Submitted:
27 February 2025
Posted:
28 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Magnetic Resonance Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.4. Seed-Based FC Analyses
2.5. Clinical Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Clinical Information
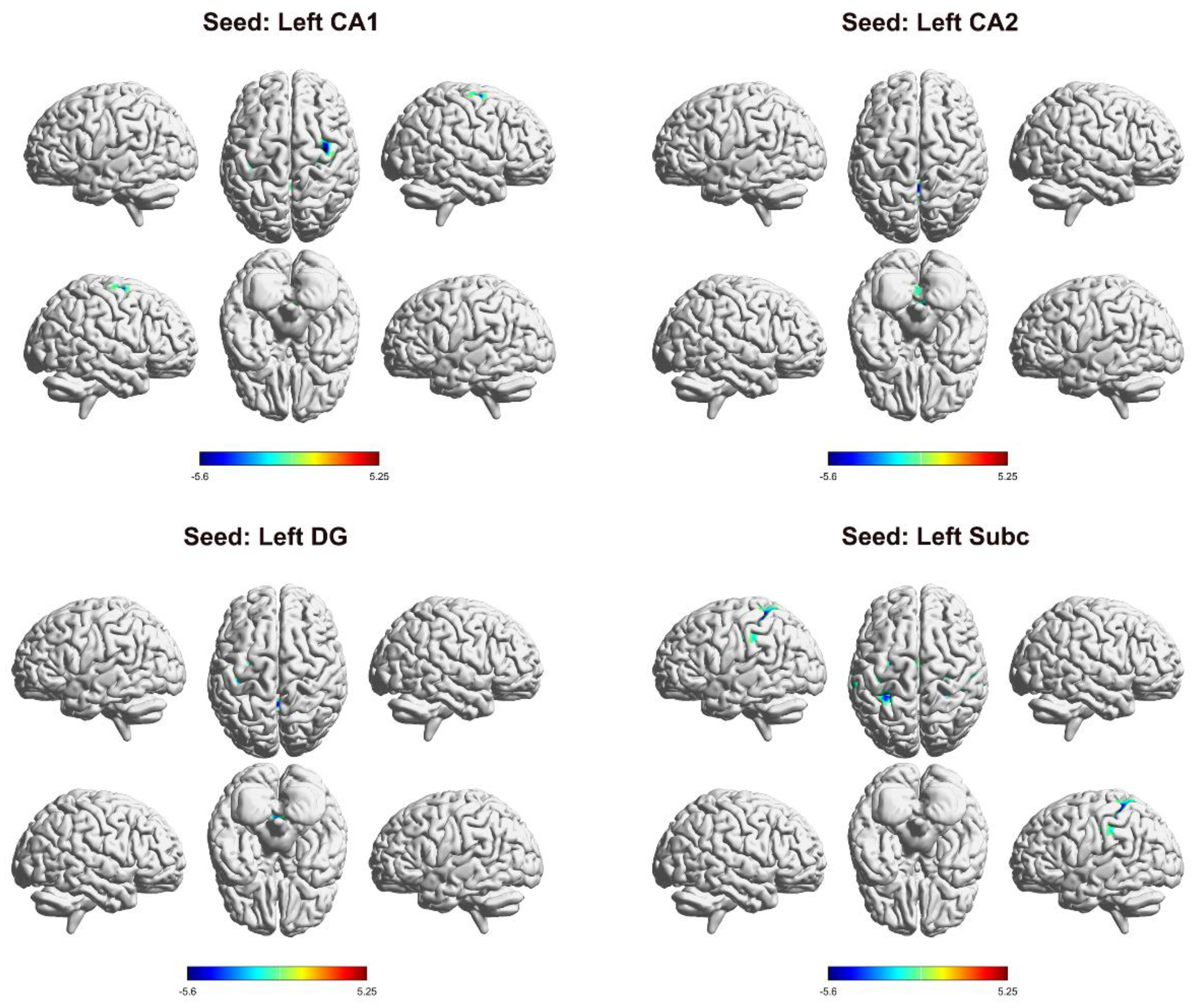
3.2. Differences in FC in the Left Hippocampal Subregion
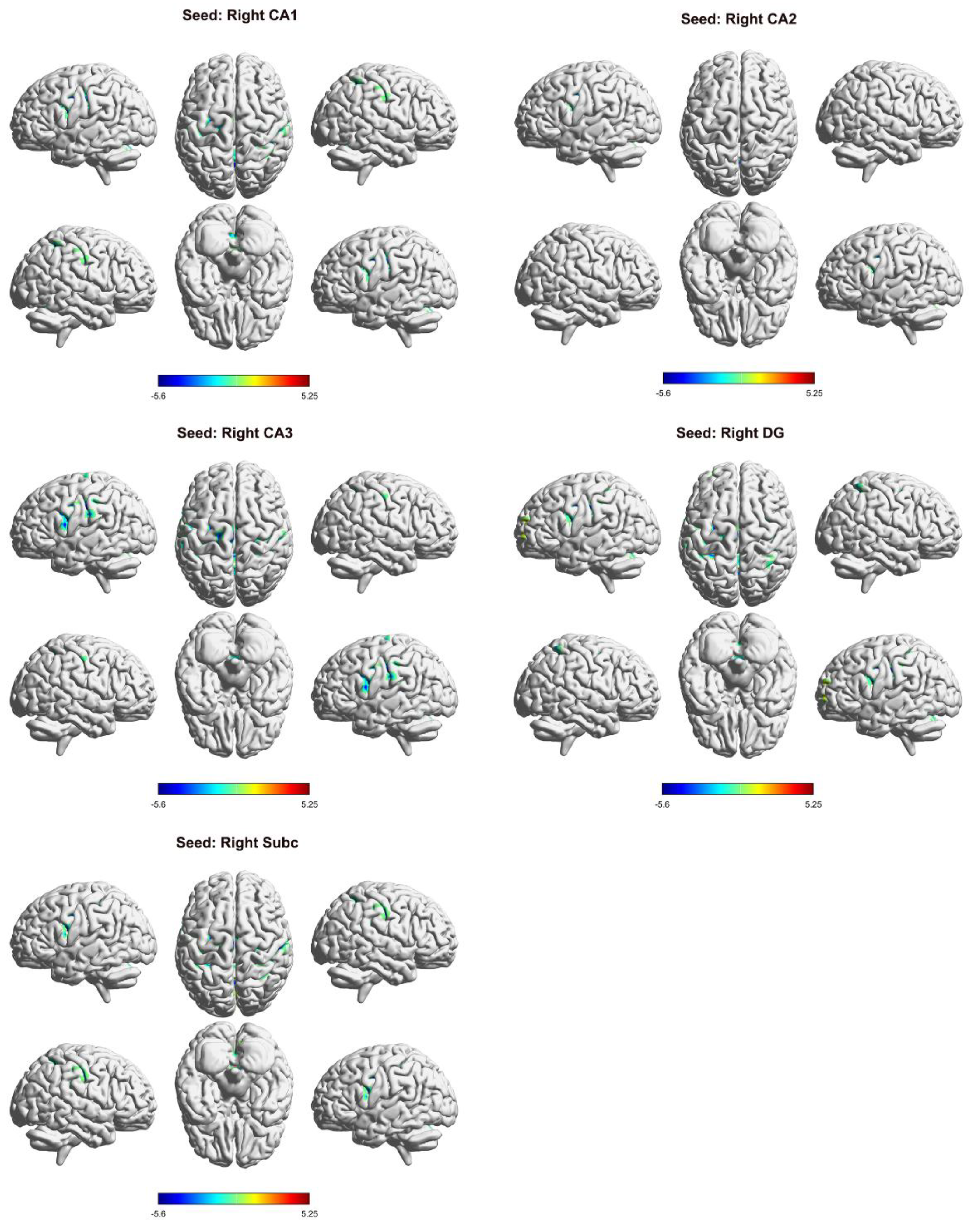
3.3. Differences in FC in the Right Hippocampal Subregion
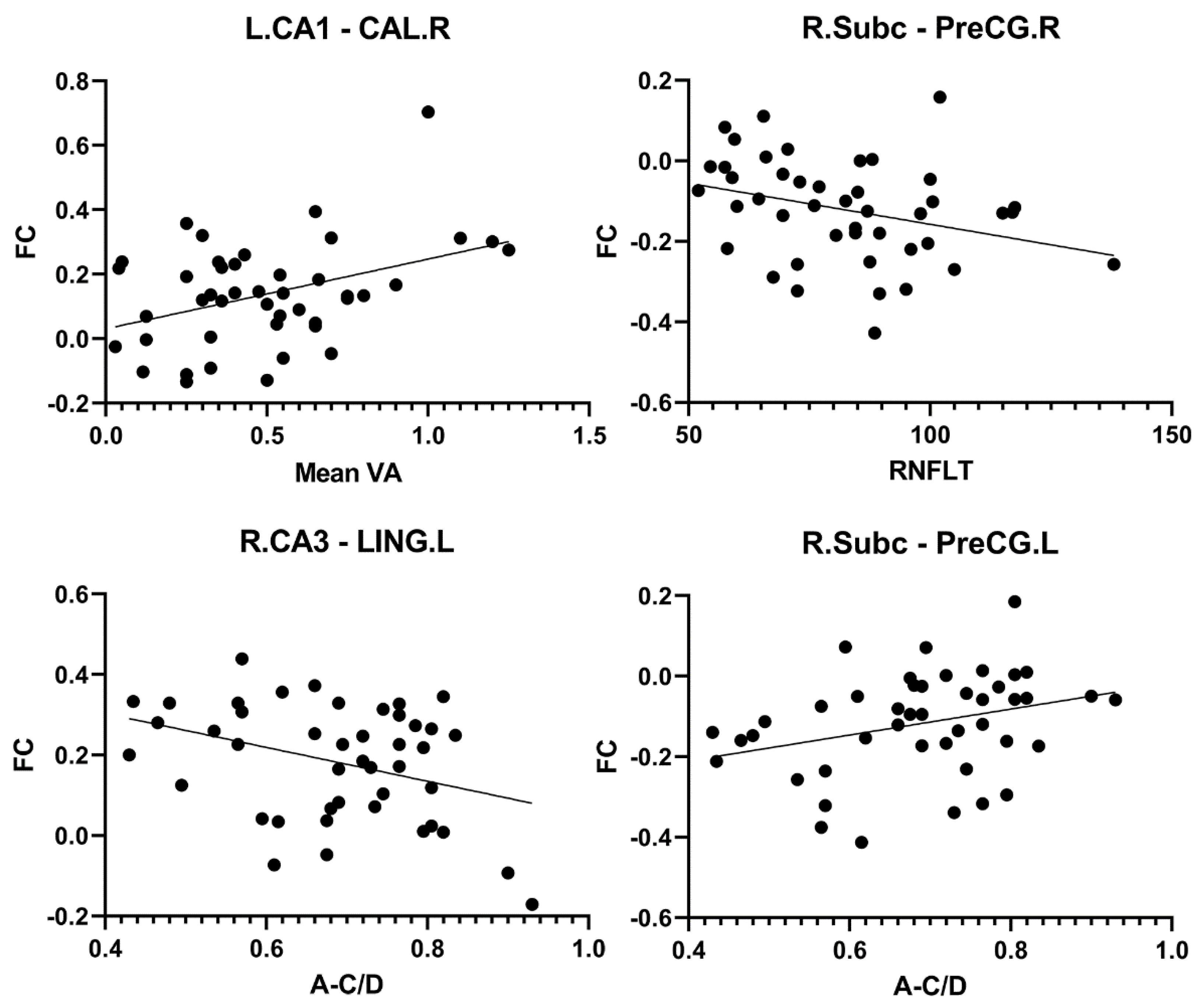
3.4. Correlation Between Hippocampal FC and Clinical Indices in PACG Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flaxman, S. R.; Bourne, R. R. A.; Resnikoff, S.; Ackland, P.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M. V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J. B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J. H.; et al. Global Causes of Blindness and Distance Vision Impairment 1990–2020: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The Lancet Global Health 2017, 5 (12), e1221–e1234. [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J. D.; Bourne, R. R. A.; Briant, P. S.; Flaxman, S. R.; Taylor, H. R. B.; Jonas, J. B.; Abdoli, A. A.; Abrha, W. A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E. G.; et al. Causes of Blindness and Vision Impairment in 2020 and Trends over 30 Years, and Prevalence of Avoidable Blindness in Relation to VISION 2020: The Right to Sight: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. The Lancet Global Health 2021, 9 (2), e144–e160. [CrossRef]
- Tham, Y.-C.; Li, X.; Wong, T. Y.; Quigley, H. A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.-Y. Global Prevalence of Glaucoma and Projections of Glaucoma Burden through 2040: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121 (11), 2081–2090. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N. Human Glaucoma and Neural Degeneration in Intracranial Optic Nerve, Lateral Geniculate Nucleus, and Visual Cortex. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2006, 90 (6), 674–678. [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, A. C.; Liu, J. Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection in Glaucoma. Yale J Biol Med. 2016, 89(1), 73-79.
