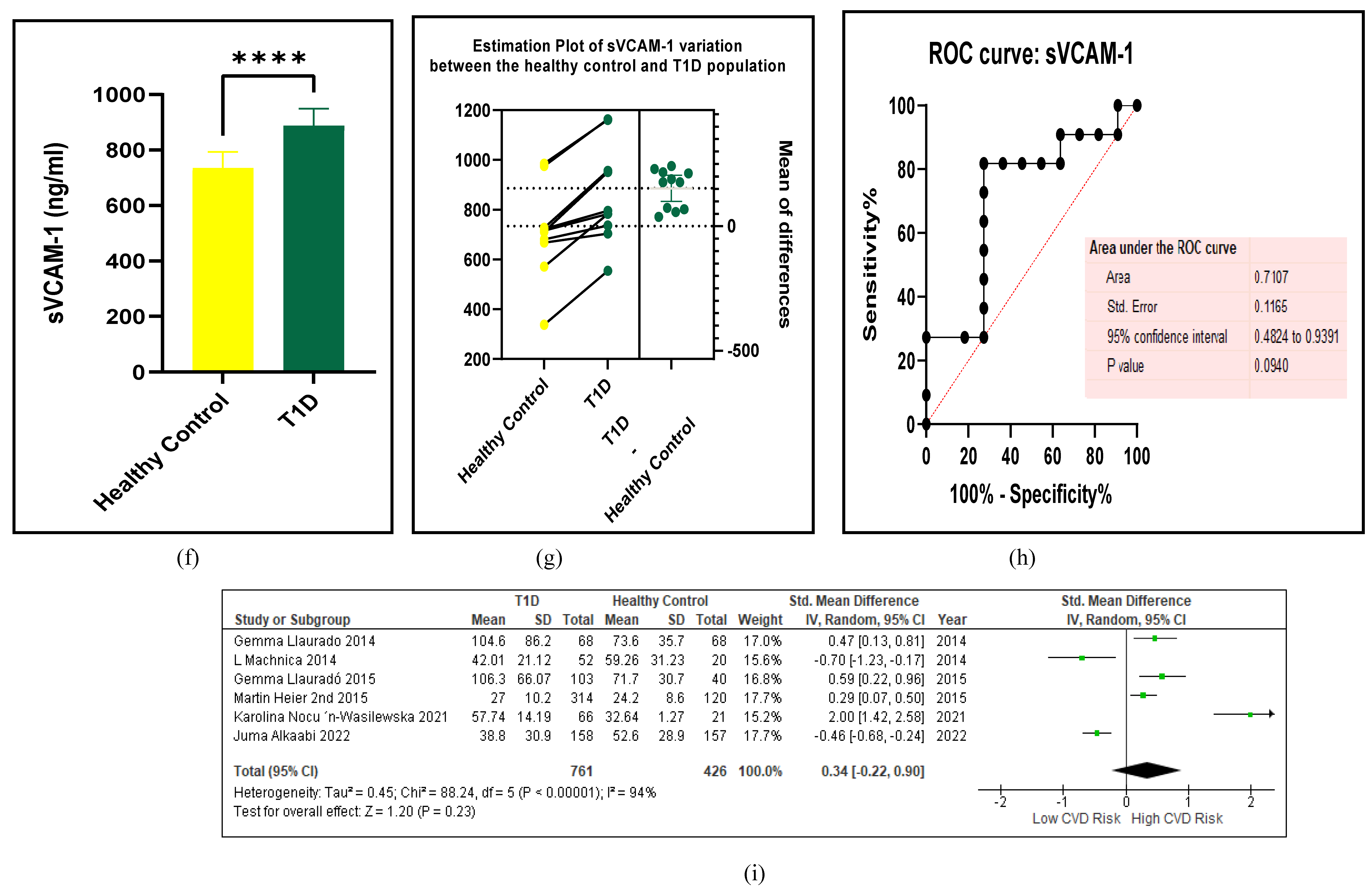
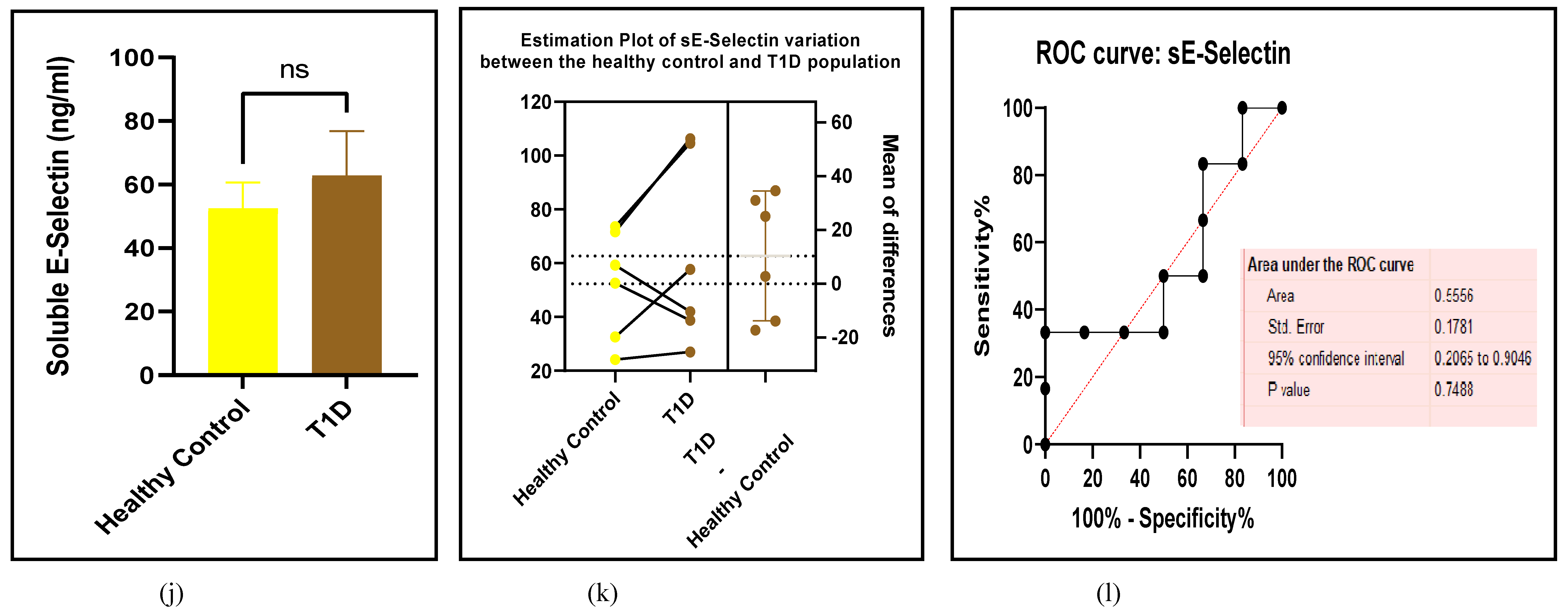
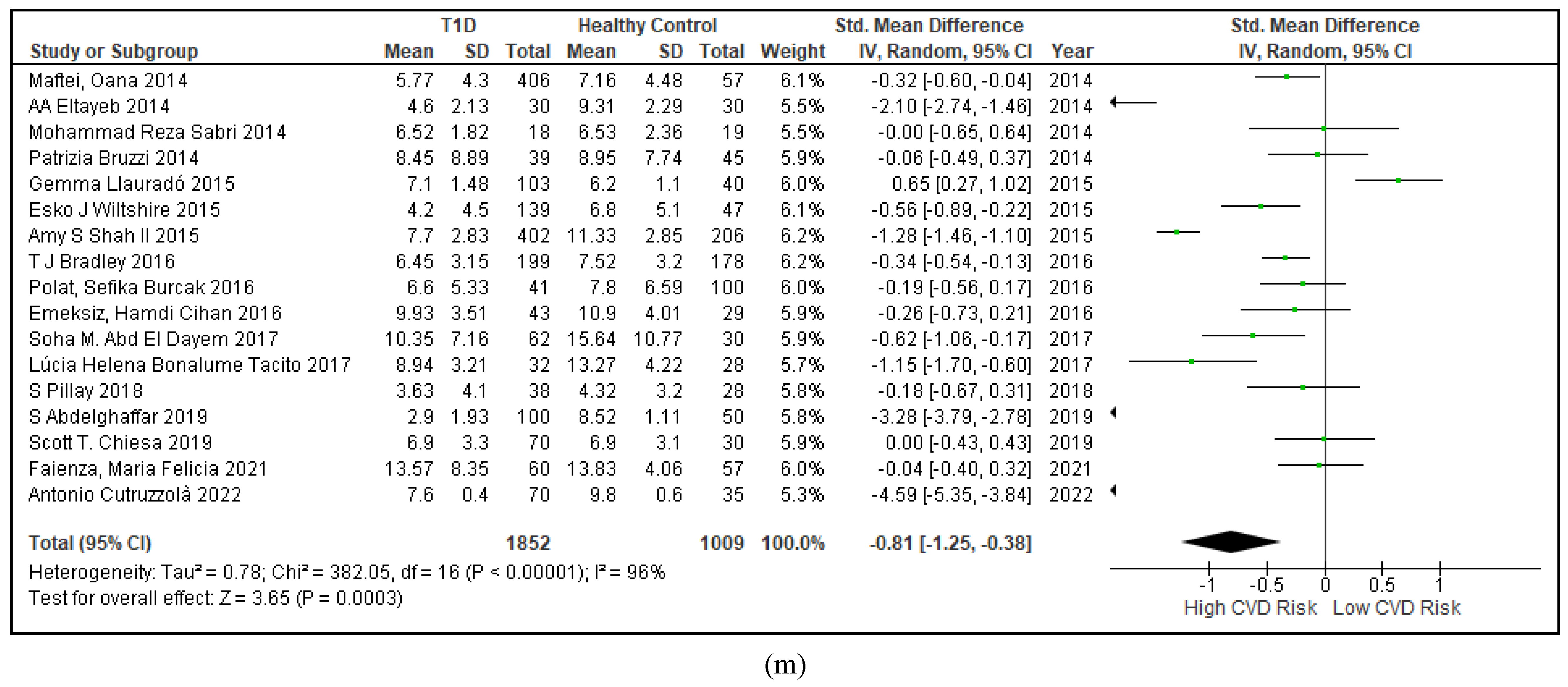
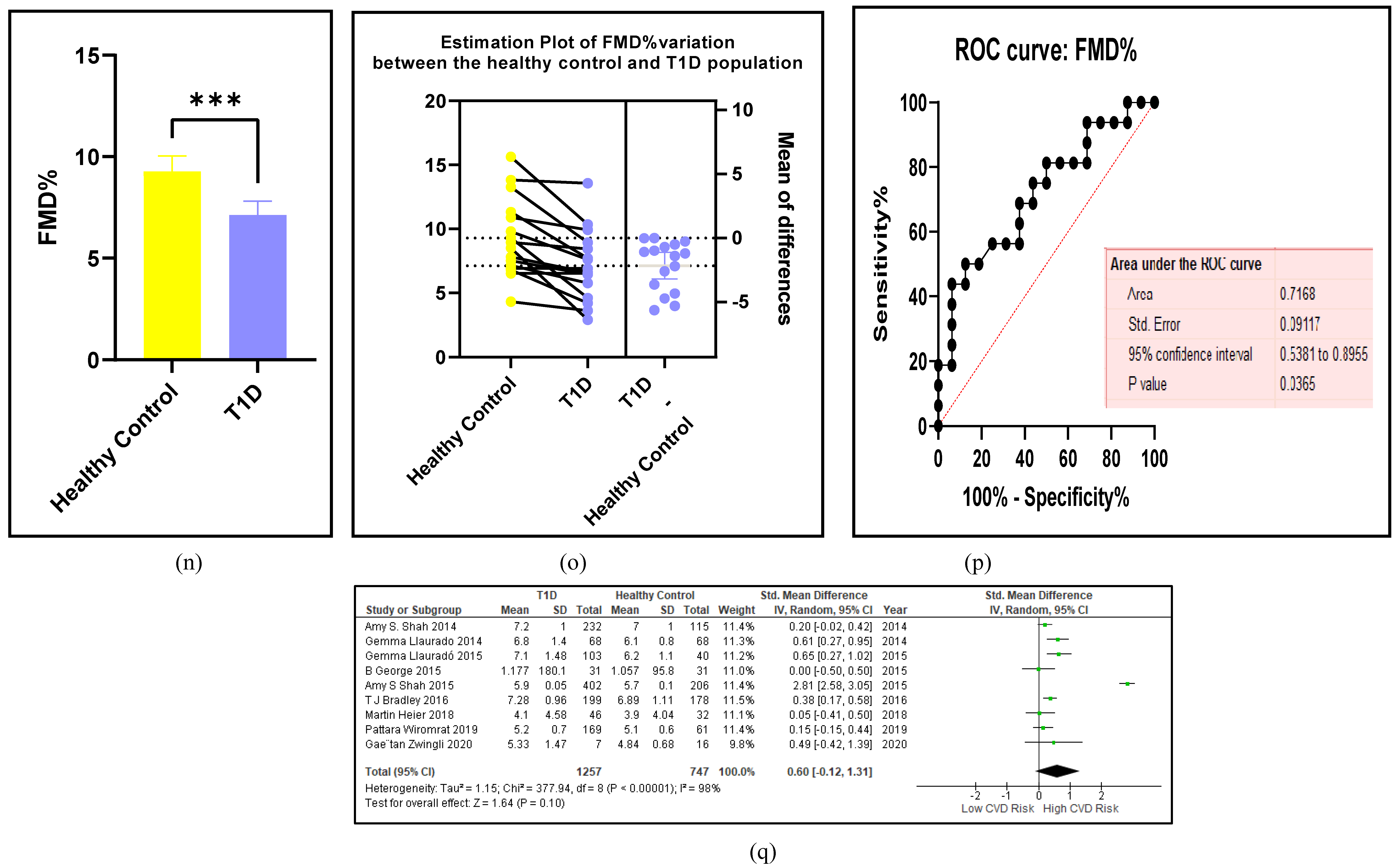
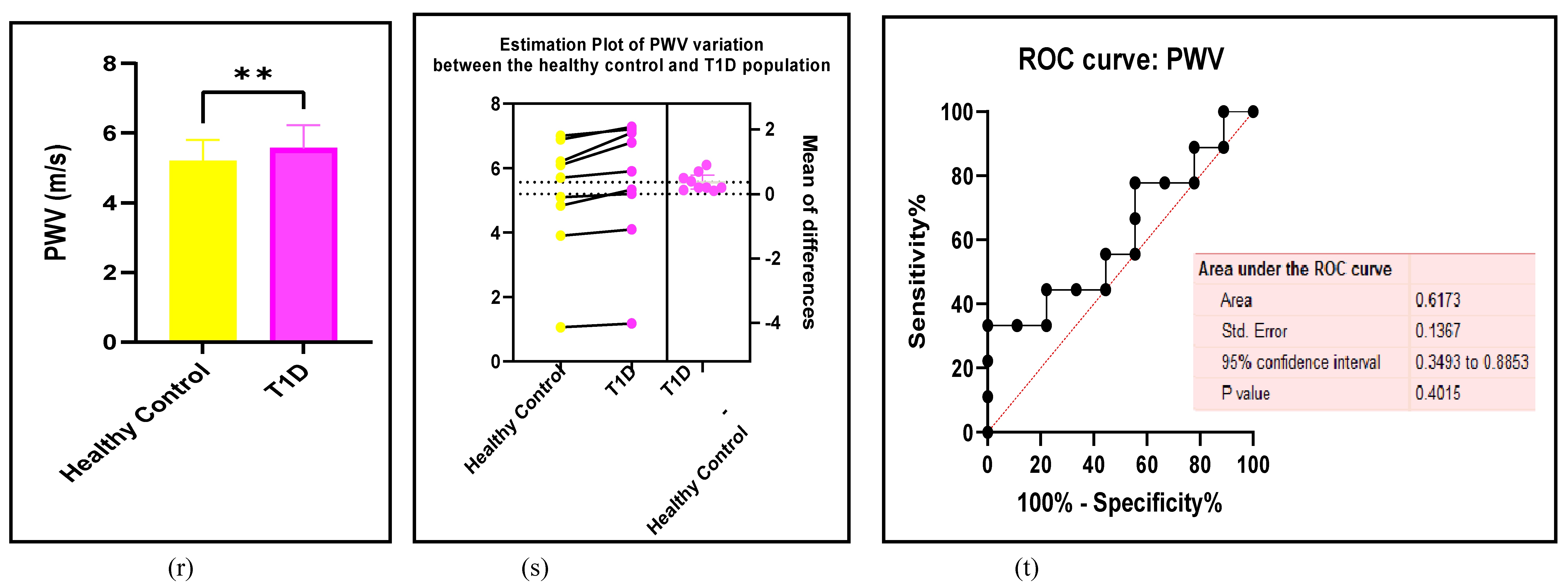
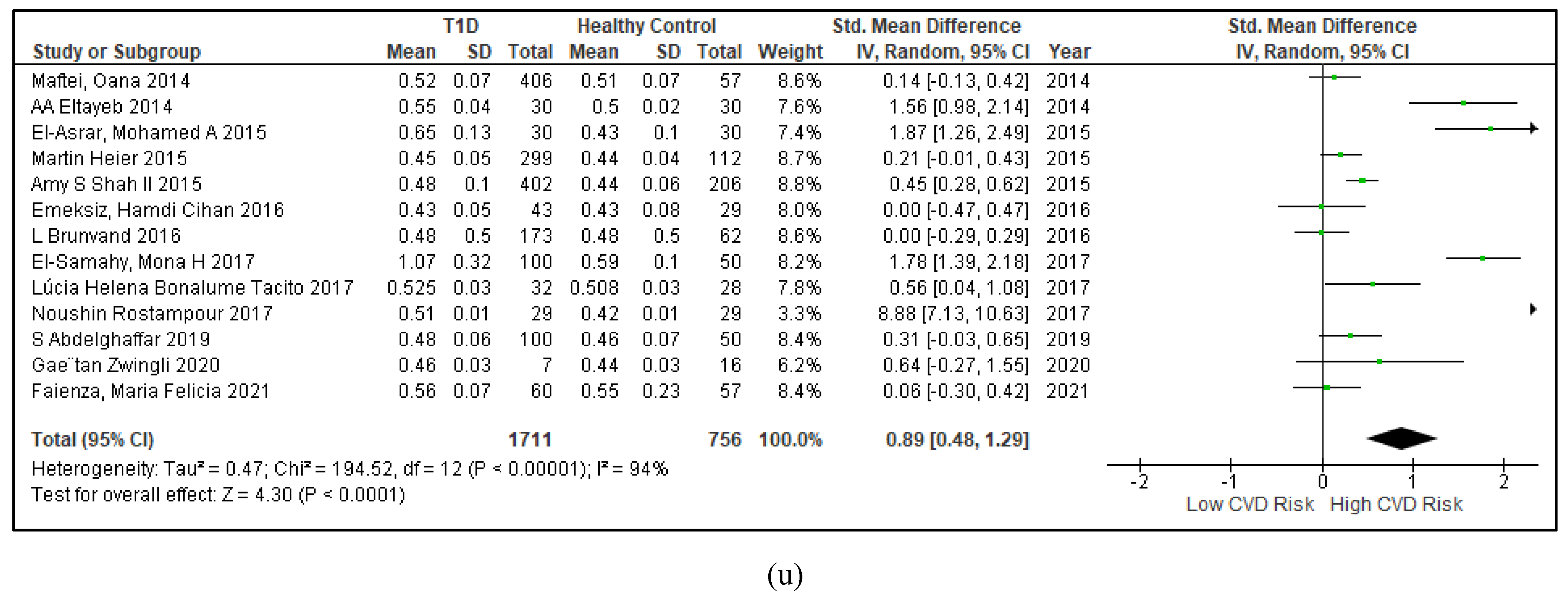
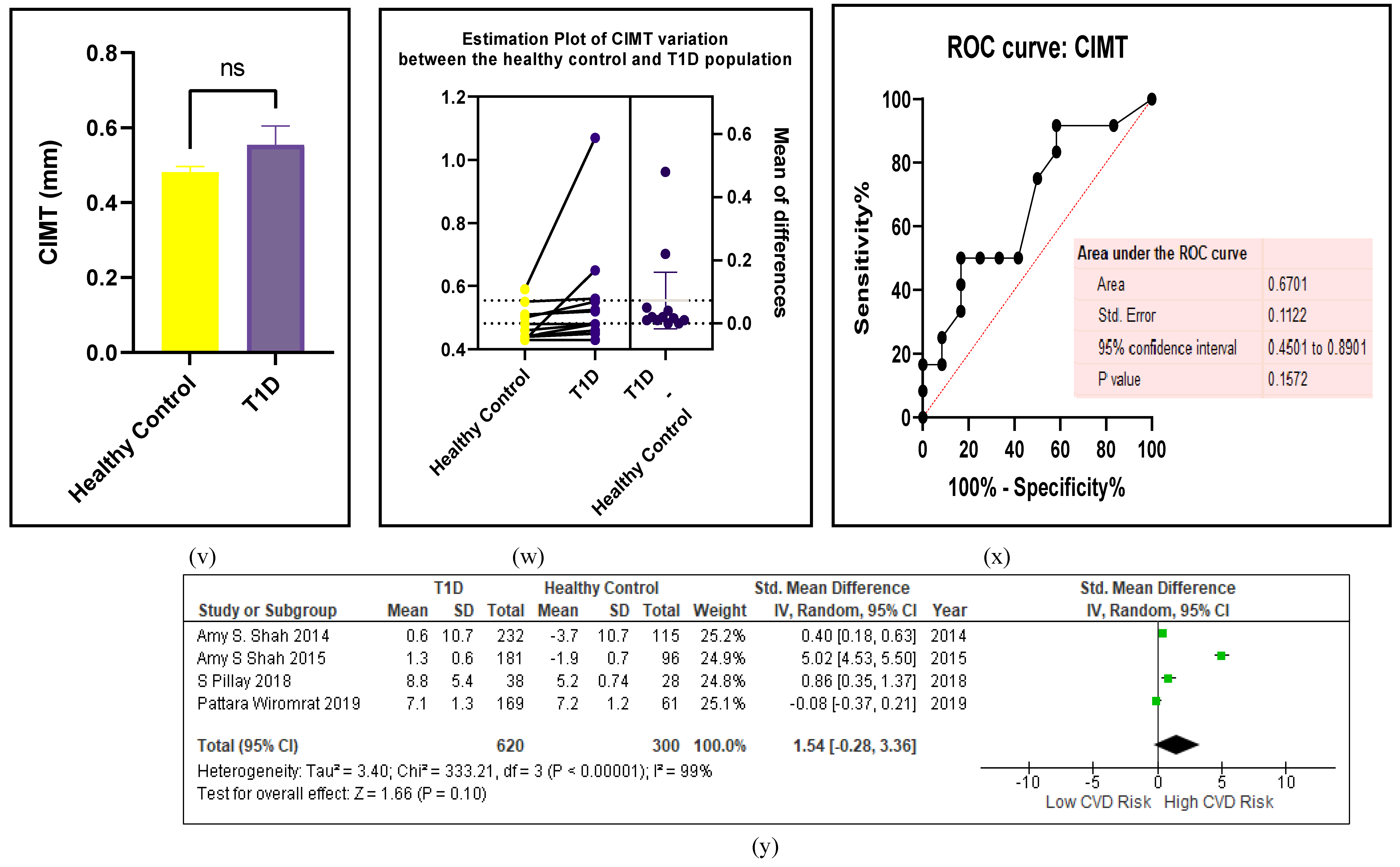
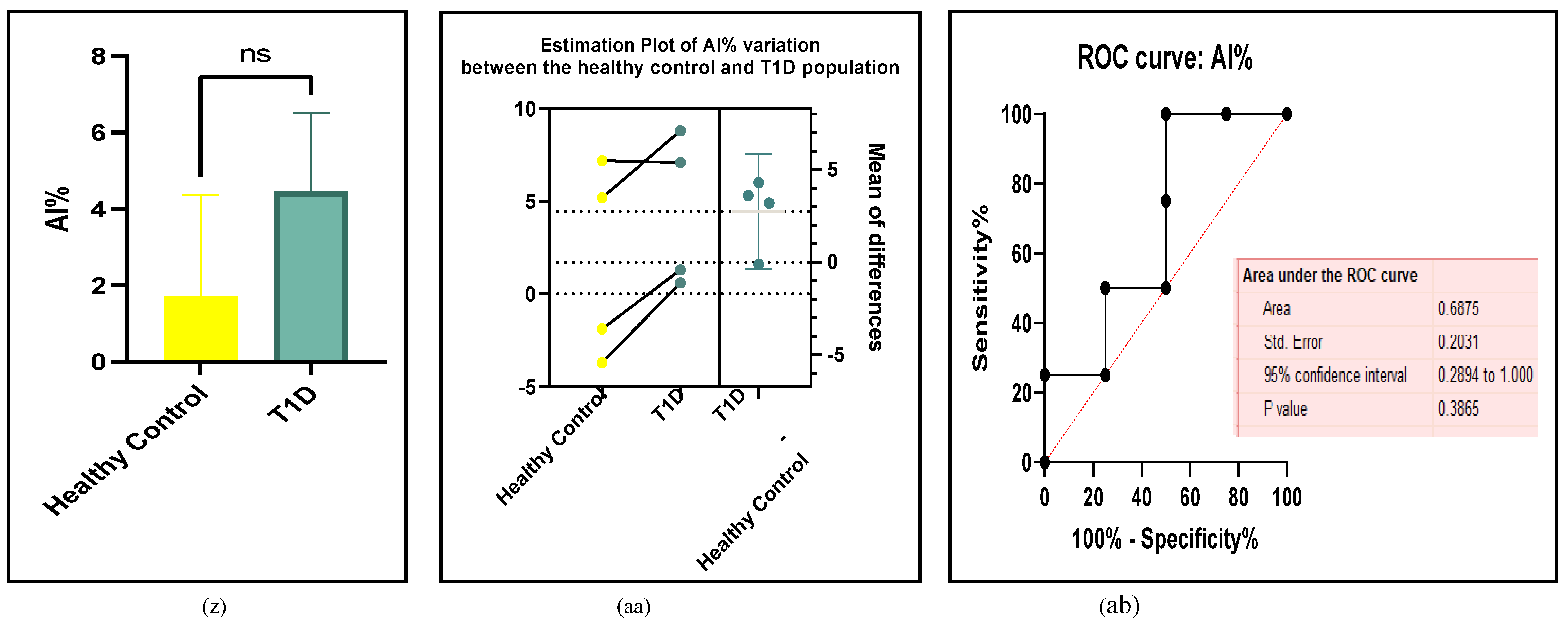
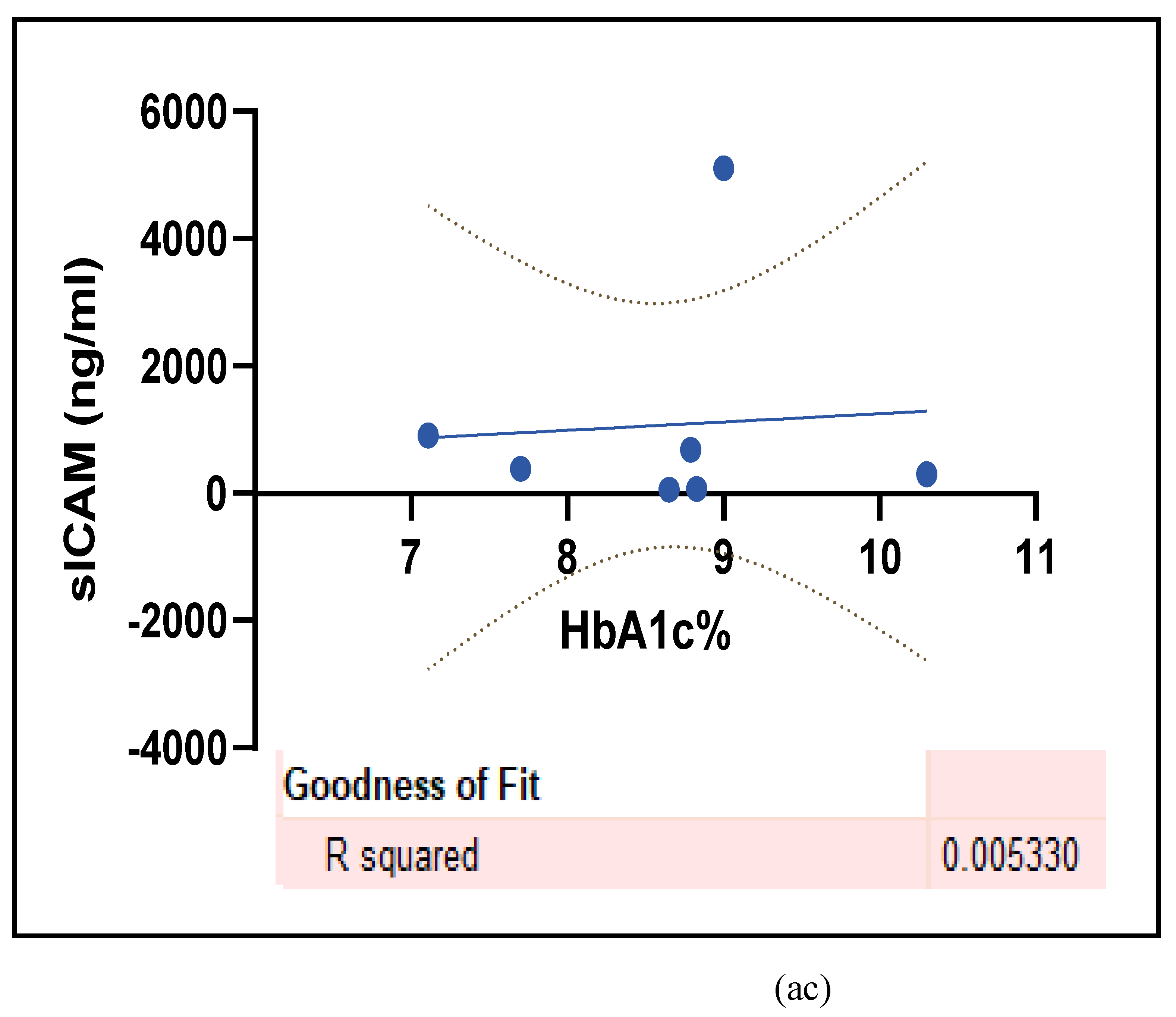
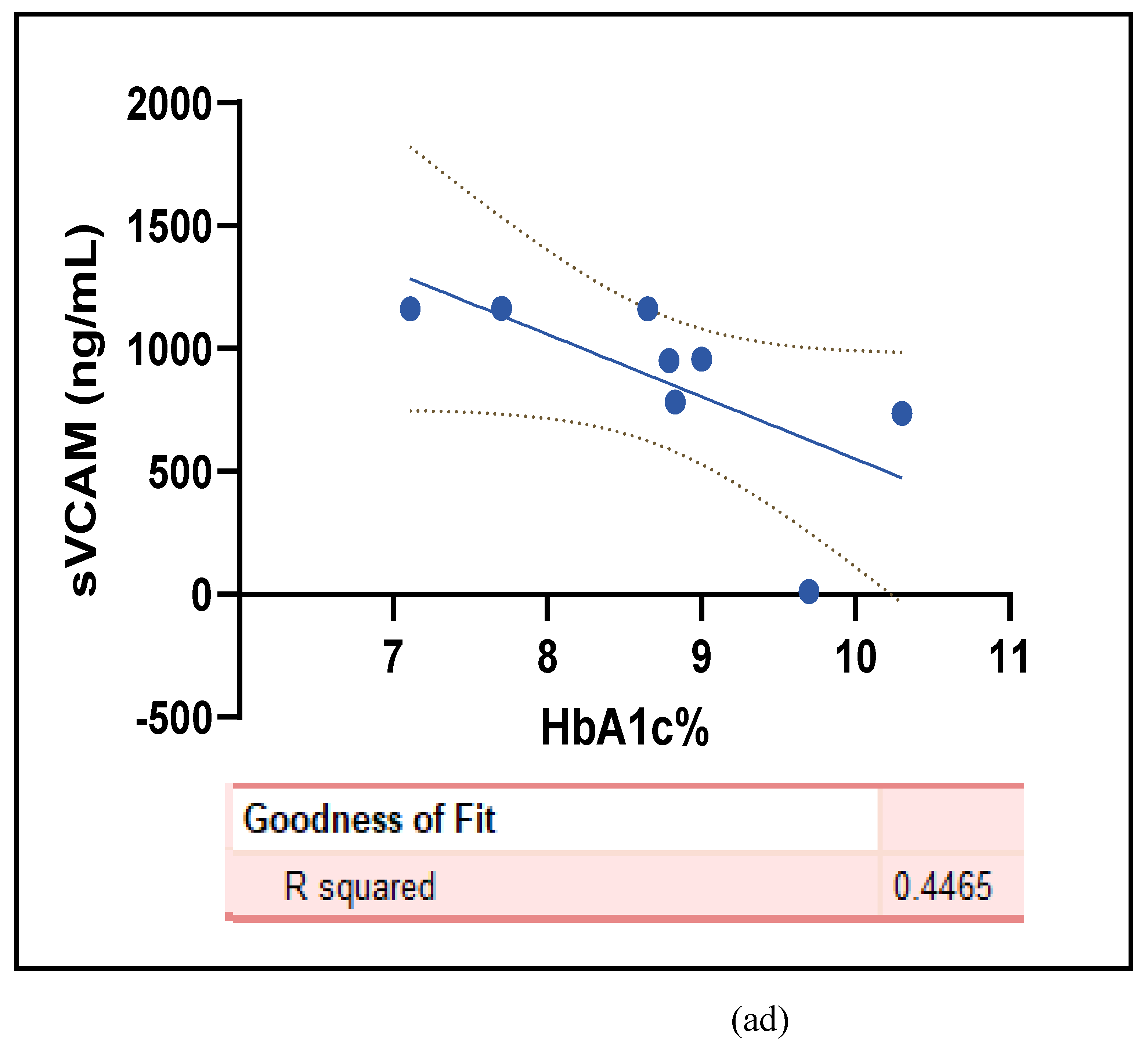
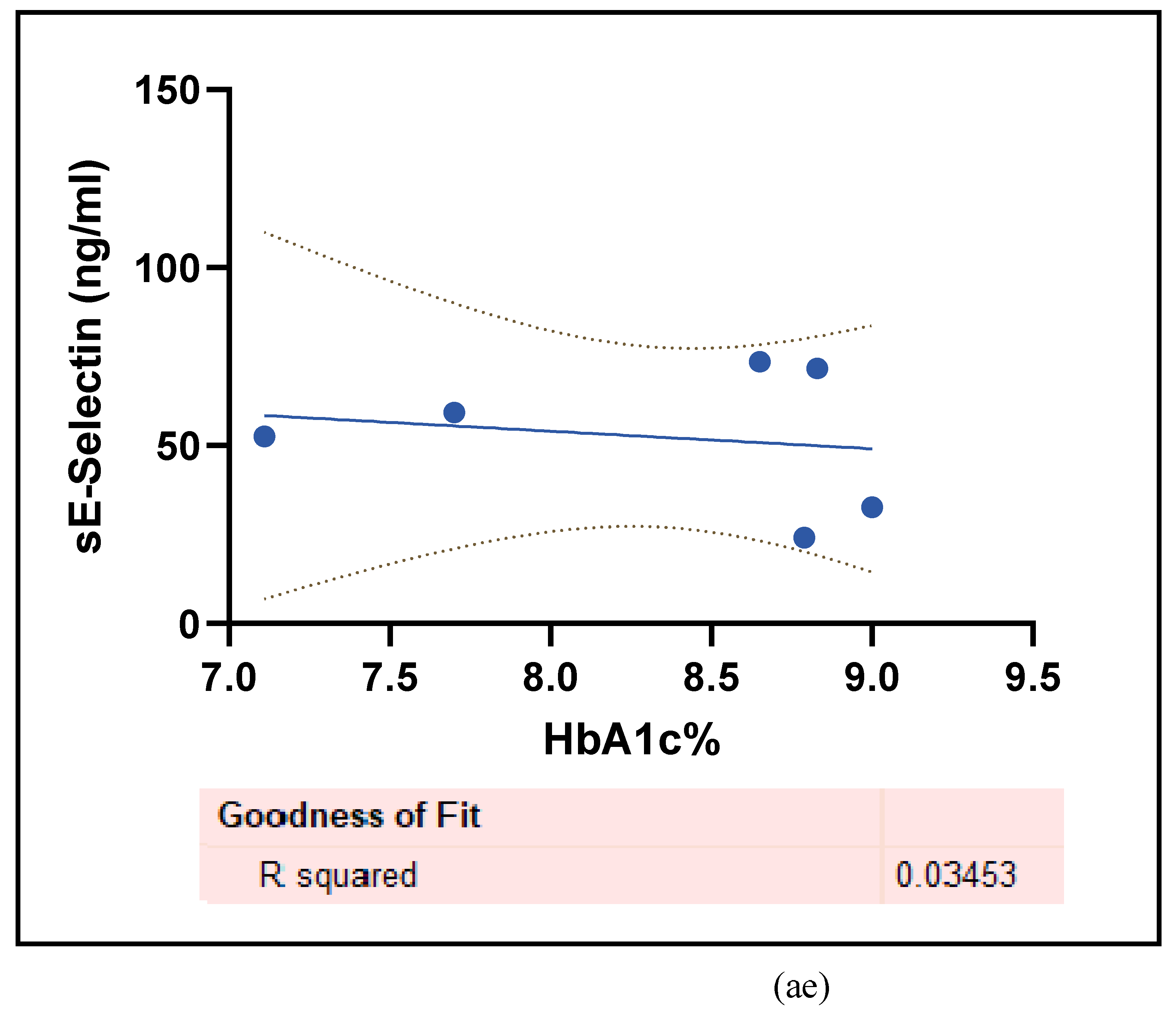
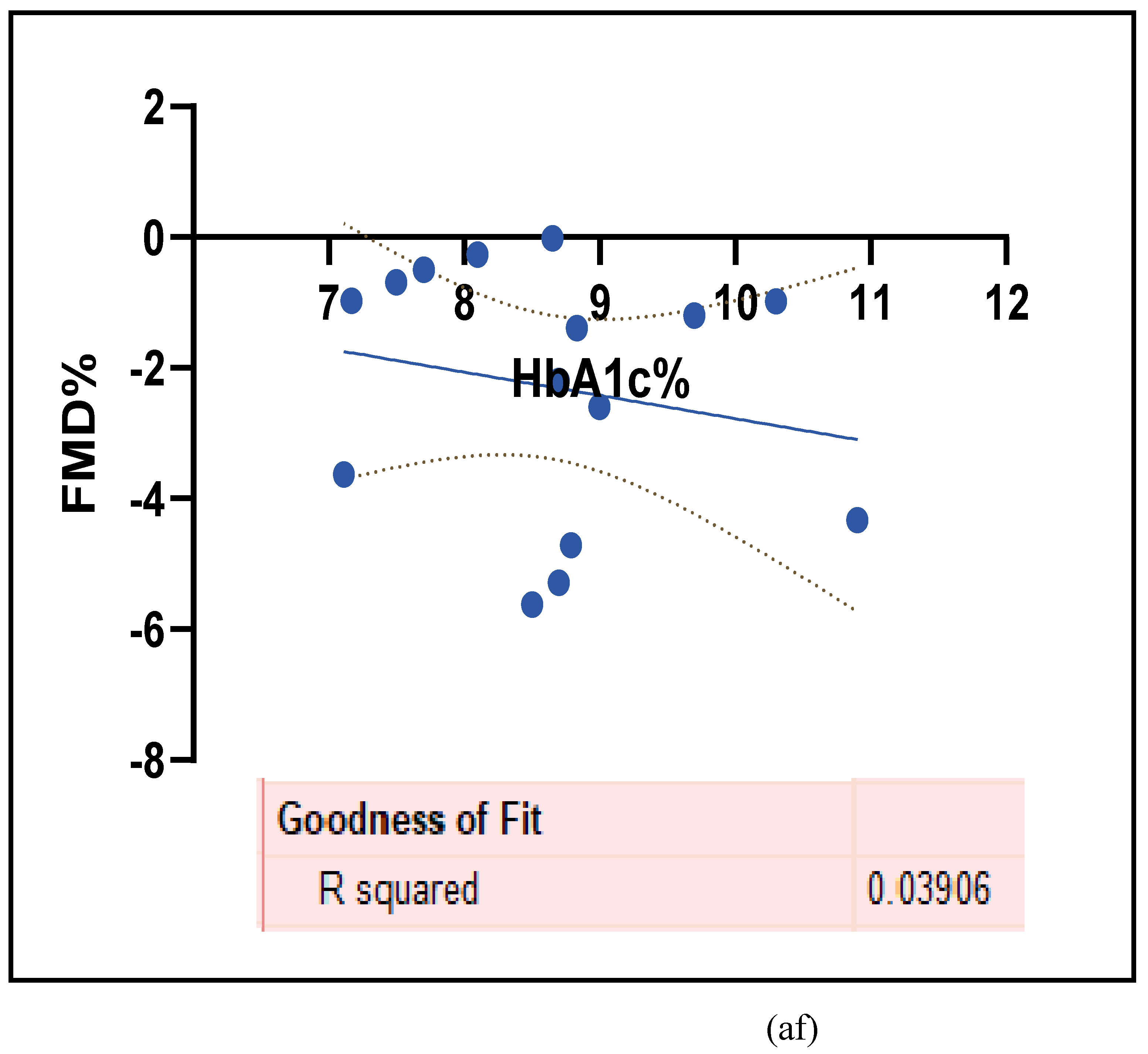
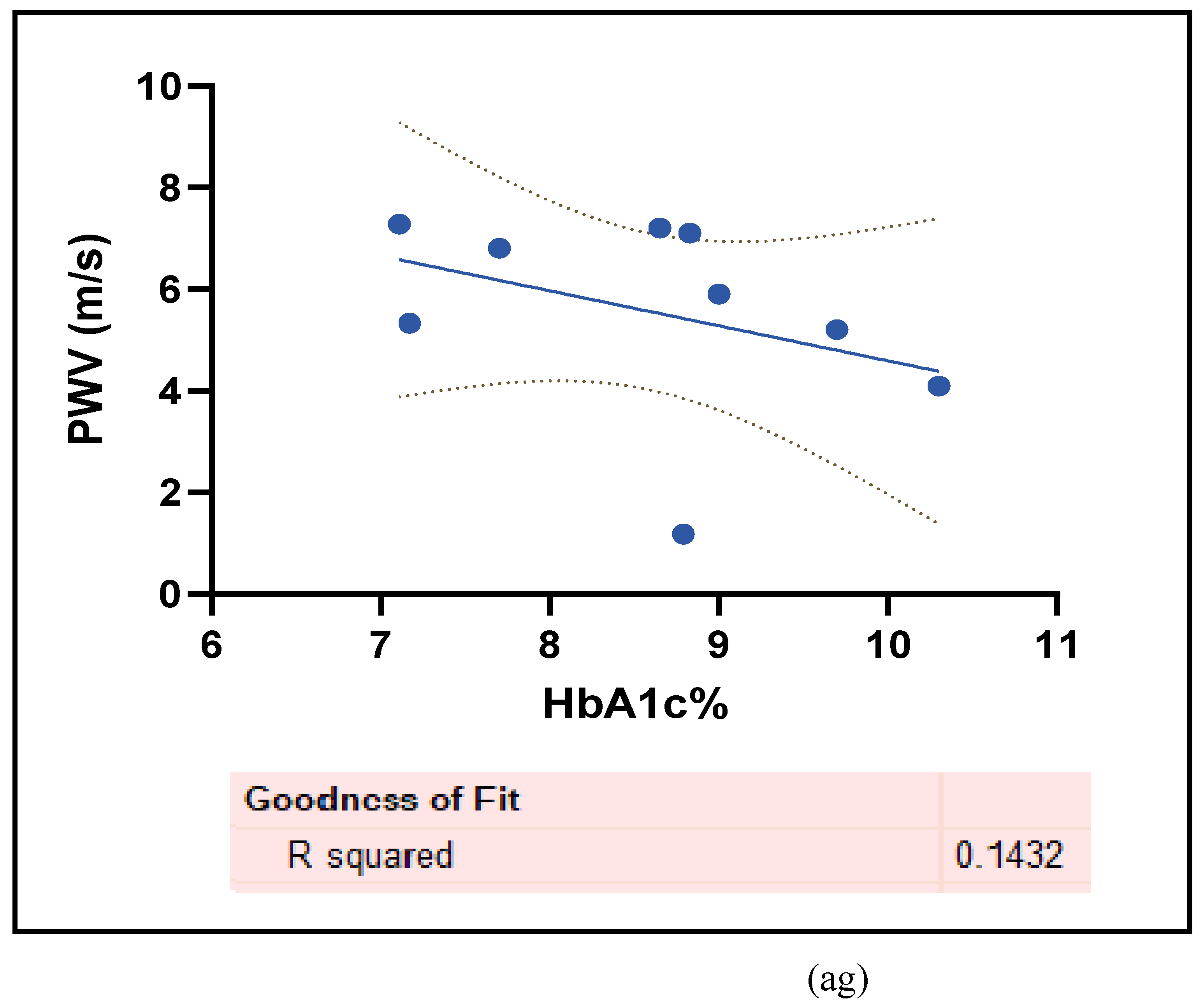
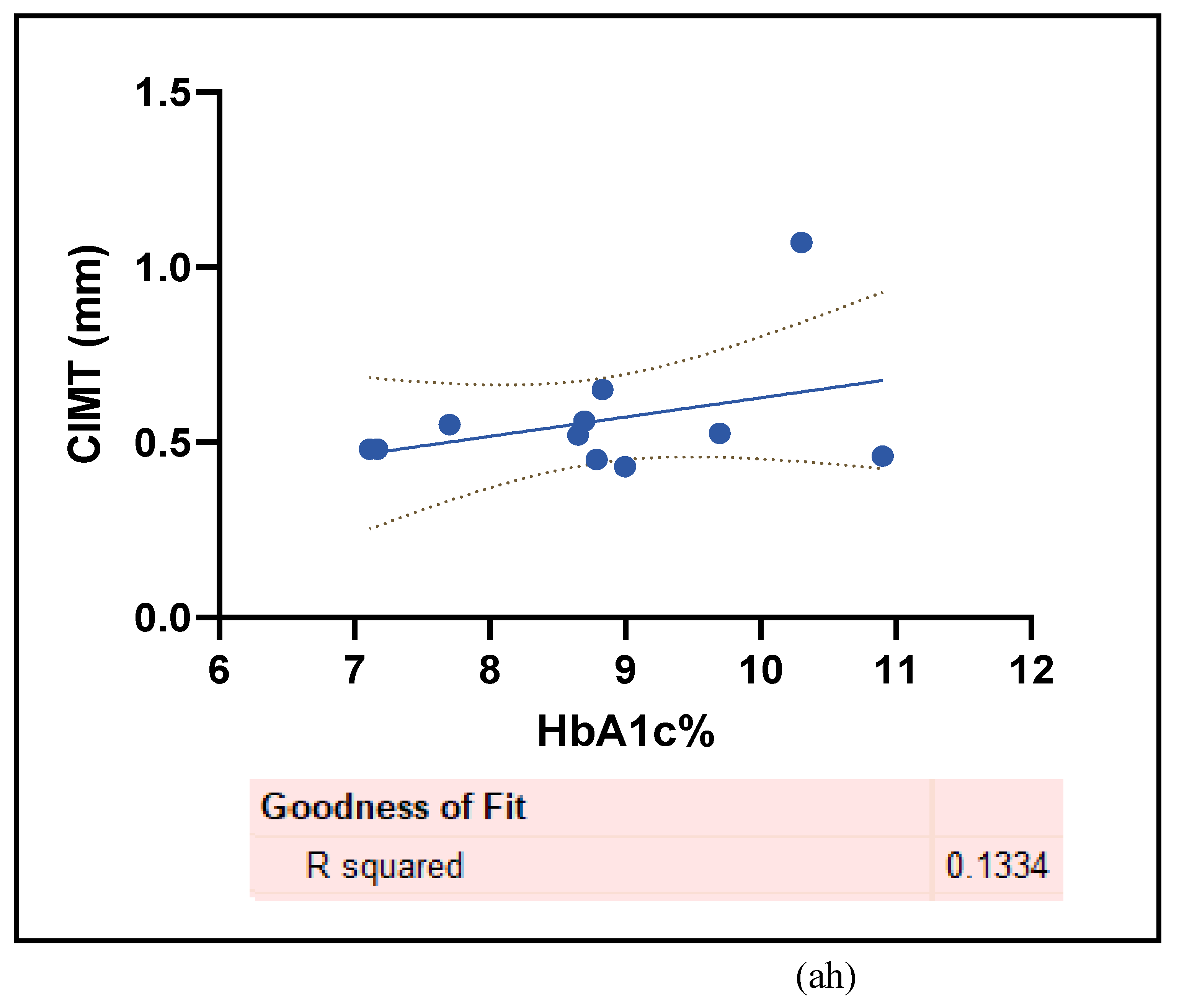
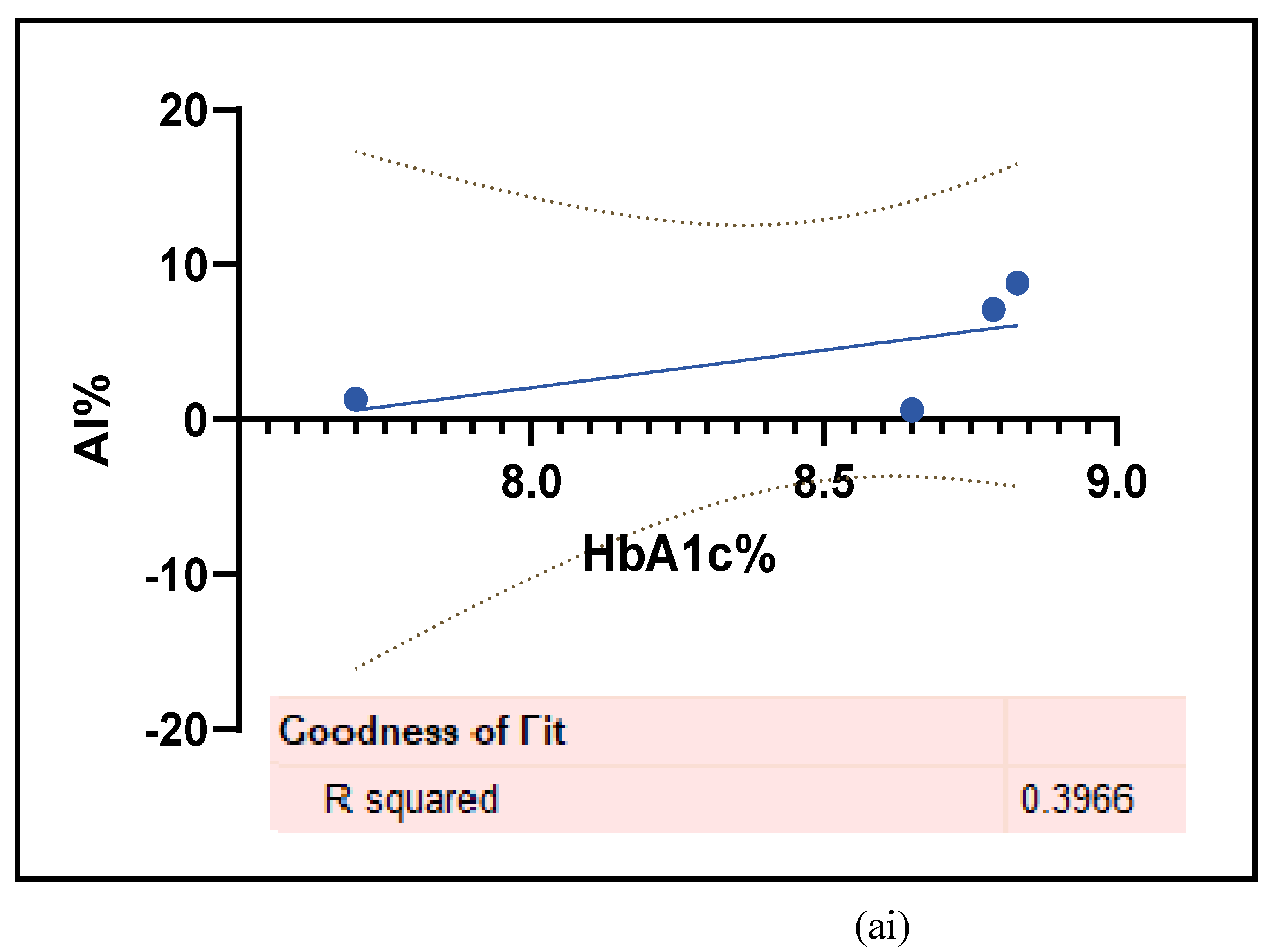
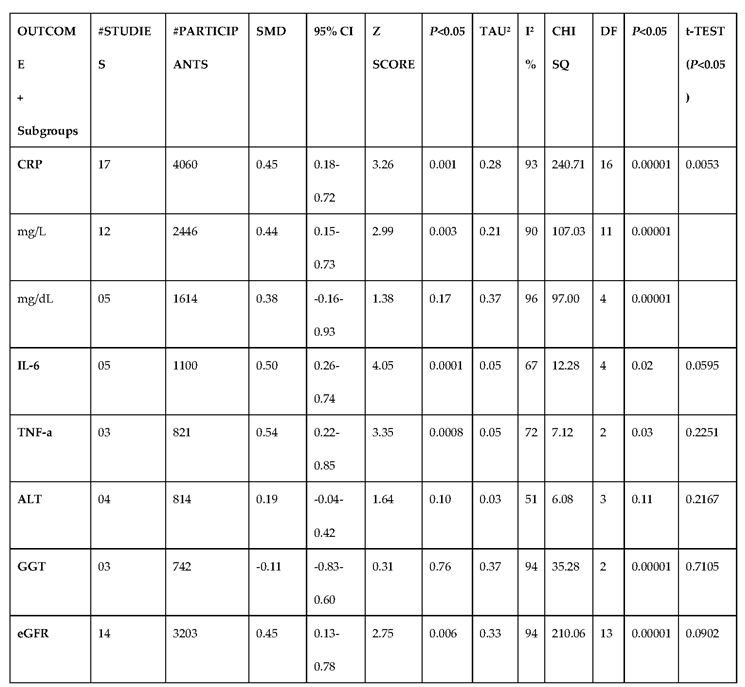
3.2.5. The Inflammatory Targets Were Mostly in Favour of the T1D-Induced ED
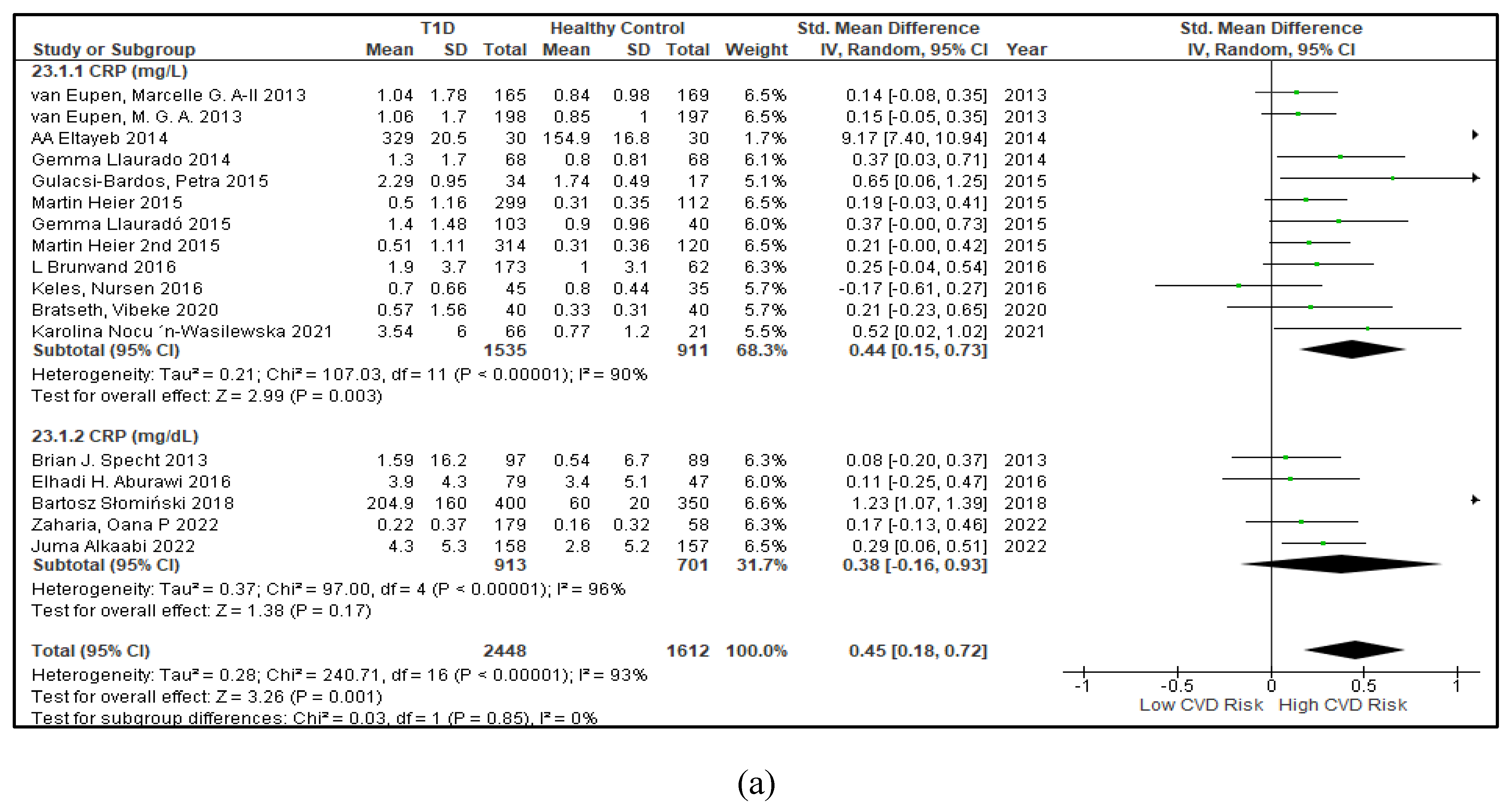
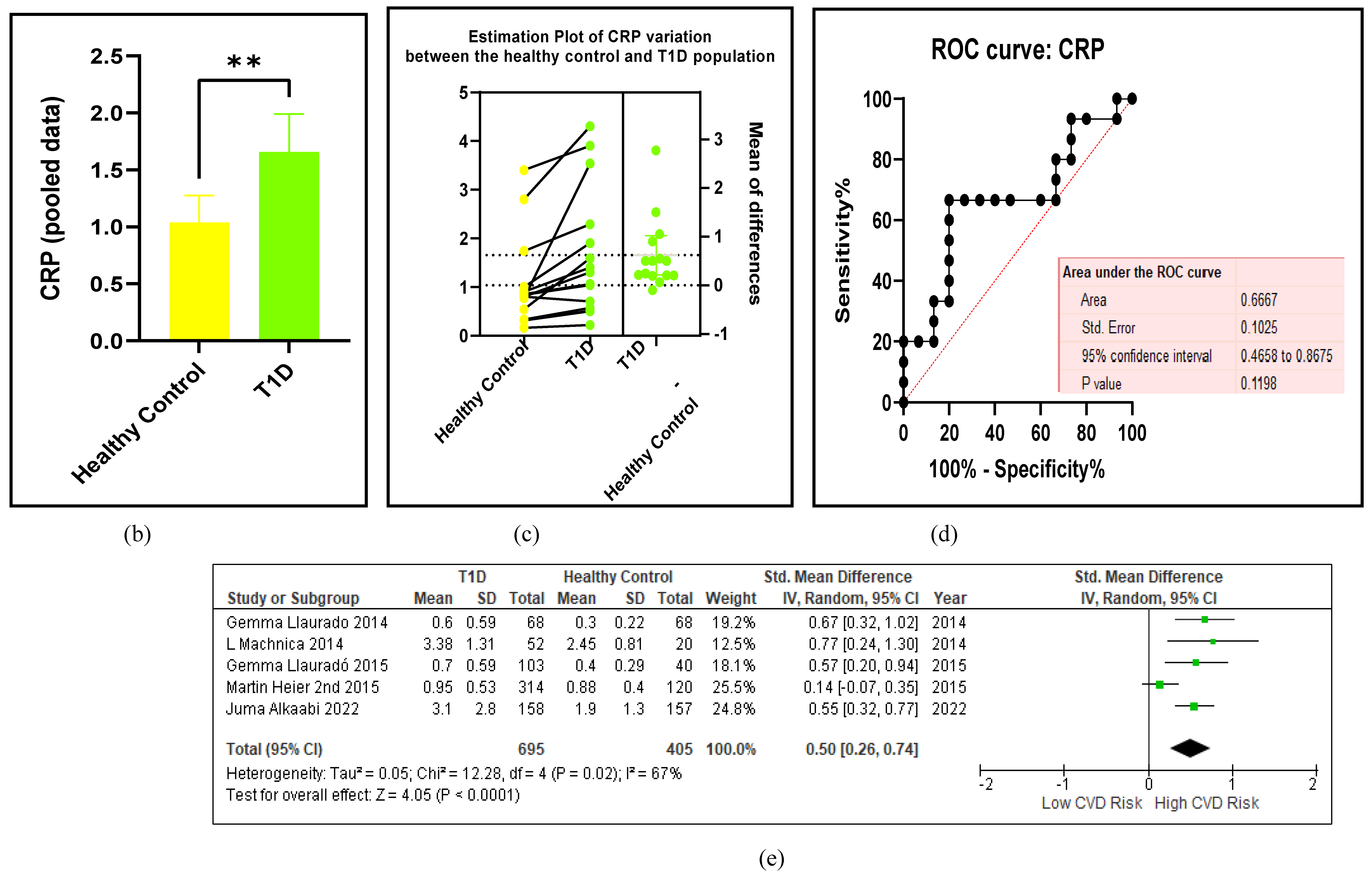
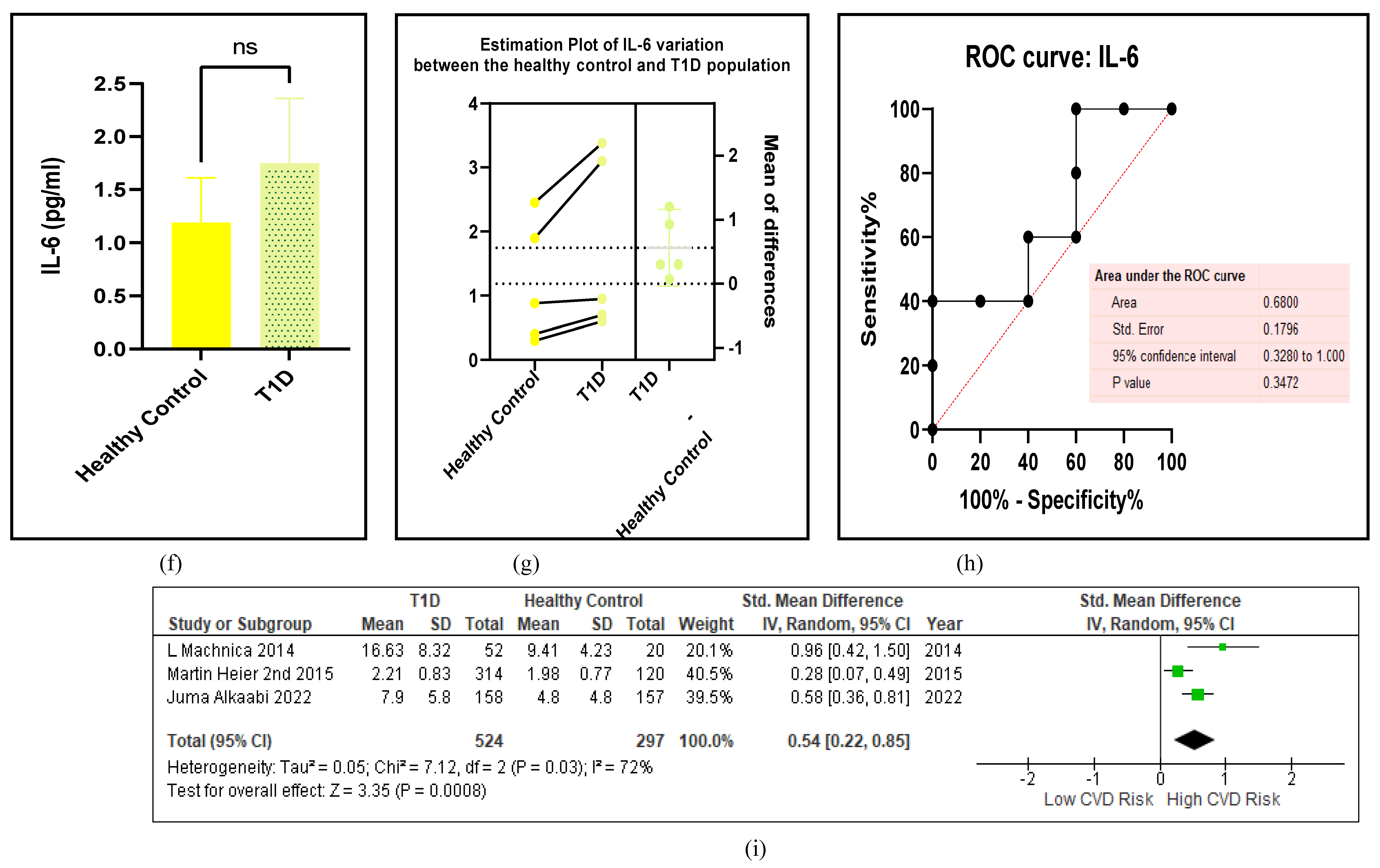
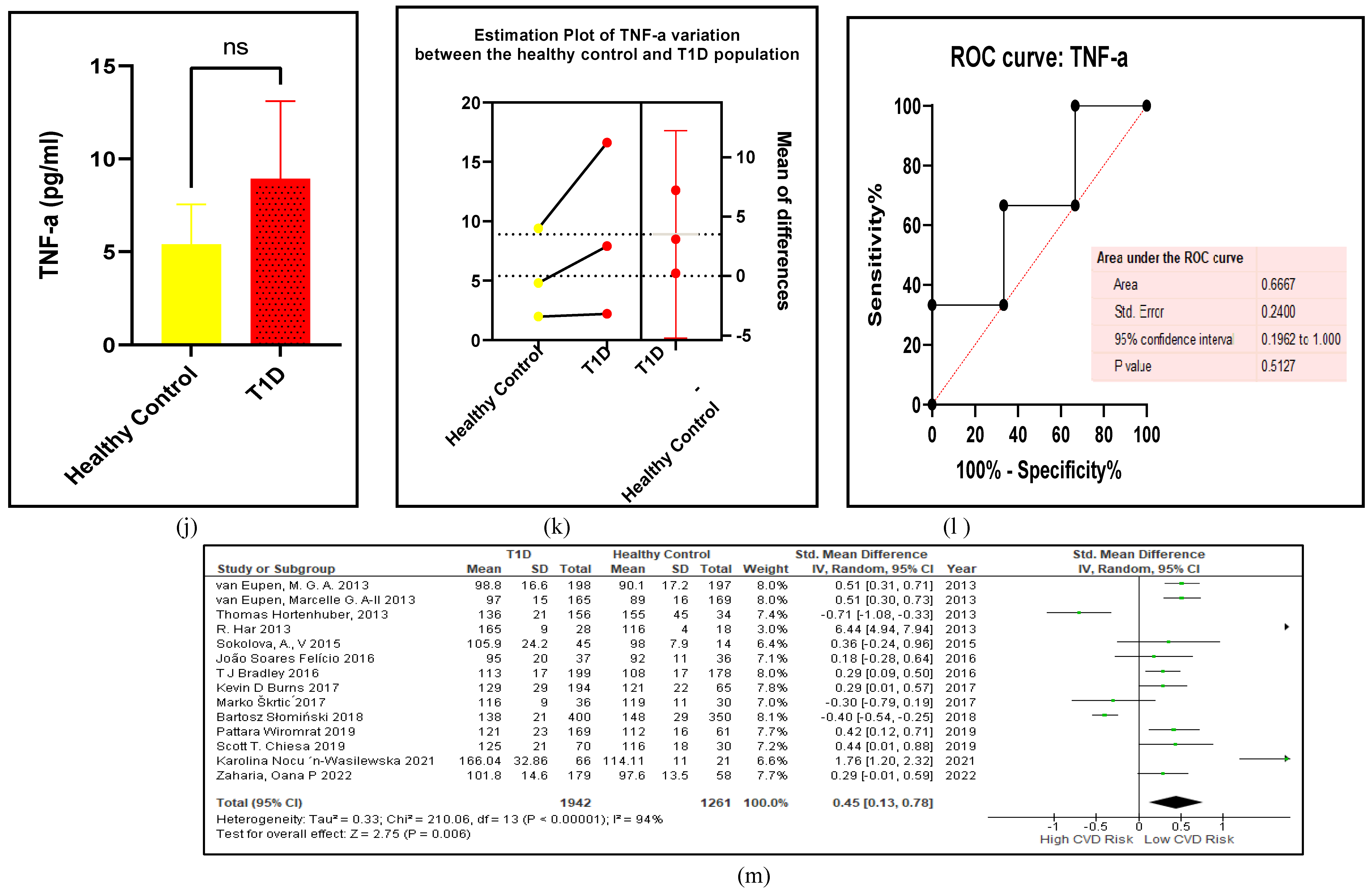
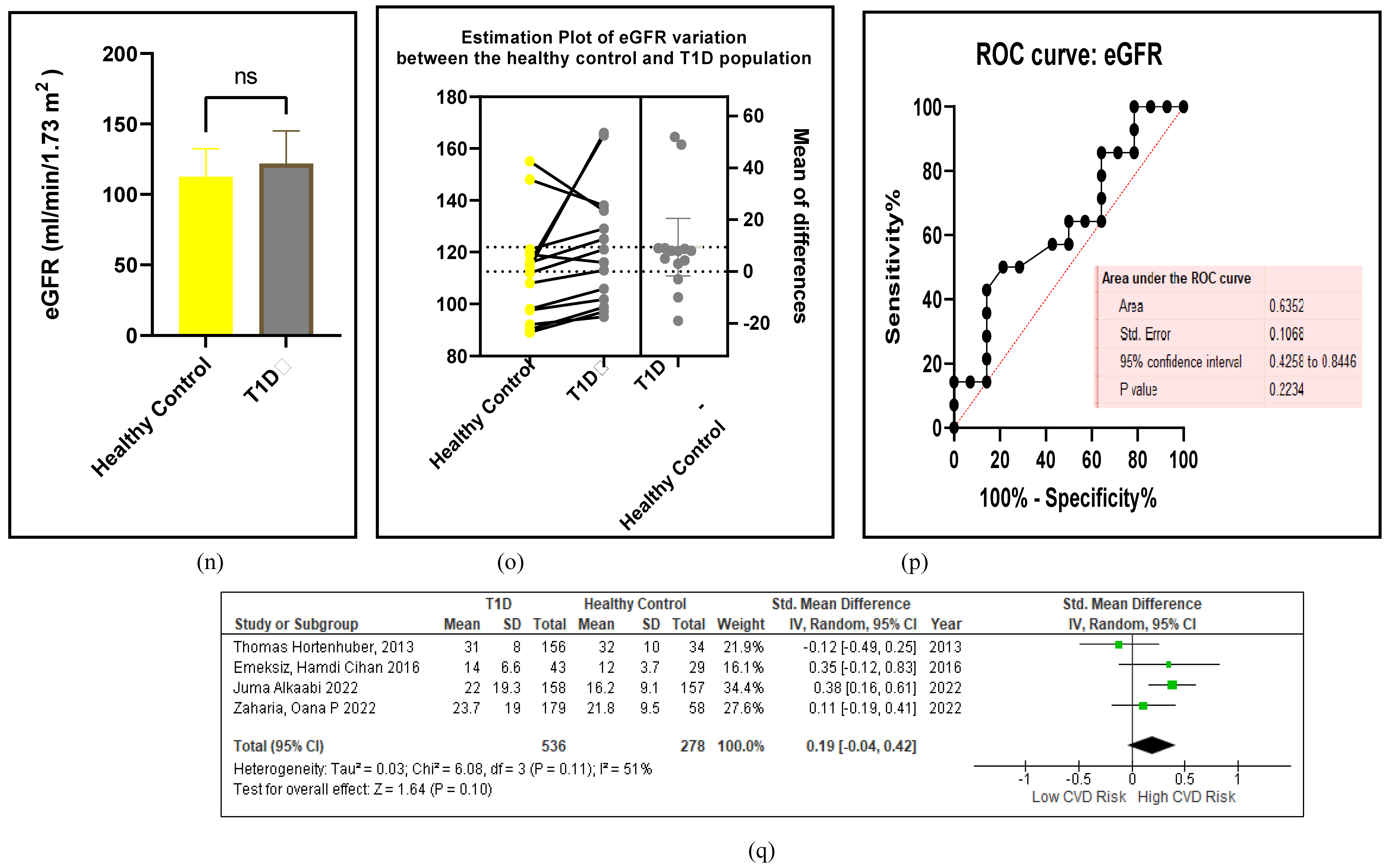
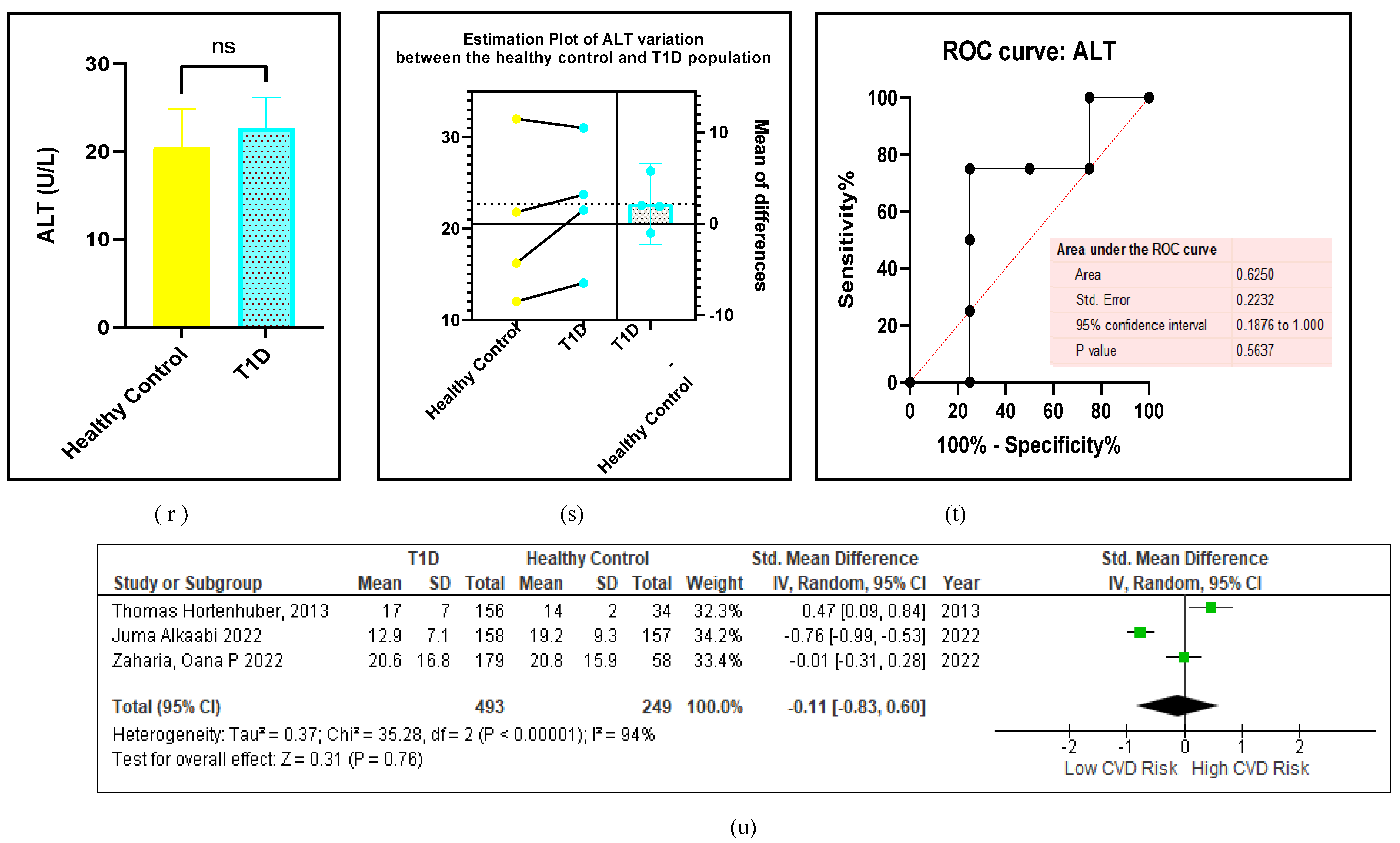
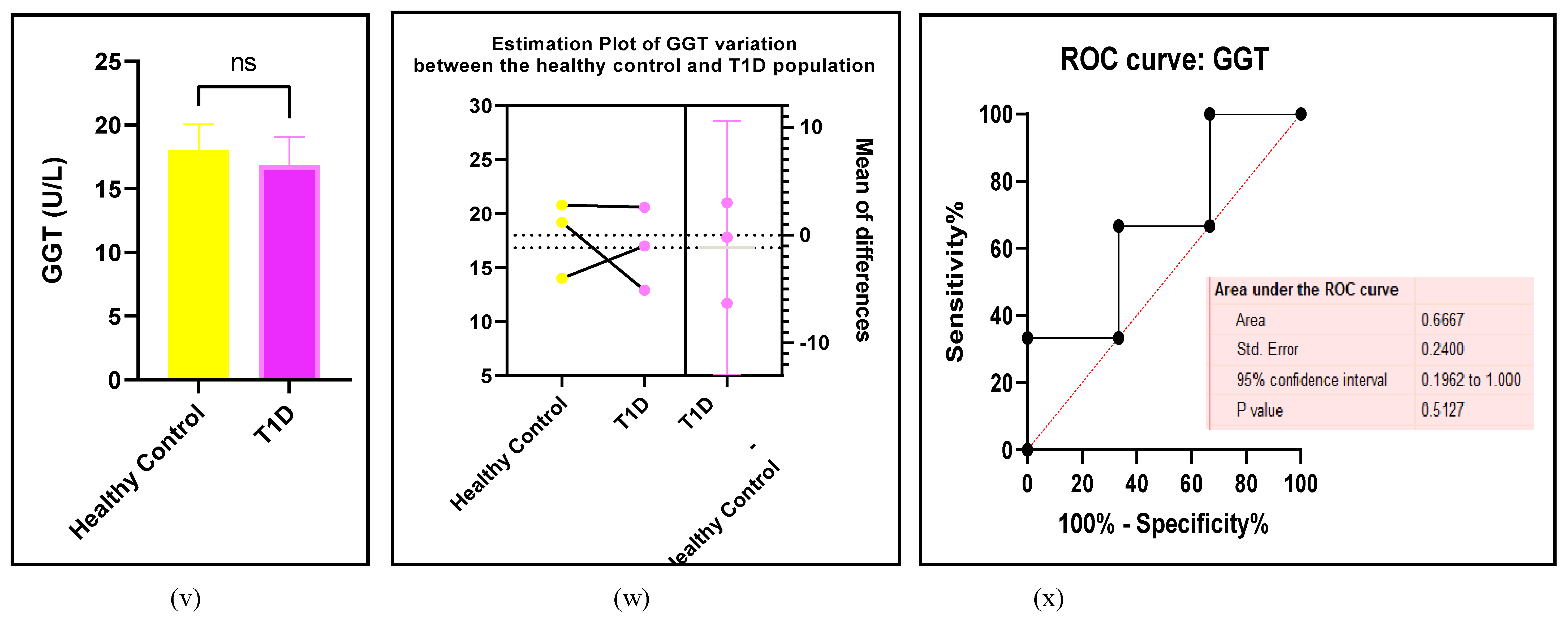
3.2.6. The Obesity Targets Are Also Fitting Biomarkers of T1D-Induced ED
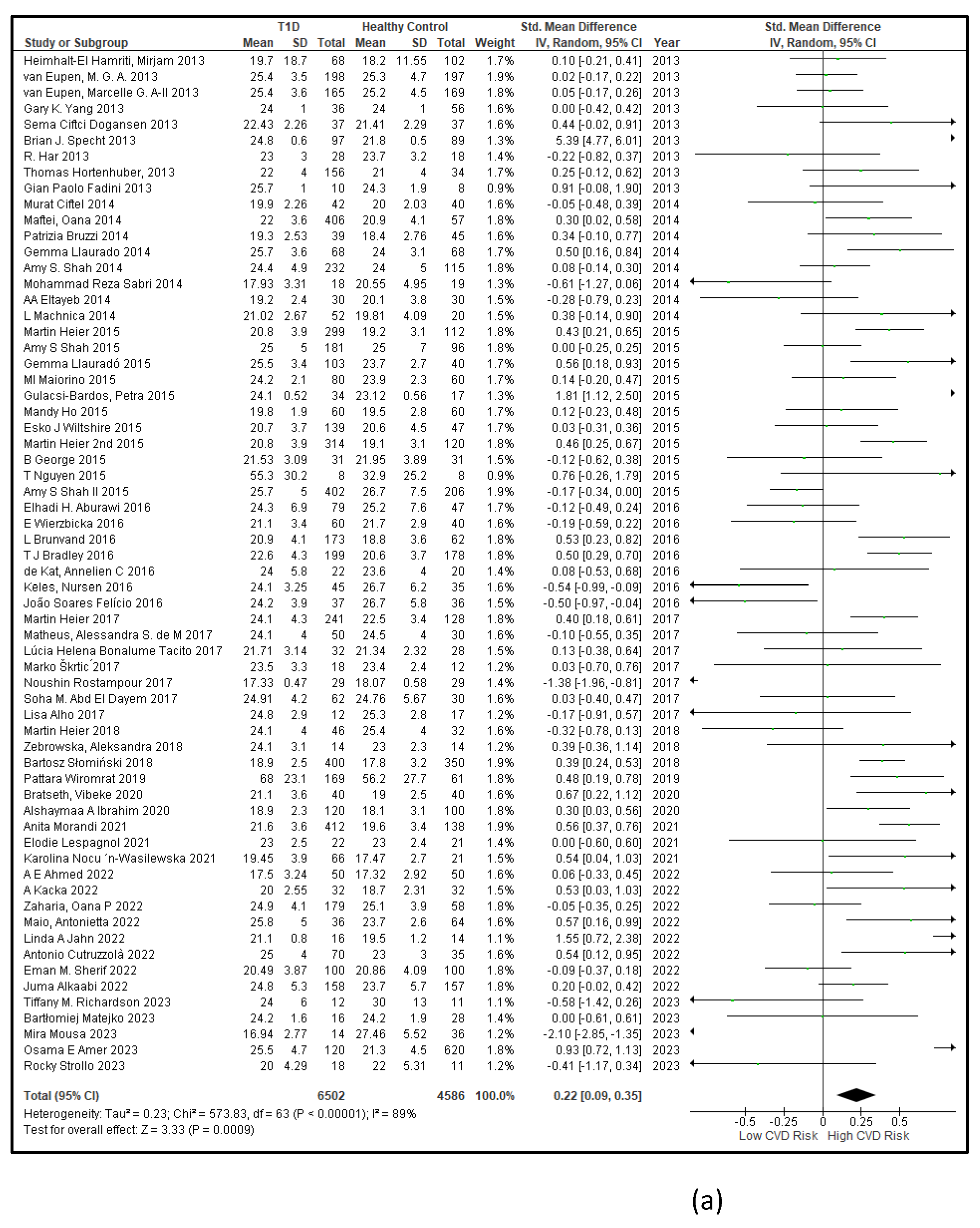
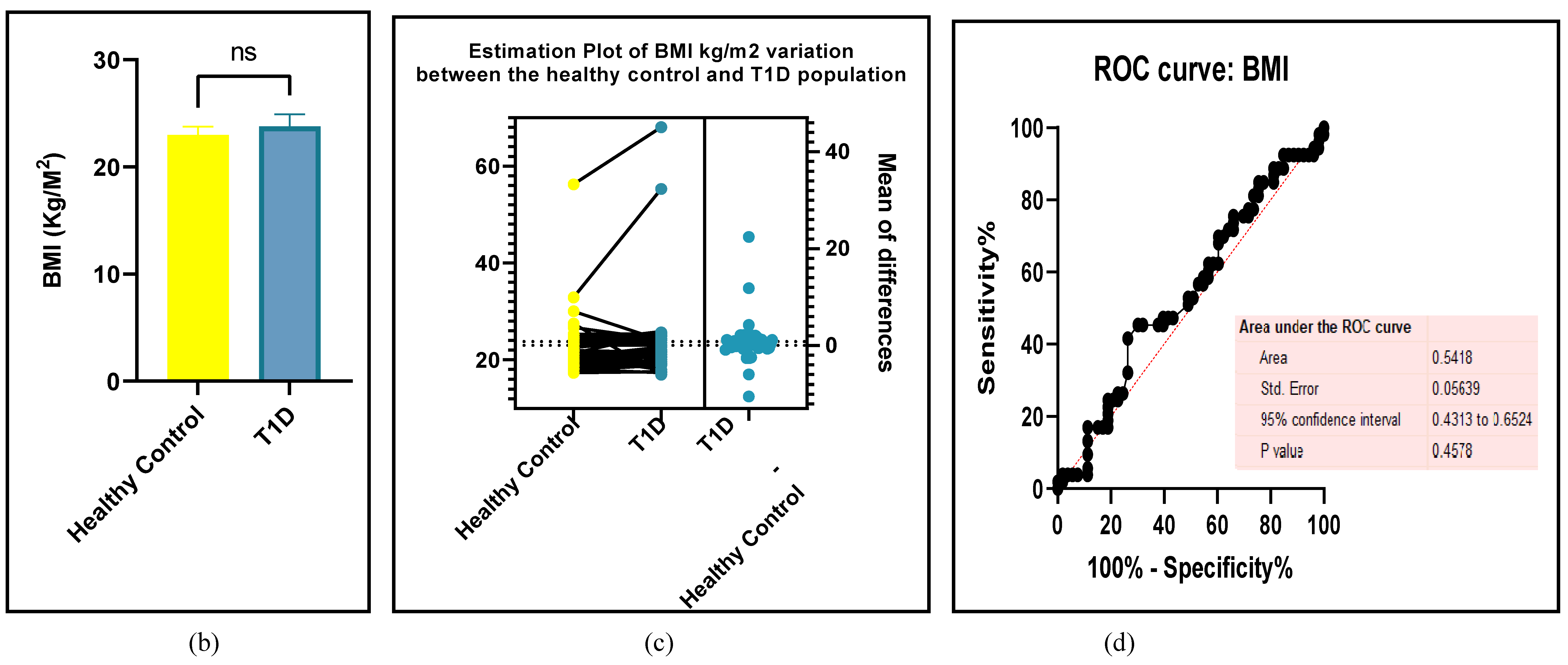
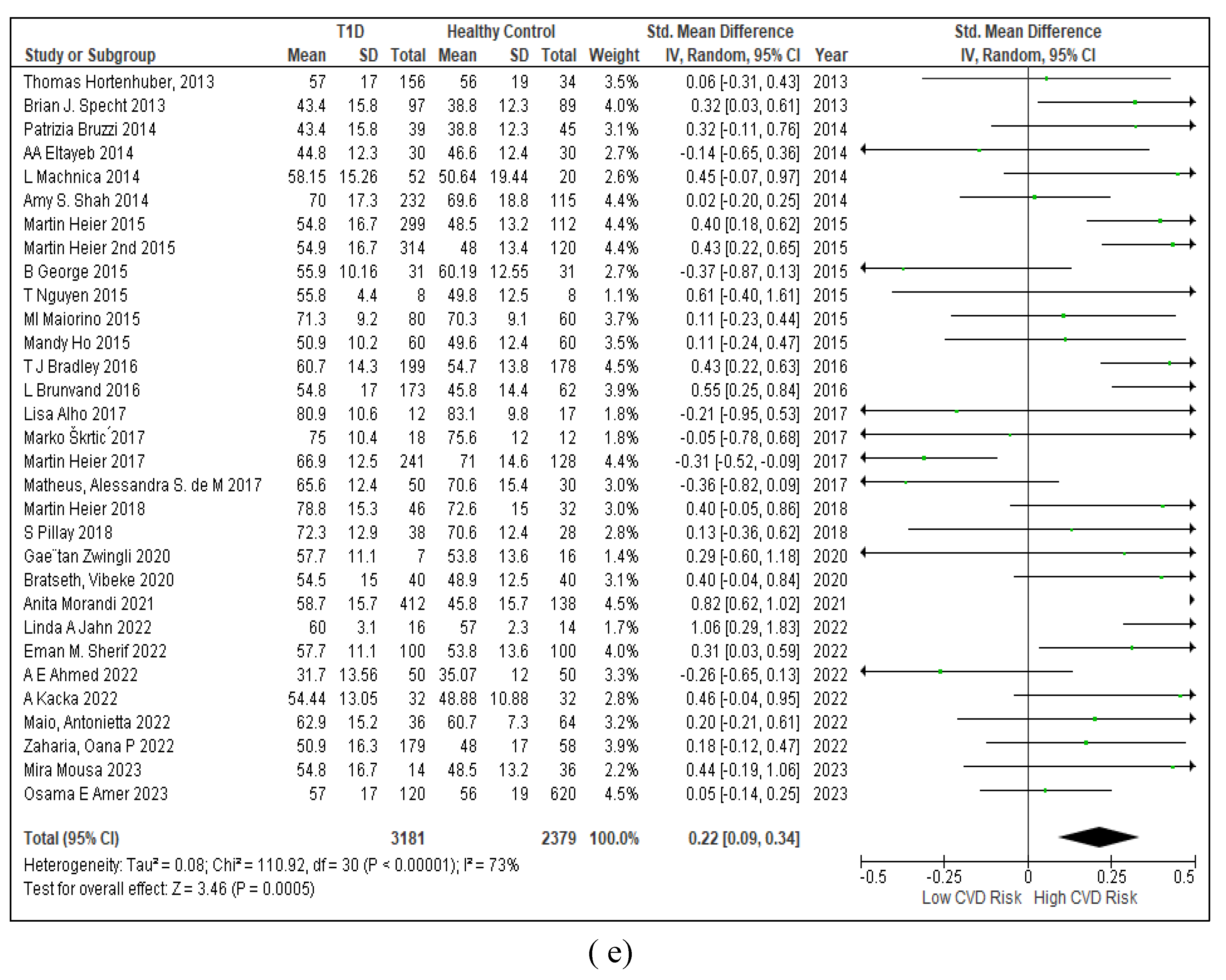
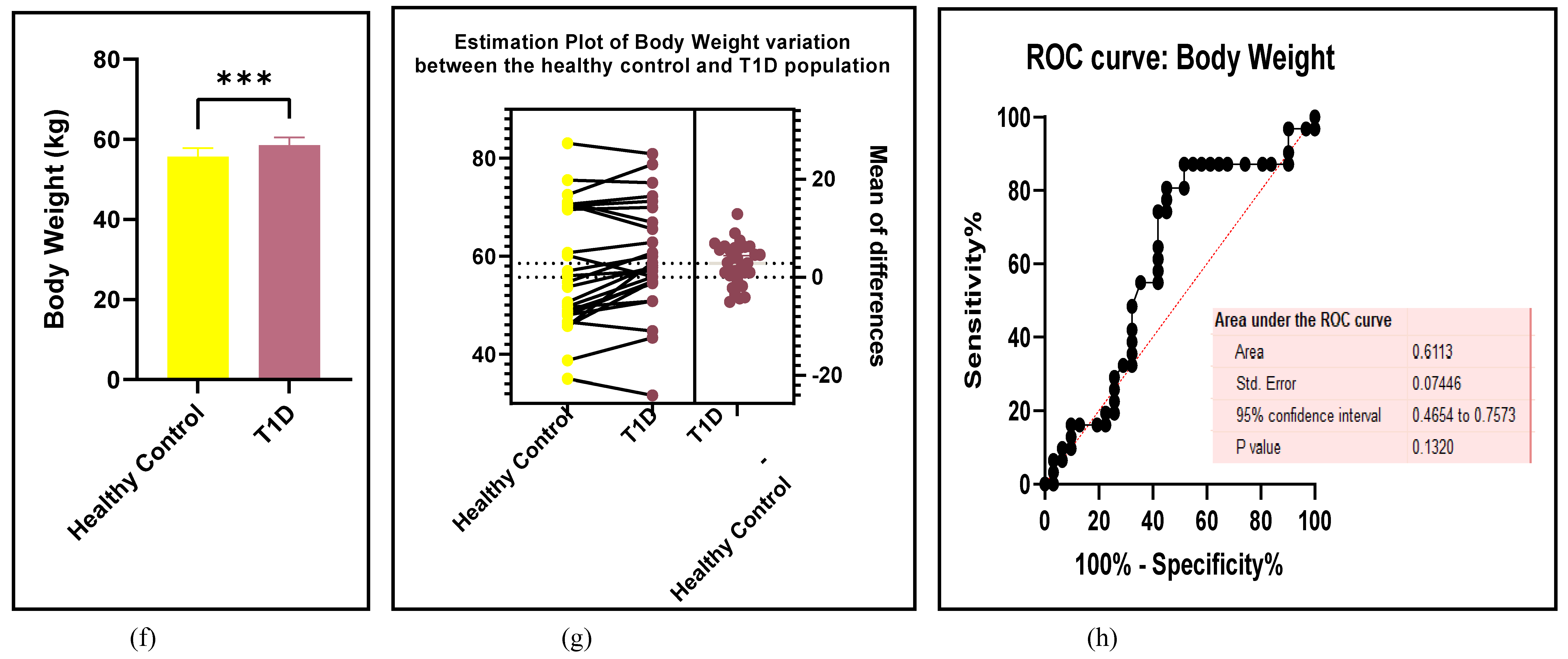
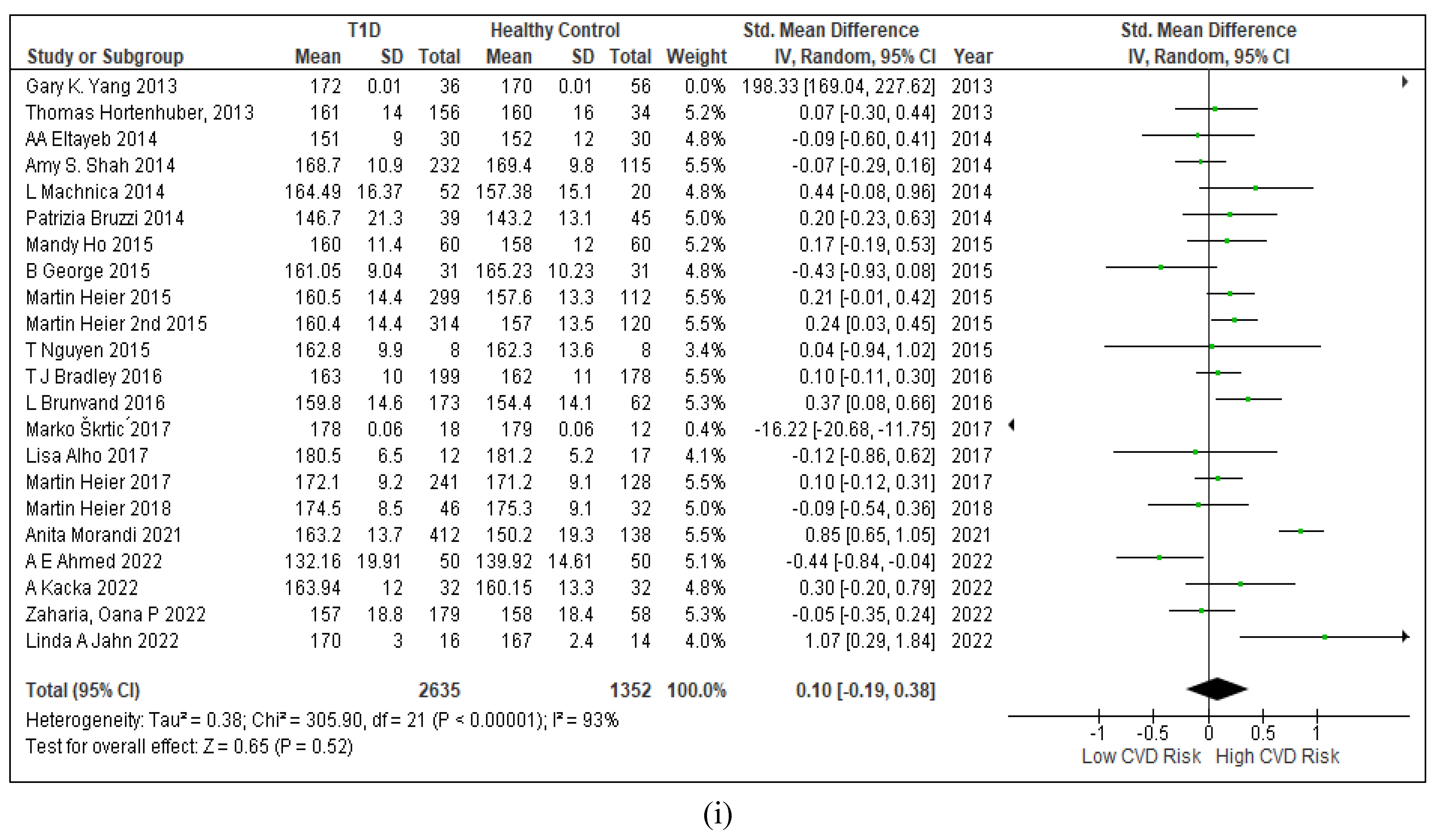
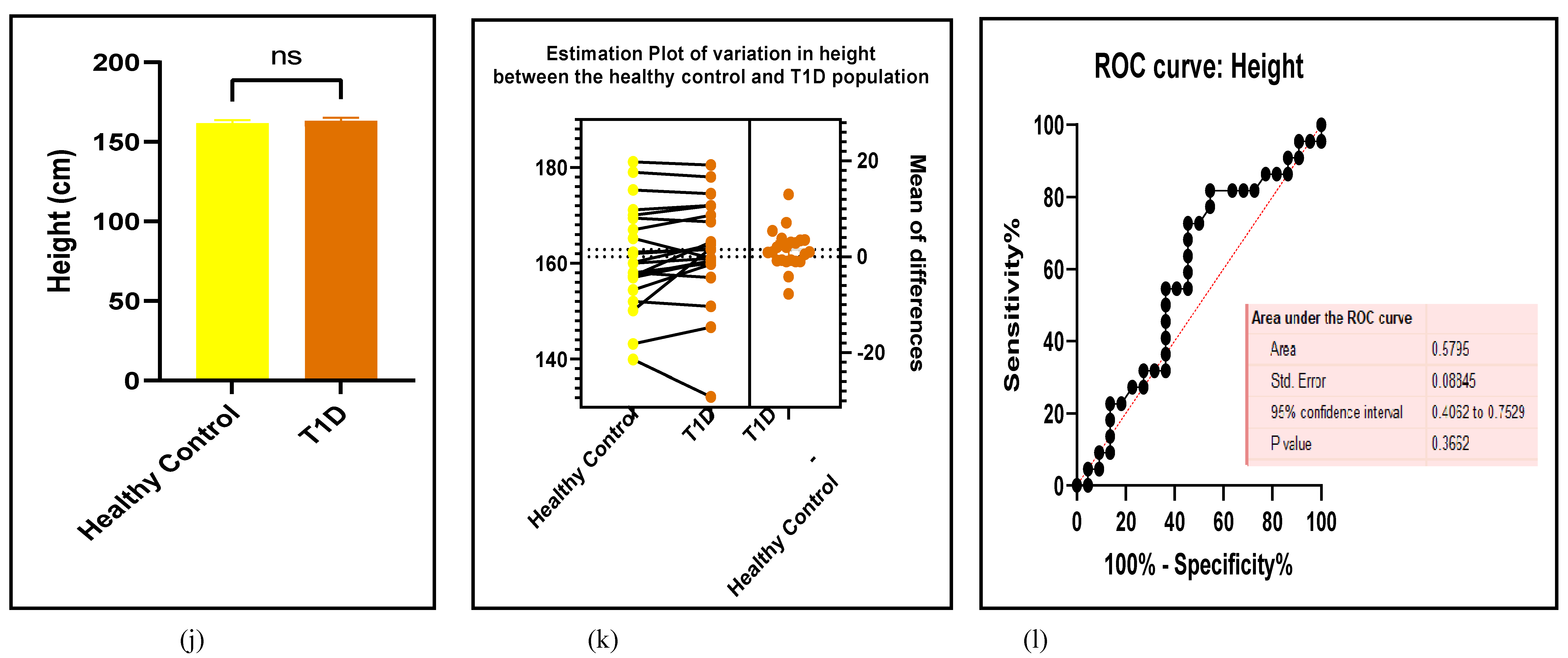
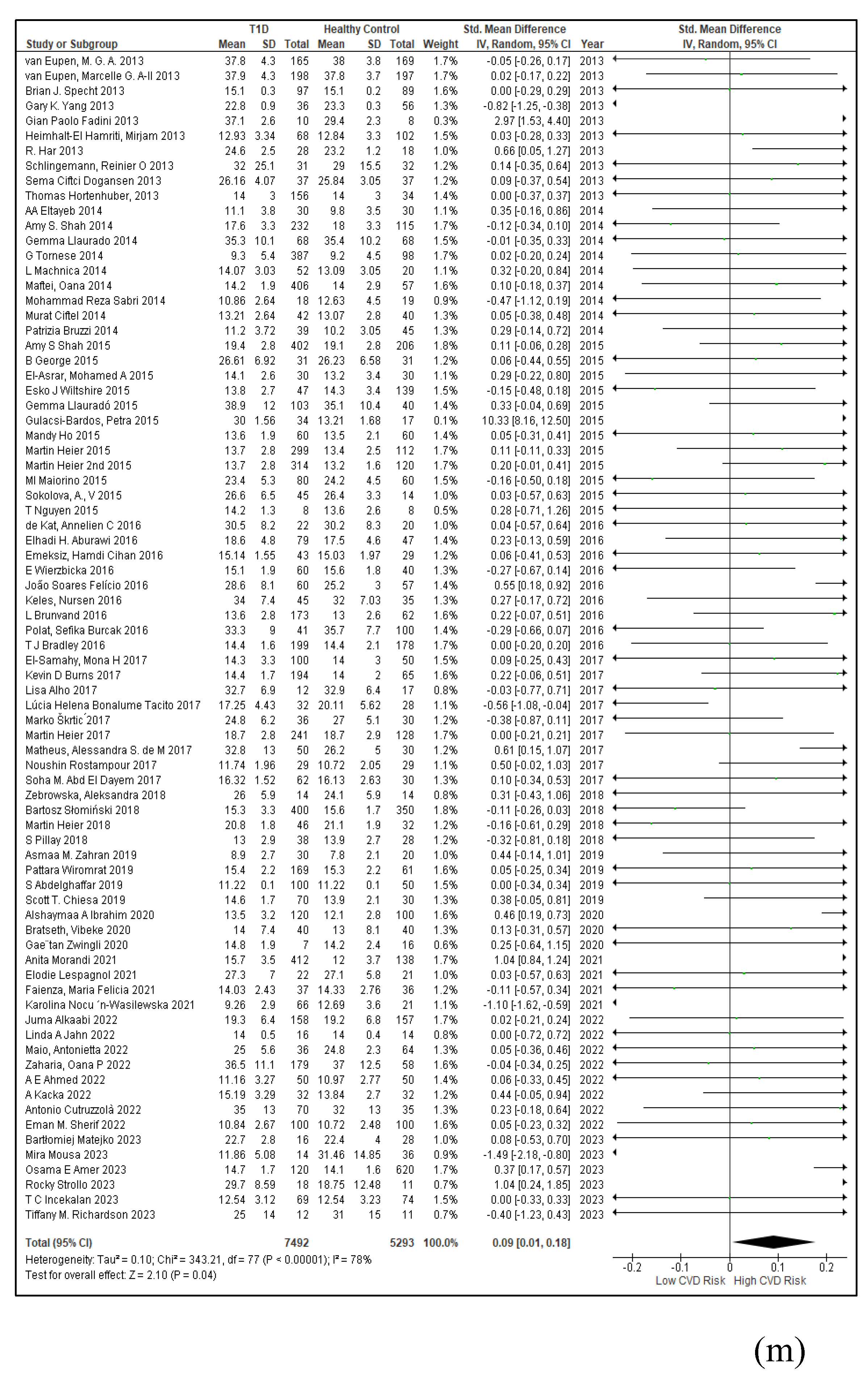
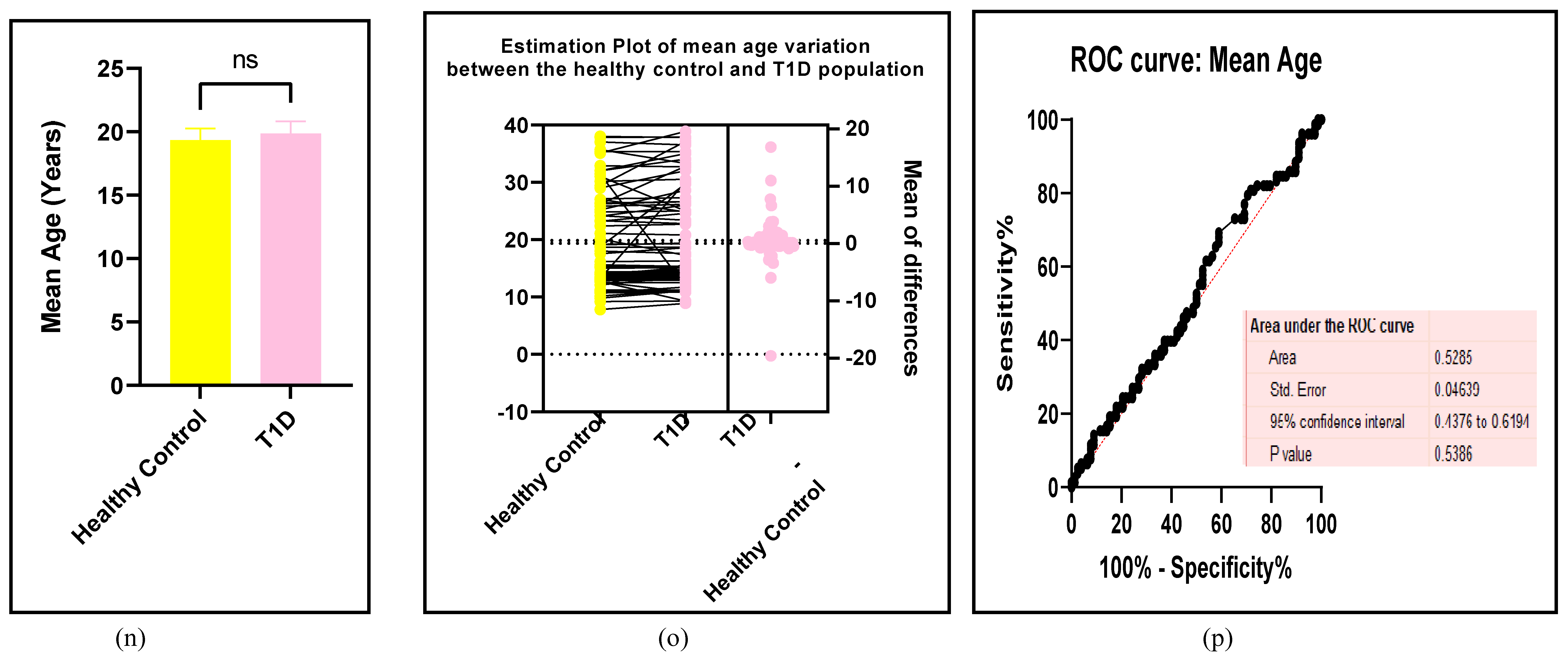
3.2.7. Assessment of the Risk of Bias
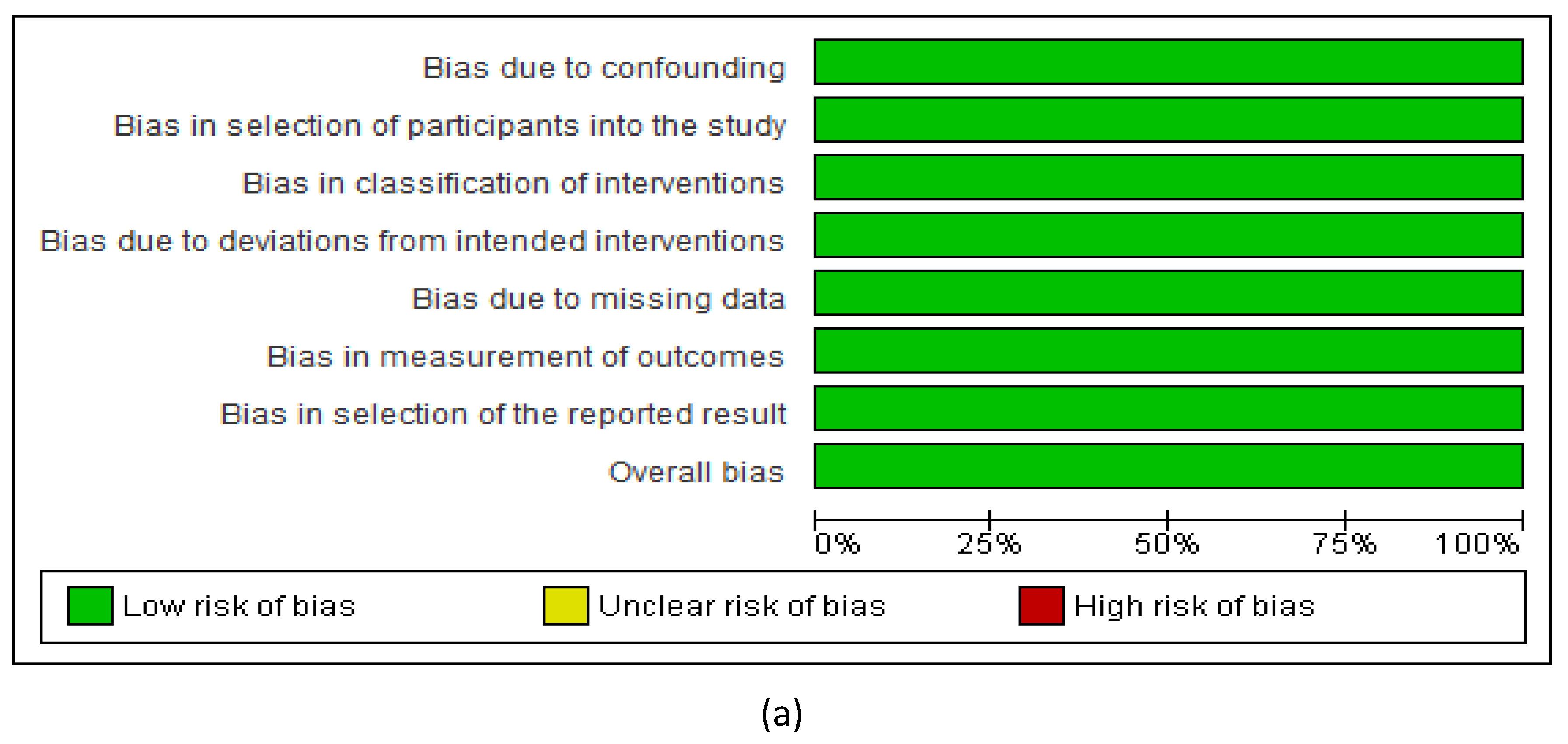
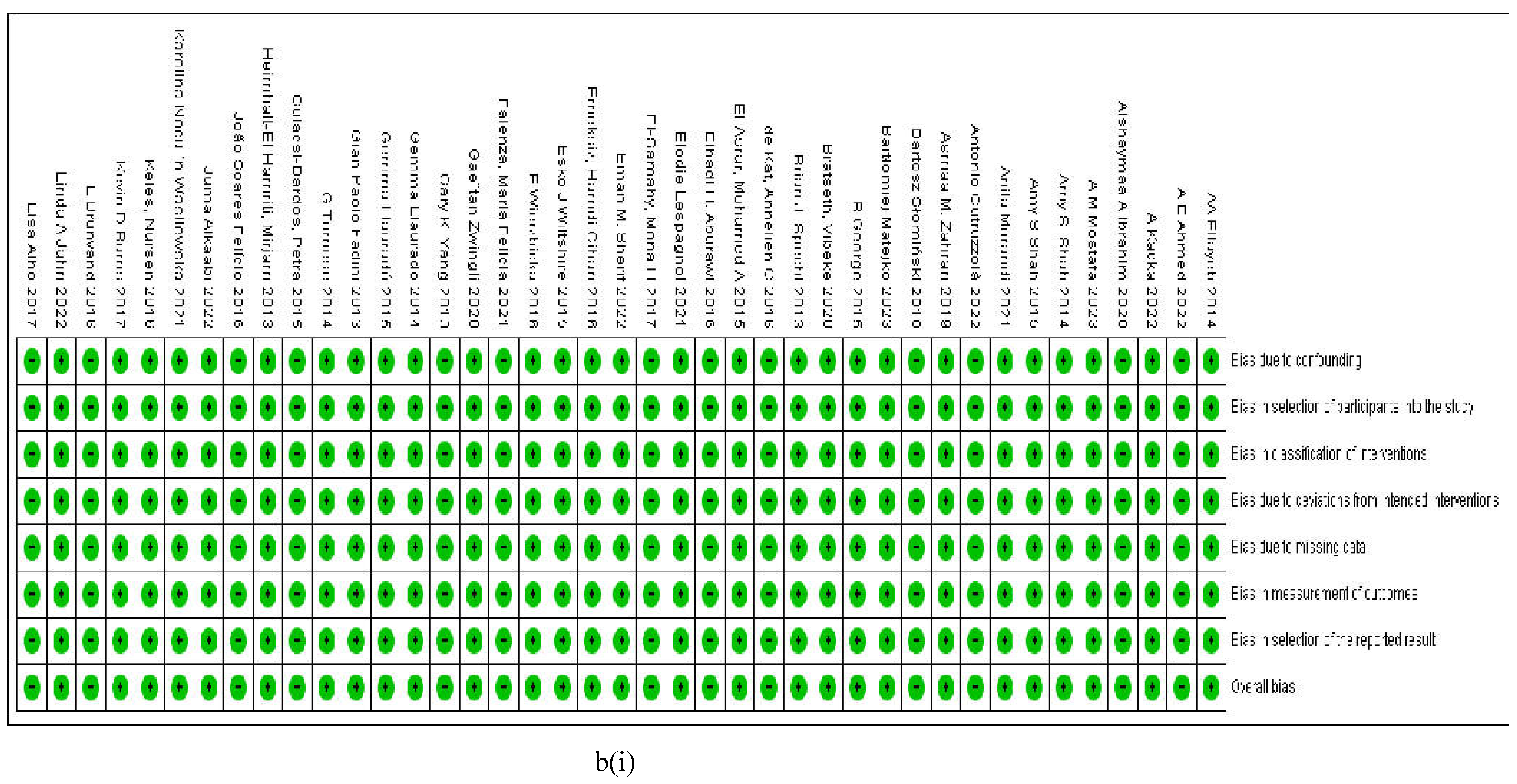
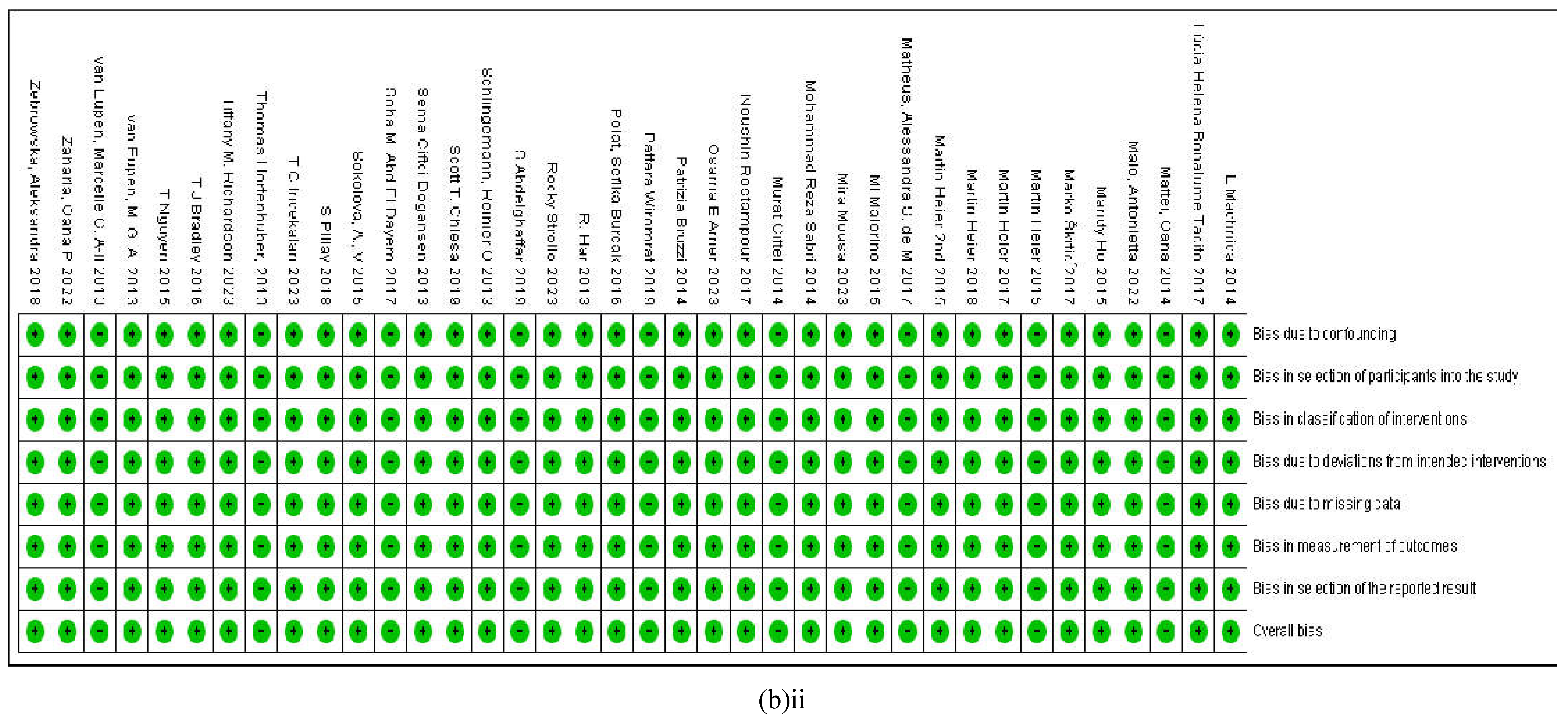
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Disclosure Ethics
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Competing interests
Abbreviations
| ACCORD | Action to control cardiovascular risk in type -2 diabetes |
| Ach | acetylcholine |
| ADVANCE | Action in diabetes and vascular disease -PreterX and DiamicronN controlled evaluation |
| AHA | American heart association |
| AI | augmentation index |
| ALT | alanine transaminase |
| APO | A-apolipoprotein-A |
| APO B | apolipoprotein B |
| ATIR | angiotensin-II type 1 receptor |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BP | blood pressure |
| BW | body weight |
| CIMT | carotid intima media thickness |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease/disorders |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| DCCT/EDIC | Diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications trial |
| ED | endothelial deregulation |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| EP | estimation plot |
| EURODIAB/IDDM | European diabetes centres study of complications in patients with Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus. |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| FINN/DIANE | Finnish diabetic nephropathy study |
| FMD | flow mediated dilatation |
| GGT | gamma glutamyl transferase |
| g | gram |
| HbA1c | glycated haemoglobin |
| HC | healthy control |
| HDL | c-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| HT | height |
| IDF | international diabetes federation |
| IDF | international diabetes federation |
| IL | 6-interleukin-6 |
| kg | kilograms |
| LDL | c-low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| l | litre |
| m | metre |
| MAP | mean arterial pressure |
| MeSH | medical subject headings |
| mg/dl | milligram per decilitre |
| min | minutes |
| mmol/L | millimole per litre |
| m/s | meters per second |
