Submitted:
06 March 2025
Posted:
07 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
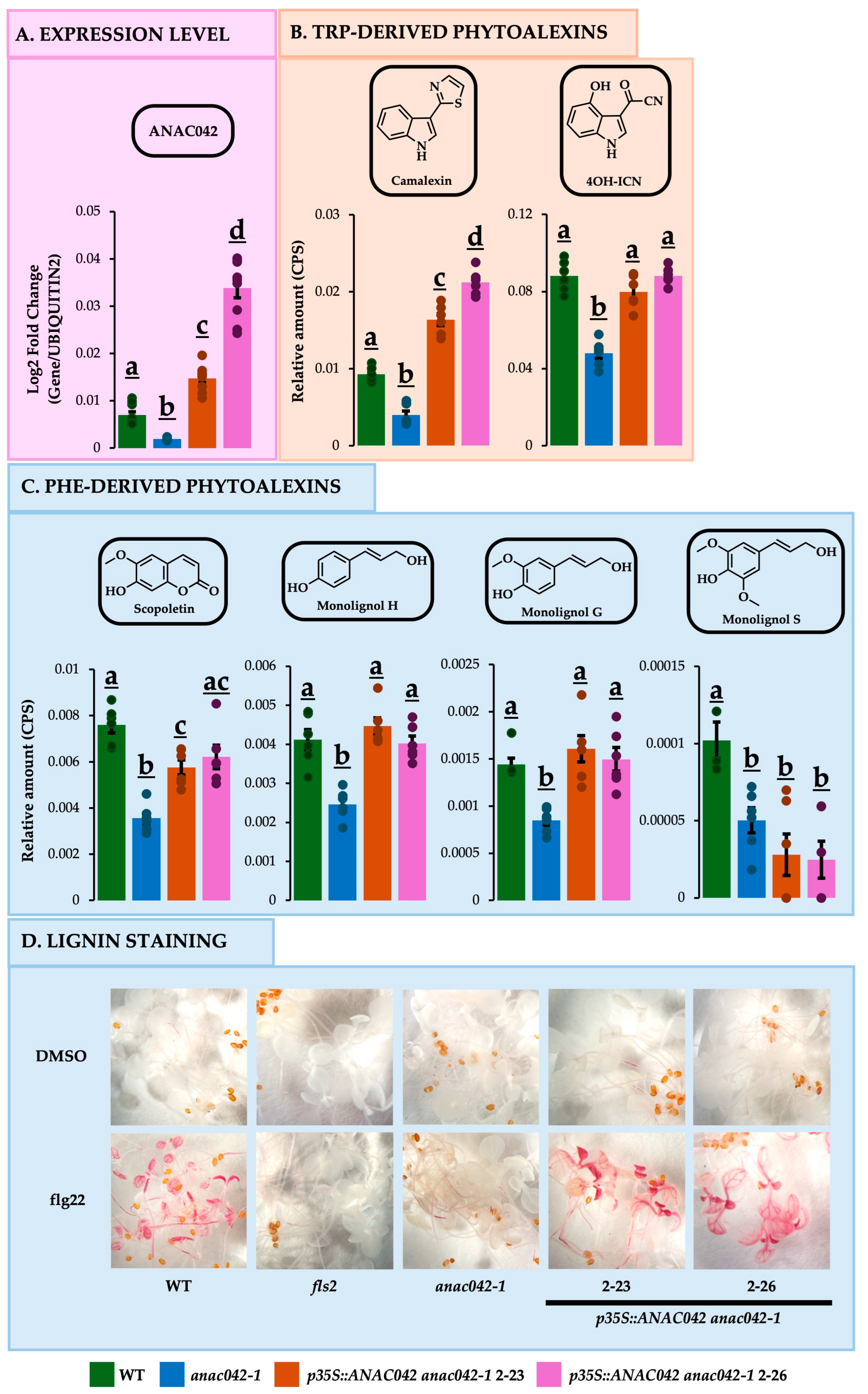
2.1. Arabidopsis Loss-of-Function Mutant anac042-1 Is Deficient in Phe- and Trp-Derived Phytoalexins
2.2. Overexpressing ANAC042 in anac042-1 Background Restored or Exceeded Wildtype Amounts of Phe- and Trp-Derived Phytoalexins
2.3. Overexpressing ANAC042 in anac042-1 background restored or exceeded wildtype levels of Phe and Trp phytoalexin gene expressions
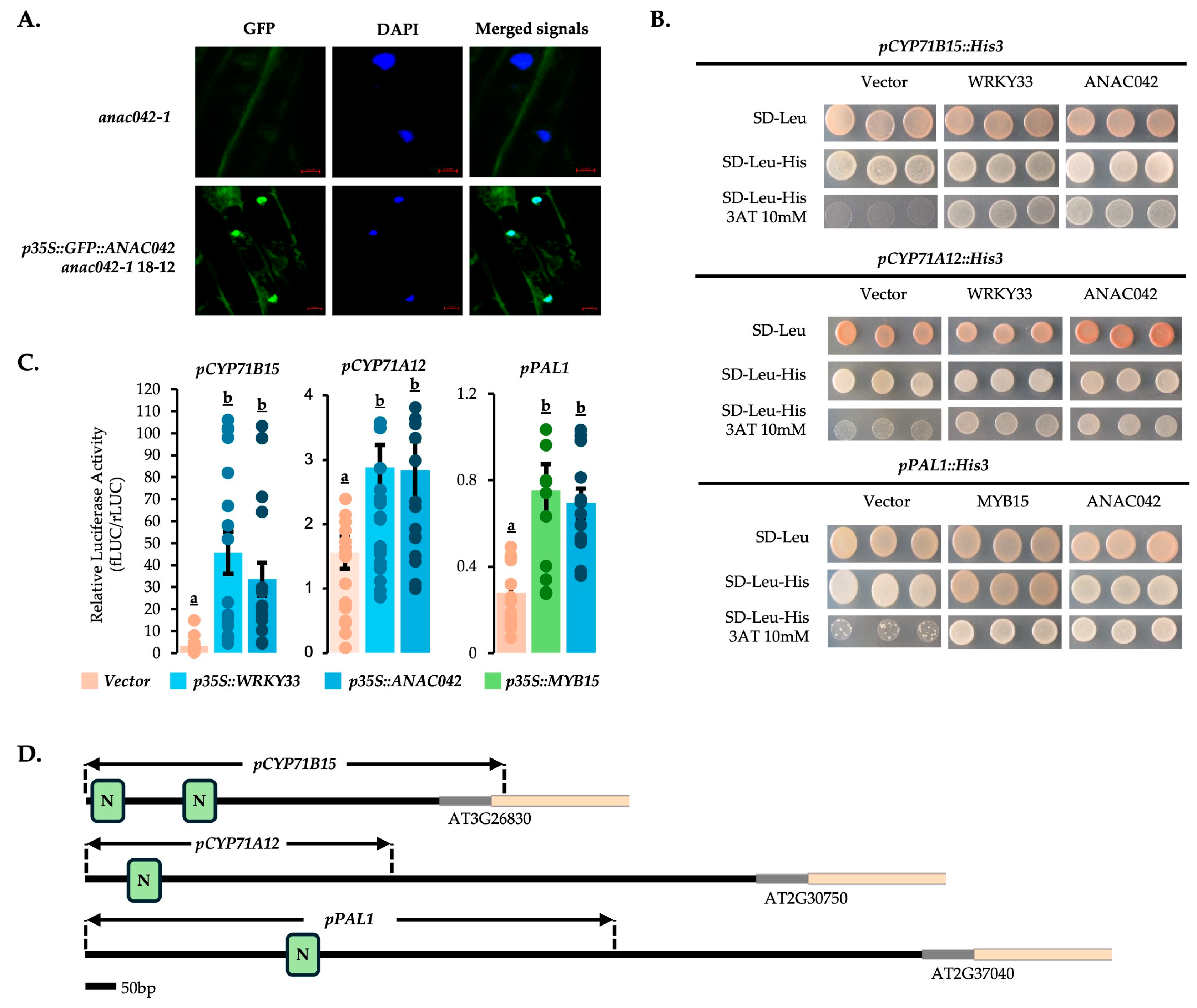
2.4. ANAC042 Directly Activates the Expression of Scopoletin, Monolignol, 4OH-ICN, and Camalexin Biosynthetic Genes
3. Discussion
3.1. ANAC042 is a Regulator of Diverse Phytoalexin Biosynthetic Pathways in Arabidopsis
3.2. NAC42-type Transcription Factors are Opportunistic Regulators that Coopt Lineage-Specific Genes into Pathogen-Inducible Biochemical Defenses
3.3. ANAC042 as a Member of a Cooperative Network that Regulates Phytoalexin Biosynthesis
3.4. Limitations and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cloning and Plasmid Constructs
4.3. Plant materials
4.4. Metabolites Analyses
4.5. Lignin Staining
4.6. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Measurements (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Subcellular Localization
4.8. Y1H
4.9. Luciferase Transactivation Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
