| Karthikeyan et al. (2024) |
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering |
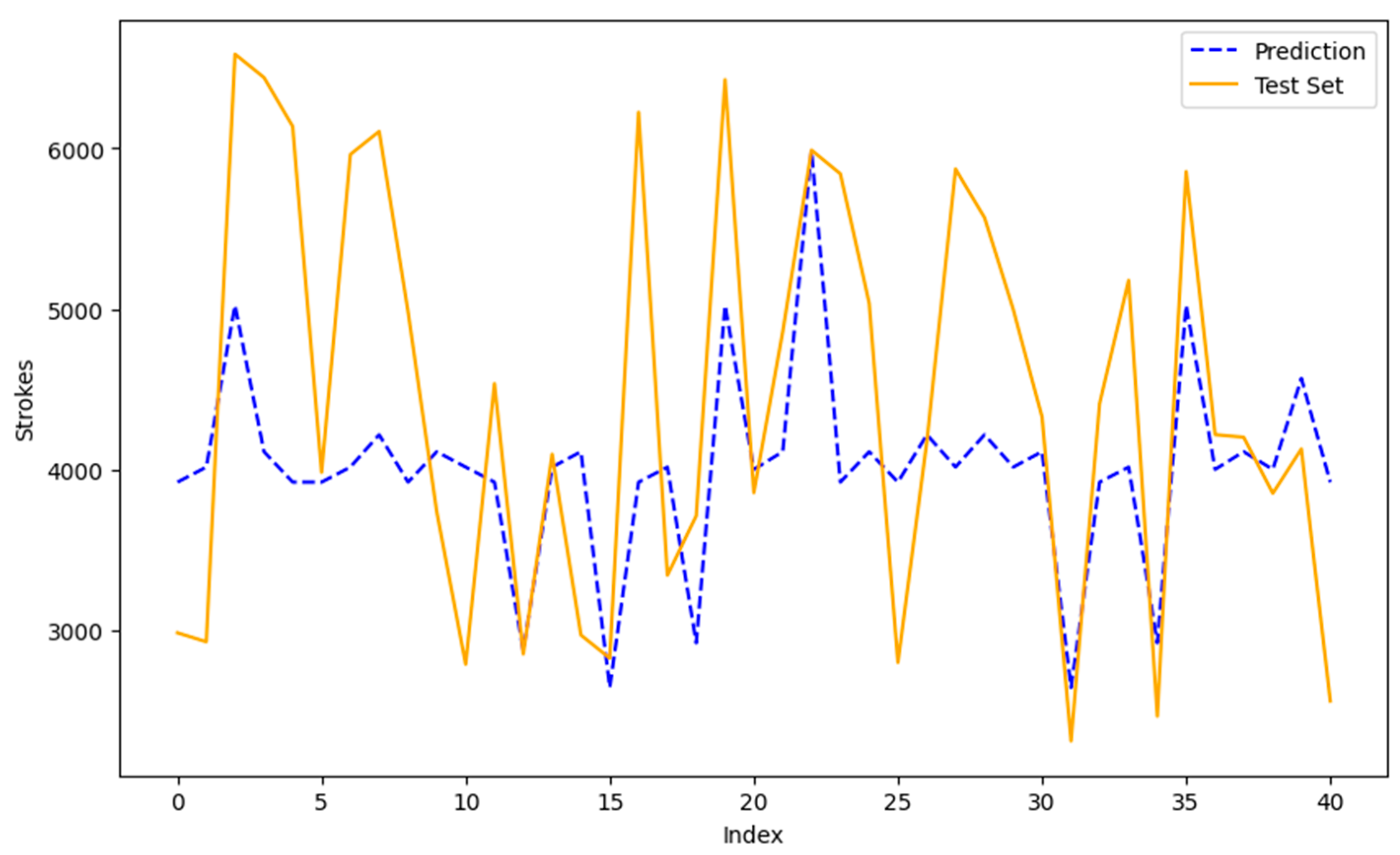
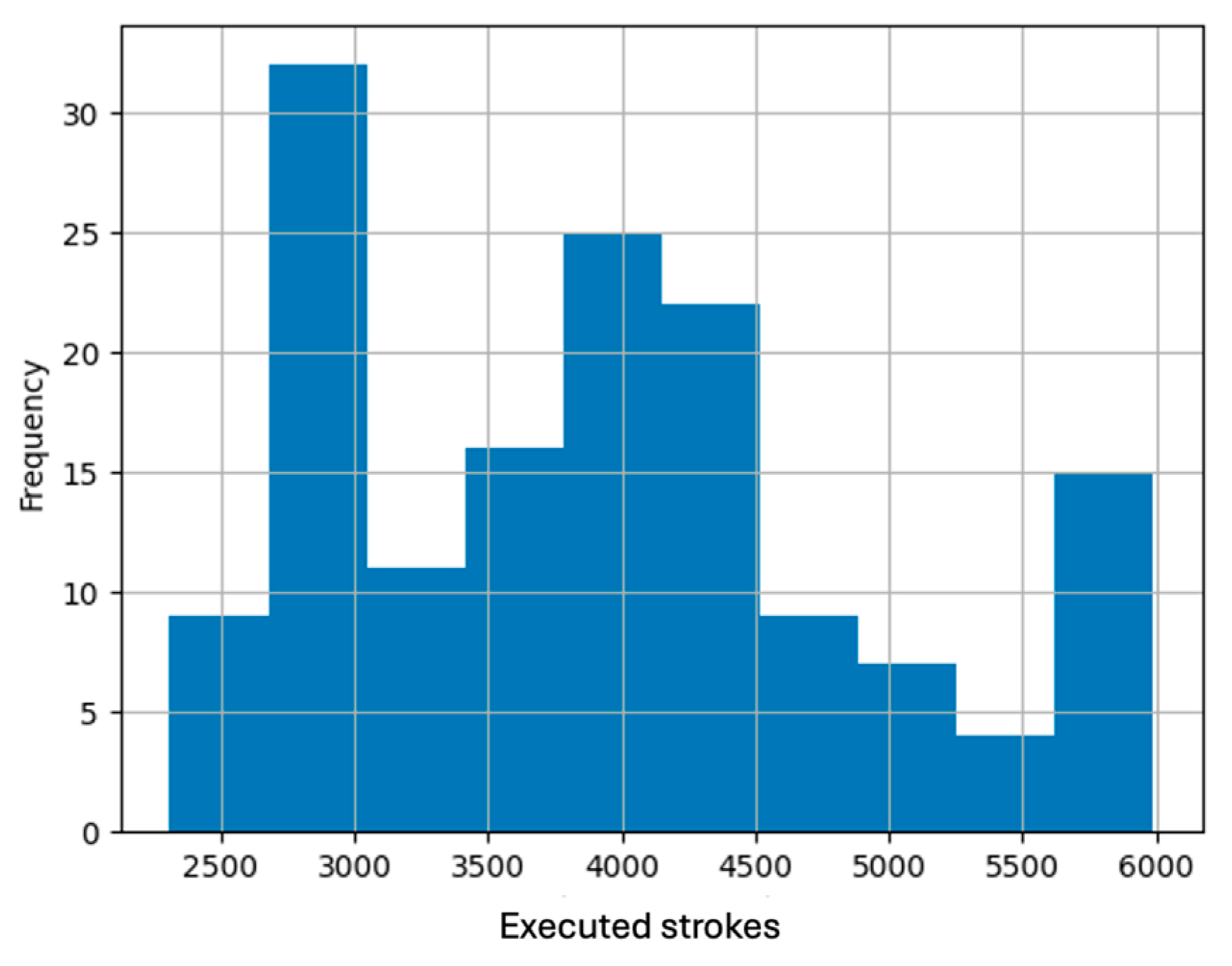
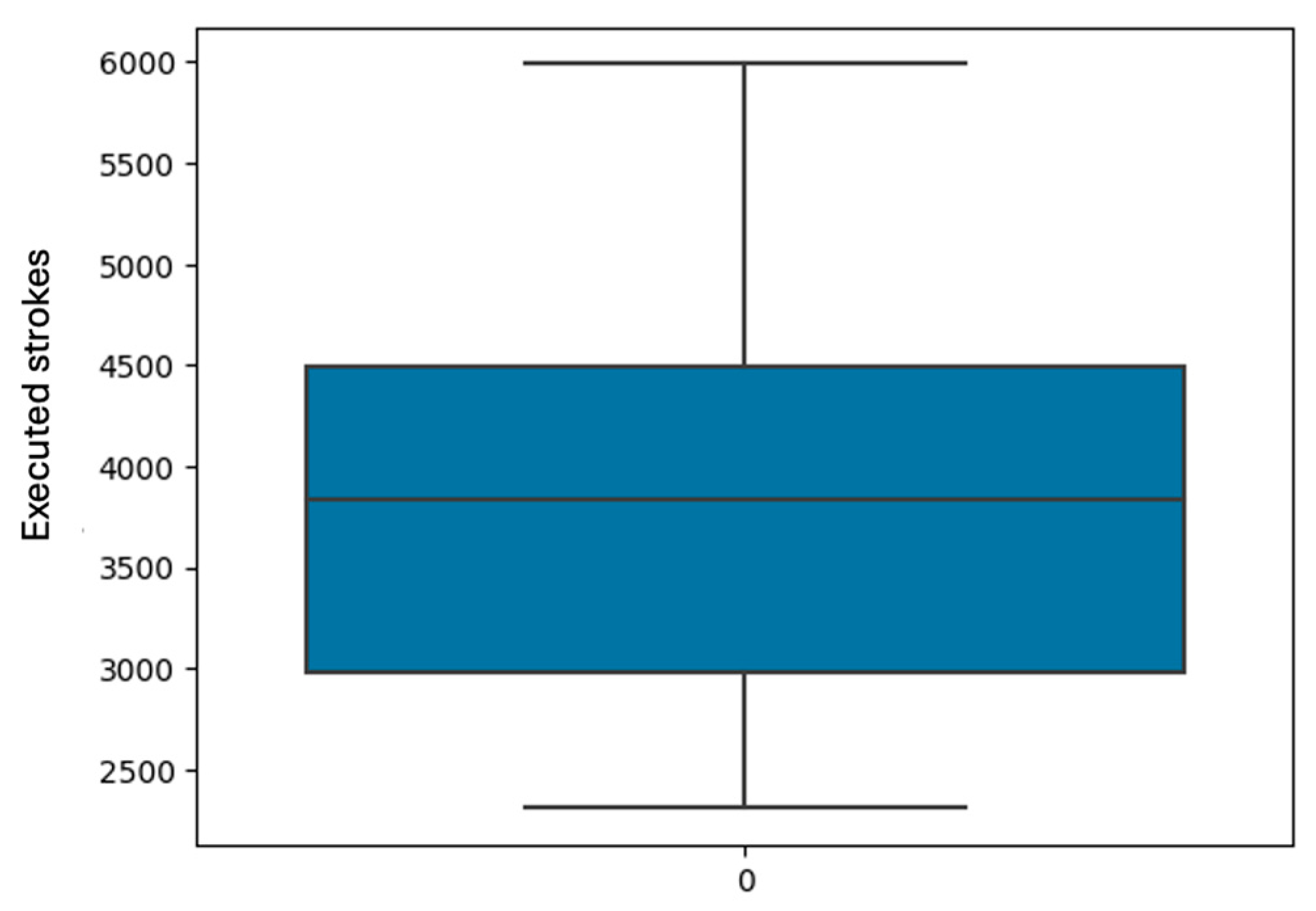
Using three different feature extraction techniques, namely statistical, histogram, and the autoregressive moving average model (ARMA), this study attempted to employ feature fusion to identify the most significant features required for detecting suspension faults using vibration signals and a machine learning approach. |
The study classified eight different states of the suspension system, comprising seven fault conditions and one normal (good) condition. The study demonstrates that the combination of ARMA-histogram-statistical features with a random forest classifier results in high classification accuracy and presents findings that can enhance predictive maintenance for vehicles. |
The experiments conducted in this study were performed under laboratory conditions using a quarter-car model. The accuracy of the proposed method and model may vary. For future work, real-time implementation could provide greater significance and practical value |
| Prytz R. et al. (2015) |
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence |
This article proposes a data-driven approach to predict the future maintenance needs of air compressors in heavy trucks, combining pattern recognition and Remaining Useful Life (RUL) estimation. The proposal classifies whether the RUL will be shorter or longer than the interval until the next scheduled service visit, using historical data collected from vehicles and records of certified workshop services. |
This study makes an innovative contribution to the literature by using historical vehicle data and service records to predict maintenance needs, overcoming the limitation of data sources not designed for mining. The application of failure prediction models and Remaining Useful Life (RUL) estimates for air compressors, components with multiple potential failure modes, extends the reach of predictive automotive maintenance, bringing significant advancements to the industry. Furthermore, the research contributes to the field of Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) by proposing a solution that does not rely on continuous monitoring or real-time sensors, thus overcoming connectivity challenges and associated costs. |
An important limitation of the study lies in the complexity of the data, which includes maintenance records and vehicle usage data designed for other purposes, such as warranty analysis, rather than for data mining. Additionally, the datasets are highly imbalanced, with noisy class labels and missing data, which hinders the accuracy of predictions. Another challenge is the variety of vehicle configurations, as well as adverse conditions and the lack of continuous monitoring, making the application of predictive maintenance models more complex and difficult to generalize across all scenarios. |
| Joseph Chukwudi I. et al. (2024) |
IEEE Access |