| n | number |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NS | not specified |
| p | probability |
| pg/ml | picogram per millilitre |
| PON-1 | paraoxonase-1 |
| PRISMA | preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses |
| PWV | pulse wave velocity |
| ROBINS-1 | risk of bias in non-randomized studies-1 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SBP | systolic blood pressure |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SEARCH-CVD | SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study |
| sE-Selectin | soluble E-selectin |
| sICAM | soluble intracellular cell adhesion marker |
| SMD | standardized mean difference |
| sVCAM | soluble vascular cell adhesion marker |
| TC | total cholesterol |
| T1D | type-1 diabetes |
| T2D | type-2-diabetes |
| TG | total triglycerides |
| TNF | a-tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| WHO | world health organization |
| WOS | web of science |
References
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Gender differences in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Physiology & behavior. 2018, 187, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, R.C.; Shankar, R.R.; Fineberg, N.; McGill, J.; Baron, A.D. HbA1c measurement improves the detection of type 2 diabetes in high-risk individuals with nondiagnostic levels of fasting plasma glucose: the Early Diabetes Intervention Program (EDIP). Diabetes Care. 2001, 24, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-M.; Jiang, B.-G.; Sun, L,-L. HNF1A: from monogenic diabetes to type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022, 13, 829565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, T.; Rosenbauer, J.; Wild, S.; et al. Diabetes in Europe: an update. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2014, 103, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komulainen, J.; Lounamaa, R.; Knip, M.; Kaprio, E.A.; Akerblom, H.K. Ketoacidosis at the diagnosis of type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus is related to poor residual beta cell function. Childhood Diabetes in Finland Study Group. Archives of disease in childhood. 1996, 75, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Noor, S.; Menzel, A.; Pivina, L.; Bjørklund, G. Obesity and insulin resistance: associations with chronic inflammation, genetic and epigenetic factors. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2021, 28, 800–826. [Google Scholar]
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nature reviews Disease primers. 2017, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, Y.; Galalain, A.; Yunusa, U. A modern overview on diabetes mellitus: a chronic endocrine disorder. European Journal of Biology. 2020, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Araki, S.-i.; Kawai, K.; et al. Declining trends of diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy with improving diabetes care indicators in Japanese patients with type 2 and type 1 diabetes (JDDM 46). BMJ Open Diabetes Research and Care. 2018, 6, e000521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Cardwell, C.R.; Black, C.J.; McCance, D.R.; Patterson, C.C. Excess mortality in Type 1 diabetes diagnosed in childhood and adolescence: a systematic review of population-based cohorts. Acta diabetologica. 2015, 52, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomber, A.; Ward, Z.J.; Ross, C.; et al. Variation in the incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents by world region and country income group: A scoping review. PLOS Global Public Health. 