Submitted:
17 March 2025
Posted:
18 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Current Trends and Functional Requirements Analysis of Intelligent Fault Information Retrieval Systems for NEVs
2.1. Domestic and International Research Trends
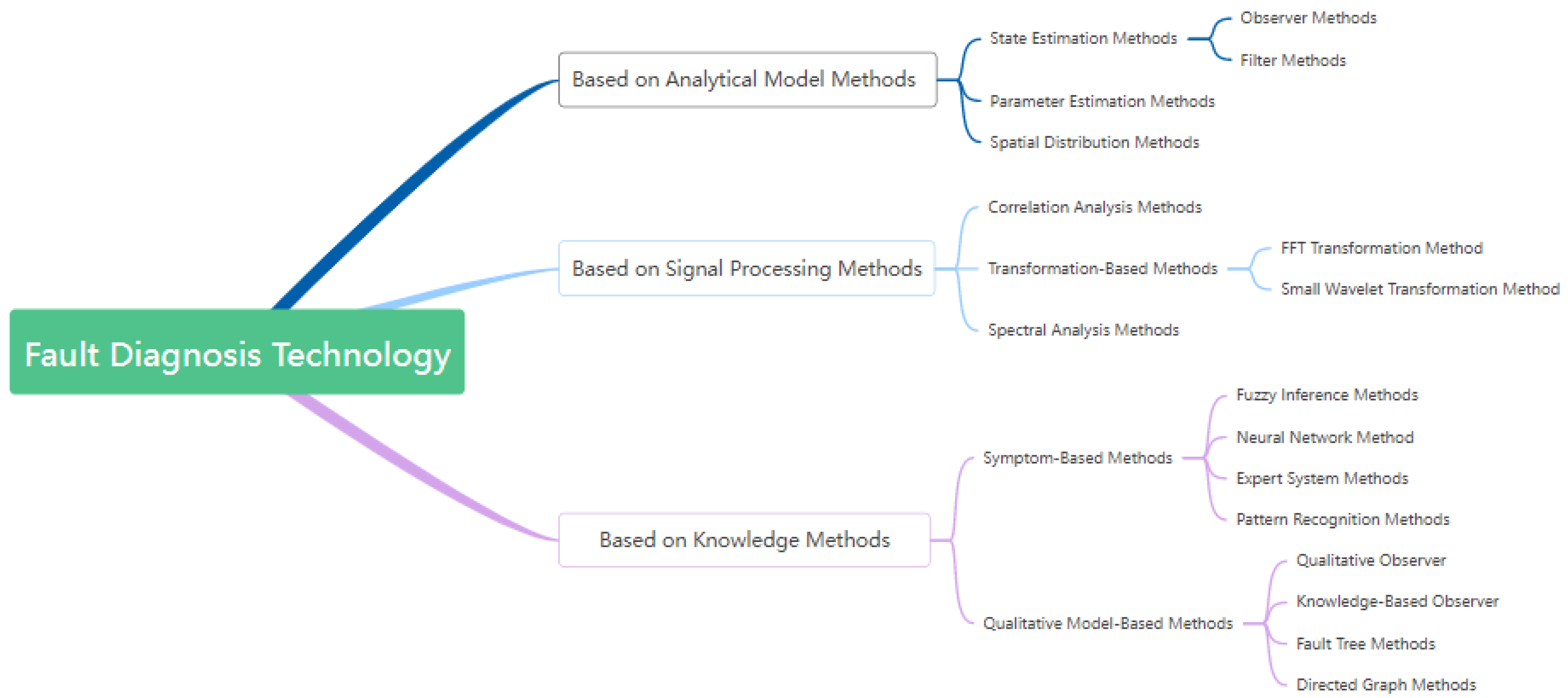
2.1.1. Fault Diagnosis and Information Retrieval Systems Research Trends
2.1.2. Knowledge Graphs and Generative Language Models Research Trends
- (1)
- Generative Language Models
- (2)
- Knowledge Graphs and Applications
- (3)
- The Combination of Generative Language Models and KGs
2.2. Functional Requirements of Intelligent Fault Information Retrieval Systems for NEVs
3. System Design of Intelligent Retrieval of Fault Information
3.1. The Logical Structure Design of the Fault Data Retrieval System
3.1.1. The Integration of Fault Diagnosis Technology
3.1.2. The Logical Integration of Large Language Models and Knowledge Graphs
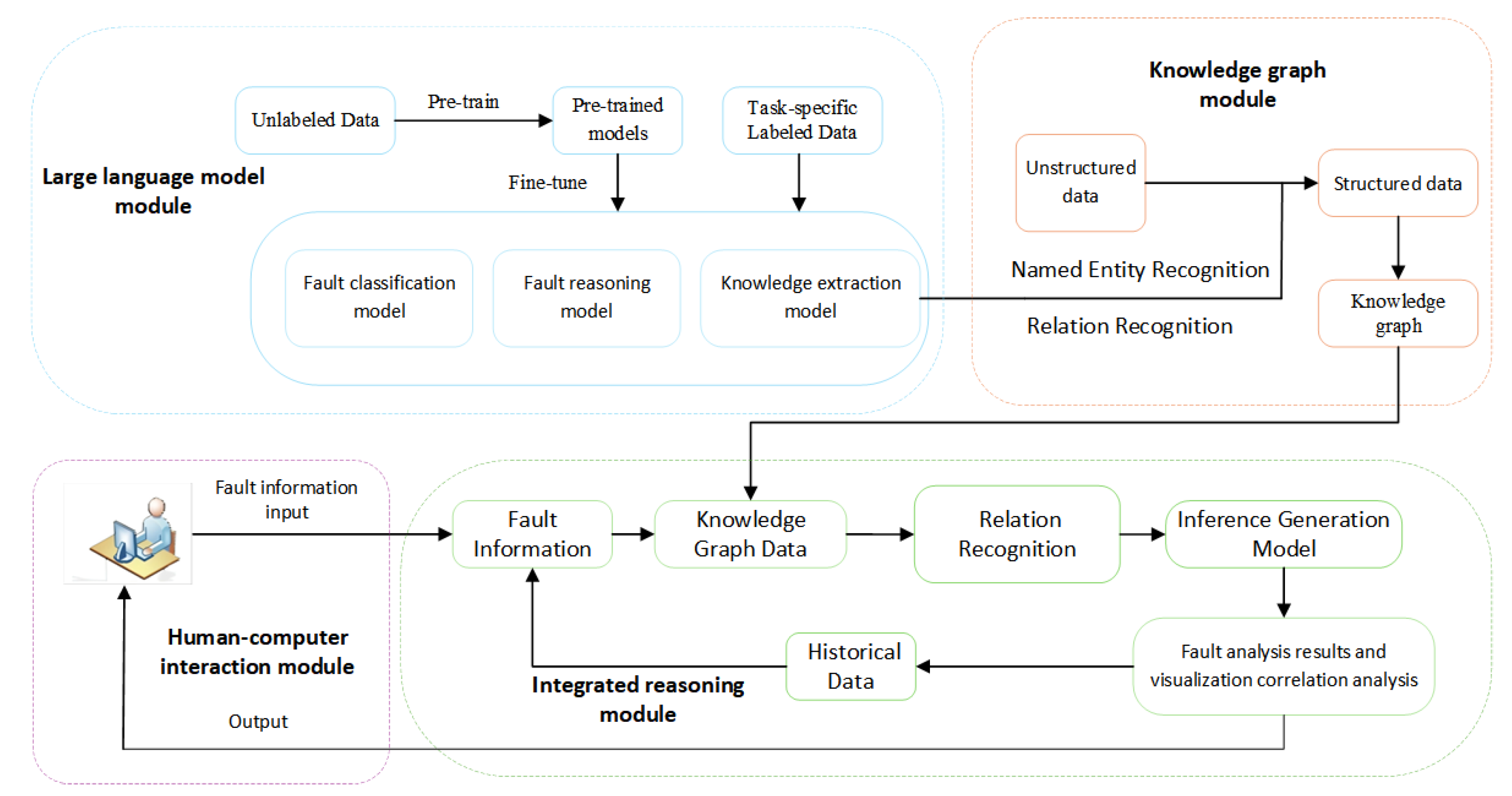
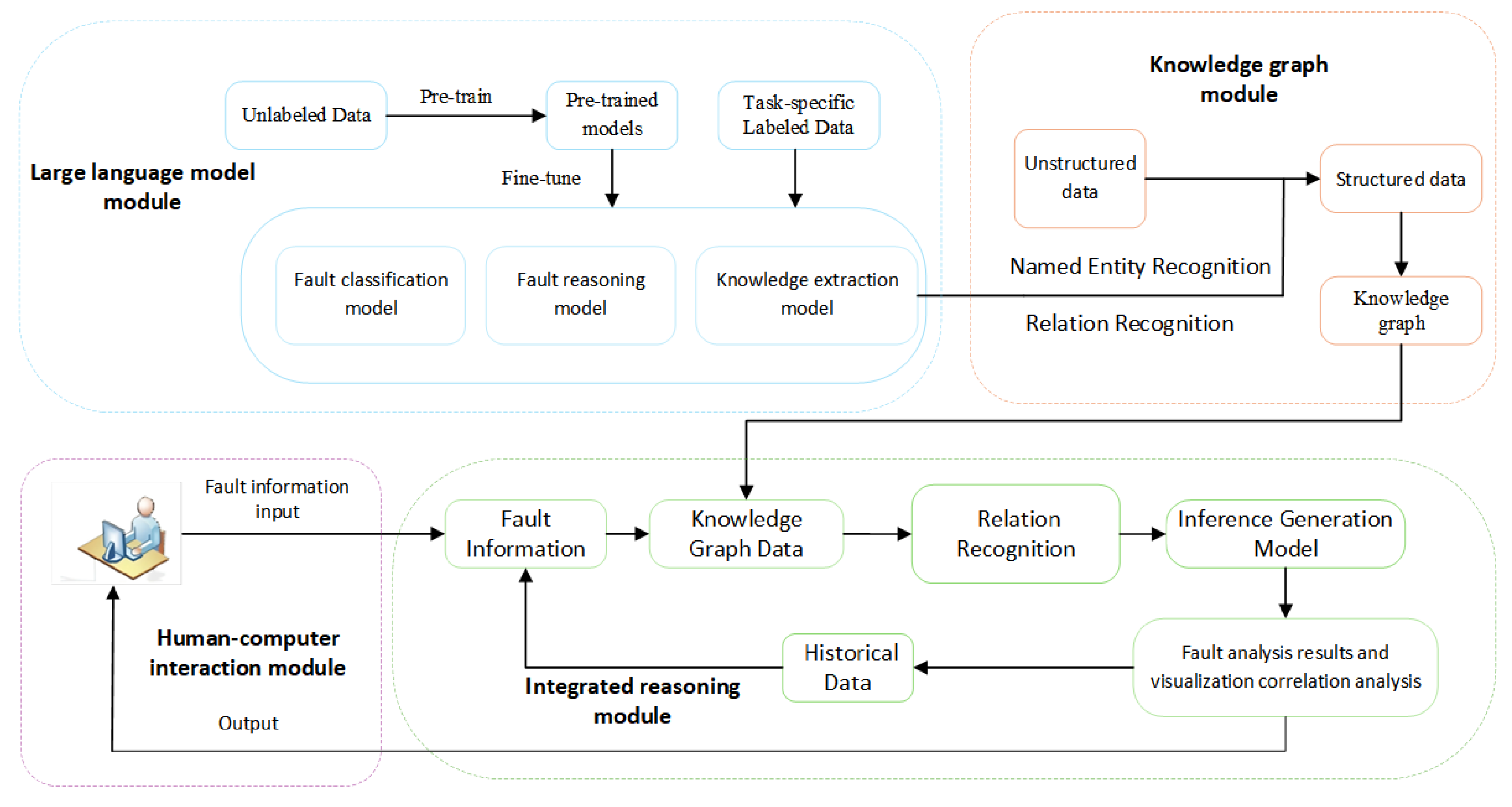
3.2. The Framework Design of the Fault Data Retrieval System
3.2.1. Large Language Models Module
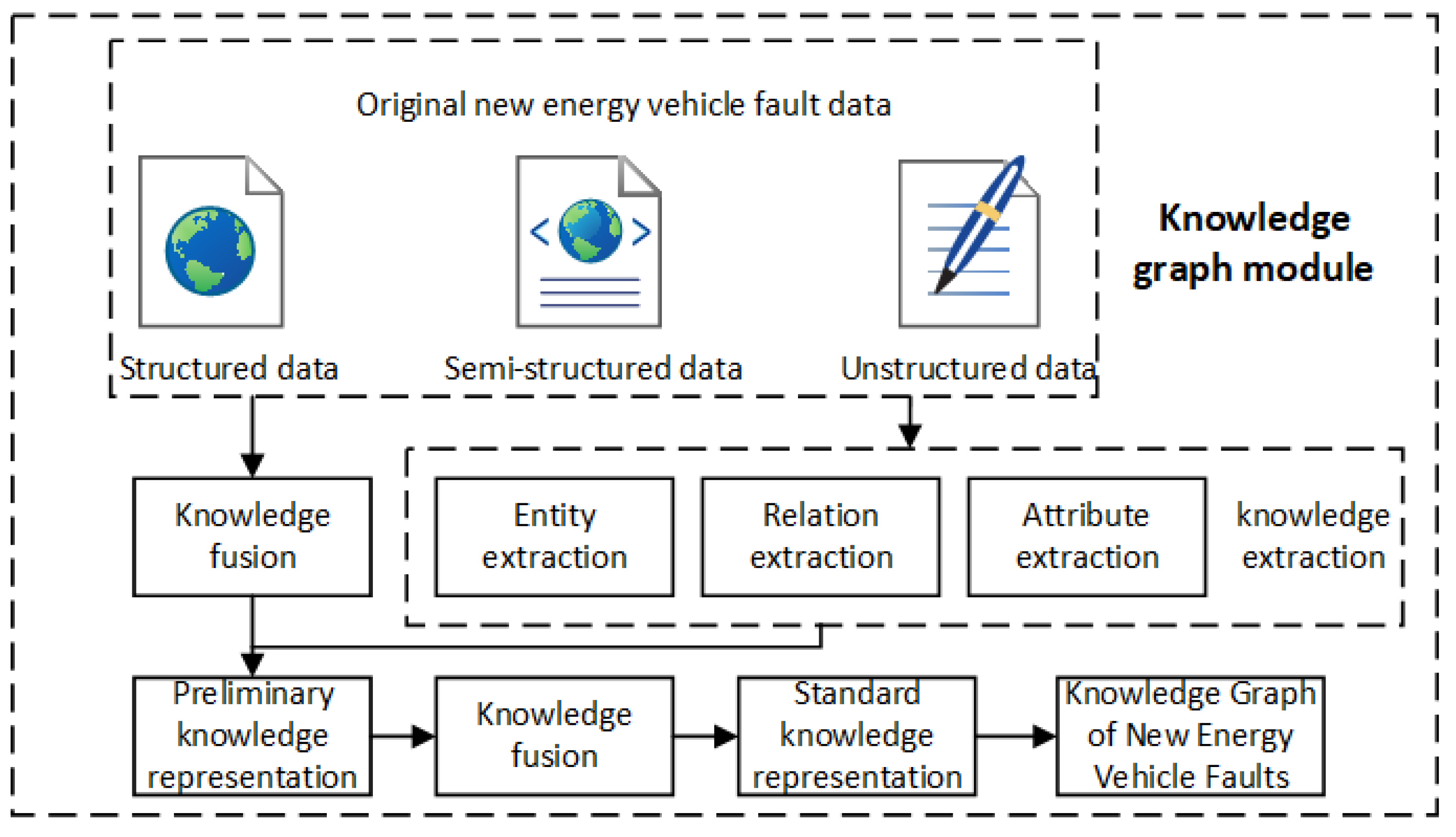
3.2.2. Knowledge Graphs Module
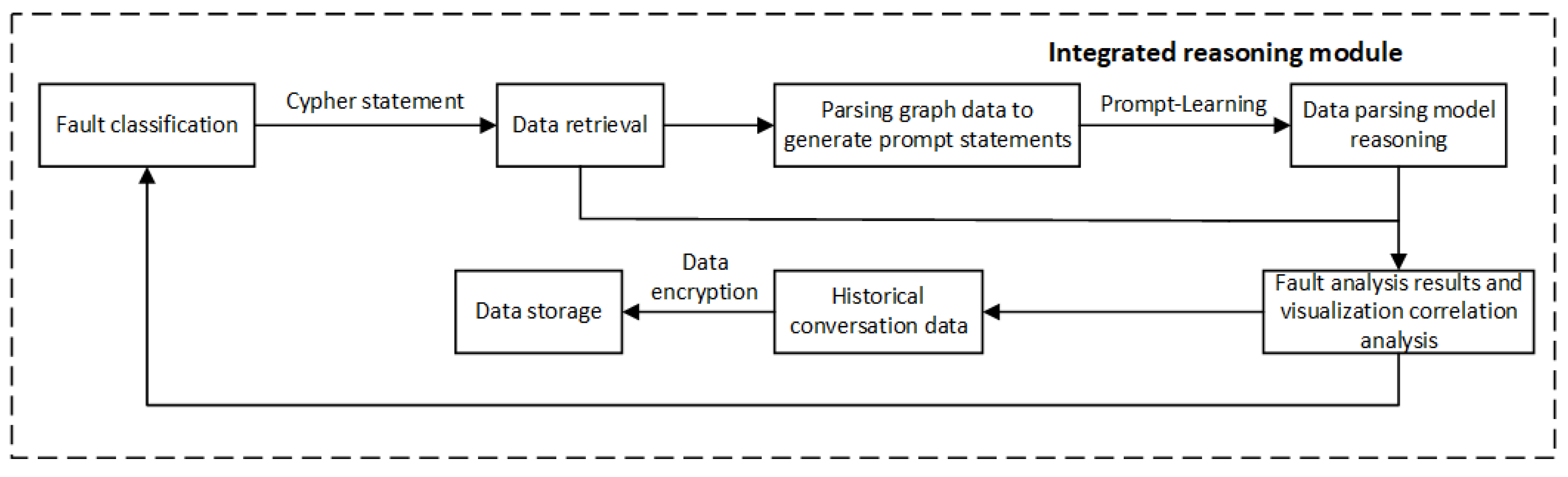
3.2.3. Integrated Reasoning Module
4. System Implementation and Testing
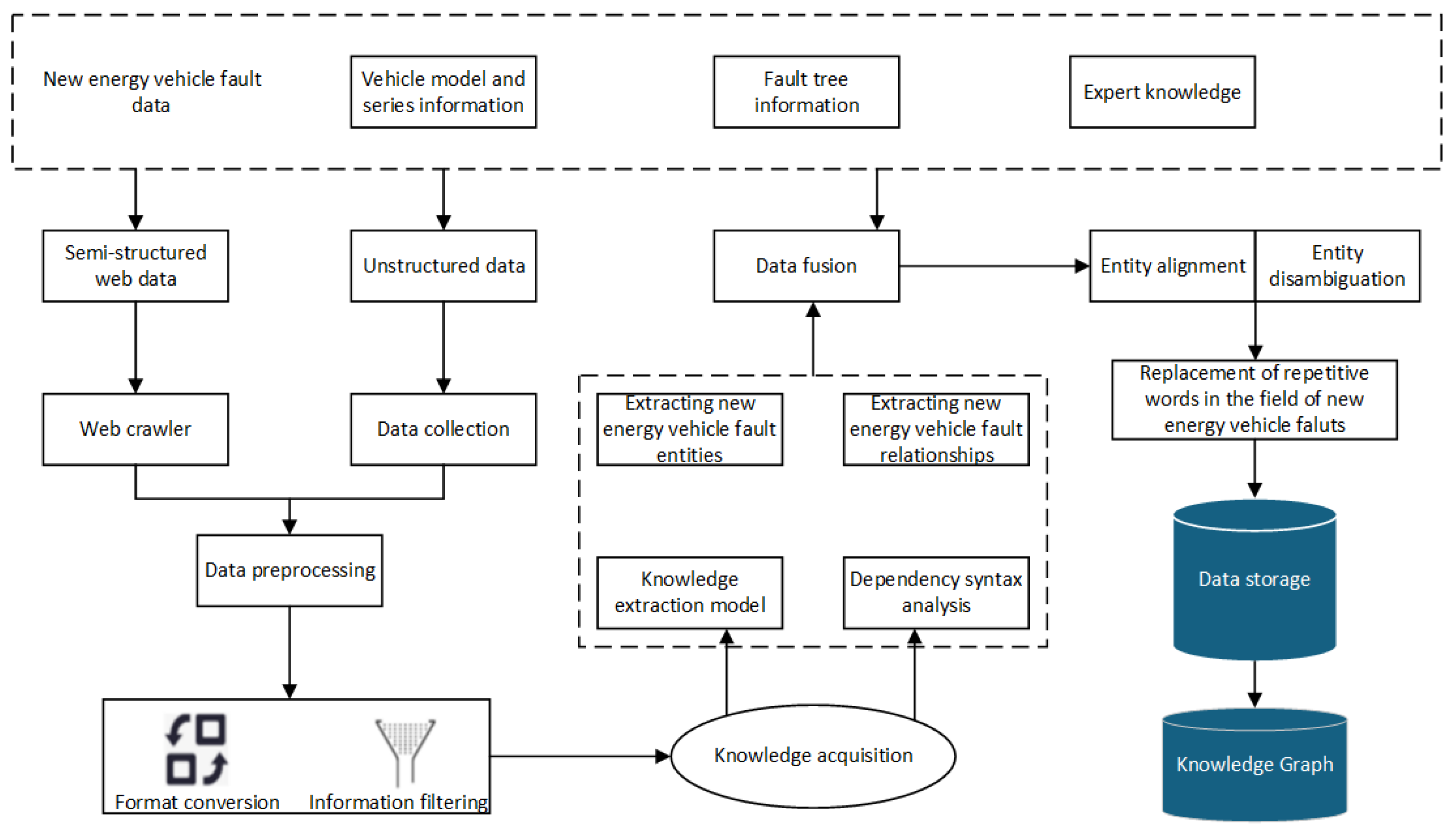
4.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
4.2. New Energy Vehicles Fault Model Training
4.2.1. New Energy Vehicle Fault Knowledge Model Training
4.2.2. New Energy Vehicle Fault Classification Model Training
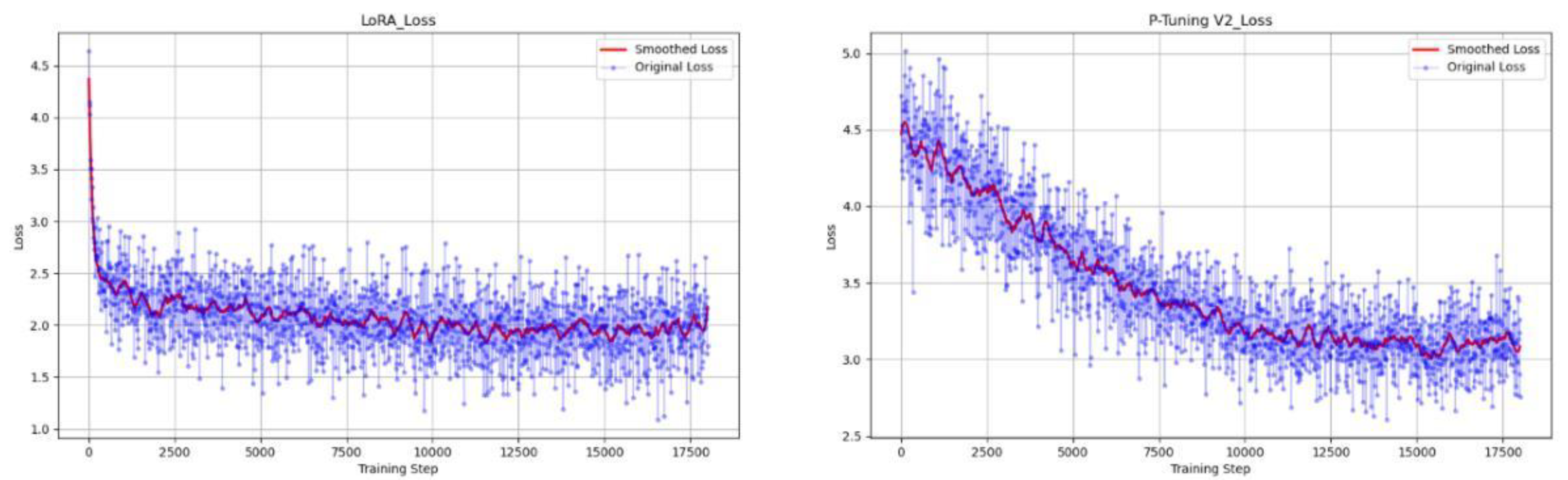
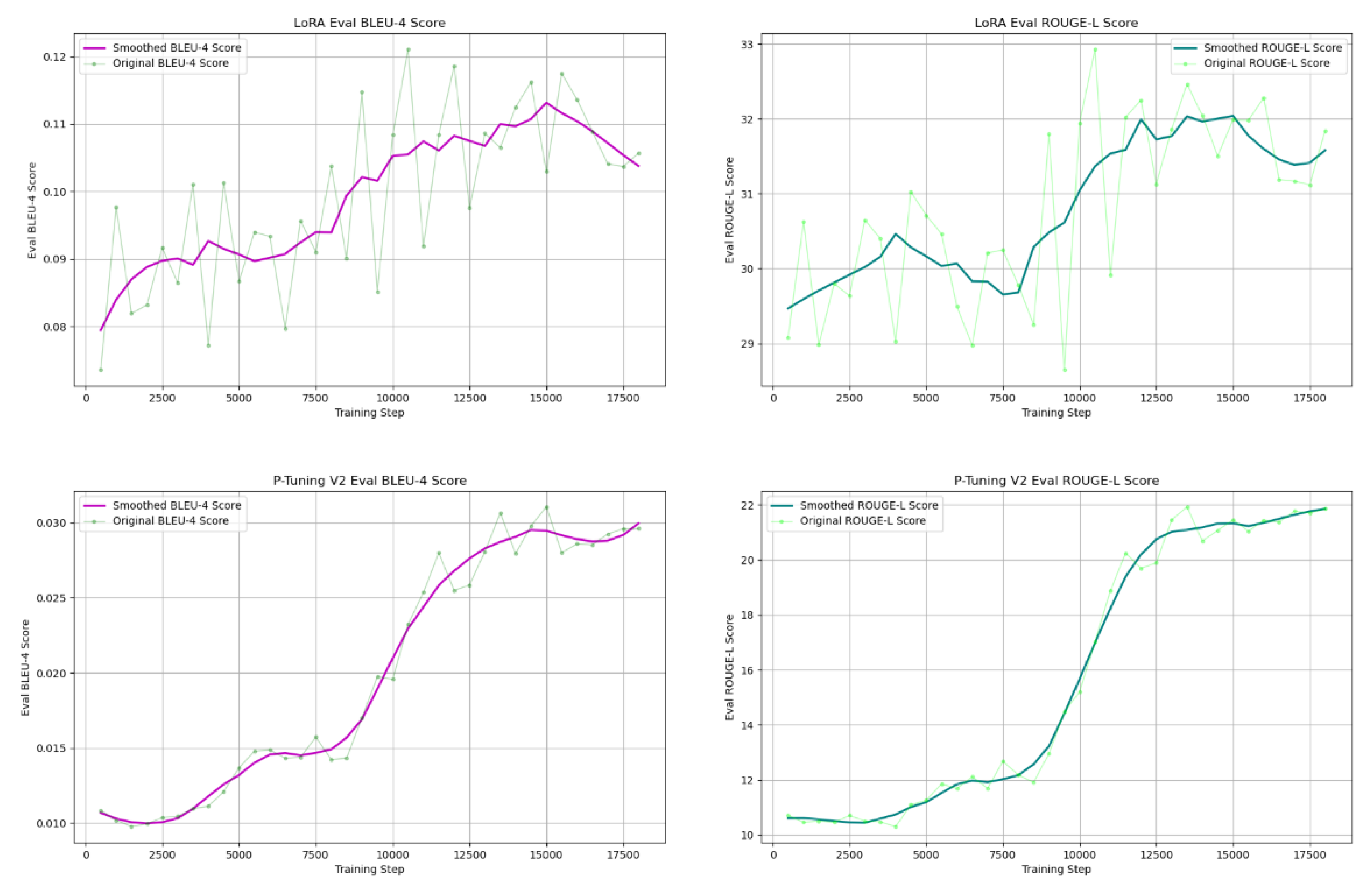
4.3. Knowledge Graph and Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
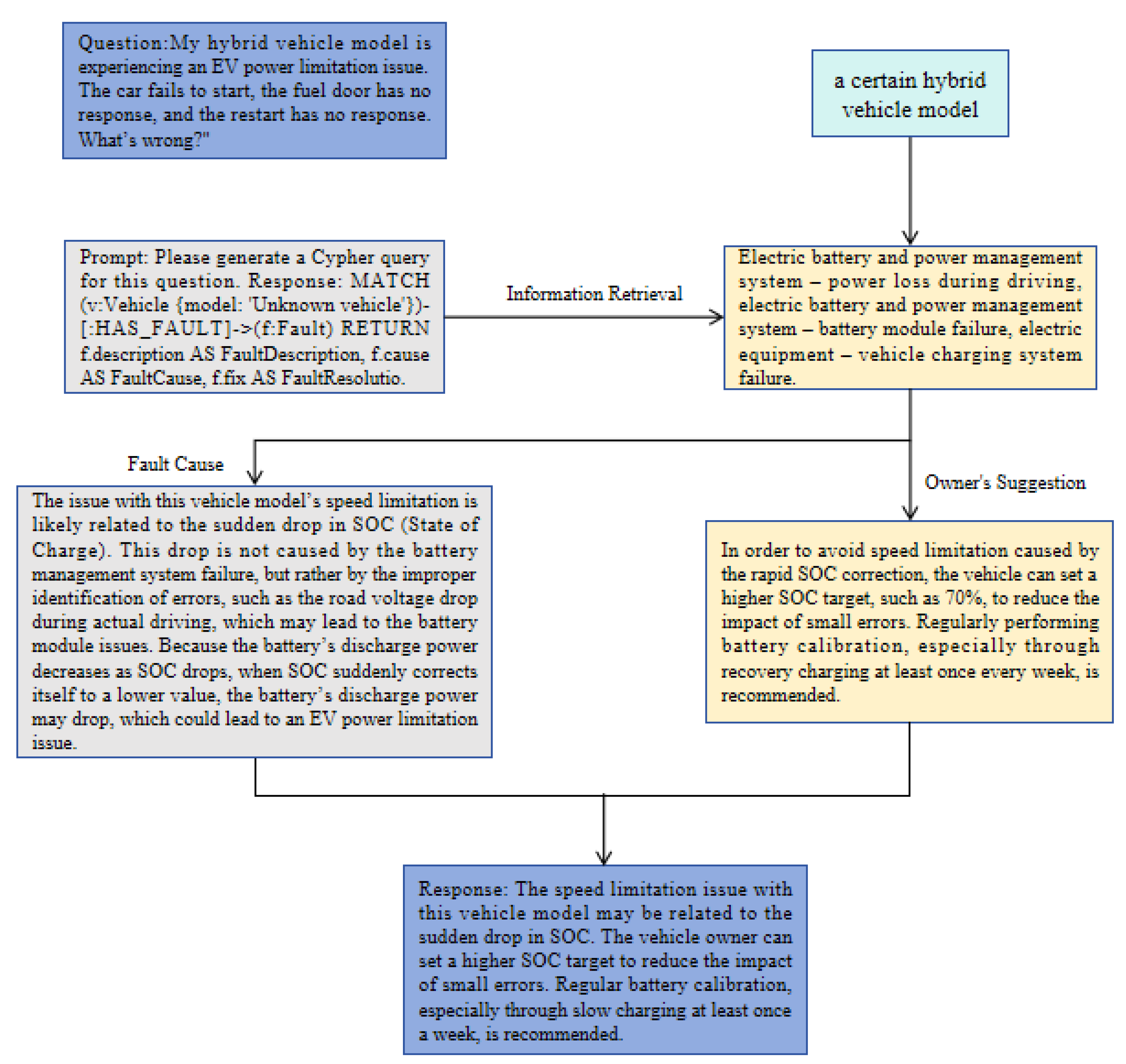