- Li, C.; Cai, P.; Shi, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Xie, B.; Shi, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; et al. Voxel-Based Morphometry of the Visual-Related Cortex in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Curr Eye Res. 2012, 37 (9), 794–802. [CrossRef]
- Williams, A. L.; Lackey, J.; Wizov, S. S.; Chia, T. M. T.; Gatla, S.; Moster, M. L.; Sergott, R.; Spaeth, G. L.; Lai, S. Evidence for Widespread Structural Brain Changes in Glaucoma: A Preliminary Voxel-Based MRI Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013, 54 (8), 5880–5887. [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Rong, R.; Zeng, Z.; Xia, X.; Ji, D. Transneuronal Degeneration in the Brain During Glaucoma. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 643685. [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Saxena, R.; Tripathi, M.; Vibha, D.; Dhiman, R. Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease and Glaucoma: Overlaps and Missing Links. Eye 2020, 34 (9), 1546–1553. [CrossRef]
- Neacșu, A. M.; Ferechide, D. Glaucoma - a Neurodegenerative Disease with Cerebral Neuroconnectivity Elements. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2022, 66 (3), 219–224. [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-J.; Liu, C. J.-L.; Wojciechowski, R.; Bailey-Wilson, J. E.; Cheng, C.-Y. Structure-Function Correlations Using Scanning Laser Polarimetry in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010, 149 (5), 817-825.e1. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Zeng, X.-J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, X.-H.; Hu, P.-H.; Pei, C.-G.; Shao, Y.; Dai, X.-J. Disturbed Spontaneous Brain Activity Pattern in Patients with Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Using Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation: A fMRI Study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015, 11, 1877–1883. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, Z.; Liu, T.; Sun, X.; Wu, L.; Xiao, Z. Altered Spontaneous Neuronal Activity and Functional Connectivity Pattern in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma: A Resting-State fMRI Study. Neurol Sci. 2021, 42 (1), 243–251. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Y. L. The Predictive Values of Changes in Local and Remote Brain Functional Connectivity in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients According to Support Vector Machine Analysis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 910669. [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Gao, L.; Gong, H.; Jiang, F.; Pei, C.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, X.; Huang, R. Network Centrality of Resting-State fMRI in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Before and After Surgery. PLoS One 2015, 10 (10), e0141389. [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-B.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Liu, H.; Huang, X. Machine Learning Analysis Reveals Abnormal Functional Network Hubs in the Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 935213. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Cai, G.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, J.; Zeng, X. Effects of Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma on Interhemispheric Functional Connectivity. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1053114. [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhong, Y. L.; Liu, H.; Huang, X. Disrupted Interhemispheric Functional Connectivity in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma: A Functional MRI Study: Voxel-Mirrored Homotopic Connectivity in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients. NeuroReport 2022, 33 (14), 604–611. