Submitted:
14 February 2025
Posted:
17 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- RQ1: What is the state of the literature on mining equipment maintenance, with a particular focus on pump systems, between 2005 and 2024?
- RQ2: What are the main research and knowledge gaps in pump systems maintenance, especially in the mining industry sector?
- RQ3: What trends can be identified in proactive maintenance approaches, and how have they evolved over recent years in the mining sector?
- RQ4: What scope should the framework for proactive maintenance of pump systems in the mining industry have?
2. Theoretical Background
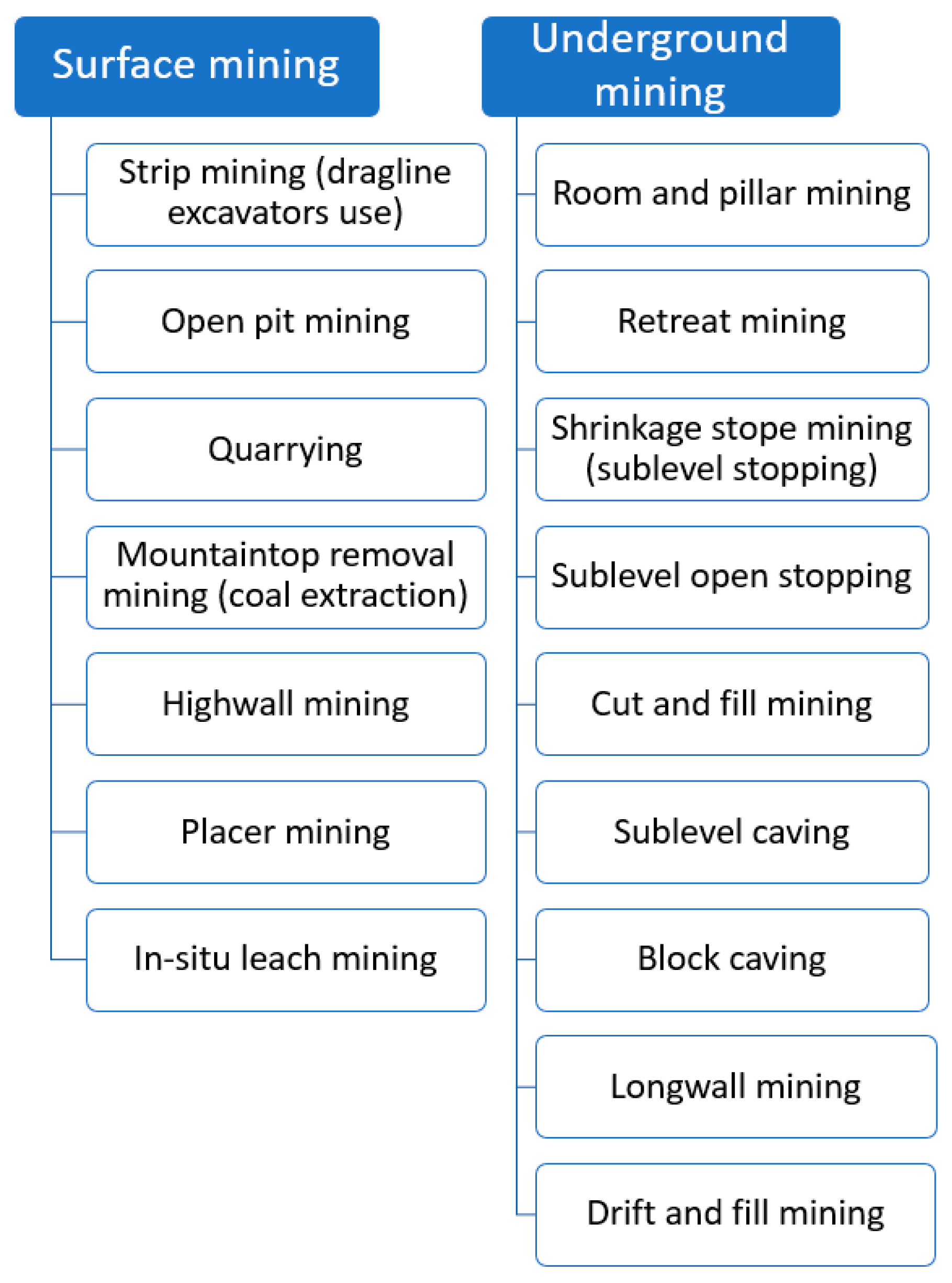
2.1. Pump Systems in the Mining Industry
- surface mining activity means that all the work related to the extraction of raw materials takes place on the surface, and the entire process of extracting minerals is based on the discovery of successive layers of the deposit of raw material,
- underground mining, also known as subsurface mining, consists of digging or blasting tunnels and shafts into the earth's crust to reach buried orebodies. Ore deposits and tailings are brought to the surface to be refined by onsite processing plants.
- water that is needed for technological processes performance,
- water that remains after technological processes performance,
- water as an inflow to mine working areas caused by ore exploitation.
- Water can also enter the pits due to rainfall in the surface mines.
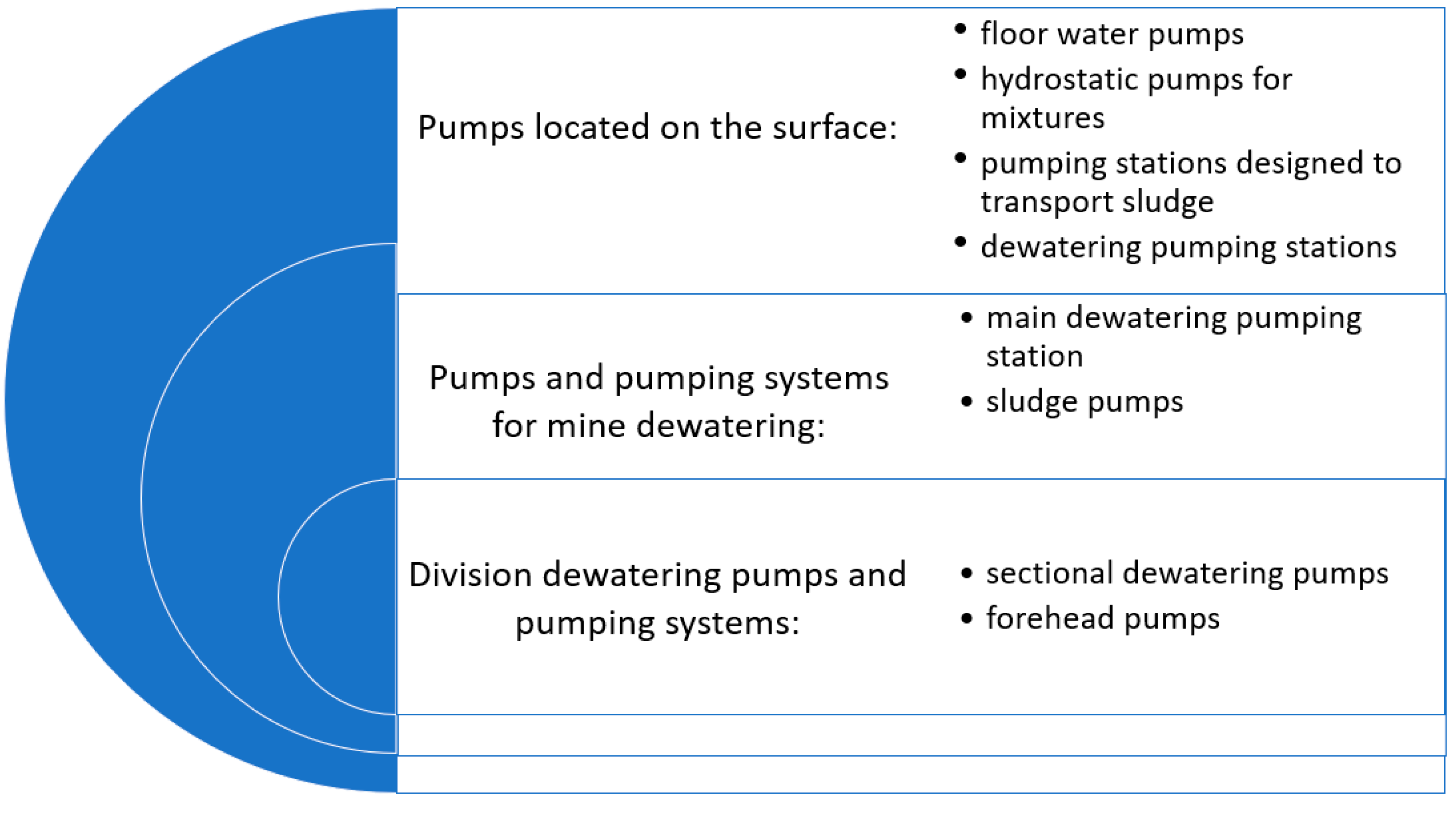
- horizontal dewatering system,
- main (vertical) dewatering system,
- technological water system,
- and other water systems, such as e.g.:
- fire water system, or
- air-conditioning system.
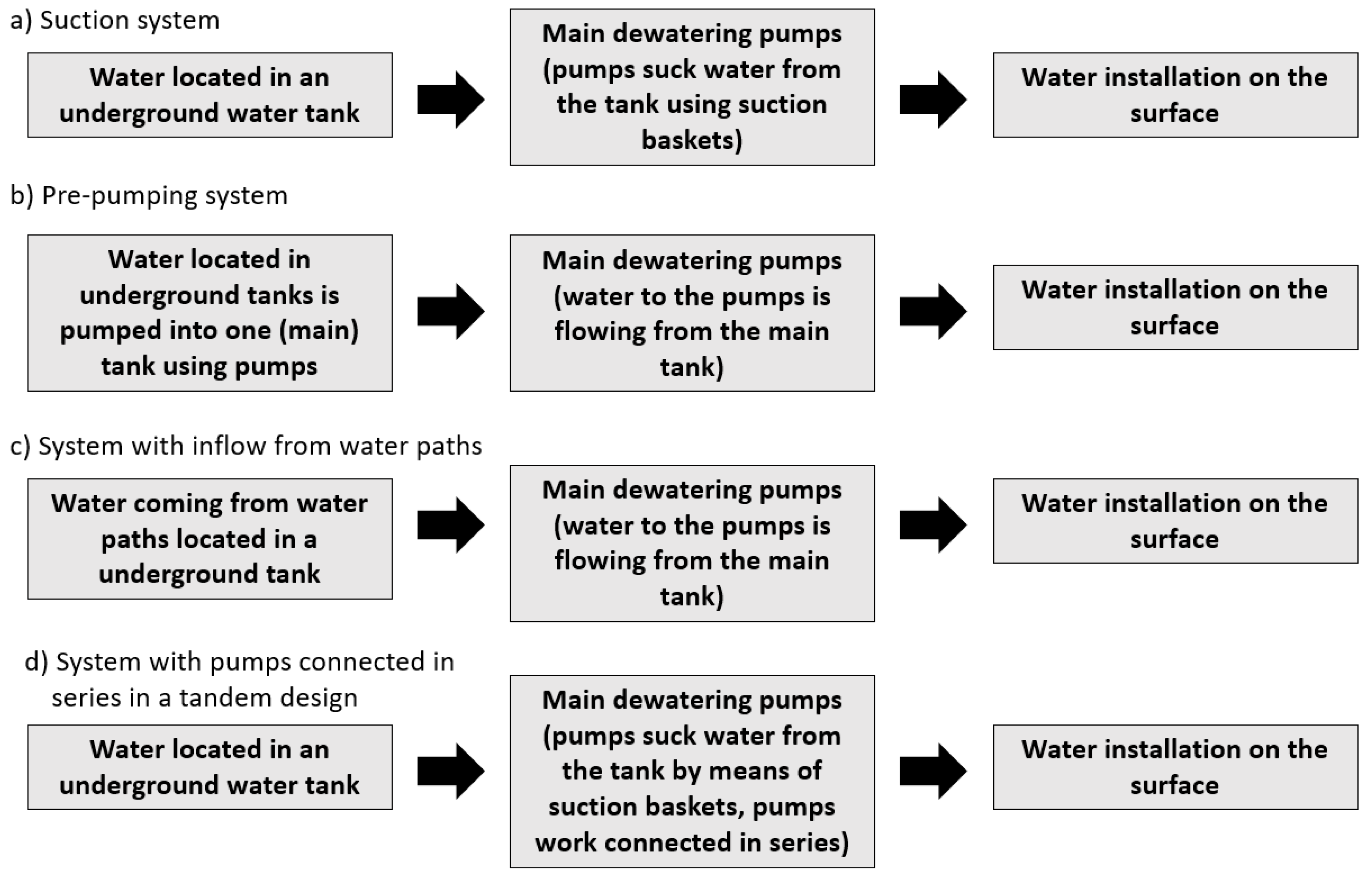
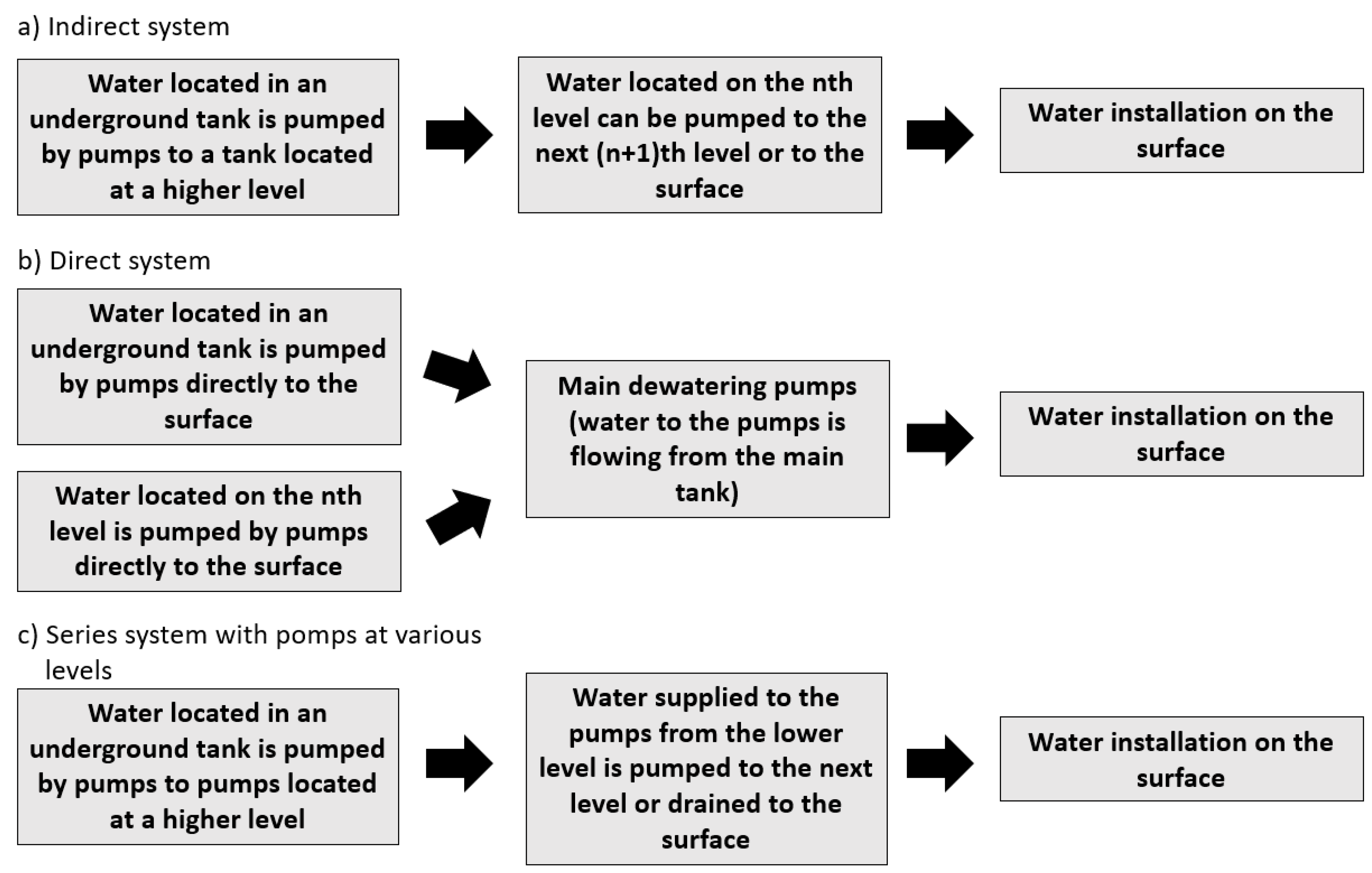
- single-stage,
- multi-level,
- indirect, and
- direct.
