Submitted:
17 March 2025
Posted:
19 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MIA-602 and MIA-690 GHRH Peptide Antagonists
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Drug Treatments
2.5. Trypan Blue Exclusion Assay to Measure Total Cell Death
2.6. Cell Viability Assay and Determination of Synergy Combination Index (CI)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
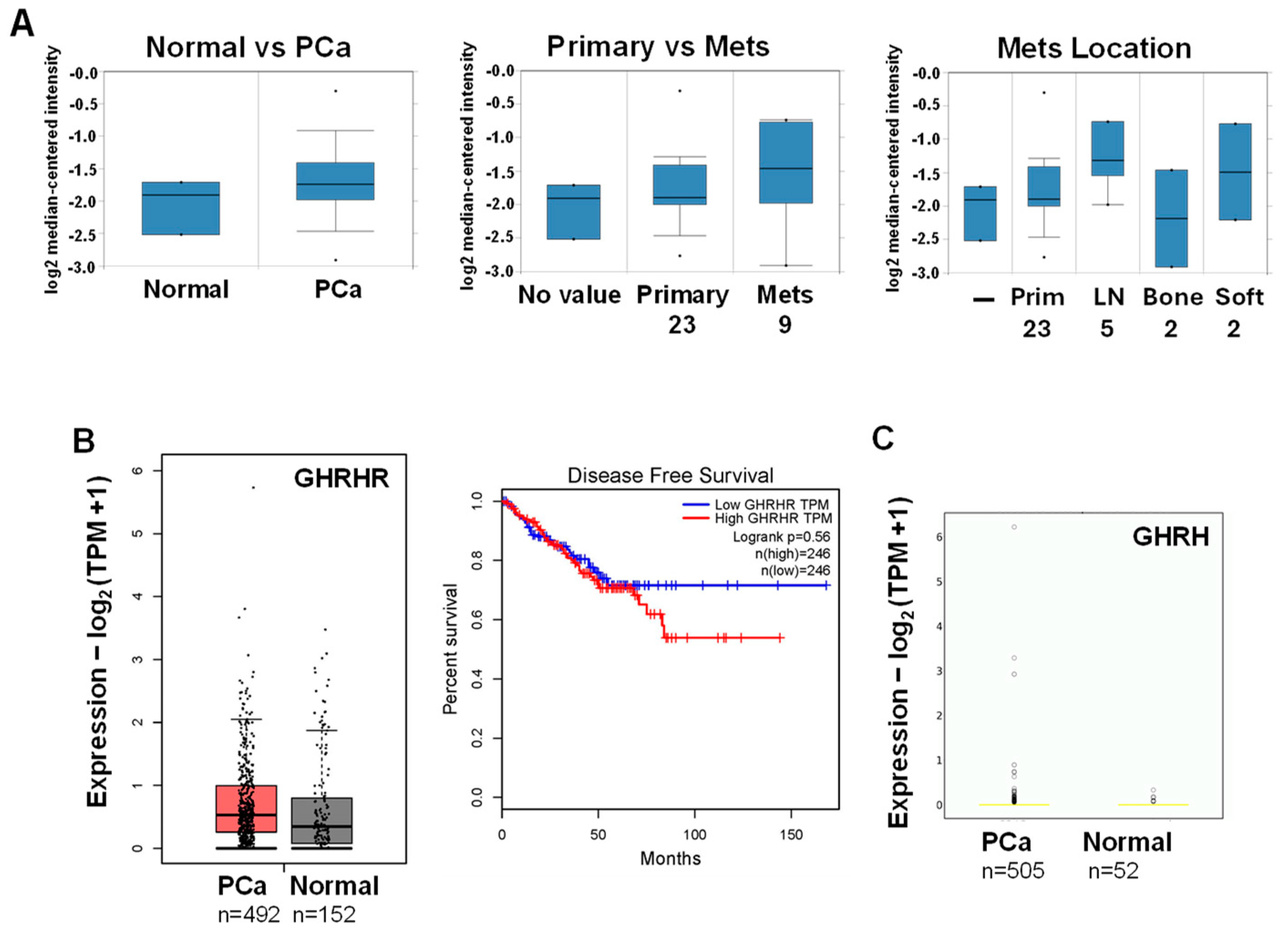
3.1. Database Analysis of GHRHR and GHRH mRNA Expression in PCa
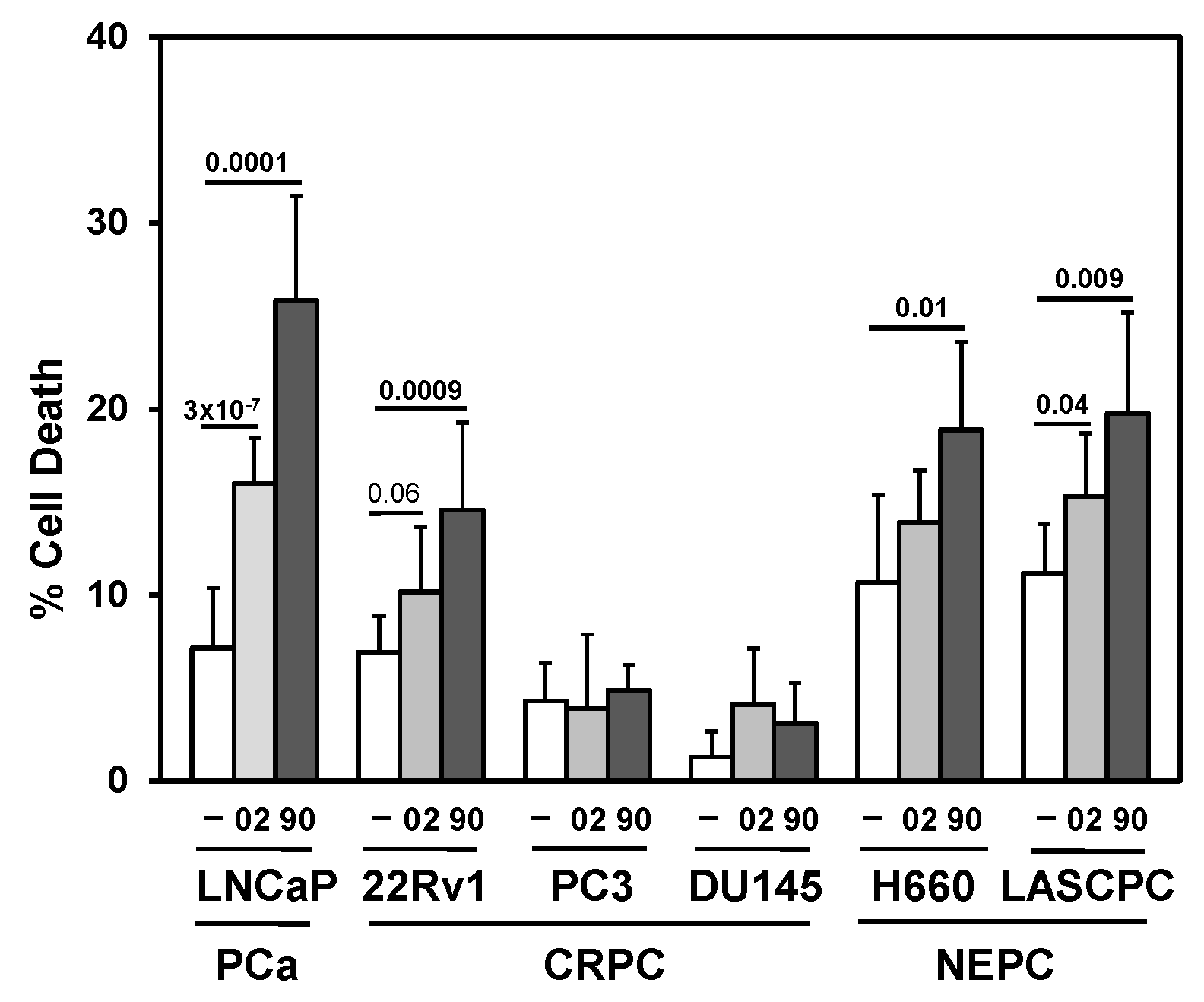
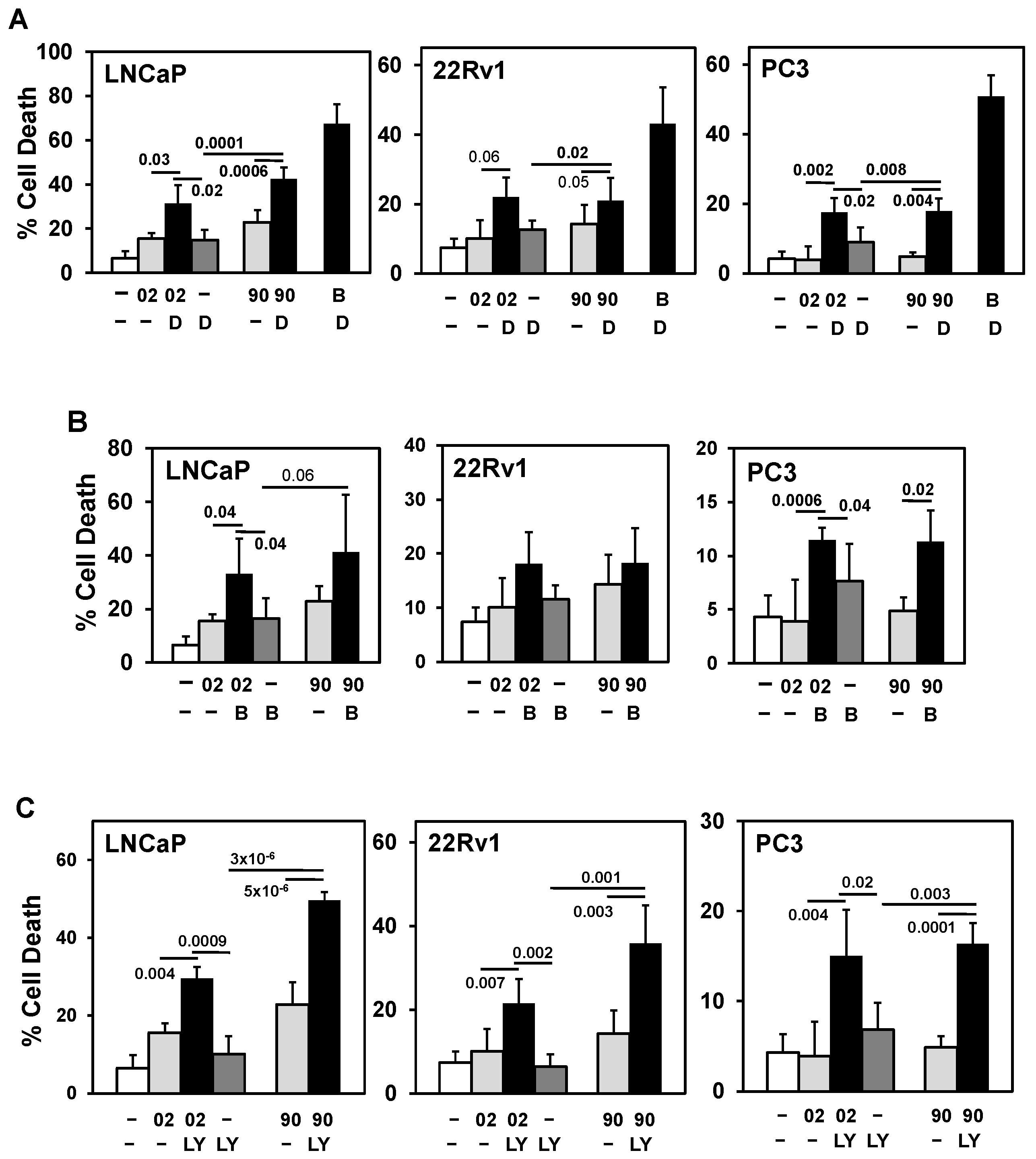
3.2. Searching for a Drug Combination with MIA-602 and MIA-690 GHRH Antagonist Peptides to Increase Cell Death in PCa/CRPC/NEPC
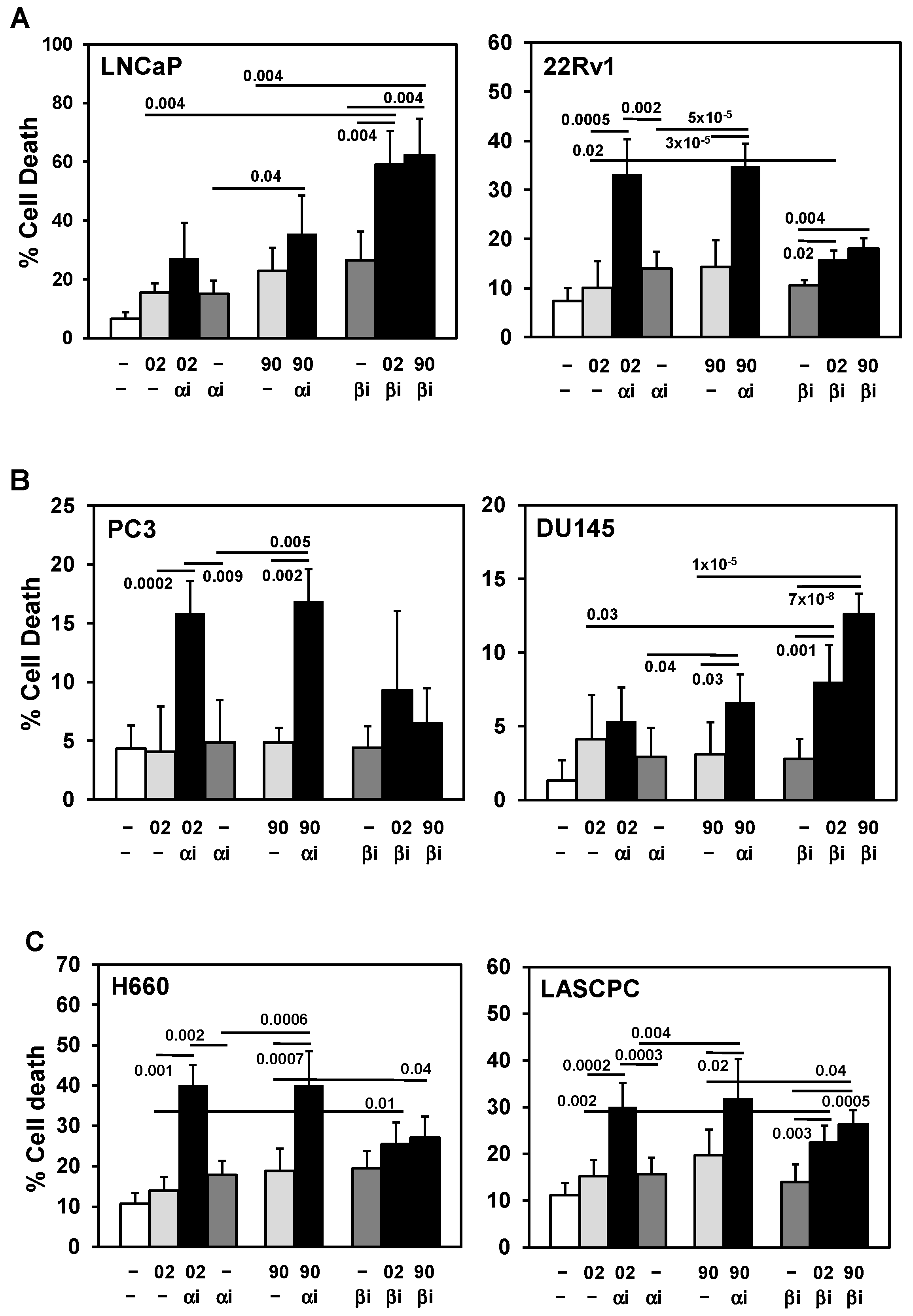
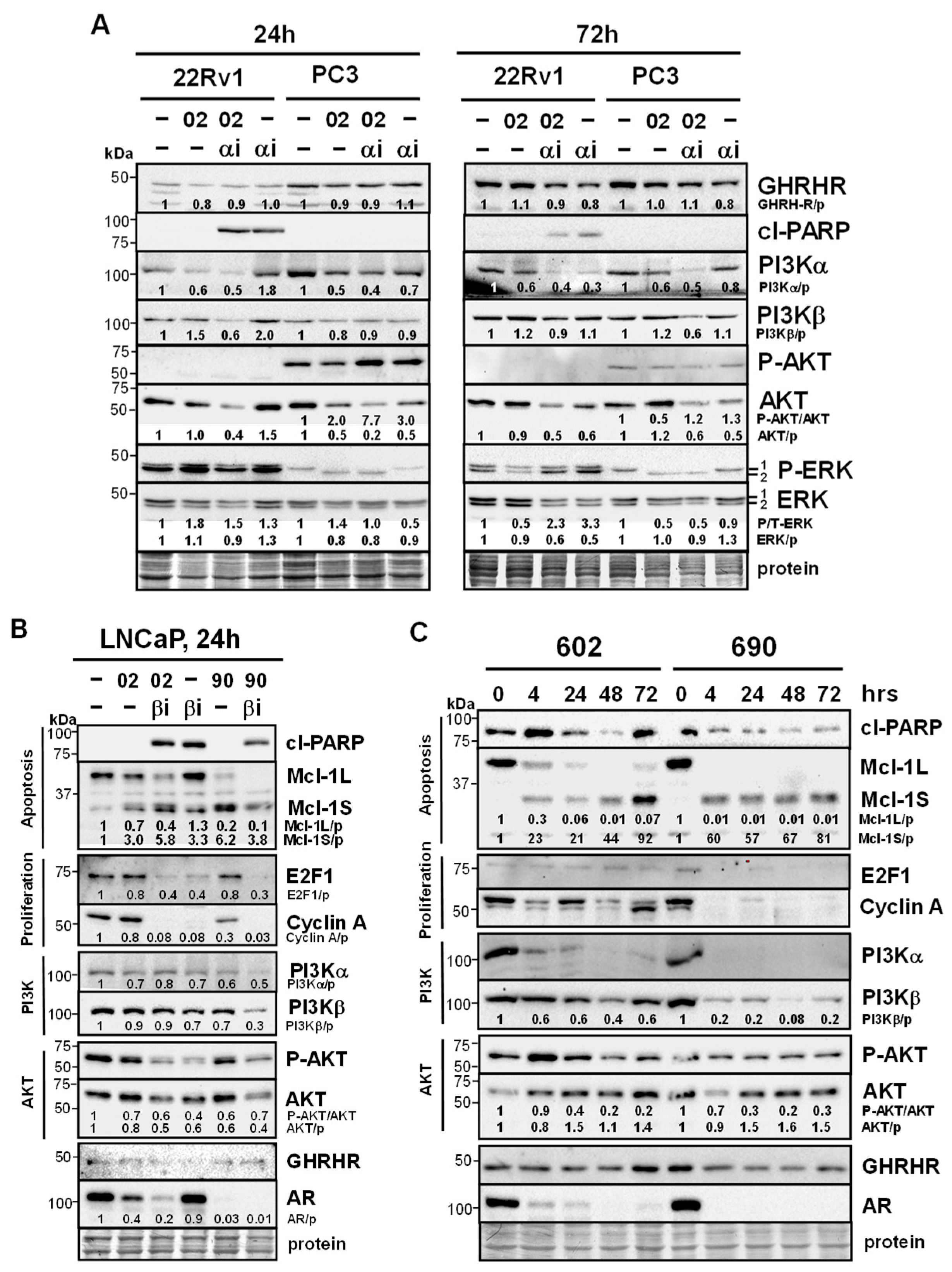
3.3. PI3Ka or b Isoform Inhibitors + MIA-602 or -690 Increases Cell Death in PCa/CRPC/NEPC
3.4. MIA-602/690 Alone and + PI3K Inhibitors Alters Multiple Signaling Pathways and AR Expression
3.5. Testing MIA-602 and -690 Acetate Salt (Ac) Form for Future Clinical Applications
3.6. AR Antagonist Enzalutamide + MIA-602 or -690 has No Effect
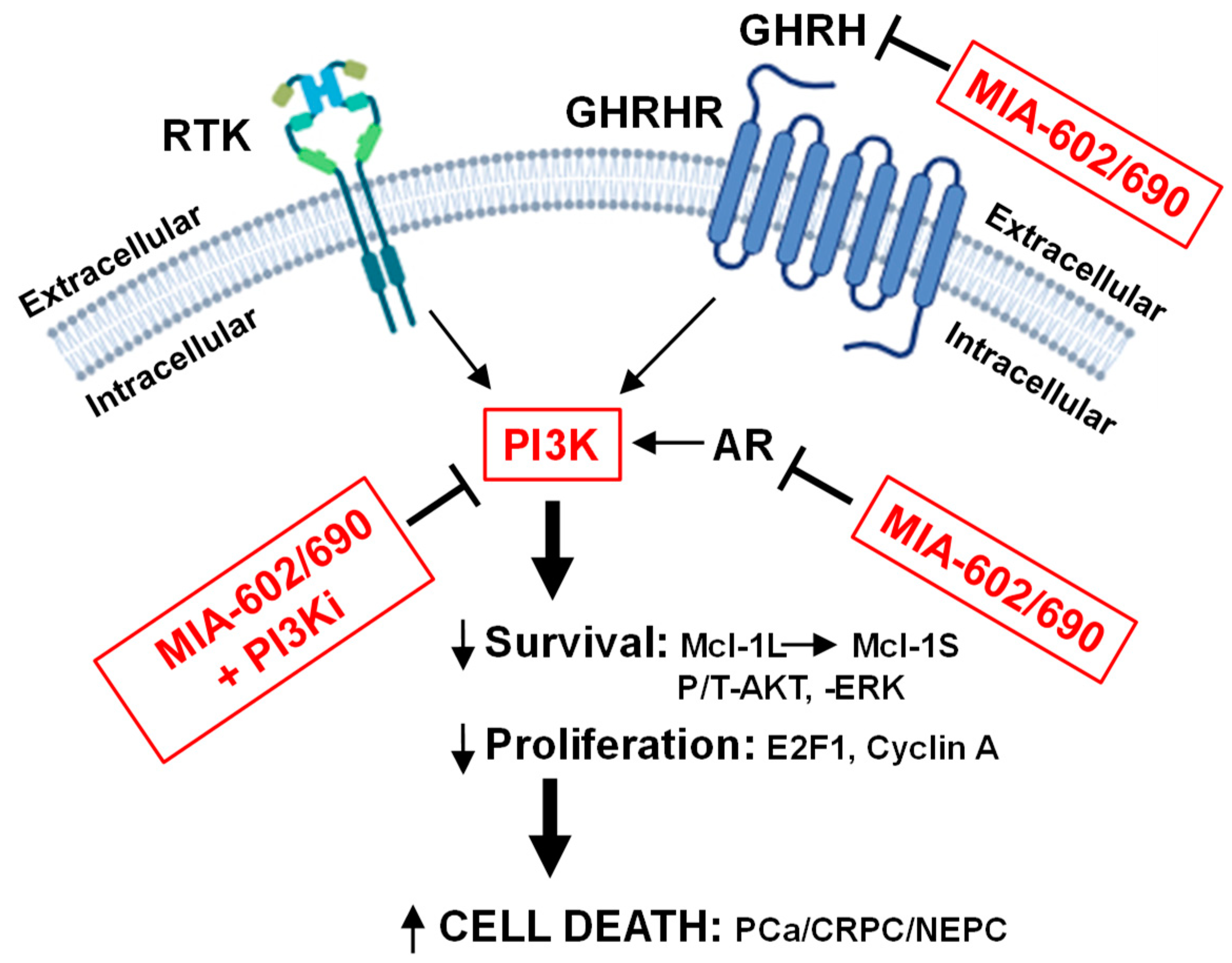
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ac | Acetate |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| AR | Androgen Receptor |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| ca | Constitutively Active |
| CDK | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase |
| CI | Combination Index |
| CRPC | Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| ERK | Extracellular-signal Regulated Kinase |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GH | Growth Hormone |
| GHRH | Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone |
| GHRHR | Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone Receptor |
| GnRH | Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone |
| GPCR | G Protein-Coupled Receptor |
| IGF1 | Insulin Growth Factor 1 |
| mTOR | Mammilian Target of Rapamycin |
| NFkB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| NEPC | Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer |
| P | Phospho |
| PCa | Prostate Cancer |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog |
| RTK | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic Acid |