4.11. Accession Numbers
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, L.; Wang, P.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Hu, M.; Ge, X.; Li, F.; Hou, Y. Feruloyl-CoA 6′-hydroxylase-mediated scopoletin accumulation enhances cotton resistance to Verticillium dahliae. Plant Physiology 2024, 196, 3007-3022. [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Locci, F.; Wanke, F.; Zhang, L.S.; Saile, S.C.; Joe, A.; Karelina, D.; Hua, C.L.; Fröhlich, K.; Wan, W.L.; et al. The EDS1-PAD4-ADR1 node mediates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. Nature 2021, 598, 495-+. [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Gust, A.A.; Nürnberger, T. Plant immunity unified. Nature Plants 2021, 7, 382-383. [CrossRef]
- Saijo, Y.; Loo, E.P.; Yasuda, S. Pattern recognition receptors and signaling in plant-microbe interactions. Plant Journal 2018, 93, 592-613. [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J.; Jackson, E.P.; Gage, D.A.; Hammerschmidt, R.; Somerville, S.C. Phytoalexin accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana during the hypersensitive reaction to Pseudomonas syringae pv syringae. Plant physiology 1992, 98, 1304-1309. [CrossRef]
- Glazebrook, J.; Zook, M.; Mert, F.; Kagan, I.; Rogers, E.E.; Crute, I.R.; Holub, E.B.; Hammerschmidt, R.; Ausubel, F.M. Phytoalexin-deficient mutants of Arabidopsis reveal that PAD4 encodes a regulatory factor and that four PAD genes contribute to downy mildew resistance. Genetics 1997, 146, 381-392.