- slurry pumps, widely used in mining to transport abrasive mixtures of solids and liquids. They are prone to wear and tear due to the abrasive nature of the materials they handle,
- submersible pumps, commonly used for mine dewatering. They are preferred for their ease of installation and maintenance,
- centrifugal pumps, used for various applications, including dewatering and slurry transport. They require careful selection and maintenance to ensure longevity and efficiency.
- the number of levels on which mining is executed,
- the distance from the mining decks,
- water inflow on each level,
- the irregularity of the inflows,
- the possibility of collecting water in the pits.
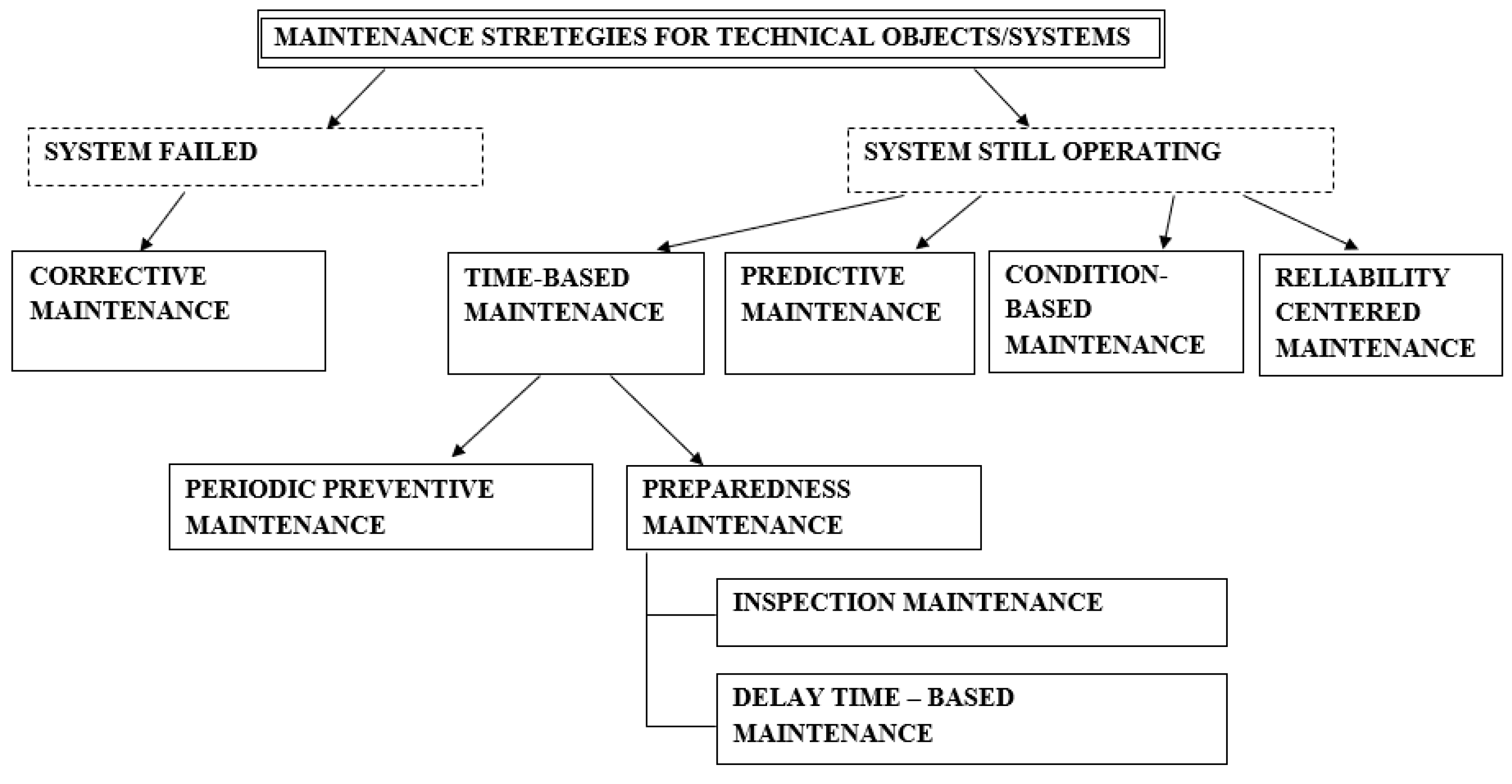
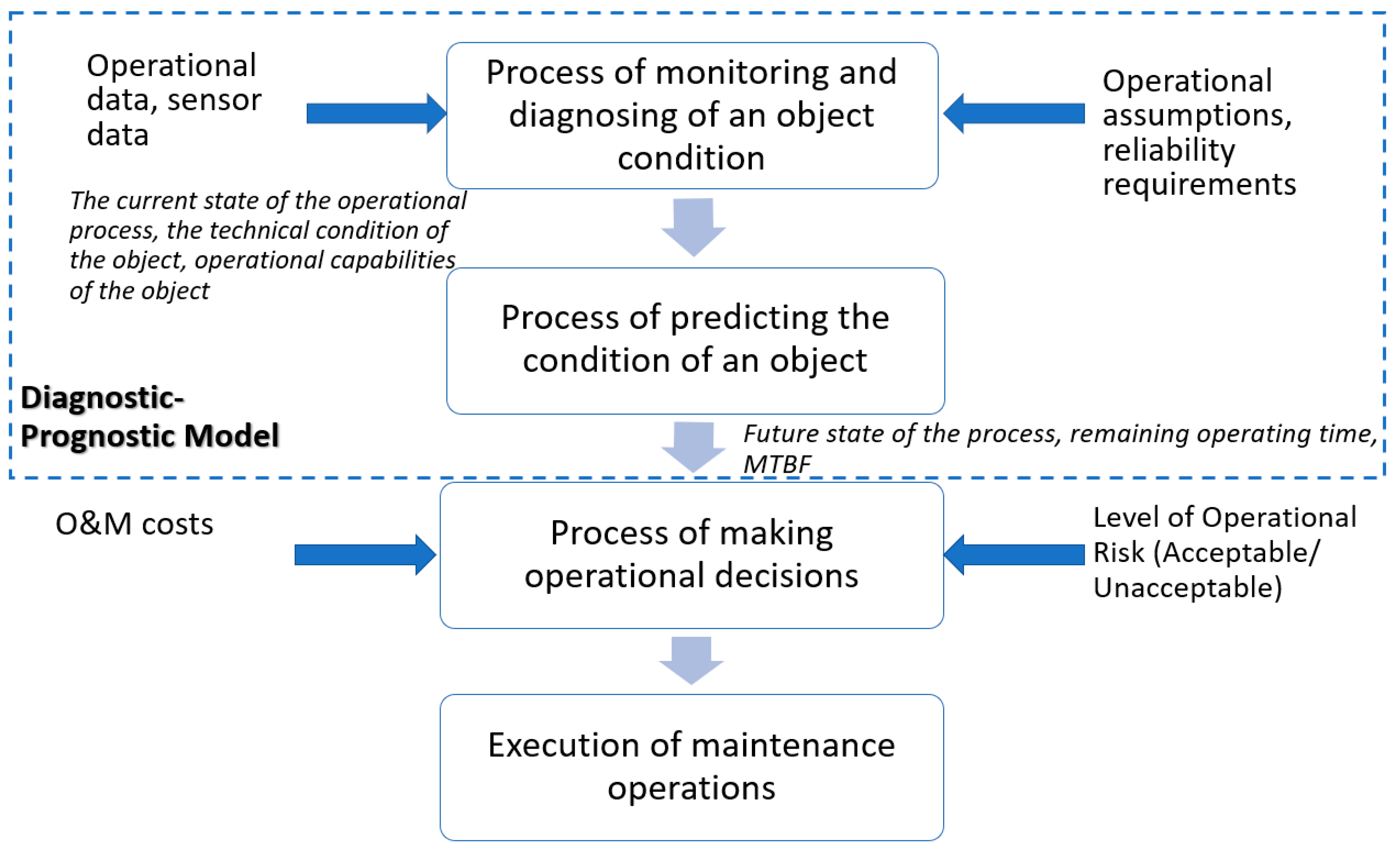
2.2. Maintenance of Pump Systems
2.2.1. Pump Systems Reliability Issues
- excessive temperature generated at seals,
- rotor looseness,
- corrosion of the casing or impeller due to turbulence or cavitation,
- damage to rolling elements (bearings),
- failures caused by improper use of the pump outside its design parameters.
