Submitted:
19 February 2025
Posted:
20 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
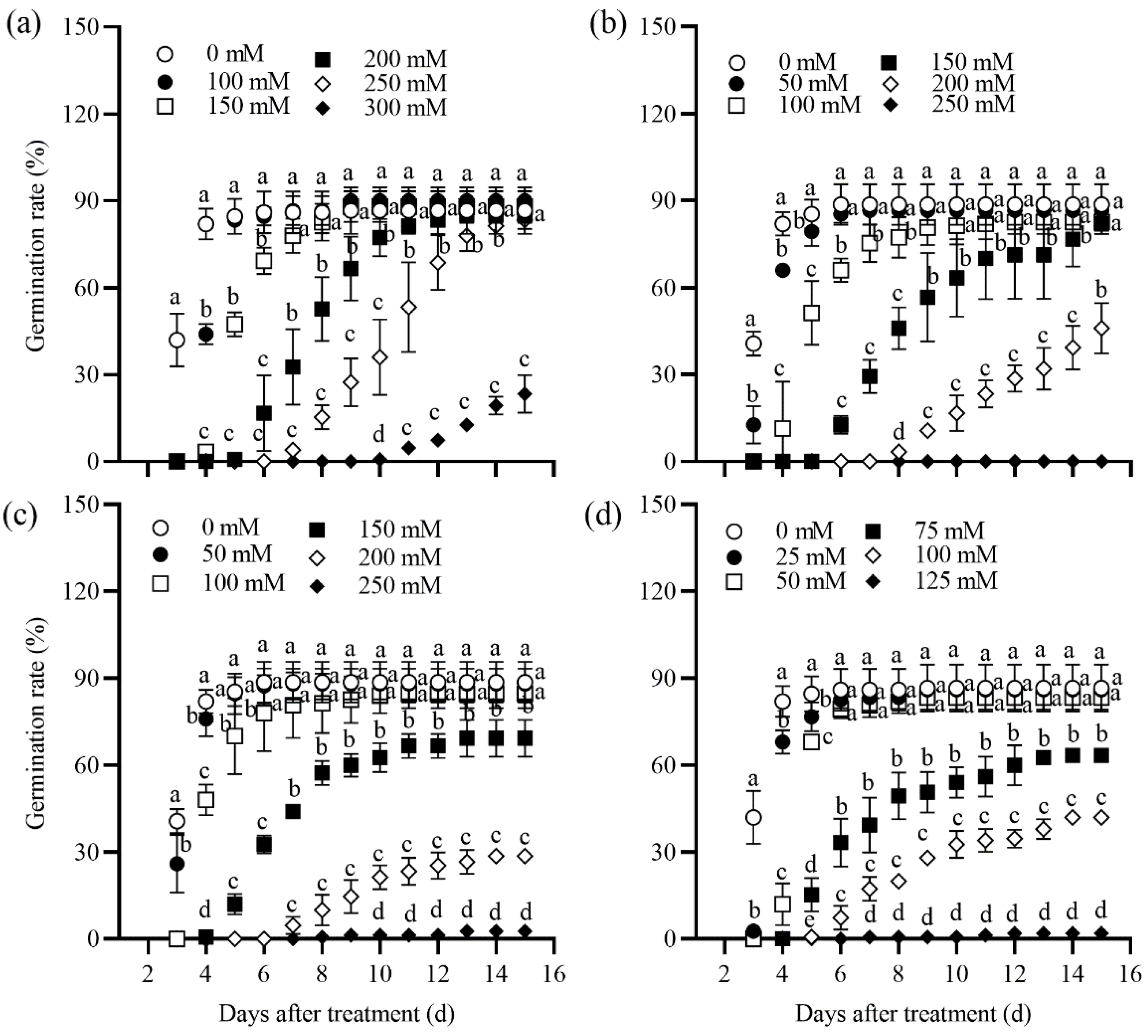
2.1. Seed Germination Rate of Tall Wheatgrass Responding to NaCl, Na2SO4, NaHCO3, and Na2CO3
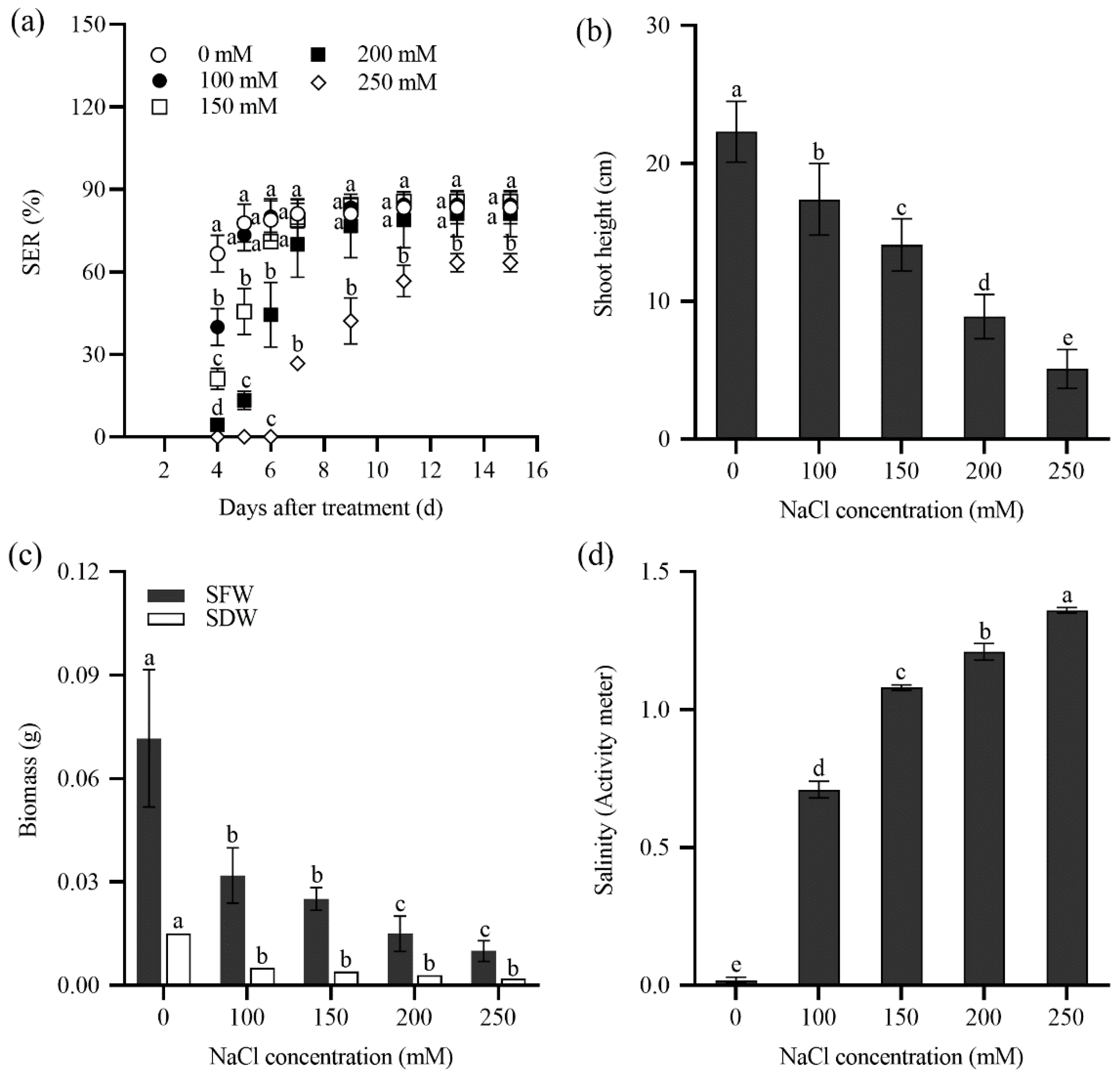
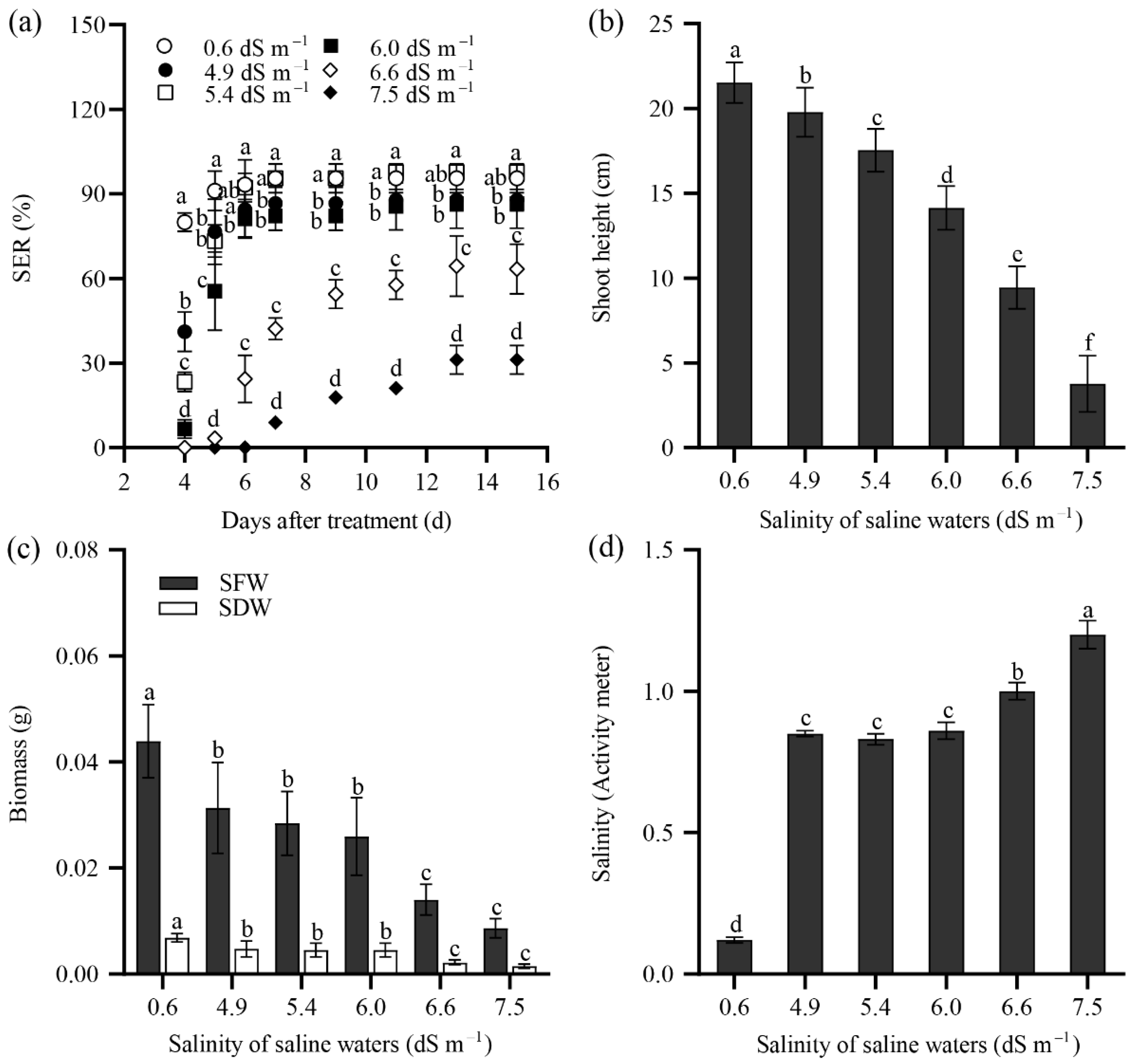
2.2. Seedling Emergence Rate of Tall Wheatgrass Responding to NaCl and Saline Water
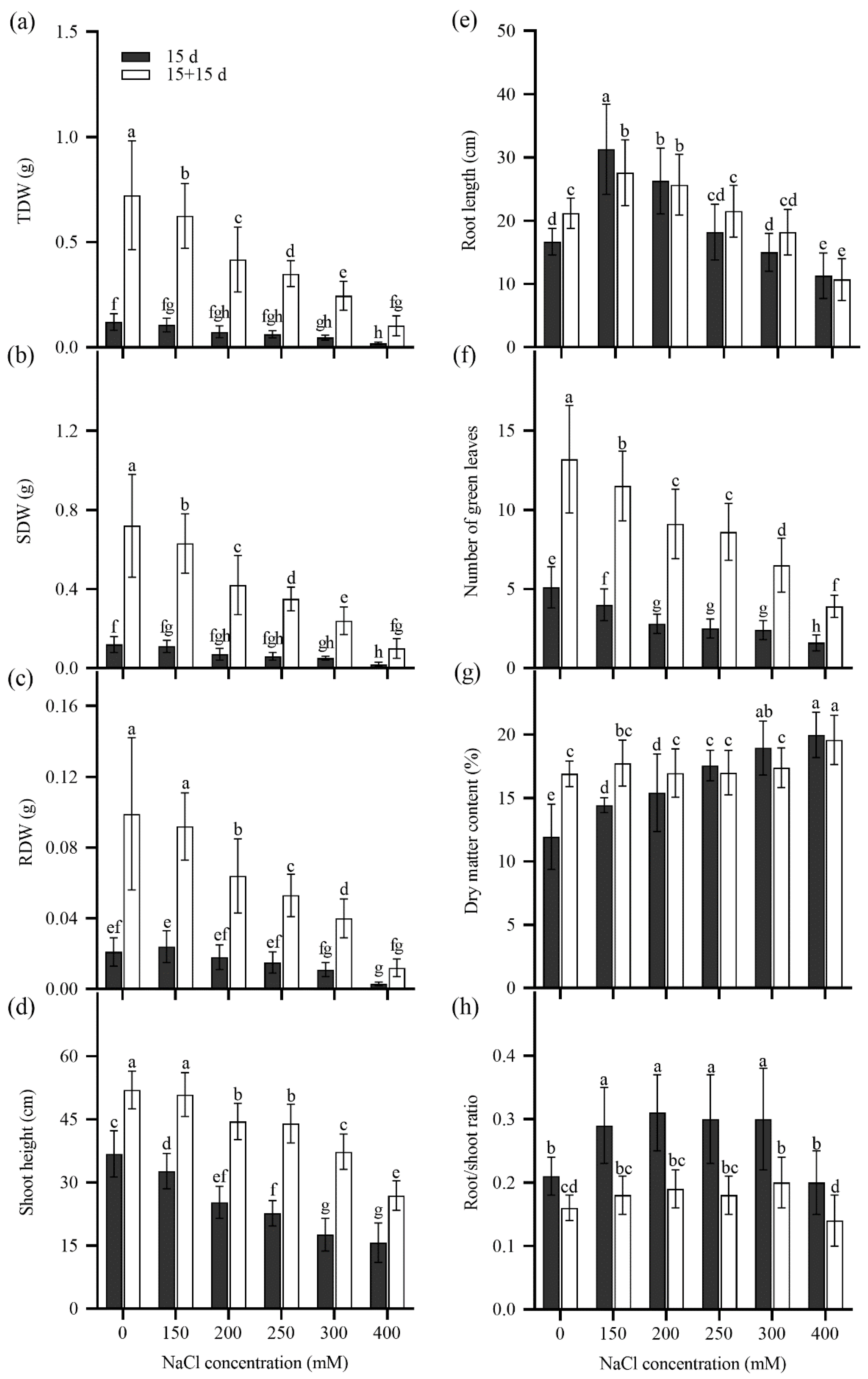
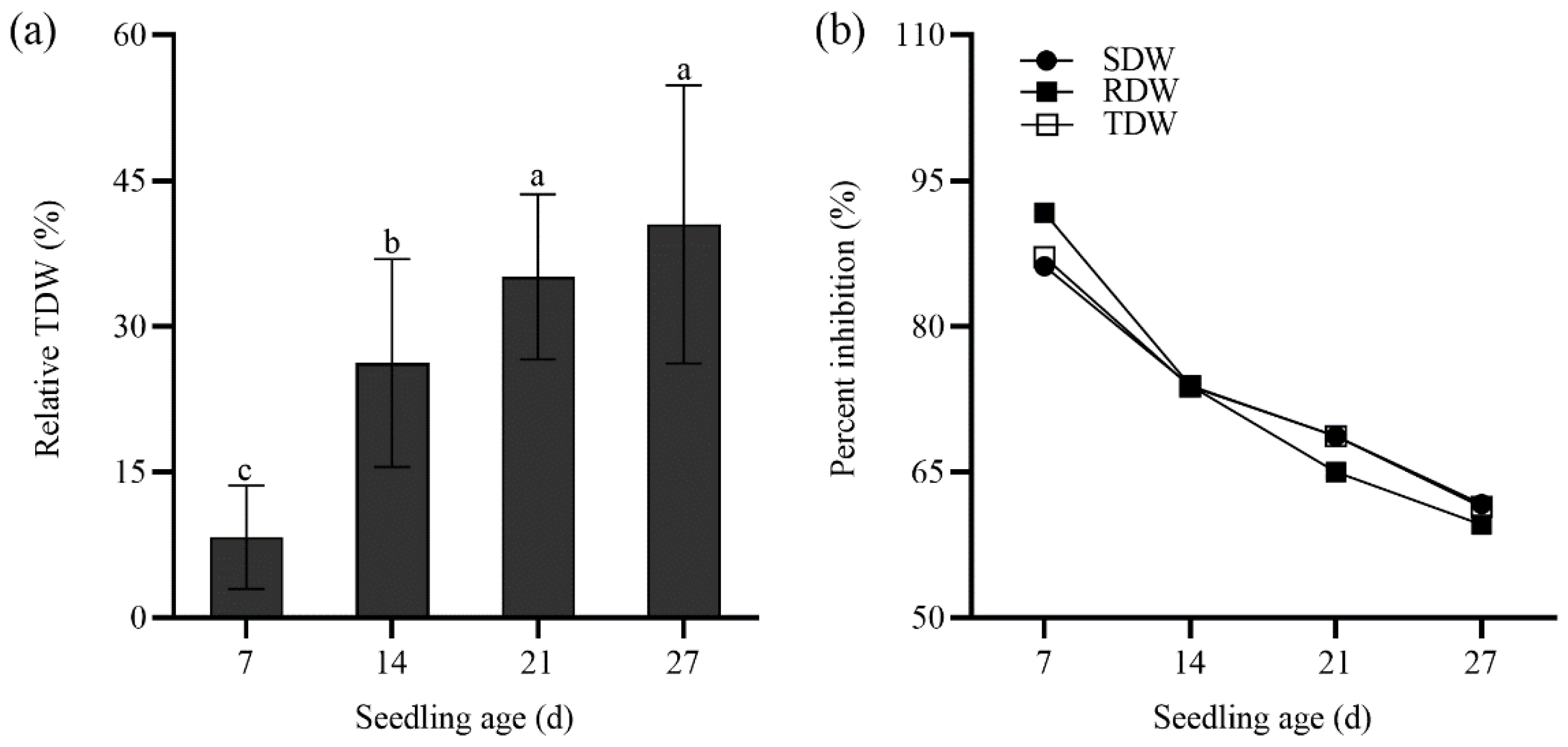
2.3. Seedling Growth of Tall Wheatgrass Responding to NaCl Stress.
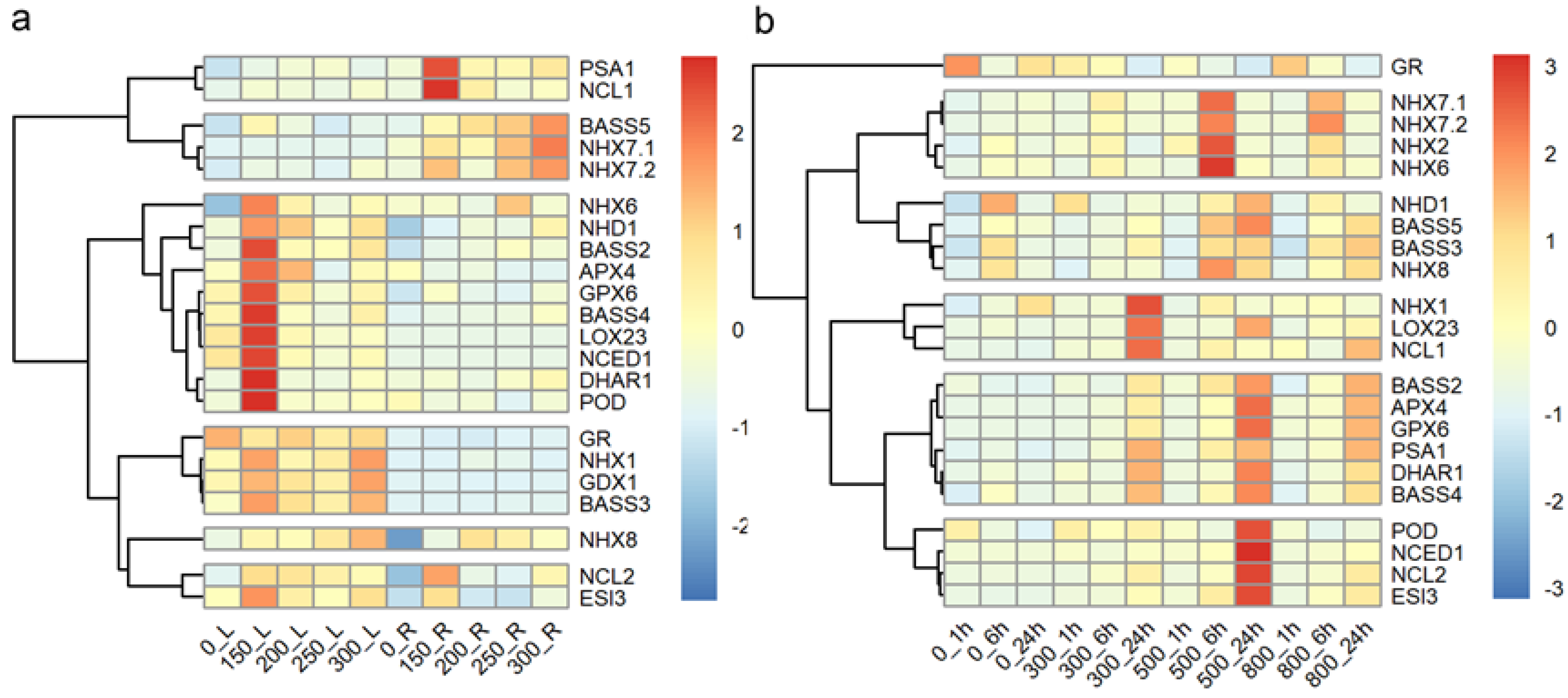
2.4. Differential Expression of Salt Response Genes in Seedlings of Tall Wheatgrass Under Salt Stress
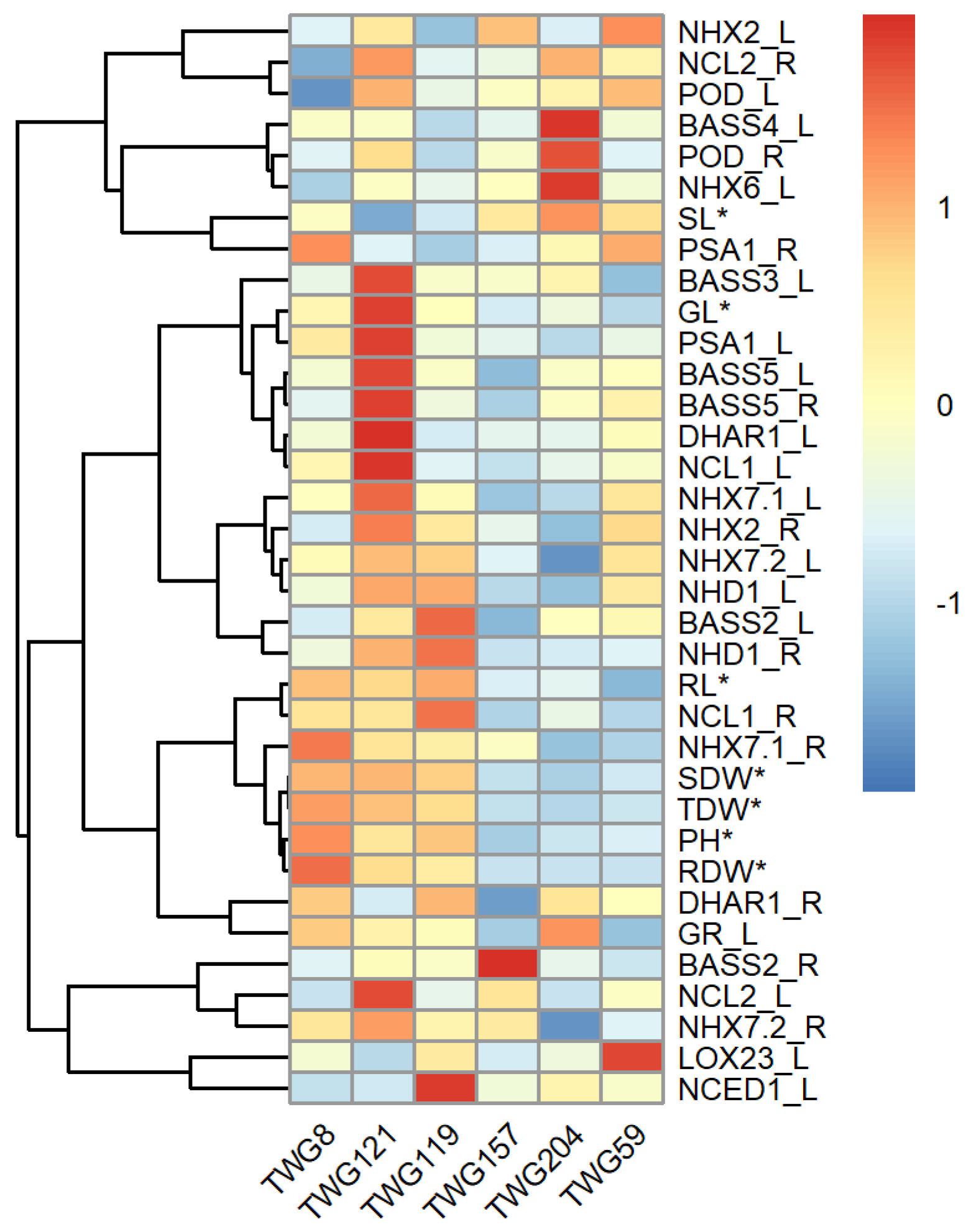
2.5. Differential Expression of Salt Response Genes Between Salt-Tolerant and Salt-Sensitive Tall Wheatgrass Lines
2.6. Evaluation of Salt Tolerance in 28 Tall Wheatgrass Lines
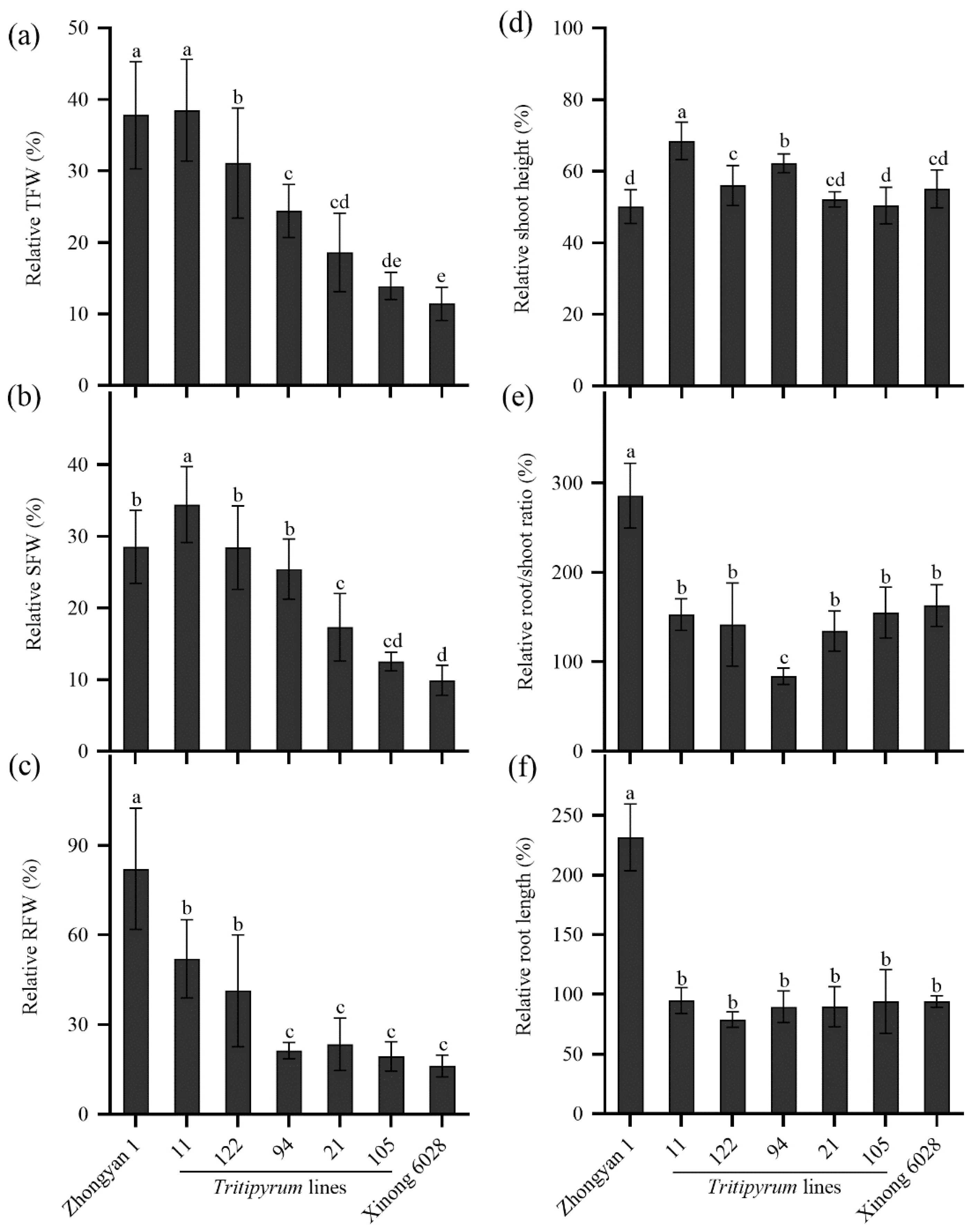
2.7. Evaluation of Salt Tolerance in Five Tritipyrum Lines Derived from Wheat×Tall Wheatgrass
3. Discussion
3.1. Seed Germination Rate Under Salt Stress as Salt Tolerance Index in Tall Wheatgrass
3.2. Seedling Emergence Rate Under Salt Stress as Salt Tolerance Index in Tall Wheatgrass
3.3. Seedling Growth Under Salt Stress as Salt Tolerance Index in Tall Wheatgrass
3.4. Differential Expression of Salt Response Genes in Tall Wheatgrass Responding to Salt Stress