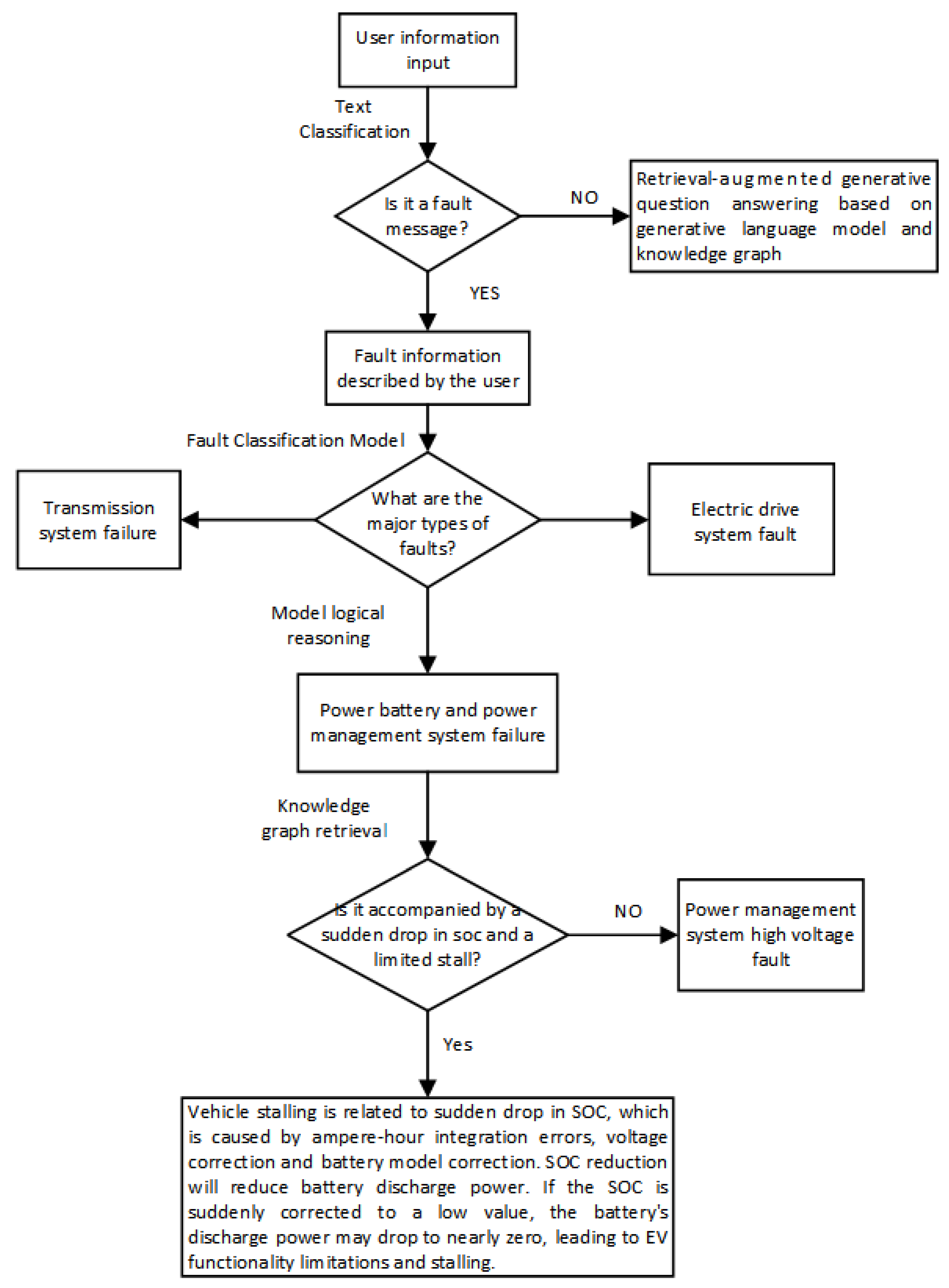
4.4. The Process of Intelligent Retrieval of Fault Information of NEVs
4.5. Elaboration of the System Information Interaction Flow's Framework
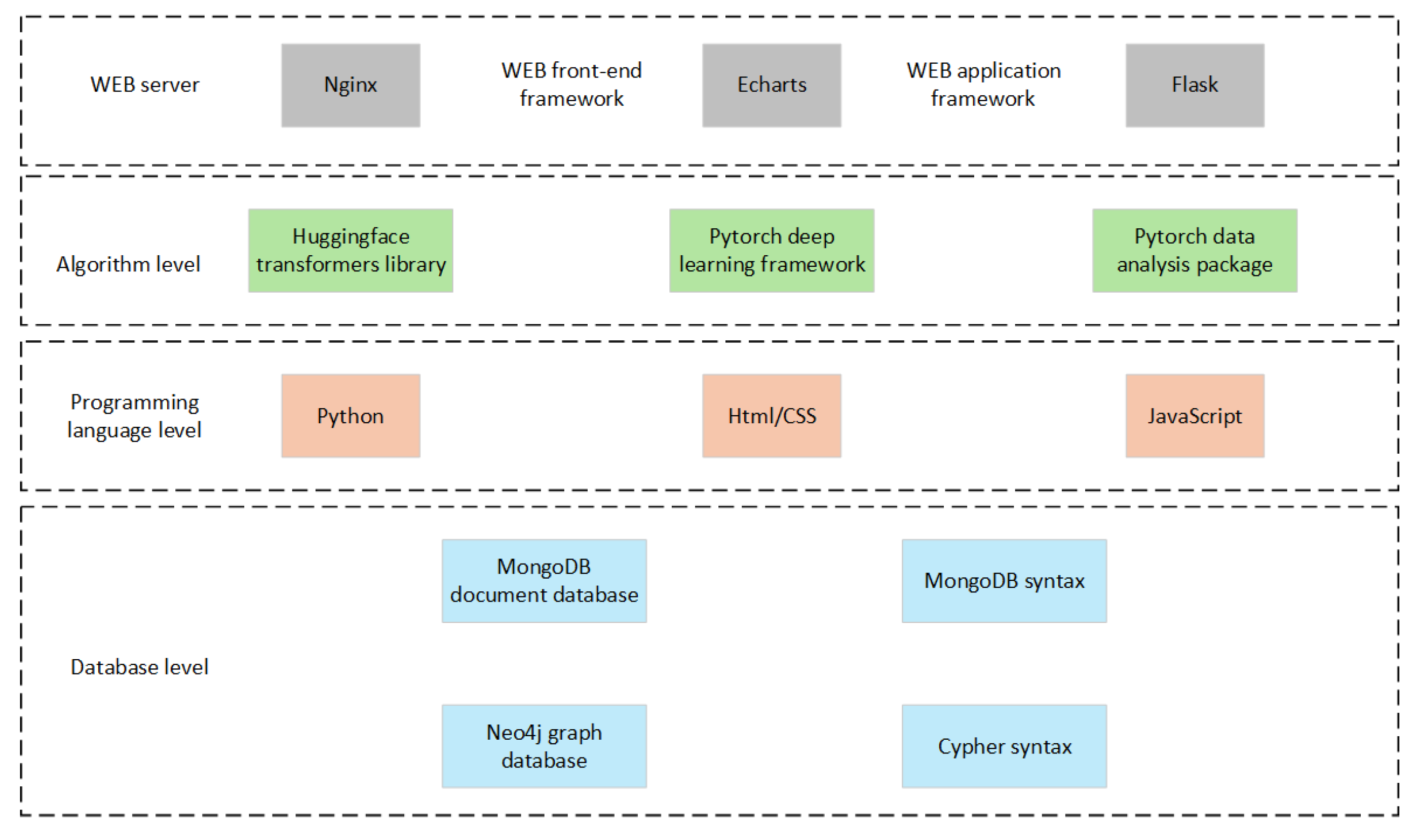
4.6. System Development Technology
4.7. System Demonstration and Testing
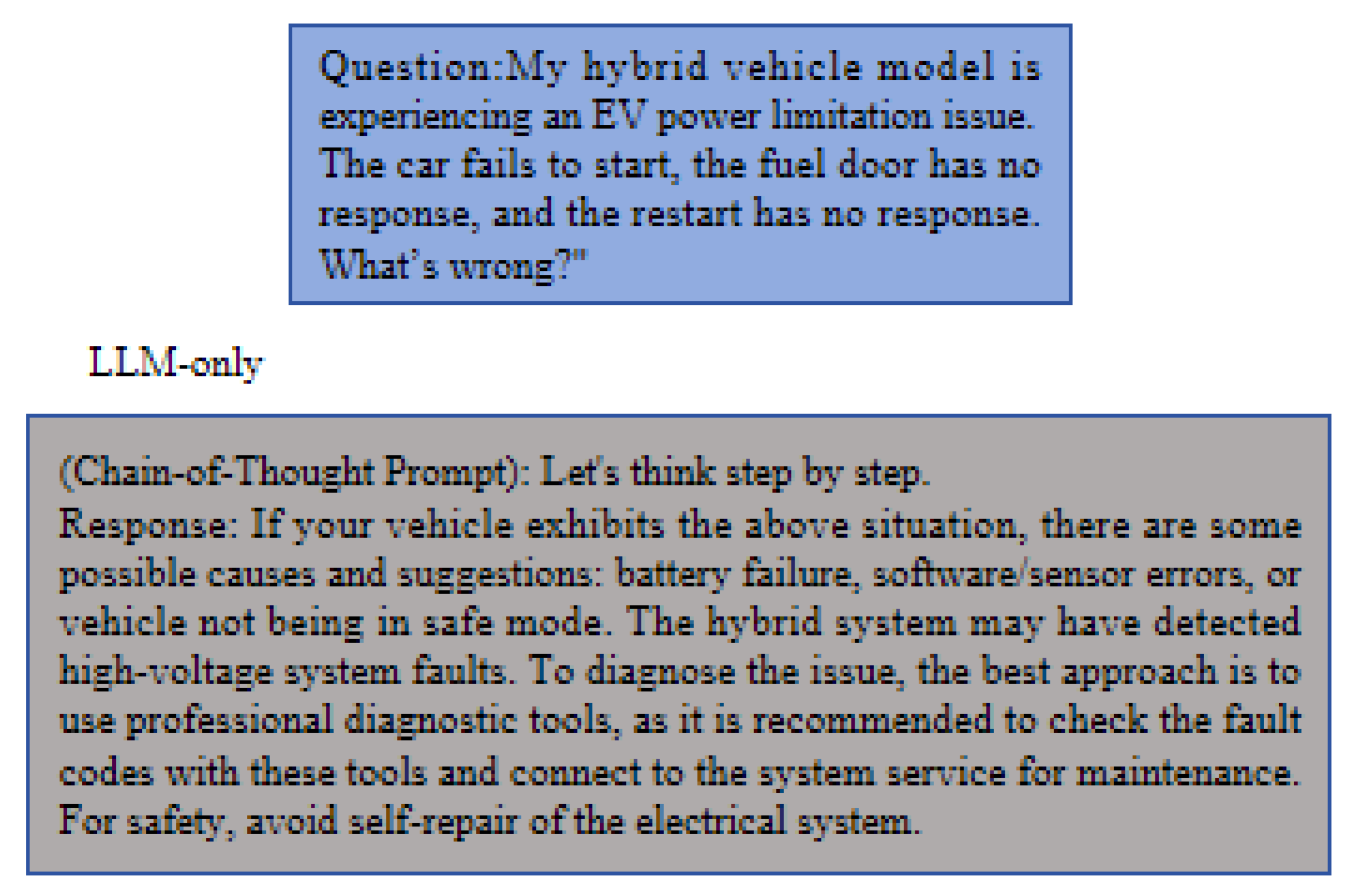
4.7.1. System Presentation
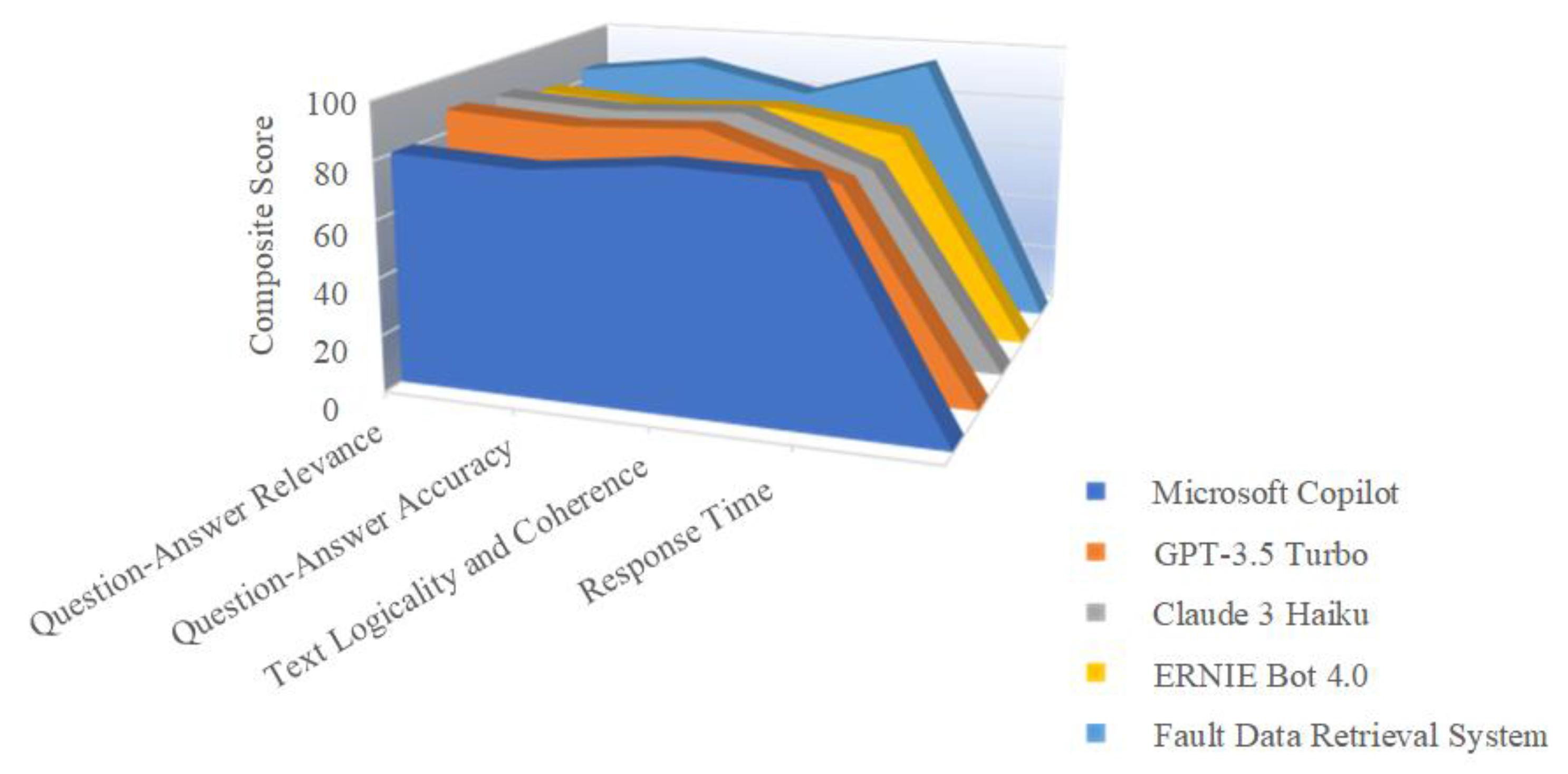
4.7.2. System Testing
5. Conclusion and Prospects
References
- Cong, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L. A Comprehensive Signal-Based Fault Diagnosis Method for Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.S.; Abubakar, S.; Gambo, F.L.; Gadanya, M.S. A Rule-Based Expert System for Automobile Fault Diagnosis. Int. J. Perceptive Cogn. Comput. 2021, 7, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Liu, X.; Liao, J. Research on Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Parts Based on Transformer Deep Learning Model. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Lei, Y.; Li, N. Applications of Stochastic Resonance to Machinery Fault Detection: A Review and Tutorial. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 122, 502–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Han, F.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W. Research on Fault Diagnosis Method of Rapier Loom Based on the Fusion of Expert System and Fault Tree. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 3429–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. Cross-Domain Fault Diagnosis Using Knowledge Transfer Strategy: A Review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129260–129290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Shahbazi, Z.; Byun, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-J. Lithium-Ion