- temperature: excessive heating in areas experiencing high friction,
- pressure: a drop in pump efficiency,
- power consumption: increased power draw indicating inefficiencies,
- vibrations: an increase in overall vibration levels, with bearing failures often preceded by changes in vibration patterns. excessive vibrations may result from pump misalignment or cavitation resonance between the pump, its base, or valves located in the suction or discharge lines,
- leakage: monitoring seal integrity and bolted connections.
2.2.2. Pump Systems Maintenance Issues
- lack of comprehensive reviews on mining-specific pump maintenance: while numerous studies broadly explore pump maintenance, few focus on the unique environmental and operational challenges the mining industry faces. This review provides a structured and in-depth analysis tailored to these conditions,
- limited exploration of advanced maintenance strategies in mining: the application of CBM and PdM in mining pump systems remains underexplored. This article highlights the potential of these approaches to improve reliability and efficiency in harsh mining environments and proposes future research directions to optimize their implementation.
3. Review Methodology
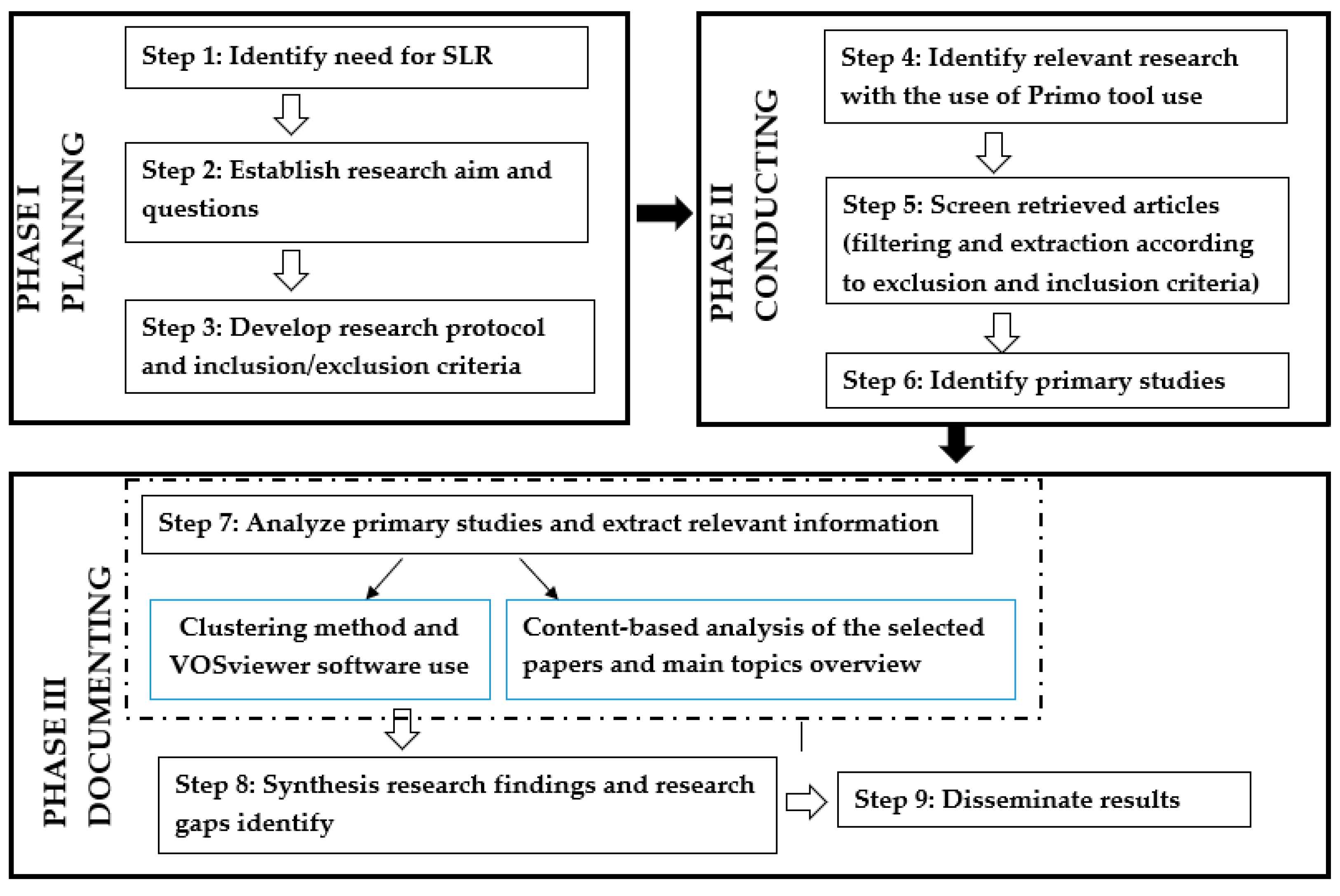
3.1. Planning of the SLR Study
3.2. Conducting the SLR Study
3.2.1. Collection of Publications for Review
| (ALL = (pump maintenance)) AND (ALL = (pump condition OR pump monitoring OR pump prognosis OR pump diagnosis OR pump fault)) AND (ALL = (mining industry)) |
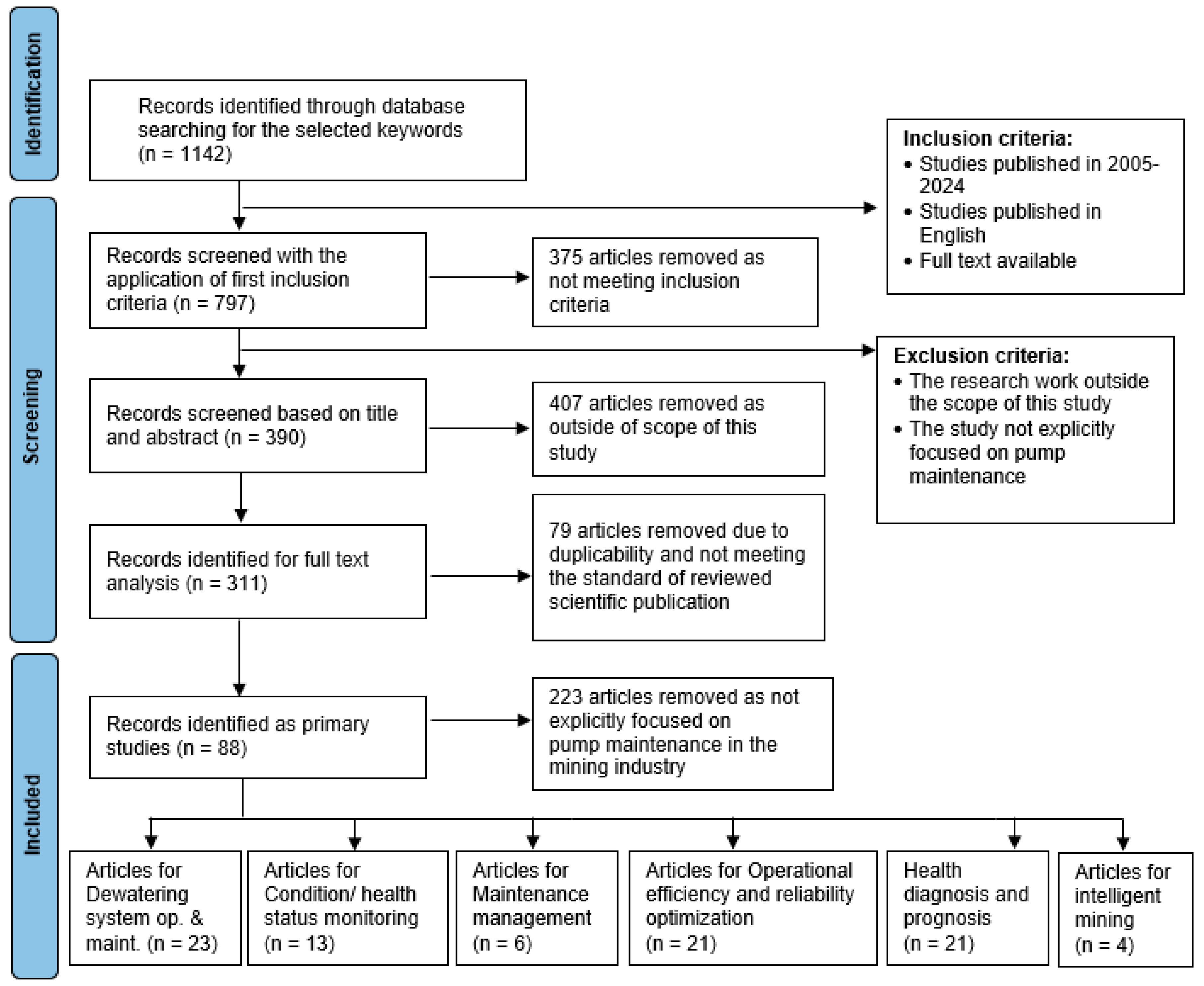
3.2.2. Screening of Collected Publications
3.2.3. Primary Studies Identification
3.3. Documenting of the SLR Study
4. Results
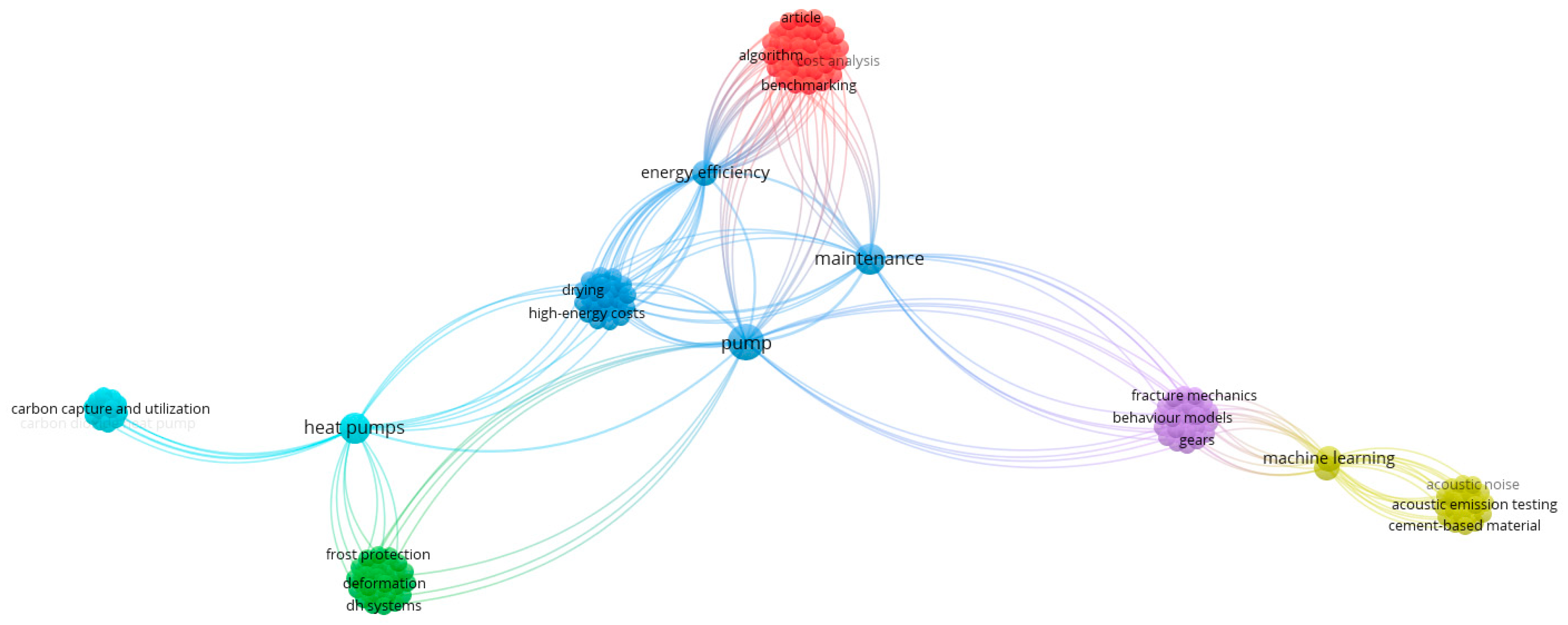
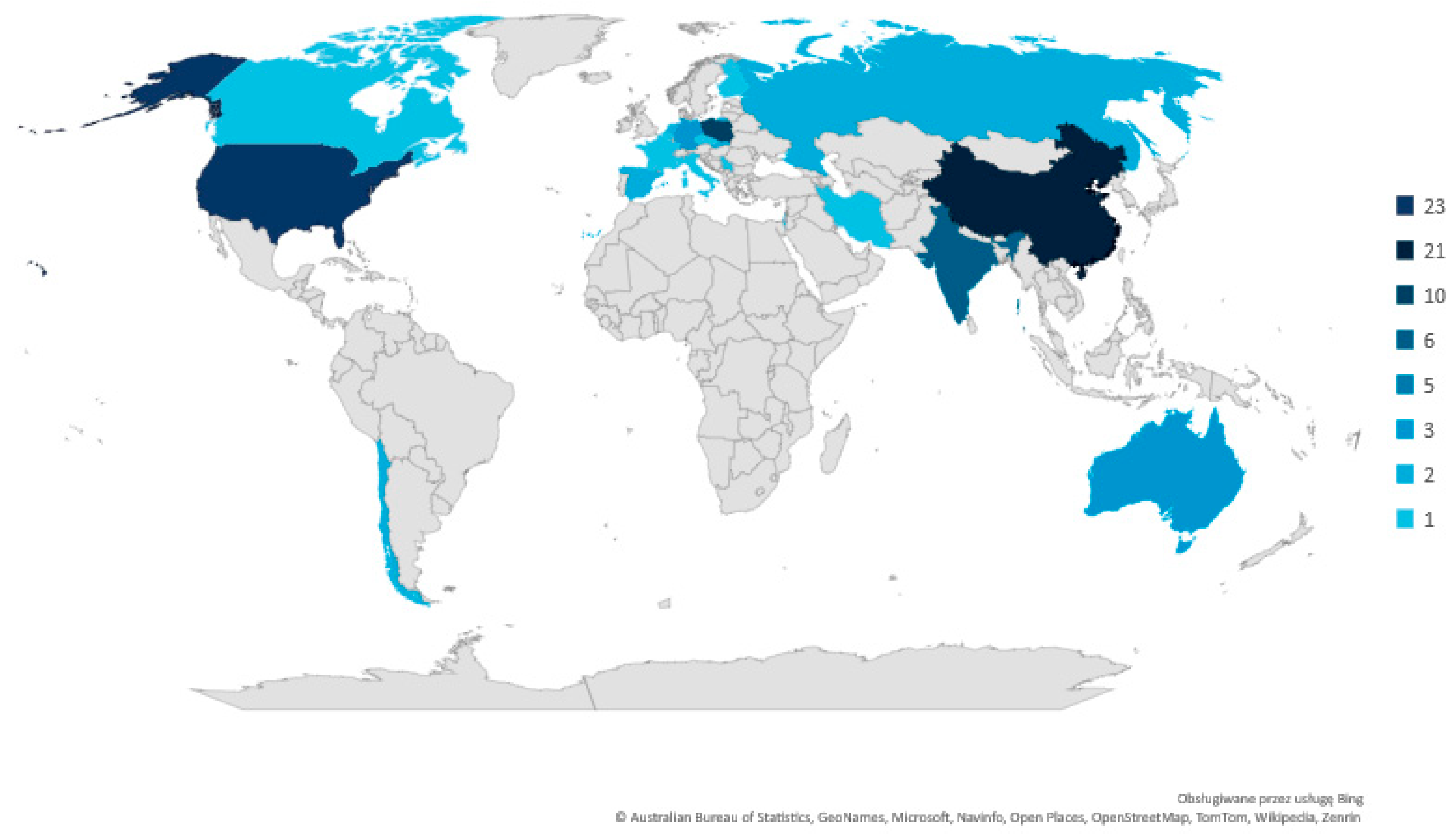
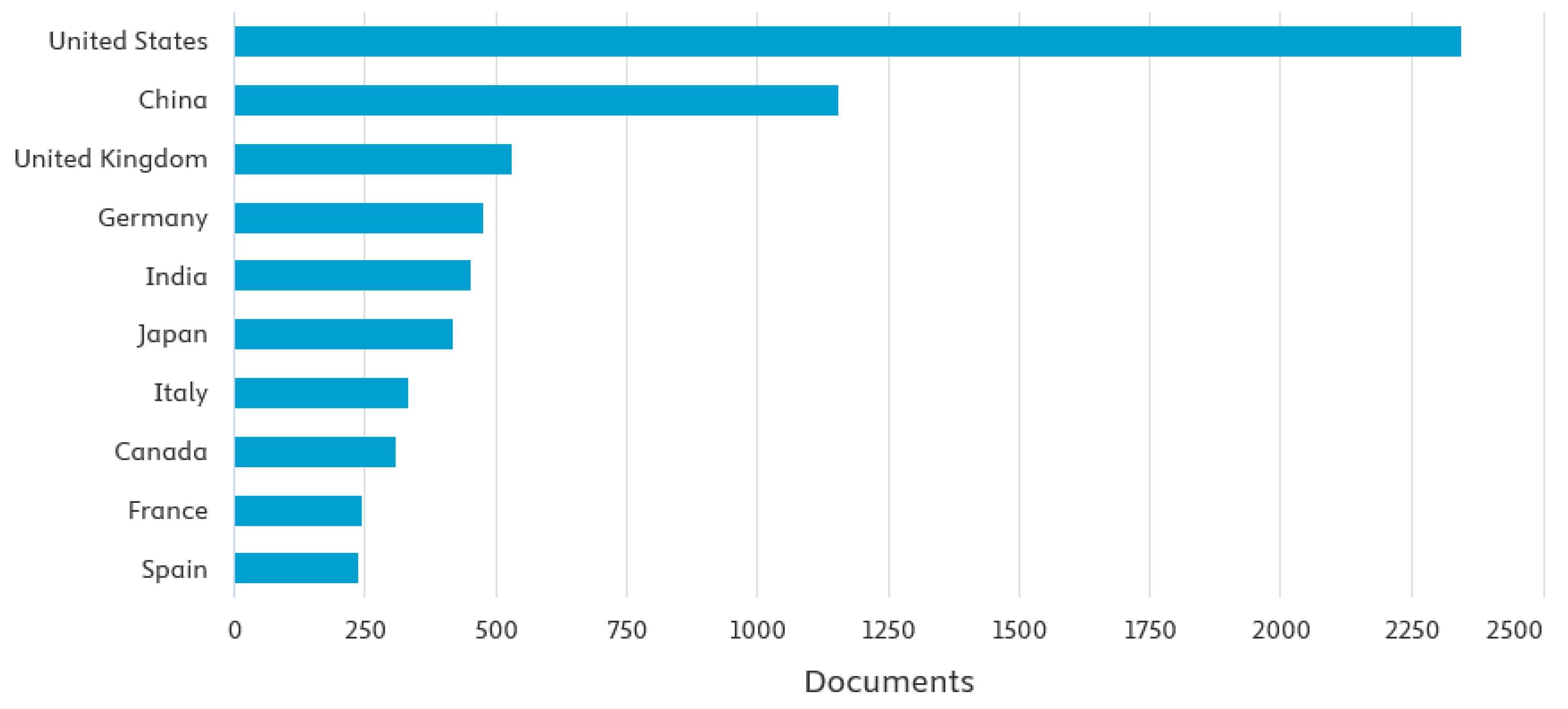
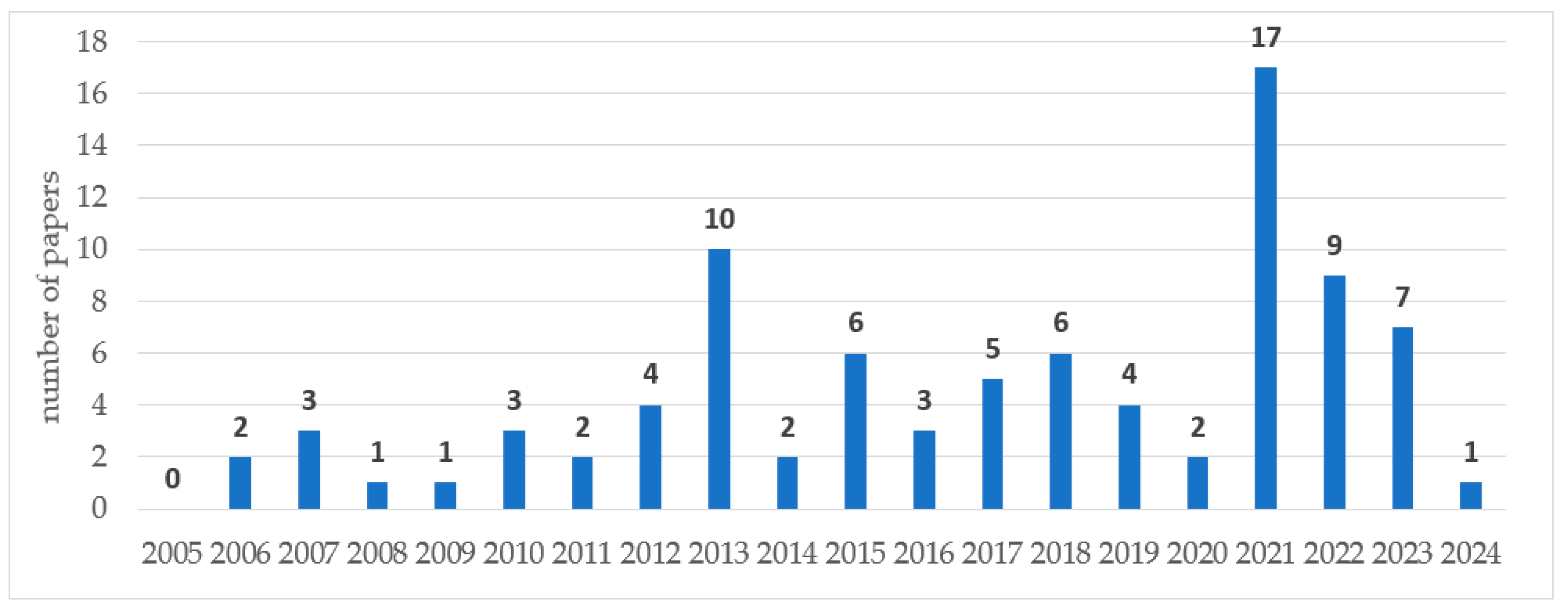
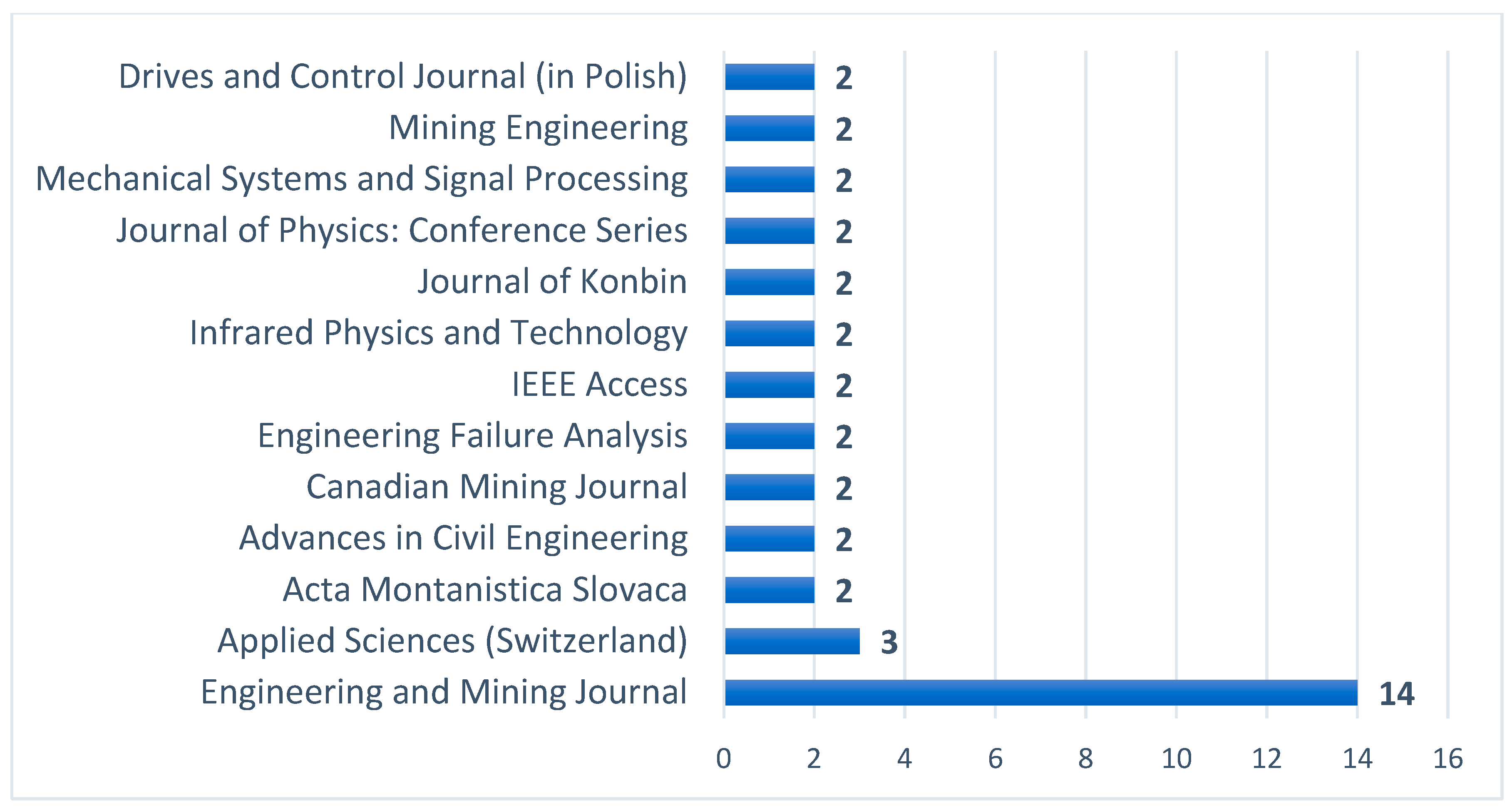
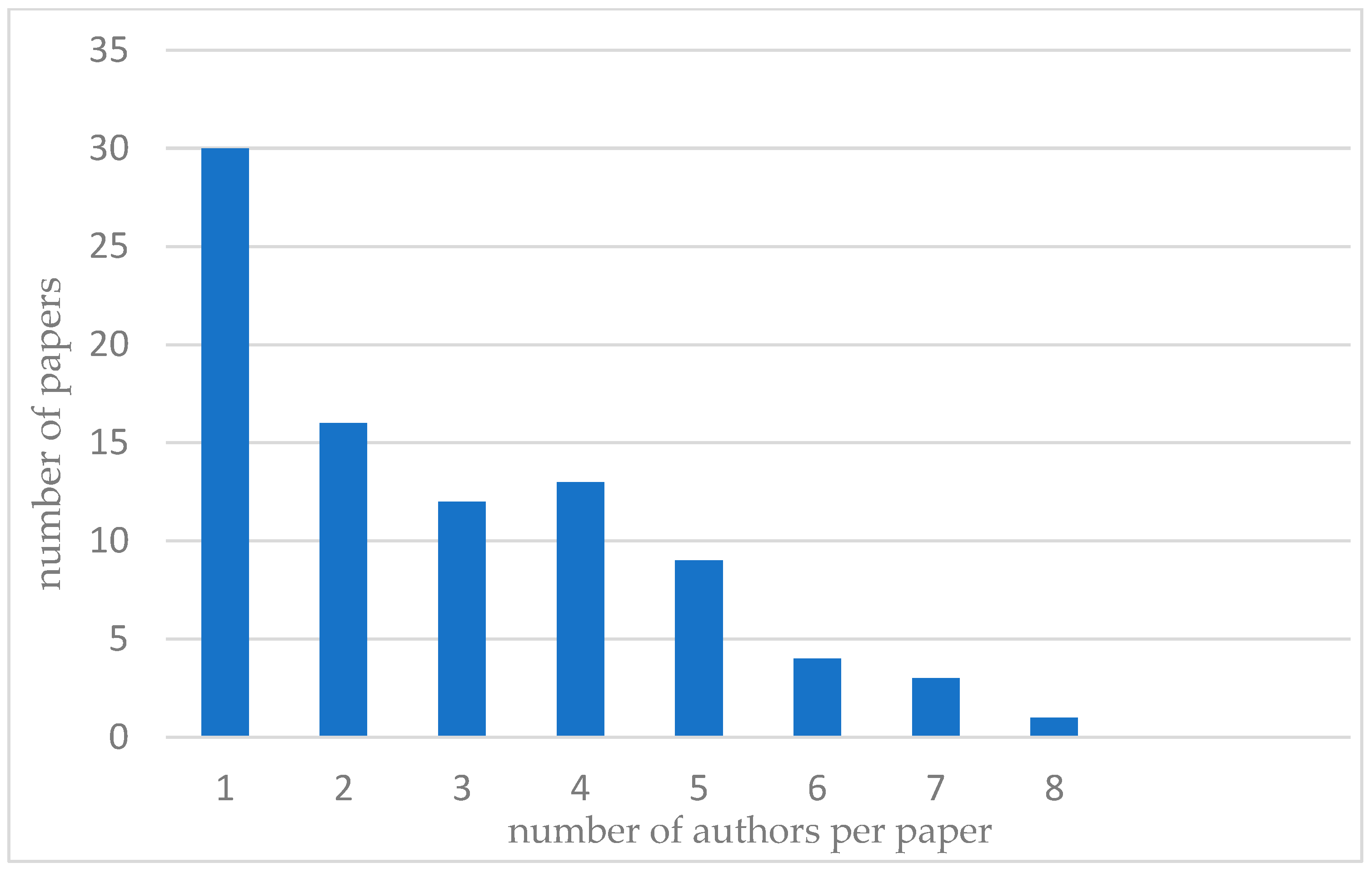
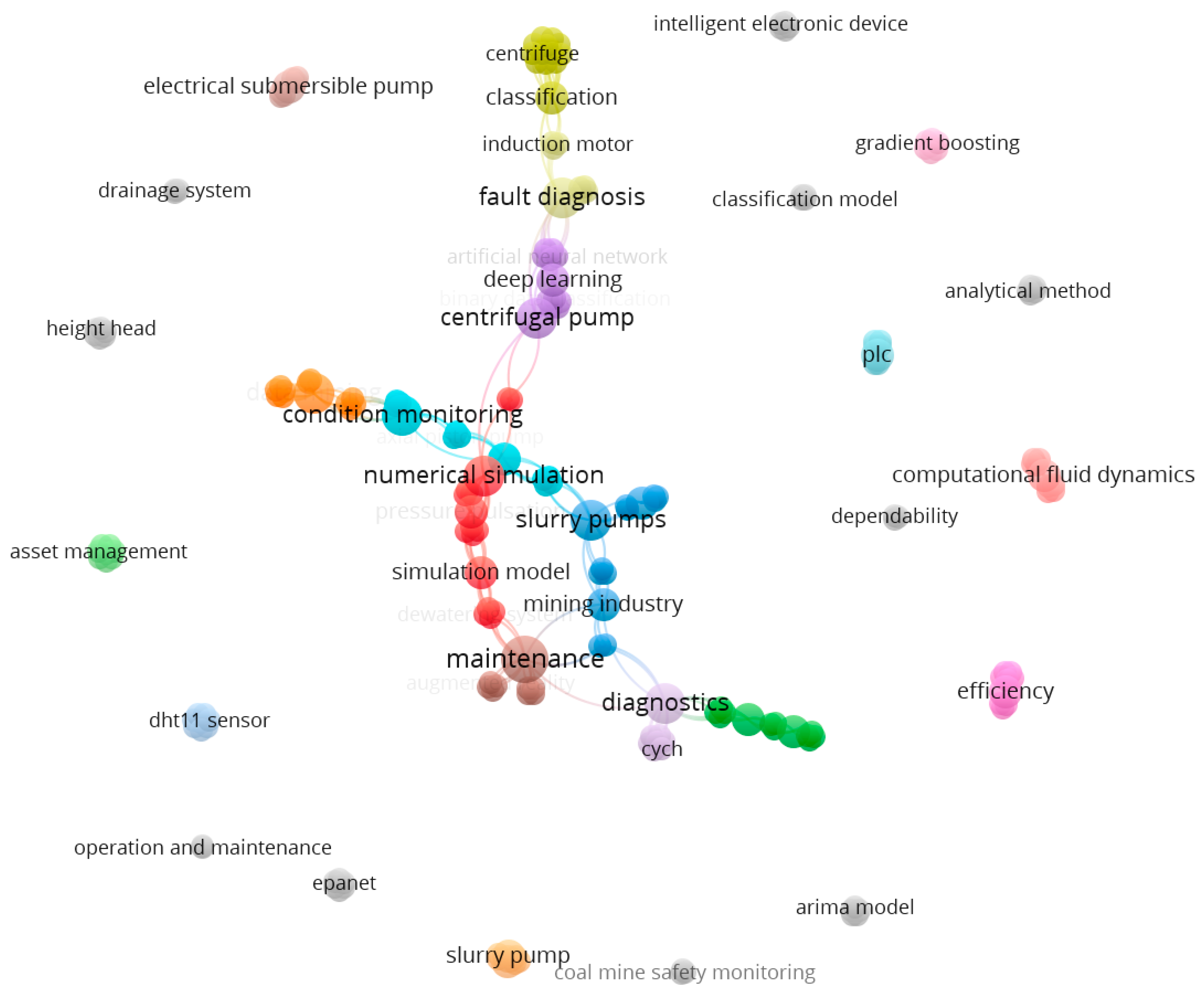
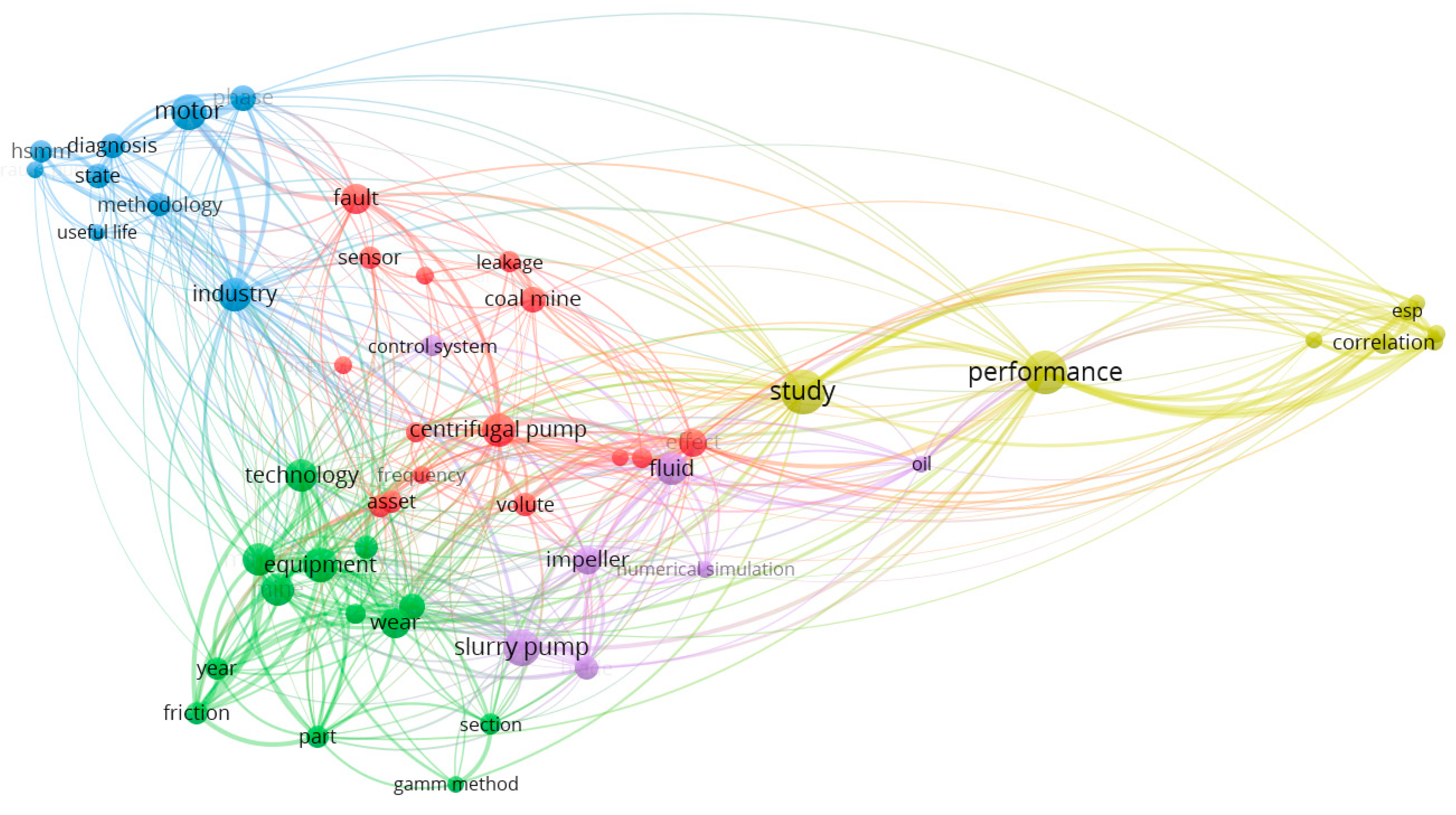
4.1. Bibliometric Analysis