3.5. Screening of Salt-Tolerant Lines of Tall Wheatgrass for Breeding Purpose
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Evaluation of Seed Germination of Tall Wheatgrass Responding to Salt Stress
4.3. Evaluation of Seedling Emergence of Tall Wheatgrass Responding to Salt Stress
4.4. Evaluation of Seedling Growth of Tall Wheatgrass Responding to Salt Stress
4.5. Total RNA Extraction and First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
4.7. Tall Wheatgrass Lines and Tritipyrum Lines Evaluation
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgement: We thank for the support from Saline–alkaline Land Technological Breakthroughs of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DAT | Days after treatment |
| SDW | Shoot dry weight |
| SER | Seedling emergence rate |
| SFW | Shoot fresh weight |
| TDW | Total dry matter weight |
| TFW | Total fresh matter weight |
References
- Asay, K.H.; Jensen, K.B. Wheatgrasses. In Cool-Season Forage Grasses, Moser, L.E.; Buxton, D.R.; Casler, M.D., Eds., ASA, CSSA, and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996, 691–724.
- Andrioli, R.J. Adaptive mechanisms of tall wheatgrass to salinity and alkalinity stress. Grass Forage Sci. 2023, 78(1), 23–36. [CrossRef]
- Falasca, S.L.; Miranda, C.; Alvarez, S.P. Agro-ecological zoning for tall wheatgrass (Thinopyrum ponticum) as a potential energy and forage crop in salt-affected and dry lands of Argentina. Arch. Crop Sci. 2017, 1(1), 10–19.
- Dewey, D.R. Salt tolerance of twenty-five strains of Agropyron. Agron. J. 1960, 52, 631–635.
- Carter, D.L.; Peterson, H.B. Sodic tolerance of tall wheatgrass1. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 382–384.
- Temel, S.; Keskın, B.; Sımsek, U.; Yılmaz, I.H. Performance of some forage grass species in halomorphic soil. Turk. J. Field Crops. 2015, 20, 131–141. [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Al-Shankiti, A. Sustainable food production in marginal lands—Case of GDLA member countries. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2013, 1(1), 24–38. [CrossRef]
- Ciria, C.S.; Sastre, C.M.; Carrasco, J.; Ciria, P. Tall wheatgrass (Thinopyrum ponticum (Podp)) in a real farm context, a sustainable perennial alternative to rye (Secale cereale L.) cultivation in marginal lands. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 146, 112184. [CrossRef]
- Nazli, R.I.; Kusvuran, A.; Tansi, V.; Ozturk, H.H.; Budak, D.B. Comparison of cool and warm season perennial grasses for biomass yield, quality, and energy balance in two contrasting semiarid environments. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 139, 105627. [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Approaches and research progresses of marginal land productivity expansion and ecological benefit improvement in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36(3), 336–348.