- Glazebrook, J.; Rogers, E.E.; Ausubel, F.M. Isolation of Arabidopsis mutants with enhanced disease susceptibility by direct screening. Genetics 1996, 143, 973-982.
- Glazebrook, J.; Ausubel, F.M. ISOLATION OF PHYTOALEXIN-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ARABIDOPSIS-THALIANA AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THEIR INTERACTIONS WITH BACTERIAL PATHOGENS. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1994, 91, 8955-8959. [CrossRef]
- Thomma, B.P.; Nelissen, I.; Eggermont, K.; Broekaert, W.F. Deficiency in phytoalexin production causes enhanced susceptibility of Arabidopsis thaliana to the fungus Alternaria brassicicola. The Plant Journal 1999, 19, 163-171. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Tootle, T.L.; Glazebrook, J. Arabidopsis PAD3, a gene required for camalexin biosynthesis, encodes a putative cytochrome P450 monooxygenase. The Plant Cell 1999, 11, 2419-2428. [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, M.; Goregaoker, S.; Botanga, C.J.; Glawischnig, E.; Olsen, C.E.; Halkier, B.A.; Glazebrook, J. Arabidopsis cytochrome P450 monooxygenase 71A13 catalyzes the conversion of indole-3-acetaldoxime in camalexin synthesis. The Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2039-2052.