2022, 2, e0001099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrish, N.; Wang, S.-L.; Stevens, L.; Fuller, J.; Keen, H.; Group, W.M.S. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001, 44, S14–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalakova, T.; Yotov, Y.; Tzotchev, K.; et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus-risk factor for cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality. Current Diabetes Reviews. 2021, 17, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Yang, T.; Xu, Y.; et al. δ-Tocotrienol, isolated from rice bran, exerts an anti-inflammatory effect via MAPKs and PPARs signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. International journal of molecular sciences. 2018, 19, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K. Human wound and its burden: updated 2022 compendium of estimates. In. Vol 12: Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers 140 Huguenot Street, 3rd Floor New …; 2023:657-670.
- Avogaro, A.; de Kreutzenberg, S.V.; Fadini, G. Endothelial dysfunction: causes and consequences in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2008, 82, S94–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alho, I. Ankle-Brachial Index and Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index and their association with cardiorespiratory fitness and leisure-time physical activity in men with type 1 diabetes. 2017.
- Tacito, L.H.B.; Pires, A.C.; Yugar-Toledo, J.C. Impaired flow-mediated dilation response and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus with a mean disease duration of 4.1 years. Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2017, 61, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J.; Ronnback, M.; Fagerudd, J.; Forsblom, C. POSTERS: COMPLICATIONS, MACROVASCULAR-ATHEROSCLEROTIC CVD AND HUMAN DIABETES. Diabetes. 2004, 53, A169. [Google Scholar]
- Gildea, N. Pulmonary oxygen uptake and muscle deoxygenation responses during ramp incremental exercise and moderate-and heavy-intensity exercise subsequent to priming exercise in type 2 diabetes, Trinity College Dublin; 2017.
- Heier, M.; Borja, M.S.; Brunborg, C.; et al. Reduced HDL function in children and young adults with type 1 diabetes. Cardiovascular diabetology. 2017, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, G.R.; Pober, D.; Galderisi, A.; et al. Glycemic Control, Cardiac Autoimmunity, and Long-Term Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A DCCT/EDIC Cohort–Based Study. Circulation. 2019, 139, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.K.; Maahs, D.M.; Perkins, B.A.; Cherney, D.Z. Renal hyperfiltration and systemic blood pressure in patients with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. PloS one. 2013, 8, e68908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörtenhuber, T.; Rami-Mehar, B.; Satler, M.; et al. Endothelial progenitor cells are related to glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes over time. Diabetes care. 2013, 36, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadini, G.P.; Albiero, M.; Vigili de Kreutzenberg, S.; et al. Diabetes impairs stem cell and proangiogenic cell mobilization in humans. Diabetes care. 2013, 36, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogansen, S.C.; Helvaci, A.; Adas, M.; Onal, S.D. The relationship between early atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction in type 1 diabetic patients as evidenced by measurement of carotid intima-media thickness and soluble CD146 levels: a cross sectional study. Cardiovascular Diabetology. 