- Scordia, D.; Papazoglou, E.G.; Kotoula, D.; Sanz, M.; Ciria, C.S.; Pérez, J.; Maliarenko, O.; Prysiazhniuk, O.; Von Cossel, M.; Greiner, B.E. Towards identifying industrial crop types and associated agronomies to improve biomass production from marginal lands in Europe. GCB Bioenergy 2022, 14(7), 710–734. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, Q.; Yang, W.; Cao, X.; Li, Z. Scientific and technological reasons, contents and corresponding policies of constructing “Coastal Grass Belt”. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 37(2), 238–245.
- Wang, T.; Cao, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Jing, H. Forage grass basic biology of constructing Coastal Grass Belt. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2022, 57, 837–847.
- Li, H.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, K.; Fang, H.; Xing, X.; Yang, W.; Cao, X.; Liu, X. Industrialization of tall wheatgrass for construction of “Coastal Grass Belt”. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2023, 38(4), 622–631.
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, S. Salt tolerance of early growth of five grass species in Hexi corridor. Acta Agrest. Sin. 1999, 7(4), 293–299.
- Peng, Y.X.; Zhang, L.J.; Yu, Y.J.; Liu, G. The salt tolerance of seeds and seedlings from Thinopyrum species. Inner Mong. Pratacult. 2002, 14(3), 42–43.
- Zhang, B.; Jacobs, B.C.; O'Donnell, M.; Guo, J. Comparative studies on salt tolerance of seedlings for one cultivar of puccinellia (Puccinellia ciliata) and two cultivars of tall wheatgrass (Thinopyrum ponticum). Anim. Prod. Sci. 2005, 45(4), 391–399. [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.H.; Liang, Z.W. Effect of different sodium salt stress on the seed germination of tall wheatgrass (Agropyron elongatum). J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2007, 21(6), 173–176.
- Liu, Y.Q.; Dong, K.H.; Wang, Q.L.; Zhang, R.Z. Effect of salt stress on seed germination of tall wheatgrass. Grassl. Turf 2007, 2, 18–21.
- Bazzigalupi, O.; Pistorale, S.M.; Andrés, A.N. Salinity tolerance during seed germination from naturalized populations of tall wheatgrass (Thinopyrum ponticum). Cien. Investig. Agrar. 2008, 35(2), 231–238.
- Xu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, B. Effects of different salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Elytrigia elongata. Chin. J. Grassl. 2020, 42, 15–20.
- Mcguire, P.E.; Dvôrák, J. High salt tolerance potential in wheatgrasses. Crop Sci. 1981, 21(5), 702–705.
