I. Introduction
The use of the old-style financial system has some problems, especially when there is a change in the exchange rate. If consumers use Automatic Teller Machines (ATM) when there is a change in the exchange rate, there will be the sharpest increase. The sharpest change in the share of cash payments occurs at $20 and $40 which coincides with the observation that most ATMs in the US dispense multiples of $20. Other thresholds apply at multiples of $5 and $10. The above thresholds will result in asymmetry in consumer behavior (Shy, O., 2020). The development of technology is increasing rapidly today, people have abandoned the old financial system and switched to the financial technology system. One of them is the emergence of a new payment method, namely through an E-Wallet (Rohmatun, 2020). E-wallet is a feature of the x electronic x payment media application developed to make it easier for x users to carry out transaction activities.
Initially, the growth in the number of fintech startups began to soar, this is indicated by a declining percentage of growth; in 2016 78% and only 28.34% knew the term fintech, while in 2017 it 39% and respondents knew the term fintech 67.20%. (Setiobudi & Wiradinata, 2018). Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) theory is used to determine the acceptance rate of a new x technology system, saying that people always want to try the emergence of new technologies.(Lucyanda, 2010). In addition, research conducted by Rahmawati, (2020) explained that where the use of Financial E-wallet technology is perceived by the general public as a financial technology that has security and useful uses.
However, the fact is that in the field many users of financial technology experience many problems. On the other hand, financial technology also provides threats and risks that lurk in its users such as fraud through OTP (One Time Passcode) codes, Phishing Attacks, and account hacking by violating the use of E-wallet and pay later balances. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a study of what affects financial technology so that it causes problems for its users.
SMEs players often use financial technology services to increase their business income. Before getting to know Financial technology in the digital economy, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) have not been able to maximize sales and had a relatively low income and when business actors use E-swallow-based financial technology they can increase marketing, In the research (Quanmei, 2022) said that revenue has a positive and significant effect when using Financial technology because it facilitates and is efficient in the payment system for users. However, the study is different from the research conducted (Pohan, 2021)
According to the Behavioral Intention Theory, it is stated that the form of positive attitude shown by the community has the desire to use services continuously and the existence of transaction services on Fintech means that people feel helped. Therefore, financial technology facilitates payment transactions, speeds up the transaction process, increases transaction efficiency, and avoids the risk of counterfeit money and crime (Nurcholidah & Harsono, 2021), research (Purnama, 2021) revealed that transactions have a positive and significant effect on Financial Technology because financial technology types of mobile payments can increase transactions micro-business payments, while the research (George Mutiso, 2021) revealed the results of the study, namely that transactions do not affect financial technology because financial technology still does not provide more benefits so that it affects a person's satisfaction in using E-wallet financial technology services.
The public, especially SMEs who use financial technology and feel worried about the high level of risk of digital services, must consider the benefits as well as the risks, and based on these considerations, decisions will be made using other financial technology services that have various benefits that can support the economy and improve performance for small and medium enterprises, in research (Wai Han Wong, 2019) shows that the risk is positive and significant to Financial technology because it is still worried about the risks that occur when using financial technology services, while research conducted by (Kurnianingsih, 2022) shows that risk does not affect Financial technology this is evidenced that the benefits and conveniences felt so that business actors and the public are more willing to use financial technology services
In Theory Global Financial Development Report (2014) defining Financial Inclusion as a need for both individuals and companies that use financial services has become a fairly interesting subject among policymakers, researchers, and other stakeholders (Erni Awanti, 2018). Financial inclusion is a condition where the majority of individuals can take advantage of available financial services and minimize the existence of groups of individuals who are not yet aware of the benefits of financial access through access that is already available at an affordable cost. Research conducted by (Shaliza Alwi, 2021) states that financial inclusion has a positive and significant effect on financial technology because financial technology provides easy access for the public and business actors. Meanwhile, research conducted by (Irman, 2021) states that financial inclusion does not affect financial technology, this is caused by a lack of understanding of financial technology and does not have an influence and impact on users of financial technology.
The purpose of this study is to provide information and understanding that something new is not necessarily immediately stable and good. Financial technology is financial software that provides many benefits for the community and MSMEs in particular. The urgency of this research is very high because it will provide extensive knowledge about financial technology, especially E-Wallets. Users of Financial Technology E-wallet, the selection of financial technology E-wallets that have an impact on SMEs who use increasingly consumptive services and not on the other hand also have risks such as Phishing Attacks and account hacking by misusing E-wallet pay later balances, so they are interested in researching in the interest in using financial technology.
Theory Review
Financial technology is increasingly advanced to improve their business performance and not only that, in the digital era can also be used for product promotion media and increase their income by using E-swallow-based financial technology services such as Go pay, shopee pay, Ovo, Dana Link Only, And still and many others and not only that Role Financial Technology also provides access to digital payment services in the marketplace and various mobile payments to increase sales and revenue to business actors who use financial technology. This is evidenced in research (Murti Wijayanti, 2022) which provides evidence that income has a significant and positive effect on Financial technology, but research conducted (Vira Indah, 2021) reveals that income does not influence Financial technology, because Online payments through Financial technology services do not affect increasing income, this is because most consumers prefer cash payments instead of using E-wallet-based financial technology services on non-cash mobile payment services.
