Submitted:
03 March 2025
Posted:
04 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The spread of metastatic prostate cancer (PCa) is responsible for the majority of PCa-related deaths, yet the precise mechanisms driving this process remain unclear. We have identified a novel interaction between two distinct promotility factors, tousled-like kinase 1 (TLK1) and MAPK-activated protein kinase 5 (MK5), which triggers a signaling cascade that promotes metastasis. In PCa, the TLK1-MK5 pathway may play a critical role, as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) has been linked to increased expression of both TLK1 and MK5 in metastatic patients linked with poor survival. In this study, we directly examined the effects of disrupting the TLK1>MK5 axis on the motility, invasiveness, and metastatic potential of PCa cells. To establish this, we used both pharmacologic and systemic approaches with genetically engineered mouse models and the use of IVIS. The results of targeting the TLK1>MK5 axis support the notion that this axis is essential for the spread of metastatic cells and the development of age-related metastases.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Viability Assay and Treatments
2.2. Animal Studies
2.3. Immunohistochemistry and Fluorescence Imaging
3. Results
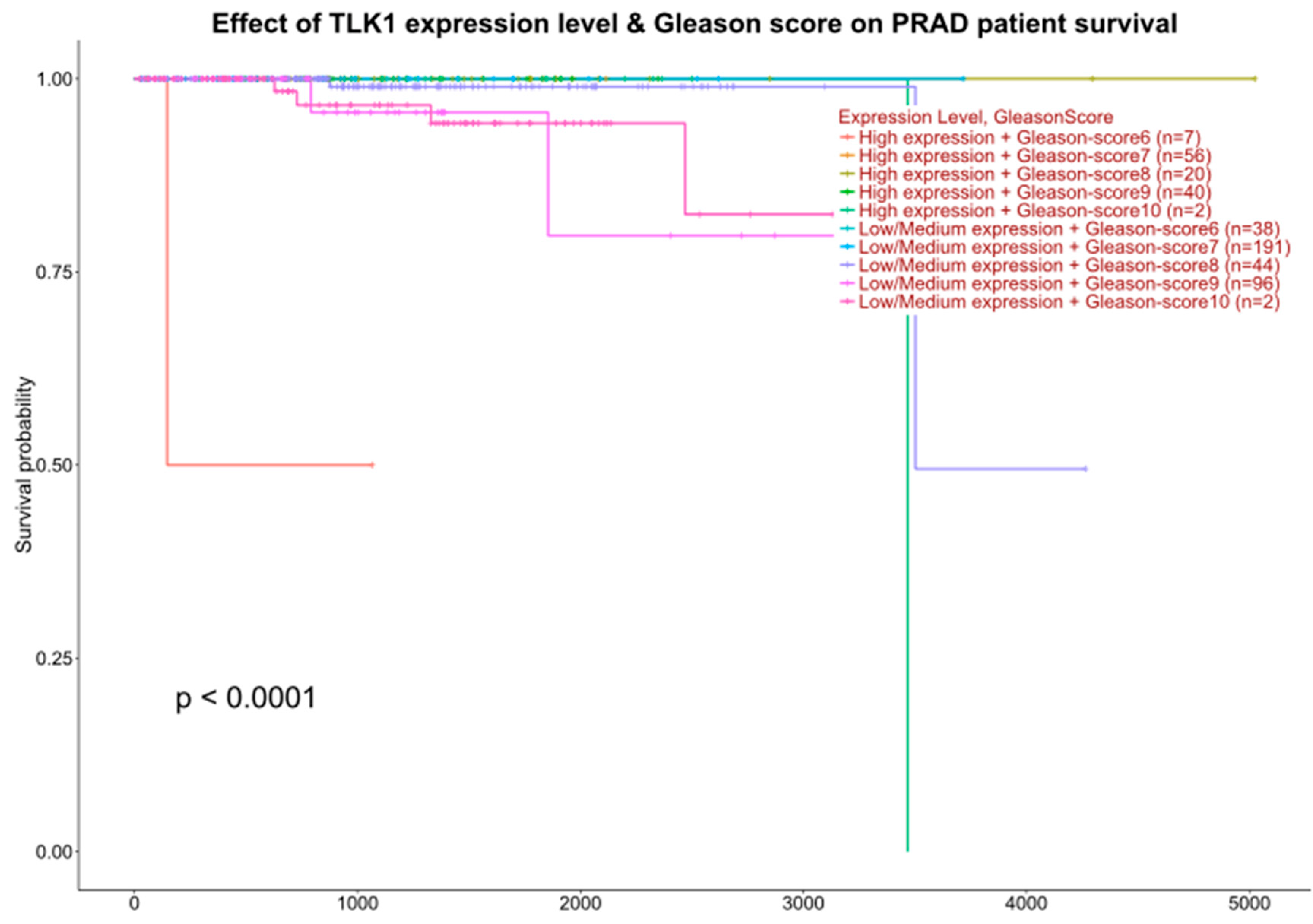
3.1. Interrogation of Expression Reports