Develop a model capable of real-time prediction of failures or potential problems in a vehicle's engine using a data pre-processing technique scaled in sklearn, analyzing and validating the performance of the proposed models using statistical tools. |
Presented an effective model by leveraging the strengths of multiple machine learning models to generate more accurate and specific solutions. |
The findings of this study consist of fundamental tools for the implementation of a predictive maintenance guide for the automotive industry, however they do not guarantee that the results obtained are related to the real world, aiming at the use of more efficient techniques and parameters. |
| Rana K. et al. (2024) |
Computers and Electrical Engineering |
Presented a literature review focusing on the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) for automotive systems with applications that go beyond Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). |
Gaps in the existing literature were identified, highlighting the evolution of the mobility scenario. From this perspective, research needs were identified for a complete evaluation of network architecture, connectivity and performance metrics, covering Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) technology, networking protocols and swarm dynamics. |
It focused on identifying gaps in the literature, addressing the impact of AI in areas such as automotive emissions, predictive maintenance, connected vehicles, safety-focused driver monitoring systems, and the use of various algorithms from an ADAS perspective. The summarized case studies provide excellent examples of applications of each system, but do not provide methodological details. |
| Tabit S. et al. (2022) |
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology (JATIT) |
The objective of our research is to develop an algorithmic solution for the detection of anomalies and
nonconformities in production units, through an automatic classification of the data collected by the sensors
(which represent the INPUTS of our model) into two categories: defects and without defects, which constitute
the set of arrivals of the value of OUTPUT |
The work contributes by presenting an approach capable of classifying images of product surfaces (such as steel strips) into two categories: defect present or defect absent. It utilizes algorithms that map pixel intensity values to achieve precise categorization. The use of machine learning for predictive maintenance allows predicting the failures of different types of equipment, anticipating the maintenance of machines, and therefore planning it in advance. |
The proposed research requires extensive annotated data on non-compliance, making it costly. The efficiency of machine learning applications is heavily influenced by selecting the correct evaluation metrics, particularly in scenarios with imbalanced data, where incorrect predictions can have significant consequences. The efficient application of machine learning for the detection of anomalies in the production process depends essentially on the analytical approach used by the data scientist to select the data and exploit it. |
