Submitted:
17 February 2025
Posted:
18 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
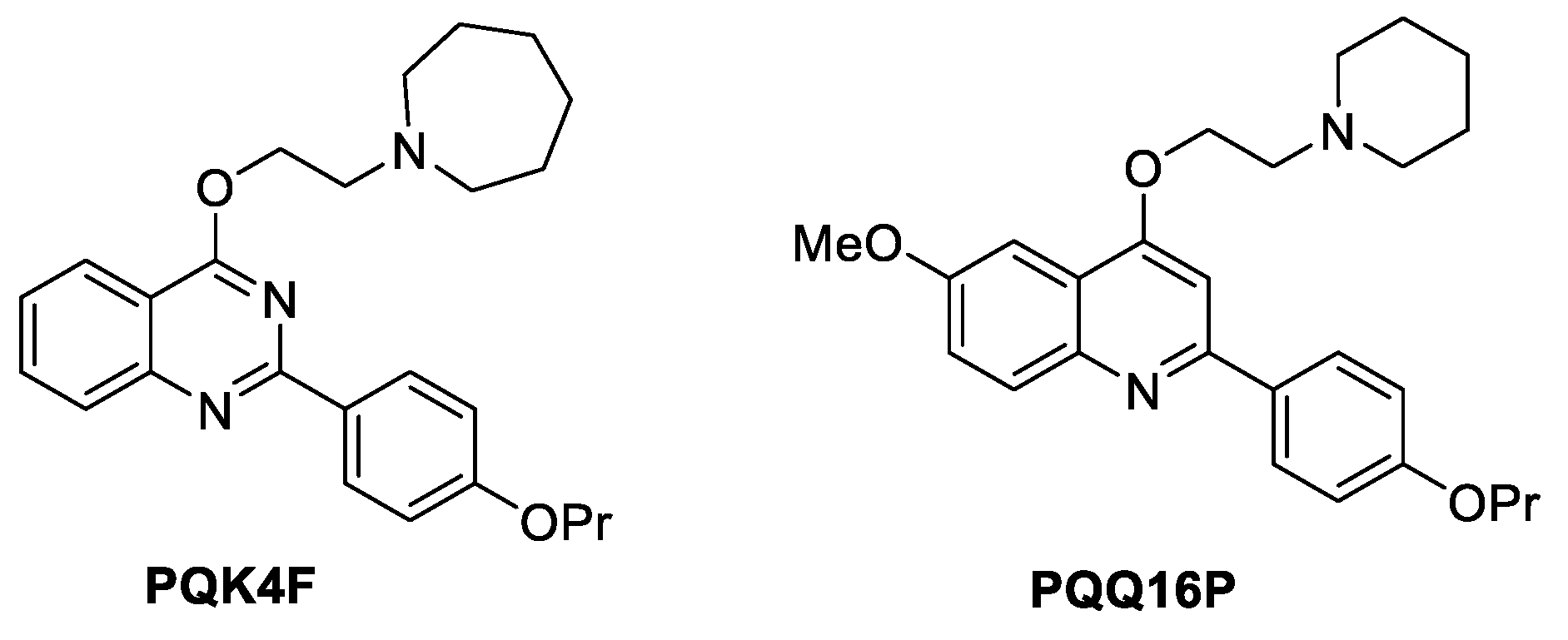
2.1. Impact of Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P on CPX's Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
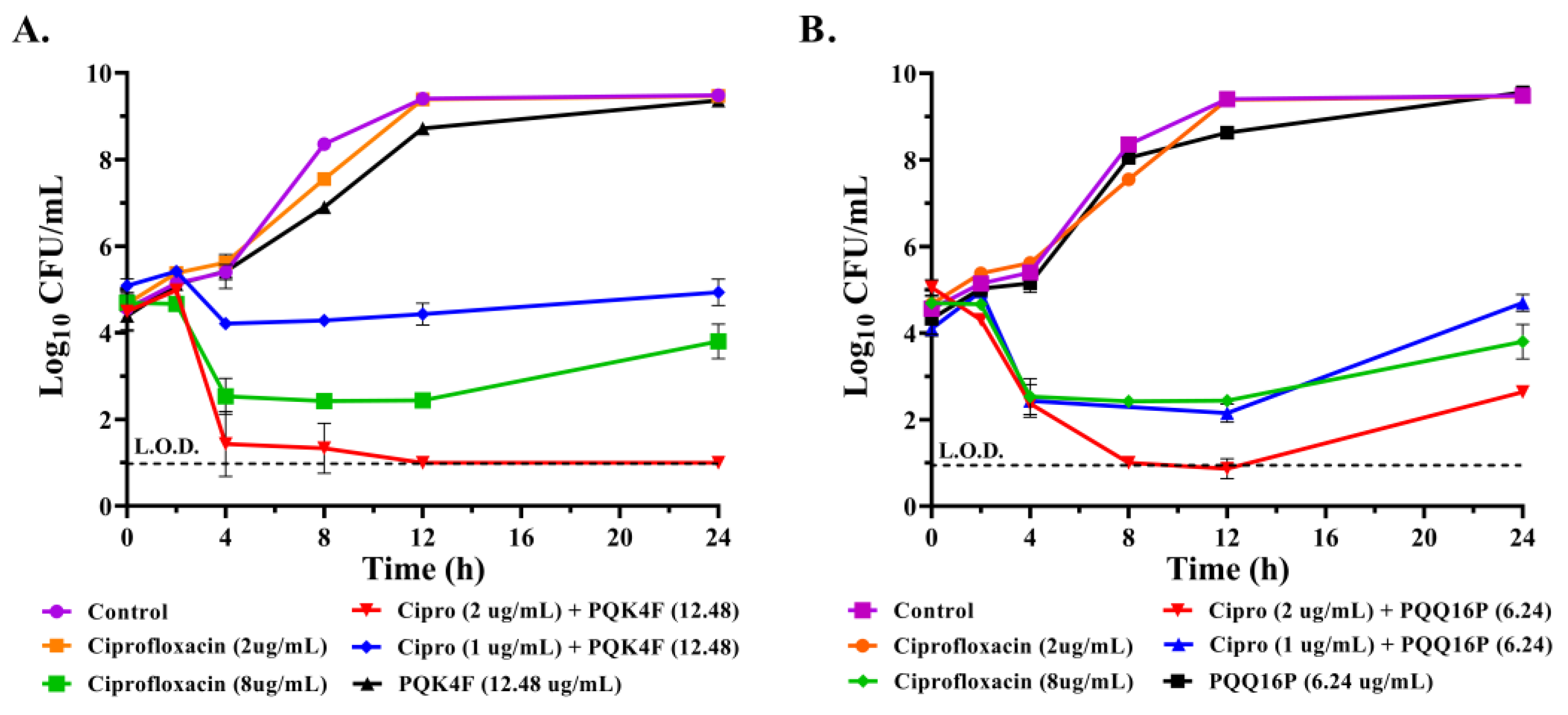
2.2. Effect of the Combination of CPX with Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P on the Time-Kill Kinetics on S. aureus SA-1199B
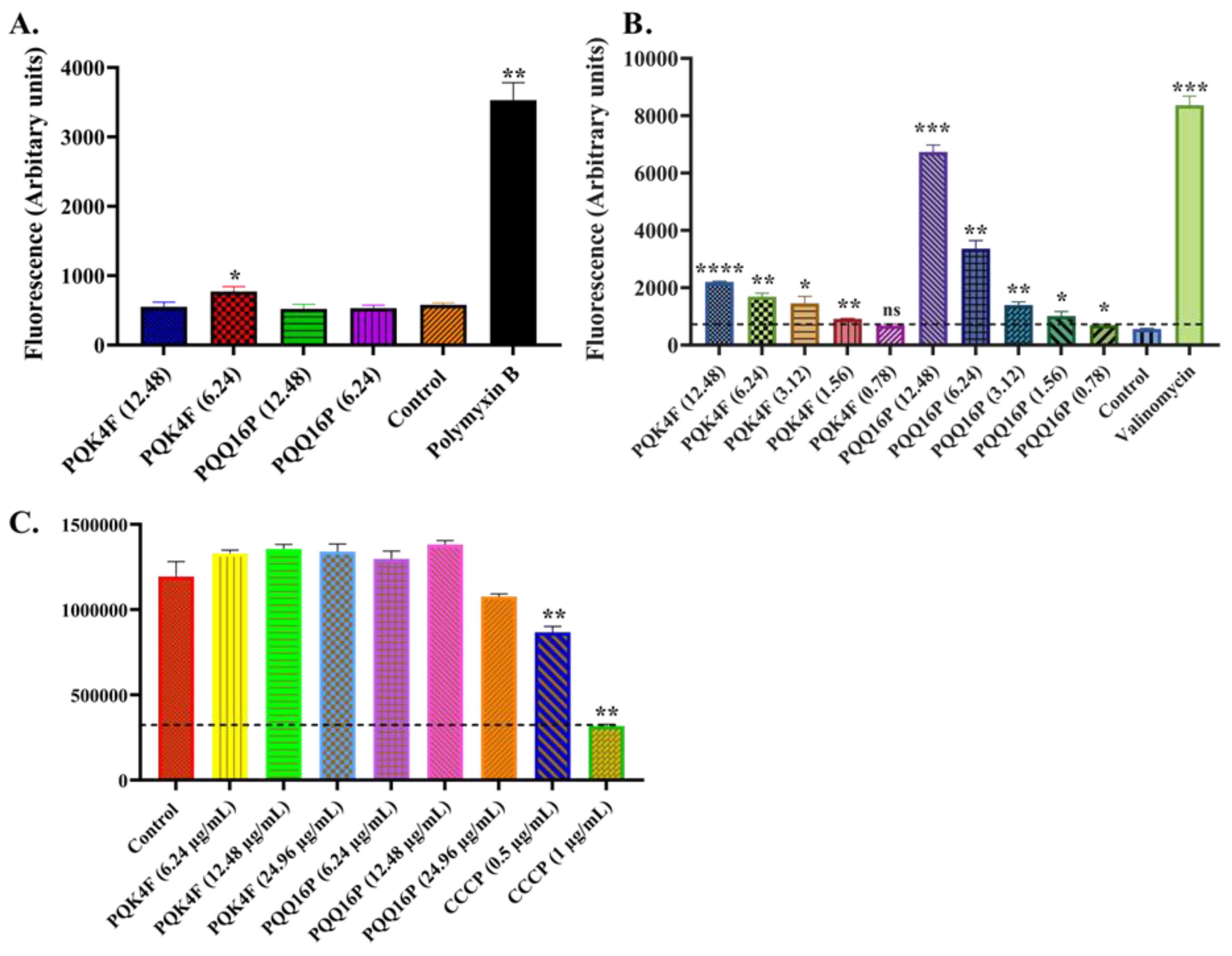
2.3. Membrane Permeabilization and Depolarization Activity of Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P on S. aureus SA-1199B
2.4. Effect of Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P on the Electron Transport Chain by ATP Bioluminescence Detection Assay
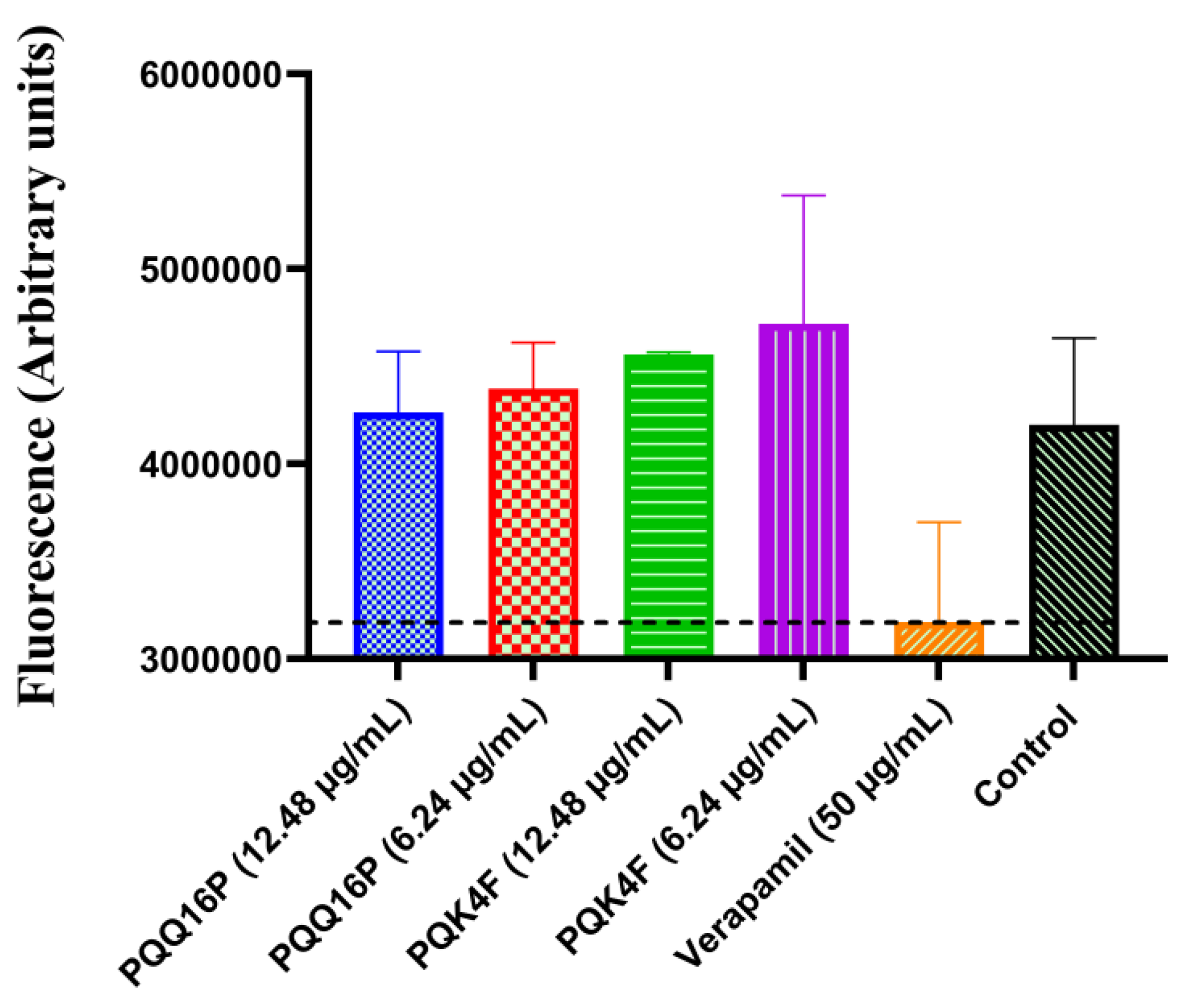
2.5. Effect of Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P on Mammalian Ca2+ Channels
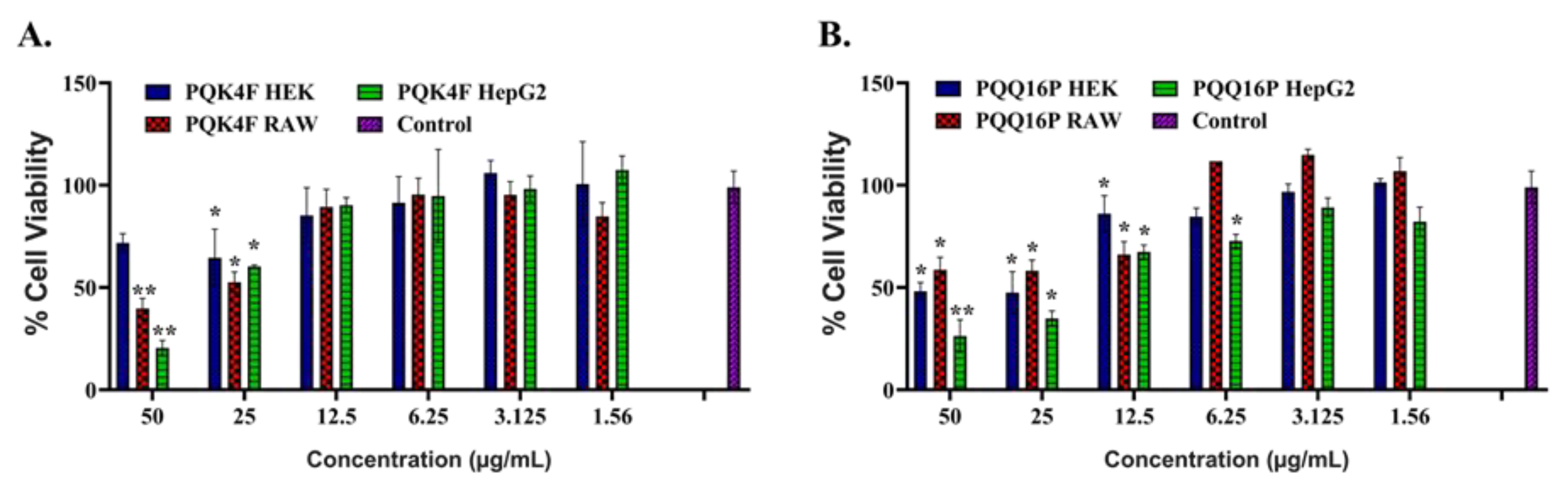
2.6. Toxicity Studies of Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P Towards Eukaryotic Cells
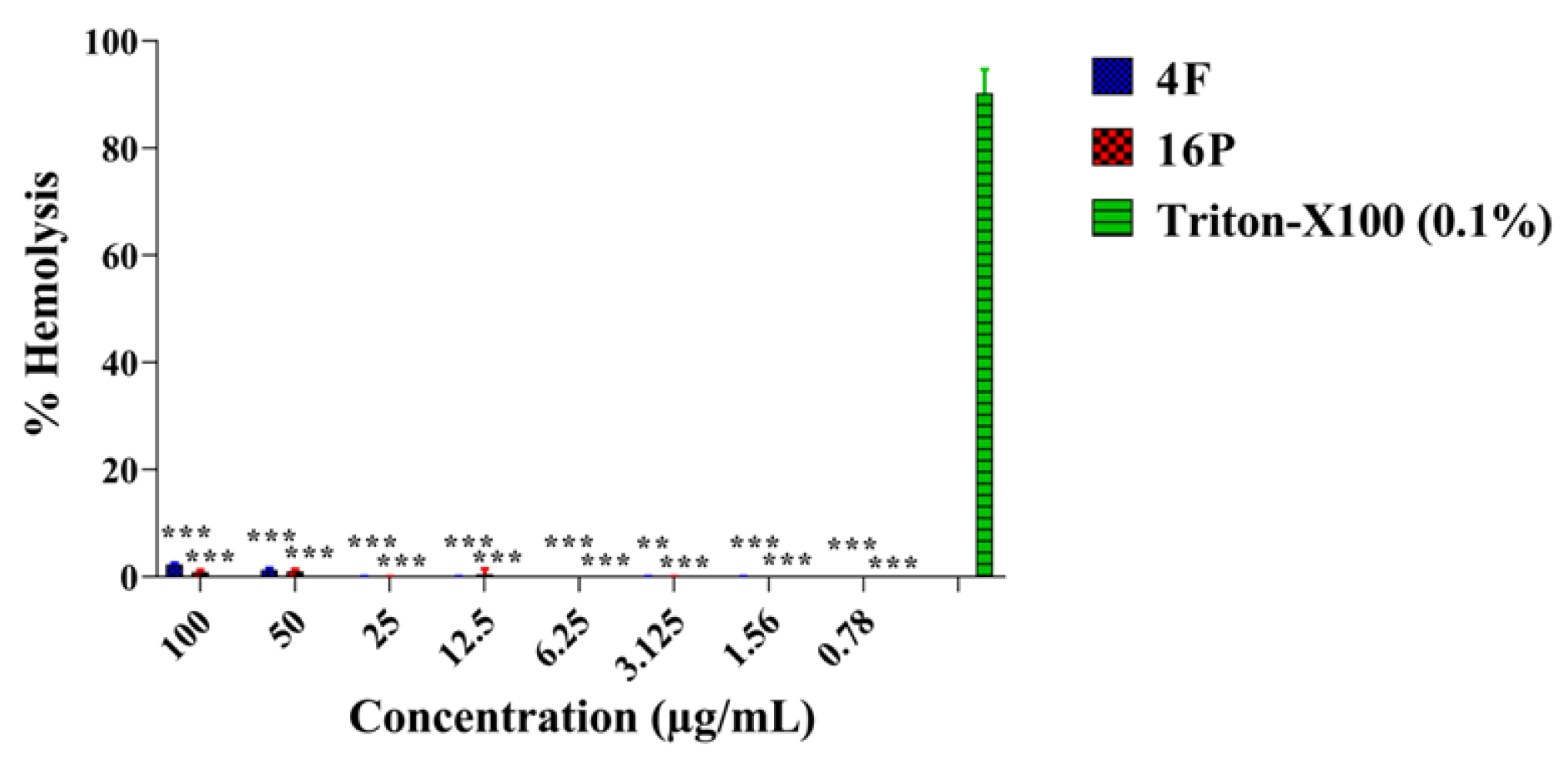
2.7. Hemolytic Activity Studies of the Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P
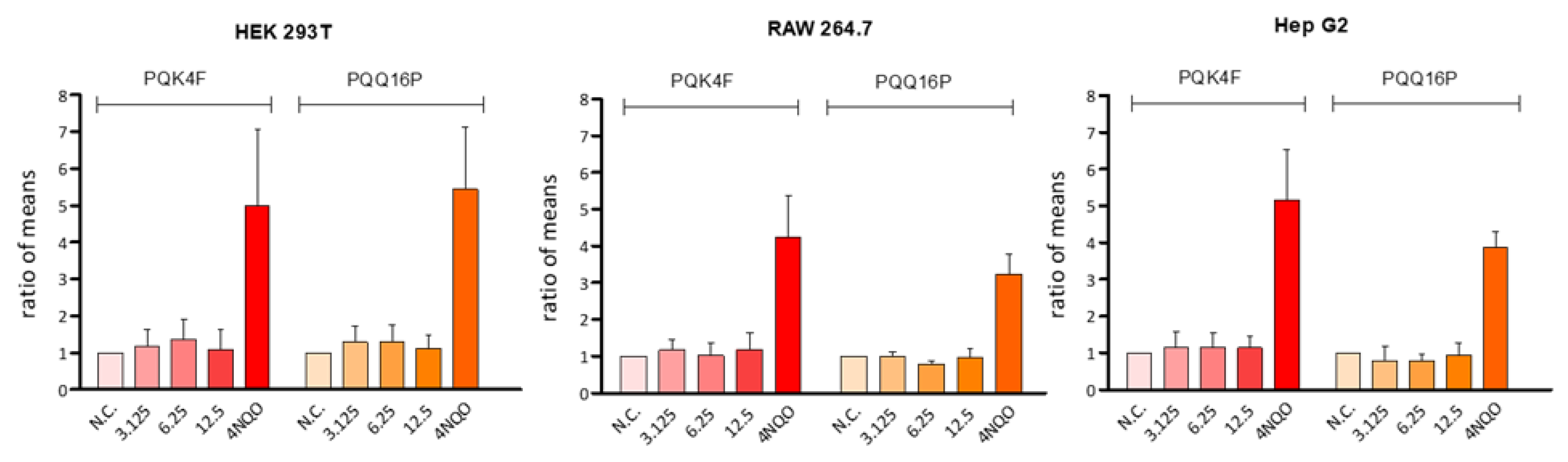
2.8. Genotoxicity Assessment
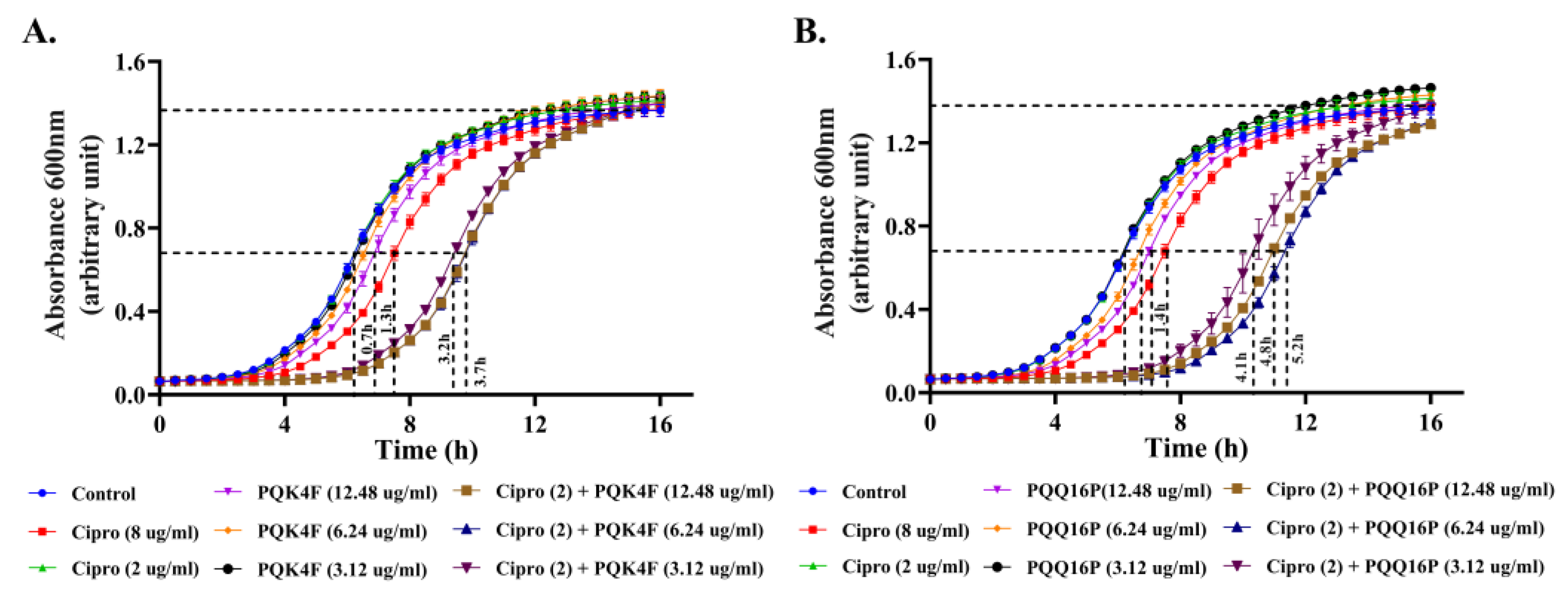
2.9. Enhanced Post-Antibiotic Life of CPX in the Presence of Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P
2.10. Mutation Frequency Analysis of Compounds PQK4F and PQQ16P to Check the Development of Its Resistant Mutants
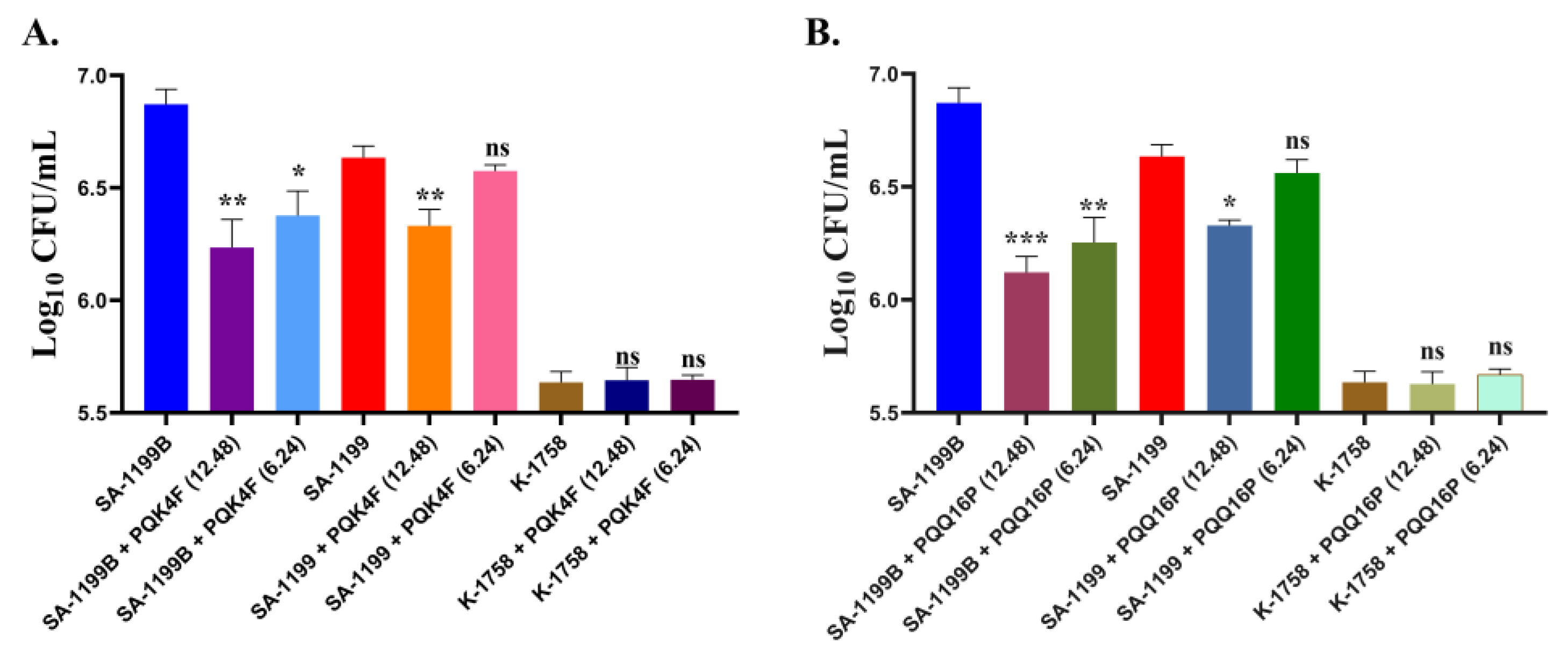
