Submitted:
09 March 2025
Posted:
11 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
This review systematically summarizes the novel preparation methods of cyclodextrin-based chromatographic stationary phases and their applications for chiral recognition in separation techniques such as capillary gas chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography. Aiming at the current situation that enantiomers of chiral compounds present significant differences at the pharmacological, pharmacodynamic and toxicological levels, the core value of chromatographic chiral separation technology in the field of drug discovery and development is emphasized. By analyzing the unique cavity structure and excellent stereoselective properties of cyclodextrins, the mechanism of its action as a chromatographic stationary phase was elaborated. Combined with the typical applications of different derivatized cyclodextrin stationary phases in drug analysis, environmental testing and biological samples, the value and potential of cyclodextrin stationary phases in stereoisomer separation are systematically demonstrated.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Chiral Resolution Mechanisms of Cyclodextrin Derivatives
2.1. Mechanism of Inclusion Complexation
2.2. Conformation-Induced Recognition Mechanism
2.3. Association Mechanism
2.4. Host-Guest Synergy Mechanism
2.5. Multimodal Interaction Mechanisms
3. Cyclodextrin-Derived Stationary Phases in Gas Chromatography
3.1. Cyclodextrin-Derived Stationary Phases
3.2. MOF/COF-Cyclodextrin Stationary Phases
3.3. Column Coupling Technology
4. Cyclodextrin-Derived Stationary Phases in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
4.1. Ether-Linked Cyclodextrin Derivative Stationary Phases
4.2. Aminocarbamate-Bonded Cyclodextrin-Derived Chiral Stationary Phases
4.3. Urea Bond Linkages Cyclodextrin Derivative Stationary Phases
4.4. Thioether-Bonded Cyclodextrin Derivative Stationary Phases
4.5. Bridged Cyclodextrin Derivative Stationary Phases
4.6. Cyclodextrin-Based Chiral Stationary Phases Utilizing Chiral Porous Materials
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, D.W.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, D.J.; Jung, H.S. Chiral Biomaterials: From Molecular Design to Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, K.; Dötterl, S.; Fuchs, R.; Navarro, D.; Machado, I.C.S.; Dobler, D.; Reiser, O.; Ayasse, M.; Milet-Pinheiro, P. Subtle Chemical Variations with Strong Ecological Significance: Stereoselective Responses of Male Orchid Bees to Stereoisomers of Carvone Epoxide. J. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 45, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucci, E.; Dal Bosco, C.; Antonelli, L.; Fanali, C.; Fanali, S.; Gentili, A.; Chankvetadze, B. Enantioselective high-performance liquid chromatographic separations to study occurrence and fate of chiral pesticides in soil, water, and agricultural products. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1685, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayala, V.; Kandula, J.S.; Radhakrishnanand, P. Advances and challenges in the pharmacokinetics and bioanalysis of chiral drugs. Chirality 2022, 34, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.B. Chiral Covalent Organic Framework Packed Nanochannel Membrane for Enantioseparation. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2022, 61, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, M.D.; Kendrick, J.; Leusen, F.J.J. Predicting the spontaneous chiral resolution by crystallization of a pair of flexible nitroxide radicals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 2899–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Suhail, M.; Asnin, L. Chiral separation of quinolones by liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 2863–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.D.; Yadav, G.D. Insight into microwave assisted immobilized <i>Candida antarctica</i> lipase B catalyzed kinetic resolution of RS-(±)-ketorolac. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.W.; Zhang, P.L.; Pan, C.Y.; Li, H.J. Equilibrium Studies on Enantioselective Extraction of Oxybutynin Enantiomers by Hydrophilic β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives. Aiche J. 2011, 57, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Long, Y.D.; Zhi, Y.G.; Xu, X.Y. Preparation and chromatographic evaluation of a chiral stationary phase based on carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin for high-performance liquid chromatography. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Li, H.; Quan, K.J.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.D.; Li, Z.G. Preparation and applications of cellulose-functionalized chiral stationary phases: A review. Talanta 2021, 225, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.Y.; Guo, L.Z.; Xie, F.Y.; Yao, B.X.; Zeng, Q.; Weng, W. Enantioseparation of Hydrobenzoin and Structurally Related Compounds on β-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Bonded Chiral Stationary Phases. Chromatographia 2011, 73, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; He, W.; Qin, X.Y.; Sun, X.L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.Y. Synthesis and Application of a Novel Single-Isomer Mono-6-Deoxy-6-((2<i>S</i>,3<i>S</i>)-(+)-2,3-<i>O</i>-Isopropylidene-1, 4Tetramethylenediamine)-β-Cyclodextrin as Chiral Selector in Capillary Electrophoresis. Chirality 2010, 22, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ong, T.T.; Ge, L.Y.; Tan, S.N.; Young, D.J.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Ng, S.C. Chiral capillary electrophoresis with cationic pyrrolidinium-β-cyclodextrin derivatives as chiral selectors. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvancz, Z.; Bodáné-Kendrovics, R.; Szente, L.; Maklári, D. Cyclodextrins as Dominant Chiral Selective Agents in the Capillary Separation Techniques. Period. Polytech.-Chem. Eng. 2021, 65, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapte, S.; Pore, Y. Inclusion complexes of cefuroxime axetil with β-cyclodextrin: Physicochemical characterization, molecular modeling and effect of L-arginine on complexation. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyee, Z.A.; Saim, N.; Said, M.; Illias, R.M.; Mustapha, W.A.W.; Hassan, O. Characterization of cyclodextrin complexes with turmeric oleoresin. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Z.; Zhou, J.; Tang, J.; Tang, W.H. Cyclodextrin clicked chiral stationary phases with functionalities-tuned enantioseparations in high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1406, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharaishvili, Q.; Jibuti, G.; Farkas, T.; Chankvetadze, B. Further proof to the utility of polysaccharide-based chiral selectors in combination with superficially porous silica particles as effective chiral stationary phases for separation of enantiomers in high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1467, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucerová, G.; Procházková, H.; Kalíková, K.; Tesarová, E. Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin as a chiral selector for separation of amino acids and dipeptides in chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1467, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Liu, F.P.; Mao, J.Y. The CGC enantiomer separation of 2-arylcarboxylic acid esters by using β-cyclodextrin derivatives as chiral stationary phases. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 912, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.L.; Wang, P.; Wen, X.L.; Guo, X.; Luo, L.D.; Yu, J.; Guo, X.J. Layer-by-layer self-assembly of gold nanoparticles/thiols β-cyclodextrin coating as the stationary phase for enhanced chiral differentiation in open tubular capillary electrochromatography. Talanta 2017, 167, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Yin, Q.H.; Cai, P.F.; Zhao, X.Y.; Pan, Y.J. Enhancement of visual chiral sensing <i>via</i> an anion-binding approach: Novel ionic liquids as the chiral selectors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 962, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Han, C.; Wang, S.S.; Bai, L.J.; Li, S.S.; Luo, J.G.; Kong, L.Y. Development of a high speed counter-current chromatography system with Cu(II)-chiral ionic liquid complexes and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as dual chiral selectors for enantioseparation of naringenin. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1471, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkowitz, K.B.; Pearl, G.; Coner, B.; Peterson, M.A. Explanation of where and how enantioselective binding takes place on permethylated beta-cyclodextrin, a chiral stationary phase used in gas chromatography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Armstrong, D.W. 4,6-Di-<i>O</i>-pentyl-3-<i>O</i>-trifluoroacetyl/propionyl cyclofructan stationary phases for gas chromatographic enantiomeric separations. Analyst 2011, 136, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.D.; Shi, X.Y. Capillary gas chromatographic properties of three new cyclodextrin derivatives with acyl groups in the 6-position of β-cyclodextrin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 498, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartsova, L.A.; Makarov, A.A.; Popova, A.M. Quantitative evaluation of interactions of organic compounds with 18-crown ethers and β-cyclodextrin as components of stationary phases for gas chromatography. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 62, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaise, T.; Cardinael, P.; Tisse, S.; Combret, J.C.; Bouillon, J.P. Indirect and direct approaches in the synthesis of a new mono-6-<i>O</i>-benzyl methylated γ-cyclodextrin as chiral selector for enantioselective gas chromatography. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry 2008, 19, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.Y.; Cui, J.; Yang, X.L.; Ling, Y. Capillary GC using pyridyl β-cyclodextrin stationary phase. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.; Matos, S.; da Silva, M.; Pereira, M.M.A. Cyclodextrin-Based Ionic Liquids as Enantioselective Stationary Phases in Gas Chromatography. ChemPlusChem 2013, 78, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.S. Metal organic framework membranes for separation applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2015, 8, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.Y.; Yang, C.X.; Chang, N.; Yan, X.P. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Analytical Chemistry: From Sample Collection to Chromatographic Separation. Accounts Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yuan, C.; Hou, B.; Liu, L.J.