FinTech developments benefit from general advancements in many areas, such as blockchain, big data, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and the digital economy. In addition, mobile money is currently a hot topic and will continue to be a hot topic. In terms of countries/regions, China has the largest number of publications, which can be illustrated by China's advanced technological environment, such as convenient mobile payment and smart life. Burst detection analysis and overlay analysis give scholars interested in FinTech a boost to understanding dynamic changes more intuitively (Li, B., & Xu, Z. (2021)
Financial technology is a new business model that will support the needs of the business community in financial transactions without having to have an account so that people who have a business can easily access online payments, online money loans, and non-cash money transfers with the existing of Financial technology on the E-wallet the financial transaction process is faster, easier and more practical even though transactions between regions as well as users with Freedom to trade and buy and sell at the market place to increase their business profit. In this case, it is shown in the research conducted by (Kusuma, 2020) states that transactions have a significant and positive effect on Financial Technology, this is evidenced that financial technology can increase sales transactions in business actors, while the research researched by (Listiawati, 2021) shows the results of transactions does not affect Financial Technology,
Risk is the possibility or uncertainty of a loss caused when using financial technology, the loss has a direct or indirect impact on financial technology such as psychological anxiety, discomfort, financial loss, dissatisfaction with the performance, and loss of time, therefore the public before using innovative products produced by financial technology first understands and knows the uses of financial technology services. Research (Van Tuan, 2021) shows the results that risk has a significant and positive effect on financial technology because financial technology provides risks and concerns, therefore some users feel directly the risks of these services. Meanwhile, the research (Krisnawati, 2021) provides results that risk does not affect financial technology.
Financial inclusion is a condition where most individuals can use financial services in financial technology to improve financial services and create financial stability for the community or people who have businesses smoothly, at a time, at affordable costs and adjusted to the needs aimed at improving the welfare of the community and business actors (Mulasiwi, 2020) . This is proven by research conducted by (Tran Hung Son, 2020) which states that financial inclusion has a significant and positive impact on financial technology, this is evidenced that financial technology provides access to financial services young through financial technology and has a positive influence . but it is different from the results of the research conducted by (Beg Sana, 2018) with the results Financial inclusion does not have an impact on financial technology.
Research Methods
The type of research used in this study used a quantifiable approach (Ghozali, 2013) the population in this study was micro, small, and medium enterprises in the Sidoarjo region of East Java province with a total of 1195 SMEs. The sampling technique used in this study is a purposive sampling technique that determines certain criteria. The criteria set were 167 samples (Sugiyono, 2017).
The source of data in this study is primary data. Primary data collection is carried out using questionnaires which are raw data that have not been processed and collected specifically. This data collection technique uses a Likert scale used to measure indicators of income, transactions, risk, and financial inclusion, the approval rate of this Likert scale consists of a choice of several scales on which each instrument is scored, namely: Strongly Agree (5), Agree (4), Neutral (3), Disagree (2) and Strongly Disagree (1). This data analysis technique uses SmartPLS Software which is used to combine indicators in each variable that has been previously determined.
Operational Definition, Variable Identification and Variable Indicators
- a.
-
Financial technology (Y)
Financial technology E-wallet or Variable dependent Y in this study is an information technology system similar to internet banking equipped with various features that allow individuals to make transactions so that users switch to non-cash users only by using applications that can be easily downloaded on smartphones (Muliadi, 2021)
- b.
-
Revenue (X1)
Income is income from investment or product sales, the use of financial technology in E-swallow services where those who have businesses can expand their product sales network through promotions on marketplace applications, gojek, shoopy and not only that users can also invest in shares on several Financial technology platforms registered by the OJK and recognized by BI (Miswan, 2019)
- c.
-
Transaction (X2)
Transactions or variable X2 is a new style or new trend of shifting transactions in doing business or business towards digital which no longer uses physical money, but uses electronic money on E-swallows in Electronic Payment services transactions including payments, investments, borrowing money, transfers, on financial service products (Pattinaja, 2021)
- d.
-
Risk (X3)
In the risk variable, it can be defined as a subjective opportunity for possible losses when deciding to use financial technology on E-swallow services based on the definition of risk perception or risk to users of features and services can result in losses in the form of unfavorable consequences for consumers
- e.
-
Financial inclusion
Financial inclusion in Financial technology E-swallow services is an effort to encourage a technology-based financial system so that it can be accessed by all levels of society to encourage quality economic growth if the public can access financial products and services easily, then the community will be more productive and create a stable financial system (Kusuma, 2020a)
- 2.
Variable Indicators
Table 1.
Variable Indicators.
Table 1.
Variable Indicators.
| No |
Variable |
Indicator |
Variable Type |
| 1. |
Financial Technology (Y)
(Ariningsih, 2022) |
Perceived usefulness. Perceived ease of use. Perceived security. Trust. intention to use. |
Dependent |
| 2. |
Income
(X1)
(Agustina, 2021) |
Promotional Media in increasing revenue. Provision of discount coupons in increased sales. maximizing business potential in the form of expanding product potential access to customers through marketing channels. |
Independent |
| 3. |
Transaction
(X2)
(Kartika Sari, 2020) |
|
Independent |
| 4. |
Risk
(X3)
(Marias, 2020) |
Financial Risk Psychological Risk Performance Risk Social risks Physical risks |
Independent |
| 5. |
Financial Inclusion
(X4)
(Kurniasari & Adyni, 2021) |
Expand public access to financial products or services. Offers a variety of financial products or services. Access at an affordable cost. Support market deepening of financial products and services. |
Independent |
Population and Sample
The population used in this study is all SMEs located in Sidoarjo District where is X generalization area X consisting of X objects or subjects that have quality x and certain which set by researcher to be studied and then drawn X conclusion. Sample x is a part x of the sum and characteristics of x possessed by that population, or x is a small x part of a member of the population taken according to a certain procedure so that can represent its population (Sandu Siyoto, 2015). This study uses a technique in the form of purposive sampling. Purposive sampling is a sampling technique by determining certain criteria that are determined by the researcher with several considerations. (Sugiyono, 2017). The results of the criteria obtained a sample of 167 m
Table 2.
Sampling Criteria.
Table 2.
Sampling Criteria.
| No |
Criterion |
Sum |
| 1 |
SMEs that are registered are fostered in the Sidoarjo Regency Cooperatives and Micro Enterprises Office. |
1195 |
| 2 |
SMEs located in the 4 largest districts of Balongbendo, Sukodono, Sidoarjo, Candi |
347 |
| 3 |
SMEs that use online marketing in the 4 largest sub-districts in Sidoarjo regency. |
167 |
| Total |
167 |
Analysis Techniques
The data analysis technique used in this study is to use several analytical methods as a measuring tool. . The data analyst technique used by researchers using SmartPLS version 3.0 with data analysts using variant-based SEM (Equation Modelling) to determine the relationship and influence between variables (Yamin, 2021). The purpose of using Smart PLS is, among others, to predict relationships between constructs, confirm theories, and can be used to explain the presence or absence of relationships between latent variables. The stages of analysis carried out in this study include model measurement (outer model) Validity test and reliability test, model structure (inner model) Determinant coefficient (R2) and Path Coefficients, T-Statistical
Results of Research and Discussion
- A.
