Submitted:
24 February 2025
Posted:
25 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
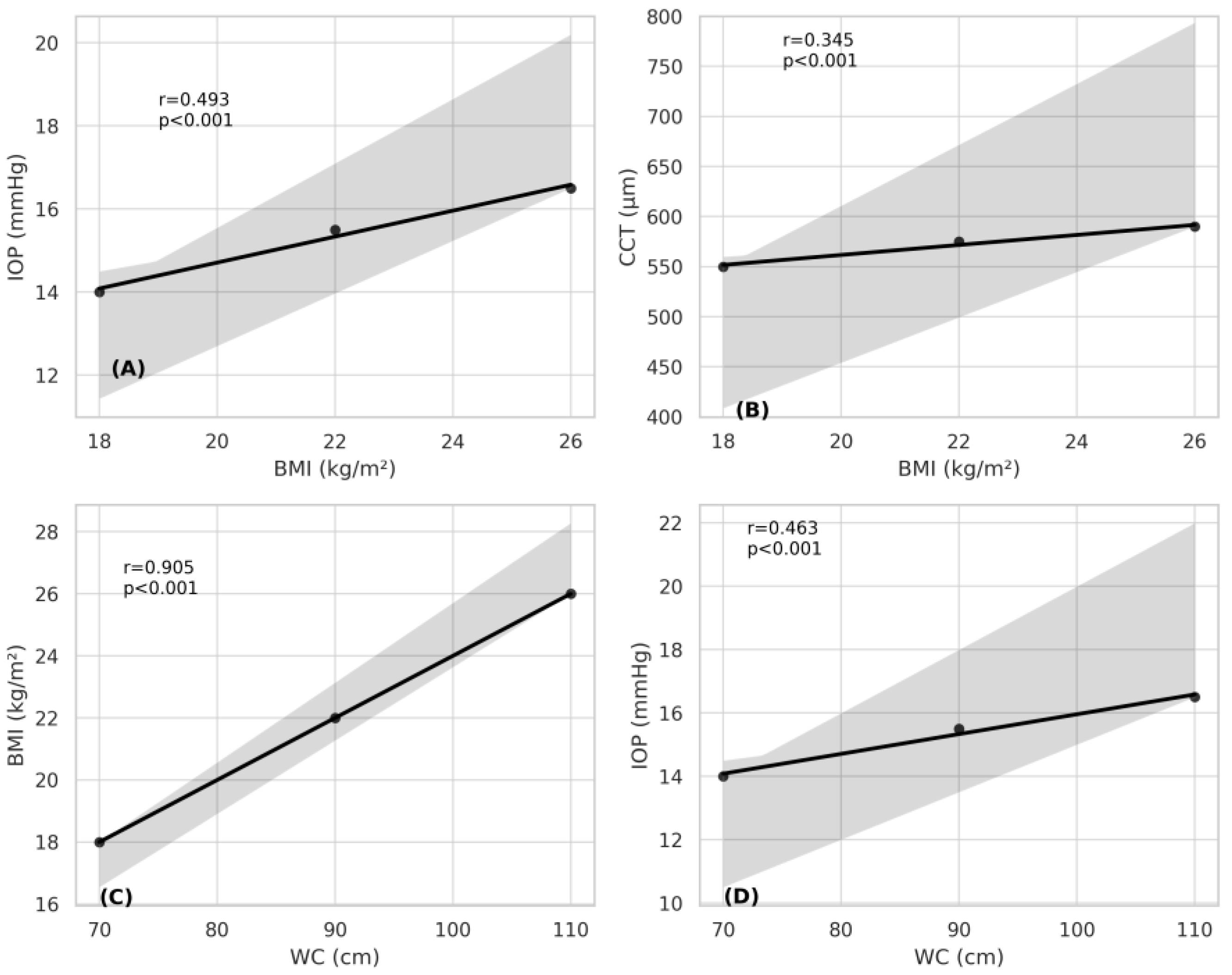
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Onís, M.; Blössner, M.; Borghi, E. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool children. The American journal of clinical nutrition 2010, 92 5, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuveer, G. Lifetime cardiovascular risk of childhood obesity. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, M.E.; Kızıltoprak, H.; Buluş, A.D.; Özkoyuncu, D.; Koç, M.; Yıldız, Z.Ö. Corneal biomechanical properties in childhood obesity. Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 2020, 57, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, N.; Wong, T.Y. Obesity and Eye Diseases. Survey of Ophthalmology 2007, 52, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtul, B.E.; Cąkmak, A.I.; Elbeyli, A.; Karaaslan, A.; El, Ç. Association of childhood obesity with retinal microvasculature and corneal endothelial cell morphology. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism 2021, 34, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panon, N.; Luangsawang, K.; Rugaber, C.; Tongchit, T.; Thongsepee, N.; Cheaha, D.; Kongjaidee, P.; Changtong, A.; Daradas, A.; Chotimol, P. Correlation between body mass index and ocular parameters. Clinical Ophthalmology 2019, 13, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrave, A.; Courson, J.A.; Pham, V.; Landry, P.; Magadi, S.; Shankar, P.; Hanlon, S.; Das, A.; Rumbaut, R.E.; Wayne Smith, C.; et al. Corneal dysfunction precedes the onset of hyperglycemia in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Kalteniece, A.; Ferdousi, M.; Adam, S.; D’Onofrio, L.; Ho, J.H.; Rao, A.P.; Dhage, S.; Azmi, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Corneal keratocyte density and corneal nerves are reduced in patients with severe obesity and improve after bariatric surgery. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 2021, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaimi, E.; Morgan, I.G.; Robaei, D.; Rose, K.A.; Smith, W.; Rochtchina, E.; Mitchell, P. Effect of stature and other anthropometric parameters on eye size and refraction in a population-based study of Australian children. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 2005, 46, 4424–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; Nalla, S.; Rodriguez-Dieguez, E.; Hasrod, N. Correlation between body mass index and corneal thickness in emmetropic subjects. African Vision and Eye Health 2023, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Londregan, A.; Rich, C.; Trinkaus-Randall, V. Changes in epithelial and stromal corneal stiffness occur with age and obesity. Bioengineering 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Colao, A. Body Mass Index (BMI): Still be used? European journal of internal medicine 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, G. Association of combined body mass index and central obesity with cardiovascular disease in middle-aged and older adults: a population-based prospective cohort study. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2024, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, B.; Dogan, U.; Erol, M.K.; Habibi, M.; Oruc, M.T. Comparison of anterior segment parameter values obtained with Scheimpflug-Placido topographer, optical low coherence reflectometry and noncontact specular microscopy in morbid obesity. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences 2017, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Nishitsuka, K.; Kawasaki, R.; Kanno, M.; Tanabe, Y.; Saito, K.; Honma, K.; Oizumi, T.; Daimon, M.; Kato, T.; Kayama, T.; et al. Determinants and Risk Factors for Central Corneal Thickness in Japanese Persons: The Funagata Study. Ophthalmic Epidemiology 2011, 18, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, L.L.d.; Gaete, M.I.L.; Figueiroa, J.N.; Alves, J.G.B. The correlation between body mass index and intraocular pressure in children. Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia 2013, 76, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyzi, O.; Bundak, R.; Gökçay, G.; Günöz, H.; Furman, A.; Darendeliler, F.; Baş, F. Reference values for weight, height, head circumference, and body mass index in Turkish children. JCRPE Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology 2015, 7, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezor-Garus, J.; Niechciał, E.; Kędzia, A.; Gotz-Więckowska, A. Obesity-induced ocular changes in children and adolescents: A review. Front Pediatr 2023, 11, 1133965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci, A.; Cetinkaya, E.; Aycan, Z.; Oner, O. Relationship between intraocular pressure and obesity in children. J Glaucoma 2007, 16, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, G.A.; Aydemir, E.; Asik, A.; Bolu, S. Changes in ocular pulse amplitude and choroidal thickness in childhood obesity patients with and without insulin resistance. Eur J Ophthalmol 2022, 32, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, R.T.; Baran, S.O.; Toraman, N.F.; Filiz, S.; Demirbilek, H. Evaluation of intraocular pressure and retinal nerve fiber layer, retinal ganglion cell, central macular thickness, and choroidal thickness using optical coherence tomography in obese children and healthy controls. Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice 2019, 22, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, S.A.; Unsal, A.I.A.; Verdi, F.; Omurlu, İ.K.; Unuvar, T.; Anık, A. The Effect of Childhood Obesity on Intraocular Pressure, Corneal Biomechanics, Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer, and Central Macular Thickness. Journal of Glaucoma 2024, 33, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.J.; Wu, J.F.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wu, H.; Sun, W.; Lu, T.L.; Wang, X.R.; Bi, H.S.; Jonas, J.B. Intraocular pressure and associated factors in children: the Shandong children eye study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014, 55, 4128–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdi, F.; Akyüz Ünsal, A.İ.; Aydın Eroğlu, S.; Dündar, S.; Ünüvar, T.; Anık, A.; Kurt Ömürlü, İ. The Association Between Body Mass Index, Intraocular Pressure and Central Corneal Thickness in Children. Meandros Medical and Dental Journal 2022, 23, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.D.; Kim, D.H.; Han, K.; Ha, S.