Battery Estimation in Online Framework Using Extreme Gradient Boosting Machine Learning Approach. Mathematics 2022, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Ye, F.; Dai, M.; Zhang, Z. Real-Time Fault Detection and Process Control Based on Multi-Channel Sensor Data Fusion. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Li, W.; Rong, Y.; Li, F.; Yu, F.; Zeng, X. Research on the Application of Artificial Intelligence Method in Automobile Engine Fault Diagnosis. Eng. Res. Express 2021, 3, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, F. Fault Diagnosis of New Energy Vehicles Based on Improved Machine Learning. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 12091–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.-S.A.; Su, C.-H.S.; Chen, Y.-H.; Guu, D.-Y. How to Implement Automotive Fault Diagnosis Using Artificial Intelligence Scheme. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, A.-A.; Cai, Z.; Al-qaness, M.A.; Alawamy, E.A.; Alalimi, A. ETR: Enhancing Transformation Reduction for Reducing Dimensionality and Classification Complexity in Hyperspectral Images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118971. [Google Scholar]
- McCann, B.; Keskar, N.S.; Xiong, C.; Socher, R. The Natural Language Decathlon: Multitask Learning as Question Answering. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv180608730 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, F.; Tan, C.; Qiu, M.; Yang, F.; Shi, Q.; Huang, S.; Gao, M. Towards Unified Prompt Tuning for Few-Shot Text Classification. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv220505313 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. 2018.