Descriptive Statistics
This study took samples on SMEs in Sidoarjo regency, with a total of 167 questionnaires distributed to respondents who met the criteria in purposive sampling and the rate of return of questionnaires that had been filled out can be seen in the following table:
Respondent Characteristic Data:
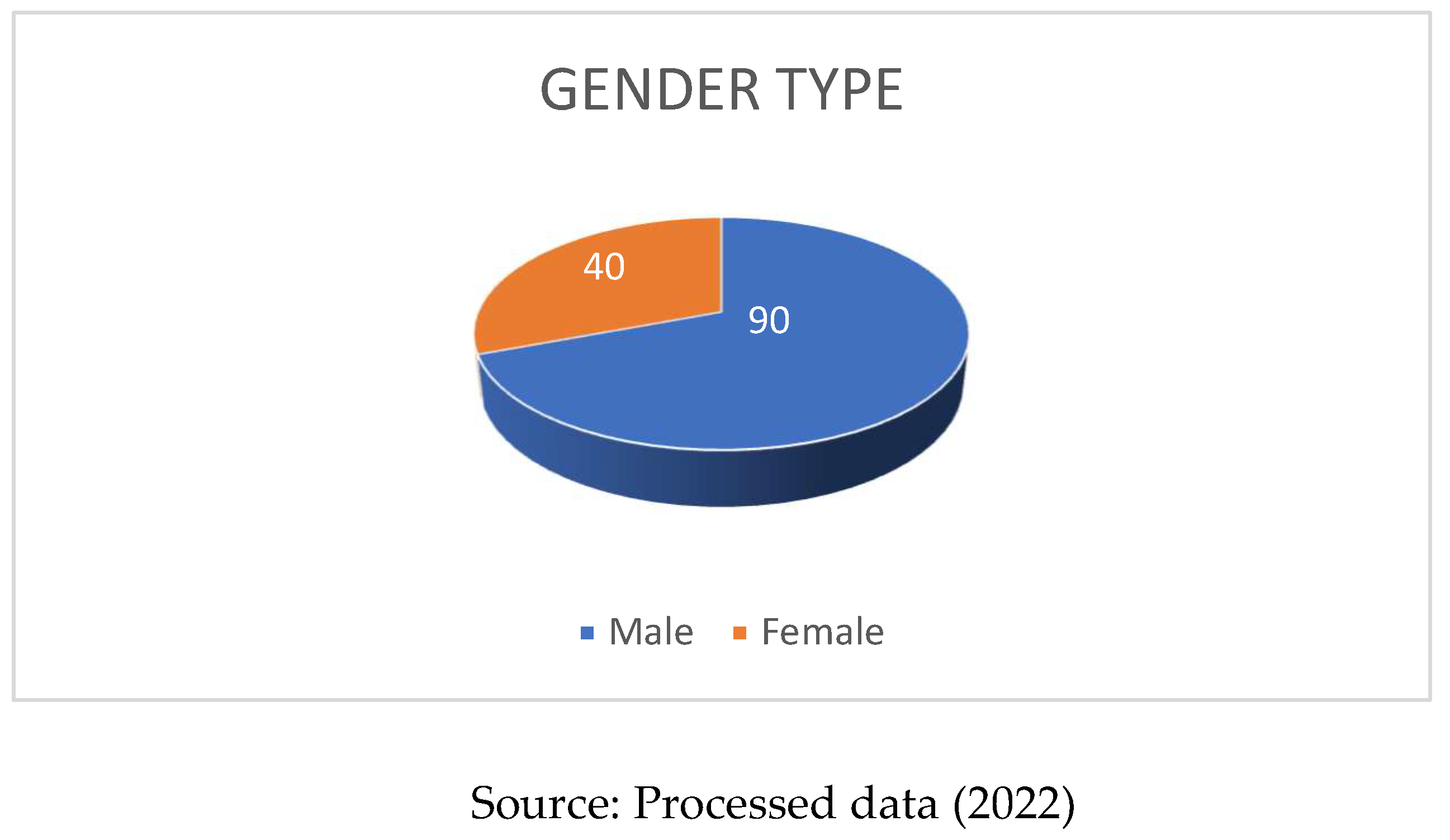
Based on
Figure 1, it can be seen that the number of respondents of the male sex is 40 people (30.1%) and the respondents who are female are 93 people (69.9%). Thus, it can be stated that SME actors in 4 sub-districts in Sidoarjo Regency are mostly female.