| Jain A. et al. (2023) |
International Journal of Prognostics and Health Management. |
The aim of this paper is to propose a Machine Learning (ML) based framework which utilizes minimally labelled or unlabeled sensor data generated from a vehicle system at a given frequency. The framework utilizes an ML model to identify any anomalous behavior or aberration, and flag it for further review. |
The framework helps in providing an automation solution to quickly analyze the field data and provide alerts for any aberration. It is useful in creating early alert model for any known problem or new anomaly in absence of labeled data. The infrastructure, pipeline creation, or models could be configured as per the specific requirements of the problem and is technology agnostic. The framework also proposes to convert a generic anomaly detection problem to specific predictive maintenance problem once the labels are captured in the data. Another aspect for which this framework could be utilized is
for creation of a Vehicle Health Index (VHI) indicating the
overall health of the vehicle. |
The framework can handle most scenarios but may encounter rare operating conditions not defined during design. These conditions would appear as anomalies, potentially forming densely populated clusters that indicate a new operating regime. Regular performance monitoring is crucial, especially when such clusters are reported. Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) should investigate to confirm if the scenario represents a new condition or an actual anomaly. |
| Voronov S. et al. (2020) |
Journal of Prognostics and Health Management |
The article proposes the development of predictive models for lead-acid battery maintenance in heavy vehicles, utilizing sparse and non-equidistant operational data. The focus is on predicting battery failure through machine learning techniques, specifically Random Survival Forest (RSF) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models |
This paper contributes to the field of predictive maintenance by addressing the challenge of predicting lead-acid battery failures in heavy-duty vehicles using sparse operational data. The proposed approach combines imputation techniques, such as mean imputation for missing values, and two predictive models: RSF and LSTM-based neural networks. The study demonstrates that LSTM models significantly outperform RSF models and other traditional algorithms like Cox regression, particularly in scenarios with sparse data. Additionally, the work highlights the importance of handling data imbalances and proposes an ensemble method to address this issue. The findings suggest that more frequent data readouts improve model performance, but due to the accumulative nature of sensor readings, data collection can be optimized by reducing readout frequency, thus lowering transmission costs and vehicle equipment requirements. These contributions provide valuable insights into data collection strategies and the application of machine learning in industrial predictive maintenance. |