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gao, J.; You, T.; Li, S.; Cai, F.; Pei, C.; Zeng, X. Brain Functional Network Analysis of Patients with Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma. Disease Markers 2022, 2022, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Cai, F.; Wu, L.; Gong, H.; Pei, C.; Zhou, F.; Zeng, X. Altered Functional Connectivity Density in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients at Resting-State. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019, 9 (4), 603–614. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Fang, J.-W.; Ye, Y.-Q.; Tian, Y.-J.; Zeng, X.-J.; Zhong, Y.-L. Altered Effective Connectivity of Primary Visual Cortex in Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma Using Granger Causality Analysis. Acta Radiol. 2020, 61 (4), 508–519. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, P.; Gong, H.; Jiang, F.; Liu, D.; Cai, F.; Pei, C.; Zhou, F.; Zeng, X. Intrinsic Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Primary Visual Cortex in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients before and after Surgery: A Resting-State fMRI Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12 (1), e0170598. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Cai, F.; Gao, J.; Ouyang, F.; Chen, Y.; Yin, M.; Hua, C.; Zeng, X. Altered Functional Connectivity of the Thalamus in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients: A Resting-State fMRI Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1015758. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ouyang, F.; Yin, M.; Lv, L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X. Altered Resting-State Amygdalar Functional Connectivity in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2024, 23 (4), 75. [CrossRef]
- Park, D. Y.; Kim, M.; Bae, Y.; Jang, H.; Lim, D. H. Risk of Dementia in Newly Diagnosed Glaucoma: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea. Ophthalmology 2023, 130 (7), 684–691. [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Obayashi, K.; Miyata, K.; Saeki, K.; Ogata, N. Lower Cognitive Function in Patients With Functionally and Structurally Severe Glaucoma: The LIGHT Study. Journal of Glaucoma 2021, 30 (10), 882–886. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. H.; Han, J. W.; Lee, E. J.; Kim, T.-W.; Kim, H.; Kim, K. W. Cognitive Impairment and Lamina Cribrosa Thickness in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Trans. Vis. Sci. Tech. 2020, 9 (7), 17. [CrossRef]
- Crump, C.; Sundquist, J.; Sieh, W.; Sundquist, K. Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias in Persons with Glaucoma: A National Cohort Study. Ophthalmology 2024, 131 (3), 302–309. [CrossRef]
- Bird, C. M.; Burgess, N. The Hippocampus and Memory: Insights from Spatial Processing. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008, 9 (3), 182–194. [CrossRef]
- Slotnick, S. D. The Hippocampus and Long-Term Memory. Cogn Neurosci. 2022, 13 (3–4), 113–114. [CrossRef]
- Pronier, É.; Morici, J. F.; Girardeau, G. The Role of the Hippocampus in the Consolidation of Emotional Memories during Sleep. Trends Neurosci. 2023, 46 (11), 912–925. [CrossRef]
- Babcock, K. R.; Page, J. S.; Fallon, J. R.; Webb, A. E. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Stem Cell Reports 2021, 16 (4), 681–693. [CrossRef]