2.11. Effectiveness of PQK4F and PQQ16P in Mitigating Macrophage Invasion by norA over-Expressing S. aureus
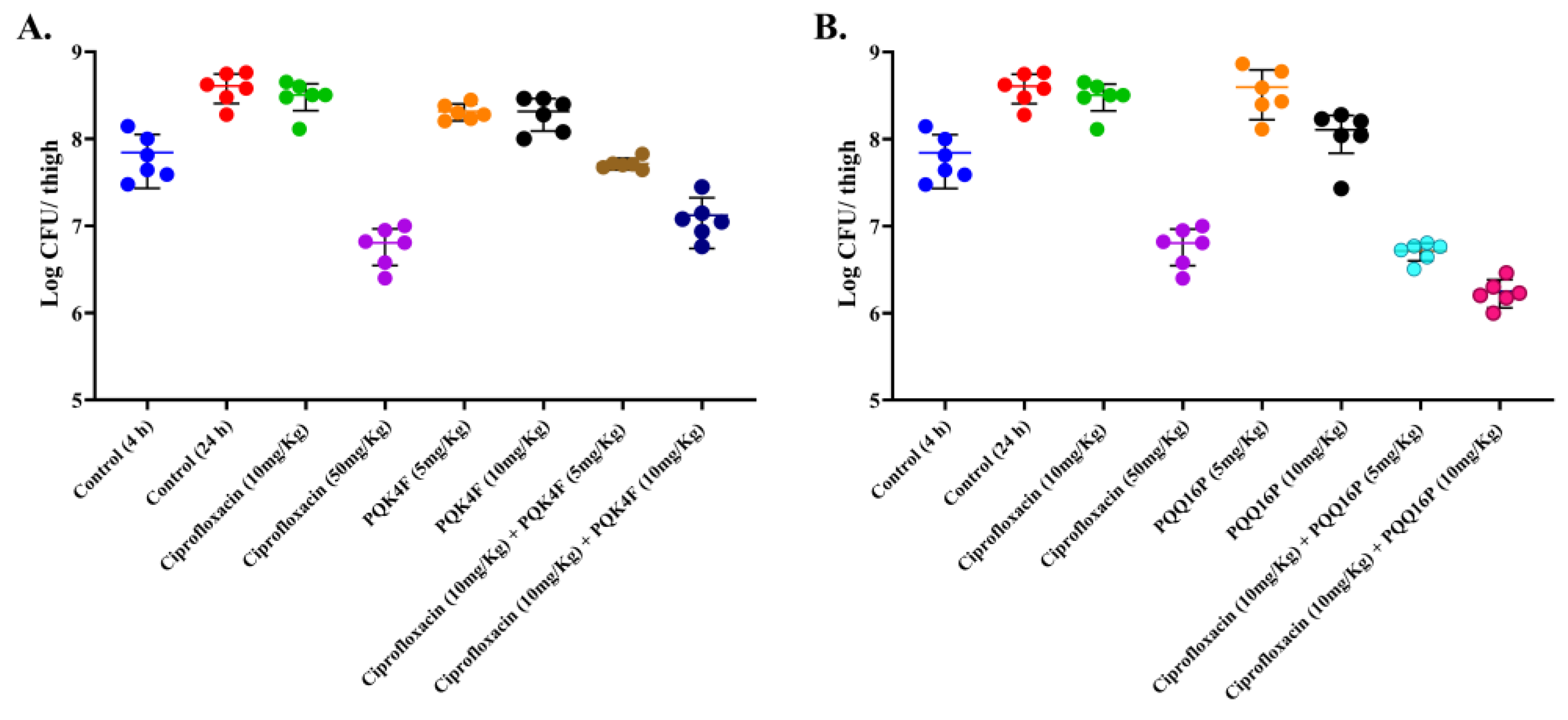
2.12. Mouse Thigh Infection Model In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Cell Lines, and Growth Medium
4.2. MIC Determination and Synergy Assay
4.3. Membrane Potentiation Assay
4.4. Membrane Permeability Assay
4.5. Determination of Intracellular ATP Levels
4.6. Mammalian Ca2+ Channel Blocking Assay
4.7. Genotoxicity Test
4.7.1. Chemical and Reagents
4.7.2. Alkaline Single-Cell Microgel Electrophoresis (Comet) Assay
4.8. Post-Antibiotic Assay
4.9. Mutation Prevention Concentration (MPC)
4.10. Time-Kill Kinetics Study
4.11. Hemolysis Assay
4.12. Mammalian Cytotoxicity
4.13. Macrophage Invasion Assay
4.14. In Vivo Thigh Infection Model
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gherardi, G. Staphylococcus Aureus Infection: Pathogenesis and Antimicrobial Resistance. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 8182. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Staphylococcus Aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547. [CrossRef]
- Thomer, L.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D. Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus Aureus Bloodstream Infections. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease 2016, 11, 343–364. [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, J.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus Aureus Bloodstream Infections: Pathogenesis and Regulatory Mechanisms. Curr Opin Microbiol 2020, 53, 51–60. [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Aguilar, G.R.; Sharara, F.