- Glawischnig, E.; Hansen, B.G.; Olsen, C.E.; Halkier, B.A. Camalexin is synthesized from indole-3-acetaldoxime, a key branching point between primary and secondary metabolism in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, 8245-8250.
- Millet, Y.A.; Danna, C.H.; Clay, N.K.; Songnuan, W.; Simon, M.D.; Werck-Reichhart, D.; Ausubel, F.M. Innate immune responses activated in Arabidopsis roots by microbe-associated molecular patterns. The Plant Cell 2010, 22, 973-990.
- Zhou, J.; Mu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, T.; He, Y.; Dai, S.; Meng, X. Multilayered synergistic regulation of phytoalexin biosynthesis by ethylene, jasmonate, and MAPK signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3066-3087.
- Ferrari, S.; Plotnikova, J.M.; De Lorenzo, G.; Ausubel, F.M. Arabidopsis local resistance to Botrytis cinerea involves salicylic acid and camalexin and requires EDS4 and PAD2, but not SID2, EDS5 or PAD4. The Plant Journal 2003, 35, 193-205.
- Ren, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.-Y.; Han, L.; Mao, G.; Glazebrook, J.; Zhang, S. A fungal-responsive MAPK cascade regulates phytoalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, 5638-5643. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Meng, J.; Meng, X.Z.; Zhao, Y.T.; Liu, J.M.; Sun, T.F.; Liu, Y.D.; Wang, Q.M.; Zhang, S.Q. Pathogen-Responsive MPK3 and MPK6 Reprogram the Biosynthesis of Indole Glucosinolates and Their Derivatives in Arabidopsis Immunity. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1144-1162. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Tong, G.; Xi, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Ren, D.; Han, S. MPK3/MPK6-mediated phosphorylation of ERF72 positively regulates resistance to Botrytis cinerea through directly and indirectly activating the transcription of camalexin biosynthesis enzymes. Journal of Experimental Botany 2022, 73, 413-428.
- Zhou, J.G.; Wang, X.Y.; He, Y.X.; Sang, T.; Wang, P.C.; Dai, S.J.; Zhang, S.Q.; Meng, X.Z. Differential Phosphorylation of the Transcription Factor WRKY33 by the Protein Kinases CPK5/CPK6 and MPK3/MPK6 Cooperatively Regulates Camalexin Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 2621-2638. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Zhang, H.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.Q. Functional characterization of calcium-dependent protein kinase (CPK) 2 gene from oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) in regulating reactive oxygen species signaling and cell death control. Gene 2018, 651, 49-56. [CrossRef]
- Cheval, C.; Perez, M.; Leba, L.-J.; Ranty, B.; Perochon, A.; Reichelt, M.; Mithöfer, A.; Robe, E.; Mazars, C.; Galaud, J.-P. PRR2, a pseudo-response regulator, promotes salicylic acid and camalexin accumulation during plant immunity. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 6979.
- Saga, H.; Ogawa, T.; Kai, K.; Suzuki, H.; Ogata, Y.; Sakurai, N.; Shibata, D.; Ohta, D. Identification and Characterization of ANAC042, a Transcription Factor Family Gene Involved in the Regulation of Camalexin Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2012, 25, 684-696. [CrossRef]
- Birkenbihl, R.P.; Diezel, C.; Somssich, I.E. Arabidopsis WRKY33 Is a Key Transcriptional Regulator of Hormonal and Metabolic Responses toward Botrytis cinerea Infection. Plant Physiology 2012, 159, 266-285. [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Hébrard, C.; Deville, M.A.; Cordelier, S.; Dorey, S.; Aziz, A.; Crouzet, J. Deciphering the Role of Phytoalexins in Plant-Microorganism Interactions and Human Health. Molecules 2014, 19, 18033-18056. [CrossRef]
- Monsalvo, I.; Lin, J.; Kovinich, N. Phytoalexin Gene Regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana-On the Verge of a Paradigm Shift? Current Plant Biology 2024, 100367.