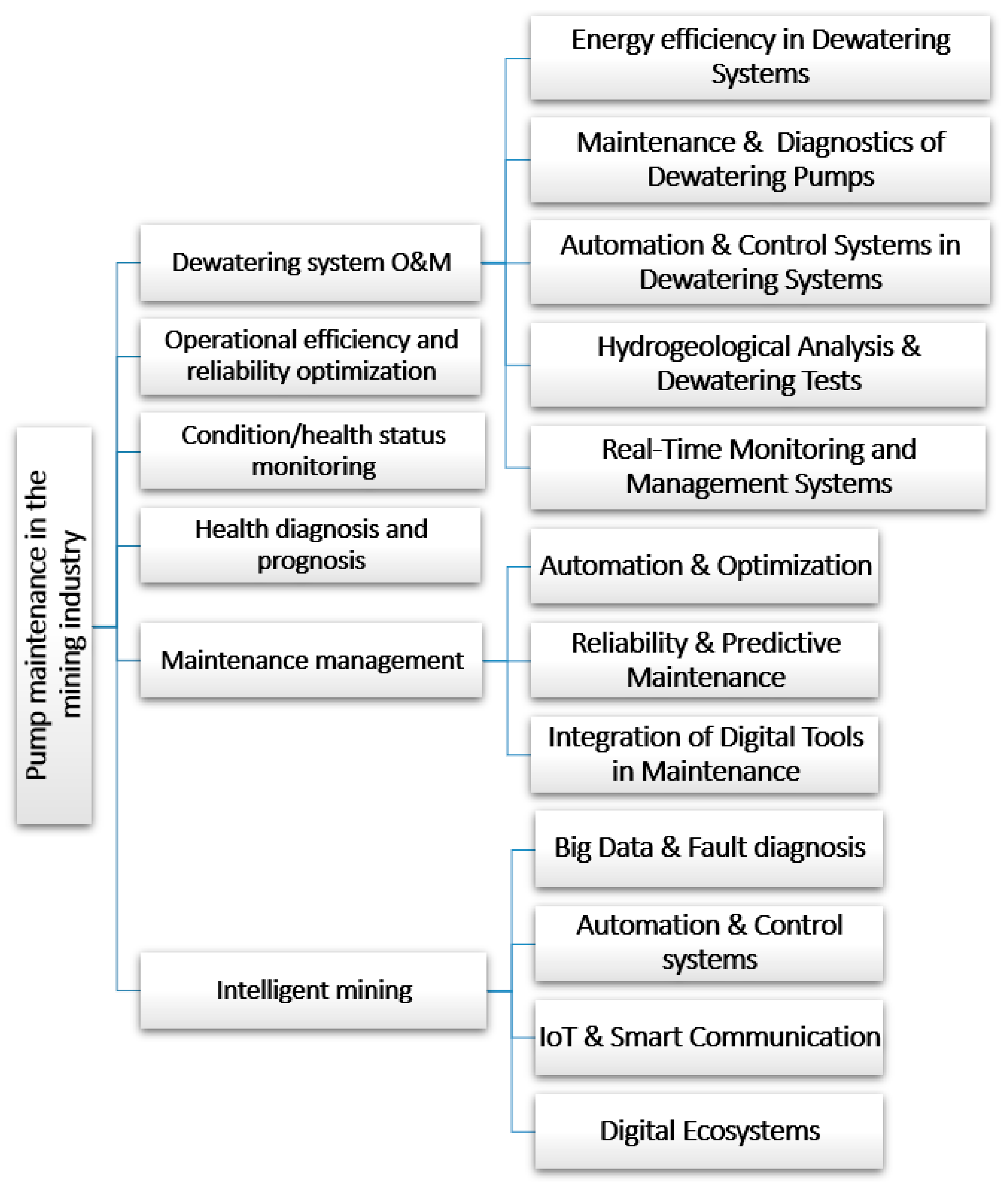
4.2. Content-Based Analysis
4.2.1. Dewatering System Operation and Maintenance
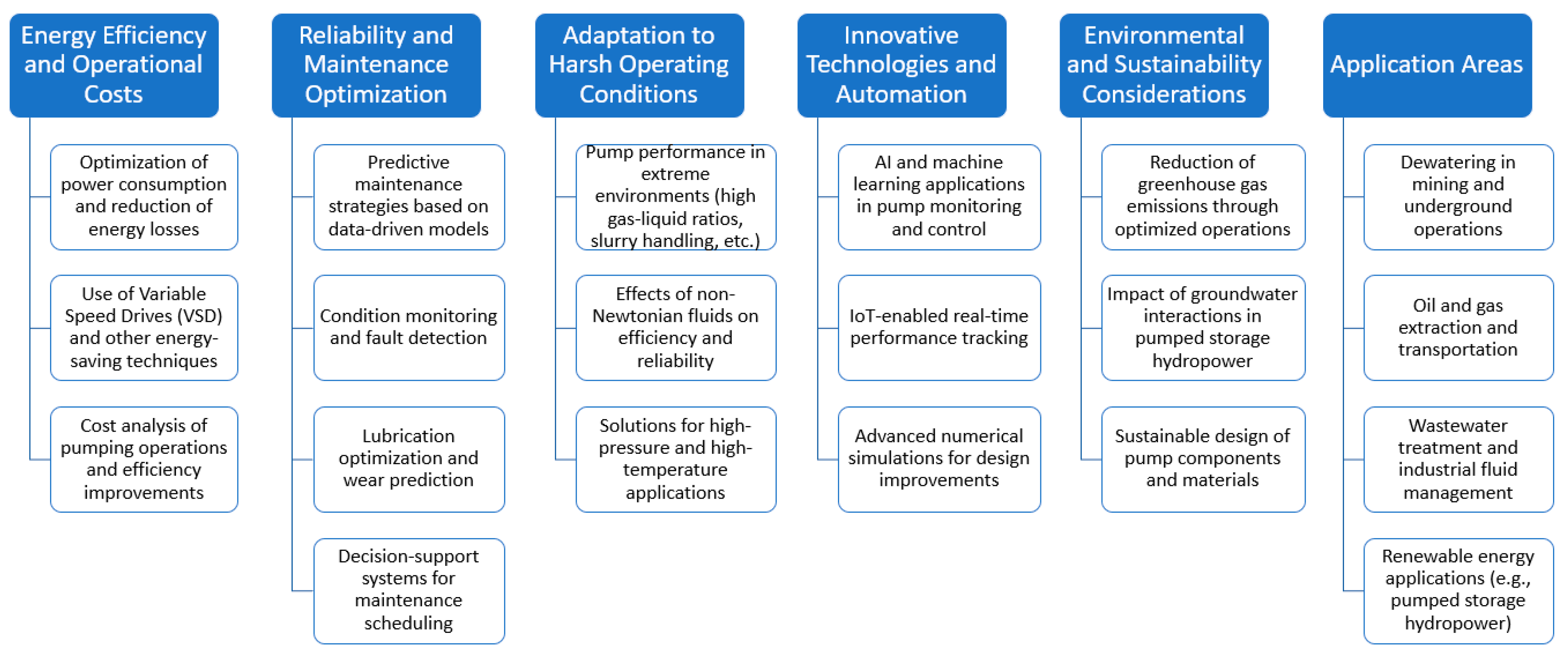
4.2.2. Operational Efficiency and Reliability Optimization
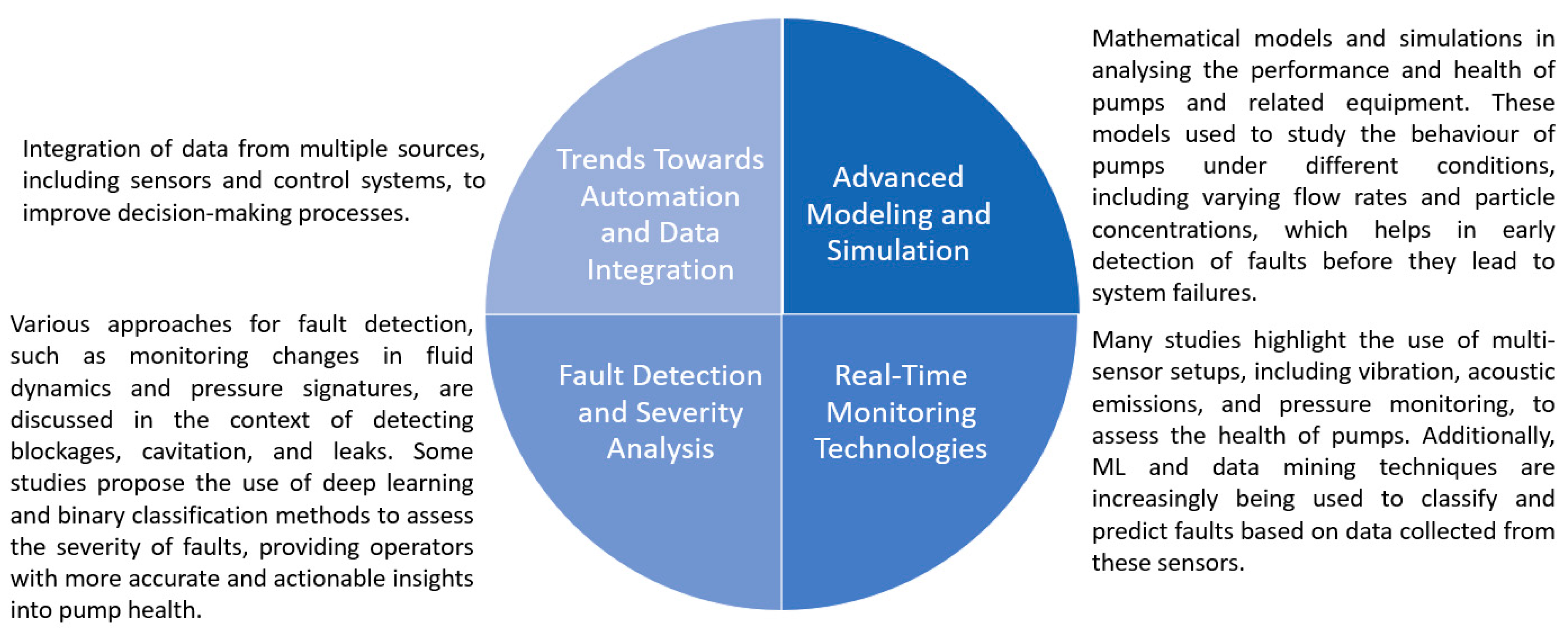
4.2.3. Condition/Health Status Monitoring
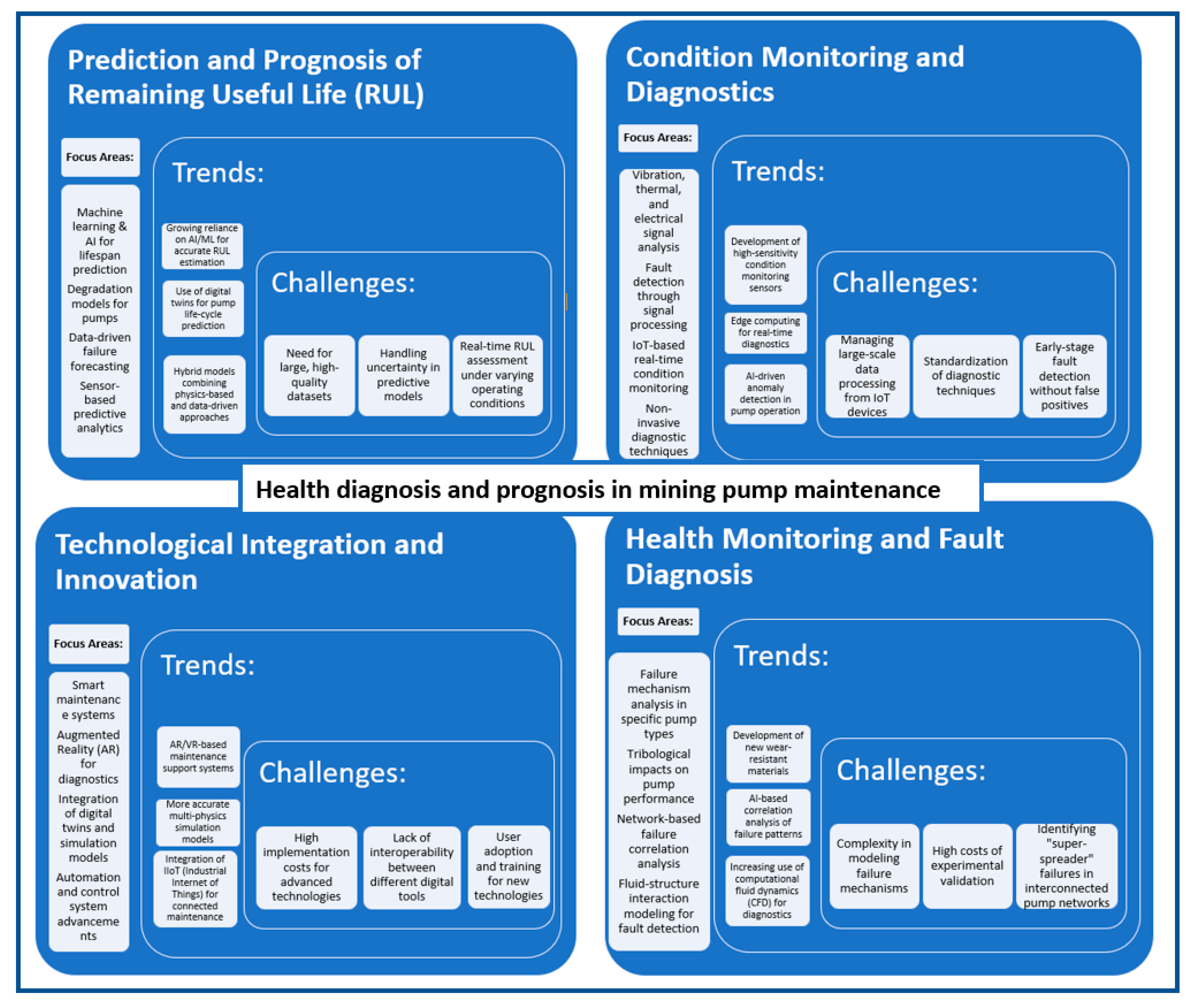
4.2.4. Health Diagnosis and Prognosis
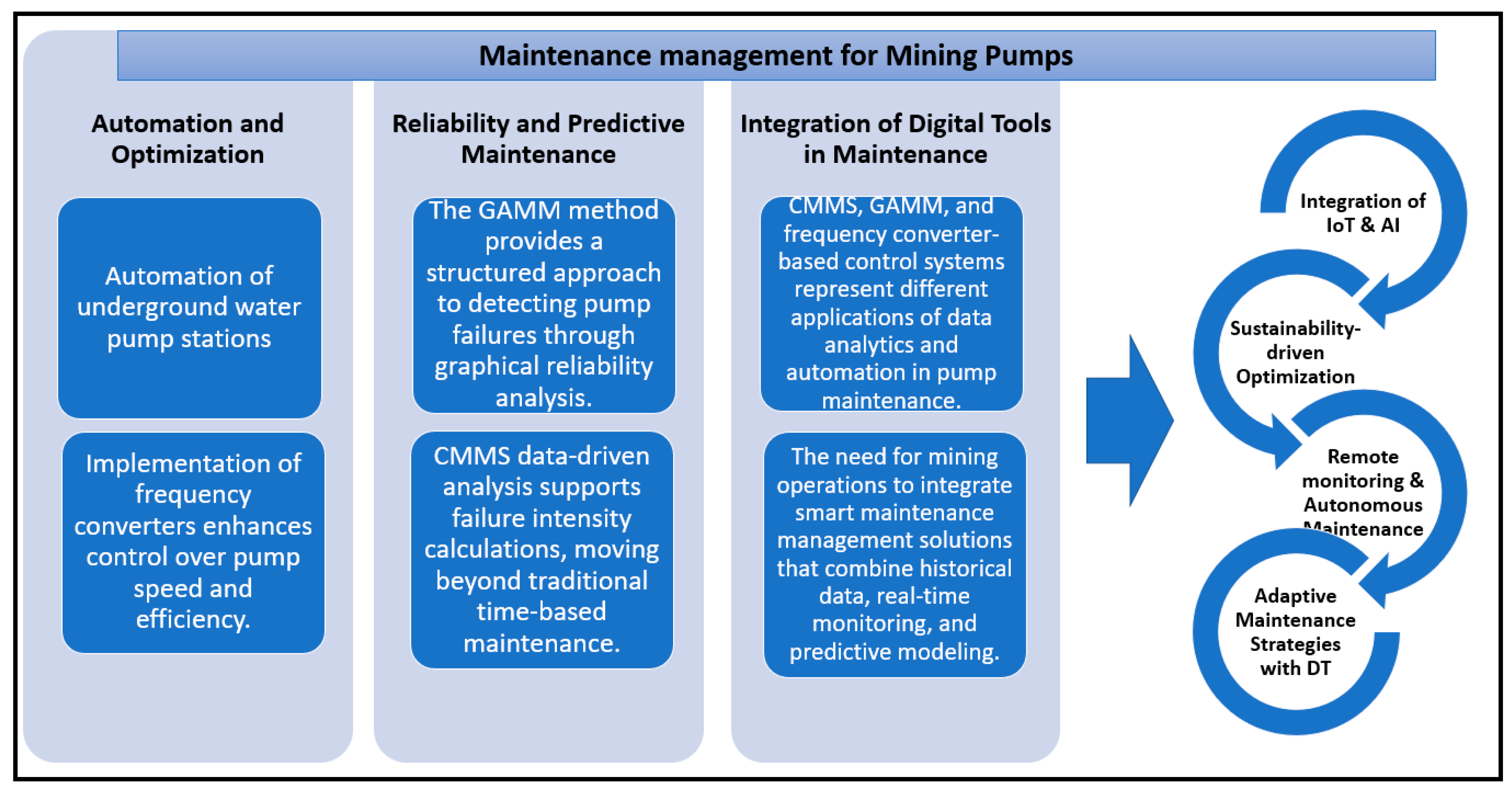
4.2.5. Maintenance Management
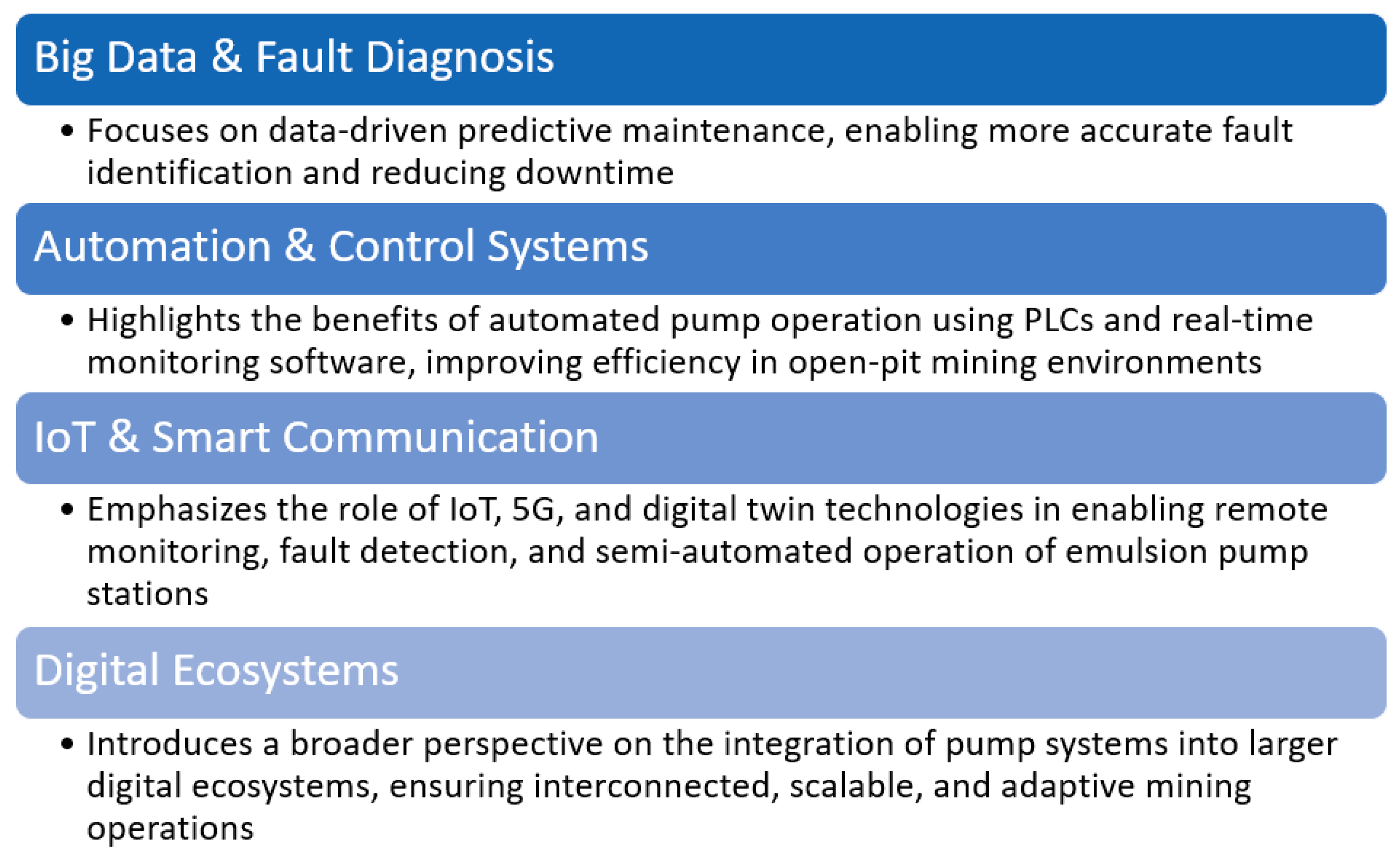
4.2.6. Intelligent Mining
5. Discussion
- optimization of pumping systems – research explores the selection of pump configurations, balancing flow rates, and designing multi-stage pumping stations to enhance water removal efficiency,
- impact of harsh mining environments – studies highlight the abrasive nature of mine water, which accelerates wear in pump components such as impellers and seals,
- remote monitoring of dewatering pumps – the use of IoT-enabled sensors and automated diagnostics has been explored to improve operational oversight and reduce manual inspections.