Characteristic data based on the use of financial technology
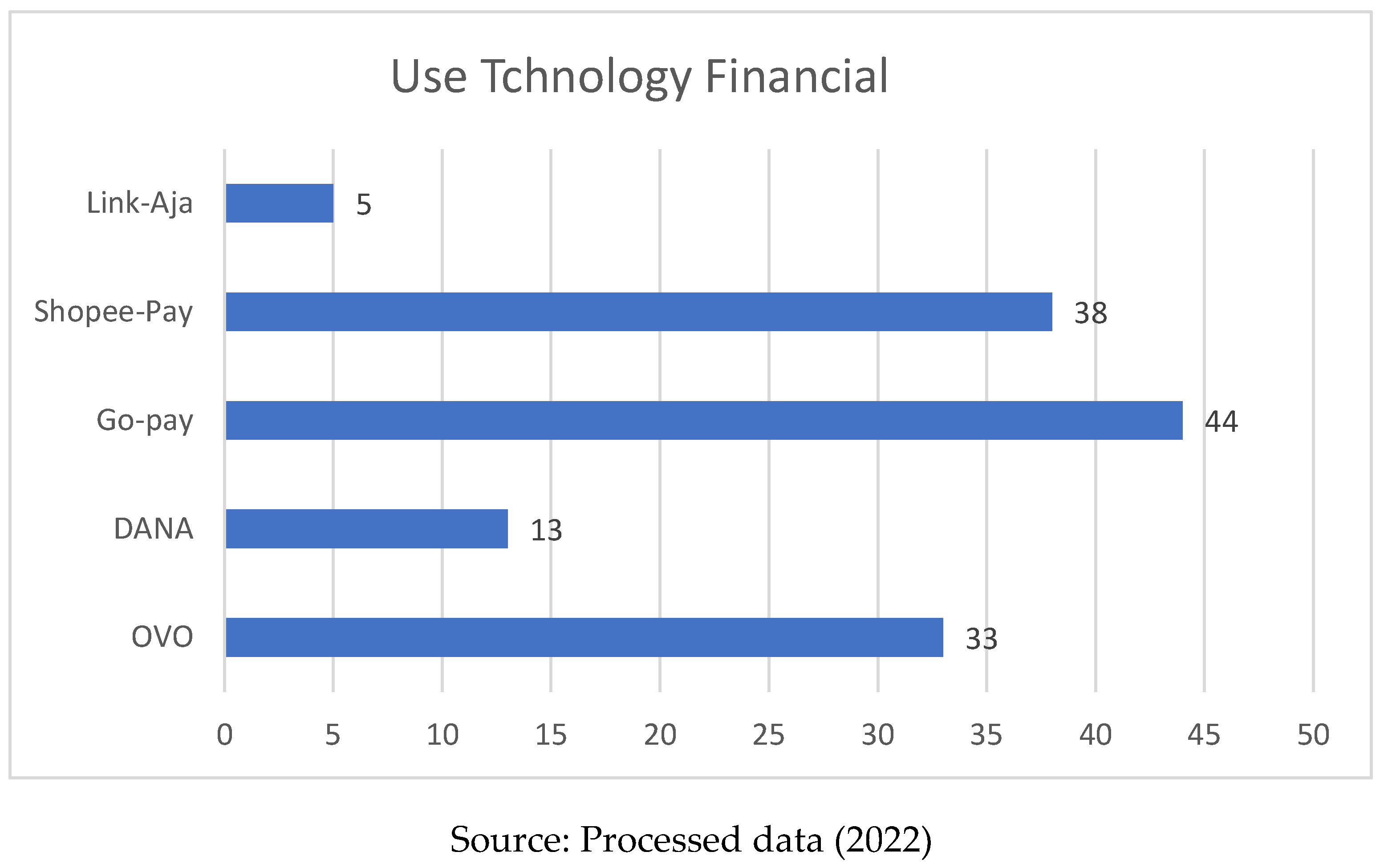
From
Figure 2, it can be seen that the majority of respondents use Go-pay with 44 then Sopee-Pay 38, OVO 33, DANA 13, and Link-Aja 5.
Characteristic data based on time of financial technology users
Figure 3.
Time-based characteristics of financial technology users.
Figure 3.
Time-based characteristics of financial technology users.
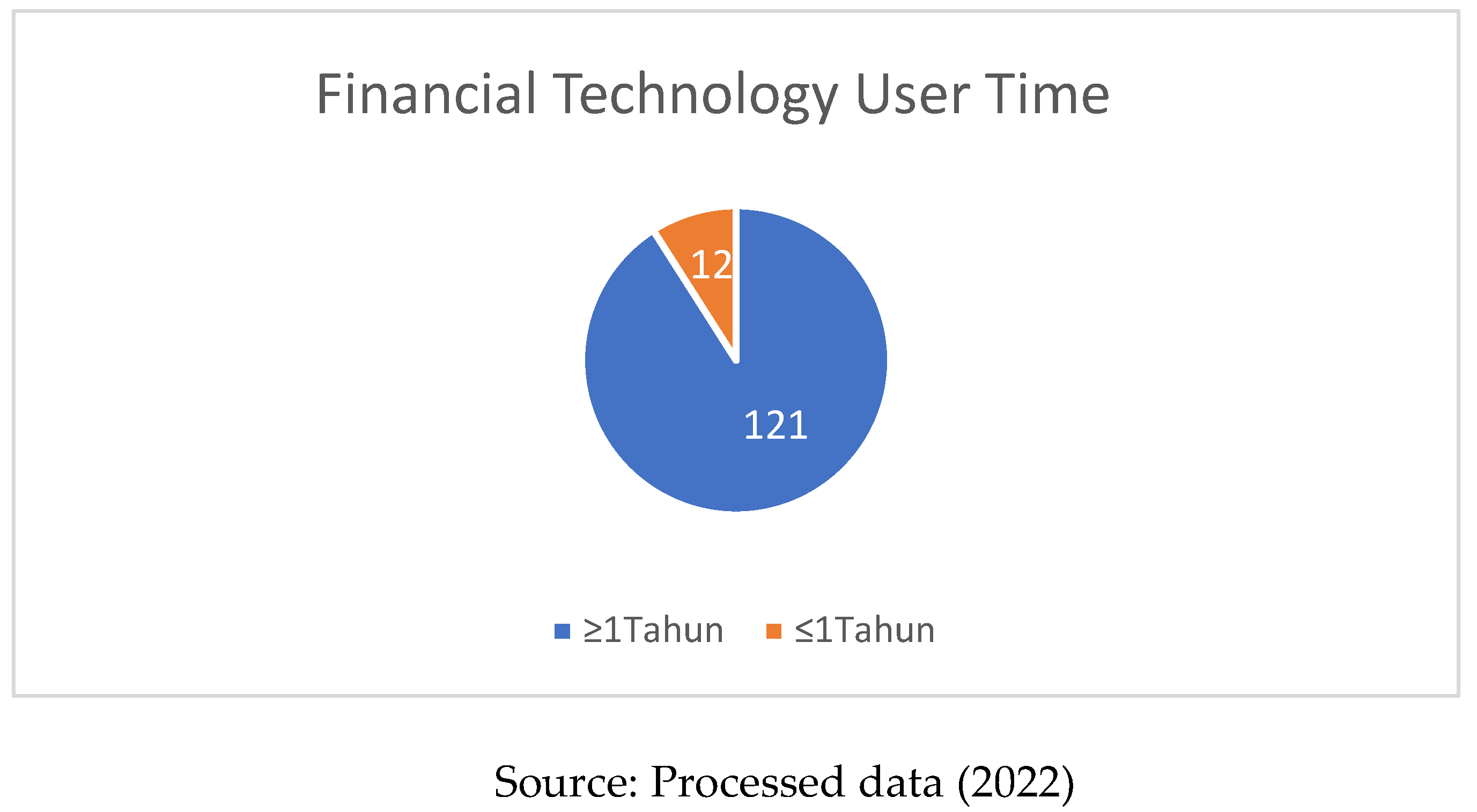
From
Table 3, it can be seen that out of 133 respondents dominated by active users for more than 1 year which amounted to a total of 121 with a percentage value of 91%, and the remaining less than 1 year amounted to 12 with a percentage value of 9%.
