Submitted:
08 February 2025
Posted:
10 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Graphical Abstract
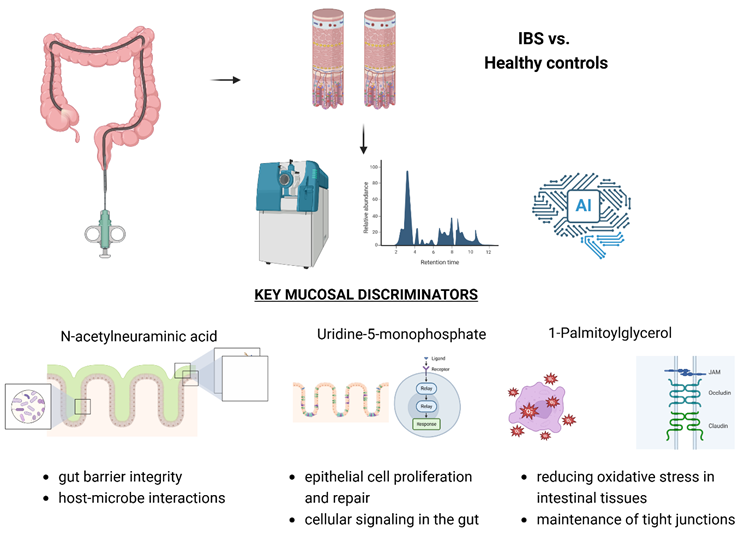
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analysis
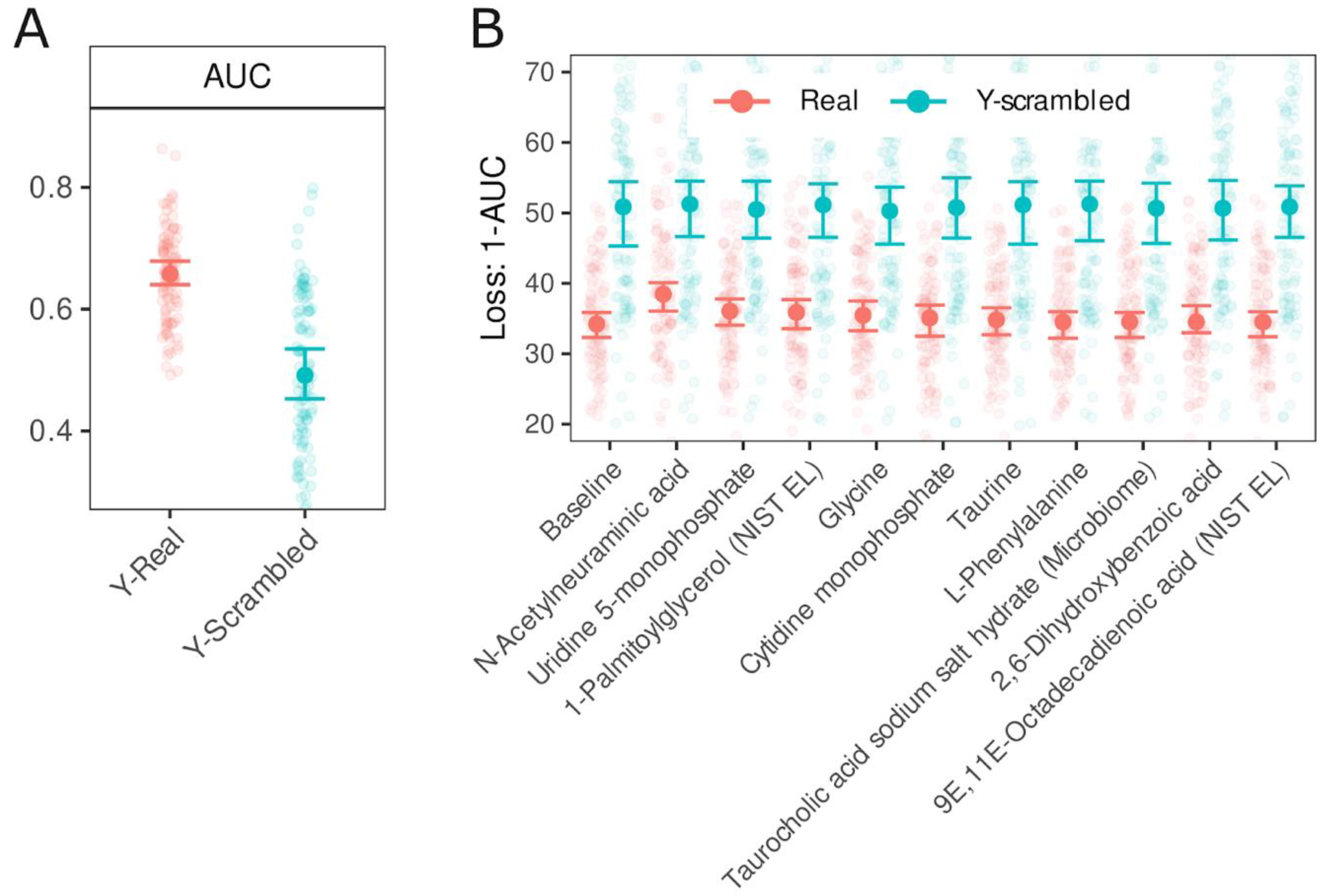
2.4. Random Forest Classification and Feature Importance Analysis
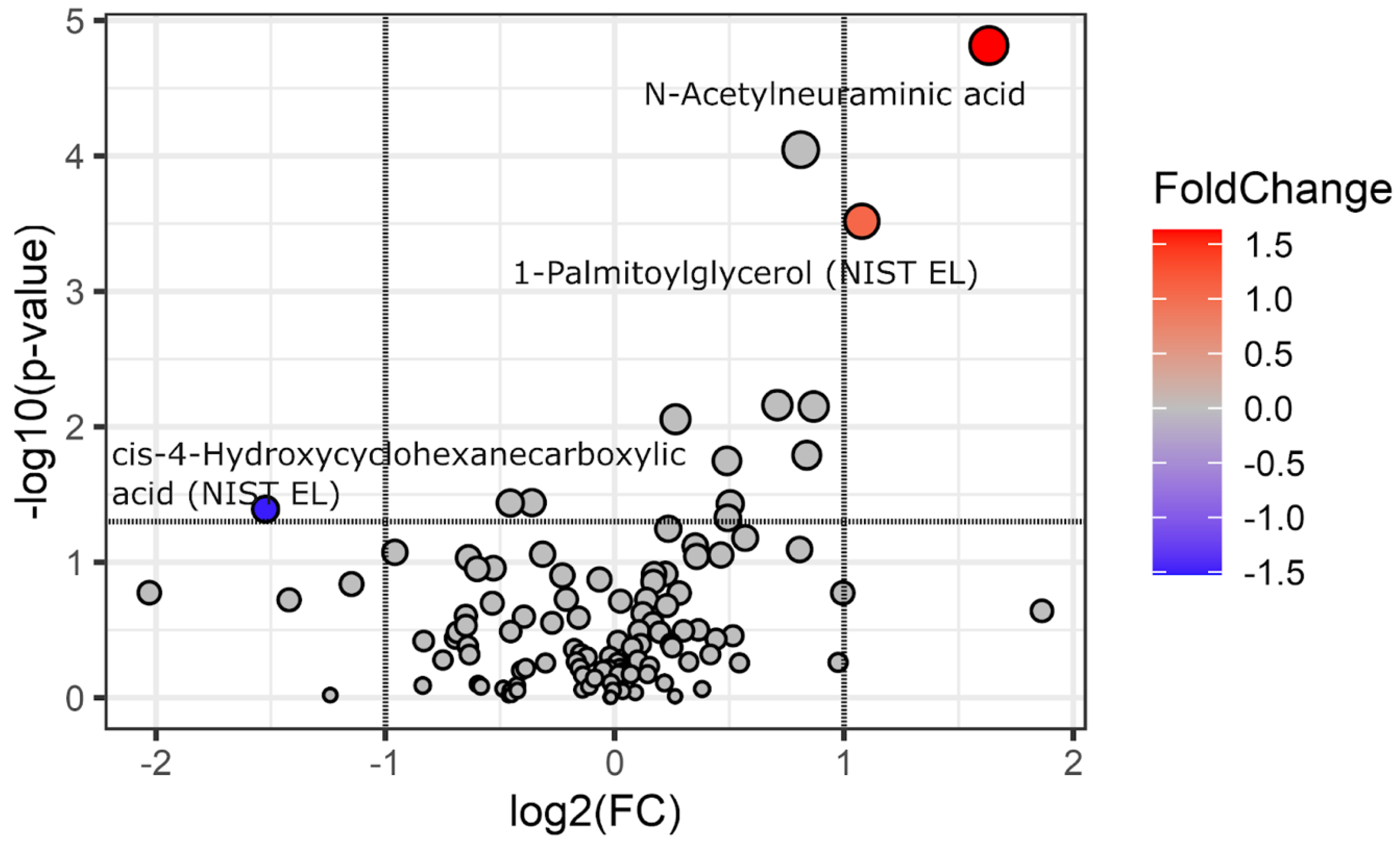
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palsson, O.S.; Tack, J.; Drossman, D.A.; Le Nevé, B.; Quinquis, L.; Hassouna, R.; Ruddy, J.; Morris, C.B.; Sperber, A.D.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; et al. Worldwide Population Prevalence and Impact of Sub-Diagnostic Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2024, 59, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.P.; Holtmann, G.J.; Tack, J.; Carbonne, F.; Chey, W.; Koloski, N.; Shah, A.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Sperber, A.D.; Palsson, O.S.; et al. Diagnostic Classification Systems for Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction Should Include Psychological Symptoms. Neurogastroenterology and Motility 2024, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, S.; Vasant, D.H.; Guadagnoli, L.; Reed, B.; Chiarioni, G.; Ten Cate, L.; Keefer, L.; Kinsinger, S.W. A Primer for the Gastroenterology Provider on Psychosocial Assessment of Patients with Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2024, 36, e14894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulak, A.; Freud, T.; Waluga, M.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Palsson, O.S.; Sperber, A.D. Sex- and Gender-Related Differences in the Prevalence and Burden of Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction in Poland. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2023, 35, e14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krynicka, P.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Cembrowska-Lech, D.; Podsiadło, K.; Dąbkowski, K.; Gaweł, K.; Botke, N.; Zawada, I.; Ławniczak, M.; et al. The Burden of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia in Poland: A Cross-Sectional Study from West Pomeranian Voivodship. BMC Gastroenterol 2025, 25, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.; Antoniewicz, J.; Borecki, K.; Tejchman, K.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Maciejewska-Markiewicz, D.; Ryterska, K.; Komorniak, N.; Czerwińska-Rogowska, M.; Wolska, A.; et al. Irritable Bowel Syndrome Prevalence among Participants of Woodstock Rock Festival in Poland Based on Rome IV Criteria Questionnaire. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperber, A.D.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Drossman, D.A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Simren, M.; Tack, J.; Whitehead, W.E.; Dumitrascu, D.L.; Fang, X.; Fukudo, S.; et al. Worldwide Prevalence and Burden of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 99–114.