- energy consumption analysis – studies have quantified the energy footprint of pumps in mining operations, emphasizing the potential for efficiency improvements through variable-speed drives (VSDs) and frequency conversion technologies,
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) in pump design – CFD has been widely applied to simulate fluid flow, identify turbulence effects, and optimize pump impeller designs,
- impact of wear on pump performance – research frequently examines degradation mechanisms (e.g., cavitation, erosion, and corrosion), providing insights into material selection and protective coatings.
- early detection of faults: several studies emphasize the importance of monitoring pump performance to identify potential issues before they result in significant breakdowns or inefficiencies. Predictive techniques help optimize maintenance schedules and minimize unplanned downtime,
- wear and tear monitoring: many studies focus on slurry pump wear, particularly the wear of impellers. Wear patterns are influenced by factors like flow rate, particle concentration, and particle size, which help inform better pump design, maintenance, and operational strategies,
- advanced monitoring methods: the use of diverse methodologies, including unsupervised clustering, multiphase flow models, nodal analysis, and deep learning-based fault detection, is central to these studies. These methods allow for the prediction of pump health and early intervention to prevent failures,
- real-time and preventive maintenance: technologies such as Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), simulation-based monitoring, and real-time data analysis (e.g., power consumption and pressure measurements) are highlighted as essential for ensuring optimal performance and preventing breakdowns,
- multisensor and intelligent systems: the integration of multisensor systems in monitoring and the use of intelligent systems, such as IEDs and simulation models, play a crucial role in enhancing preventive maintenance capabilities and ensuring the safety of mining operations,
- focus on safety: real-time monitoring of various equipment, including pumps, is critical to ensuring safety in mining operations, particularly in relation to issues like gas leaks, temperature, and pressure monitoring.
- prediction of Remaining Useful Life: advanced models like Hidden Semi-Markov Models, Relevance Vector Machines, and Support Vector Machines have been used to predict the RUL of hydraulic pumps, slurry pump impellers, and other components. These models improve the accuracy of predictions, reducing unplanned breakdowns and optimizing maintenance schedules,
- condition monitoring and diagnostics: research has focused on real-time monitoring of pump health, with applications like vibration-based monitoring, thermal imaging, and automated diagnostics using PLC control. These systems aim to identify faults early, preventing failures and extending the operational life of pumps,
- technological integration and innovation: the incorporation of advanced technologies, including AR, dynamic modeling, and machine learning, have been explored to enhance diagnostic capabilities and predictive maintenance. These innovations allow for more efficient maintenance strategies, particularly in remote and extreme environments like oil rigs and mining operations,
- specific pump types health monitoring: studies have also focused on the health monitoring of specific pump types, such as hydraulic plunger pumps and piston diaphragm pumps, exploring failure mechanisms and proposing solutions to improve reliability and reduce operational costs.
-
Real-Time Data Acquisition and Integration:
- real-time data collection through IoT sensors embedded in the pump systems is a critical component. Data from these sensors will provide a continuous flow of information on pump health, operational performance, and environmental factors,
- data must be integrated from various sources, including maintenance history, sensor data, operational logs, and environmental conditions, to comprehensively view the pump system’s performance.
-
Predictive Maintenance Algorithms:
- the core of the framework is the implementation of predictive maintenance strategies. Using machine learning models and statistical analysis, these algorithms will predict potential failures before they occur, allowing the operators to schedule maintenance tasks proactively,
- predictive maintenance will reduce unplanned downtimes, enhance the lifespan of pumps, and optimize resource allocation.
-
Data Analytics and Visualization:
- the framework should include advanced data analytics tools to identify patterns and anomalies in the operational data, providing actionable insights,
- visualization dashboards will allow operators and maintenance personnel to easily interpret data, spot emerging issues, and make informed maintenance and operational adjustments decisions.
-
Simulation and Scenario Testing:
- simulation models of the pump systems will enable the testing of various maintenance strategies and failure scenarios. This allows the mining operators to evaluate the effectiveness of different approaches without disrupting actual operations,
- this component also aids in optimizing maintenance schedules and identifying the best timing for interventions to minimize the impact on overall productivity.
-
Condition Monitoring and Performance Tracking:
- continuous monitoring of the pump systems, including key parameters such as pressure, temperature, flow rate, and vibration levels, will provide real-time insight into their operational health,
- automated condition monitoring tools will send alerts for any deviations from normal operating conditions, allowing quick actions to be taken before a potential failure occurs.
-
Feedback Mechanisms for Continuous Improvement:
- the framework should incorporate feedback loops that capture the outcomes of maintenance activities and compare them with the predictions made by the system. By continually analyzing maintenance results, organizations can refine their predictive models and improve maintenance strategies,
- continuous improvement process helps the organization enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of its predictive maintenance capabilities.
-
Collaboration and Communication Tools:
- efficient communication tools are essential for coordinating maintenance activities, especially in complex mining operations. The framework should include collaboration platforms that allow seamless information sharing between maintenance teams, management, and operators to ensure all stakeholders are informed about the pump systems' status and any required actions.
-
Compliance and Reporting:
- the framework must ensure compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements for maintenance practices. It should include reporting functionalities to generate maintenance logs, compliance reports, and performance reviews,
- the data-driven approach will help demonstrate environmental, safety, and operational standards adherence.
-
Scalability and Adaptability:
- the framework should be designed to be scalable, supporting various pump systems used in mining operations of different sizes and complexities.
- it should also be adaptable to future technological advancements, ensuring that the system can evolve with emerging technologies such as 5G communications, AI, and enhanced data analytics tools.
6. Framework for Proactive Maintenance in Pump Systems from the Mining Industry
- pumps operating in cascade should be responsible for transporting water from different depth levels to the surface,
- the system should allow automatic start-up of subsequent pumps in the event of failure of one of the lower level pumps to avoid interruption of dewatering.
- pumps on the surface responsible for removing process water to the main pipeline must work reliably, as their downtime could lead to flooding of the mine,
- in case of pump overload, the system should automatically switch to another pump to ensure continuous operation.
- the maintenance system should use various diagnostic methods to monitor the condition of pumps, including vibroacoustic diagnostics, acoustic tests, and thermal measurements, which have been pre-tested,
- monitoring of the condition of rolling elements should be regular and allow detection of anomalies at an early stage.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Description |
| AI AR ARIMA BNN CBM CFD CM CMMS CR DeT DT ESP FSI GAMM HSMM HSM HVAC IEDs IMs IoT LiDAR MED ML MoASoID MTBF MTTF MTTR NN |
Artificial Intelligence Augmented Reality Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving-Average Back-propagation Neural Network Condition-Based Maintenance Computational Fluid Dynamics Condition Monitoring Computerized Maintenance Management Systems Corrective Maintenance Decision Tree Digital Twin Electrical Submersible Pump Fluid-Structure Interaction Graphical Analysis for Maintenance Management Hidden Semi-Markov Model Health Status Monitoring Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning Intelligent Electronic Devises Induction Motors Internet of Things Light Detection and Ranging Minimum Entropy Deconvolution Machine Learning Method of Areas Selection of Image Differences Mean Time Between Failures Mean Time To Failure Mean Time To Repair Nearest Neighbour |
| O&M PAT Pdis PdM PIP PM |
Operation and Maintenance Pump as turbine Pump discharge pressure Predictive Maintenance Pump Intake Pressure Preventive Maintenance |
| PRISMA RBFNN RVM RUL |
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes Radial Basis Function Neural Networks Relevance Vector Machine Residual Lifetime |
| SLR SVM WPD |
Systematic Literature Review Support Vector Machines Wavelet Packet Decomposition |
References
- Dhillon, B.S. Mining Equipment Reliability, Maintainability, and Safety; Springer-Verlag London Limited, 2008; ISBN 9781848002876.
- Dhillon, B.S. Mining Equipment Safety: A Review, Analysis Methods and Improvement Strategies. Int. J. Mining, Reclam. Environ. 2009, 23, 168–179. [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. Operational State Monitoring and Fuzzy Fault Diagnostic System of Mine Drainage. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 581–584. [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, B.S. Mining Equipment Maintenance. Springer Ser. Reliab. Eng. 2008, 26, 115–133. [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.P.; Kahraman, M.M.; Drews, F.A.; Powell, K.; Haight, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Baxla, K.; Sobalkar, M. Automation in the Mining Industry: Review of Technology, Systems, Human Factors, and Political Risk. Mining, Metall. Explor. 2019, 36, 607–631. [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, S.; Papic, L.; Janackovic, G.L.; Savic, S. The Analysis of Human Error as Causes in the Maintenance of Machines: A Case Study in Mining Companies. South African J. Ind. Eng. 2016, 27, 193–202. [CrossRef]
- Odeyar, P.; Apel, D.B.; Hall, R.; Zon, B.; Skrzypkowski, K. A Review of Reliability and Fault Analysis Methods for Heavy Equipment and Their Components Used in Mining. Energies 2022, 15, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Sottile, J.; Holloway, L.E. An Overview of Fault Monitoring and Diagnosis in Mining Equipment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1994, 30, 1326–1332. [CrossRef]
- Dayo-Olupona, O.; Genc, B.; Celik, T.; Bada, S. Adoptable Approaches to Predictive Maintenance in Mining Industry: An Overview. Resour. Policy 2023, 86, 104291. [CrossRef]
- Dayo-Olupona, O.; Genc, B.; Bada, S.; Celik, T. Predictive Maintenance: A Viable Maintenance Option for Machines/Equipment/Plants in Mining and Mineral Processing. Proc. 27th Int. Min. Congr. Exhib. Turkey, IMCET 2022 2022, 759–765.
- Kokkinis, A.; Frantzis, T.; Skordis, K.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Koustoumpardis, P. Review of Automated Operations in Drilling and Mining. Machines 2024, 12, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Pourjavad, E.; Shirouyehzad, H.; Shahin, A. Selecting Maintenance Strategy in Mining Industry by Analytic Network Process and TOPSIS. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2013, 15, 171–192. [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.P. Effective Maintenance Practices for Mining Equipments. 2011, 4–7.
- Angeles, E.; Kumral, M. Optimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining Equipment. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2020, 20, 1408–1416. [CrossRef]
- Chaowasakoo, P.; Seppala, H.; Koivo, H. Age-Based Maintenance for a Fleet of Haul Trucks. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2018, 24, 511–528. [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, E. Cost-Effective Prevention of Equipment Failure in the Mining Industry. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 1995, 61, 329–347. [CrossRef]
- Online Condition Monitoring Offers Early Warning of Impending Equipment Problems. Eng. Min. J. 2011, 212, 106–108.
- Bauer, B.; Geropp, B.; Seeliger, A. Condition Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance in Mining Industry Using Vibration Analysis for Diagnosis of Gear Boxes. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1997, 30, 989–992. [CrossRef]
- Bartelmus, W. Object and Operation Supported Maintenance for Mining Equipment. Min. Sci. 2014, 21, 7–21. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H. Use of Data Mining Techniques for Mine Machine Condition Monitoring, University of Missouri-Rolla, 2003.
- Beckman, M. Predictive Maintenance Polishes up Mining. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2021, 77, 38–40.
- Robatto Simard, S.; Gamache, M.; Doyon-Poulin, P. Current Practices for Preventive Maintenance and Expectations for Predictive Maintenance in East-Canadian Mines. Mining 2023, 3, 26–53. [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Rong, X.; Wei, L.; Shi, X. Review of Fault Diagnosis and Early Warning of Coal Mine Ventilator. In Proceedings of the Proceedings - 2019 Chinese Automation Congress, CAC 2019; 2019; pp. 5226–5230.
- Gerike, B.L.; Mokrushev, A.A. Diagnostics of the Technical State of Bearings of Mining Machines Base Assemblies. In Proceedings of the IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering; 2017; Vol. 253, pp. 1–8.
- Burrows, J.H. Predictive and Preventive Maintenance of Mobile Mining Equipment Using Vibration, McGill University, Montreal, 1996.
- Dos Santos Silva, F.J.; Garcia Viana, H.R.; Aquino Queiroz, A.N. Availability Forecast of Mining Equipment. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2016, 22, 418–432. [CrossRef]
- Curilem, M.; Huanquilef, C.; Acuña, G.; Cubillos, F.; Araya, B.; Segovia, G.; Pérez, C. Prediction of the Criticality of a Heavy Duty Mining Equipment. In Proceedings of the 2015 Latin America Congress on Computational Intelligence (LA-CCI); 2015; pp. 1–5.
- 2022; 28. AI Enabled Predictive Maintenance in Mining; 2022;
- Dong, L.; Mingyue, R.; Guoying, M. Application of Internet of Things Technology on Predictive Maintenance System of Coal Equipment. Procedia Eng. 2017, 174, 885–889. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chen, S.; Wu, P. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis System Based on Big Data. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8980–8985. [CrossRef]
- Isermann, R. Fault-Diagnosis of Pumps. In Fault-Diagnosis Applications, Model-Based Condition Monitoring: Actuators, Drives, Machinery, Plants, Sensors, and Fault-tolerant Systems; Isermann, R., Ed.; Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2011; pp. 143–179 ISBN 9783642127670.
- Jain, S. V.; Patel, R.N. Investigations on Pump Running in Turbine Mode: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 841–868. [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.F.; Shaker, H.R. Predictive Maintenance for Pump Systems and Thermal Power Plants: State-of-the-Art Review, Trends and Challenges. Sensors (Switzerland) 2020, 20. [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, J.J.; Meesenburg, W.; Ommen, T.; Markussen, W.B.; Poulsen, J.L.; Zühlsdorf, B.; Elmegaard, B. A Review of Common Faults in Large-Scale Heat Pumps. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112826. [CrossRef]
- Mallioris, P.; Aivazidou, E.; Bechtsis, D. Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Multi-Sector Mapping. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2024, 50, 80–103. [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Kizil, M.S.; Yahyaei, M.; Knights, P.F. Digital Twins in the Minerals Industry–a Comprehensive Review. Min. Technol. Trans. Institutions Min. Metall. 2023, 132, 267–289. [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Goyal, D.; Shimi, S.L.; Akula, A. Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motors: A Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 1221–1238. [CrossRef]
- Bagri, I.; Tahiry, K.; Hraiba, A.; Touil, A.; Mousrij, A. Vibration Signal Analysis for Intelligent Rotating Machinery Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Comprehensive Systematic Literature Review. Vibration 2024, 7, 1013–1062. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, N.; Das, A.K. A Review on Wear Failure of Hydraulic Components: Existing Problems and Possible Solutions. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6. [CrossRef]
- Rajak, P.K.; Sarkar, S.; Paul, B. Comparison of the Dewatering of Underground and Open Pit Coal Mine Pumping Systems in (BCCL), Dhanbad, Jharkhand, India. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; 2018; Vol. 377.