The data primarily consists of accumulated sensor readings collected throughout the battery's lifetime, typically recorded during irregular workshop visits. The dataset contains several uncertainties, including a high rate of non-random missing values. |
| Jain M. et al. (2022) |
Computational Intelligence |
This article intends to
provide the literature review of ML techniques used for
predictive maintenance of automobiles and diagnosis of
the vehicle’s health using ML. |
The article synthesizes the state-of-the-art in the application of machine learning models, such as Random Forest (RF) and Support Vector Machines (SVM), for predicting faults, diagnosing vehicle health, and estimating remaining useful life (RUL). It highlights the importance of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) systems, which serve as a crucial tool for collecting data that enables the application of predictive and prognostic techniques. |
The OBD system proves to be a valuable tool in collecting data on which machine learning models can be applied. However, data concentration has been confined to only a limited number of parts, and there is significant scope for collecting data from other parts of the vehicle that requires further investigation. Supervised learning techniques such as SVM, RF, and others have been successfully applied to prognosis applications. However, further research is necessary, as there remains considerable room for improvement in these methodologies. |
| Cherdo Y. et al. (2023) |
Sensors |
The proposal of this article is to explore the application of recurrent and convolutional neural networks for unsupervised anomaly detection in real multidimensional time series generated by vehicle sensors, extracted from the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus. |
It contributes to the literature by applying unsupervised anomaly detection techniques based on LSTM and CNN to time series data from real vehicles, enabling the identification of complex multidimensional behaviors without focusing on specific types of anomalies. Furthermore, it demonstrates that smaller models can achieve similar performance in anomaly detection, albeit with lower prediction accuracy, offering a more efficient alternative. Finally, the study introduces an innovative method to correlate variables with the detected anomalies, aiding in the interpretation of results and the diagnosis of abnormal behaviors. |
The limitations of this article include the difficulty of fully evaluating the model due to the labels representing only a specific abnormal behavior, as well as the lack of more advanced preprocessing and feature engineering driven by experts, which could improve the results. Additionally, the reduction in computational costs, although addressed, lacks further in-depth study on public benchmarks, which is essential for validating and generalizing the results. Finally, the proposed method for correlating variables with abnormal behaviors, while promising, still requires a more detailed evaluation to be refined. |
| Theissler A. et al. (2021) |