- Kim, T. A.; Syty, M. D.; Wu, K.; Ge, S. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Its Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease. Zool Res. 2022, 43 (3), 481–496. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhong, X.; Hou, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Mai, N.; Zhou, H.; et al. Static and Dynamic Functional Connectivity Variability of the Anterior-Posterior Hippocampus with Subjective Cognitive Decline. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022, 14 (1), 122. [CrossRef]
- Neunuebel, J. P.; Knierim, J. J. CA3 Retrieves Coherent Representations from Degraded Input: Direct Evidence for CA3 Pattern Completion and Dentate Gyrus Pattern Separation. Neuron. 2014, 81 (2), 416–427. [CrossRef]
- Hodgetts, C. J.; Voets, N. L.; Thomas, A. G.; Clare, S.; Lawrence, A. D.; Graham, K. S. Ultra-High-Field fMRI Reveals a Role for the Subiculum in Scene Perceptual Discrimination. J Neurosci. 2017, 37 (12), 3150–3159. [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Fernandez-Ruiz, A.; Karaba, L. A. CA2 Orchestrates Hippocampal Network Dynamics. Hippocampus 2023, 33 (3), 241–251. [CrossRef]
- Middleton, S. J.; McHugh, T. J. CA2: A Highly Connected Intrahippocampal Relay. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2020, 43, 55–72. [CrossRef]
- Amunts, K.; Kedo, O.; Kindler, M.; Pieperhoff, P.; Mohlberg, H.; Shah, N. J.; Habel, U.; Schneider, F.; Zilles, K. Cytoarchitectonic Mapping of the Human Amygdala, Hippocampal Region and Entorhinal Cortex: Intersubject Variability and Probability Maps. Anat Embryol (Berl) 2005, 210 (5–6), 343–352. [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, S. B.; Stephan, K. E.; Mohlberg, H.; Grefkes, C.; Fink, G. R.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. A New SPM Toolbox for Combining Probabilistic Cytoarchitectonic Maps and Functional Imaging Data. Neuroimage 2005, 25 (4), 1325–1335. [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z. S.; Phillips, N. A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J. L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005, 53 (4), 695–699. [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.-G.; Wang, X.-D.; Zuo, X.-N.; Zang, Y.-F. DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (Resting-State) Brain Imaging. Neuroinformatics 2016, 14 (3), 339–351. [CrossRef]
- Buckner, R. L. The Cerebellum and Cognitive Function: 25 Years of Insight from Anatomy and Neuroimaging. Neuron. 2013, 80 (3), 807–815. [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, S.; Badura, A.; Lutzu, S.; Pathak, S. S.; Thieme, A.; Verpeut, J. L.; Wagner, M. J.; Yang, Y.-M.; Fioravante, D. Cognitive-Affective Functions of the Cerebellum. J Neurosci. 2023, 43 (45), 7554–7564. [CrossRef]
- Koziol, L. F.; Budding, D.; Andreasen, N.; D’Arrigo, S.; Bulgheroni, S.; Imamizu, H.; Ito, M.; Manto, M.; Marvel, C.; Parker, K.; et al. Consensus Paper: The Cerebellum’s Role in Movement and Cognition. Cerebellum 2014, 13 (1), 151–177. [CrossRef]
- Abderrakib, A.; Ligot, N.; Naeije, G. Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome after Acute Cerebellar Stroke. Front Neurol. 2022, 13, 906293. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qu, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Xian, J. Arterial Spin Labeling Reveals Disordered Cerebral Perfusion and Cerebral Blood Flow-Based Functional Connectivity in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Brain Imaging and Behavior 2023, 18 (1), 231–242. [CrossRef]