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Chiral covalent organic frameworks: design, synthesis and property. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6248–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozawa, T.; Jones, J.T.A.; Swamy, S.I.; Jiang, S.; Adams, D.J.; Shakespeare, S.; Clowes, R.; Bradshaw, D.; Hasell, T.; Chong, S.Y.; et al. Porous organic cages. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Xie, S.M.; Zi, M.; Yuan, L.M. Recent advances of application of porous molecular cages for enantioselective recognition and separation. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Ronson, T.K.; Zou, Y.Q.; Nitschke, J.R. Metal-organic cages for molecular separations. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.R.; Xie, S.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, L.; Nong, R.Y.; Yuan, L.M. Metal-Organic Framework Cd(LTP)<sub>2</sub> <i><sub>n</sub></i> for Improved Enantioseparations on a Chiral Cyclodextrin Stationary Phase in GC. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, W.; Hou, H.P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.K.; Geng, L.N.; Sun, L.Q.; Luo, A.Q. A β-cyclodextrin covalent organic framework used as a chiral stationary phase for chiral separation in gas chromatography. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, W.Q.; Huang, Z.F.; Lai, Y.L.; Fu, S.G.; Dong, J.Q.; Duan, A.H.; Hou, X.D.; Yuan, L.M.; Cui, Y. Cyclodextrin Incorporation into Covalent Organic Frameworks Enables Extensive Liquid and Gas Chromatographic Enantioseparations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.J.; Biba, M.; Gouker, J.R.; Kath, G.; Augustine, P.; Hosek, P. Solving multicomponent chiral separation challenges using a new SFC tandem column screening tool. Chirality 2007, 19, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Tymiak, A.A.; Zhang, Y.R. Optimization and Simulation of Tandem Column Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Separations Using Column Back Pressure as a Unique Parameter. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4033–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, Z.G.; Liu, Z.M.; Zhu, R.Z.; Zhang, F.M.; Liu, Z.H.; Si, X.X. Botanical discrimination and classification of <i>Mentha</i> plants applying two-chiral column tandem GC-MS analysis of eight menthol enantiomers. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Q.; Ong, T.T.; Ng, S.C. Synthesis of cationic β-cyclodextrin derivatives and their applications as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography and supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1203, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.T.; Wang, R.Q.; Muderawan, I.W.; Ng, S.C. Synthesis and application of mono-6-(3-methylimidazolium)-6-deoxyperphenylcarbamoyl-β-cyclodextrin chloride as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography and supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1182, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cheng, B.P.; Zhou, R.D.; Cao, Z.G.; Zeng, C.; Li, L.S. Preparation and evaluation of a novel <i>N</i>-benzyl-phenethylamino-β-cyclodextrin-bonded chiral stationary phase for HPLC. Talanta 2017, 174, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.S.; Chen, B.P.; Zhou, R.D.; Nie, G.Z. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Isatin Derivative of β-Cyclodextrin-bonded SBA-15 Stationary Phase for HPLC. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 42, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, Y.Z.; Cao, Z.G.; Zhang, T.C.; Li, L.S. Enantiomeric Separation of Chiral Triazole Pesticides by a <i>mono</i>-6-(4-Nitrophenyl)-ureido-β-cyclodextrin-Bonded Stationary Phase Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 2481–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liu, W.N.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.K.; Zheng, S.R.; Lin, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.G. Synthesis of a novel cyclodextrin-derived chiral stationary phase with multiple urea linkages and enantioseparation toward chiral osmabenzene complex. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1283, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Fan, J.; Liu, W.N.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, W.G. Comparative HPLC enantioseparation on substituted phenylcarbamoylated cyclodextrin chiral stationary phases and mobile phase effects. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 98, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.X.; Yang, X.M.; Guo, L.Z.; Kang, S.S.; Weng, W. Development of a Composite Chiral Stationary Phase from BSA and β-Cyclodextrin-Bonded Silica. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Z.M. Enantioseparation performance of novel benzimido-β-cyclodextrins derivatized by ionic liquids as chiral stationary phases. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 819, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhou, W.H.; Zhou, Z.M. Preparation of chiral oxazolinyl-functionalized β-cyclodextrin-bonded stationary phases and their enantioseparation performance in high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4136–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: Diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2001, 40, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
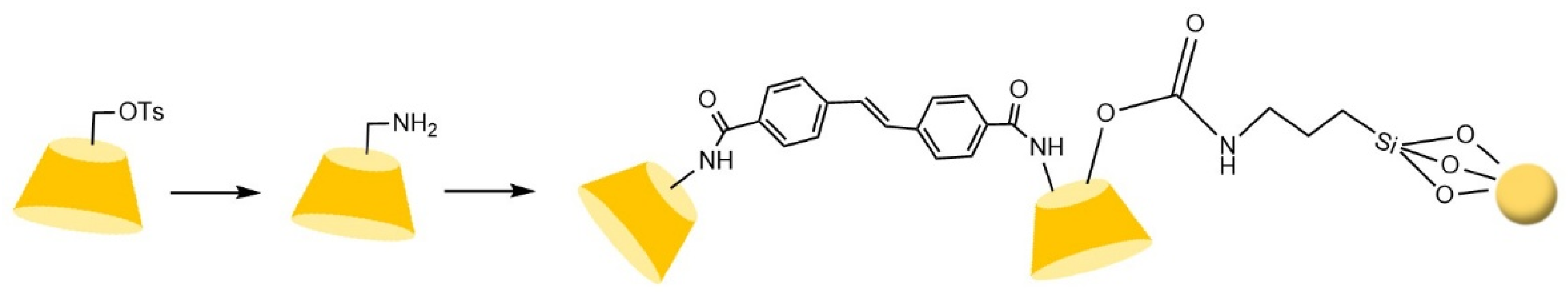
- Zhang, Y.P.; Guo, Z.M.; Ye, J.X.; Xu, Q.; Liang, X.M.; Lei, A.W. Preparation of novel β-cyclodextrin chiral stationary phase based on click chemistry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1191, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.M.; Jin, Y.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.F.; Xu, Q.; Liang, X.M.; Lei, A.W. Synthesis, chromatographic evaluation and hydrophilic interaction/reversed-phase mixed-mode behavior of a "Click β-cyclodextrin" stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Z.M.; Dai, L.; Zhou, W.H.; Wang, J.L. Synthesis and enantioseparation characteristics of a novel mono-6-deoxy-(2,4-dihydroxybenzimide)-β-cyclodextrin as a chiral stationary phase in high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2011, 86, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Zhou, Z.M.; Yuan, H.; Meng, Z.H. Preparation and chiral recognition of a novel chiral stationary phase for HPLC, based on mono(6<SUP>A</SUP>-<i>N</i>-1-(2-hydroxyl)-phenylethylimino-6<SUP>A</SUP >-deoxy)-β-cyclodextrin and covalently bonded silica gel. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2008, 19, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsburg, J.W.; Armstrong, D.W.; Péter, A.; Tóth, G. LC enantiomeric separation of unusual amino acids using cyclodextrin-based stationary phases. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2008, 31, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.Q.; He, L.F.; Beesley, T.E.; Trahanovsky, W.S.; Sun, P.; Wang, C.L.; Armstrong, D.W. Development of dinitrophenylated cyclodextrin derivatives for enhanced enantiomeric separations by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1115, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Q.; Ong, T.T.; Tang, W.H.; Ng, S.C. Cationic cyclodextrins chemically-bonded chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 718, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.H.; Tang, W.H.; Ng, S.C. Novel β-cyclodextrin chiral stationary phases with different length spacers for normal-phase high performance liquid chromatography enantioseparation. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3496–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Fan, J.; Liu, W.N.; Chen, X.D.; Ruan, L.J.; Zhang, W.G. A new single-urea-bound 3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamoylated β-cyclodextrin chiral stationary phase and its enhanced separation performance in normal-phase liquid chromatography. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
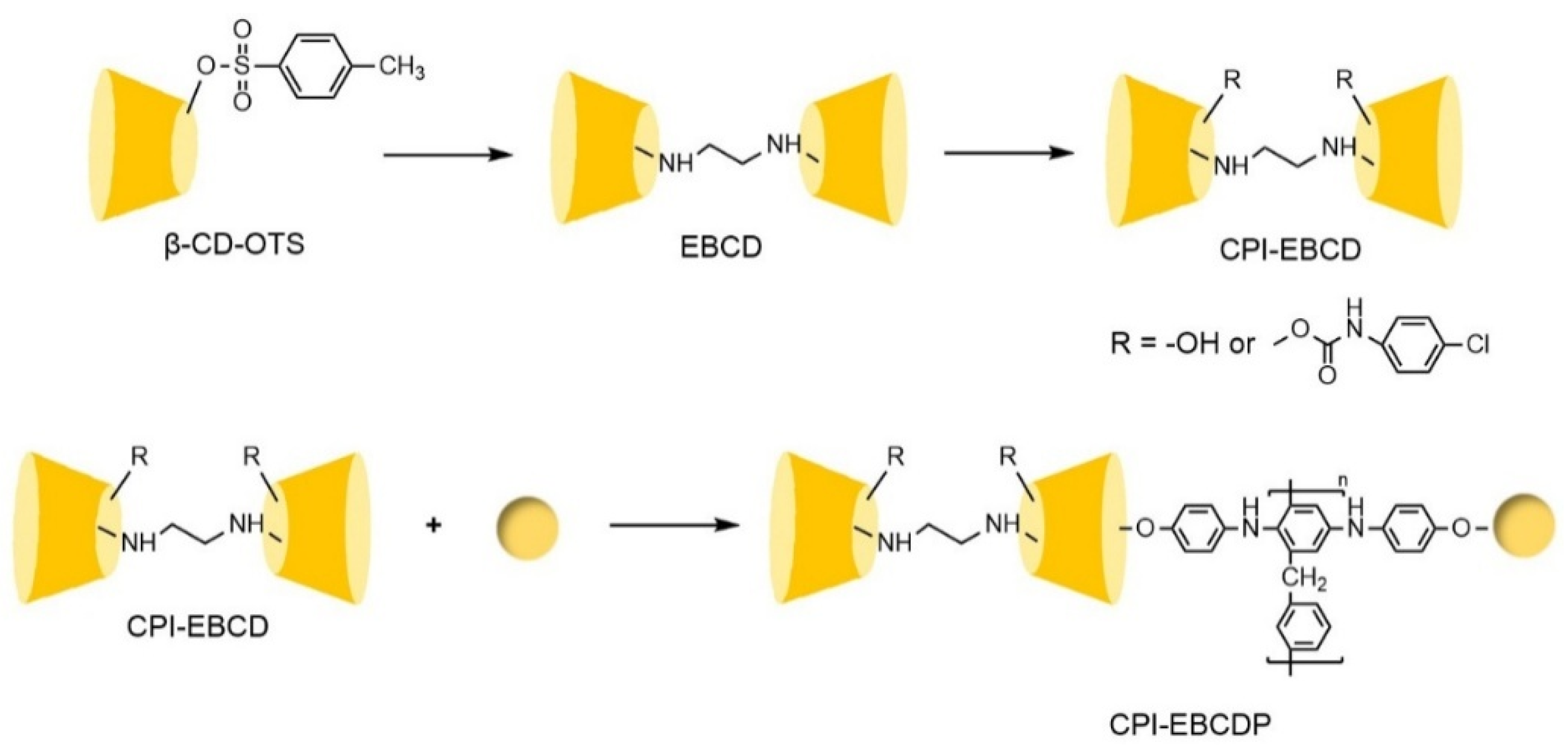
- Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, W.G.; Luo, W.J.; Fan, J. Preparation and enantioseparation characteristics of a novel chiral stationary phase based on mono (6<SUP>A</SUP>-azido-6<SUP>A</SUP>-deoxy)-per(<i>p</i>-chlorophenylcarba moylated) β-cyclodextrin. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1213, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Tan, D.; Chelvi, S.K.T.; Yong, E.L.; Lee, H.K.; Gong, Y.H. Preparation and application of rifamycin-capped (3-(2-O-β-cyclodextrin)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-propylsilyl-appended silica particles as chiral stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2010, 83, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Li, L.S.; Ng, S.C.; Tan, T.T.Y. Sub-1-micron mesoporous silica particles functionalized with cyclodextrin derivative for rapid enantioseparations on ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7502–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Wu, M.H.; Wu, R.A.; Done, J.; Ou, J.J.; Zou, H.F. Preparation of Perphenylcarbamoylated β-Cyclodextrin-silica Hybrid Monolithic Column with "One-Pot" Approach for Enantioseparation by Capillary Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3616–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, Y.F.; Muderawan, I.W.; Ng, S.C. Synthesis and application of mono-2<i><SUP>A</SUP></i>-azido-2<i><SUP>A</SUP></i>-deoxyperphenylcarba moylated β-cyclodextrin and mono-2<i><SUP>A</SUP></i>-azido-2<i><SUP>A</SUP></i>-deoxyperacetylated β-cyclodextrin as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1101, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faugeras, P.A.; Boëns, B.; Elchinger, P.H.; Brouillette, F.; Montplaisir, D.; Zerrouki, R.; Lucas, R. When Cyclodextrins Meet Click Chemistry. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 4087–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, B.D.; Viswanathan, K.; Miller, K.M.; Long, T.E. Michael addition reactions in macromolecular design for emerging technologies. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 487–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, C.N.; Kloxin, C.J. Toward an Enhanced Understanding and Implementation of Photopolymerization Reactions. Aiche J. 2008, 54, 2775–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.X.; Huo, F.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Yang, Y.T.; Lv, H.G.; Li, S.D. Thiol-addition reactions and their applications in thiol recognition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6032–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.Z.; Dou, A.; Shi, X.Z.; Li, H.; Shan, Y.H.; Lu, X.; Xu, G.W. Development and evaluation of new imidazolium-based zwitterionic stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1286, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