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, V.A.; Gheorghe, G.; Georgescu, T.F.; Bacalbasa, N.; Gheorghe, F.; Diaconu, C.C. The Latest Data Concerning the Etiology and Pathogenesis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2024, 13, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Xiao, H.; Xu, J.; He, J.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, B.; Cao, M.; Hong, W. Meta-Analysis of Gut Microbiota Alterations in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, M.R.; Cremon, C.; Marasco, G.; Savarino, E.; Guglielmetti, S.; Bonomini, F.; Palombo, M.; Fuschi, D.; Rotondo, L.; Mantegazza, G.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Loss of Vascular and Epithelial Integrity in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2024, 167, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarewska, A.; Lewandowski, K.; Kaniewska, M.; Rosołowski, M.; Marlicz, W.; Rydzewska, G. Irritable Bowel Syndrome Following COVID-19: An Underestimated Consequence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pol Arch Intern Med 2022, 132, 16323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarewska, A.; Lewandowski, K.; Kaniewska, M.; Tulewicz-Marti, E.; Więcek, M.; Szwarc, P.; Rosołowski, M.; Marlicz, W.; Rydzewska, G. Long-Lasting Dyspeptic Symptoms - Another Consequence of the COVID-19 Pandemic? Prz Gastroenterol 2023, 18, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, K.; James, S.C.; Young, W.; Gearry, R.B.; Heenan, P.E.; Keenan, J.I.; Talley, N.J.; McNabb, W.C.; Roy, N.C. Characterisation of the Plasma and Faecal Metabolomes in Participants with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopera, K.; Gromowski, T.; Wydmański, W.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Muszyńska, A.; Zielińska, K.; Wierzbicka-Woś, A.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Kadaj-Lipka, R.; Cembrowska-Lech, D.; et al. Gut Microbiome Dynamics and Predictive Value in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of Shallow and Deep Shotgun Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-Y.; Qi, Q.-Q.; Long, X.; Li, X.; Chen, F.-X.; Yu, Y.-B.; Zuo, X.-L. Ultrastructure of Intestinal Mucosa in Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Physiol Int 2019, 106, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vich Vila, A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Faber, K.N.; Weersma, R.K. Untargeted Faecal Metabolomics for the Discovery of Biomarkers and Treatment Targets for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gut 2024, 73, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R.; Zhong, H.; Xiong, X.; et al. Integrated Analysis of Colorectal Cancer Reveals Cross-Cohort Gut Microbial Signatures and Associated Serum Metabolites. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1024–1037.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, C.; Xiong, T.; Lu, L.; Deng, Y.; Luo, W.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Q.; et al. Altered Metabolome and Microbiome Features Provide Clues in Understanding Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Depression Comorbidity. ISME J 2022, 16, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.-Z.; Fu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Hwang, S.H.; Yin, H.-H.; Ni, K.-D.; Pan, Q.-J.; He, X.; Zhang, L.-T.; et al. Metabolomics Reveals Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase as a Therapeutic Target for High-Sucrose Diet-Mediated Gut Barrier Dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2024, 121, e2409841121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzadilla, N.; Qazi, A.; Sharma, A.; Mongan, K.; Comiskey, S.; Manne, J.; Youkhana, A.G.; Khanna, S.; Saksena, S.; Dudeja, P.K.; et al. Mucosal Metabolomic Signatures in Chronic Colitis: Novel Insights into the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Metabolites 2023, 13, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres Lessa, A.Y.; Edwinson, A.; Sato, H.; Yang, L.; Berumen, A.; Breen-Lyles, M.; Byale, A.; Ryks, M.; Keehn, A.; Camilleri, M.; et al. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Correlates of Increased Colonic Permeability in Postinfection Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 1542; -7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The Neuroactive Potential of the Human Gut Microbiota in Quality of Life and Depression. Nat Microbiol 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Lin, Q.; Luo, F.; Wang, H. Insights into the Structure, Metabolism, Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms of Sialic Acid: A Review. Foods 2024, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, R.; Qin, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, J. Effects of Oligosaccharide-Sialic Acid (OS) Compound on Maternal-Newborn Gut Microbiome, Glucose Metabolism and Systematic Immunity in Pregnancy: Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e026583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface Components and Metabolites of Probiotics for Regulation of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Microbial Cell Factories 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y. Protective Effect of 1,3-Dioleoyl-2-Palmitoylglycerol against DSS-Induced Colitis via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Maintaining Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Integrity. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8700–8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuckin, M.A.; Eri, R.; Simms, L.A.; Florin, T.H.J.; Radford-Smith, G. Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009, 15, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.; Li, X.; Burchmore, R.; Goodwin, R.J.A.; Wall, D.M. Microbiome-Derived Metabolite Effects on Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Immune Cell Response to Infection. Microbiology 2024, 170, 001504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, C.; Mahurkar-Joshi, S.; Dong, T.S.; Lenhart, A.; Lagishetty, V.; Jacobs, J.P.; Labus, J.S.; Jaffe, N.; Mayer, E.A.; Chang, L. Colonic Mucosal Microbiota Is Associated with Bowel Habit Subtype and Abdominal Pain in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2022, 323, G134–G143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, C.; Savolainen, O.; Sapnara, M.; Törnblom, H.; Simrén, M.; Magnusson, M.K.; Öhman, L. Temporal Stability of Fecal Metabolomic Profiles in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2024, 36, e14741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, O.; Adibi Sedeh, P.; Pourfarzam, M. Metabolic Biomarkers in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Diagnosis. Clin Chim Acta 2024, 560, 119753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, M.; Lang, M.; Holley, H.; Crepaz, D.; Hausmann, B.; Pjevac, P.; Moser, D.; Haller, F.; Hof, F.; Beer, A.; et al. Mucosal Biofilms Are an Endoscopic Feature of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1245–1256.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.X.; Lee, J.S.; Campbell, E.L.; Colgan, S.P. Microbiota-Derived Butyrate Dynamically Regulates Intestinal Homeostasis through Regulation of Actin-Associated Protein Synaptopodin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 11648–11657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vich Vila, A.; Hu, S.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Collij, V.; Jansen, B.H.; Augustijn, H.E.; Bolte, L.A.; Ruigrok, R.A.A.A.; Abu-Ali, G.; Giallourakis, C.; et al. Faecal Metabolome and Its Determinants in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut 2023, 72, 1472–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | IBS N = 441 | Other N = 691 | P2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.175 | ||
| Females | 30 / 44 (68%) | 38 / 69 (55%) | |
| Males | 14 / 44 (32%) | 31 / 69 (45%) | |
| Age (years) | 0.029 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 52 (16) | 59 (13) | |
| Body mass (kg) | 0.741 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 77 (18) | 77 (15) | |
| Height (cm) | 0.538 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 168 (10) | 168 (13) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.932 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 27.0 (5.4) | 27.7 (8.5) | |
| DM (Yes/No) | 7 / 44 (16%) | 9 / 69 (13%) | 0.783 |
| Hypertension (Yes/No) | 14 / 44 (32%) | 32 / 69 (46%) | 0.169 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