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Weaver, N.D.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Hayoon, A.G.; et al. Global Mortality Associated with 33 Bacterial Pathogens in 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, G.R.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Weaver, N.D.; Ikuta, K.S.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Chung, E.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Hayoon, A.G.; et al. The Burden of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Americas in 2019: A Cross-Country Systematic Analysis. The Lancet Regional Health - Americas 2023, 25, 100561. [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. The Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [CrossRef]
- Mestrovic, T.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Ikuta, K.S.; Gray, A.P.; Davis Weaver, N.; Han, C.; Wool, E.E.; Gershberg Hayoon, A.; Hay, S.I.; et al. The Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in the WHO European Region in 2019: A Cross-Country Systematic Analysis. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, 897–913. [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2009, 48, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE Pathogens: Antimicrobial Resistance, Epidemiology, Clinical Impact and Therapeutics. Nat Rev Microbiol 2024, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.M.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: An Overview of Basic and Clinical Research. Nat Rev Microbiol 2019, 17, 203–218. [CrossRef]
- Abebe, A.A.; Birhanu, A.G. Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Drug Resistance Development and Novel Strategies to Combat. Infect Drug Resist 2023, 16, 7641. [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.; Nehra, K.; Rana, J.S.; Dahiya, T. Antibiotic Resistance in Agriculture: Perspectives on Upcoming Strategies to Overcome Upsurge in Resistance. Curr Res Microb Sci 2021, 2, 100030. [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Bhat, A.; Ravi, K. Antibiotics Misuse and Antimicrobial Resistance Development in Agriculture: A Global Challenge. Environment and Health 2024. [CrossRef]
- Haaber, J.; Penadés, J.R.; Ingmer, H. Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus Aureus. Trends Microbiol 2017, 25, 893–905. [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.J.A.; Wulandari, S.W.; Lovell, S.D.; Laabei, M. Novel Antimicrobial Strategies to Treat Multi-drug Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections. Microb Biotechnol 2023, 16, 1456. [CrossRef]
- Papkou, A.; Hedge, J.; Kapel, N.; Young, B.; MacLean, R.C. Efflux Pump Activity Potentiates the Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance across S. Aureus Isolates. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, S.; Shivaee, A.; Khosravi, M.A.; Eshaghi, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Hosseini, F. Evaluation of Multidrug Efflux Pump Expression in Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus Aureus. Gene Rep 2020, 18, 100537. [CrossRef]