- Steppuhn, H.; Asay, K. Emergence, height, and yield of tall, NewHy, and green wheatgrass forage crops grown in saline root zones. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2005, 85(4), 863–875. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Meng, L.; Mao, P.; Tian, X. Salt tolerance in two tall wheatgrass species is associated with selective capacity for K+ over Na+. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 1708. [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.C. Testing salt tolerance variability among tall wheatgrass lines. Agron. J. 1978, 70(5), 719–722. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R. Salinity resistance, water relations, and salt content of crested and tall wheatgrass accessions. Crop Sci. 1991, 31(3), 730–734. [CrossRef]
- Roundy, B.A. Response of basin wildrye and tall wheatgrass seedlings to salination. Agron. J. 1983, 75(1), 67–71. [CrossRef]
- Grattan, S.R.; Grieve, C.M.; Poss, J.A.; Robinson, P.H.; Suarez, D.L.; Benes, S.E. Evaluation of salt-tolerant forages for sequential water reuse systems: I. Biomass production. Agric. Water Manage. 2004, 70(2), 109–120. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Gao, H.; Na, T.; Guo, D. Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance at seedling stage in Elytrigia accessions. Pratacult. Sci. 2008, 25, 51–54.
- Meng, L.; Shang, C.; Mao, P.; Zhang, G.; An, S. A comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance for germplasm and materials of Elytrigia at the seedling stage. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2009, 18(4), 67–74.
- Riedell, W.E. Growth and ion accumulation responses of four grass species to salinity. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2016, 39(14), 2115–2125. [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.I.; Raman, A.; Hodgkins, D.; Mitchell, D.; Nicol, H.I. Influence of high levels of Na+ and Cl− on ion concentration, growth, and photosynthetic performance of three salt-tolerant plants. Flora 2017, 228, 1‒9.
- Borrajo, C.I.; Sánchez-Moreiras, A.M.; Reigosa, M.J. Morpho-physiological, biochemical and isotopic response of tall wheatgrass populations to salt stress. J. Agro. Crop Sci. 2021, 207, 236–248. [CrossRef]
- Borrajo, C.I.; Sánchez-Moreiras, A.M.; Reigosa, M.J. Ecophysiological responses of tall wheatgrass germplasm to drought and salinity. Plants 2022, 11(12), 1548. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Feng, X.H.; Wu, Y.J.; Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Li, J.S.; Liu, X.J. Interactive effects of drought and salt stresses on the growth and physiological characteristics of Thinopyrum ponticum. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30(11), 1795−1806.
- Rogers, A.L.; Bailey, E.T. Salt tolerance trials with forage plants in south Western Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1963, 3, 125–130. [CrossRef]
- Gu, A. Cultivation of salt-tolerant forage grass—Thinopyrum ponticum. Grassl. China 2004, 26(2), 9.
- Bhuiyan, M.N.; Raman, A.; Hodgkins, D.S.; Mitchell, D.C.; Nicol, H.I. Salt accumulation and physiology of naturally occurring grasses in saline soils in Australia. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 501–511. [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.Y.; Yang, G.T.; Li, H.W.; Li, B.; Li, Z.S.; Zheng, Q. Screening of salt-tolerant Thinopyrum ponticum under two coastal region salinity stress levels. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 832013. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Li, Z. Salinity threshold of tall wheatgrass for cultivation in coastal saline and alkaline land. Agriculture 2023, 13(2), 337. [CrossRef]
- Suyama, H.; Benes, S.E.; Robinson, P.H.; Getachew, G.; Grattan, S.R.; Grieve, C.M. Biomass yield and nutritional quality of forage species under long-term irrigation with saline-sodic drainage water: Field evaluation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 135, 329–345. [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.; Ford, R. Salt tolerance of forage crops. In: U.S. Salinity Lab Report to Collaborators, Riverside: CA, USDA, 1958, 32–36.
- Li, W.; Yin, J.; Ma, D.; Zheng, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, X.; Li, Z. Acceptable salinity level for saline water irrigation of tall wheatgrass in edaphoclimatic scenarios of the coastal saline–alkaline land around Bohai Sea. Agriculture 2023, 13(11), 2117. [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Wang, H.; Lai, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Hou, R. New approach of high-quality agricultural development in the yellow river delta. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35(2): 145–153.
- Gulick, P.; Dvorák, J. Gene induction and repression by salt treatment in roots of the salinity-sensitive Chinese Spring wheat and the salinity-tolerant Chinese Spring x Elytrigia elongata amphiploid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1987, 84(1), 99–103.
- Gulick, P.J.; Dvorák, J. Coordinate gene response to salt stress in Lophopyrum elongatum. Plant Physiol. 1992, 100(3), 1384–1388. [CrossRef]
- Galvez, A.F.; Gulick, P.J.; Dvorak, J. Characterization of the early stages of genetic salt-stress responses in salt-tolerant Lophopyrum elongatum, salt-sensitive wheat, and their amphiploid. Plant Physiol. 1993, 103(1), 257–265. [CrossRef]
- Tabaei-Aghdaei, S.R.; Harrison, P.; Pearce, R.S. (2000), Expression of dehydration-stress-related genes in the crowns of wheatgrass species [Lophopyrum elongatum (Host) A. Love and Agropyron desertorum (Fisch. ex Link.) Schult.] having contrasting acclimation to salt, cold and drought. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 561–571.
- Shen, W.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Routly, E.L.; Ho, T.H.; Simmonds, J.A.; Gulick, P.J. The salt stress-inducible protein kinase gene, Esi47, from the salt-tolerant wheatgrass Lophopyrum elongatum is involved in plant hormone signaling. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125(3), 1429–41.
- Hussein, Z.; Dryanova, A.; Maret, D.; Gulick, P.J. Gene expression analysis in the roots of salt-stressed wheat and the cytogenetic derivatives of wheat combined with the salt-tolerant wheatgrass, Lophopyrum elongatum. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 189–201. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Geng, G.; Yang, R.; Yang, Z.; Yang, C.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kakar, K.U.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Comparative analysis of physiological, enzymatic, and transcriptomic responses revealed mechanisms of salt tolerance and recovery in Tritipyrum. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 800081. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Li, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.S. Overexpression of AeNHX1, a root-specific vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from Agropyron elongatum, confers salt tolerance to Arabidopsis and Festuca plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26(9), 1663–1672.
- Sheikh-Mohamadi, M.H.; Etemadi, N.; Aalifar, M.; Pessarakli, M. Salt stress triggers augmented levels of Na+, K+ and ROS alters salt-related gene expression in leaves and roots of tall wheatgrass (Agropyron elongatum). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 183, 9–22. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.X,; Zheng, M.L.; Mao, P.C.; Meng, L. Analysis of drought and salt resistance of EeHKT1;4 gene from Elytrigia elongata in Arabidopsis. Acta Prat. Sin. 2022, 31, 188–198.
- King, I.P.; Law, C.N.; Cant, K.A.; Orford, S.E.; Reader, S.M. Miller, T.E. Tritipyrum, a potential new salt-tolerant cereal. Plant Breed. 1997, 116, 127–132.
- Didaran, F.; Kordrostami, M.; Ghasemi-Soloklui, A.A.; Pashkovskiy, P.; Kreslavski, V.; Kuznetsov, V.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. The mechanisms of photoinhibition and repair in plants under high light conditions and interplay with abiotic stressors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2024, 259, 113004. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Q.; Wang, J.L.; Li, S.J. Genome-wide identification of Na+/H+ antiporter (NHX) genes in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) and their regulated expression under salt stress. Genes 2019, 10 (5), 401.