| T | Total |
References
- Sartor, O.; de Bono, J.S. Metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018, 378, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prekovic, S.; van den Broeck, T.; Linder, S.; van Royen, M.E.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; Handle, F.; Joniau, S.; Zwart, W.; Claessens, F. Molecular underpinnings of enzalutamide resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2018, 25, R545–R557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, H.; Demichelis, F. Therapy considerations in neuroendocrine prostate cancer: what next? Endocr Relat Cancer. 2021, 28, T67–T78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ci, X.; Choi, S.Y.C.; Crea, F.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y. Molecular events in neuroendocrine prostate cancer development. Nat Rev Urol. 2021, 18, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Alabi, B.R.; Yin, Q.; Stoyanova, T. Molecular mechanisms underlying the development of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, P.M.; Crowley, W.F., Jr. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its analogues. N Engl J Med. 1991, 324, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schally, A.V., Arimura, A.; Kastin, A.J.; Matsuo, H.; Baba, Y.; Redding, T.W.; Nair, R.M.; Debeljuk, L.; White, W.F. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: one polypeptide regulates secretion of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. Science. 1971, 173, 1036–1038. [CrossRef]
- Schally, A.V.; Cai, R.; Zhang, X.; Sha, W.; Wangpaichitr, M. The development of growth hormone-releasing hormone analogs: therapeutic advances in cancer, regenerative medicine, and metabolic disorders. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schally, A.V.; Varga, J.L.; Engel, J.B. Antagonists of growth hormone-releasing hormone: An emerging new therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008, 4, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesmundo, I.; Pedrolli, F.; Cai, R.; Sha, W.; Schally, A.V.; Granata, R. Growth hormone-releasing hormone and cancer. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M.N.; Schernhammer, E.S.; Hankinson, S.E. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004, 4, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga J.L., Schally, A.V.; Csernus, V.J.; Zarándi, M.; Halmos, G.; Groot, K.; Rékási, Z. Synthesis and biological evaluation of antagonists of growth hormone-releasing hormone with high and protracted in vivo activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999, 96, 692–697. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarandi, M., Cai R, Kovacs M, Popovics P, Szalontay L, Cui T, Sha W, Jaszberenyi M, Varga, J.; Zhang, X.; Block, N.L.; Rick, F.G.; Halmos, G.; Schally, A.V. Synthesis and structure-activity studies on novel analogs of human growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) with enhanced inhibitory activities on tumor growth. Peptides. 2017, 89, 60–70. [CrossRef]
- Rick, F.G.; Schally, A.V.; Szalontay, L.; Block, N.L.; Szepeshazi, K.; Nadji, M.; Zarandi, M.; Hohla, F.; Buchholz, S.; Seitz, S. Antagonists of growth hormone-releasing hormone inhibit growth of androgen-independent prostate cancer through inactivation of ERK and Akt kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012, 109, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrenholtz, C.D.; Rick, F.G.; Garcia, M.I.; Zarandi, M.; Cai, R.Z.; Block, N.L.; Schally, A.V.; Burnstein, K.L. Preclinical efficacy of growth hormone-releasing hormone antagonists for androgen-dependent and castration-resistant human prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014, 111, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schally, A.V.; Perez, R.; Block, N.L.; Rick, F.G. Potentiating effects of GHRH analogs on the response to chemotherapy. Cell Cycle. 2015, 14, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohla, F.; Schally, A.V.; Szepeshazi, K.; Varga, J.L.; Buchholz, S.; Köster, F.; Heinrich, E.; Halmos, G.; Rick, F.G.; Kannadka, C.; Datz, C.; Kanashiro, C.A. Synergistic inhibition of growth of lung carcinomas by antagonists of growth hormone-releasing hormone in combination with docetaxel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006, 103, 14513–14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohla, F.; Buchholz, S.; Schally, A.V.; Seitz, S.; Rick, F.G.; Szalontay, L.; Varga, J.L.; Zarandi, M.; Halmos, G.; Vidaurre, I.; Krishan, A.; Kurtoglu, M.; Chandna, S.; Aigner, E.; Datz, C. GHRH antagonist