2013, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, B.J.; Wadwa, R.P.; Snell-Bergeon, J.K.; Nadeau, K.J.; Bishop, F.K.; Maahs, D.M. Estimated insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular disease risk factors in adolescents with and without type 1 diabetes. The Journal of pediatrics. 2013, 162, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Har, R.; Scholey, J.; Daneman, D.; et al. The effect of renal hyperfiltration on urinary inflammatory cytokines/chemokines in patients with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2013, 56, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eupen, M.G.; Schram, M.T.; Colhoun, H.M.; Scheijen, J.L.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Schalkwijk, C.G. Plasma levels of advanced glycation endproducts are associated with type 1 diabetes and coronary artery calcification. Cardiovascular diabetology. 2013, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimhalt-El Hamriti, M.; Schreiver, C.; Noerenberg, A.; et al. Impaired skin microcirculation in paediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovascular diabetology. 2013, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlingemann, R.O.; Van Noorden, C.J.; Diekman, M.J.; et al. VEGF levels in plasma in relation to platelet activation, glycemic control, and microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes care. 2013, 36, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eupen, M.; Schram, M.; Colhoun, H.; et al. The methylglyoxal-derived AGE tetrahydropyrimidine is increased in plasma of individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus and in atherosclerotic lesions and is associated with sVCAM-1. Diabetologia. 2013, 56, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çiftel, M.; Ertuğ, H.; Parlak, M.; Akçurin, G.; Kardelen, F. Investigation of endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus and the association with diastolic dysfunction. Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research. 2014, 11, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, M.R.; Tavana, E.N.; Ahmadi, A.; Hashemipour, M. The effect of vitamin C on endothelial function of children with type 1 diabetes: an experimental study. International journal of preventive medicine. 2014, 5, 999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruzzi, P.; Predieri, B.; Patianna, V.D.; et al. Longitudinal evaluation of endothelial function in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A long-term follow-up study. Pediatrics International. 2014, 56, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.S.; Dabelea, D.; Talton, J.W.; et al. Smoking and arterial stiffness in youth with type 1 diabetes: the SEARCH Cardiovascular Disease Study. The Journal of pediatrics. 2014, 165, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llauradó, G.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Vilardell, C.; et al. Advanced glycation end products are associated with arterial stiffness in type 1 diabetes. J Endocrinol. 2014, 221, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornese, G.; Iafusco, D.; Monasta, L.; et al. The levels of circulating TRAIL at the onset of type 1 diabetes are markedly decreased in patients with ketoacidosis and with the highest insulin requirement. Acta diabetologica. 