- Iglói, K.; Doeller, C. F.; Paradis, A.-L.; Benchenane, K.; Berthoz, A.; Burgess, N.; Rondi-Reig, L. Interaction Between Hippocampus and Cerebellum Crus I in Sequence-Based but Not Place-Based Navigation. Cereb Cortex 2015, 25 (11), 4146–4154. [CrossRef]
- Onuki, Y.; Van Someren, E. J. W.; De Zeeuw, C. I.; Van der Werf, Y. D. Hippocampal-Cerebellar Interaction during Spatio-Temporal Prediction. Cereb Cortex 2015, 25 (2), 313–321. [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M. F. A.; Heba, S.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Tegenthoff, M.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Cerebellar-Hippocampal Processing in Passive Perception of Visuospatial Change: An Ego- and Allocentric Axis? Hum Brain Mapp. 2020, 41 (5), 1153–1166. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhan, Y.; Duan, F.; Cheng, J.; Tang, Z. The Alterations of Brain Network Degree Centrality in Patients with Neovascular Glaucoma: A Resting-State fMRI Study. Neurol Sci. 2023, 44 (8), 2915–2922. [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Morelli, J. N.; Ai, F.; Yin, D.; Hu, C.; Xu, D.; Li, Y. Resting-State Functional MRI: Functional Connectivity Analysis of the Visual Cortex in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients: Functional Connectivity in Glaucoma. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34 (10), 2455–2463. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shu, Y.; Cai, G.; Guo, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Lv, L.; Zeng, X. Altered Static and Dynamic Functional Network Connectivity in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Patients. Sci Rep. 2024, 14 (1), 11682. [CrossRef]
- Kurysheva, N. I.; Lepeshkina, L. V. Detection of Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma Progression by Optical Coherence Tomography. J Glaucoma. 2021, 30 (5), 410–420. [CrossRef]
- Igelström, K. M.; Graziano, M. S. A. The Inferior Parietal Lobule and Temporoparietal Junction: A Network Perspective. Neuropsychologia 2017, 105, 70–83. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qu, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, C.; Li, T.; Wang, N.; Xian, J. Altered Coupling of Cerebral Blood Flow and Functional Connectivity Strength in Visual and Higher Order Cognitive Cortices in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41 (4), 901–913. [CrossRef]
- Chadick, J. Z.; Gazzaley, A. Differential Coupling of Visual Cortex with Default or Frontal-Parietal Network Based on Goals. Nat Neurosci. 2011, 14 (7), 830–832. [CrossRef]
- Harmelech, T.; Friedman, D.; Malach, R. Differential Magnetic Resonance Neurofeedback Modulations across Extrinsic (Visual) and Intrinsic (Default-Mode) Nodes of the Human Cortex. J Neurosci. 2015, 35 (6), 2588–2595. [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R. O.; Sample, P. A.; Bowd, C.; Weinreb, R. N.; Zangwill, L. M. Arterial Spin Labeling fMRI Measurements of Decreased Blood Flow in Primary Visual Cortex Correlates with Decreased Visual Function in Human Glaucoma. Vision Res. 2012, 60, 51–60. [CrossRef]
- Fathian, A.; Jamali, Y.; Raoufy, M. R.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. The Trend of Disruption in the Functional Brain Network Topology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci Rep. 2022, 12 (1), 14998. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Suppiah, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Mohamad, M.; Hassan, H. A.; Nasser, N. S.; Saripan, M. I. Diagnostic Power of Resting-State fMRI for Detection of Network Connectivity in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021, 42 (9), 2941–2968. [CrossRef]