- A.
Data Testing Analysis
Based on the results of
Table 4, it can be concluded that there are 4 indicators of income, 4 indicators of transactions, 4 indicators of risk, 4 indicators of financial inclusion, and 5 indicators of financial technology There are 4 invalid indicators where the value of factor loading is less than 0.7. Therefore, 4 such indicators should be removed from the model. The following is the output of the loading factor value after the 4 invalid indicators are removed:
Based on
Table 5, it can be seen that outer loadings show indicators that have been modified from each variable, namely
Income,
Transactions, Risks,
Financial Inclusion, and Financial technology has an outer loadings value greater than 0.7. This suggests that the correlation between the research item/indicator score and the construct has a high reflective measure. So that the indicators in the study can be declared valid as a measure of their latent variables.
Table 5.
Modified Loading Factor Values.
Table 5.
Modified Loading Factor Values.
| Indicators |
Loading Factor |
Result |
| X1.1 |
0,827 |
Valid |
| X1.2 |
0,765 |
Valid |
| X1.3 |
0,773 |
Valid |
| X2.2 |
0,758 |
Valid |
| X2.3 |
0,733 |
Valid |
| X2.4 |
0,864 |
Valid |
| X3.1 |
0,905 |
Valid |
| X3.2 |
0,915 |
Valid |
| X3.3 |
0,836 |
Valid |
| X3.4 |
0,783 |
Valid |
| X4.2 |
0,823 |
Valid |
| X4.3 |
0,771 |
Valid |
| X4.4 |
0,720 |
Valid |
| Y.1 |
0,743 |
Valid |
| Y.2 |
0,760 |
Valid |
| Y.4 |
0,845 |
Valid |
| Y.5 |
0,749 |
Valid |
Table 6.
Cross-Loading Values.
Table 6.
Cross-Loading Values.
| No |
|
X1 |
X2 |
X3 |
X4 |
Y |
Result |
| 1. |
X1.1 |
0,827 |
0,499 |
0,020 |
0,300 |
0,467 |
valid |
| 2. |
X1.2 |
0,765 |
0.456 |
-0,215 |
0,355 |
0,413 |
valid |
| 3. |
X1.3 |
0,773 |
0,503 |
-0,005 |
0,403 |
0,463 |
valid |
| 4. |
X2.2 |
0,445 |
0,758 |
-0,070 |
0,351 |
0,405 |
valid |
| 5. |
X2.3 |
0,431 |
0,733 |
-0,005 |
0,403 |
0,399 |
valid |
| 6. |
X2.4 |
0,564 |
0,864 |
-0,219 |
0,591 |
0,584 |
valid |
| 7. |
X3.1 |
-0,165 |
-0,136 |
0,905 |
-0,245 |
-0,383 |
valid |
| 8. |
X3.2 |
-0,049 |
-0,176 |
0,915 |
-0,219 |
-0,373 |
valid |
| 9. |
X3.3 |
0,027 |
-0,006 |
0,836 |
-0,065 |
-0,205 |
valid |
| 10. |
X3.4 |
-0,024 |
-0,130 |
0,783 |
-0,072 |
-0,244 |
valid |
| 11. |
X4.2 |
0,431 |
0,461 |
-0,153 |
0,823 |
0,376 |
valid |
| 12. |
X4.3 |
0,299 |
0,482 |
-0,266 |
0,771 |
0,403 |
valid |
| 13. |
X4.4 |
0,339 |
0,406 |
0,037 |
0,720 |
0,239 |
valid |
| 14. |
Y.1 |
0,393 |
0,423 |
-0,256 |
0,331 |
0,743 |
valid |
| 15. |
Y.2 |
0,491 |
0,500 |
-0,178 |
0,240 |
0,760 |
valid |
| 16. |
Y.4 |
0,484 |
0,551 |
-0,258 |
0,358 |
0,845 |
valid |
| 17. |
Y.5 |
0,394 |
0.388 |
-0,444 |
0,478 |
0,749 |
valid |
Based on Table 3.6, it can be seen that each indicator has a cross-loading greater than 0.7 compared to the cross-loading value in other latent variables. So it can be concluded that the indicators on each construct are declared valid.
Table 7.
Composite Reliability.
Table 7.
Composite Reliability.
| |
Cronbach's Alpha |
Composite Reliability |
| X1 (Revenue) |
0.696 |
0.832 |
| X2 (Transaction) |
0.696 |
0.829 |
| X3 (Risk) |
0.886 |
0.920 |
| X4 (Financial Inclusion) |
0.672 |
0.816 |
| Y (Financial Technology) |
0.778 |
0.858 |
Based on Table 3.7, it can be concluded that the results of the Composite Reliability test are above 0.7 for each variable and the value of Cronbach's alpha is above 0.6. Thus the measurement items on each variable are declared reliable.
- B.