2014, 51, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltayeb, A.A.; Ahmad, F.-A.; Sayed, D.M.; Osama, A.M. Subclinical vascular endothelial dysfunctions and myocardial changes with type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Pediatric cardiology. 2014, 35, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machnica, L.; Deja, G.; Polanska, J.; Jarosz-Chobot, P. Blood pressure disturbances and endothelial dysfunction markers in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2014, 237, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftei, O.; Pena, A.S.; Sullivan, T.; et al. Early atherosclerosis relates to urinary albumin excretion and cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Adolescent type 1 Diabetes cardio-renal Intervention Trial (AdDIT). Diabetes care. 2014, 37, 3069–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.; Black, S.; Wadwa, R.P.; et al. Insulin sensitivity and arterial stiffness in youth with type 1 diabetes: the SEARCH CVD study. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications. 2015, 29, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.; Wadwa, R.P.; Dabelea, D.; et al. Arterial stiffness in adolescents and young adults with and without type 1 diabetes: the SEARCH CVD study. Pediatric diabetes. 2015, 16, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, M.; Margeirsdottir, H.D.; Brunborg, C.; Hanssen, K.F.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Seljeflot, I. Inflammation in childhood type 1 diabetes; influence of glycemic control. Atherosclerosis. 2015, 238, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.; Benitez-Aguirre, P.Z.; Donaghue, K.C.; et al. Arterial elasticity in obese adolescents with clinical features of insulin resistance. Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research. 2015, 12, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire, E.J.; Peña, A.S.; MacKenzie, K.; Bose-Sundernathan, T.; Gent, R.; Couper, J.J. A NOS3 polymorphism determines endothelial response to folate in children with type 1 diabetes or obesity. The Journal of Pediatrics. 2015, 166, 319–325 e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heier, M.; Margeirsdottir, H.D.; Gaarder, M.; et al. Soluble RAGE and atherosclerosis in youth with type 1 diabetes: a 5-year follow-up study. Cardiovascular diabetology. 2015, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, B.; Bantwal, G.; Ayyar, V.; Mathew, V. Occurrence of increased arterial stiffness in a cohort of adult patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus when compared to normoglycemic controls. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology. 2014, 9, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Obeid, J.; Walker, R.G.; et al. Fitness and physical activity in youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus in good or poor glycemic control. Pediatric Diabetes. 2015, 16, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaurado, G.; Sevastianova, K.; Sädevirta, S.; et al. Liver fat content and hepatic insulin sensitivity in overweight patients with type 1 diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2015, 100, 607–616. [Google Scholar]