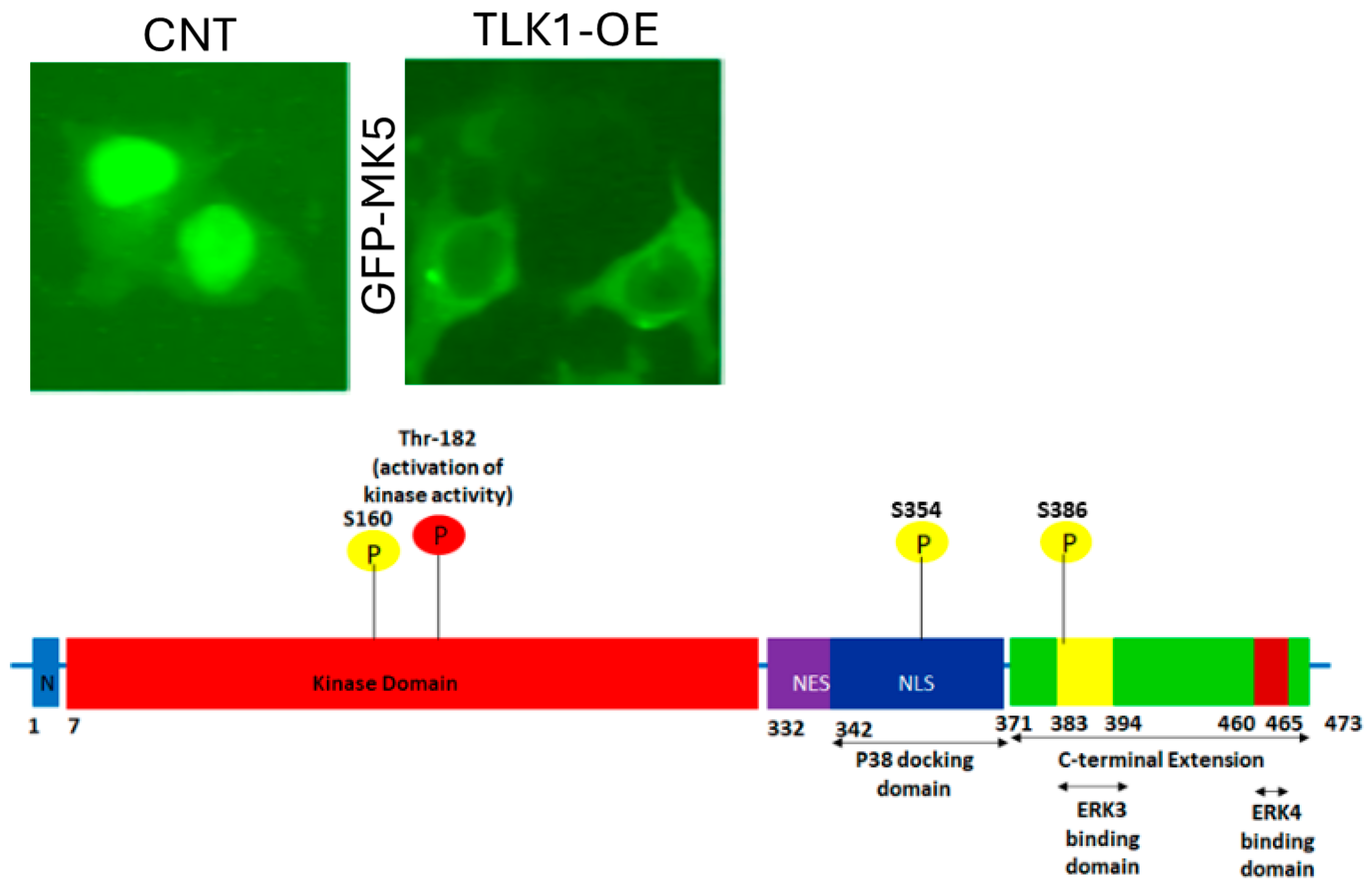
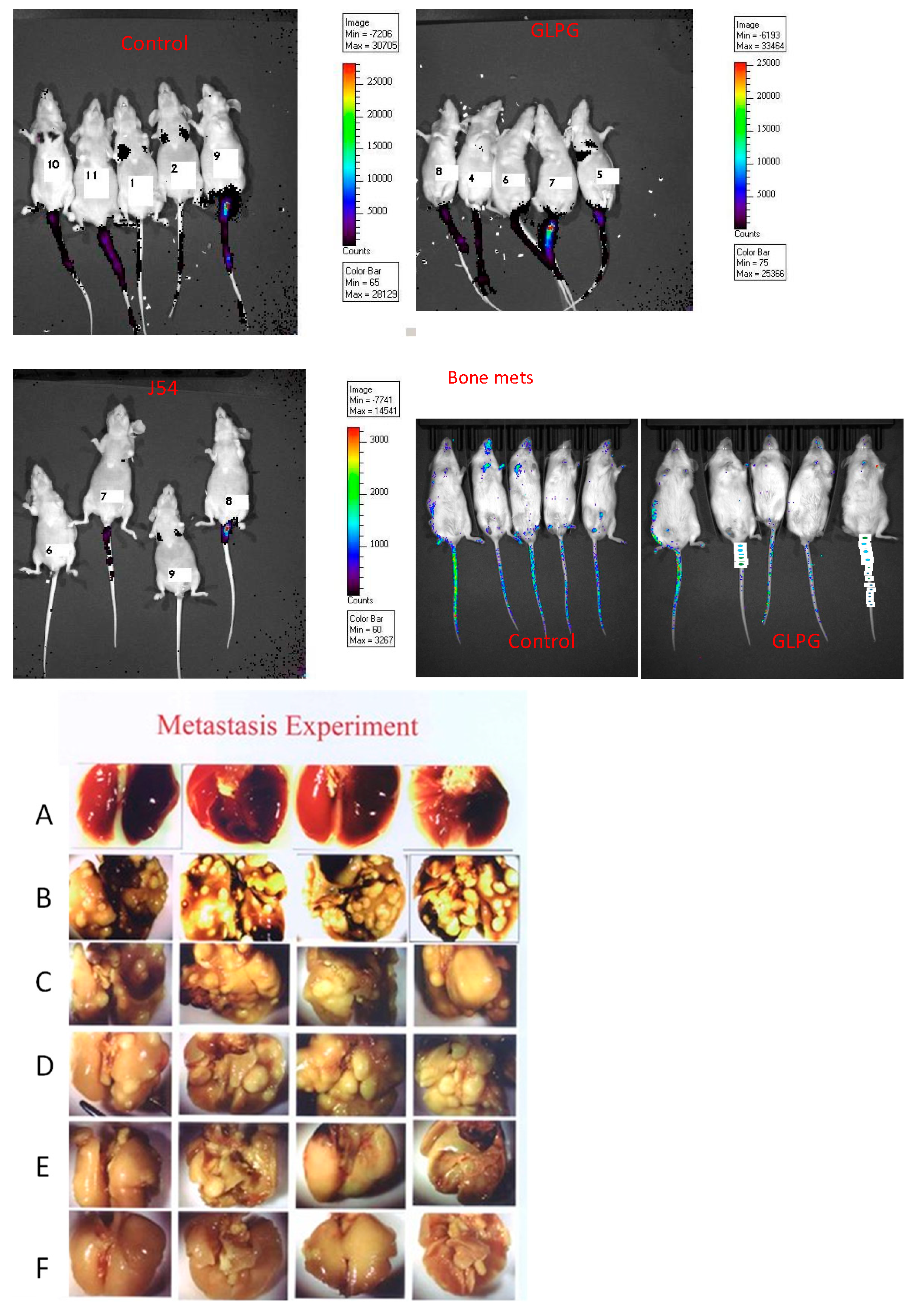
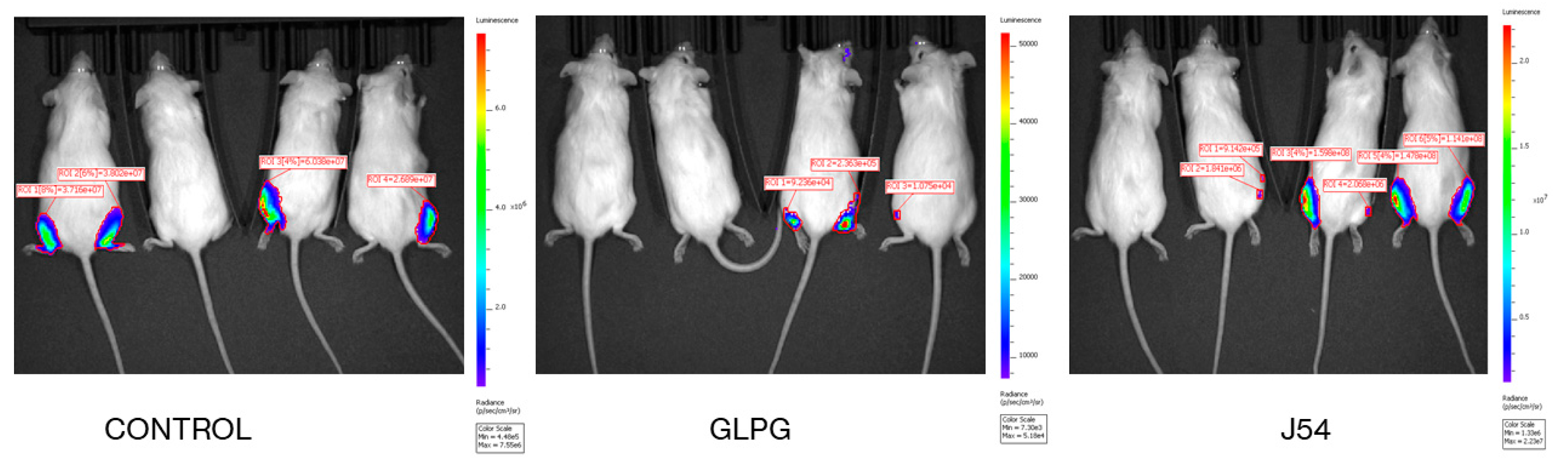
3.2. Reduction of Metastatic Spread with Inhibitors of TLK or MK5
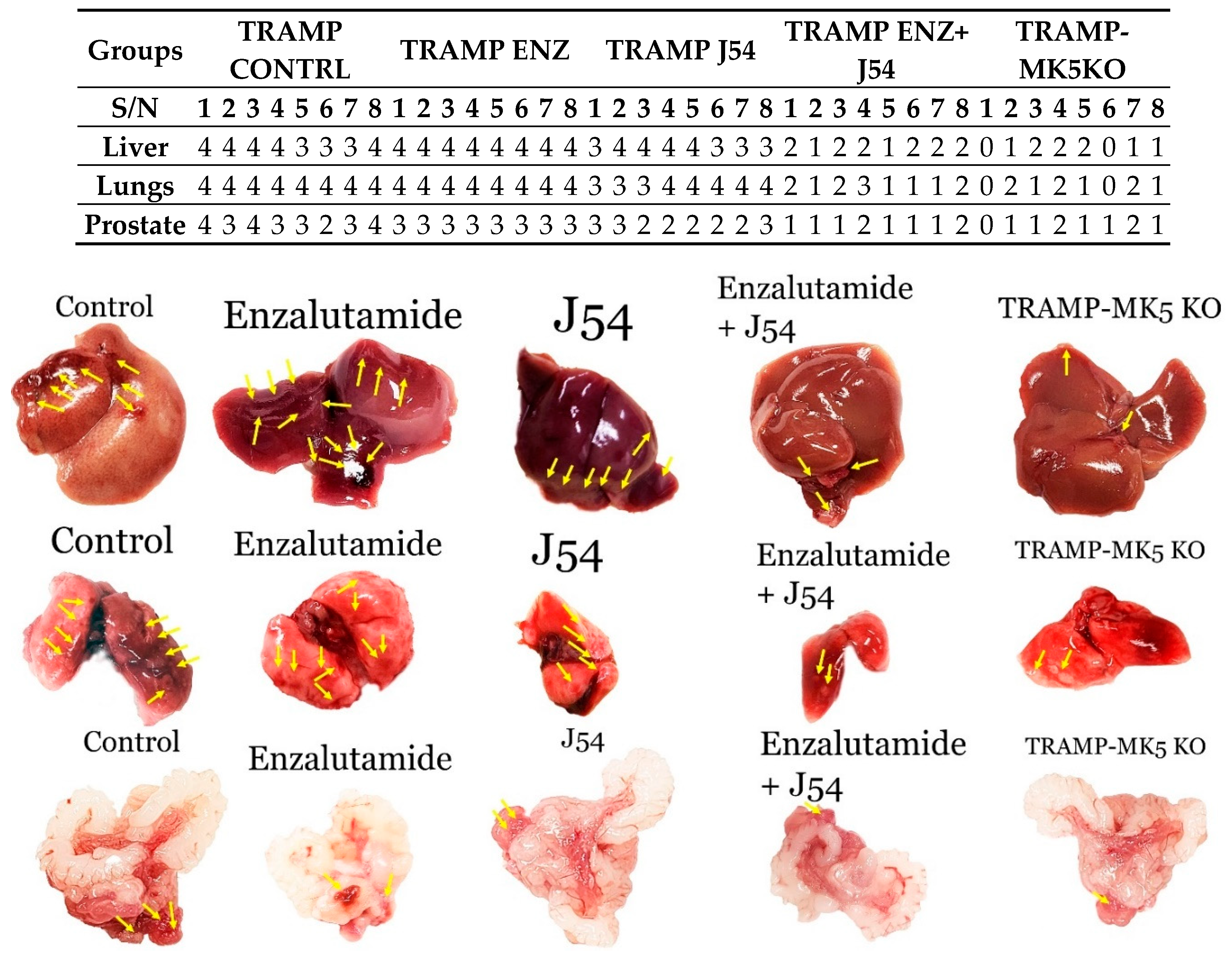
3.3. Role of TLK1>MK5 in Cancer Dissemination in a Mouse Model of Spontaneous PCa Progression
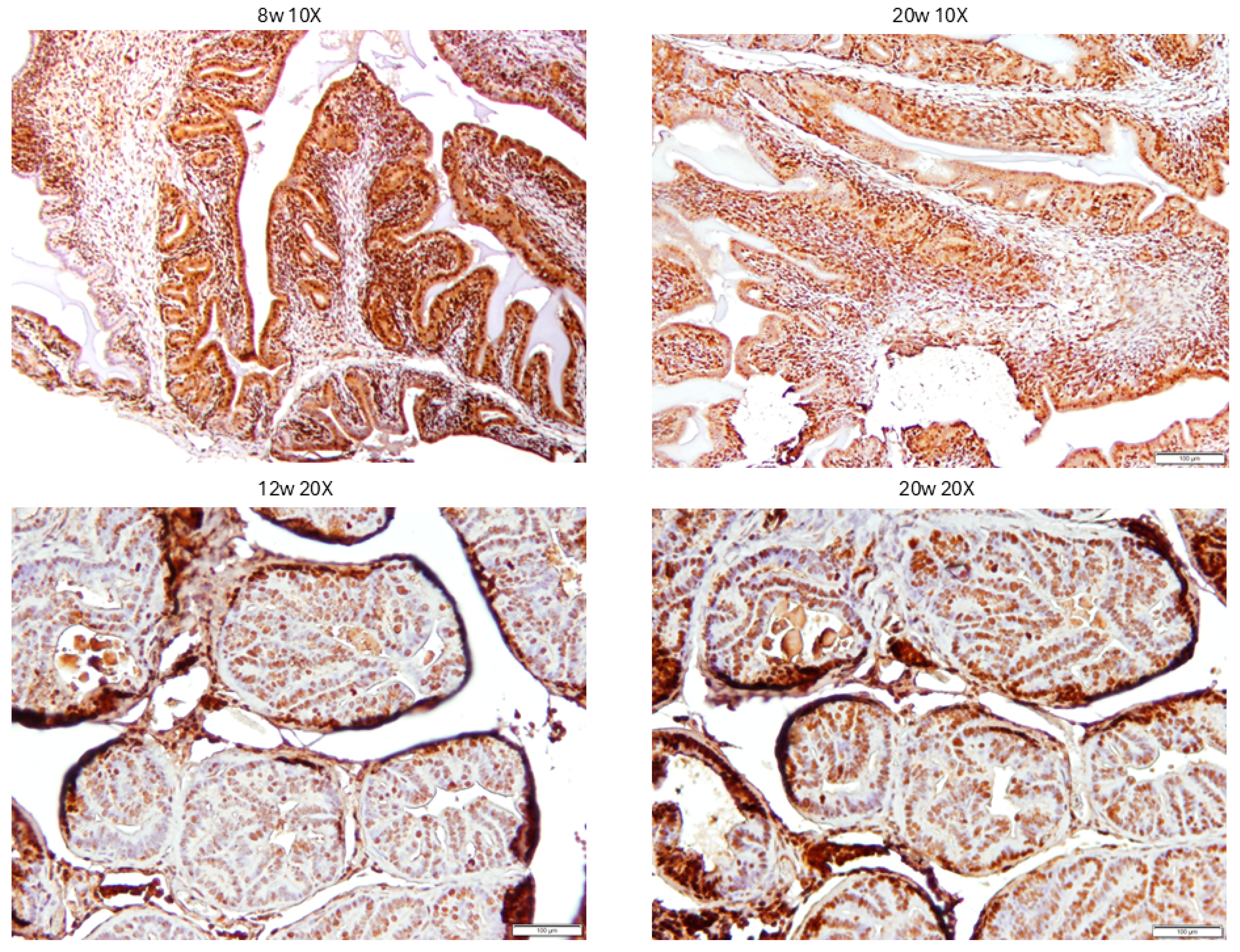
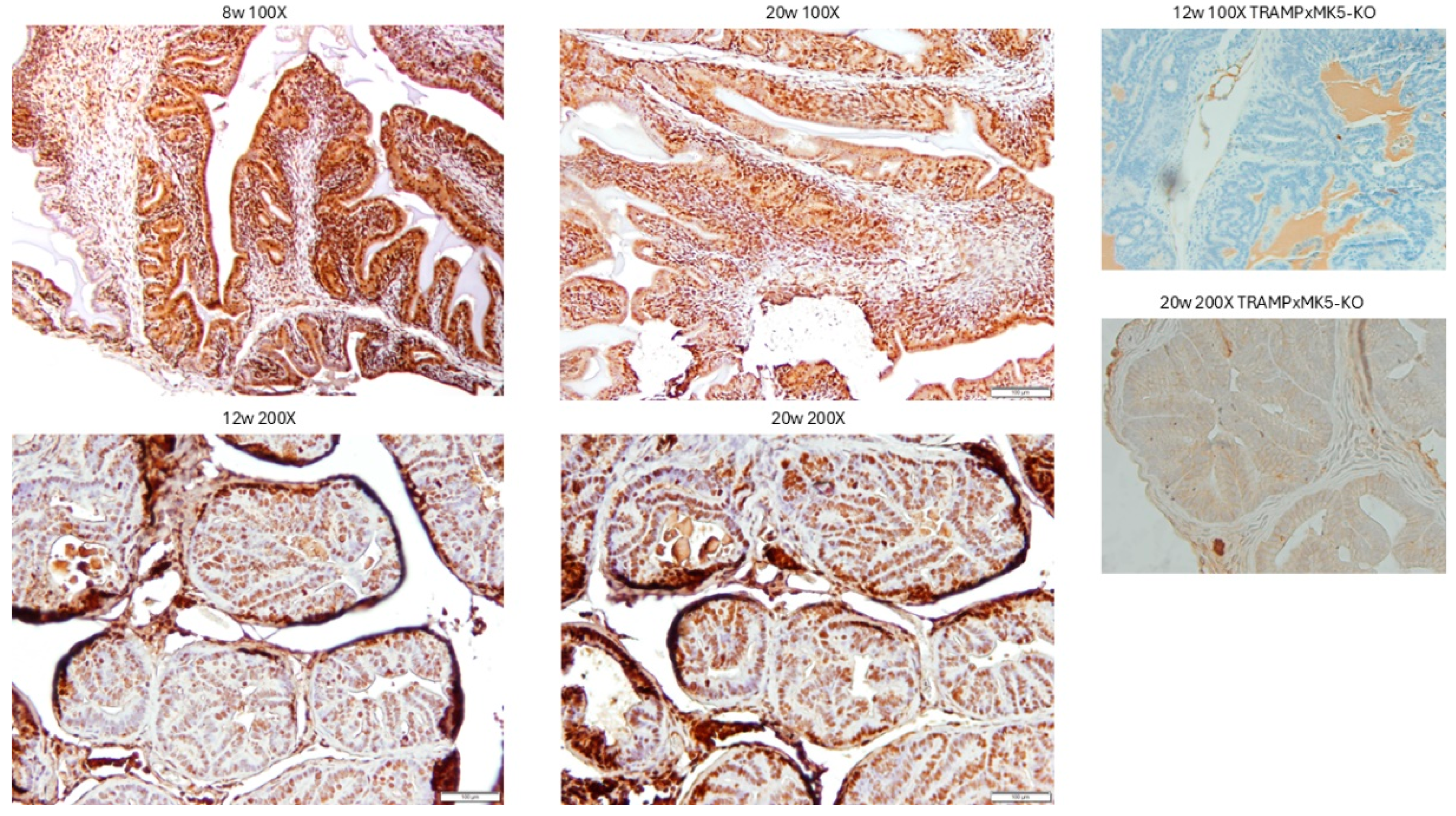
3.4. Evaluation of PCa Progression in TRAMP via IHC for pMK5 Ab.
3.5. Evaluation of PCa TMA with pMK5 Ab.
3.6. Direct Bone Engraftment
4. Disscussion
4.1. Choice of GLPG vs J54 in Clinical Translation