- Hamamoto, S.; Horie, T.; Hauser, F.; Deinlein, U.; Schroeder, J.I.; Uozumi, N. HKT transporters mediate salt stress resistance in plants: from structure and function to the field. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 113–120. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, P.; Hu, T.; Wang, Z.; Hou, Y.J.; Wan, Y.; Liu, W.; Xie, S.; Lu, T. Arabidopsis duodecuple mutant of PYL ABA receptors reveals PYL repression of ABA-independent SnRK2 activity. Cell Rep. 2018, 23 (11), 3340–3351. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z. GmNAC06, a NAC domain transcription factor enhances salt stress tolerance in soybean. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 105(3), 333–345. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Long, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Xin, Y.; Li, L.; Cao, S.Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhou, D.; Xia, J. A NAC transcription factor OsNAC3 positively regulates ABA response and salt tolerance in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 546. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, R.; Song, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dong, X.; Liu, S.; Feng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Di, H. The transcription factor ZmNAC89 gene is involved in salt tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(20), 15099. [CrossRef]
- Solis, C.A.; Yong, M.T.; Zhou, M.; Venkataraman, G.; Shabala, L.; Holford, P.; Shabala, S.; Chen, Z.H. Evolutionary significance of NHX Family and NHX1 in salinity stress adaptation in the genus Oryza. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(4), 2092. [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Duan, L.; Li, Z. SOS1 gene overexpression increased salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco by maintaining a higher K(+)/Na(+) ratio. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169(3), 255–261.
- Salazar, O.R.; Chen, K.; Melino, V.J.; Reddy, M.P.; Hřibová, E.; Čížková, J.; Beránková, D.; Arciniegas Vega, J.P.; Cáceres Leal, L.M.; Aranda, M.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; Fedoroff, N.V.; Tester, M.; Schmöckel, S.M. SOS1 tonoplast neo-localization and the RGG protein SALTY are important in the extreme salinity tolerance of Salicornia bigelovii. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15(1), 4279. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, D.; Cui, S. A Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-like protein (AtNCL) involved in salt stress in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287(53), 44062–44070.
- Li, H.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Li, Z. The analysis of determining factors and evaluation of tolerance to photoinhibition in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Photosynthetica 2017, 55, 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [CrossRef]
| Genes | Forward sequence | Reverse sequence | Product (bp) | Gene annotation |
| ACT4 | CTAGTGGACGCACAACAGGT | AAGGATGGCATGTGGAAGGG | 98 | Actin |
| APX4 | AGCCCAAACACACCTCAGAC | CAACGCGGATGACCCTAGAA | 80 | Probable L-ascorbate peroxidase 4 |
| BASS2 | TGAGTGTGGGATGCAGAGTT | CCATGCACACAACACTGACA | 104 | Probable sodium/metabolite cotransporter BASS2 |
| BASS3 | CGTATTGGGGAAGTGGCATG | CCCAAATGGCAGCAGAGTTT | 149 | Probable sodium/metabolite cotransporter BASS3 |
| BASS4 | GGTCATCCCATGTGTTGCTG | GTCAAGCCTCACTCGGATAGA | 157 | Probable sodium/metabolite cotransporter BASS4 |
| BASS5 | ACAGGGATGCAAAGTAGCCT | TCAGGGACATCAGCACAACT | 106 | Probable sodium/metabolite cotransporter BASS5 |
| DHAR1 | GCCTTGATGTGCTGTGGTTG | CCGCTAGCACCAAAACACAC | 116 | Probable glutathione S-transferase DHAR1 |
| ESI3 | AGCCTCGAGTGAAGTAAGCA | GAATTCCACGCCGAGTTTGT | 114 | Salt stress-induced hydrophobic peptide ESI3 |
| GPX1 | GAGTCGAGTGCTGGAGGATT | CCGCAACGAGTTTCTGGATG | 148 | Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase 1 |
| GPX6 | TCGCTTCAAGGCCGAGTATC | CCACTTGATGTTGTCCCCGA | 121 | Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase 6 |
| GR | AATACAGAGCTGCAACGCCT | ACCTTTCCACGGCCTTCAAT | 86 | Glutathione reductase |
| LOX23 | GACCAGCGAAACAACAACCC | CTTATCCTGGGGCCACGATC | 147 | Lipoxygenase 2.3 |
| NCED1 | TCAGACACACCAACACGTCC | CCTACCCATGCACCACTGTT | 88 | 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase 1 |
| NCL1 | GACCATGAACAACACGCTGT | ATGACACAGACGAGCAGGAT | 111 | Sodium/calcium exchanger-like protein NCL1 |
| NCL2 | ATCTGGTACGTGTTTCCGGT | CAGCAACACACGCGATATCA | 116 | Sodium/calcium exchanger-like protein NCL2 |
| NHD1 | TGTTCCACTTGTTGCTGCAA | TGCAGACCCGATGATAAGCA | 127 | Sodium/proton antiporter NHD1 |
| NHX1 | TTATTGTGCTGCTGTGACCA | CGACCTCCCTTTTCCATGTG | 97 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger NHX1 |
| NHX2 | TGGTGCGATGGGGCTAATAT | GCCGAGAATATTGCCCCAAG | 84 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger NHX2 |
| NHX6 | CCGGCAAATATCCAGGCAAT | AAATTGTCTGTCCATGGCCG | 122 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger NHX6 |
| NHX7.1 | GGCTTGGGAAAATTGTCAGC | TCACCAAAAGCCTCCAATGC | 89 | SOS1 |
| NHX7.2 | GTTTTGGCCGTCATGACCTT | GCAAACTTTCCTGGCTGTCA | 82 | SOS1 |
| NHX8 | AGGGACGGATAAATGCAGCT | GGACACTGGACTGCAAACTG | 96 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger NHX8 |