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372. [CrossRef]
- Agboola, O.; Babatunde, D.E.; Isaac Fayomi, O.S.; Sadiku, E.R.; Popoola, P.; Moropeng, L.; Yahaya, A.; Mamudu, O.A. A Review on the Impact of Mining Operation: Monitoring, Assessment and Management. Results Eng. 2020, 8, 100181. [CrossRef]
- Asr, E.T.; Kakaie, R.; Ataei, M.; Tavakoli Mohammadi, M.R. A Review of Studies on Sustainable Development in Mining Life Cycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 213–231. [CrossRef]
- Zhironkin, S.; Szurgacz, D. Mining Technologies Innovative Development; 2022; ISBN 9783036532257.
- Afum, B.O.; Ben-Awuah, E. A Review of Models and Algorithms for Surface-Underground Mining Options and Transitions Optimization: Some Lessons Learnt and the Way Forward. Mining 2021, 1, 112–134. [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, R.; Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S. Mining Equipment Diagnostics in a Mine Shaft Dewatering System - Case Study. J. Konbin accepted f.
- Bridgwood, E.W.; Singh, R.N.; Atkins, A.S. Selection and Optimization of Mine Pumping Systems. Int. J. Mine Water 1983, 2, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Korbiel, T.; Wojciechowski, J. Analiza Kosztów Eksploatacji Systemu Głównego Odwadniania Kopalni Węgla Kamiennego. Syst. Wspomagania w Inżynierii Prod. 2019, 8, 413–419.
- Andrzej, K.; Mikuła, S. Badania Eksploatacyjne Górniczych Pomp Odwadniających. Zesz. Nauk. Politech. Śląskiej, Ser. Górnictwo z. 269 2005, 1697, 465–474.
- Gogolewska, A.B. Surface and Underground Mining Technology; Wroclaw, 2010;
- Tse, P.W.; Shen, C. Remaining Useful Life Estimation of Slurry Pumps Using the Health Status Probability Estimation Provided by Support Vector Machine. In Engineering Asset Management - Systems, Professional Practices and Certification, Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Tse, P.W., Mathew, J., Wong, K., Lam, R., Ko, C.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Switzerland, 2015; pp. 87–98 ISBN 978-3-319-09506-6.
- Di Maio, F.; Hu, J.; Tse, P.; Pecht, M.; Tsui, K.; Zio, E. Ensemble-Approaches for Clustering Health Status of Oil Sand Pumps. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 4847–4859. [CrossRef]
- Tse, P.W.; Hu, J. A Fusion Approach with Application to Oil Sand Pump Prognostics. In Engineering Asset Management -Systems, Professional Practices and Certification. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Tse, P.W., Mathew, J., Wong, K., Lam, C.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Switzerland, 2015; pp. 31–41.
- Beck, D.; Wulff, S.; Thamsen, P.U.; Reich, M.; Worringer, J.P. Recommendations for Long-Term Operation of High-Performance Submersible Motor Pumps in Mine Dewatering. In Proceedings of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Fluids Engineering Division (Publication) FEDSM; 2020; Vol. 1.
- Morgan, S.E. The ABCs of Pump Selection for Mine Dewatering. Coal Age 2008, 113, 46–47.
- Boyce, K. Selecting a Reliable Dewatering Pump for Mining Applications. Eng. Min. J. 2013, 214, 36–37.
- Vujic, S.B. Adaptive Computer Supported Surveilance-Management Model of Dewatering System at Coal Open Pit Mine. Therm. Sci. 2006, 10, 33–42. [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.R. Oil Hydraulic Systems: Principles and Maintenance; McGraw-Hill Education, 2013;
- Minav, T. Electric-Drive-Based Control and Electric Energy Regeneration in a Hydraulic System; Lappeenranta University of Technology, 2011; ISBN 9789522651037.
- Dutta, N.; Kaliannan, P.; Paramasivam, S. A Comprehensive Review on Fault Detection and Analysis in the Pumping System. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2022, 43, 6878–6898. [CrossRef]
- Premium Pumping Technology for the Mining Industry. IIoT Enabled Pump Solutions;
- Hermawan, Y.; Danang Wijaya, F.; Setiawan, N.A.; Dharmastiti, R. Prediction of Lubricant Service Life Using Data Mining to Improve Reliability of Water Injection Pumps in Crude Oil Production Facility. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Information Engineering: Technological Breakthrough for Greater New Life, ICEEIE 2021; IEEE, 2021; pp. 2–6.
- ALTobi, M.A.S.; Bevan, G.; Wallace, P.; Harrison, D.; Ramachandran, K.P. Centrifugal Pump Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis Using Frequency Domain Analysis; Springer International Publishing, 2019; Vol. 15; ISBN 9783030112202.
- Rogowski, R.; Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S. Maintenance Problems of Mining Equipment on the Example of a Mine Dewatering System (in Polish). In (accepted for publication); Nowakowski, T., Rosiński, A., Sieriejczyk, M., Eds.; Warsaw University of Technology Publ. House, 2023.
- Wang, Q.; Geng, P.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R. Development of Intelligent Automatic Water Intake System for Open-Pit Mine. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2591. [CrossRef]
- Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S. Technical System Maintenance. Delay-Time-Based Modelling; Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2019; ISBN 9783030107871.
- BS EN 13306:2017: Maintenance. Maintenance Terminology; 2018;
- Ran, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lin, P.; Wen, Y.; Deng, R. A Survey of Predictive Maintenance: Systems, Purposes and Approaches. 2019, XX, 1–36.
- Ahmad, R.; Kamaruddin, S. An Overview of Time-Based and Condition-Based Maintenance in Industrial Application. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 63, 135–149. [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.; Bechtel, J.; Ganesan, S. Condition Based Maintenance: A Survey. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2012, 18, 384–400. [CrossRef]
- VOSviewer, Https://Www.Vosviewer.Com/.
- McKee, K.K.; Forbes, G.; Mazhar, I.; Entwistle, R.; Howard, I. A Review of Major Centrifugal Pump Failure Modes with Application to the Water Supply and Sewerage Industries. In Proceedings of the ICOMS Asset Management Conference , Gold Coast, QLD, Australia; 2011; pp. 1–12.
- McKee, K.K.; L., F.G.; Mazhar, I.; Entwistle, R.; Howard, I. A Review of Machinery Diagnostics and Prognostics Implemented on a Centrifugal Pump. In Engineering Asset Management 2011. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Lee, J., Ni, J., Sarangapani, J., Mathew, J., Eds.; Springer-Verlag London, 2014; pp. 593–614 ISBN 978-1-4471-4992-7.
- Aliyu, R.; Mokhtar, A.A.; Hussin, H. Prognostic Health Management of Pumps Using Artificial Intelligence in the Oil and Gas Sector: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Hallaji, S.M.; Fang, Y.; Winfrey, B.K. Predictive Maintenance of Pumps in Civil Infrastructure: State-of-the-Art, Challenges and Future Directions. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104049. [CrossRef]
- Lakal, N.; Shehri, A.H.; Brashler, K.W.; Wankhede, S.P.; Morse, J.; Du, X. Sensing Technologies for Condition Monitoring of Oil Pump in Harsh Environment. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2022, 346, 113864. [CrossRef]
- Sunal, C.E.; Dyo, V.; Velisavljevic, V. Review of Machine Learning Based Fault Detection for Centrifugal Pump Induction Motors. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 71344–71355. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, L.; Xiao, J.; Fang, G.; Li, J. Current Status and Applications for Hydraulic Pump Fault Diagnosis: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Verhulst, T.; Judt, D.; Lawson, C.; Chung, Y.; Al-Tayawe, O.; Ward, G. Review for State-of-the-Art Health Monitoring Technologies on Airframe Fuel Pumps. Int. J. Progn. Heal. Manag. 2022, 13, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Almazrouei, S.; Dweiri, F.; Aydin, R.; Alnaqbi, A. A Review on the Advancements and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence Based Models for Predictive Maintenance of Water Injection Pumps in the Oil and Gas Industry. SN Appl. Sci. 2023, 5. [CrossRef]
- Klis, P.; Xing, Y.; Abd, A.H.; Ren, C. A Survey of Control Systems for Offshore Well Service Pumps: State-of-the-Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the ASME 2024 43rd International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering. Volume 8: Offshore Geotechnics; Petroleum Technology. V008T11A018. ASME; June 9 2024.
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lv, S.; Shi, W.; Ni, H.; Li, X.; Tao, C.; Hou, Z. Research Progress on Identification and Suppression Methods for Monitoring the Cavitation State of Centrifugal Pumps; 2024; Vol. 16; ISBN 2210310024.
- Blischke, W.R.; Murthy, P.D.N. Reliability: Modeling, Prediction, and Optimization; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2000;
- Ali, A.; Abdelhadi, A. Condition-Based Monitoring and Maintenance: State of the Art Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 688. [CrossRef]
- Discenzo, F.M.; Chung, D.; Loparo, K.A. Pump Condition Monitoring Using Self-Powered Wireless Sensor Nodes. Metrics Key to Success - Proc. 60th Meet. Soc. Mach. Fail. Prev. Technol. 2006, 425–434.
- ALTobi, M.A.S.; Bevan, G.; Wallace, P.; Harrison, D.; Ramachandran, K.P. Centrifugal Pump Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis Using Frequency Domain Analysis. In Applied Condition Monitoring; Springer International Publishing, 2019; Vol. 15, pp. 122–131 ISBN 9783030112202.
- Kalmár, C.; Hegedus, F. Condition Monitoring of Centrifugal Pumps Based on Pressure Measurements. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 2019, 63, 80–90. [CrossRef]
- Pech, M.; Vrchota, J.; Bednář, J. Predictive Maintenance and Intelligent Sensors in Smart Factory: Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–39. [CrossRef]
- Divya, D.; Marath, B.; Santosh Kumar, M.B. Review of Fault Detection Techniques for Predictive Maintenance. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Harihara, P.P.; Parlos, A.G. Fault Diagnosis of Centrifugal Pumps Using Motor Electrical Signals. Centrif. Pumps 2012, 15–32. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, W. Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance of Centrifugal Pumps Based on Smart Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Budgen, D.; Brereton, P. Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering. Proc. - Int. Conf. Softw. Eng. 2006, 2006, 1051–1052. [CrossRef]
- Madhukar, P.; McCulloch, M.; Gorman, J.; Pai, N.P.; Enanoria, W.T.A.; Kennedy, G.E.; Tharyan, P.; Colford, J.M. Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: An Illustrated, Step-by-Step Guide. Natl. Med. J. India 2004, 17, 86–95.
- Zamani, E.D.; Smyth, C.; Gupta, S.; Dennehy, D. Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics for Supply Chain Resilience: A Systematic Literature Review. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E.; Pearson, A. The Systematic Review: An Overview. Am. J. Nurs. 2014, 114, 53–58. [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. BMJ 2009, 339, 332–336. [CrossRef]
- Https://Omnis-Pwr.Primo.Exlibrisgroup.Com/Discovery/Search?Vid=48OMNIS_TUR:48TUR&lang=pl&mode=advanced.
- Flores-Castañeda, R.O.; Olaya-Cotera, S.; López-Porras, M.; Tarmeño-Juscamaita, E.; Iparraguirre-Villanueva, O. Technological Advances and Trends in the Mining Industry: A Systematic Review. Miner. Econ. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.T.; Webster, J. Analysing the Past to Prepare for the Future: Writing a Literature Review a Roadmap for Release 2.0. J. Decis. Syst. 2020, 29, 129–147. [CrossRef]
- Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S.; Winiarska, K. Maintenance Performance in the Age of Industry 4.0: A Bibliometric Performance Analysis and a Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 1409. [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T.; Khan, F.; Zuo, M.J. A Bibliometric Analysis of Process System Failure and Reliability Literature. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 106, 104152. [CrossRef]
- Midha, A.; Maheshwari, I.; Ojha, K.; Gupta, K.; Deshpande, S. V. Bibliometric Review of Predictive Maintenance Using Vibration Analysis. Libr. Philos. Pract. 2021, 5790, 1–15.
- Grubisic, V.V.F.; Aguiar, J.P.F.; Simeu-Abazi, Z. A Review on Intelligent Predictive Maintenance: Bibliometric Analysis and New Research Directions. 2020 Int. Conf. Control. Autom. Diagnosis, ICCAD 2020 - Proc. 2020, 3–8. [CrossRef]
- Vithi, N.L.; Chibaya, C. Advancements in Predictive Maintenance : A Bibliometric Review of Diagnostic Models Using Machine Learning Techniques. 2024, 493–507.
- Lorenzetti, D.L.; Ghali, W.A. Reference Management Software for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: An Exploration of Usage and Usability. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2013, 13. [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.A. da; Pedrosa, M.R. Using Reference Manager ( Mendeley ) in Systematic Reviews 2018.
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Chen, Q.; Bai, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X. Wear Mechanism Investigation in a Centrifugal Slurry Pump Impeller by Numerical Simulation and Experiments. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 128, 105637. [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Du, J.; Chang, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Pan, C.; Yang, Y. Numerical and Experimental Analysis of Influence of Impeller Structures on Slurry Pump Performance. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tian, L.; Chang, H.; Hong, S.; Ye, D.; You, B. Numerical and Experimental Study of Hydraulic Performance and Wear Characteristics of a Slurry Pump. Machines 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- Gierlotka, S. The Drive of Mining Electric Pumps. Silesian Electr. J. 2016, XXIII, 28–31.
- G, C.; B, C.; P, K.; sasi, B.; Kumar, P.V.K. IoT Based Underground Drainage Monitoring System. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2020, 9, 247–249. [CrossRef]
- Myszkowski, P. Money-Saving and Innovative Products and Systems Used in Minerals Processing – Selection. J. Polish Miner. Eng. Soc. 2017, 2017, 73–80. [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.A. Latest Dewatering Pumps Put a New Spin on Performance. Eng. Min. J. 2012, 213, 75–76.
- Walker, S. Pumping Technology: For Water, Slurries, Solids and More. Eng. Min. J. 2012, 34.
- Treutel, C. Hose Pumps Becoming an Option for Abrasive Mining Applications. Eng. Min. J. 2007, 208, 82–85.
- Emal Qazizada, M.; Pivarčiová, E. Reliability of Parallel and Serial Centrifugal Pumps for Dewatering in Mining Process. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2018, 23, 141–152.
- Wright, M. Water Management in Mining Applications: Selecting the Correct Pumps to Meet a Mine Site’s Needs. Min. Eng. 2021, 18–23.
- De Jager, J.P.; Groenewald, H.J.; Cilliers, C. Investigating the Effect of Pump Availability on Load Shift Performance. Proc. Conf. Ind. Commer. Use Energy, ICUE 2016, 2016-Octob, 98–103.
- Li, S.G.; Mei, S. Bin; Gao, Z.Z. Design of Mining Automatic Drainage Monitoring and Control System Based on PLC and Kingview. Proc. - 2013 7th Int. Conf. Image Graph. ICIG 2013 2013, 779–783. [CrossRef]
- Michlowicz, E.; Wojciechowski, J. Analysis of Energy Consumption of Main Dewatering Pumps in Underground Mines. Min. - Informatics, Autom. Electr. Eng. 2021, 2, 55–62.
- Walker, S. Pumps and Pielines Keep Mines on the Move. Eng. Min. J. 2013, APRIL, 68–79.
- Hasan, A.N. Evaluating the Performance of Single Classifiers Against Multiclassifiers in Monitoring Underground Dam Levels and Energy Consumption for a Deep Gold Mine Pump Station. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016 - 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society; 2016; pp. 907–911.