causes DNA damage leading to p21 mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 2009, 8, 3149–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R., Schally, A.V.; Popovics, P.; Cai, R.; Sha, W.; Rincon, R.; Rick, F.G. Antagonistic analogs of growth hormone releasing hormone increase the efficacy of treatment of triple negative breast cancer in nude mice with doxorubicin: a preclinical study. Oncoscience. 2014, 1, 665–673. [CrossRef]
- Gesmundo, I.; Pedrolli, F.; Vitale, N.; Bertoldo, A.; Orlando, G.; Banfi, D.; Granato, G.; Kasarla, R.; Balzola, F.; Deaglio, S.; Cai, R.; Sha, W.; Papotti, M.; Ghigo, E.; Schally, A.V.; Granata, R. Antagonist of growth hormone-releasing hormone potentiates the antitumor effect of pemetrexed and cisplatin in pleural mesothelioma. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 11248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Moreno, L.; Gómez-Calcerrada, M.I.; Arenas, M.I.; Carmena, M.J.; Prieto, J.C.; Schally, A.V.; Bajo, A.M. Antagonist of growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor MIA-690 suppresses the growth of androgen-independent prostate cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, 25, 11200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; Kulke, M.H.; Baird, R.D.; Prabhu, J.S.; Carbone, D.; Pecoraro, C.; The, D.B.L.; Sethi, G.; Cavalieri, V.; Lin, K.H.; Javidi-Sharifi, N.R.; Toska, E.; Davids, M.S.; Brown, J.R.; Diana, P.; Stebbing, J.; Fruman, D.A.; Kumar, A.P. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus. H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; Antipin, Y.; Mitsiades, N.; Landers, T.; Dolgalev, I.; Major, J.E.; Wilson, M.; Socci, N.D.; Lash, A.E.; Heguy, A.; Eastham, J.A.; Scher, H.I.; Reuter, V.E.; Scardino, P.T.; Sander, C.; Sawyers, C.L.; Gerald, W.L. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010, 18, 11–22. [CrossRef]
- Grasso, C.S.; Wu, Y.M.; Robinson, D.R.; Cao, X.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Khan, A.P.; Quist, M.J.; Jing, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Brenner, J.C.; Asangani, I.A.; Ateeq, B.; Chun, S.Y.; Siddiqui, J.; Sam, L.; Anstett, M.; Mehra, R.; Prensner, J.R.; Palanisamy, N.; Ryslik, G.A.; Vandin, F.; Raphael, B.J.; Kunju, L.P.; Rhodes, D.R.; Pienta, K.