- The Major Facilitator Superfamily, M.; Kolar, M.; Auxiliadora Dea-Ayuela, M.; Stephen, J.; Salam, F.; Lekshmi, M.; Kumar, S.H.; Varela, M.F. The Major Facilitator Superfamily and Antimicrobial Resistance Efflux Pumps of the ESKAPEE Pathogen Staphylococcus Aureus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 343. [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L.; Couto, I. Multidrug Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus Aureus: An Update. Open Microbiol J 2013, 7, 59–71. [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, S.; Ganjloo, S.; Pourmand, M.R.; Mashhadi, R.; Ghazvini, K. Epidemiology of Efflux Pumps Genes Mediating Resistance among Staphylococcus Aureus; a Systematic Review. Microb Pathog 2020, 139, 103850. [CrossRef]
- Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, G.W. Multidrug Efflux Pumps of Gram-Positive Bacteria. Drug Resistance Updates 2016, 27, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Laws, M.; Shaaban, A.; Rahman, K.M. Antibiotic Resistance Breakers: Current Approaches and Future Directions. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2019, 43, 490–516. [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, G.; Acharya, Y.; Haldar, J. Antibiotic Adjuvants: A Versatile Approach to Combat Antibiotic Resistance. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 10757–10783. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yasmeen, N.; Pandey, A.; Ahmad Chaudhary, A.; Alawam, A.S.; Ahmad Rudayni, H.; Islam, A.; Lakhawat, S.S.; Sharma, P.K.; Shahid, M. Antibiotic Adjuvants: Synergistic Tool to Combat Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023, 13, 1293633. [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.D. Antibiotic Adjuvants: Rescuing Antibiotics from Resistance. Trends Microbiol 2016, 24, 862–871. [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Dastidar, S.G.; Fanning, S.; Kristiansen, J.E.; Molnar, J.; Pagès, J.-M.; Schelz, Z.; Spengler, G.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L. Potential Role of Non-Antibiotics (Helper Compounds) in the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections: Mechanisms for Their Direct and Indirect Activities. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2008, 31, 198–208. [CrossRef]
- Christaki, E.; Marcou, M.; Tofarides, A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria: Mechanisms, Evolution, and Persistence. J Mol Evol 2019, 88, 26–40. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, W. The Mechanism of Bacterial Resistance and Potential Bacteriostatic Strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1215. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, R. Efflux Pump Inhibitors for Bacterial Pathogens: From Bench to Bedside. Indian J Med Res 2019, 149, 129. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Bogaki, M.; Nakamura, S.; Ubukata, K.; Konno, M. Nucleotide Sequence and Characterization of the Staphylococcus Aureus NorA Gene, Which Confers Resistance to Quinolones. J Bacteriol 1990, 172, 6942–6949.