- Marin-Marin, L.; Miró-Padilla, A.; Costumero, V. Structural But Not Functional Connectivity Differences within Default Mode Network Indicate Conversion to Dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 91 (4), 1483–1494. [CrossRef]
- Zheng W.; Cui B.; Han Y.; Song H.; Li K.; He Y.; Wang Z. Disrupted Regional Cerebral Blood Flow, Functional Activity and Connectivity in Alzheimer's Disease: A Combined ASL Perfusion and Resting State fMRI Study. Front Neurosci. 2019, 13, 738. [CrossRef]
- Tondelli, M.; Ballotta, D.; Maramotti, R.; Carbone, C.; Gallingani, C.; MacKay, C.; Pagnoni, G.; Chiari, A.; Zamboni, G. Resting-State Networks and Anosognosia in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1415994. [CrossRef]
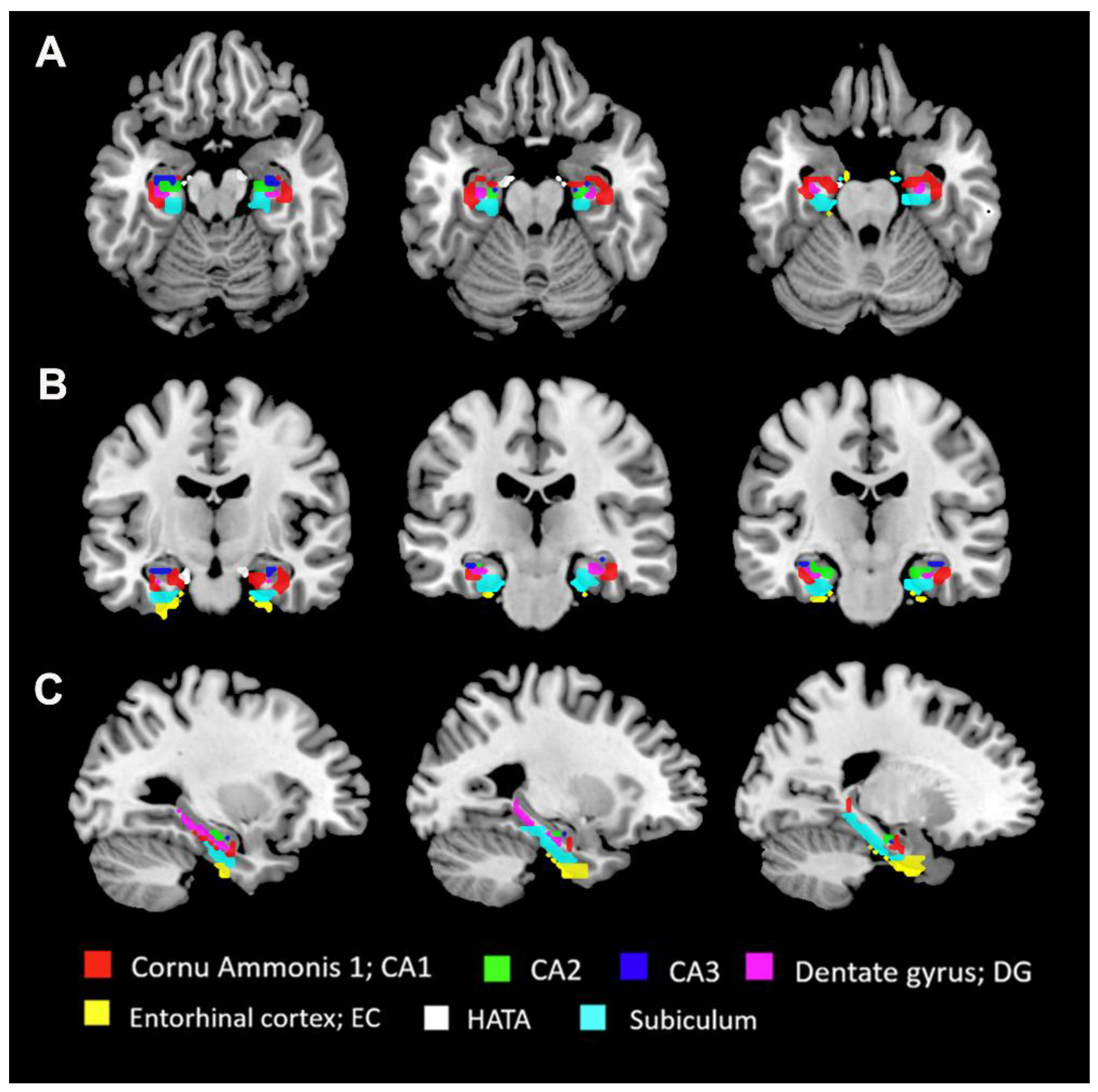
| Condition | PACG(n=44) | HC(n=46) | p value | Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(years) | 55.64±9.04 | 54.61±8.93 | 0.589 | 0.542 |
| Gender(male/female) | 16/28 | 18/28 | 0.787 | 0.073 |
| Education level(years) | 8.89±3.36 | 9.43±2.7 | 0.394 | -0.856 |
| Disease duration(years) | 0.45 (0.04,1) | - | - | - |
| Mean VA | 0.5±0.3 | 1.11±0.18 | <0.001 | -11.838 |
| IOP(mmHg) | 28.56±8.75 | 15.53±2.05 | <0.001 | 9.82 |
| RNFLT(μm) | 82.23±19.46 | 117.1±8.52 | <0.001 | -11.097 |
| A-C/D | 0.69±0.12 | 0.46±0.1 | <0.001 | 9.784 |
| V-C/D | 0.66±0.17 | 0.5±0.08 | <0.001 | 5.767 |
| MoCA | 22.43±3.07 | 27.04±1.43 | <0.001 | -9.205 |
| seed | brain region | MNI | Voxels | t value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||||
| L_CA1 | cerebellum | 15 | -45 | -33 | 82 | -5.1998 |
| CAL_R | 18 | -60 | 6 | 68 | 5.2531 | |
| PreCG_R | 39 | -6 | 66 | 157 | -5.603 | |
| PreCG_L | -30 | -18 | 51 | 78 | -5.3584 | |
| L_CA2 | cerebellum | 0 | -48 | -12 | 173 | -5.9324 |
| L_DG | cerebellum | 0 | -51 | -21 | 119 | -5.2706 |
| PreCG_L | -30 | -21 | 51 | 150 | -5.5942 | |
| L_Subc | PoCG_R | 27 | -42 | 45 | 267 | -6.2276 |
| SMG_L | -48 | -33 | 30 | 165 | -5.0492 | |
| PreCG_L | -27 | -12 | 51 | 116 | -5.0965 | |
| SMA_L | -3 | -6 | 57 | 67 | -4.5938 | |
| R_CA1 | cerebellum | 15 | -48 | -27 | 337 | -6.1275 |
| PreCG_L | -45 | 0 | 36 | 144 | -5.5733 | |
| SMG_L | -51 | -21 | 36 | 286 | -5.1464 | |
| PoCG_R | 39 | -33 | 48 | 210 | -4.9792 | |
| R_CA2 | cerebellum | 21 | -60 | -33 | 107 | -5.1806 |
| IFGoperc_L | -45 | 3 | 27 | 64 | -4.8923 | |
| R_CA3 | cerebellum | 21 | -57 | -33 | 290 | -5.2591 |
| LING_L | -15 | -51 | 0 | 145 | 5.3832 | |
| CAL_R | 18 | -60 | 9 | 99 | 5.4462 | |
| PoCG_L | -51 | -18 | 36 | 1743 | -5.5171 | |
| PAL_R | 18 | 6 | 3 | 56 | -4.47 | |
| ROL_R | 57 | 6 | 15 | 91 | -4.4437 | |
| R_DG | cerebellum | 21 | -60 | -33 | 352 | -5.8117 |
| ACG | 0 | 42 | 12 | 218 | 5.023 | |
| PreCG_L | -36 | 3 | 30 | 113 | -5.0394 | |
| IPL_R | 36 | -45 | 39 | 107 | -4.5107 | |
| PreCG_R | 36 | -9 | 45 | 120 | -5.3434 | |
| IPL_L | -27 | -12 | 51 | 457 | -5.6223 | |
| SMA_L | -3 | -6 | 54 | 116 | -5.3053 | |
| R_Subc | cerebellum | 21 | -60 | -33 | 199 | -5.0727 |
| CAL_L | -9 | -69 | 18 | 318 | 5.0858 | |
| PreCG_R | 45 | 3 | 30 | 67 | -4.5003 | |
| PreCG_L | -45 | 0 | 39 | 77 | -4.4107 | |
| PoCG_R | 39 | -33 | 48 | 1078 | -5.3631 | |
| seed | Brain region | clinical parameter | r value | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L_CA1 | CAL_R | Mean VA | 0.396 | 0.008 |
| R_Subc | PreCG_R | RNFLT | -0.312 | 0.039 |
| R_CA3 | LING_L | A-C/D | -0.358 | 0.017 |
| R_Subc | PreCG_L | A-C/D | 0.311 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