4.2. Specificity vs. General Toxicity Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halabi, S.; Kelly, W. K, Ma, H.; Zhou, H.; Solomon NC, Fizazi, K.; Tangen CM, Rosenthal, M.; Petrylak DP, Hussain M et al. Meta.-Analysis Evaluating the Impact of Site of Metastasis on Overall Survival in Men With Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Welch DR, Hurst DR: Defining the Hallmarks of Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3011–3027. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hood JD, Cheresh DA: Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer 2002, 2, 91–100. [CrossRef]
- Sillje HH, Takahashi, K. ; Tanaka, K.; Van Houwe, G.; Nigg EA: Mammalian homologues of the plant Tousled gene code for cell-cycle-regulated kinases with maximal activities linked to ongoing DNA replication. Embo J 1999, 18, 5691–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunavala-Dossabhoy, G.; Li, Y.; Williams, B.; De Benedetti A: A dominant negative mutant of TLK1 causes chromosome missegregation and aneuploidy in normal breast epithelial cells. BMC Cell Biol 2003, 4:16.
- Sunavala-Dossabhoy, G.; Fowler, M.; De Benedetti A: Translation of the radioresistance kinase TLK1B is induced by gamma-irradiation through activation of mTOR and phosphorylation of 4E-BP1. BMC Mol Biol 2004, 5:1.
- Sunavala-Dossabhoy, G.; Balakrishnan, S.; Sen, S.; Nuthalapaty, S.; De Benedetti A: The radioresistance kinase TLK1B protects the cells by promoting repair of double strand breaks. BMC Mol Biol 2005, 6:19.
- Sen, S.; De Benedetti A: TLK1B promotes repair of UV-damaged DNA through chromatin remodeling by Asf1. BMC Mol Biol 2006, 7:37.
- Canfield, C.; Rains, J.; De Benedetti, A. TLK1B promotes repair of DSBs via its interaction with Rad9 and Asf1. BMC Mol Biol 2009, 10:110.
- Li, Y.; DeFatta, R.; Anthony, C.; Sunavala, G.; De Benedetti, A. A translationally regulated Tousled kinase phosphorylates histone H3 and confers radioresistance when overexpressed. Oncogene 2001, 20, 726–738. [Google Scholar]
- Sunavala-Dossabhoy, G.; De Benedetti, A. Tousled homolog, TLK1, binds and phosphorylates Rad9; tlk1 acts as a molecular chaperone in DNA repair. DNA Repair 2009, 8:87-102.