| POD | TTGCTCTGCCATTGTCCACA | GTCGATTGCCAACTGAACGG | 121 | Peroxidase 51 |
| PSA1 | ATCGCCTCAGGTTGACAAGA | CCTCAGGCTGTTGAACGATG | 129 | Protein short root in salt medium PSA1 |
| Lines | Seed germination test | RER (%) | Seedling growth test | ||||||||||||||
| RGR (%) | RDR (%) | RGI (%) | RSH (%) | RVI (%) | SFW (g) | RFW (g) | TFW (g) | SDW (g) | RDW (g) | TDW (g) | |||||||
| NaCl | Na2CO3 | NaCl | Na2CO3 | NaCl | Na2CO3 | NaCl | Na2CO3 | NaCl | Na2CO3 | ||||||||
| TWG8 | 43.5 | 28.2 | 56.5 | 71.8 | 15.0 | 11.9 | 23.5 | 18.9 | 2.2 | 0.9 | 118.5 | 0.168 | 0.100 | 0.268 | 0.036 | 0.011 | 0.046 |
| TWG216 | 50.4 | 30.7 | 49.6 | 69.3 | 18.6 | 12.7 | 29.0 | 20.0 | 4.4 | 2.7 | 96.6 | 0.104 | 0.056 | 0.160 | 0.024 | 0.008 | 0.031 |
| TWG223 | 45.6 | 44.1 | 54.4 | 55.9 | 19.7 | 18.4 | 24.7 | 25.3 | 4.2 | 3.5 | 85.7 | 0.123 | 0.085 | 0.208 | 0.026 | 0.010 | 0.036 |
| TWG86 | 45.2 | 15.9 | 54.8 | 84.1 | 17.4 | 6.8 | 31.8 | 15.6 | 5.9 | 0.9 | 96.7 | 0.152 | 0.082 | 0.234 | 0.032 | 0.009 | 0.041 |
| TWG22 | 38.5 | 13.9 | 61.5 | 86.1 | 15.2 | 5.6 | 21.9 | 13.1 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 104.9 | 0.164 | 0.092 | 0.255 | 0.035 | 0.010 | 0.045 |
| Group 1 | 44.7a | 26.6a | 55.3b | 73.4b | 17.2a | 11.1a | 26.2a | 18.6a | 4.0a | 1.8a | 100.5a | 0.142a | 0.083a | 0.225a | 0.030a | 0.009a | 0.039a |
| TWG31 | 49.6 | 10.9 | 50.4 | 89.1 | 19.6 | 4.5 | 30.2 | 9.3 | 5.9 | 0.5 | 57.0 | 0.116 | 0.055 | 0.171 | 0.023 | 0.008 | 0.031 |
| TWG90 | 48.0 | 11.2 | 52.0 | 88.8 | 17.9 | 4.3 | 26.2 | 10.2 | 5.1 | 0.3 | 54.2 | 0.140 | 0.086 | 0.226 | 0.028 | 0.009 | 0.037 |
| TWG182 | 48.6 | 11.4 | 51.4 | 88.6 | 20.1 | 4.8 | 28.3 | 8.6 | 5.3 | 0.8 | 52.9 | 0.101 | 0.063 | 0.163 | 0.023 | 0.008 | 0.030 |
| TWG48 | 39.5 | 17.1 | 60.5 | 82.9 | 19.4 | 9.3 | 21.5 | 8.0 | 4.9 | 1.0 | 60.4 | 0.085 | 0.042 | 0.126 | 0.018 | 0.005 | 0.023 |
| TWG88 | 38.6 | 8.7 | 61.4 | 91.3 | 16.1 | 4.0 | 27.4 | 6.4 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 54.0 | 0.160 | 0.093 | 0.252 | 0.035 | 0.011 | 0.046 |
| TWG30 | 48.1 | 26.7 | 51.9 | 73.3 | 21.3 | 10.4 | 37.0 | 17.5 | 6.0 | 1.5 | 64.1 | 0.139 | 0.066 | 0.204 | 0.032 | 0.009 | 0.040 |
| TWG209 | 42.1 | 36.4 | 57.9 | 63.6 | 16.6 | 14.7 | 31.9 | 30.1 | 4.8 | 4.1 | 43.0 | 0.126 | 0.076 | 0.202 | 0.028 | 0.011 | 0.039 |
| TWG214 | 42.7 | 32.1 | 57.3 | 67.9 | 16.8 | 15.6 | 27.9 | 24.7 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 39.7 | 0.116 | 0.064 | 0.179 | 0.024 | 0.007 | 0.031 |
| Group 2 | 44.7a | 19.3ab | 55.3bb | 80.7ab | 18.5a | 8.4a | 28.8a | 14.3ab | 5.1a | 1.4ab | 53.2b | 0.123ab | 0.068a | 0.190ab | 0.026ab | 0.009a | 0.035ab |
| TWG9 | 34.3 | 5.7 | 65.7 | 94.3 | 14.3 | 2.7 | 15.3 | 2.1 | 4.2 | 0.1 | 20.3 | 0.142 | 0.083 | 0.224 | 0.029 | 0.009 | 0.038 |
| TWG15 | 29.9 | 16.8 | 70.1 | 83.2 | 10.4 | 6.3 | 18.0 | 15.6 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 44.6 | 0.089 | 0.055 | 0.144 | 0.021 | 0.007 | 0.028 |
| TWG65 | 9.9 | 3.3 | 90.1 | 96.7 | 4.2 | 1.2 | 9.6 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 50.3 | 0.122 | 0.071 | 0.192 | 0.025 | 0.007 | 0.032 |
| TWG105 | 15.2 | 11.6 | 84.8 | 88.4 | 5.4 | 4.9 | 11.0 | 13.3 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 16.5 | 0.138 | 0.079 | 0.218 | 0.030 | 0.011 | 0.040 |
| TWG106 | 13.8 | 2.3 | 86.2 | 97.7 | 5.8 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 22.8 | 0.110 | 0.067 | 0.177 | 0.023 | 0.007 | 0.029 |
| TWG164 | 18.4 | 5.7 | 81.6 | 94.3 | 7.4 | 2.3 | 18.6 | 5.4 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 22.2 | 0.108 | 0.063 | 0.171 | 0.023 | 0.008 | 0.030 |
| TWG180 | 15.8 | 18.7 | 84.2 | 81.3 | 6.3 | 8.0 | 10.6 | 14.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 28.1 | 0.127 | 0.086 | 0.212 | 0.027 | 0.009 | 0.035 |
| TWG185 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 86.1 | 89.8 | 5.1 | 4.2 | 11.0 | 10.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 30.5 | 0.115 | 0.048 | 0.163 | 0.023 | 0.006 | 0.028 |
| TWG186 | 26.3 | 1.7 | 73.7 | 98.3 | 9.5 | 0.6 | 17.3 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 12.6 | 0.116 | 0.062 | 0.177 | 0.025 | 0.008 | 0.032 |
| TWG213 | 27.3 | 16.4 | 72.7 | 83.6 | 10.2 | 6.2 | 19.8 | 12.1 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 9.3 | 0.097 | 0.054 | 0.151 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.029 |
| Group 3 | 20.5b | 9.2b | 79.5a | 90.8a | 7.9b | 3.7b | 14.1b | 7.8b | 1.4b | 0.4b | 25.7c | 0.116b | 0.067a | 0.183b | 0.025b | 0.008a | 0.032b |
| TWG52 | 68.5 | 58.7 | 31.5 | 41.3 | 28.1 | 28.0 | 42.4 | 31.5 | 11.8 | 7.6 | 92.6 | 0.137 | 0.083 | 0.219 | 0.028 | 0.010 | 0.038 |
| TWG70 | 67.7 | 40.0 | 32.3 | 60.0 | 30.9 | 18.5 | 32.0 | 22.1 | 10.9 | 3.9 | 103.7 | 0.093 | 0.055 | 0.148 | 0.022 | 0.009 | 0.031 |
| TWG40 | 50.6 | 8.0 | 49.4 | 92.0 | 20.7 | 3.1 | 22.2 | 1.5 | 5.7 | 0.0 | 82.8 | 0.113 | 0.067 | 0.180 | 0.028 | 0.010 | 0.037 |
| TWG157 | 64.9 | 2.1 | 35.1 | 97.9 | 29.2 | 1.0 | 26.2 | 1.1 | 8.4 | 0.0 | 108.7 | 0.122 | 0.079 | 0.201 | 0.027 | 0.014 | 0.041 |
| TWG206 | 27.7 | 48.2 | 72.3 | 51.8 | 9.5 | 20.3 | 15.4 | 24.3 | 1.2 | 4.6 | 24.1 | 0.123 | 0.052 | 0.174 | 0.026 | 0.006 | 0.032 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