- Nori, H.; King, N.; McKinney, S.M.; Carignan, D.; Horvitz, E. Capabilities of Gpt-4 on Medical Challenge Problems. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv230313375 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S. Gpt-4 Technical Report. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv230308774 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Z.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xiong, F.; Guo, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N. Codekgc: Code Language Model for Generative Knowledge Graph Construction. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2024, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Yuksekgonul, M.; Mao, Y.; Wu, E.; Zou, J. GPT Detectors Are Biased against Non-Native English Writers. Patterns 2023, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Xu, C.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.; Lin, C.; Gong, Y.; Ni, L.M.; Shum, H.-Y.; Guo, J. Think-on-Graph: Deep and Responsible Reasoning of Large Language Model on Knowledge Graph. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv230707697 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, A. Prompt Engineering for Large Language Models. Available SSRN 4504303 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Yuan, W.; Fu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Hayashi, H.; Neubig, G. Pre-Train, Prompt, and Predict: A Systematic Survey of Prompting Methods in Natural Language Processing. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, W.; Gao, J. Cases Integration System for Fault Diagnosis of CNC Machine Tools Based on Knowledge Graph. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Tay, Y.; Bommasani, R.; Raffel, C.; Zoph, B.; Borgeaud, S.; Yogatama, D.; Bosma, M.; Zhou, D.; Metzler, D. Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv220607682 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hamad, K.; Kaya, M. A Detailed Analysis of Optical Character Recognition Technology. Int. J. Appl. Math. Electron. Comput. 2016, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, K.; Chen, H.; Yi, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Survey on Evaluation of Large Language Models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2024, 15, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Ji, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Liu, L.; Sun, M.; Liu, Q.; Yang, R. Construction and Application of a Knowledge Graph. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, A.; Blomqvist, E.; Cochez, M.; D’amato, C.; Melo, G.D.; Gutierrez, C.; Kirrane, S.; Gayo, J.E.L.; Navigli, R.; Neumaier, S.; et al. Knowledge Graphs. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-J.; Zhou, W.; Hou, J. Construction of Fault Diagnosis System for Control Rod Drive Mechanism Based on Knowledge Graph and Bayesian Inference. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2023, 34, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, L. Research on Event Logic Knowledge Graph Construction Method of Robot Transmission System Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 17656–17673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, K.; Zakari, R.Y.; Lu, G.; Yin, J. Deep Neural Network-Based Relation Extraction: An Overview. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Qin, Y.; Yang, G.; Wei, F.; Yang, Z.; Su, Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chan, C.-M.; Chen, W.; et al. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large-Scale Pre-Trained Language Models. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2023, 5, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Ross, H.; Sulem, E.; Veyseh, A.P.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sainz, O.; Agirre, E.; Heintz, I.; Roth, D. Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing via Large Pre-Trained Language Models: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.P. Comparison of Text Preprocessing Methods. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2023, 29, 509–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, K.; Fu, Y.; Tam, W.L.; Du, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J. P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-Tuning Universally across Scales and Tasks. ArXiv Prepr. ArXiv211007602 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. ICLR 2022, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Shi, N.; Chen, L.; Lee, R. Enhancing Educational Q&A Systems Using a Chaotic Fuzzy Logic-Augmented Large Language Model. Front. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 1404940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Core Focus | Limitation | Reference Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure LLM Reasoning | Using the idea of linking, LLMs can solve some reasoning problems | Difficult to handle professional knowledge-intensive reasoning and complex reasoning tasks | ChatGPT4.0, ChatGPT3.5, ChatGLM, Wenxin-Yiyan, etc |
| LLM⊕KG | Large models play various roles, through querying knowledge in KG to enhance reasoning capabilities, enabling the addition of external knowledge into the model | Embedding LLM into KG limits its interpretability and introduces complexity when updating the knowledge base | Li et al. used LLM to generate SPARQL queries for KGs, and the main subject of the study is to complete KGs |