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Tomlins, S.A. The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature. 2012, 487, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Luo, P.; Yan, H.; Yang, X. Development and safety of PI3K inhibitors in cancer. Arch Toxicol. 2023, 97, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.S.; Bonano-Rios, A.; Theik, N.W.Y.; Hussein, A.; Blaya, M. Molecular targeting of the phosphoinositide-3-protein kinase (PI3K) pathway across various cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, 25, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wen, X.; Ren, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, G.; Fu, L. Targeting PI3K family with small-molecule inhibitors in cancer therapy: current clinical status and future directions. Mol Cancer. 2024, 23, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekant, W.; Dekant, R. Mammalian toxicity of trifluoroacetate and assessment of human health risks due to environmental exposures. Arch Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Phillips, J.W.; Smith, B.A.; Park, J.W.; Stoyanova, T.; McCaffrey, E.F.; Baertsch, R.; Sokolov, A.; Meyerowitz, J.G.; Mathis, C.; Cheng, D.; Stuart, J.M.; Shokat, K.M.; Gustafson, W.C.; Huang. J.; Witte, O.N. N-myc drives neuroendocrine prostate cancer initiated from human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Cell. 2016, 29, 536–547. [CrossRef]
- VanDeusen, H.R.; Ramroop, J.R.; Morel, K.L.; Bae, S.Y.; Sheahan, A.V.; Sychev, Z.; Lau, N.A.; Cheng, L.C.; Tan, V.M.; Li, Z.; Petersen, A.; Lee, J.K.; Park, J.W.; Yang, R.; Hwang, J.H.; Coleman, I.; Witte, O.N.; Morrissey, C.; Corey, E.; Nelson, P.S.; Ellis, L.; Drake, J.M. Targeting RET kinase in neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, L.A.; de las Pozas, A.; Perez-Stable, C. Sequential combination of flavopiridol and docetaxel reduces the levels of XIAP and AKT proteins and stimulates apoptosis in human LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmos, G.; Schally, A.V.; Czompoly, T.; Krupa, M.; Varga, J.L.; Rekasi, Z. Expression of growth hormone-releasing hormone and its receptor splice variants in human prostate cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002, 87, 4707–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMenamin, M.E.; Soung, P.; Perera, S.; Kaplan, I.; Loda, M.; Sellers, W.R. Loss of PTEN expression in paraffin-embedded primary prostate cancer correlates with high Gleason score and advanced stage. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yen, C.; Liaw, D.; Podsypanina, K.; Bose, S.; Wang, SI.; Puc, J.; Miliaresis, C.; Rodgers, L.; McCombie, R.; Bigner, S.H.; Giovanella, B.C.; Ittmann, M.; Tycko, B.; Hibshoosh, H.; Wigler, M.H.; Parsons, R. PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science. 1997, 275, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sramkoski, R.M.; Pretlow, T.G.; Giaconia, J.M.; Pretlow, T.P.; Schwartz, S.; Sy, M.S.; Marengo, S.R.; Rhim, J.S.; Zhang, D.; Jacobberger, J.W. A new human prostate carcinoma cell line, 22Rv1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1999, 35, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Moreno, L.; Román, I.D.; Bajo, A.M. GHRH and the prostate. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Moreno, L.; Arenas, M.I.; Carmena, M.J.; Schally, A.V.; Prieto, J.C.; Bajo, A.M. Growth hormone-releasing hormone antagonists abolish the transactivation of human epidermal growth factor receptors in advanced prostate cancer models. Invest New Drugs. 2014, 32, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, E.; Giantulli, S.; Sciarra, A.; Silvestri, I. AR and PI3K/AKT in prostate cancer: a tale of two interconnected pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raith, F.; O’Donovan, D.H.; Lemos, C.; Politz, O.; Haendler, B. Addressing the reciprocal crosstalk between the AR and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways for prostate cancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Moreno, L.; Carmena, M.J.; Schally, A.V.; Prieto, J.C.; Bajo, A.M. Stimulation of neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer cells by GHRH and its blockade by GHRH antagonists. Invest New Drugs. 2020, 38, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Ke, X.; Jiang, J.; Dong, H.; Yao, Z.; Lin, Y.; Lin, W.; Wu, X.; Yan, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Chu, W.K.; Cai, R.; Zhang, X.; Cheung, H.S.; Block, N.L.; Pang, C.P.; Schally, A.V.; Zhang, H. Growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor antagonists