- Costa, S.S.; Sobkowiak, B.; Parreira, R.; Edgeworth, J.D.; Viveiros, M.; Clark, T.G.; Couto, I. Genetic Diversity of NorA, Coding for a Main Efflux Pump of Staphylococcus Aureus. Front Genet 2019, 10, 421435. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Koide, A.; Kuang, H.; Torres, V.J.; Koide, S.; Wang, D.N.; Traaseth, N.J. Proton-Coupled Transport Mechanism of the Efflux Pump NorA. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Lamut, A.; Peterlin Mašič, L.; Kikelj, D.; Tomašič, T. Efflux Pump Inhibitors of Clinically Relevant Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. Med Res Rev 2019, 39, 2460–2504. [CrossRef]
- Brawley, D.N.; Sauer, D.B.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Koide, A.; Jedhe, G.S.; Suwatthee, T.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Arora, P.S.; et al. Structural Basis for Inhibition of the Drug Efflux Pump NorA from Staphylococcus Aureus. Nature Chemical Biology 2022 2022, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Lepri, S.; Buonerba, F.; Goracci, L.; Velilla, I.; Ruzziconi, R.; Schindler, B.D.; Seo, S.M.; Kaatz, G.W.; Cruciani, G. Indole Based Weapons to Fight Antibiotic Resistance: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study. J Med Chem 2016, 59, 867–891. [CrossRef]
- Buonerba, F.; Lepri, S.; Goracci, L.; Schindler, B.D.; Seo, S.M.; Kaatz, G.W.; Cruciani, G. Improved Potency of Indole-Based NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors: From Serendipity toward Rational Design and Development. J Med Chem 2017, 60, 517–523. [CrossRef]
- Hequet, A.; Burchak, O.N.; Jeanty, M.; Guinchard, X.; Le Pihive, E.; Maigre, L.; Bouhours, P.; Schneider, D.; Maurin, M.; Paris, J.M.; et al. 1-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethanamine Derivatives as Potent Staphylococcus Aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1534–1545. [CrossRef]
- Chandal, N.; Tambat, R.; Kalia, R.; Kumar, G.; Mahey, N.; Jachak, S.; Nandanwar, H. Efflux Pump Inhibitory Potential of Indole Derivatives as an Arsenal against NorA over-Expressing Staphylococcus Aureus. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, e0487622. [CrossRef]
- Felicetti, T.; Mangiaterra, G.; Cannalire, R.; Cedraro, N.; Pietrella, D.; Astolfi, A.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; et al. C-2 Phenyl Replacements to Obtain Potent Quinoline-Based Staphylococcus Aureus NorA Inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2020, 35, 584–597. [CrossRef]
- Felicetti, T.; Cedraro, N.; Astolfi, A.; Cernicchi, G.; Mangiaterra, G.; Vaiasicca, S.; Massari, S.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; Tabarrini, O.; et al. New C-6 Functionalized Quinoline NorA Inhibitors Strongly Synergize with Ciprofloxacin against Planktonic and Biofilm Growing Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Strains. Eur J Med Chem 2022, 241, 114656. [CrossRef]
- Cedraro, N.; Cannalire, R.; Astolfi, A.; Mangiaterra, G.; Felicetti, T.; Vaiasicca, S.; Cernicchi, G.; Massari, S.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; et al. From Quinoline to Quinazoline-Based S. Aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors by Coupling a Focused Scaffold Hopping Approach and a Pharmacophore Search. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, F.; Hequet, A.; Voisin-Chiret, A.S.; Bouillon, A.; Lesnard, A.; Cresteil, T.; Jolivalt, C.; Rault, S. First Identification of Boronic Species as Novel Potential Inhibitors of the Staphylococcus Aureus NorA Efflux Pump. J Med Chem 2014, 57, 2536–2548. [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, F.; Héquet, A.; Voisin-Chiret, A.S.; Bouillon, A.; Lesnard, A.; Cresteil, T.; Jolivalt, C.; Rault, S. Boronic Species as Promising Inhibitors of the Staphylococcus Aureus NorA Efflux Pump: Study of 6-Substituted Pyridine-3-Boronic Acid Derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 2015, 95, 185–198. [CrossRef]
- Holler, J.G.; Slotved, H.C.; Molgaard, P.; Olsen, C.E.; Christensen, S.B. Chalcone Inhibitors of the NorA Efflux Pump in Staphylococcus Aureus Whole Cells and Enriched Everted Membrane Vesicles. Bioorg Med Chem 2012, 20, 4514–4521. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Khan, I.A.; Koul, S.; Koul, J.L.; Taneja, S.C.; Ali, I.; Ali, F.; Sharma, S.; Mirza, Z.M.; Kumar, M.; et al. Novel Structural Analogues of Piperine as Inhibitors of the NorA Efflux Pump of Staphylococcus Aureus. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2008, 61, 1270–1276. [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, P.L.; Koul, J.L.; Koul, S.; Reddy, M. V; Thota, N.; Khan, I.A.; Kumar, A.; Kalia, N.P.; Qazi, G.N. Piperine Analogs as Potent Staphylococcus Aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2008, 16, 9847–9857. [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.F.S.; Tintino, S.R.; da Silva, A.R.P.; Cristina, C.R.; Scherf, J.R.; de S. Silveira, Z.; de Freitas, T.S.; de Lacerda Neto, L.J.; Barros, L.M.; Irwin, I.R.; et al. Enhancement of the Antibiotic Activity by Quercetin against Staphylococcus Aureus Efflux Pumps. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2021, 53, 157–167. [CrossRef]
- Muniz, D.F.; dos Santos Barbosa, C.R.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; de Sousa, E.O.; Pereira, R.L.S.; Júnior, J.T.C.; Pereira, P.S.; de Matos, Y.M.L.S.; da Costa, R.H.S.; de Morais Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.; et al. In Vitro and in Silico Inhibitory Effects of Synthetic and Natural Eugenol Derivatives against the NorA Efflux Pump in Staphylococcus Aureus. Food Chem 2021, 337, 127776. [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.; Urzúa, A.; Sanhueza, L.; Walter, M.; Fincheira, P.; Muñoz, P.; Mendoza, L.; Wilkens, M. Essential Oil, Extracts, and Sesquiterpenes Obtained From the Heartwood of Pilgerodendron Uviferum Act as Potential Inhibitors of the Staphylococcus Aureus NorA Multidrug Efflux Pump. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 337. [CrossRef]
- Kalia, N.P.; Mahajan, P.; Mehra, R.; Nargotra, A.; Sharma, J.P.; Koul, S.; Khan, I.A. Capsaicin, a Novel Inhibitor of the NorA Efflux Pump, Reduces the Intracellular Invasion of Staphylococcus Aureus. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2012, 67, 2401–2408. [CrossRef]
- Diniz-Silva, H.T.; Magnani, M.; de Siqueira, S.; de Souza, E.L.; de Siqueira-Júnior, J.P. Fruit Flavonoids as Modulators of Norfloxacin Resistance in Staphylococcus Aureus That Overexpresses <i>NorA<i/>. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2017, 85, 324–326. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kalia, N.P.; Joshi, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.R.; Kumar, A.; Bharate, S.B.; Khan, I.A. Boeravinone B, A Novel Dual Inhibitor of NorA Bacterial Efflux Pump of Staphylococcus Aureus and Human P-Glycoprotein, Reduces the Biofilm Formation and Intracellular Invasion of Bacteria. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 1868. [CrossRef]
- de Morais Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.; Tintino, S.R.; Limaverde, P.W.; Figueredo, F.G.; Campina, F.F.; da Cunha, F.A.B.; da Costa, R.H.S.; Pereira, P.S.; Lima, L.F.; de Matos, Y.M.L.S.; et al. Inhibition of the Essential Oil from Chenopodium Ambrosioides L. and α-Terpinene on the NorA Efflux-Pump of Staphylococcus Aureus. Food Chem 2018, 262, 72–77. [CrossRef]