| LLM⊗KG | Cooperation between KG and LLM, enabling knowledge graph completion and reasoning through both LLM and KG integration | Need to consider the accurate path to knowledge graph completion while integrating external knowledge | Sun et al. used KG/LLM in the beam search algorithm for knowledge reasoning, enabling enhanced path expansion for KG generation[20] |
| Serial Number | Existing Problems in the System | Brief Description | System Requirements | New System Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Information search is inconvenient | The client-side web page refreshes, the interface is not user-friendly, and there is no focus on NEV fault optimization | Customer-side retrieval is complicated, and the interface is inconvenient | The interface should be concise, user-friendly, and able to quickly locate the required functions |
| 2 | No specific model for vehicle faults | There is no specific fault diagnosis system for vehicles | Technical method | Needs a fault detection model for vehicle fault diagnosis, providing precise and natural interaction for troubleshooting |
| 3 | Lack of relevant knowledge | NEV fault knowledge is scattered and unorganized | Data acquisition | Needs to organize knowledge on NEVs faults and establish a knowledge base with feedback. |
| 4 | Data resource scarcity | Needs to build a knowledge base for NEV faults | Knowledge base | Needs to build a specialized knowledge base for NEVs with capabilities for easy integration and expert use |
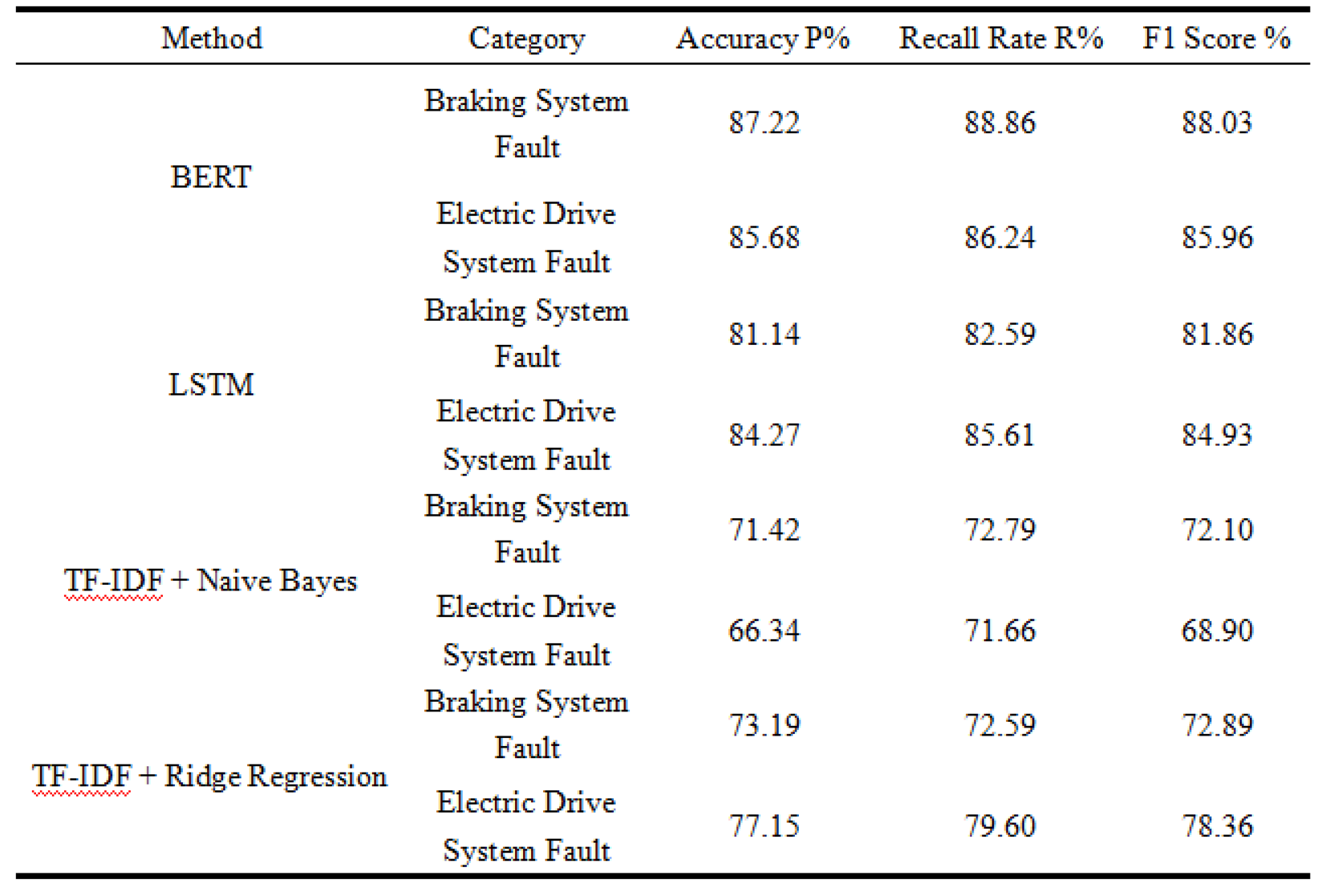
| Method | Category | Accuracy P% | Recall Rate R% | F1 Score % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BERT | Braking System Fault | 87.22 | 88.36 | 88.03 |