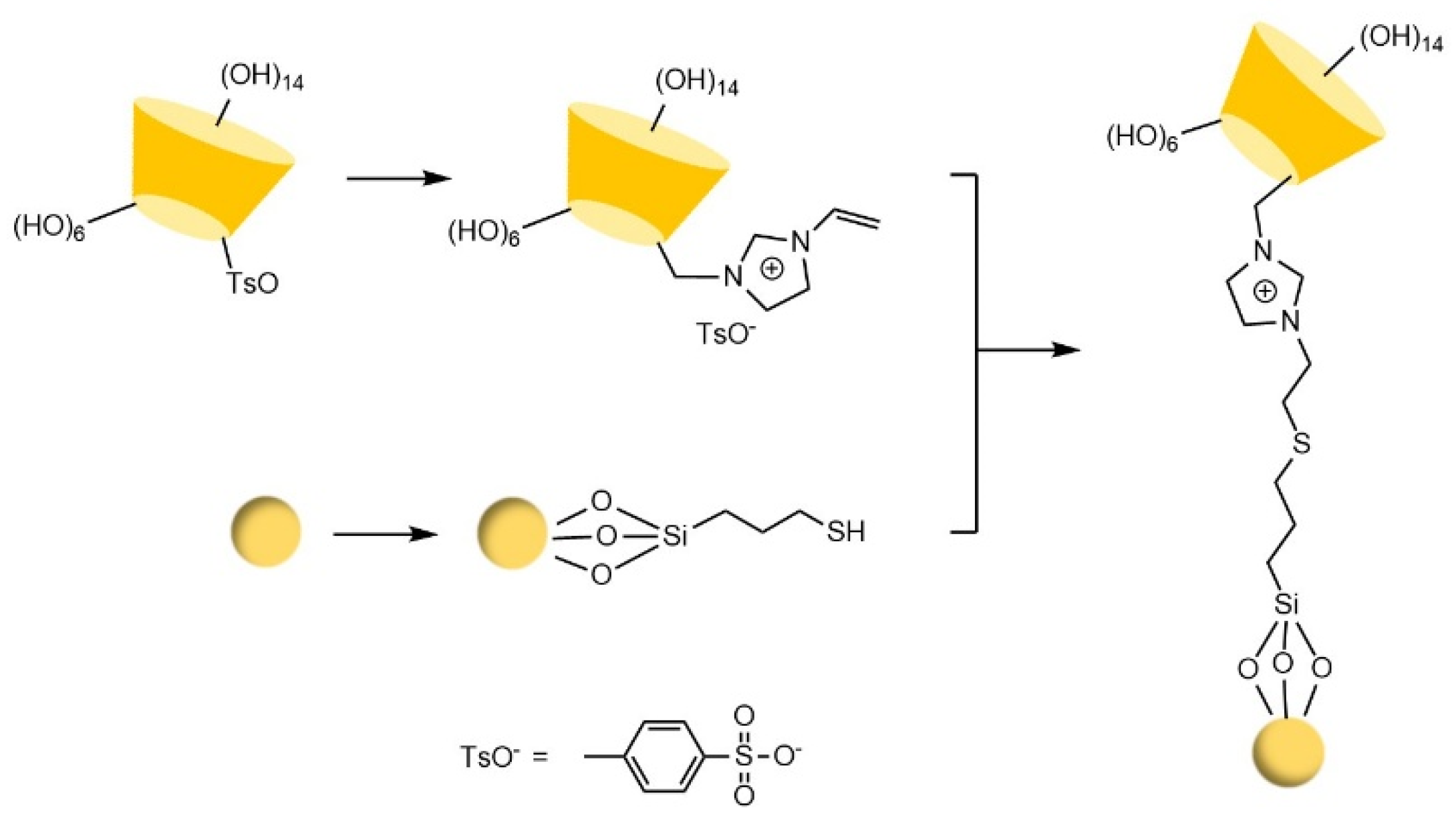
- Yao, X.B.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Wang, Y. Thiol-ene click chemistry derived cationic cyclodextrin chiral stationary phase and its enhanced separation performance in liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1326, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jin, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y. Click preparation and application of chiral stationary phase based on intrinsic recognition ability of cyclodextrin. Se pu = Chinese journal of chromatography 2020, 38, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
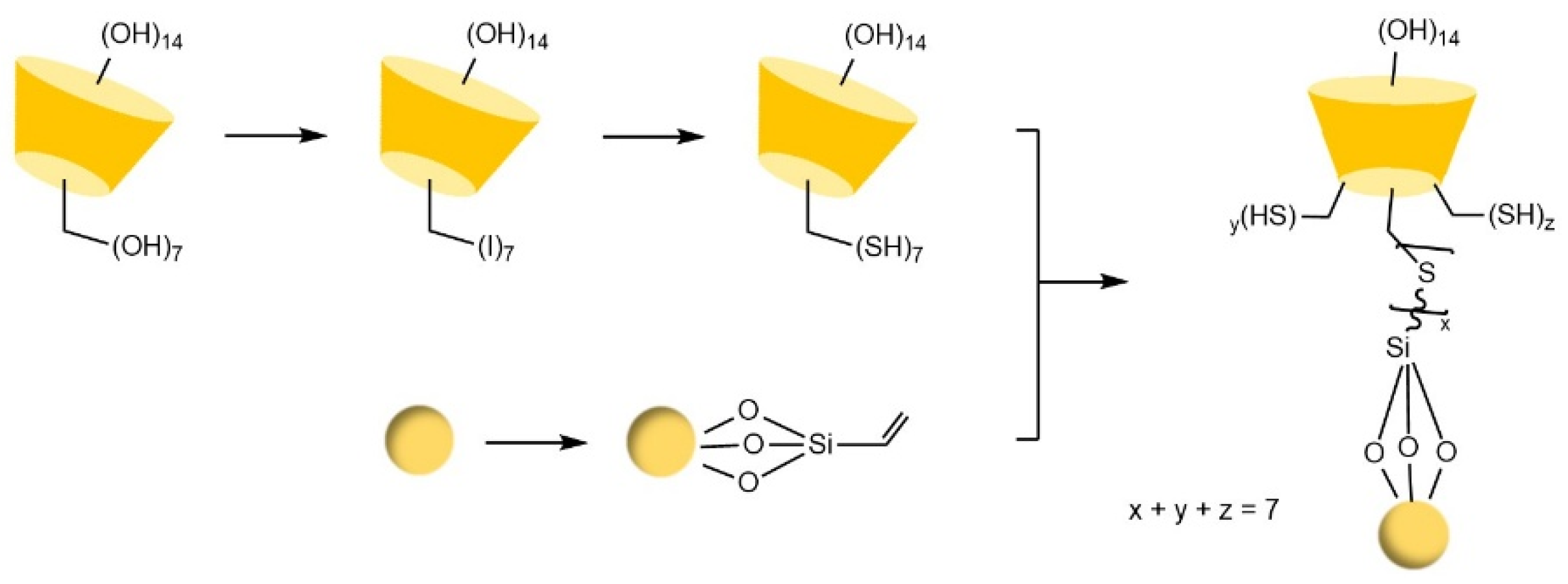
- Chen, M.; Lu, X.L.; Ma, X.F.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y. Click preparation of multiple-thioether bridged cyclodextrin chiral materials for efficient enantioseparation in high-performance liquid chromatography†. Analyst 2021, 146, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
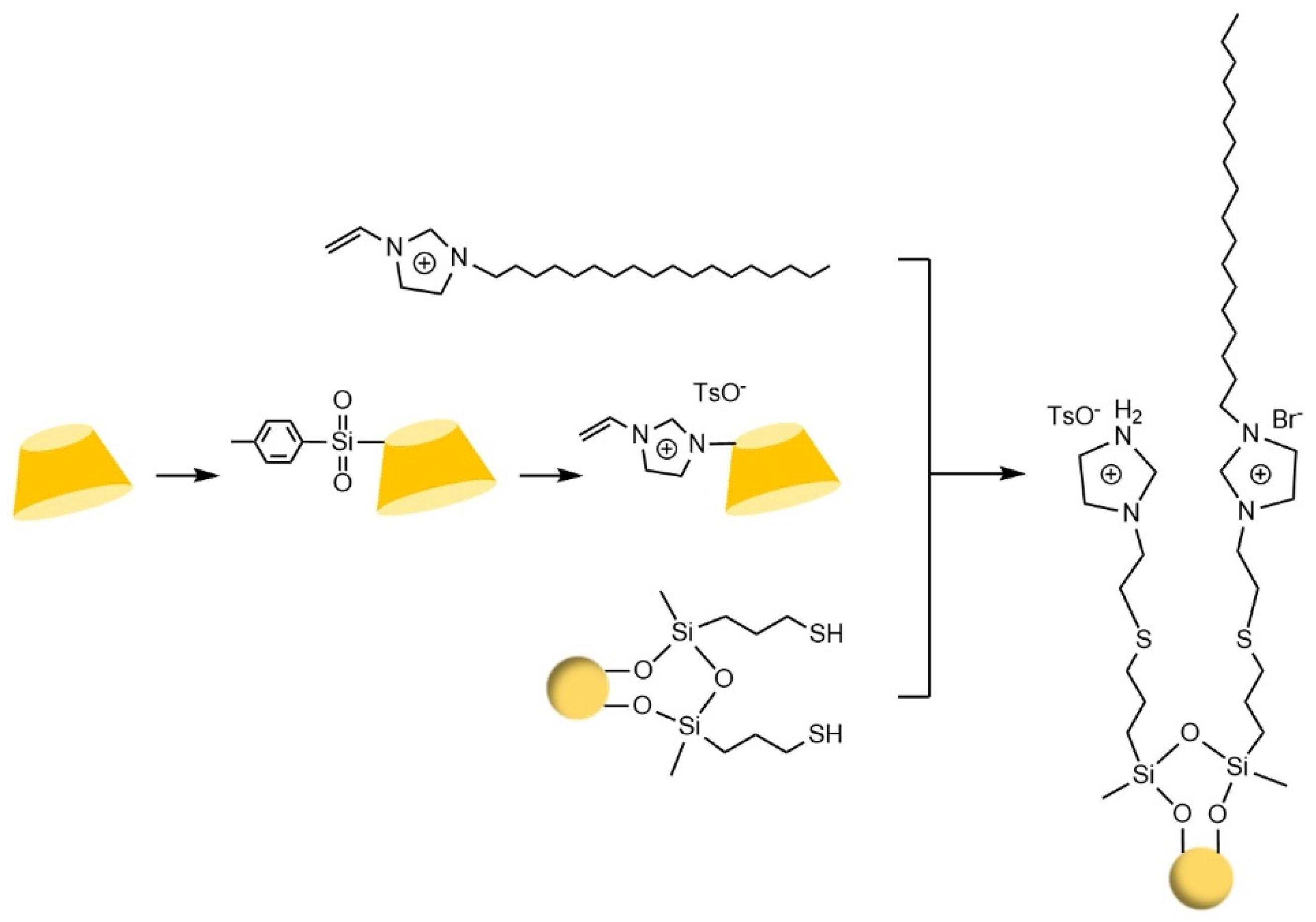
- Zhou, J.Q.; Ren, X.J.; Luo, Q.R.; Gao, D.; Fu, Q.F.; Zhou, D.; Zu, F.J.; Xia, Z.N.; Wang, L.J. Ionic liquid functionalized β-cyclodextrin and C18 mixed-mode stationary phase with achiral and chiral separation functions. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1634, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Pei, W.J.; Zheng, X.X.; Zhao, S.Z.; Zhang, Z.Z. Preparation and Enantioseparation Characteristics of a Novel β-Cyclodextrin Derivative Chiral Stationary Phase in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
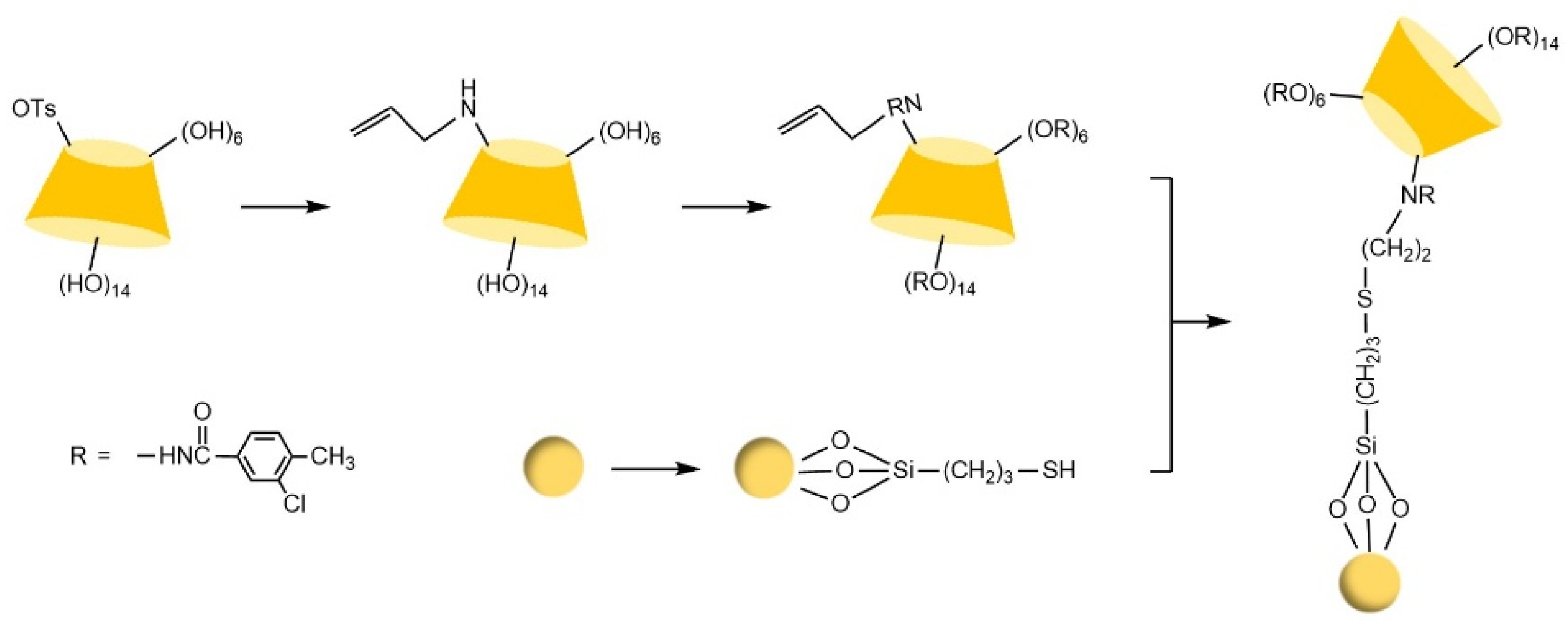
- Huang, G.; Ou, J.J.; Zhang, X.D.; Ji, Y.S.; Peng, X.J.; Zou, H.F. Synthesis of novel perphenylcarbamated β-cyclodextrin based chiral stationary phases via thiol-ene click chemistry. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2752–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.L.; Sun, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.N.; Ma, X.F. Surface-up click access to allylimidazolium bridged cyclodextrin dimer phase for efficient enantioseparation. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
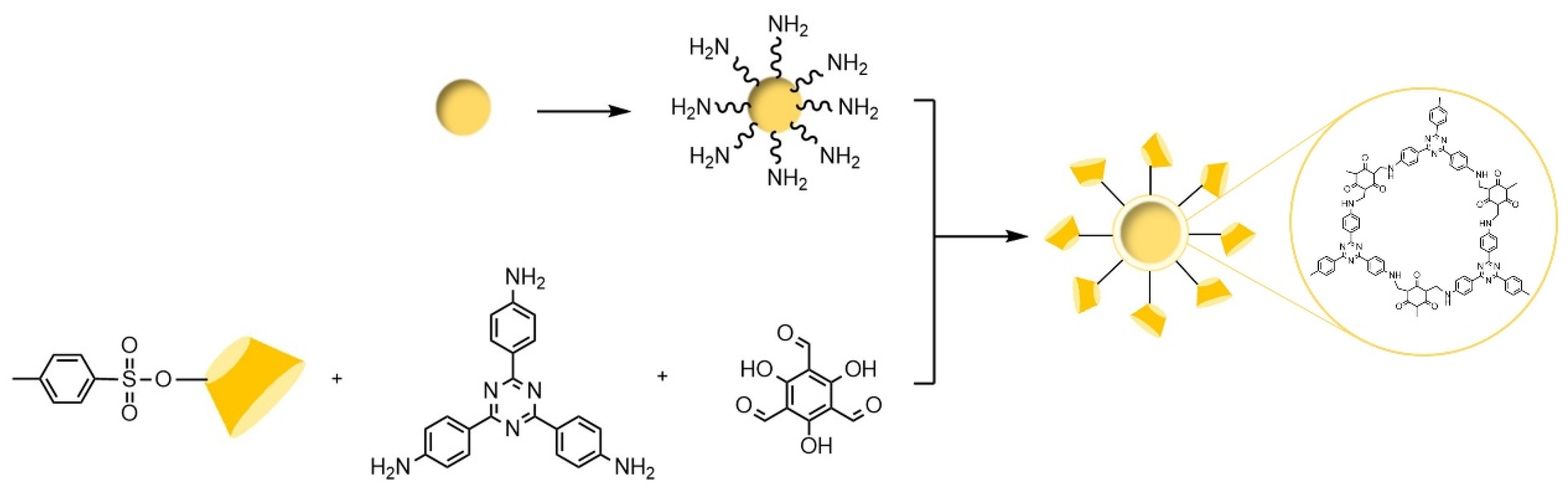
- Wan, M.J.; Zheng, Y.C.; Dai, X.M.; Yang, H.L.; Zhou, J.Q.; Ou, J.; Yang, Y.X.; Liao, M.F.; Xia, Z.N.; Wang, L.J. Click Chemistry for the Preparation of β-Cyclodextrin Grafting Uniform Spherical Covalent Organic Framework Materials for Chiral Separation. Chem. Mat. 2023, 35, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.L.; Huang, Z.Q.; Li, D.; Li, L.S. Preparation of a <i>bis</i>-triazolyl bridged β-cyclodextrin stationary phase and its application for enantioseparation of chiral compounds by HPLC. Chirality 2024, 36, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Shi, H.; Zhu, H.Y.; Huang, R.; Chi, C.M.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis of Novel Bis(β-cyclodextrin)s Linked with Glycol and Their Inclusion Complexation with Organic Dyes. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, S.D.P.; Yang, Z.W.; Leung, D.K.; Wilson, D.M.; Breslow, R. Cyclodextrin dimers as cleavable carriers of photodynamic sensitizers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 12488–12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y. Photocontrolled Reversible Conversion of Nanotube and Nanoparticle Mediated by -Cyclodextrin Dimers. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 9376–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Cooperative binding and multiple recognition by bridged bis(β-cyclodextrin)s with functional linkers. Accounts Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, Y.; Ding, F.; Chen, G.S. Binding behavior of aliphatic oligopeptides by bridged and metallobridged bis(β-cyclodextrin)s bearing an oxamido bis(2-benzoic) carboxyl linker. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.W.; Huskens, J. Photo-induced switchable binding behavior of bridged bis(<i>β</i>-cyclodextrin) with an azobenzene dicarboxylate linker. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 56, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, Y. Bridged bis(β-cyclodextrin)s-based polysaccharide nanoparticles for controlled paclitaxel delivery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 28593–28598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
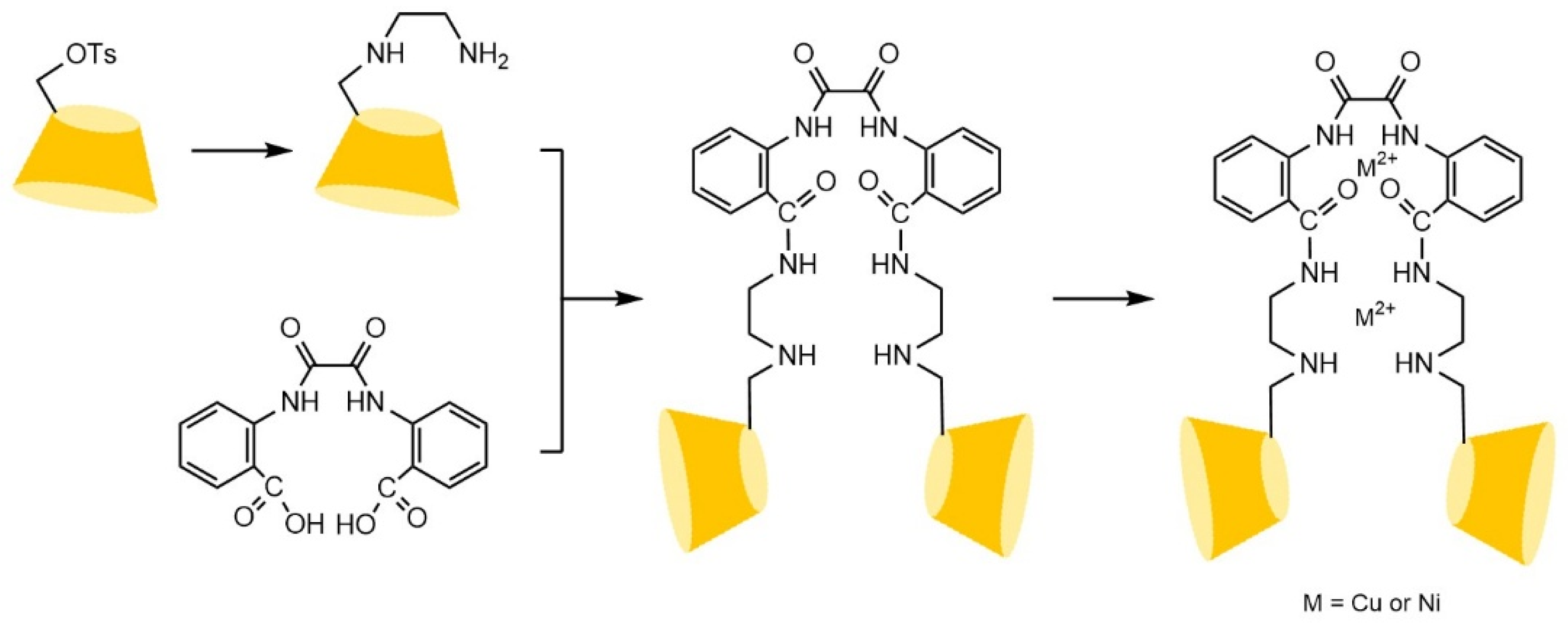
- Shuang, Y.Z.; Zhang, T.C.; Li, L.S. Preparation of a stilbene diamido-bridged bis(β-cyclodextrin)-bonded chiral stationary phase for enantioseparations of drugs and pesticides by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhao, X.R.; Shen, Y.Q.; Cong, H.L.; Yu, B. Short bridging and partial derivatization synergistically modified ll-cyclodextrin bonded chiral stationary phases for improved enantioseparation. Talanta 2024, 273, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.X.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Yan, X.P. γ-Cyclodextrin metal-organic framework for efficient separation of chiral aromatic alcohols. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36297–36301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Li, C.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, C.F.; Guo, T.; Zhang, J.W.; Sun, L.X. Cross-linked γ-cyclodextrin metal-organic framework-a new stationary phase for the separations of benzene series and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Wan, M.J.; Zhou, J.Q.; Dai, X.M.; Yang, H.L.; Xia, Z.N.; Wang, L.J. One-pot method for the synthesis of β-cyclodextrin and covalent organic framework functionalized chiral stationary phase with mixed-mode retention mechanism. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1662, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
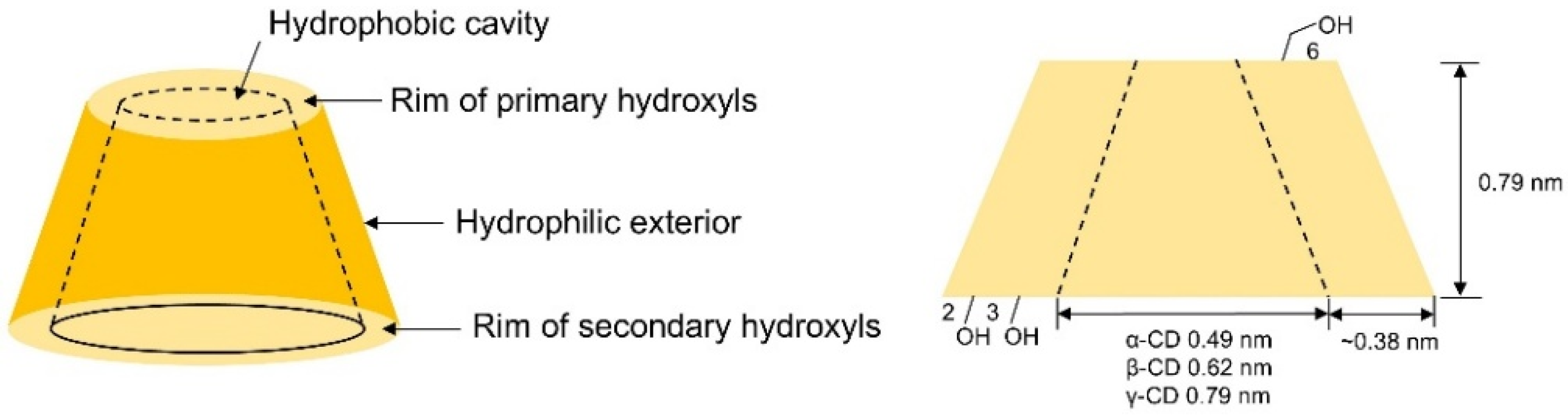
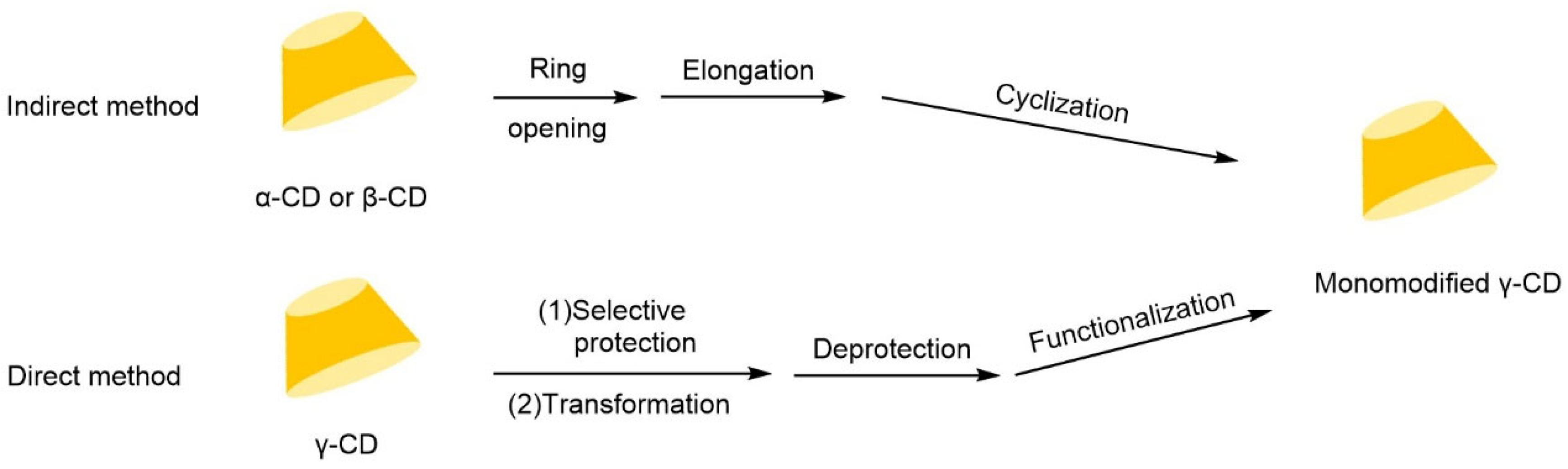
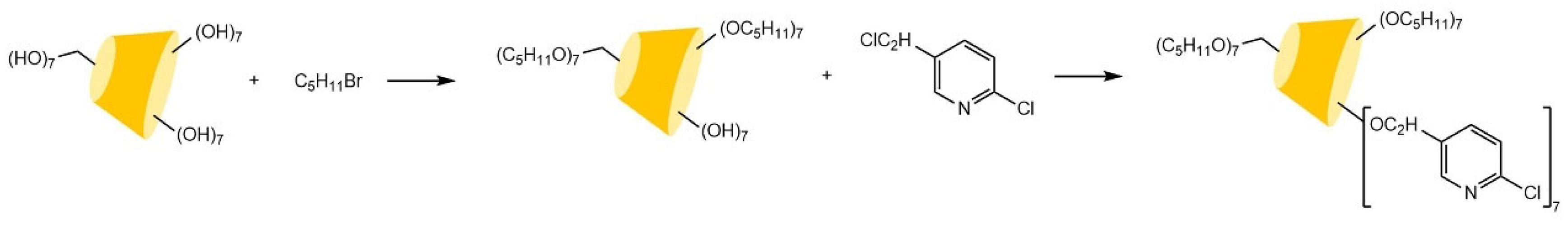
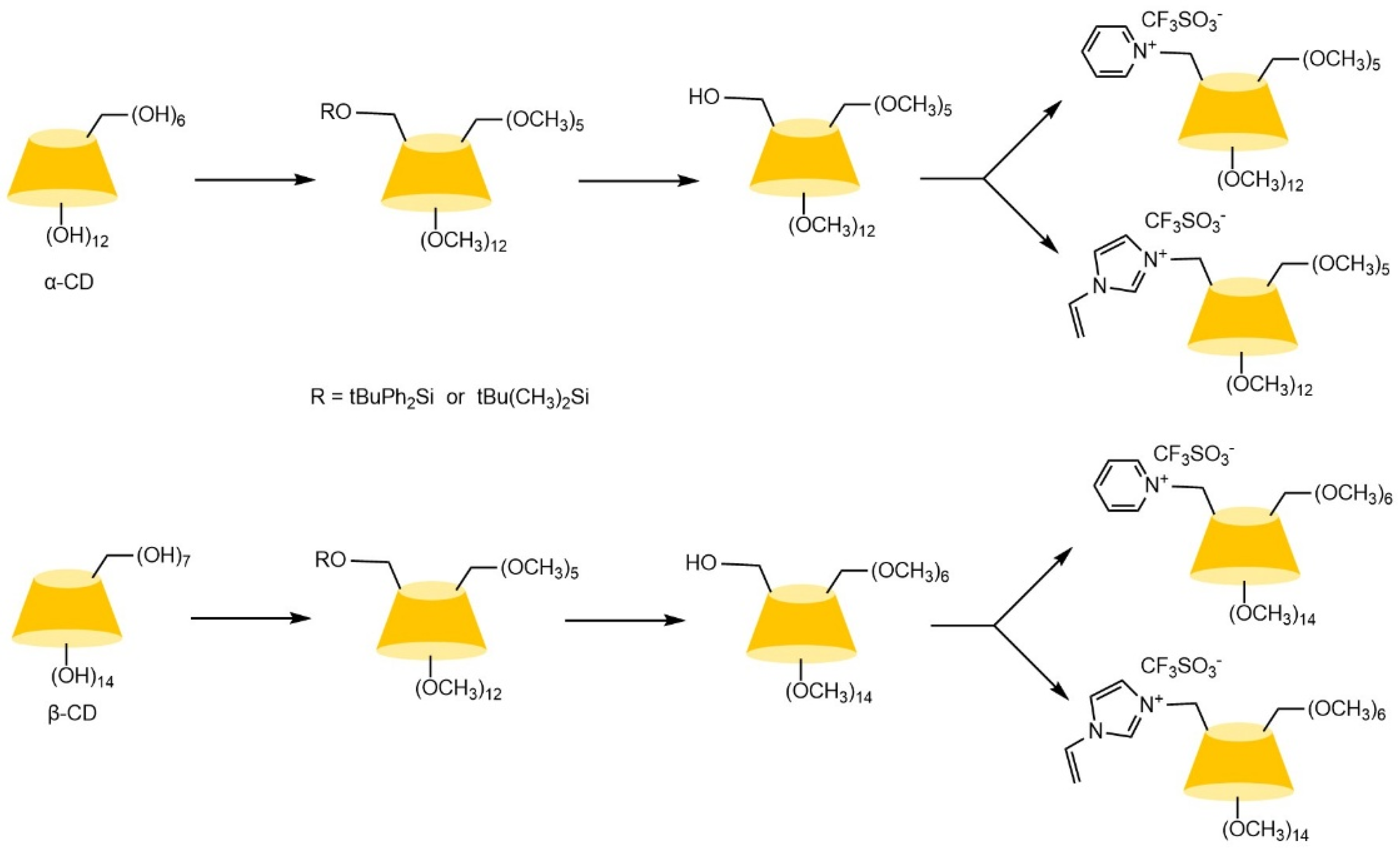
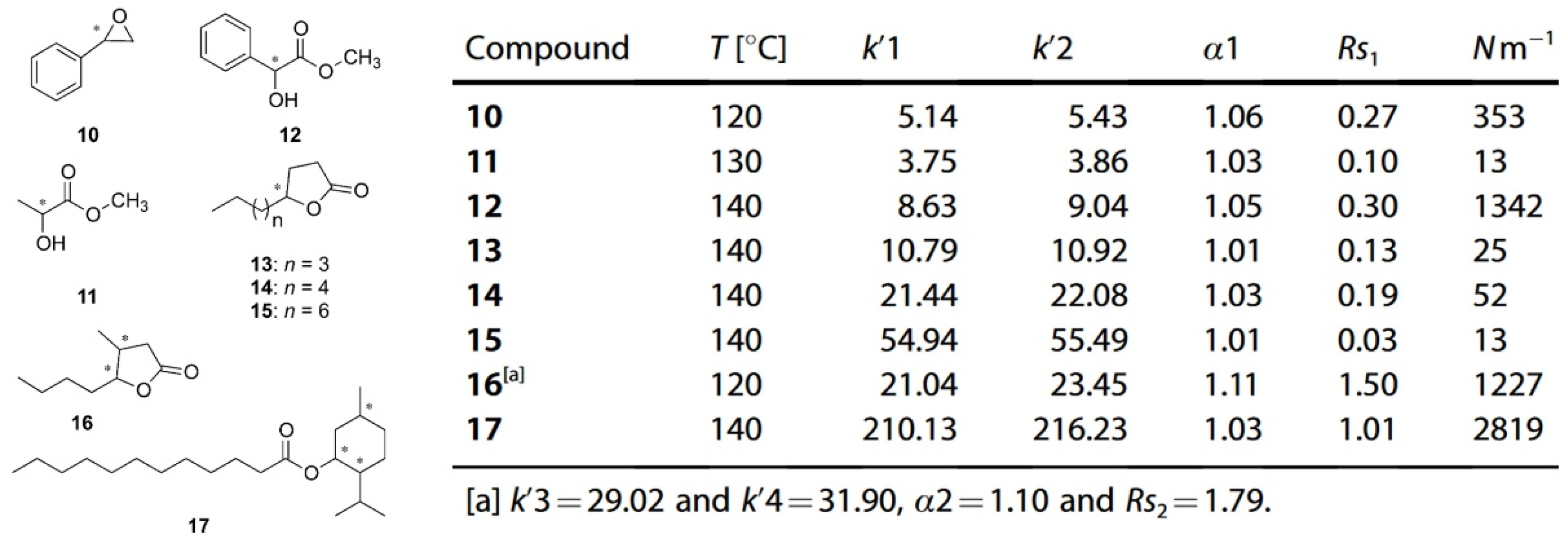
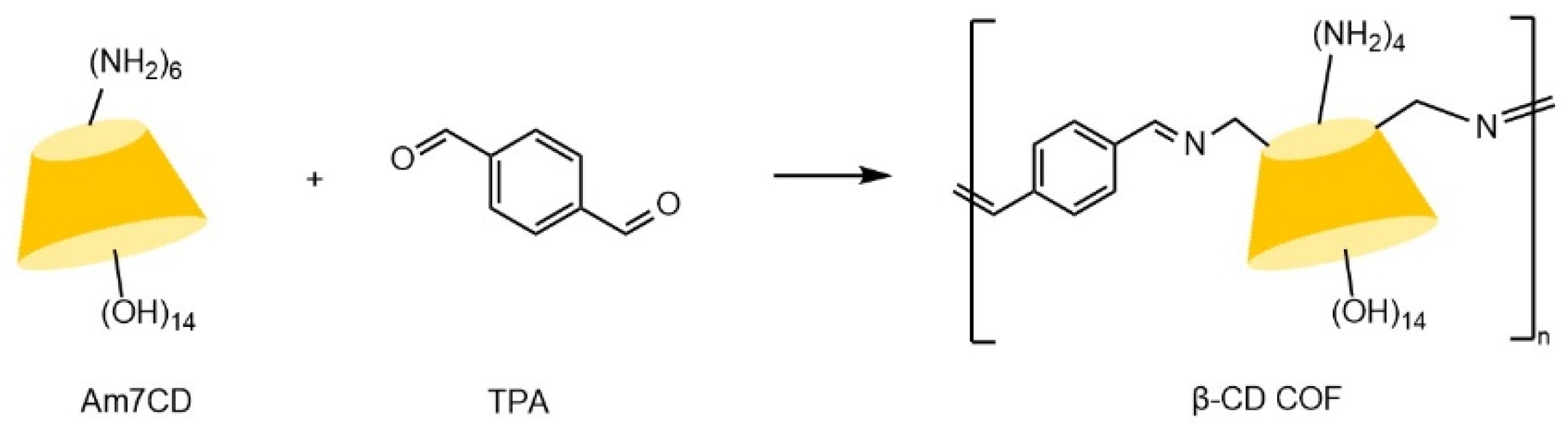
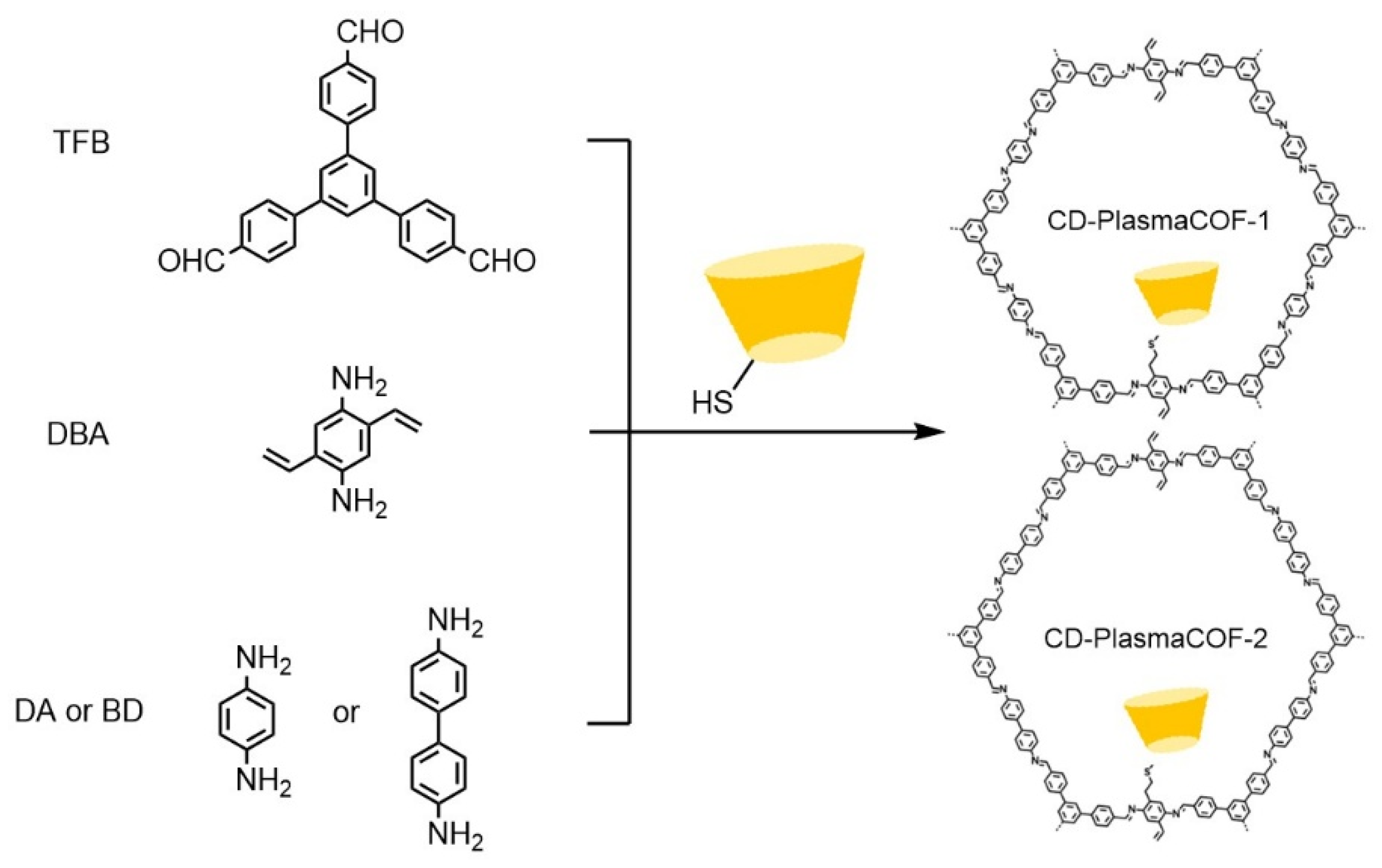
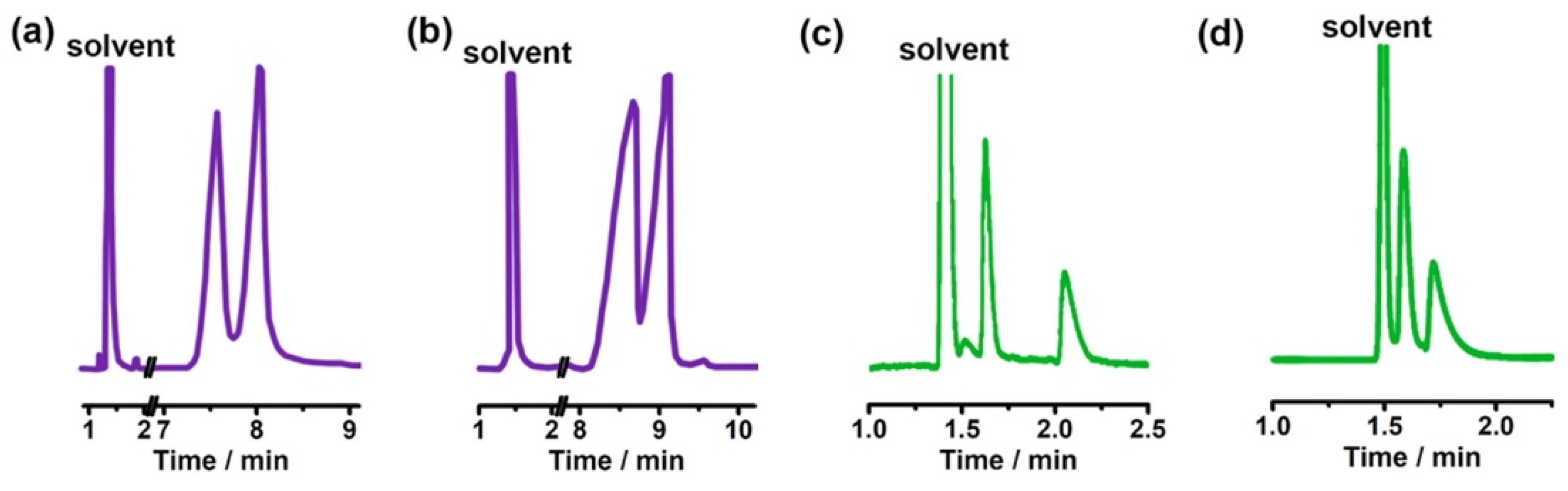
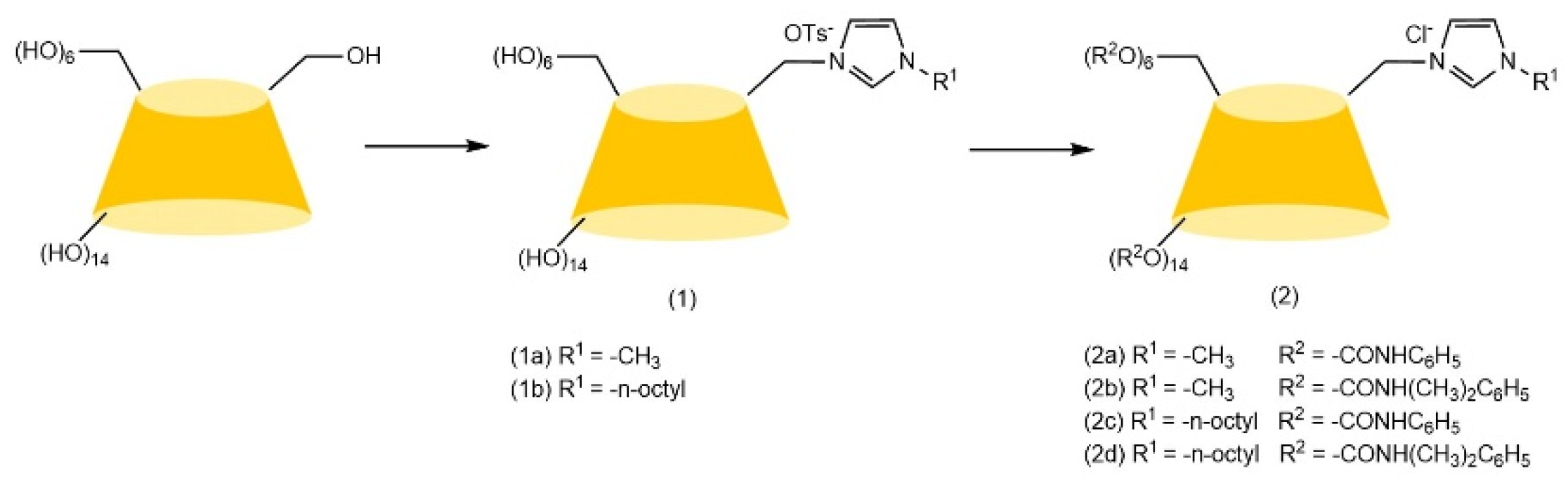
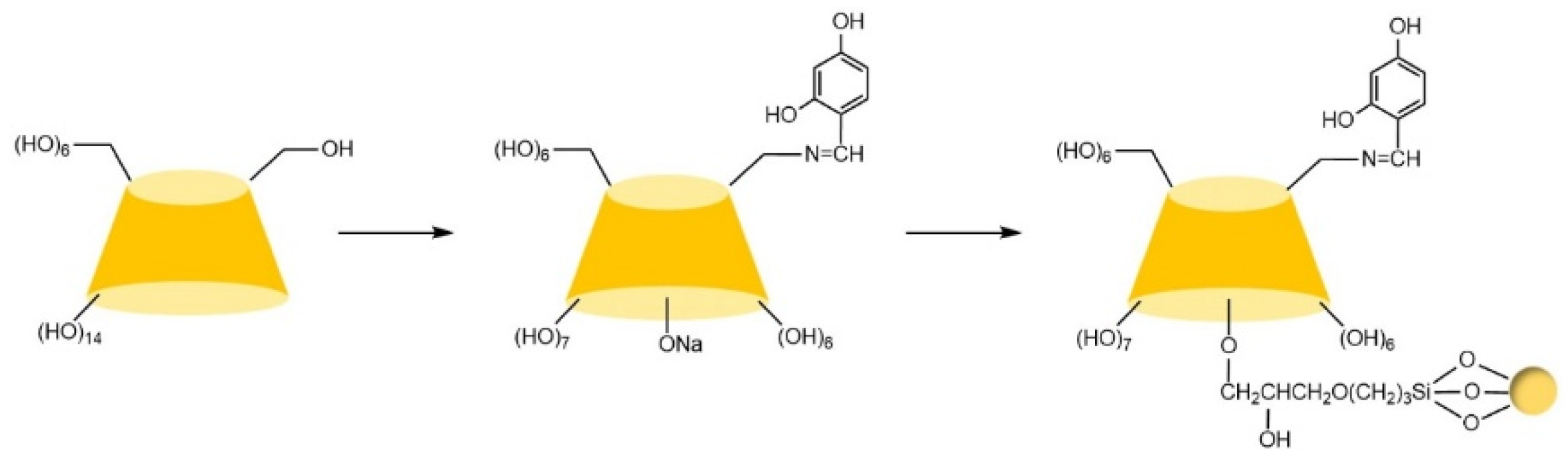
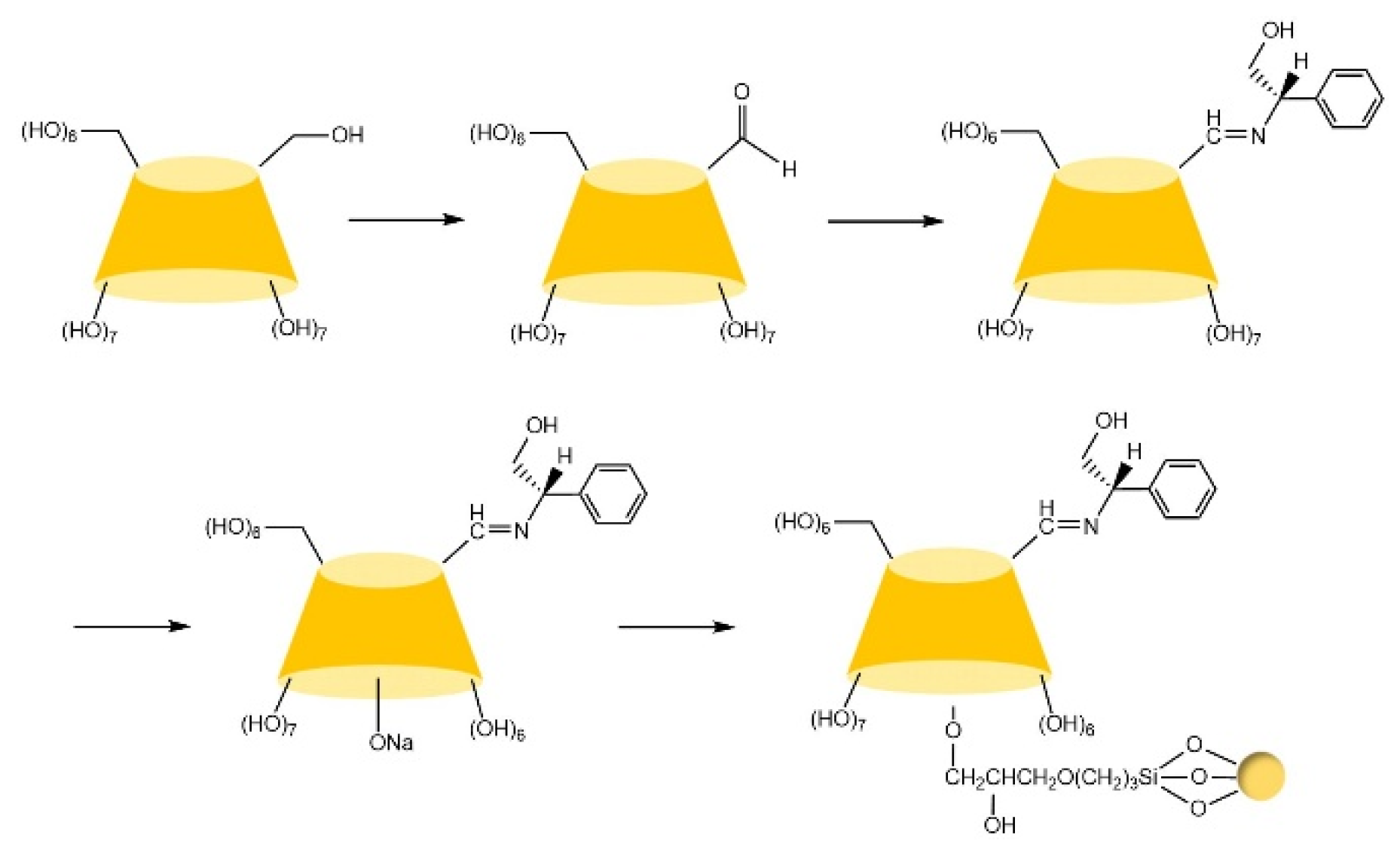
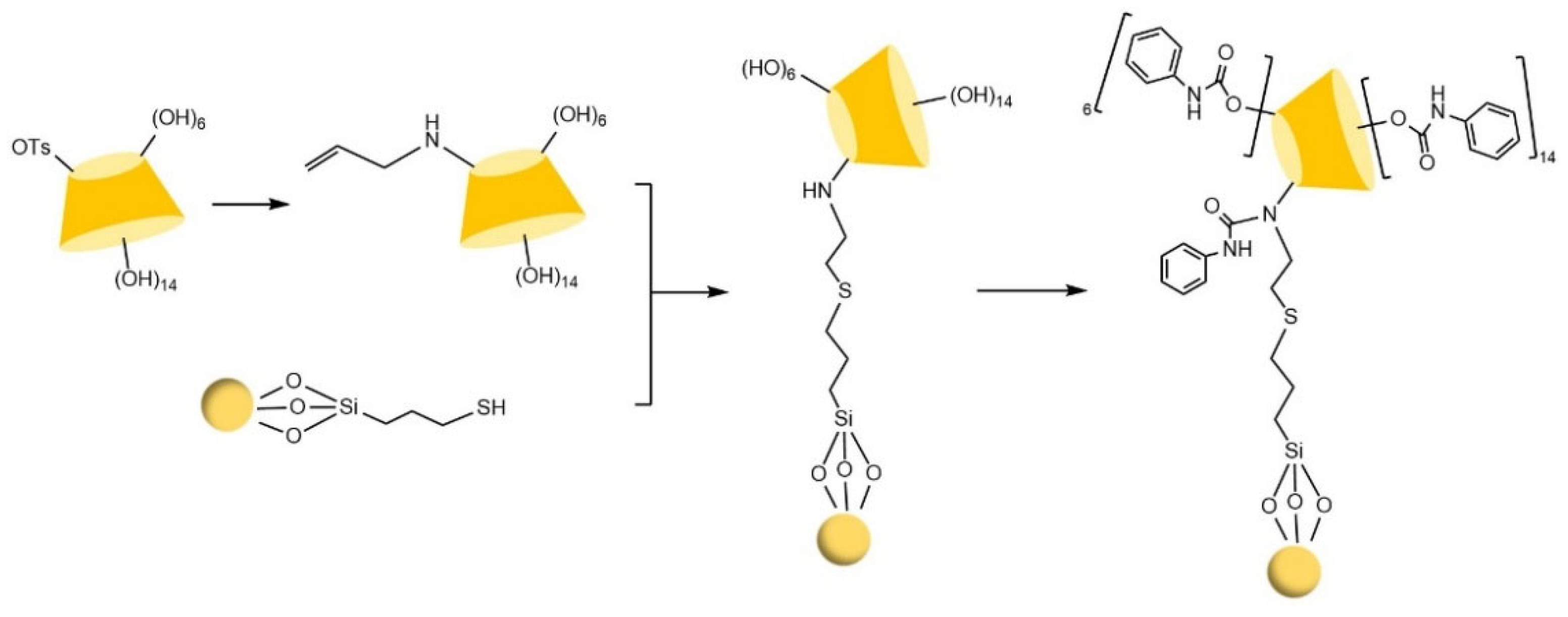
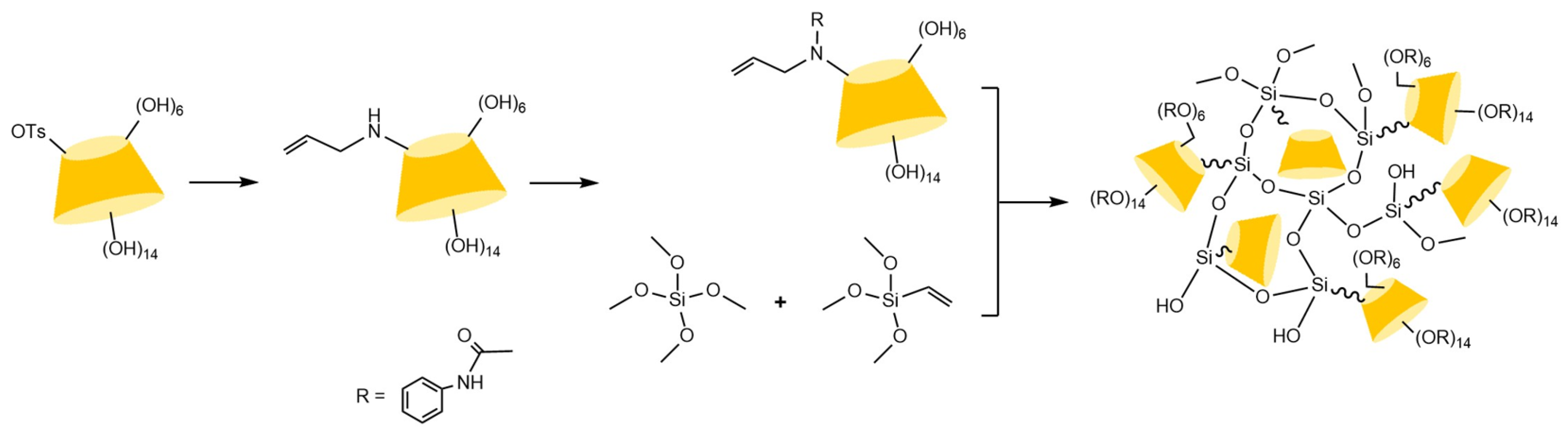
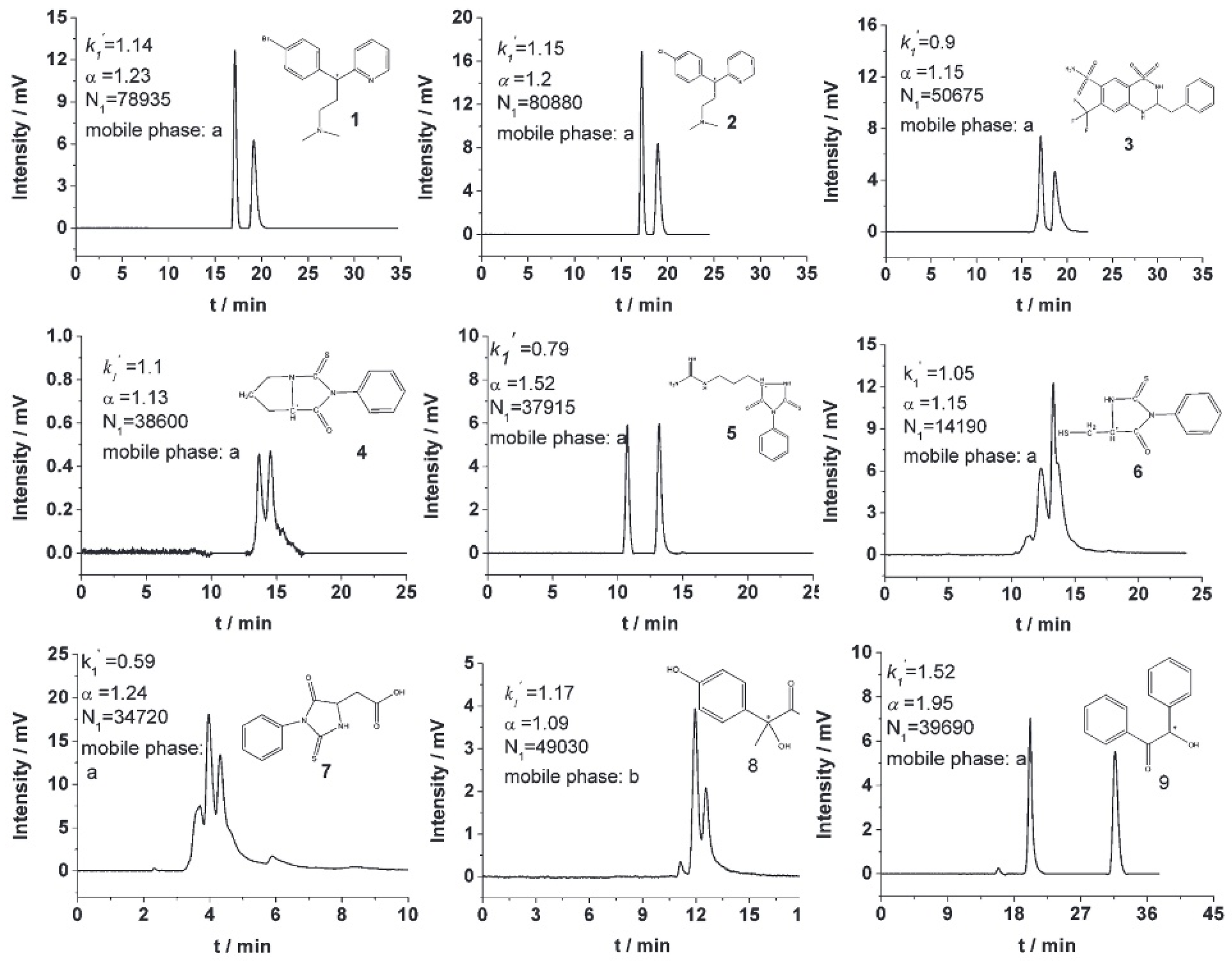
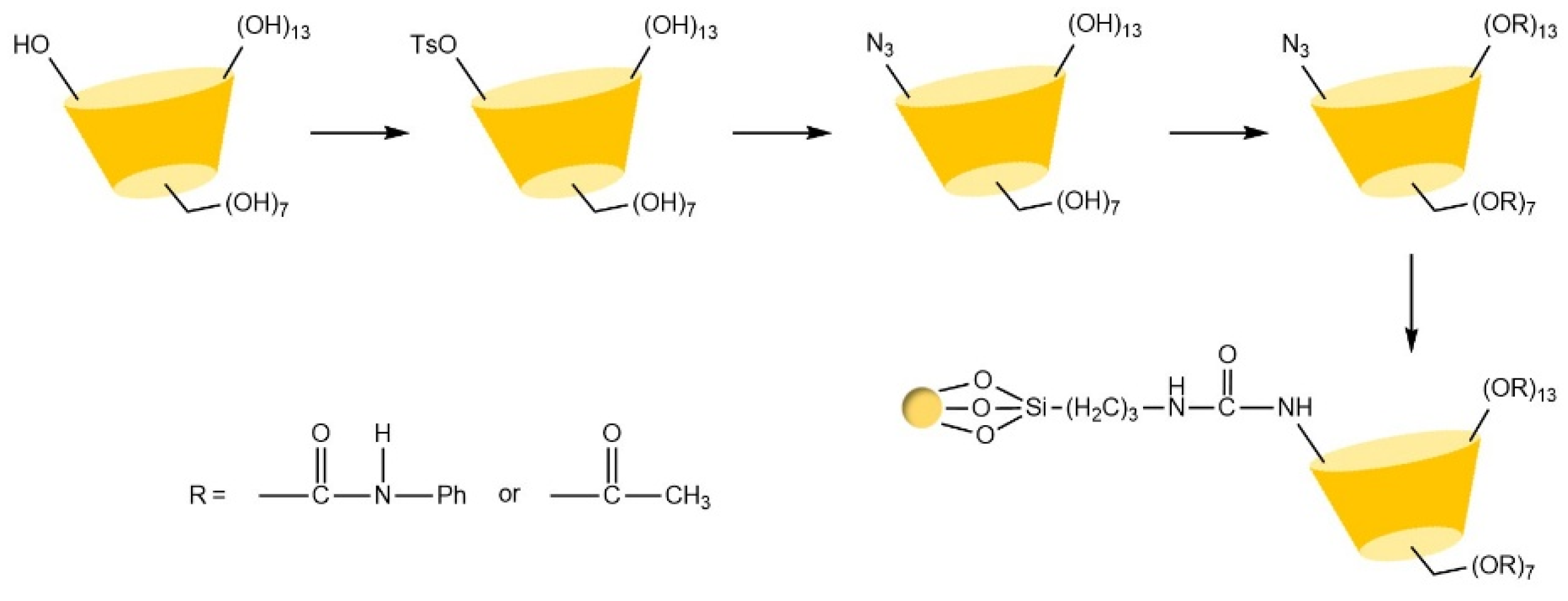
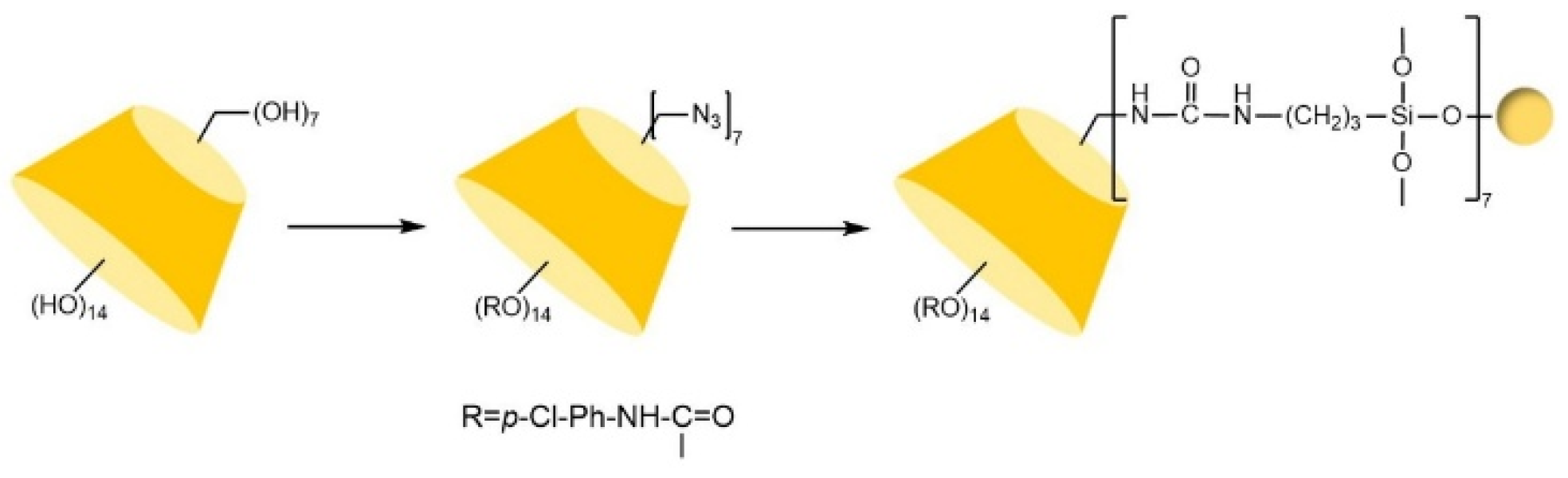
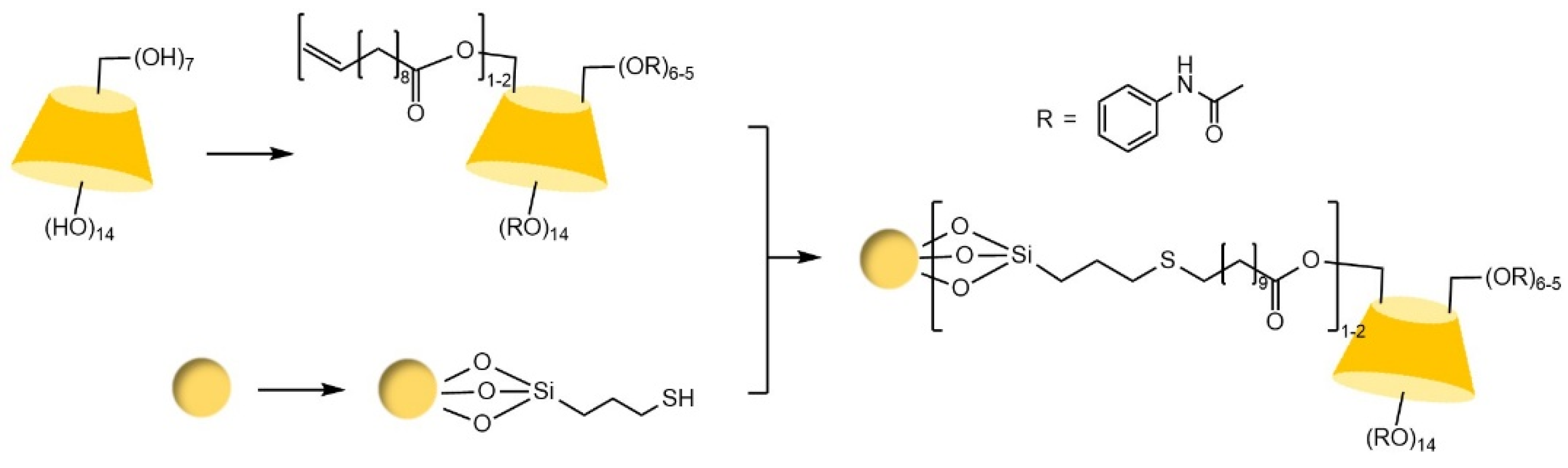
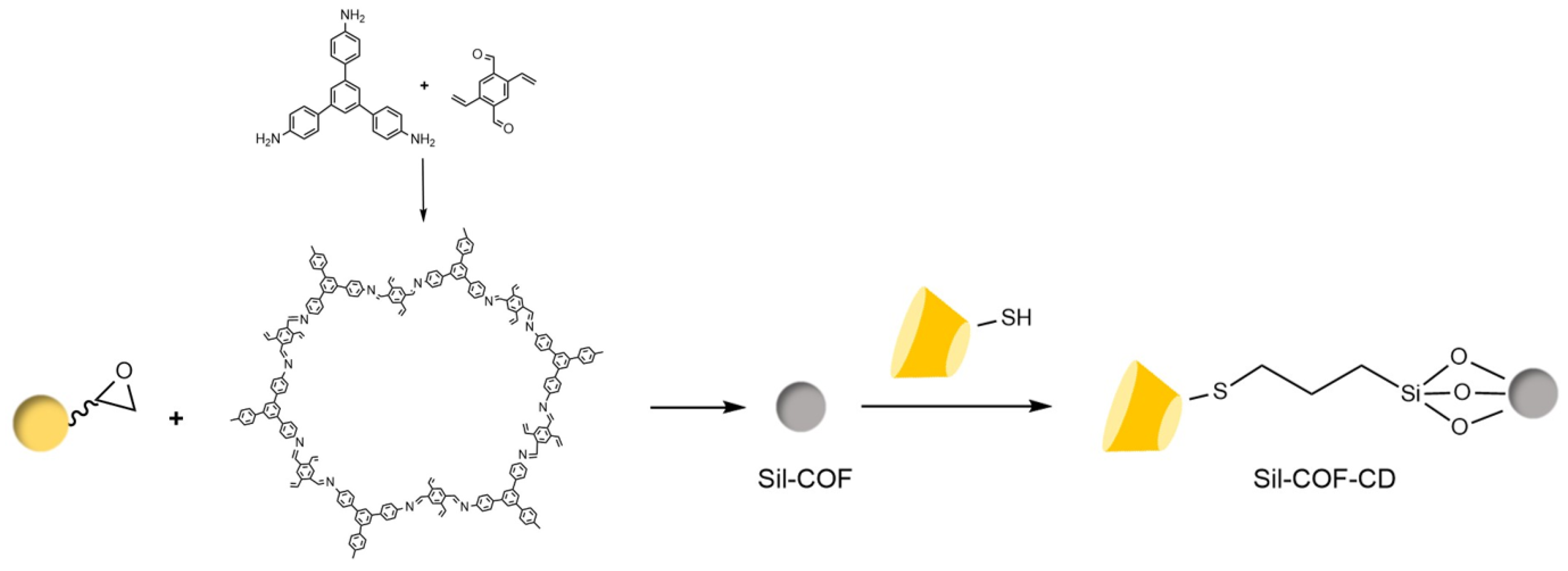
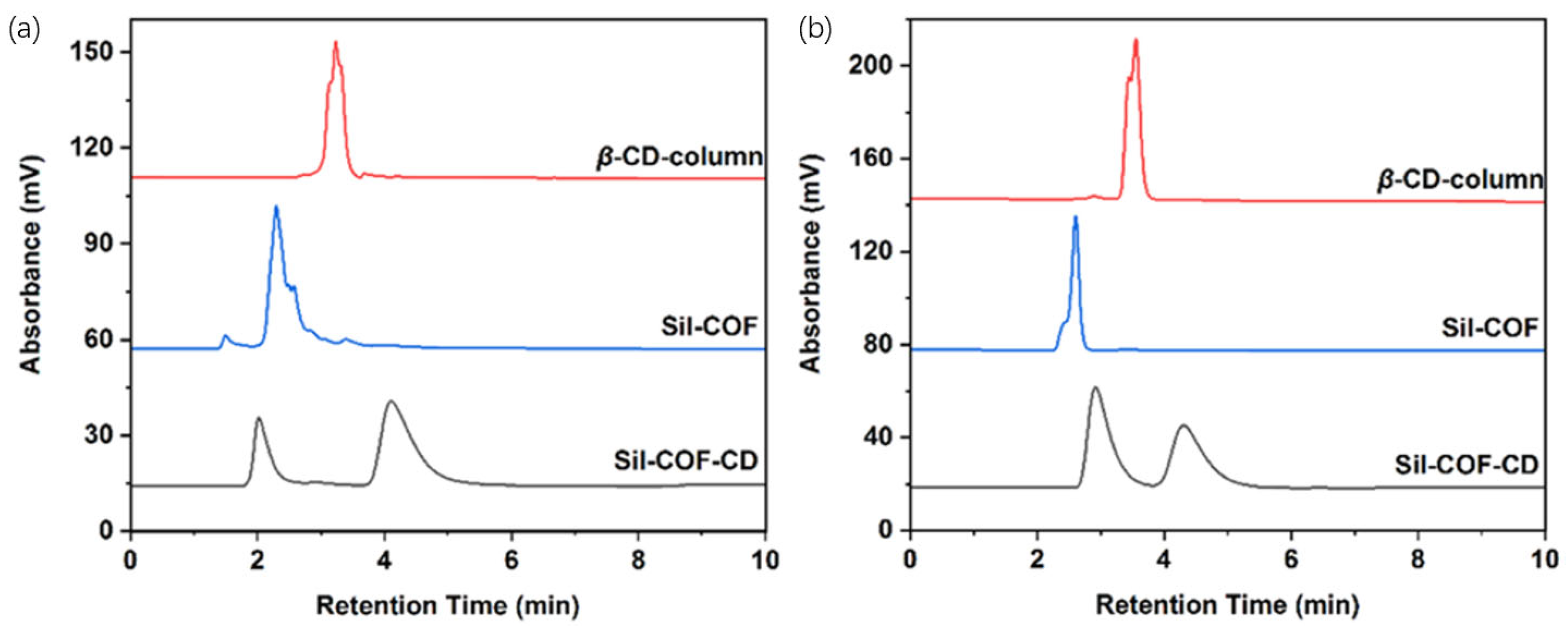
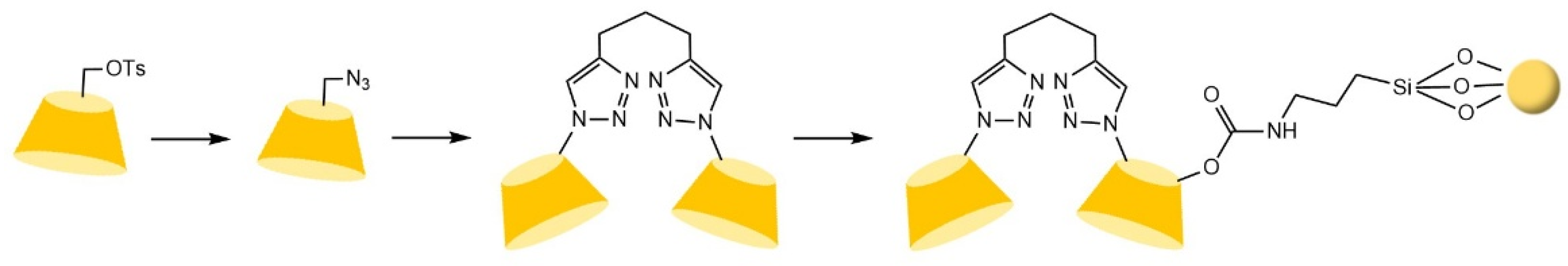
| Cyclodextrin | Glucose Unit | Molecular Weight | Cavity Height (Å) | Cavity Diameter (Å) | Cavity Volume (Å3) | Specific Optical Rotation ([α]25D) | Water Solubility (g/100mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-CD | 6 | 973 | 7.9±0.1 | 4.70~5.30 | 174.0 | +150.5° | 14.5 |
| β-CD | 7 | 1135 | 7.9±0.1 | 6.00~6.50 | 262.0 | +162.5° | 1.85 |
| γ-CD | 8 | 1297 | 7.9±0.1 | 7.50~8.30 | 427.0 | +177.4° | 23.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