- Mouwakeh, A.; Kincses, A.; Nové, M.; Mosolygó, T.; Mohácsi-Farkas, C.; Kiskó, G.; Spengler, G. Nigella Sativa Essential Oil and Its Bioactive Compounds as Resistance Modifiers against Staphylococcus Aureus. Phytother Res 2019, 33, 1010–1018. [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, J.N.; de Oliveira, A.B.M.; Ferreira, A.K.; Silva, E.; de Sousa, L.M.S.; França Rocha, M.C.; De, J.P.; Júnior, S.; William Kaatz, G.; da Silva Almeida, J.R.G.; et al. Modulation of the Resistance to Norfloxacin in Staphylococcus Aureus by Bauhinia Forficata Link. Nat Prod Res 2021, 35, 681–685. [CrossRef]
- Cernicchi, G.; Felicetti, T.; Sabatini, S. Microbial Efflux Pump Inhibitors: A Journey around Quinoline and Indole Derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 6996. [CrossRef]
- Felicetti, T.; Cannalire, R.; Pietrella, D.; Latacz, G.; Lubelska, A.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; et al. 2-Phenylquinoline S. Aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors: Evaluation of the Importance of Methoxy Group Introduction. J Med Chem 2018, 61, 7827–7848. [CrossRef]
- Kaatz, G.W.; Seo, S.M. Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Genetically Related Strains of Staphylococcus Aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1997, 41, 2733–2737. [CrossRef]
- Uribe, E.G. ATP Synthesis Driven by a K+-Valinomycin-Induced Charge Imbalance across Chloroplast Grana Membranes. FEBS Lett 1973, 36, 143–147. [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.Y.; Cotman, C.W. Programmed Cell Death: Its Possible Contribution to Neurotoxicity Mediated by Calcium Channel Antagonists. Brain Res 1992, 587, 233–240. [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Barnett, P.; Perlmutter, J.; Dunman, P.M. Identification of Acinetobacter Baumannii Serum-Associated Antibiotic Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 6360. [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Fleet, J.L.; Bailey, D.G.; McArthur, E.; Wald, R.; Rehman, F.; Garg, A.X. Calcium-Channel Blocker–Clarithromycin Drug Interactions and Acute Kidney Injury. JAMA 2013, 310, 2544–2553. [CrossRef]
- AlMatar, M.; Albarri, O.; Makky, E.A.; Köksal, F. Efflux Pump Inhibitors: New Updates. Pharmacological Reports 2020, 73, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Pidwill, G.R.; Gibson, J.F.; Cole, J.; Renshaw, S.A.; Foster, S.J. The Role of Macrophages in Staphylococcus Aureus Infection. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 620339. [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.; Nabi, B.; Daswani, M.; Viquar, I.; Pal, N.; Sharma, P.; Tiwari, S.; Sarma, D.K.; Shubham, S.; Kumar, M. Role of Bacterial Efflux Pump Proteins in Antibiotic Resistance across Microbial Species. Microb Pathog 2023, 181, 106182. [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, H.F.L.; Vos, M.C.; Ott, A.; Van Belkum, A.; Voss, A.; Kluytmans, J.A.J.W.; Van Keulen, P.H.J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Meester, M.H.M.; Verbrugh, H.A. Risk and Outcome of Nosocomial Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteraemia in Nasal Carriers versus Non-Carriers. Lancet 2004, 364, 703–705. [CrossRef]
- Abbey, T.C.; Deak, E. What’s New from the CLSI Subcommittee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing M100, 29th Edition. Clin Microbiol Newsl 2019, 41, 203–209. [CrossRef]
- Hemaiswarya, S.; Kruthiventi, A.K.; Doble, M. Synergism between Natural Products and Antibiotics against Infectious Diseases. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 639–652. [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Klinger-Strobel, M.; Bohnert, J.A.; Wendler, S.; Rödel, J.; Pletz, M.W.; Löffler, B.; Tuchscherr, L. Clinically Approved Drugs Inhibit the Staphylococcus Aureus Multidrug NorA Efflux Pump and Reduce Biofilm Formation. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 492781. [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Maier, E.; Benz, R.; Hancock, R.E.W. Mechanism of Interaction of Different Classes of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides with Planar Bilayers and with the Cytoplasmic Membrane of Escherichia Coli. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7235–7242. [CrossRef]
- Morin, N.; Lanneluc, I.; Connil, N.; Cottenceau, M.; Pons, A.M.; Sablé, S. Mechanism of Bactericidal Activity of Microcin L in Escherichia Coli and Salmonella Enterica. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2011, 55, 997–1007. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Huang, J.X.; Ramu, S.; Butler, M.S.; Cooper, M.A. Ramoplanin at Bactericidal Concentrations Induces Bacterial Membrane Depolarization in Staphylococcus Aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 6819. [CrossRef]
- French, S.; Farha, M.; Ellis, M.J.; Sameer, Z.; Côté, J.P.; Cotroneo, N.; Lister, T.; Rubio, A.; Brown, E.D. Potentiation of Antibiotics against Gram-Negative Bacteria by Polymyxin B Analogue SPR741 from Unique Perturbation of the Outer Membrane. ACS Infect Dis 2020, 6, 1405–1412. [CrossRef]
- Tambat, R.; Jangra, M.; Mahey, N.; Chandal, N.; Kaur, M.; Chaudhary, S.; Verma, D.K.; Thakur, K.G.; Raje, M.; Jachak, S.; et al. Microbe-Derived Indole Metabolite Demonstrates Potent Multidrug Efflux Pump Inhibition in Staphylococcus Aureus. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 2153. [CrossRef]
- OECD Overview of the Set of OECD Genetic Toxicology Test Guidelines and Updates Performed in 2014-2015 Series On. 2016, 60. [CrossRef]
- di Vito, R.; Levorato, S.; Fatigoni, C.; Acito, M.; Sancineto, L.; Traina, G.; Villarini, M.; Santi, C.; Moretti, M. In Vitro Toxicological Assessment of PhSeZnCl in Human Liver Cells. Toxicol Res 2023, 39, 105. [CrossRef]
- Rondini, T.; Branciari, R.; Franceschini, E.; Acito, M.; Fatigoni, C.; Roila, R.; Ranucci, D.; Villarini, M.; Galarini, R.; Moretti, M. Olive Mill Wastewater Extract: In Vitro Genotoxicity/Antigenotoxicity Assessment on HepaRG Cells. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2024, 21, 1050. [CrossRef]
- Lovell, D.P.; Omori, T. Statistical Issues in the Use of the Comet Assay. Mutagenesis 2008, 23, 171–182. [CrossRef]
- Rázquin-Olazarán, I.; Shahrour, H.; Martínez-De-Tejada, G. A Synthetic Peptide Sensitizes Multi-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa to Antibiotics for More than Two Hours and Permeabilizes Its Envelope for Twenty Hours. J Biomed Sci 2020, 27, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Drugeon, H.B.; Juvin, M.E.; Bryskier, A. Relative Potential for Selection of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Streptococcus Pneumoniae Strains by Levofloxacin: Comparison with Ciprofloxacin, Sparfloxacin and Ofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother 1999, 43, 55–59. [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.L.; Schneider, T.; Peoples, A.J.; Spoering, A.L.; Engels, I.; Conlon, B.P.; Mueller, A.; Schäberle, T.F.; Hughes, D.E.; Epstein, S.; et al. A New Antibiotic Kills Pathogens without Detectable Resistance. Nature 2015, 517, 455–459. [CrossRef]
| CPX Conc. | 0.25×MIC | 0.5×MIC | 1×MIC | 2×MIC | 4×MIC | 8×MIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFU count | ||||||
| CPX | UC | UC | UC | 2.75 × 10-9 | 2.3 × 10-8 | < 10-9 |
| + PQK4F (6.24 µg/mL) | UC | 1 × 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 |
| + PQK4F (12.48 µg/mL) | 5.26 × 10-9 | 3 × 10-7 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 |
| + PQQ16P (3.12 µg/mL) | UC | 1.67 × 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 |
| + PQQ16P (6.24 µg/mL) | UC | 1 × 10-7 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 | < 10-9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