- Rea, I.; Monaghan, D. Dewatering Bore Pumps - Reducing Costs and Emissions by Maximising Pumping Efficiency over Time. Trans. Institutions Min. Metall. Sect. A Min. Technol. 2009, 118, 220–224. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Tian, Z.; Lin, S.; Ji, J.; Guo, Y.; Xie, F. Fault Diagnosis Study of Mine Drainage Pump Based on MED–WPD and RBFNN. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, R.; Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S. Mining Equipment Diagnostics in a Mine Shaft Dewatering System – Case Study. J. Konbin 2023, 53, 69–86. [CrossRef]
- Szymański, Z. Modern Control Method and Diagnostics Research of the Mine Main Pumps. Napędy i Sterow. 2013, 54–61.
- Saha, D.; V. A. V. Prasad, S.; Saluja, N. Design of Coal Mine Underground Drainage Pump Monitoring and Controlling System Using ARM7 and Touch Screen. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 71, 25–28. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, G.J. Design of Coal Mine Underground Drainage Pump Monitoring and Controlling System Based on PLC and Touch Screen. Proc. 2011 Int. Conf. Mechatron. Sci. Electr. Eng. Comput. MEC 2011 2011, 1245–1247. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. zun; Wang, Z. jie; Lin, Y.; Pan, C. fang; Pan, G. ying Three Step-Drawdown Dewatering Test in Unsteady Flow Condition: A Case Study of the Siwan Coal Mine in North China Coalfield. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77. [CrossRef]
- Mahamadou, O.; Abdoulkader, H.A.; Seibou, B.; Abdourazakou, M.H.; Harouna, S.; Souleymane, I.I.; Marou, I.H. Study of the Operating Cost of the Electric Pump for Mine Dewatering: Case of the SOMAÏR Uranium Mine. Phys. Sci. Int. J. 2024, 28, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Marchi, A.; Simpson, A.R.; Lambert, M.F. Pump Operation Optimization Using Rule-Based Controls. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 210–217. [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. Pressure Fluctuation–Vorticity Interaction in the Volute of Centrifugal Pump as Hydraulic Turbines (PATs). Processes 2022, 10, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Kusiak, A. Data-Driven Minimization of Pump Operating and Maintenance Cost. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 40, 37–46. [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Nguyen, T.C.; Wang, J.; Vuong, D. New Correlations for Predicting Two-Phase Electrical Submersible Pump Performance under Downhole Conditions Using Field Data. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 12, 1225–1235. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, K.; Su, W.; Zhao, X. Numerical Simulation of Drilling Fluid Flow in Centrifugal Pumps. Water (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, W. Possible Application of Low-Cost Laser Scanners and Photogrammetric Measurements for Inspections in Shaft Sinking Process. J. Konbin 2023, 53, 147–156. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, F. The Effect of Discharge Areas on the Operational Performance of a Liquid-Ring Vacuum Pump: Numerical Simulation and Experimental Verification. Vacuum 2022, 206, 111425. [CrossRef]
- Pujades, E.; Orban, P.; Bodeux, S.; Archambeau, P.; Erpicum, S.; Dassargues, A. Underground Pumped Storage Hydropower Plants Using Open Pit Mines: How Do Groundwater Exchanges Influence the Efficiency? Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 135–146. [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.A. Pumps and Valves: Ready for Prime Time. Eng. Min. J. 2021, 50–56.
- Pierce, W. An Overview of a Cost-Effective Method of Sealing Slurry Pumps: Centrifugal or Dynamic Expeller Seals. Min. Eng. 2021, 21–25.
- Casteel, K. Pumping Progress New Models, Materials and Methods Enhance Efficiency. Eng. Min. J. 2006, 207, 36–42.
- High-Tech Materials Maximize Pump Safety and Performance. Eng. Min. J. 2014, 136–138.
- Carter, R.A. Spotlight on Slurry. Eng. Min. J. 2010, 211, 102–105.
- Michalicka, P. Boosting Bearing and Pump Reliability in Fracking Operations. Can. Min. J. 2013, 134, 42–46.
- Crane, J. How to Improve Reliability, Bottom Line, and Water Reduction. Can. Min. J. 2023, 33–34.
- Cai, J.; Wu, J.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Z.; Kong, D. Numerical Analysis of Multi-Factors Effects on the Leakage and Gas Diffusion of Gas Drainage Pipeline in Underground Coal Mines. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 166–181. [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.A. What’s Next for Slurry Pumps? Eng. Min. J. 2021, 38–42.
- Metso Updates Plant Control Monitoring Software. Eng. Min. J. 2018, 98–99.
- Iranzi, J.; Son, H.; Lee, Y.; Wang, J. A Nodal Analysis Based Monitoring of an Electric Submersible Pump Operation in Multiphase Flow. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Mazur, D.C.; Sottile, J.; Novak, T. An Electrical Mine Monitoring System Utilizing the IEC 61850 Standard. In Proceedings of the Conference Record - IAS Annual Meeting (IEEE Industry Applications Society); IEEE, 2013; pp. 1–10.
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, R.; Sarkar, B.K.; Maity, S. Condition Monitoring of Hydraulic Transmission System with Variable Displacement Axial Piston Pump and Fixed Displacement Motor. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 46, 9758–9765. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Sarkar, B.K.; Maity, S. Leakage Based Condition Monitoring and Pressure Control of the Swashplate Axial Piston Pump. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 Gas Turbine India Conference, GTINDIA 2019; 2019; Vol. 2, pp. 1–9.
- Tiwari, R.; Bordoloi, D.J.; Dewangan, A. Blockage and Cavitation Detection in Centrifugal Pumps from Dynamic Pressure Signal Using Deep Learning Algorithm. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 173, 108676. [CrossRef]
- Rosic, M.; Leiden, A.; Abraham, T.; Herrmann, C. Data Mining Approach for Device Detection Using Power Signatures and Manufacturing Execution System Data. Procedia CIRP 2022, 107, 1047–1052. [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. Research on Massive Data Processing System of Coal Mine Safety Monitoring Based on Computer Technology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1992, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; He, D. A Segmental Hidden Semi-Markov Model (HSMM)-Based Diagnostics and Prognostics Framework and Methodology. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 2248–2266. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dong, M.; Lv, W.; Geng, X.; Li, Y. A Novel Method Using Adaptive Hidden Semi-Markov Model for Multi-Sensor Monitoring Equipment Health Prognosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 64–65, 217–232. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Punj, P.; Kumar, N.; Das, A.K.; Kumar, A. Lifetime Prediction of a Hydraulic Pump Using ARIMA Model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Barszcz, T.; Urbanek, J.; Szumilas, Ł. Selection of Efficient Monitoring Methods for Machinery Generating High Vibration Signal Disturbance. Diagnostics 2010, 4, 55–58.
- Glowacz, A.; Glowacz, Z. Diagnosis of the Three-Phase Induction Motor Using Thermal Imaging. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 81, 7–16. [CrossRef]
- Tse, P.W.; Wang, D. Performance Degradation Assessment of Slurry Pumps. In Engineering Asset Management -Systems, Professional Practices and Certification. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Tse, P.W., Mathew, J., Wong, K., Lam, C.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Switzerland, 2015; pp. 149–158.
- Bold, S.; Urschel, S. Assessment of Approaches for Technical Diagnostic of Pump Faults with Induction Motor as Transducer. 23rd Int. Conf. Electr. Mach. Syst. ICEMS 2020 2020, 810–815. [CrossRef]
- Koteleva, N.; Valnev, V.; Frenkel, I. Investigation of the Effectiveness of an Augmented Reality and a Dynamic Simulation System Collaboration in Oil Pump Maintenance. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Pourebrahimi, A.; Mokhtar, S.; Sahami, S.; Mahmoodi, M. Status Detection and Fault Diagnosing of Rotatory Machinery by Vibration Analysis Using Data Mining. ICCTD 2010 - 2010 2nd Int. Conf. Comput. Technol. Dev. Proc. 2010, 131–135. [CrossRef]
- Isermann, R. Fault-Diagnosis Applications. Model-Based Condition Monitoring: Actuators, Drivers, Machinery, Plants, Sensors, and Fault-Tolerant Systems; 2011; ISBN 9783642127663.
- Dong, J.; Deng, Y.; Cao, W.; Wang, Z.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Ji, H.; Liu, Y. Wear Failure Analysis of Suction Valve for High Pressure and Large Flow Water Hydraulic Plunger Pump. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 134, 106095. [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Kivikytö-Reponen, P.; Härkisaari, P.; Valtonen, K.; Erdemir, A. Global Energy Consumption Due to Friction and Wear in the Mining Industry. Tribol. Int. 2017, 115, 116–139. [CrossRef]
- Kamenicky, J.; Zajicek, J. Failure Rate Evaluation of the Pumps Used in Power Industry. Proc. 2015 16th Int. Sci. Conf. Electr. Power Eng. EPE 2015 2015, 503–506. [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, J.; Zaitouny, A.; Hodkiewicz, M.R.; Small, M. Detecting Asset Cascading Failures Using Complex Network Analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 120624–120637. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wei, X. A New Integrated Numerical Modeling Approach toward Piston Diaphragm Pump Simulation: Three-Dimensional Model Simplification and Characteristic Analysis. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Vellman, D.H.; Venter, J.; Pelzer, R. Automated Demand Side Management of Clear Water Pumping and Storage for Shifting Load out of Eskom’s Domestic Peak in the Mining Industry. In Proceedings of the 2012 Proceedings of the 9th Industrial and Commercial Use of Energy Conference; 2012; pp. 1–4.
- Korzhev, A.A.; Bolshunova, O.M.; Voytyuk, I.N. Simulation of an Adjustable Synchronous Electric Motor Drive of a Pumping Unit in a Reservoir Pressure Maintenance System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1333. [CrossRef]
- Barberá, L.; Crespo, A.; Viveros, P.; Stegmaier, R. A Case Study of GAMM (Graphical Analysis for Maintenance Management) in the Mining Industry. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 121, 113–120. [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.B.; Crespo Marquez, A.; Gunckel, P.V.; Stegmaier, R. Advanced Maintenance Modelling for Asset Management: Techniques and Methods for Complex Industrial Systems. In Advanced Maintenance Modelling for Asset Management: Techniques and Methods for Complex Industrial Systems; Crespo Marquez, A., Gonzalez-Prida Diaz, V., Gomez Fernandez, J.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG, 2018; pp. 331–348 ISBN 9783319580456.
- Jasinski, M.; Jasinska, E.; Jasinski, M.; Jasinski, L. Computer-Aided Appliances to Underground Machines Maintenance – Selected Issues. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence, ECAI 2018; 2018.
- Asset Management Plan Cuts Maintenance Costs at Tronox Mine. Eng. Min. J. 2021, 58–60.
- Fan, C. Key Technologies for Intelligent Mining of Difficult-to-Mine Coal Seams. J. Civ. Eng. Urban Plan. 2024, 6, 69–75. [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Ding, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, C.; Guo, J. Research on an Intelligent Mining Complete System of a Fully Mechanized Mining Face in Thin Coal Seam. Sensors 2023, 23. [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Gangsar, P.; Porwal, R.; Atulkar, A. Artificial Intelligence Application in Fault Diagnostics of Rotating Industrial Machines: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 34, 931–960. [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Ge, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, E. Construction of Digital Twin System for Intelligent Mining in Coal Mines. Metaverse 2022, 3, 16. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X. Research on Pump Product Intelligent Fault Diagnosis System Based on Dig Data. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2121. [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Wei, X.; Yang, C.; Su, C. Optimization Technology of Frequency Conversion Constant Pressure Control System of Mine Emulsion Pump Station in Electrical Engineering and Automation Specialty. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Fiscor, B.S. Managing a Digital Ecosystem for Mining New Tools Offer Mines Ways to Collect and Analyze Useful Data. Eng. Min. J. 2022, 30–34.


| Ref. | Publication Year | Research Objectives | Methodology Used | Databases Analyzed | Papers Analyzed | Analyzed sector or type of pumps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [72] | 2011 | Review on major fault modes in centrifugal pumps, especially in the context of the water and sewage industry applications | n/a | n/a | n/a | Water and sewage industry/Centrifugal pumps |
| [73] | 2014 | Review on diagnostics and prognostics of centrifugal pumps with focusing on the application area, detection of fault modes, and test results. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Centrifugal pumps |
| [32] | 2014 | A comprehensive review of the development, applications, and performance characteristics of pumps operating in turbine mode (PAT) for small-scale hydroelectric power systems, with a focus on their feasibility in remote communities lacking grid connections. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Pump as turbine (PAT) |
| [33] | 2020 | Review on Prognostics and Health Management for pump systems operating in thermal power plants. | Structured overview | n/a | n/a | Energy sector |
| [34] | 2021 | Analysis and characteristics of faults in large-scale heat pumps, with particular attention to recurrent faults in critical components, to assess existing fault detection and diagnosis methods, identify their limitations, and propose future research directions. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Large-scale heat pumps |
| [74] | 2022 | Critical analysis of machine learning’s most current advances in the field of artificial intelligence-based system health management. | Systematic literature review | Web of Science, Science Direct, Scopus | 88 | Oil and Gas sector |
| [60] | 2022 | Review various types of faults and their identification possibilities by various traditional and ML-based techniques. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Centrifugal pumps |
| [75] | 2022 | Investigation of the potentials and challenges of integrating emerging technologies (Digital Twin, Building Information Modeling, Machine Learning) in the PdM of pumps. | Systematic literature review | Web of Science, Scopus | 118 | Civil infrastructure applications |
| [76] | 2022 | Review on condition monitoring techniques for pumps with a particular focus on the sensing technologies. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Oil and Gas sector |
| [77] | 2022 | Review on machine learning-based fault diagnosis of centrifugal pumps. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Centrifugal pumps |
| [78] | 2022 | Review on recent developments in hydraulic pumps’ fault diagnosis and health management. | Systematic literature review | n/a | n/a | Hydraulic pumps |
| [79] | 2022 | Review on health monitoring methods suitable for airframe fuel pumps under flight conditions. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Aviation sector |
| [80] | 2023 | Review on the Artificial Intelligence (AI) based models for PdM of water injection pumps. | Systematic literature review | Scopus, IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect, and ACM Digital Library | 16 | Oil and Gas sector |
| [81] | 2024 | General overview of control systems used to operate pump units. | n/a | n/a | n/a | Offshore industry |
| [82] | 2024 | Review of the centrifugal pump cavitation monitoring methods (flow-head method, high-speed photography, pressure pulsation method, acoustic emission method, vibration method). | n/a | n/a | n/a | Centrifugal pumps |
| Research Area | Main Trends | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Dewatering System Operation and Maintenance | - Increasing use of automated water management - Integration of IoT-enabled sensors for real-time monitoring - AI-driven predictive dewatering models |
- Abrasive and corrosive conditions reducing pump lifespan - Need for real-time system adjustments under changing mine conditions - High cost of automated dewatering solutions |
| Operational Efficiency and Reliability Optimization | - Adoption of variable-speed drives (VSDs) to optimize energy use - AI-based pump performance optimization - Material science advancements to reduce wear |
- High energy costs of pumping operations - Need for customized CFD models for different pump types - Complex relationship between fluid dynamics and wear mechanisms |
| Condition/Health Status Monitoring | - Widespread use of sensor-based monitoring - Integration of cloud-based diagnostics - AI-driven failure prediction models improving accuracy |
- Managing large-scale sensor data efficiently - False positives in anomaly detection - Standardization issues in monitoring technologies |
| Health Diagnosis and Prognosis | - Use of Relevance Vector Machines (RVMs), Hidden Semi-Markov Models (HSMMs), and Support Vector Machines (SVMs) for RUL estimation - Combining historical failure data with real-time analytics - AI-powered predictive maintenance platforms |
- Data quality and availability issues for AI training - Variability in failure patterns under different operating conditions - High computational costs for real-time RUL modeling |
| Maintenance Management | - Shift from preventive to predictive maintenance - Widespread adoption of Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) - AI-assisted fault classification for automated decision-making |
- Resistance to the adoption of AI-driven maintenance in traditional mining setups - Lack of standard frameworks for maintenance cost analysis - High initial investment costs |
| Intelligent Mining and Digital Transformation | - Increasing adoption of digital twins for failure prediction - AI-driven predictive analytics becoming standard - Remote and autonomous mining operations reducing human intervention |
- Data security concerns with cloud-based diagnostics - Integration challenges with legacy pump monitoring systems - High costs of AI-based automation and digital twin implementation |
| Defined area | Main requirements |
|---|---|
| Monitoring and diagnostics module |
|
| Predictive analytics |
|
| Automatic response to alarms |
|
| Service Scheduling |
|
| Reporting and historical analysis |
|
| Integration with the mine management system |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