- Ahmed, S.; Kovinich, N. Regulation of phytoalexin biosynthesis for agriculture and human health. Phytochemistry Reviews 2021, 20, 483-505. [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Miao, H.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Xia, C.C.; Zeng, W.; Sun, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.Q.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, Q.M. WRKY33-mediated indolic glucosinolate metabolic pathway confers resistance against Alternaria brassicicola in Arabidopsis and Brassica crops. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 2022, 64, 1007-1019. [CrossRef]
- Barco, B.; Kim, Y.; Clay, N.K. Expansion of a core regulon by transposable elements promotes Arabidopsis chemical diversity and pathogen defense. Nature Communications 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Abu Qamar, S.; Chen, Z.X.; Mengiste, T. Arabidopsis WRKY33 transcription factor is required for resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant Journal 2006, 48, 592-605. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.L.; Fiil, B.K.; Petersen, K.; Nielsen, H.B.; Botanga, C.J.; Thorgrimsen, S.; Palma, K.; Suarez-Rodriguez, M.C.; Sandbech-Clausen, S.; Lichota, J. Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 regulates gene expression through transcription factor release in the nucleus. The EMBO journal 2008, 27, 2214-2221. [CrossRef]
- Barco, B.; Clay, N.K. Hierarchical and Dynamic Regulation of Defense-Responsive Specialized Metabolism by WRKY and MYB Transcription Factors. Frontiers in Plant Science 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.H.; Allu, A.D.; Garapati, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Dortay, H.; Zanor, M.I.; Asensi-Fabado, M.A.; Munné-Bosch, S.; Antonio, C.; Tohge, T.; et al. JUNGBRUNNEN1, a Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive NAC Transcription Factor, Regulates Longevity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 482-506. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Nemoto, K.; Sawasaki, T.; Yamane, H.; Nojiri, H.; Okada, K. OsMYC2, an essential factor for JA-inductive sakuranetin production in rice, interacts with MYC2-like proteins that enhance its transactivation ability. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 40175.
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Q.; Liang, Z.; Hong, G. Single-repeat MYB transcription factor, OsMYB1R, enhanced phytoalexin sakuranetin accumulation and Magnaporthe oryzae resistance. Current Plant Biology 2024, 38, 100351. [CrossRef]
- Chezem, W.R.; Memon, A.; Li, F.S.; Weng, J.K.; Clay, N.K. SG2-Type R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor MYB15 Controls Defense-Induced Lignification and Basal Immunity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1907-1926. [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.A.; Harris, B.; Lowery, M.; Infante, A.M.; Percifield, R.J.; Kovinich, N. Glyceollin Transcription Factor GmMYB29A2 Regulates Soybean Resistance to Phytophthora sojae1[OPEN]. Plant Physiology 2020, 183, 530-546. [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.A.; Harris, B.; Lowery, M.; Coburn, K.; Infante, A.M.; Percifield, R.J.; Ammer, A.G.; Kovinich, N. The NAC family transcription factor GmNAC42–1 regulates biosynthesis of the anticancer and neuroprotective glyceollins in soybean. BMC genomics 2019, 20, 1-21.
- Liu, S.A.; Kracher, B.; Ziegler, J.; Birkenbihl, R.P.; Somssich, I.E. Negative regulation of ABA signaling by WRKY33 is critical for Arabidopsis immunity towards Botrytis cinerea 2100. Elife 2015, 4. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Monsalvo, I.; Jahan, M.A.; Ly, M.; Wi, D.; Martirosyan, I.; Jahan, I.; Kovinich, N. ABA-regulated JAZ1 Proteins Bind NAC42 Transcription Factors to Suppress the Activation of Phytoalexin Biosynthesis in Plants. bioRxiv 2024, 2024.2009. 2026.615281. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Monsalvo, I.; Ly, M.; Jahan, M.A.; Wi, D.; Martirosyan, I.; Kovinich, N. RNA-Seq Dissects Incomplete Activation of Phytoalexin Biosynthesis by the Soybean Transcription Factors GmMYB29A2 and GmNAC42-1. Plants-Basel 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, N.; Dwivedi, S.; Trivedi, P.K. Transcriptional regulation of secondary plant product biosynthesis: insights into flavonoid, alkaloid, and terpenoid pathways. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) 2025, 160, 6.