Hypothesis Testing
From the results of these data, it can be interpreted that Revenue (X1), Transactions (X2), Risk (X3) has a significant effect Financial Technology (Y), but Financial Inclusion (X4) does not affect Financial Technology (Y). with a positive relation
Discussion
From
Table 8, it can be seen that the test results in this study show that income has a significant and positive effect on financial technology. The results of this study are in line with the research (Nasution, 2021) which concluded that income has a significant effect on financial technology, this is because the higher the income level of users of financial technology services, the more interest in using financial technology services.
This is evidenced by the respondent's responses to the income variable in the indicator Income increases during the promotion through discount vouchers on financial technology services, this shows that when income increases, it is accompanied by dependence on the existing promotional service system on financial technology such as providing discount coupons at discounted prices on payment systems, it will increase the interest of financial technology users and become more consumptive but this research is inversely proportional to research (Husna & Novita, 2021) which states that income does not affect financial technology.
When management adopts technology for business purposes, the manager must first conduct a financial analysis to determine whether the cost of the technology to be used will provide an increase in revenue. By breaking down the process into its component parts, a manager can determine which system to implement at a particular stage with the aim of providing the greatest revenue benefit for a particular company. If the financial calculations are favorable, management must then consider the benefits to employees and customers and must also consider employee and customer perceptions of the utility and ease of use of the technology. Without these elements, the technology faces dim prospects, no matter what the prospective financial benefits. (Kimes, S. E. , 2008)
- 2.
The Effect of Transactions on Financial Technology.
From
Table 8, it can be seen that the test results in this study show that transactions have a significant and positive effect on financial technology. The results of this study are in line with research (Melati Kusuma, 2021) stating that transactions have a significant positive effect, this shows that when digital transactions increase for business actors, it will affect the use of financial technology services where they are helped when to transact online.
The advent of sophisticated personal computer devices, tablets and mobile phones has become a major influence on the lives of customers in conducting transactions. This has a linear impact on the global market and the development of the economic system. The competence to design and produce good mobile applications has increased, due to the demand for market transactions, so the development of information technology will automatically adjust to this condition. The financial market has many new transaction technologies being launched every day, but most cannot succeed or survive. Blockchain has been in the global market for more than ten years and is seriously attacking the financial market and threatening the future of traditional businesses. (Albayati, H., et al., 2020)
This is evidenced by respondents' responses to transaction variables in the Convenience indicator in transacting with several eCommerce using financial technology e-swallow services. There is a need for banking regulators to remove FinTech regulation from traditional regulatory functions. In addition, I recommend a new FinTech dynamic regulatory approach and where possible an international comparison of various FinTech regulatory regimes is needed and examine FinTech laws and regulations to investigate a dynamic model of FinTech regulation that can be used by society at large.
This proves that when users feel comfortable when transacting money non-cash, it will have an influence on interest in using financial technology services and have a consumptive impact on positive dependence and reduce the crime of cash transactions, but this research is inversely proportional to research (Gora, 2020) stating that witnessing has no effect on financial technology in this study explains that the service system on financial technology that is not understood by the public will make people not consumptive in using financial technology services.
- 3.
The Effect of Risk on Financial Technology.
From
Table 8, it can be seen that the test results in this study show that risk has a significant effect on financial technology. The results of this study are in line with the research (Fernando, 2019) with the results of research risk has a significant effect on financial technology because of the risks that exist in financial technology services such as the risk of
cybercrime risk of laundering funds, and acts of terrorism that have an impact on the concerns and psychology of users who can influence the interest in using these financial technology services.
The risk to financial technology is that legacy IT systems may not be sufficiently adaptable, or any changes to the bank's management of the innovation may not be readily made by IT. Greater use of third parties to address this, either through outsourcing or other fintech partnerships. This will increase risks around data security, privacy, money laundering and customer protection. At a system-wide level, the rise of technology in finance may lead to more interdependent technologies among market participants and fintech partners. which may ultimately cause information technology risk events to escalate into systemic crises. Regardless of which financial technology scenario is used, cyber risks will remain a threat to the use of information technology. New technologies and business models can increase cyber risk if controls do not keep pace with changes. (Hernández de Cos, P. 2019)
The implementation of new technologies is complex and expensive, the failure of many information technology implementations costs millions of dollars, increasing the need for good forecasting of market needs. However, low adoption or implementation of IT has become a major problem for many organizations when it comes to accessing tangible or intangible benefits. (Albayati, H., et al., 2020)
This is evidenced by respondents' responses to risk variables in the indicator The existence of a risk of the functioning of a product in financial technology E-wallet services and the existence of fraud risks in financial technology e-swallows, shows that the risk of functioning in a financial technology service that provides concern for users and the risk of fraud that causes users to feel worried and affects the interest of financial technology users, However, this research is inversely proportional to research (Melisa, 2021) showing that risk does not affect financial technology, indicating that risk does not affect financial technology, which means that the risks that exist in financial technology do not affect the interest in using financial technology.
- 4.
The effect of financial inclusion on financial technology.
From
Table 8, it can be seen that the test results in this study show that financial inclusion has no effect on financial technology. The results of this study are in line with the research (Joesoef, 2020) with the results of research that states that financial inclusion does not affect financial technology, this is because the lack of public literacy towards financial technology financial inclusion causes public interest in using financial technology services.
The goal of financial inclusion prevents the poor and disadvantaged from easily accessing the formal financial system, The unbanked and underbanked use alternative channels to fulfill their financial needs, yet they remain overcharged. The inability of banks to respond to the needs of the unbanked due to government regulations and legacy IT systems, and the inherent organizational friction has created opportunities for Fintech companies. Widespread adoption of mobile phones, advances in technology infrastructure, availability of big data, financial education and technology education have increased financial innovation and financial deepening. (Agarwal, S., et al., 2020)
This is evidenced by respondents' responses to financial inclusion variables in the indicator Access to financial services at affordable costs when using financial technology e-wallet services, Financial inclusion means that individuals and businesses can access financial products and services such as transactions, payments, savings, credit and insurance at affordable costs for service users financial technology and encouraging the interest of users of financial technology services, but this research is inversely proportional to research (Hermawan, 2022) shows that financial inclusion has a significant effect on financial technology, where in his research states that the higher the level of financial inclusion or access to financial services in financial technology will affect the interest in using financial technology services aforementioned.