| Electric Drive System Fault | 85.68 | 86.24 | 85.96 | |
| LSTM | Braking System Fault | 81.14 | 82.59 | 81.86 |
| Electric Drive System Fault | 84.27 | 85.61 | 84.93 | |
| TF-IDF+Naïve Bayes | Braking System Fault | 71.42 | 72.79 | 72.10 |
| Electric Drive System Fault | 66.34 | 71.66 | 68.90 | |
| TF-IDF+Ridge Regression | Braking System Fault | 73.19 | 72.59 | 72.89 |
| Electric Drive System Fault | 77.15 | 79.60 | 78.36 |
| Environment | Parameter | Environment | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows11 64-bit | Memory | 32GB |
| CPU | Intel(R) Core (TM) i9-11900H CPU @ 2.50GHz(2502 MHz) | Graphics card | NVIDIA GeForce RTX3070 Laptop GPU 8G GDDR6 |
| Test items | Operating procedures | Expected results | Test results |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Interface Responsiveness Testing | Accessing the system interface via WEB pages | The system icons, buttons, and other user interface elements are displayed normally, and the user interaction functions are free of obstacles | Pass |
| Type of fault identification | Inputting fault information into the fault classification model in the background | The fault information inputted can be correctly received and parsed by the fault classification model. | Pass |
| Knowledge base search | The data parsed is retrieved from the knowledge base | The knowledge base can successfully retrieve data related to the parsed information | Pass |
| Fault data retrieval and graph visualization function | Submit the fault information after inputting it | The page can stream and analyze the data, and display dynamic visual effects of the fault information-related graphs | Pass |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