- Zhang, X.; Henriques, R.; Lin, S.-S.; Niu, Q.-W.; Chua, N.-H. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nature protocols 2006, 1, 641-646.
- Denoux, C.; Galletti, R.; Mammarella, N.; Gopalan, S.; Werck, D.; De Lorenzo, G.; Ferrari, S.; Ausubel, F.M.; Dewdney, J. Activation of defense response pathways by OGs and Flg22 elicitors in Arabidopsis seedlings. Molecular plant 2008, 1, 423-445.
- Parasecolo, L.; Monsalvo, I.M.; Kovinich, N.; Ifa, D.R. Development of a Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantification of Camalexin and Scopoletin in Arabidopsis thaliana. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 2025, 39, e9973. [CrossRef]
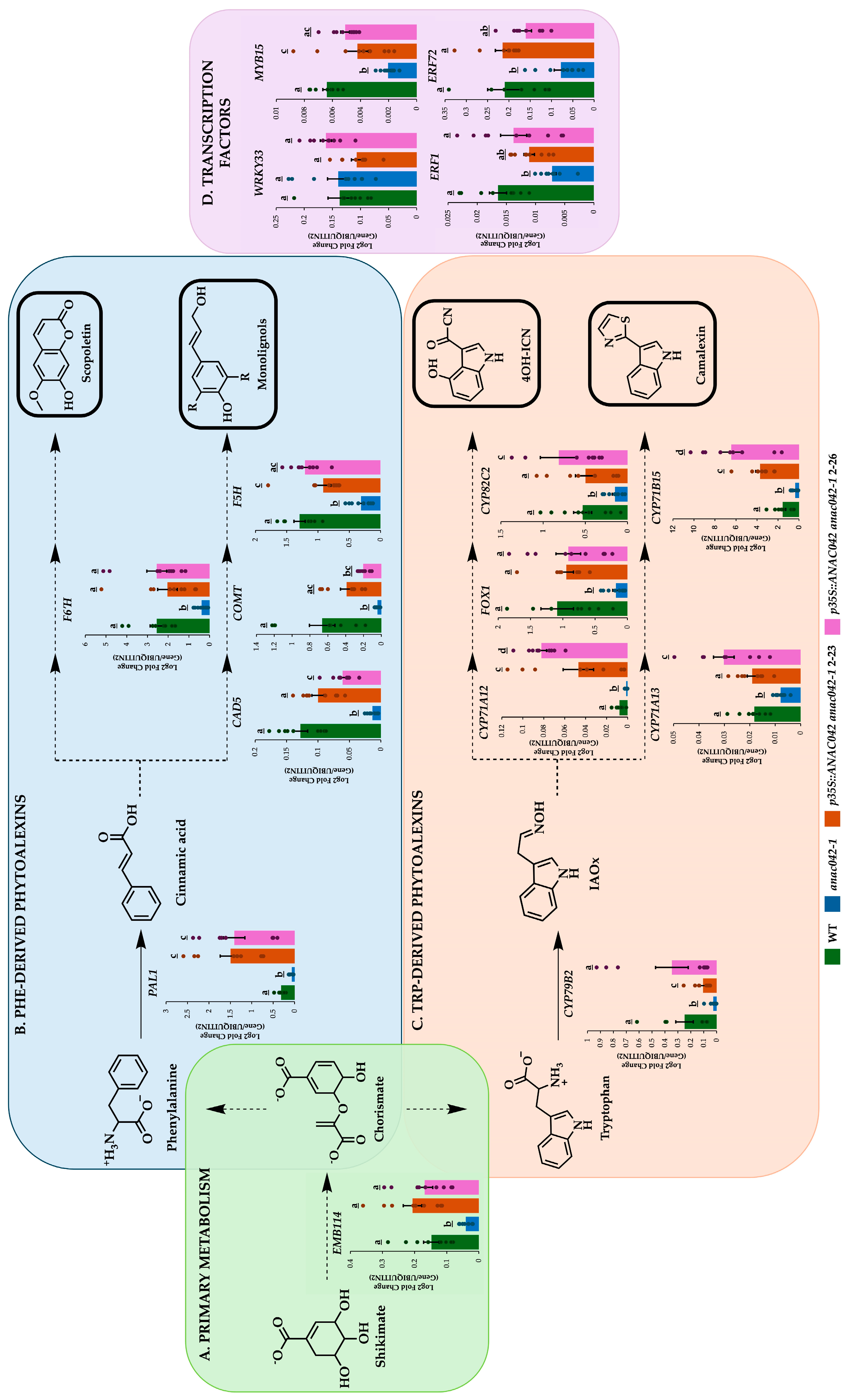
 )
indicate the direction of genes involved in phytoalexin biosynthesis starting
at PAL1 (Phe-derived phytoalexins) and CYP79B2 (Trp-derived
phytoalexins); Purple arrows (
)
indicate the direction of genes involved in phytoalexin biosynthesis starting
at PAL1 (Phe-derived phytoalexins) and CYP79B2 (Trp-derived
phytoalexins); Purple arrows ( )
indicate direct regulation of the gene; Green dotted arrows (
)
indicate direct regulation of the gene; Green dotted arrows ( )
indicated regulation of the gene by qRT-PCR, but that
it remains unknown whether the corresponding genes are regulated directly or
indirectly. Gene names: GSTF11, GLUTATHIONE