inhibit human gastric cancer through downregulation of PAK1-STAT3/NF-κB signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016, 113, 14745–14750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Huang, H.; Schally, A.V.; Chao, A.; Chou, H.; Leung, P.C.K.; Wang, H. Growth hormone-releasing hormone antagonist inhibits the invasiveness of human endometrial cancer cells by down-regulating twist and N-cadherin expression. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 4410–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.C.; Ren, J.L.; Yu, Q.X.; Li, J.; Ng, T.K.; Chu, W.K.; Qin, Y.J.; Chu, K.O.; Schally, A.V.; Pang, C.P.; Chan, S.O. Signaling mechanisms of growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor in LPS-induced acute ocular inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020, 117, 6067–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, M.L. Tipping the balance of cell death: alternative splicing as a source of MCL-1S in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.H.; Tokheim, C.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Sengupta, S.; Bertrand, D.; Weerasinghe, A.; Colaprico, A.; Wendl, M.C.; Kim, J.; Reardon, B.; Ng, P.K.; Jeong, K.J.; Cao, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Gao, Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, E.M.; Mularoni, L.; Rubio-Perez, C.; Nagarajan, N.; Cortés-Ciriano, I.; Zhou, D.C.; Liang, W.W.; Hess, J.M.; Yellapantula, V.D.; Tamborero, D.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Suphavilai, C.; Ko, J.Y.; Khurana, E.; Park, P.J.; Van Allen, E.M.; Liang, H.; MC3 Working Group; Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Lawrence, M.S.; Godzik, A.; Lopez-Bigas, N. Stuart, J.; Wheeler, D.; Getz, G.; Chen, K.; Lazar, A.J.; Mills, G.B.; Karchin, R.; Ding, L. Comprehensive characterization of cancer driver genes and mutations. Cell. 2018, 173, 371–385. [CrossRef]
- Pearson, H.B.; Li, J.; Meniel, V.S.; Fennell, C.M.; Waring, P.; Montgomery, K.G.; Rebello, R.J.; Macpherson, A.A.; Koushyar, S.; Furic, L.; Cullinane, C.; Clarkson, R.W.; Smalley, M.J.; Simpson, K.J.; Phesse, T.J.; Shepherd, P.R.; Humbert, P.O.; Sansom, O.J.; Phillips, W.A. Identification of Pik3ca mutation as a genetic driver of prostate cancer that cooperates with Pten loss to accelerate progression and castration-resistant growth. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.; Wongvipat, J.; Trigwell, C.B.; Hancox, U.; Carver, B.S.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.; Will, M.; Yellen, P.; de Stanchina, E.; Baselga, J.; Scher, H.I.; Barry, S.T.; Sawyers, C.L.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Rosen, N. Feedback suppression of PI3Kα signaling in PTEN-mutated tumors is relieved by selective inhibition of PI3Kβ. Cancer Cell. 2015, 27, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, D.; Rivera, A.A.; Li, D.; Lee, C.; Haywood, S.; Chen, X.; Chang, Q.; Xu, G.; Chen, H.A.; de Stanchina, E.; Sawyers, C.; Rosen, N.; Hsieh, A.C.; Chen, Y.; Carver, B.S. Defining the therapeutic selective dependencies for distinct subtypes of PI3K pathway-altered prostate cancers. Nat Commun. 2021, 12, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Alpelisib: first global approval. Drugs. 2019, 79, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.D.; Higano, C.S.; de Bono, J.S.; Cook, N.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Wisinski, K.B.; Martin-Liberal, J.; Linch, M.; Heath, E.I.; Baird, R.D.; García-Carbacho, J.; Quintela-Fandino, M.; Barry, S.T.; de Bruin, E.C.; Colebrook, S.; Hawkins, G.; Klinowska, T.; Maroj, B.; Moorthy, G.; Mortimer, P.G.; Moschetta, M.; Nikolaou, M.; Sainsbury, L.; Shapiro, G.I.; Siu, L.L.; Hansen, A.R. A phase I study investigating AZD8186, a potent and selective inhibitor of PI3Kβ/δ, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.C.E.; Vasilevski, N.; Serra, V.; Rodon, J.; Eichhorn, P.J.A. Mechanisms of resistance to PI3K inhibitors in cancer: adaptive responses, drug tolerance and cellular plasticity. Cancers. 2021, 13, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell Line | Type | AR | PTEN | AKT | p53 | Additional |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LNCaP | AS PCa | + | mut/─ | ca | +/+ | ARmut T877A |
| 22Rv1 | CRPC | + | +/+ | wt | +/+ |
1) AR-V7 (splice variant ─LBD 2) PIK3CA mut |
| PC3 | CRPC | ─ | ─/─ | ca | ─/─ | |
| DU145 | CRPC | ─ | +/─ | wt | dn/oe | Bax null |
| H660 | NEPC | ─ | ─/─ | ca | mut | |
| LASCPC | NEPC | ─ | ca | N-myc/AKTmyr oe |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