- Lee, J. ; Kim MS, Park SH, Jang YK: Tousled-like kinase 1 is a negative regulator of core transcription factors in murine embryonic stem cells. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee S-B, Segura-Bayona, S. ; Villamor-Payà, M.; Saredi, G.; Todd MAM, Attolini CS-O, Chang T-Y, Stracker TH, Groth A: Tousled-like kinases stabilize replication forks and show synthetic lethality with checkpoint and PARP inhibitors. Science Advances 2018, 4, eaat4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Connelly ZM, Shen, X. ; De Benedetti A: Identification of the proteome complement of humanTLK1 reveals it binds and phosphorylates NEK1 regulating its activity. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Jaiswal PK, Ghosh, I. ; Koul HK, Yu, X.; De Benedetti A: Targeting the TLK1/NEK1 DDR axis with Thioridazine suppresses outgrowth of androgen independent prostate tumors. International journal of cancer 2019, 145, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh V, Jaiswal PK, Ghosh I, Koul HK, Yu X, De Benedetti A: The TLK1-Nek1 axis promotes prostate cancer progression. Cancer Lett 2019, 453:131-141. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh I, De Benedetti A: Untousling the Role of Tousled-like Kinase 1 in DNA Damage Repair. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 13369. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-Bayona S, Stracker TH: The Tousled-like kinases regulate genome and epigenome stability: Implications in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 2019, 76, 3827–3841. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim JA, Tan Y, Wang X, Cao X, Veeraraghavan J, Liang Y, Edwards DP, Huang, S.; Pan, X.; Li K et al. Comprehensive functional analysis of the tousled-like kinase 2 frequently amplified in aggressive luminal breast cancers. Nat Commun 2016, 7:12991. [CrossRef]
- Lin M, Yao Z, Zhao N, Zhang C: TLK2 enhances aggressive phenotypes of glioblastoma cells through the activation of SRC signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther 2019, 20, 101–108. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang W, Zhang D, Montell DJ: Tousled-like kinase regulates cytokine-mediated communication between cooperating cell types during collective border cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 2016, 27, 12–19. [CrossRef]
- Khalil MI, Singh V, King J, De Benedetti A: TLK1-mediated MK5-S354 phosphorylation drives prostate cancer cell motility and may signify distinct pathologies. Molecular Oncology 2022, 16, 2537–2557. [CrossRef]
- Gelman IH: How the TRAMP Model Revolutionized the Study of Prostate Cancer Progression. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 6137–6139. [CrossRef]
- Gingrich JR, Barrios RJ, Kattan MW, Nahm HS, Finegold MJ, Greenberg NM: Androgen-independent prostate cancer progression in the TRAMP model. Cancer Res 1997, 57, 4687–4691.
- Gingrich JR, Barrios RJ, Morton RA, Boyce BF, DeMayo FJ, Finegold MJ, Angelopoulou R, Rosen JM, Greenberg NM: Metastatic prostate cancer in a transgenic mouse. Cancer Res 1996, 56, 4096–4102.
- Cerasuolo M, Maccarinelli F, Coltrini D, Mahmoud AM, Marolda V, Ghedini GC, Rezzola S, Giacomini A, Triggiani, L. ; Kostrzewa M et al. Modeling Acquired Resistance to the Second-Generation Androgen Receptor Antagonist Enzalutamide in the TRAMP Model of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 1564–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh V, Jaiswal PK, Ghosh I, Koul HK, Yu X, De Benedetti A: The TLK1-Nek1 axis promotes prostate cancer progression. Cancer letters 2019, 453:131-141.
- Singh V, Bhoir S, Chikhale RV, Hussain J, Dwyer D, Bryce RA, Kirubakaran S, De Benedetti A: Generation of Phenothiazine with Potent Anti-TLK1 Activity for Prostate Cancer Therapy. iScience 2020, 23, 101474. [CrossRef]
- Singh V, Khalil MI, De Benedetti A: The TLK1/Nek1 axis contributes to mitochondrial integrity and apoptosis prevention via phosphorylation of VDAC1. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 363–375.
- Khalil MI, De Benedetti A: The TLK1–MK5 Axis Regulates Motility, Invasion, and Metastasis of Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 5728.
- Ronkina N, Gaestel M: MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases: Servant or Partner? Annu Rev Biochem 2022, 91:505-540.
- Schumacher S, Laass K, Kant S, Shi Y, Visel A, Gruber AD, Kotlyarov A, Gaestel M: Scaffolding by ERK3 regulates MK5 in development. Embo J 2004, 23, 4770–4779.
- Kant S, Schumacher S, Singh MK, Kispert A, Kotlyarov A, Gaestel M: Characterization of the atypical MAPK ERK4 and its activation of the MAPK-activated protein kinase MK5. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 35511–35519.
- Seternes OM, Mikalsen T, Johansen B, Michaelsen E, Armstrong CG, Morrice NA, Turgeon B, Meloche S, Moens U, Keyse SM: Activation of MK5/PRAK by the atypical MAP kinase ERK3 defines a novel signal transduction pathway. Embo J 2004, 23, 4780–4791.
- Åberg E, Perander M, Johansen B, Julien C, Meloche S, Keyse SM, Seternes O-M: Regulation of MAPK-activated Protein Kinase 5 Activity and Subcellular Localization by the Atypical MAPK ERK4/MAPK4*. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2006, 281, 35499–35510.
- Boudghene-Stambouli F, Soulez M, Ronkina N, Dörrie A, Kotlyarov A, Seternes OM, Gaestel M, Meloche S: On the Therapeutic Potential of ERK4 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 15.
- Coulombe P, Meloche S: Atypical mitogen-activated protein kinases: Structure, regulation and functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007, 1773, 1376–1387.