S–TRANSFERASE F11; GGP1, Γ–GLUTAMYL PEPTIDASE 1; C4H,
CINNAMIC ACID 4–HYDROXYLASE; 4CL, 4–COUMARATE–COENZYME A LIGASE; CCR,
CINNAMOYL–COA REDUCTASE; SGT, SCOPOLETIN–GLUCOSYLTRANSFERASE.
)
indicated regulation of the gene by qRT-PCR, but that
it remains unknown whether the corresponding genes are regulated directly or
indirectly. Gene names: GSTF11, GLUTATHIONE
S–TRANSFERASE F11; GGP1, Γ–GLUTAMYL PEPTIDASE 1; C4H,
CINNAMIC ACID 4–HYDROXYLASE; 4CL, 4–COUMARATE–COENZYME A LIGASE; CCR,
CINNAMOYL–COA REDUCTASE; SGT, SCOPOLETIN–GLUCOSYLTRANSFERASE.
 )
indicate the direction of genes involved in phytoalexin biosynthesis starting
at PAL1 (Phe-derived phytoalexins) and CYP79B2 (Trp-derived
phytoalexins); Purple arrows (
)
indicate the direction of genes involved in phytoalexin biosynthesis starting
at PAL1 (Phe-derived phytoalexins) and CYP79B2 (Trp-derived
phytoalexins); Purple arrows ( )
indicate direct regulation of the gene; Green dotted arrows (
)
indicate direct regulation of the gene; Green dotted arrows ( )
indicated regulation of the gene by qRT-PCR, but that
it remains unknown whether the corresponding genes are regulated directly or
indirectly. Gene names: GSTF11, GLUTATHIONE
S–TRANSFERASE F11; GGP1, Γ–GLUTAMYL PEPTIDASE 1; C4H,
CINNAMIC ACID 4–HYDROXYLASE; 4CL, 4–COUMARATE–COENZYME A LIGASE; CCR,
CINNAMOYL–COA REDUCTASE; SGT, SCOPOLETIN–GLUCOSYLTRANSFERASE.