Reliability Engineering & System Safety |
The purpose of this article is to investigate the application of predictive maintenance (PdM) in the automotive industry, using machine learning (ML) to ensure the functional safety of vehicles throughout their lifecycle while limiting maintenance costs. |
The main contributions of this paper are introducing the most relevant machine learning subfields for predictive maintenance, making the field of ML-based PdM accessible to experts from different backgrounds; conducting a systematic survey and categorization of papers on ML-based PdM for automotive systems, analyzing them from both a use case and machine learning perspective; identifying the most frequent use cases, commonly used ML methods, and the most active authors; and identifying open challenges and discussing future research directions, providing research questions that may inspire new studies. |
The main limitations of the research include the reliance of most articles on fully labeled datasets, which creates a significant bottleneck due to the difficulty in obtaining such data, especially in field scenarios. While supervised (or semi-supervised) learning yields more reliable results, the need for labeled data for these methods is a major obstacle. Furthermore, none of the reviewed papers used reinforcement learning, indicating a gap in the research, despite the potential for applying this approach to predictive maintenance in automotive systems. |
| Muideen A.A. et al. (2023) |
Mathematics |
This article proposes an innovative approach for detecting failures in automotive air pressure systems (APS) by introducing a Broad Integrated Logistic Regression (BELR), which combines a Broad Learning System (BLS) and a Logistic Regression (LogR) classifier to predict APS failures. |
O trabalho contribui ao introduzir uma abordagem capaz de classificar falhas em sistemas de pressão de ar automotivos (APS) em duas categorias: falha de APS presente ou falha de APS ausente. Ele alavanca algoritmos que extraem características discriminativas de dados de entrada para obter previsões precisas. Ao empregar técnicas de aprendizado de máquina, o estudo permite a manutenção preditiva, permitindo a detecção precoce de falhas de APS, o planejamento oportuno de atividades de manutenção e minimizando custos associados a quebras inesperadas. |
Its limitations include reliance on the KNN imputation method for handling missing data, which, although effective, leaves room for improvement through the exploration of advanced imputation techniques like generative adversarial networks (GANs). While BELR outperforms comparison algorithms such as Gaussian Naive Bayes, Random Forest, KNN, SVM, and Logistic Regression in metrics like F1-score, its superiority is context-dependent, and further validation across diverse datasets |
| Gopalakrishnan S. et al. (2022) |
Tech Science Press |
Test predictive methodology in anomaly detection, production line accuracy and machinery efficiency for the automotive industry, especially among Accessory Manufacturers (AMs), in comparison to other existing Machine Learning (ML) approaches. |