- Maiorino, M.I.; Della Volpe, E.; Olita, L.; Bellastella, G.; Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Glucose variability inversely associates with endothelial progenitor cells in type 1 diabetes. Endocrine. 2015, 48, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, A.; Kochegura, T.; Parfyonova, E.; Shestakova, M. Examination number of circulating progenitor endothelial cells in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus. 2015, 18, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulácsi-Bárdos, P.; Nieszner, É.; Tóth-Zsámboki, E.; et al. Non-invasive, Complex Examination of Micro-and Macrovascular System of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus with or Without Vascular Complications. Journal of Cardiovascular Emergencies. 2015, 1, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asrar, M.A.; Andrawes, N.G.; Ismail, E.A.; Salem, S.M. Kallistatin as a marker of microvascular complications in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Relation to carotid intima media thickness. Vascular medicine. 2015, 20, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kat, A.C.; Gremmels, H.; Verhaar, M.C.; Broekmans, F.J.; Yarde, F. Early vascular damage in young women with DM-1 and its relation to anti-Müllerian hormone: a cross-sectional study. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeksiz, H.C.; Bideci, A.; Damar, Ç.; et al. Soluble endoglin level increase occurs prior to development of subclinical structural vascular alterations in diabetic adolescents. Journal of clinical research in pediatric endocrinology. 2016, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, N.; Dogan, B.; Kalcik, M.; et al. Is serum Klotho protective against atherosclerosis in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus? Journal of Diabetes and its Complications. 2016, 30, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, S.B.; Ugurlu, N.; Aslan, N.; Cuhaci, N.; Ersoy, R.; Cakir, B. Evaluation of biochemical and clinical markers of endothelial dysfunction and their correlation with urinary albumin excretion in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Archives of endocrinology and metabolism. 2016, 60, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, E.; Szalecki, M.; Pludowski, P.; Jaworski, M.; Brzozowska, A. Vitamin D status, body composition and glycemic control in Polish adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Minerva endocrinologica. 2016, 41, 445–455. [Google Scholar]
- Brunvand, L.; Fugelseth, D.; Stensaeth, K.H.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Margeirsdottir, H.D. Early reduced myocardial diastolic function in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus a population-based study. BMC cardiovascular disorders. 2016, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, T.J.; Slorach, C.; Mahmud, F.H.; et al. Early changes in cardiovascular structure and function in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Cardiovascular diabetology. 2016, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felício, J.S.; Luz, R.M.; De Melo FTC, et al. Vitamin D on early stages of diabetic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Frontiers in endocrinology. 2016, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburawi, E.H.; AlKaabi, J.; Zoubeidi, T.; et al. Subclinical inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in young patients with diabetes: a study from United Arab Emirates. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0159808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostampour, N.; Fekri, K.; Hashemi-Dehkordi, E.; Obodiat, M. Association between vascular endothelial markers and carotid intima-media thickness in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research: JCDR. 2017, 11, SC01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Dayem, S.M.; Abd El Kader, M.; Ibrahim, S.; Mokhtar, E.; Abd El Megeed, E. Leptin and lipid profile in overweight patient with type 1 diabetes. Open access Macedonian journal of medical sciences. 2017, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrtić, M.; Lytvyn, Y.; Bjornstad, P.; et al. Influence of sex on hyperfiltration in patients with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology. 2017, 312, F599–F606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.D.; Lytvyn, Y.; Mahmud, F.H.; et al. The relationship between urinary renin-angiotensin system markers, renal function, and blood pressure in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology. 2017, 312, F335–F342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheus, A.S.d.M.; Clemente, E.L.S.; Rodrigues, M.d.L.G.; Valença, D.C.T.; Gomes, M.B. Assessment of microvascular endothelial function in type 1 diabetes using laser speckle contrast imaging. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications. 2017, 31, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Samahy, M.H.; Tantawy, A.A.; Adly, A.A.; et al. Expression of CD4+ CD28null T lymphocytes in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Relation to microvascular complications, aortic elastic properties, and carotid intima media thickness. Pediatric Diabetes. 2017, 18, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, M.; Espeland, C.N.; Brunborg, C.; et al. Preserved endothelial function in young adults with type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2018, 13, e0206523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomiński, B.; Ryba-Stanisławowska, M.; Skrzypkowska, M.; Myśliwska, J.; Myśliwiec, M. The KL-VS polymorphism of KLOTHO gene is protective against retinopathy incidence in patients with type 1 diabetes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease. 2018, 1864, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Anderson, J.; Couper, J.; Maftei, O.; Gent, R.; Peña, A.S. Children with type 1 diabetes have delayed flow-mediated dilation. Canadian Journal of Diabetes. 2018, 42, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żebrowska, A.; Hall, B.; Maszczyk, A.; Banaś, R.; Urban, J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, insulin like growth factor-1 and inflammatory cytokine responses to continuous and intermittent exercise in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2018, 144, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, S.T.; Charakida, M.; McLoughlin, E.; et al. Elevated high-density lipoprotein in adolescents with Type 1 diabetes is associated with endothelial dysfunction in the presence of systemic inflammation. European Heart Journal. 2019, 40, 3559–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, A.M.; Mohamed, I.L.; El Asheer, O.M.; et al. Circulating endothelial cells, circulating endothelial progenitor cells, and circulating microparticles in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis. 2019, 25, 1076029618825311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiromrat, P.; Bjornstad, P. ; RONCAL-JIMENEZ CA, et al. Serum uromodulin (SUMOD) inversely correlates with aortic stiffness in type 1 diabetes (T1D) youth. Diabetes.