- Sun P, Yoshizuka N, New L, Moser BA, Li Y, Liao R, Xie C, Chen J, Deng Q, Yamout M et al. PRAK is essential for ras-induced senescence and tumor suppression. Cell 2007, 128, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizuka N, Chen RM, Xu Z, Liao R, Hong L, Hu WY, Yu G, Han J, Chen L, Sun P: A novel function of p38-regulated/activated kinase in endothelial cell migration and tumor angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2012, 32, 606–618.
- Wang Y, Wang W, Wu H, Zhou Y, Qin X, Wang Y, Wu J, Sun XY, Yang, Y. ; Xu H et al. The essential role of PRAK in tumor metastasis and its therapeutic potential. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkina N, Johansen C, Bohlmann L, Lafera J, Menon MB, Tiedje C, Laaß K, Turk BE, Iversen, L. ; Kotlyarov A et al. Comparative Analysis of Two Gene-Targeting Approaches Challenges the Tumor-Suppressive Role of the Protein Kinase MK5/PRAK. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136138. [Google Scholar]
- Seo J, Kim MH, Hong H, Cho H, Park S, Kim SK, Kim J: MK5 Regulates YAP Stability and Is a Molecular Target in YAP-Driven Cancers. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 6139–6152. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil MI, Ghosh I, Singh V, Chen J, Zhu H, De Benedetti A: NEK1 Phosphorylation of YAP Promotes Its Stabilization and Transcriptional Output. Cancers 2020, 12, 3666.
- Khalil MI, De Benedetti A: Tousled-like kinase 1: A novel factor with multifaceted role in mCRPC progression and development of therapy resistance. Cancer Drug Resistance 2022, 5, 93–101.
- Zheng M, Wang YH, Wu XN, Wu SQ, Lu BJ, Dong MQ, Zhang H, Sun P, Lin SC, Guan KL et al. Inactivation of Rheb by PRAK-mediated phosphorylation is essential for energy-depletion-induced suppression of mTORC1. Nat Cell Biol 2011, 13, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H, Huang S: Role of mTOR signaling in tumor cell motility, invasion and metastasis. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2011, 12, 30–42.
- Jiang J, Jia P, Zhao Z, Shen B: Key regulators in prostate cancer identified by co-expression module analysis. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:1015.
- Khalil MI, Singh V, King J, De Benedetti A: TLK1-mediated MK5-S354 phosphorylation drives prostate cancer cell motility and may signify distinct pathologies. Molecular Oncology, n/a(n/a).
- Elkin M, Vlodavsky I: Tail vein assay of cancer metastasis. Current protocols in cell biology 2001, 12, 19.12–11.
- Namour F, Vanhoutte FP, Beetens J, Blockhuys S, De Weer M, Wigerinck P: Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of GLPG0259, a mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 5 (MAPKAPK5) inhibitor, given as single and multiple doses to healthy male subjects. Drugs in R&D 2012, 12, 141–163.
- Westhovens R, Keyser FD, Rekalov D, Nasonov EL, Beetens J, Van der Aa A, Wigerinck P, Namour F, Vanhoutte F, Durez P: Oral administration of GLPG0259, an inhibitor of MAPKAPK5, a new target for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A phase II, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2013, 72, 741–744. [CrossRef]
- Olatunde D, De Benedetti A: TLK1>Nek1 Axis Promotes Nuclear Retention and Activation of YAP with Implications for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2918. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart SB, Cheville JC, Sebo TJ, Frank I, Boorjian SA, Thompson RH, Gettman MT, Tollefson MK, Umbriet EC, Psutka SP et al. Gleason grading after neoadjuvant hormonal therapy retains prognostic value for systemic progression following radical prostatectomy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2014, 17, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow A, Chen D, Lang JE: The current status of the clinical utility of liquid biopsies in cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2019, 19, 1031–1041. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng Z, Yi Z, Xu B: The biological and technical challenges facing utilizing circulating tumor DNA in non-metastatic breast cancer patients. Cancer Letters 2025, 616:217574.
- Yu FX, Zhao B, Guan KL: Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 811–828. [CrossRef]
- Kim MH, Kim CG, Kim SK, Shin SJ, Choe EA, Park SH, Shin EC, Kim J: YAP-Induced PD-L1 Expression Drives Immune Evasion in BRAFi-Resistant Melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res 2018, 6, 255–266. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh I, Kwon Y, Shabestari AB, Chikhale R, Chen J, Wiese C, Sung P, De Benedetti A: TLK1-mediated RAD54 phosphorylation spatio-temporally regulates Homologous Recombination Repair. Nucleic Acids Research 2023.
- Mardis ER: Neoantigens and genome instability: Impact on immunogenomic phenotypes and immunotherapy response. Genome Medicine 2019, 11, 71. [CrossRef]
- Namour F, Vanhoutte FP, Beetens J, Blockhuys S, De Weer M, Wigerinck P: Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of GLPG0259, a mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 5 (MAPKAPK5) inhibitor, given as single and multiple doses to healthy male subjects. Drugs R D 2012, 12, 141–163.
- Sahadevan P, Allen BG: MK5: A novel regulator of cardiac fibroblast function? IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 785–794. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