Conclusion
The presence of financial technology is inevitable, the presence of new technology will always attract attention to the general public including SMEs so that all people want to use it immediately without seeing the problems and risks posed. Based on the results of the analysis and theoretical review, it shows that financial technology users feel the benefits when using it can improve sales performance and affect their income. In addition, transactions have a positive and significant effect on financial technology, every transaction in financial technology makes it easier, safer and more convenient when transacting so that it has a positive impact on users. In addition to these benefits, risk has a significant effect on financial technology, this shows that the risks involved in financial technology services raise concerns about using financial technology. Meanwhile, financial inclusion has no effect on financial technology, this proves that financial services or access to services from financial technology cannot be maximally accepted by users due to limited access or services from financial technology.
Limitations
The limitation of this study is that this type of research is only carried out on the direct relationship between free variables and bound variables. There is no discussion of the possibility of a variable between the mediational variable in the study. The emergence of mediation variables in the study will provide several alternative paths that can be used to make policy
Implementation of research results
Through the results of the research, it will make a great contribution to SMEs, especially because they can understand how much can provide benefits when they use financial technology in their financial transactions. In addition, it will also understand the risks that may be caused by the technology.
References
- Agarwal, S., Qian, W., & Tan, R. (2020). Financial inclusion and financial technology. In Household finance (pp. 307-346). Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
- Agustina, T. S. (2021). The behavior of using the Gojek and Grab applications among women culinary merchants in the city of Surabaya during the Covid-19 pandemic. Proceedings of the National Seminar & Call for Paper, 8(1), 21–42.
- Albayati, H., Kim, S. K., & Rho, J. J. (2020). Accepting financial transactions using blockchain technology and cryptocurrency: A customer perspective approach. Technology in Society, 62, 101320. [CrossRef]
- Ariningsih. (2022). Intention to Use E-wallet Viewed from Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, Perceived Security, and Trust. Maksipreneur: Management, Cooperatives, and Entrepreneurship, 11 No. 2(2), 227–238.
- Beg Sana, M. S. (2018). Emerging Role of E-Wallets in Increasing Financial Inclusion in India. GYAN MANAGEMENT, 12(2), 49–56. Https://Www.Researchgate.Net/Profile/Mohd_Shafeeq/Publication/337290752_EMERGING_ROLE_OF_EWALLETS_IN_INCREASING_FINANCIAL_INCLUSION_IN_INDIA/Links/5dcf1d0a4585156b35164316/EMERGING-ROLE-OF-E-WALLETS-IN-INCREASING-FINANCIAL-INCLUSION-IN-INDIA.
- Erni Awanti. (2018). Analysis of the Effect of Financial Inclusion on Financial System Stability in Developing Countries in Southeast Asia. Journal of Applied Economics, 2(2), 99–121. [CrossRef]
- Fernando, E. (2019). The Influence of Perceived Risk and Trust in Adoption of FinTech Services in Indonesia. 13(1), 31–37.
- George Mutiso. (2021). Mobile G aaPayment and Mobile Money Transfer on Performance of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises in Kenya. International Journal of Research Publications, 84(1), 23–46. [CrossRef]
- Ghozali, I. (2013). Multivariate Analysis with the SPSS program. Diponegoro University.
- Gora, R. (2020). The Effect of Diffusion of Fintech Information through Social Media on Changes in Payment Transaction Patterns among Young People in Jakarta. International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding, 7(9), 81–92. [CrossRef]
- Hermawan. (2022). Intention to Use Digital Finance MSMEs: The Impact of Financial Literacy and Financial Inclusion. Scientific Journal of Accounting and Business, 17(1), 171–182. [CrossRef]
- Husna, N., & Novita. (2021). Income and Net Profit of Culinary MSMEs in Bandar Lampung Before and After Using Fintech Payments. Journal of Management and Business (Performance), 18(1), 14–18.
- Hernández de Cos, P. (2019). Financial technology: the 150-year revolution, Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, Bank For International Settlement.
- Irman, M. (2021). Increasing Financial Inclusion Through Financial Literacy And Financial Technology On MSMEs. International Journal of Economics Development Research (IJEDR), 2(2), 126–141. [CrossRef]
- Joesoef, H. (2020). The Impact Of Financial Technology Towards Financial Inclusion Development In Some S In West Java, Indonesia. 17(7), 6595–6608.
- Kartika Sari. (2020). Analysis of the Effect of Ovo and Gopay Fintech Acceptance on Interest in Using Kartika Fintech. Business Management, 1(1), 1–12.
- Krisnawati, M. (2021). The Effect of Consumer Trust and Perceived Risk on e-Wallet Adoption: Consideration for Technology Startup Entrepreneurs. Journal of Entrepreneurship and Entrepreneurship, 10(2), 101–108. [CrossRef]
- Kurnianingsih, H. (2022). The effect of Easy Perception, Benefit Perception, Trust, Experience, and Risk on the Decision to Use E-Wallet. International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Curren, 4(2), 58–64.
- Kurniasari, F., & Adyni, N. (2021). The Effect of Literacy and Self-Efficacy on Financial Inclusion on the Use of Shopee Pay Digital Payment Services in Jabodetabek. drama (Development Research of Management): Journal of Management, 16(1), 128–140.
- Kusuma. (2020a). The Effect Of Financial Literacy On Financial Inclusion On Financial Technology On MSMEs In Bandar Lampung. Economics And Business, 4 No.5, 247–252.