Developed a predictive maintenance system applying a hybrid ML model, with supervised and unsupervised training, within the framework of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). |
The proposed model was designed for two main scenarios: training phase and execution phase. The results were efficient in detecting defective parts earlier. However, more data is needed to complete the study of the unsupervised learning model. |
| Singh S. et al. (2023) |
IEEE Engineering Management Review |
Propose four predictive maintenance methodologies for different sensor groups that produce real-time failure and anomaly results, addressing Machine Learning (ML) for automotive industries. |
Presented unique predictive maintenance framework applicable to equipment in automotive industries emphasizing increased productivity and efficiency, improved availability of equipment and components, reduced utility and labor costs, automated processing of maintenance checks and reduced operating costs using cloud-based services. |
The proposed framework assumes that each component can suffer a single failure, so predicting Remaining Useful Lifetime (RUL) is challenging in the presence of Big Data. The proposed model can forecast and foresee anomalies, but fails to calculate RUL. |
| Redondo R. et al. (2020) |
MDPI AG: Applied Sciences (Switzerland) |
This study extends Hybrid Unsupervised Exploratory Plots (HUEPs) as a visualization technique that combines Exploratory Projection Pursuit (EPP) and Clustering methods for the automotive industry. |
Added the Classical Multidimensional Scaling, Sammon Mapping and Factor Analysis methods. A new and real case study was analyzed, comprising two of the usual machines in the automotive industry. Proving that, depending on the dataset, it may be better to use a combination of methods to generate one HUEP or another. |
The results obtained show that HUEPs is a technique that supports the continuous monitoring of machines to anticipate failures, however the use of HUEPs for quality purposes was not explored. They could also have addressed the combination of HUEPs with the outputs of supervised models. |
| Shafi U. et al. (2022) |
Journal of Advanced Transportation: Hindawi Limited |
Presented an approach for fault prediction of four subsystems of a vehicle: fuel system, ignition system, exhaust system and cooling system. Compare the accuracy of all the classifiers based on Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curves. Propose a new vehicle monitoring and fault prediction system using four classifiers: Decision Tree, SVM, RF and K-NN. |
Prediction of vehicle system failures and proper real-time vehicle monitoring and prognostic maintenance system. It used sensor data and machine learning algorithms in conjunction with smartphone applications, enabling easy-to-use remote vehicle health monitoring. |
The data source comes from a sample of 70 cars of the same model. The accuracy of the data could be further refined with more in-depth work on the data set and by applying other forecasting techniques. |