)
indicated regulation of the gene by qRT-PCR, but that
it remains unknown whether the corresponding genes are regulated directly or
indirectly. Gene names: GSTF11, GLUTATHIONE
S–TRANSFERASE F11; GGP1, Γ–GLUTAMYL PEPTIDASE 1; C4H,
CINNAMIC ACID 4–HYDROXYLASE; 4CL, 4–COUMARATE–COENZYME A LIGASE; CCR,
CINNAMOYL–COA REDUCTASE; SGT, SCOPOLETIN–GLUCOSYLTRANSFERASE.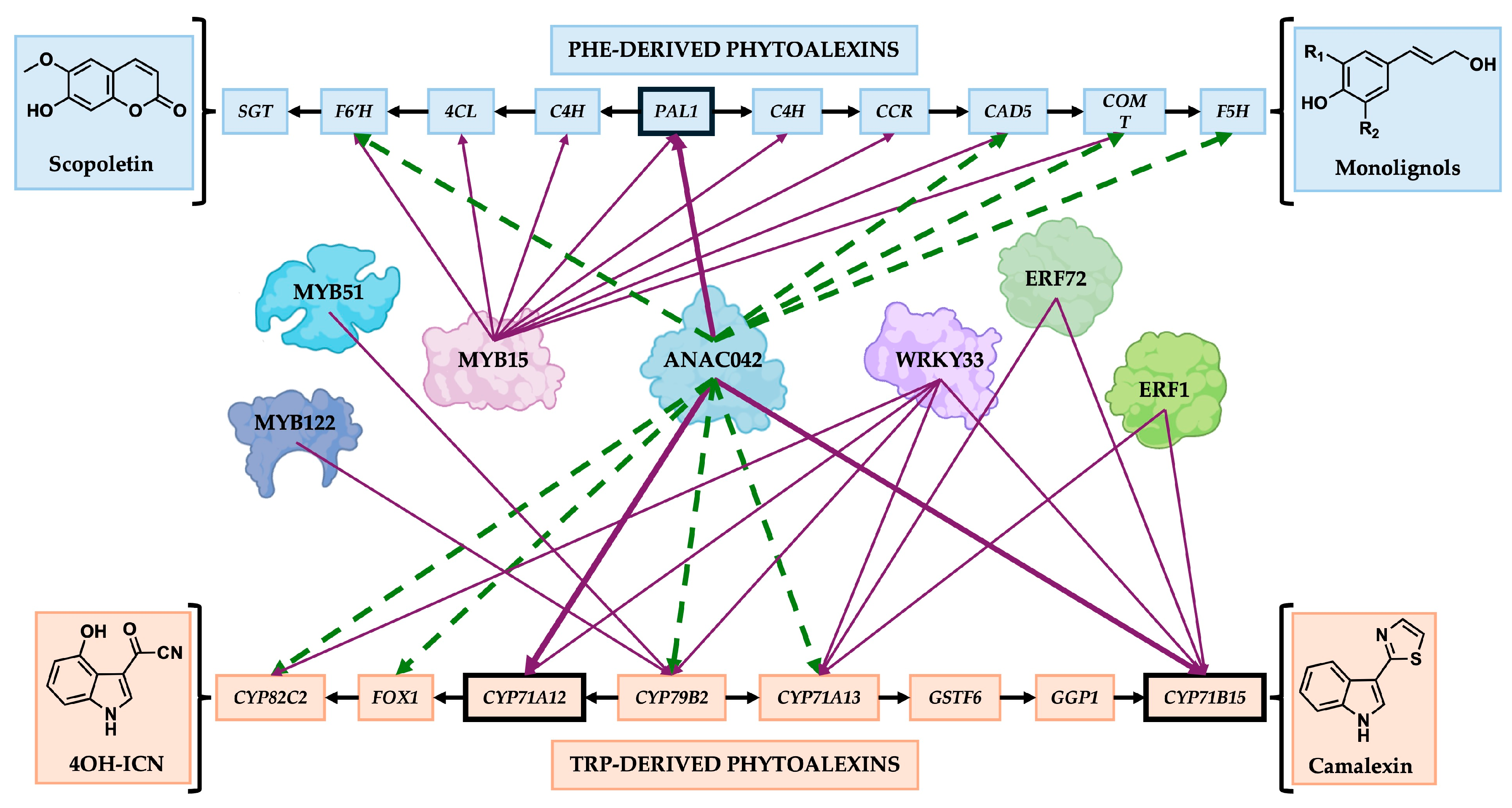
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