- Kusuma, P. O. (2020b). Mobile payment transaction on MSMEs. International Research Journal of Management, IT and Social Sciences, 7(3), 104–109. [CrossRef]
- Kireyeva, A. A., Kredina, A., Vasa, L., & Satpayeva, Z. T. (2021). Impact of financial technologies on economic development: Theories, methods and analysis. Journal of International Studies, 14(4), 286-303. [CrossRef]
- Kimes, S. E. (2008). The Role of Technology in Restaurant Revenue Management. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 49(3), 297–309. [CrossRef]
- Li, B., & Xu, Z. (2021). Insights into financial technology (FinTech): a bibliometric and visual study. Financial innovation, 7(1), 1-28. [CrossRef]
- Listiawati, R. (2021). QRIS Efficiency in Improving Digital Payment Transaction Services for Culinary Micro-Small and Medium Enterprises in Depok City. ... Conference on Global..., 3(2), 67–73. https://lib.stiekesatuan.ac.id/index.php/icogoia2021/article/view/974.
- Lucyanda, J. (2010). Technology Acceptance Model (Tam) And Theory Planned Behavior (TPB) testing. JRAK August, 2(1995), 1–14.
- Marias. (2020). The Effect of Risk and Transaction Effectiveness on Interest in Using Financial Technology. Journal of Office Administration, 8(2), 139–152.
- Melati Kusuma, S. (2021). Decision Making Analysis On The Use Of The Mobile Wallet As A Payment Transaction Tool (Case Study Of Diponegoro University Students, Semarang. Journal of Economics Development and Social Research, 1(1), 11–19.
- Melisa, K. (2021). The Effect Of Consumer Trust And Perceived Risk On E-Wallet Adoption: Consideration For Technology Startup Entrepreneurs. Insight Journal, 10, 111–118.
- Miswan, A. (2019). Development and Impact of Financial Technology (Fintech) on the Islamic Financial Industry in Central Java. Islamic Vehicles: Journal of Islamic Studies, 1.5 No.1(1), 31–45.
- Mulasiwi. (2020). Optimization of Technology (Fintech) to Increase Financial Literacy and Inclusion of Purwokerto Medium Enterprises. Performance, 27(1), 12. [CrossRef]
- Muliadi. (2021). Analysis of the Effect of Perceived Ease of Use on Behavior Intention through Perceived Usefulness as a Medium of Intervening in Ovo Digital Payment. Journal of Marketing Management, 15(1), 20–27. [CrossRef]
- Murti Wijayanti. (2022). International Journal of Education, Information Technology and Others ( IJEIT ). International Journal of Education, Information Technology and Others (IJEIT), 5(2), 389–399. [CrossRef]
- Nasution, E. Y. (2021). The Role of Financial Technology on Income in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). International Journal of Business Economics (IJBE), 3(1), 29–33. [CrossRef]
- Nurcholidah, L., & Harsono, M. (2021). Fintech Studies in the Concept of Behaviouristics. Journal of Socio-Humanities Science, 5(1), 66–71. [CrossRef]
- Pattinaja, H. C. (2021). Financial Technology Legal Regulation in Indonesia. Journal of Law and Business (Selisik), 7 No.2(7), 112–124. http://journal.univpancasila.ac.id/index.php/selisik/article/download/3045/1616.
- P. (2021). The Influence of Information Technology, Individual Performance, and Sales Volume on Increasing Profits in SMEs in Cilegon. JFBA: Journal of Financial and Behavioural..., 1(1), 51–62. http://jurnal.ut.ac.id/index.php/jfba/article/view/1859.
- Purnama, S. (2021). The Effect of Transaction Experience Using Digital Wallets on User Satisfaction in Millennial Generation. Aptisi Transactions on Management (ATM), 5(2), 161–168. [CrossRef]
- Quanmei, M. (2022). Analysis of the Relationship between Financial Technology Development and Income Distribution. Academic Journal of Humanities & Social..., 5(1), 39–47. [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati. (2020). The Effect of Perceived Benefits, Convenience And Security On E-Wallet Use Decisions. ECONBANK: Journal of Economics and Banking, 2(2), 157–168. [CrossRef]
- Rohmatun, N. (2020). E-wallet: a payment system with Hifzul Maal principles. Journal of Islamic Economics, 5(2), 52–66. [CrossRef]
- Sandu Siyoto, A. S. (2015). THE BASIS OF RESEARCH METHODOLOGY (Ayup (ed.); 1st ed.). Media Publishing Literacy.
- Setiobudi, A., & Wiradinata, T. (2018). The intention of SMEs in the adoption of financial technology in East Java. National Conference of Creative Industry, 2622, 5–6. [CrossRef]
- Shaliza Alwi, M. N. M. S. (2021). Fintech As Financial Inclusion: Factors Affecting Behavioral Intention To Accept Mobile E-Wallet During Covid-19 Outbreak. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education, 12(7), 2130–2141.
- Sugiyono. (2017). Quantitative, Qualitative, and R&D Research Methods. ALFABETA,CV. www.cvalfabeta.com.
- Shy, O. (2020). How currency denomination and the ATM affect the way we pay. Journal of Economics and Business, 111, 105908. [CrossRef]
- Tran Hung Son, N. T. L. & N. V. K. (2020). Mobile money, financial inclusion and digital payment: The case of Vietnam. International Journal of Financial Research, 11(1), 417–424. [CrossRef]
- Van Tuan. (2021). Effect of Perceived Risk, Perceived Value to Intention to Use Momo E-Wallet. Gyanshauryam, International Scientific Refereed Research Journal, 4(1), 50–60. [CrossRef]
- Vira Indah, P. (2021). The Effect of Financial Literacy and Financial Technology on MSME Profits. Advances in Engineering Research, 207(Issat), 608–613. [CrossRef]
- Wai Han Wong. (2019). A Study of Consumer Intention of Mobile Payment in Hong Kong, Based on Perceived Risk, Perceived Trust, Perceived Security and Technological Acceptance Model. Journal of Advanced Management Science, 7(2), 33–38. [CrossRef]
- Yamin, S. (2021). Statistical Data Ebook Series: SMARTPLS 3, AMOS & STATA (Easy & Practical) (Aly Rasyid (ed.); 1st ed.). PT Dewangga Energi Internasional.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).