- Abdelghaffar, S.; Shora, H.; Abdelatty, S.; et al. MicroRNAs and risk factors for diabetic nephropathy in egyptian children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity. 2494. [Google Scholar]
- Zwingli, G.; Yerly, J.; Mivelaz, Y.; et al. Non-invasive assessment of coronary endothelial function in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus using isometric handgrip exercise—MRI: A feasibility study. Plos one. 2020, 15, e0228569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Wahby, A.A.; Ashmawy, I.; Saleh, R.M.; Soliman, H. Association of exosomal miR-34a with markers of dyslipidemia and endothelial dysfunction in children and adolescents with T1DM. Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology. 2020, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratseth, V.; Margeirsdottir, H.D.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; et al. Annexin V+ Microvesicles in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study. Journal of Diabetes Research. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocuń-Wasilewska, K.; Zwolińska, D.; Zubkiewicz-Kucharska, A.; Polak-Jonkisz, D. Evaluation of Vascular Endothelial Function in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021, 10, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lespagnol, E.; Tagougui, S.; Fernandez, B.O.; et al. Circulating biomarkers of nitric oxide bioactivity and impaired muscle vasoreactivity to exercise in adults with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2021, 64, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, A.; Corradi, M.; Orsi, S.; et al. Oxidative stress in youth with type 1 diabetes: Not only a matter of gender, age, and glycemic control. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2021, 179, 109007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faienza, M.F.; Scicchitano, P.; Lamparelli, R.; et al. Vascular and Myocardial Function in Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Insulin Pump Therapy Versus Multiple Daily Injections Insulin Regimen. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021, 130, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alkaabi, J.; Sharma, C.; Yasin, J.; et al. Relationship between lipid profile, inflammatory and endothelial dysfunction biomarkers, and type 1 diabetes mellitus: A case-control study. American Journal of Translational Research. 2022, 14, 4838. [Google Scholar]
- Jahn, L.A.; Logan, B.; Love, K.M.; et al. Nitric oxide-dependent micro-and macrovascular dysfunction occurs early in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2022, 322, E101–E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutruzzolà, A.; Parise, M.; Scavelli, F.B.; Barone, M.; Gnasso, A.; Irace, C. Time in range does not associate with carotid artery wall thickness and endothelial function in type 1 diabetes. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology. 2022, 16, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, E.M.; Matter, R.M.; Salah, N.Y.; Abozeid, N.E.H.; Atif, H.M.; Tantawy, N.M. Changes in early optical coherence tomography angiography among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Relation to fibroblast growth factor 21. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews. 2023, 39, e3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kącka, A.; Charemska, A.; Jarocka-Cyrta, E.; Głowińska-Olszewska, B. Comparison of novel markers of metabolic complications and cardiovascular risk factors between obese non-diabetic and obese type 1 diabetic children and young adults. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022, 13, 1036109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, O.P.; Lanzinger, S.; Rosenbauer, J.; et al. Comorbidities in recent-onset adult type 1 diabetes: a comparison of German cohorts. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2022, 13, 760778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maio, A.; Maiorino, M.I.; Longo, M.; et al. Change in Circulating Levels of Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Sexual Function in Women With Type 1 Diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2022, 107, e3910–e3918. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, T.M.; Saunders, D.C.; Haliyur, R.; et al. Human pancreatic capillaries and nerve fibers persist in type 1 diabetes despite beta cell loss. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2023, 324, E251–E267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.; Albarguthi, S.; Albreiki, M.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing in Family Trios Reveals De Novo Mutations Associated with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Biology. 2023, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejko, B.; Tota, Ł.; Morawska-Tota, M.; Pałka, T.; Malecki, M.T.; Klupa, T. Assessment of selected muscle damage markers and zonulin concentration after maximum-intensity exercise in men with type 1 diabetes treated with a personal insulin pump. Acta Diabetologica. 2023; 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Strollo, R.; Vinci, C.; Man, Y.S.; et al. Autoantibody and T cell responses to oxidative post-translationally modified insulin neoantigenic peptides in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2023, 66, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, O.E.; Sabico, S.; Khattak, M.N.; Al-Daghri, N.M. Circulating Nitric Oxide and Metabolic Syndrome in Arab Children and Adolescents: A Case–Control Study. Children. 2023, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İncekalan, T.K.; Akbaş, E.D.; Şimdivar, G.H.N. Detection of Early Retinal Neurovascular Changes in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Without Diabetic Retinopathy. Retina-Vitreus/Journal of Retina-Vitreous. 2023; 32. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, A.M.; El Agouza, I.; Hafez, H.; Banna, M. Assesment of serum taurine level as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2023, 22, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konukoglu, D.; Uzun, H. Endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Hypertension: from basic research to clinical practice.
- Bakker, W.; Eringa, E.C.; Sipkema, P.; van Hinsbergh, V.W. Endothelial dysfunction and diabetes: roles of hyperglycemia, impaired insulin signaling and obesity. Cell and tissue research. 2009, 335, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boarescu, P.-M.; Boarescu, I.; Pop, R.M.; et al. Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and histological changes in experimental hypertension, dyslipidemia, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. Pathophysiology of diabetic dyslipidemia. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. 2018, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.; Perry, L.; Lowe, J.; Harris, M.; Colman, P.G.; Craig, M.E. Blood pressure in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes: data from the Australasian Diabetes Data Network registry. Acta Diabetologica. 2023, 60, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabelea, D.; Talton, J.W.; D’Agostino Jr, R.; et al. Cardiovascular risk factors are associated with increased arterial stiffness in youth with type 1 diabetes: the SEARCH CVD study. Diabetes care. 2013, 36, 3938–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptist, A.; Salvi, S.; Yajnik, C. Vascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes among Indian Patients. Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development. 2020; 11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Miao, F.; Paterson, A.D.; et al. Epigenomic profiling reveals an association between persistence of DNA methylation and metabolic memory in the DCCT/EDIC type 1 diabetes cohort. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2016, 113, E3002–E3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dluhy, R.G.; McMahon, G.T. Intensive glycemic control in the ACCORD and ADVANCE trials. N Engl J Med. 2008, 358, 2630–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using effect size—or why the P value is not enough. Journal of graduate medical education. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallström, S.; Svensson, A.-M.; Pivodic, A.; et al. Risk factors and incidence over time for lower extremity amputations in people with type 1 diabetes: an observational cohort study of 46,088 patients from the Swedish National Diabetes Registry. Diabetologia. 2021, 64, 2751–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, M.J.; Samyn, M.; Nichols, W.W.; et al. Radial artery tonometry demonstrates arterial stiffness in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes care. 2004, 27, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.; Perry, L.; Gallagher, R.; et al. Service usage and vascular complications in young adults with type 1 diabetes. BMC Endocrine Disorders. 2014, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, W. γ-Tocotrienol-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells is associated with a suppression in mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling. British journal of nutrition. 2008, 99, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, M.L.; Ulrich, E.H.; Noone, D.G. An update on hypertension in children with type 1 diabetes. Canadian Journal of Diabetes. 2018, 42, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkesson, K.; Hanberger, L.; Samuelsson, U. The influence of age, gender, insulin dose, BMI, and blood pressure on metabolic control in young patients with type 1 diabetes. Pediatric diabetes. 2015, 16, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.G.; Costacou, T.; Orchard, T.J. Risk factor modeling for cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes in the Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications (EDC) study: a comparison with the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study (DCCT/EDIC). Diabetes. 2019, 68, 409–419. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ammous, F.; Lin, L.; et al. The Interplay of Epigenetic, Genetic, and Traditional Risk Factors on Blood Pressure: Findings from the Health and Retirement Study. Genes. 2022, 13, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Cockcroft, J.; Van Bortel, L.; et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. European heart journal. 2006, 27, 2588–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, R.; Larrúbia, M.R.; Bussade, I.; et al. Predictors of subclinical atherosclerosis evaluated by carotid intima-media thickness in asymptomatic young women with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Archives of endocrinology and metabolism. 2017, 61, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamacchia, O.; Sorrentino, M.R. Diabetes mellitus, arterial stiffness and cardiovascular disease: clinical implications and the influence of SGLT2i. Current Vascular Pharmacology. 2021, 19, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, C.; Kozakova, M. Arterial stiffness, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk: Pathophysiologic mechanisms and emerging clinical indications. Vascular pharmacology. 2016, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Aboyans, V.; Blacher, J.; et al. The role of ventricular–arterial coupling in cardiac disease and heart failure: Assessment, clinical implications and therapeutic interventions. A consensus document of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Aorta & Peripheral Vascular Diseases, European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging, and Heart Failure Association. European journal of heart failure. 2019, 21, 402–424. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bortel, L.M.; Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; et al. Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. Journal of hypertension. 2012, 30, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Doucet, J.; Bauduceau, B.; et al. Key priorities in managing glucose control in older people with diabetes. JNHA-The Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging. 2009, 13, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dost, A.; Bechtold-Dalla Pozza, S.; Bollow, E.; et al. Blood pressure regulation determined by ambulatory blood pressure profiles in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Impact on diabetic complications. Pediatric diabetes. 2017, 18, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabek, M.E.; Akyürek, N.; Eklioglu, B.S.; Alp, H. Impaired systolic blood dipping and nocturnal hypertension: An independent predictor of carotid intima–media thickness in type 1 diabetic patients. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications. 2014, 28, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öberg, C.M.; Lindström, M.; Grubb, A.; Christensson, A. Potential relationship between eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine-ratio and glomerular basement membrane thickness in diabetic kidney disease. Physiological Reports. 2021, 9, e14939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjutsalo, V.; Barlovic, D.P.; Gordin, D.; Forsblom, C.; King, G.; Groop, P.-H. Presence and determinants of cardiovascular disease and mortality in individuals with type 1 diabetes of long duration: the FinnDiane 50 years of diabetes study. Diabetes Care. 2021, 44, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrado, J.; Farro, I.; Zócalo, Y.; et al. Preeclampsia is associated with increased central aortic pressure, elastic arteries stiffness and wave reflections, and resting and recruitable endothelial dysfunction. International journal of hypertension. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczyk, P.; Pańczyk-Tomaszewska, M. Methods to evaluate arterial structure and function in children–State-of-the art knowledge. Advances in medical sciences. 2017, 62, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, L.; Gordin, D.; Bordino, M.; et al. Oxygen-induced impairment in arterial function is corrected by slow breathing in patients with type 1 diabetes. Scientific reports. 2017, 7, 6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulou, E.Z.; Doundoulakis, I.; Antza, C.; et al. Subclinical arterial damage in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatric Diabetes. 2019, 20, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell-Bergeon, J.K.; Nadeau, K. Cardiovascular disease risk in young people with type 1 diabetes. Journal of cardiovascular translational research. 2012, 5, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M.; Group, D.E.R. The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: overview. Diabetes care. 2014, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibal, L.; Agarwal, S.C.; Home, P.D. Carotid intima-media thickness as a surrogate marker of cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity: targets and therapy. 2011; 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gourgari, E.; Dabelea, D.; Rother, K. Modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease in children with type 1 diabetes: can early intervention prevent future cardiovascular events? Current Diabetes Reports. 2017, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugier-Robiolle, S.; Vergès, B.; Le Bras, M.; et al. Glycaemic control influences the relationship between plasma PCSK9 and LDL cholesterol in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 2017, 19, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullum, C.M.; Rossetti, H.C.; Batjer, H.; Festa, J.R.; Haaland, K.Y.; Lacritz, L.H. 16 Cerebrovascular Disease. Textbook of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2017; 350. [Google Scholar]
- Walldius, G.; Jungner, I. The apoB/apoA-I ratio: a strong, new risk factor for cardiovascular disease and a target for lipid-lowering therapy–a review of the evidence. Journal of internal medicine. 2006, 259, 493–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanderani, A.B.; Wise, S.J.; Tildesley, H.D. Apolipoprotein B levels in adults with type 1 diabetes not receiving lipid-lowering therapy. Clinical biochemistry. 2009, 42, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadario, F.; Prodam, F.; Pasqualicchio, S.; et al. Lipid profile and nutritional intake in children and adolescents with Type 1 diabetes improve after a structured dietician training to a Mediterranean-style diet. Journal of endocrinological investigation. 2012, 35, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, P.S. When power calculations won’t do: Fermi approximation of animal numbers. Lab animal. 2019, 48, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornstad, P.; Nguyen, N.; Reinick, C.; et al. Association of apolipoprotein, B.; LDL-C and vascular stiffness in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Acta diabetologica. 2015, 52, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin, I.; Eizirik, D.L. Candidate genes for type 1 diabetes modulate pancreatic islet inflammation and β-cell apoptosis. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 2013; 15, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Segura, P.; De Dios, O.; Herrero, L.; et al. Children with type 1 diabetes have elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein compared with a control group. BMJ Open Diabetes Research and Care. 2020, 8, e001424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Nikoopour, E.; Huszarik, K.; Elliott, J.F.; Jevnikar, A.M. Immunomodulation and regeneration of islet beta cells by cytokines in autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research. 2011, 31, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Pirot, P.; Cardozo, A.K.; Eizirik, D.L. Mediators and mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 diabetes. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia & Metabologia. 2008, 52, 156–165. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, F.; Ducluzeau, P.-H.; Gastaldelli, A.; et al. Liver enzymes are associated with hepatic insulin resistance, insulin secretion, and glucagon concentration in healthy men and women. Diabetes. 2011, 60, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quetglas-Llabrés, M.M.; Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Bouzas, C.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Improves Plasma Biomarkers Related to Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Process in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Antioxidants. 2023, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorasia, D.G.; Dudek, N.L.; Veith, P.D.; et al. Pancreatic beta cells are highly susceptible to oxidative and ER stresses during the development of diabetes. Journal of Proteome Research. 2015, 14, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.H.; Park, B.-Y.; Yang, J.J.; et al. Interaction of body mass index and diabetes as modifiers of cardiovascular mortality in a cohort study. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health. 2012, 45, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, S.A.; Palumbo, P.J. Weight gain and management concerns in patients on insulin therapy. Insulin. 2007, 2, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laron, Z. Insulin–a growth hormone. Archives of physiology and biochemistry. 2008, 114, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelishadi, R.; Ardalan, G.; Gheiratmand, R.; et al. Association of physical activity and dietary behaviours in relation to the body mass index in a national sample of Iranian children and adolescents: CASPIAN Study. Bulletin of the world health organization. 2007, 85, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frier, B.M. How hypoglycaemia can affect the life of a person with diabetes. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews. 2008, 24, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, A.M.; Borawska, M.H. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1): an overview. European cytokine network. 2004, 15, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bui, T.M.; Wiesolek, H.L.; Sumagin, R. ICAM-1: A master regulator of cellular responses in inflammation, injury resolution, and tumorigenesis. Journal of Leucocyte Biology. 2020, 108, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.; Hovind, P.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Parving, H.-H.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Rossing, P. Biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction as predictors of pulse pressure and incident hypertension in type 1 diabetes: a 20 year life-course study in an inception cohort. Diabetologia. 2018, 61, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Casper, T.C.; Pitts, C.; et al. Association of acute kidney injury during diabetic ketoacidosis with risk of microalbuminuria in children with type 1 diabetes. JAMA pediatrics. 2022, 176, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankute, I.; Radzeviciene, L.; Monstaviciene, A.; Dobrovolskiene, R.; Danyte, E.; Verkauskiene, R. Serum cystatin C as a biomarker for early diabetic kidney disease and dyslipidemia in young type 1 diabetes patients. Medicina. 2022, 58, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ix, J.H.; Shlipak, M.G.; Katz, R.; et al. Kidney function and aortic valve and mitral annular calcification in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). American journal of kidney diseases. 2007, 50, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