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Jung, D.W.; Park, S.W.; et al. Relationship between Intraocular Pressure and Parameters of Obesity in Korean Adults: The 2008-2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Current Eye Research 2015, 40, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Lee, E.H.; Jargal, G.; Paek, D.; Cho, S.I. The distribution of intraocular pressure and its association with metabolic syndrome in a community. J Prev Med Public Health 2010, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Kim, M.H.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Rampal, S.; Shin, H.; Kim, J.M.; Friedman, D.S.; et al. A Longitudinal Study of Association between Adiposity Markers and Intraocular Pressure: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elflein, H.M.; Pfeiffer, N.; Hoffmann, E.M.; Hoehn, R.; Kottler, U.B.; Lorenz, K.; Zwiener, I.; Wild, P.S.; Mirshahi, A. Correlations Between Central Corneal Thickness and General Anthropometric Characteristics and Cardiovascular Parameters in a Large European Cohort From the Gutenberg Health Study. Cornea 2014, 33, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencer, B.; Ozgurhan, E.B.; Kara, S.; Tufan, H.A.; Arikan, S.; Bozkurt, E.; Demirok, A. Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea in patients with keratoconus in a Turkish population. Cornea 2014, 33, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlblad, M.S.; Schaefer, D.P. Eyelid laxity, obesity, and obstructive sleep apnea in keratoconus. Cornea 2013, 32, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Tu, R.; Xu, L.; Gu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yin, S.; Pang, C.; Zhao, D.; et al. A high body mass index strengthens the association between the time of eye rubbing and keratoconus in a Chinese population: a case control study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Normal (n=30) |
Overweight (n=30) P |
Obese (n=30) P |
Pc | |
| Age (years) | 11.3±2.56 | 11.7±3.14 0,530a |
11.6±3.40 0.639a |
0.797 |
| Gender Male/Female-n (%) | 14 (46.7)/ 16 (53.3) | 14 (46.7)/ 16 (53.3) 1b |
12 (40)/ 18 (60) 0.610b |
0.840 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.6±1.98 | 23.3±1.92 < .001a |
27.2±1.93 < .001a |
< .001 |
| WC (cm) | 66±9.55 | 103±16.7 < .001a |
111±11 < .001a |
< .001 |
| IOP (mmHg) | 13.6±1.52 | 15.8±2.35 < .001a |
16.5±2.19 < .001a |
< .001 |
| Normal (n=30) |
Overweight (n=30) Pa |
Obese (n=30) Pa |
Pb | |
| CCT (μm) | 537±23.9 | 549±21.7 0.046 |
561±22.5 < .001 |
< .001 |
| K flat (D) | 42.4±0.808 | 42.3±1.33 0.652 |
42.2±1.01 0.763 |
0.751 |
| K steep (D) | 43±0.808 | 43.4±1.49 0.724 |
43.1±1.17 0.563 |
0.445 |
| Kmax (D) | 42.8±0.837 | 42.9±1.39 0.263 |
42.7±1.06 0.283 |
0.722 |
| CV (mm3) | 59.1±2.32 | 59.3±3.59 0.779 |
59.5±2.68 0.310 |
0.833 |
| ACV (mm3) | 199±29.9 | 201±28.2 0.218 |
203±29 0.622 |
0.201 |
| ACD (mm) | 3.13±0.254 | 3.14±0.238 0.896 |
3.20±0.267 0.376 |
0.544 |
| ACA (˚) | 39.8±5.10 | 40.1±5.26 0.830 |
40.2±5.37 0.765 |
0.186 |
| Normal (n=30) |
Overweight (n=30) Pa |
Obese (n=30) Pa |
Pb | |
| ECD (cells/mm2) | 3128 ± 257 |
3123 ± 270 0.753 |
3121 ± 265 0.664 |
0.903 |
| CV | 28.6 ±3.54 |
28.5 ± 4.52 0.919 |
28.2 ± 4.71 0.591 |
0.852 |
| HEX (%) | 69.7 ± 9.91 |
67.8 ± 10.15 0.106 |
67.4 ± 10.61 0.074 |
0.162 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





