Submitted:
07 February 2025
Posted:
10 February 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Mass-Spectroscopic Database
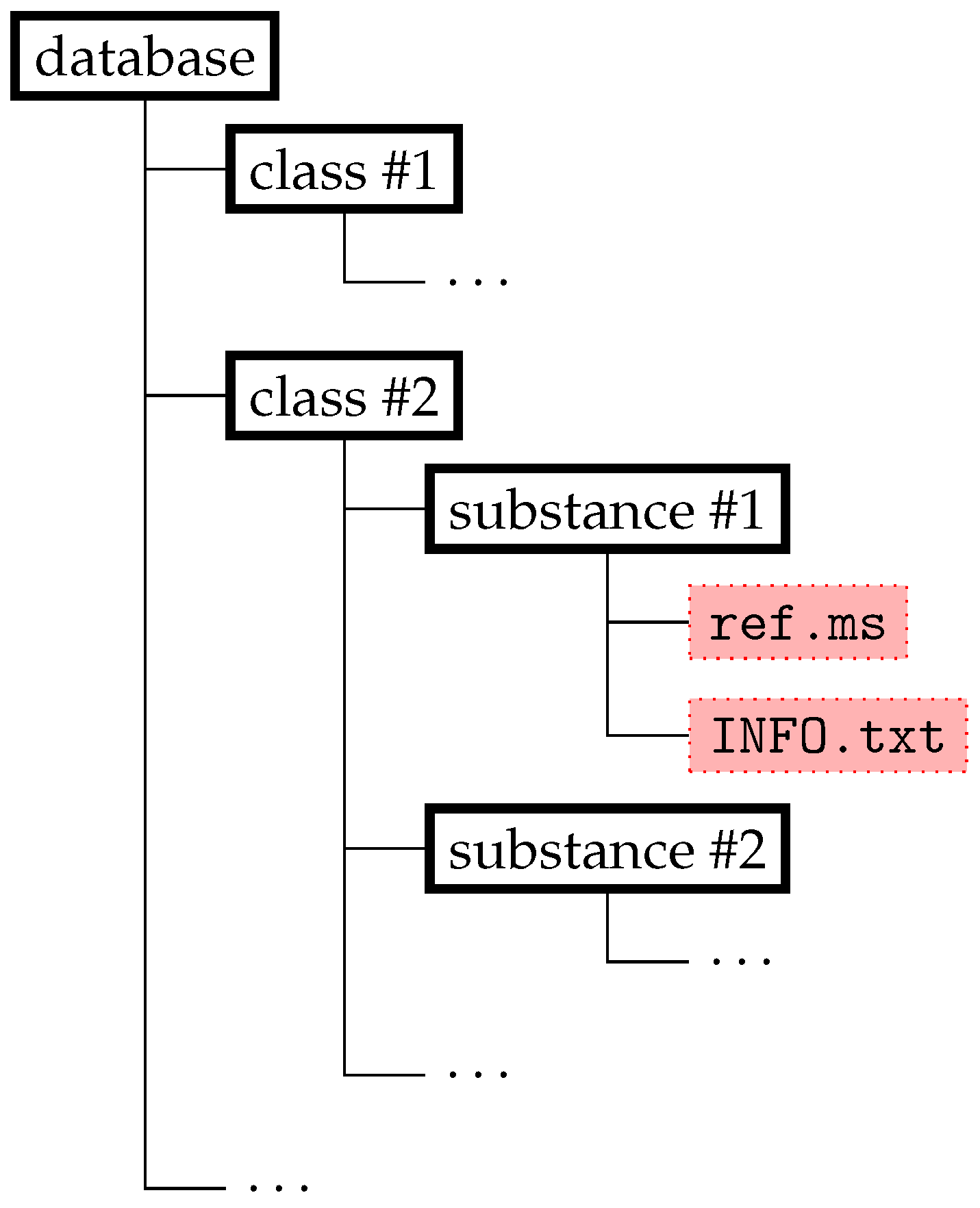
2.1.1. Database Structure and File Formats
2.1.2. Sources of Experimental Mass Spectra
2.1.3. Sources of Theoretical Mass Spectra
2.2. Mass-Spectra Assigning Algorithm
2.2.1. Window-Function Based Assignment
2.2.2. Assignment Metric
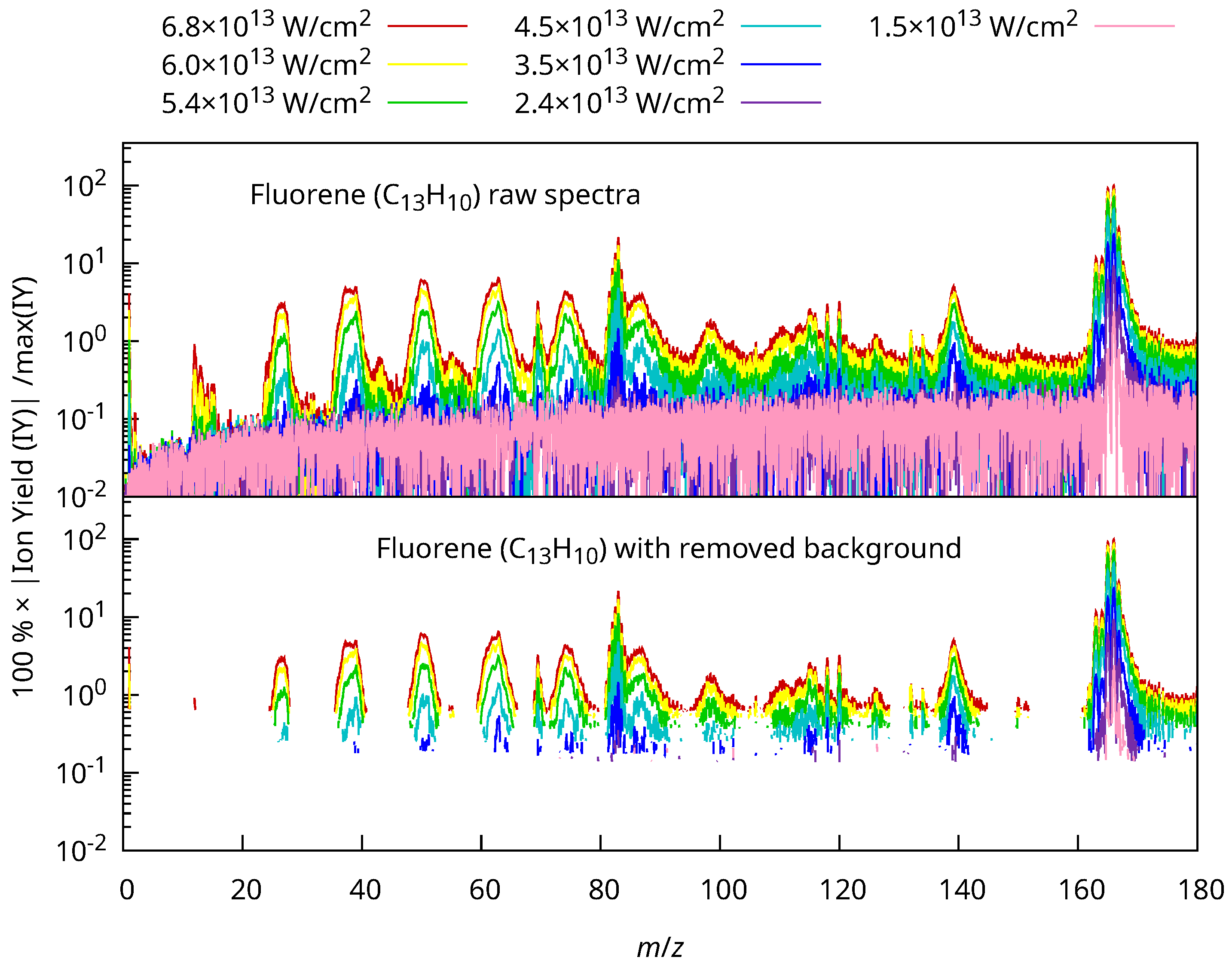
2.2.3. Background Removal Algorithm
- Calculate the standard deviation of from baseline () as .
- Consider only values , with being an arbitrary selectivity coefficient, forming a new set , where the upper index “(1)” indicates the iteration number and is the number of elements in the new set.
- Calculate the new standard deviation as .
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until the number of elements in the set remains constant or a maximum number of iterations p is reached.
- Set values of the original mass spectrum below the final threshold to zero.
2.3. Software
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Results
- Top-K accuracy (also known as Hit rate at rank K), which is equal to the number of trials with the correctly identified compound being present in top-best K candidates divided by the total number of trials and multiplied by 100%, i.e.,
- Mean reciprocal rank (MRR), defined aswhere is the rank of the correctly identified compound in trial i.
- Mean rank (MR), defined as
3. Results and Discussion
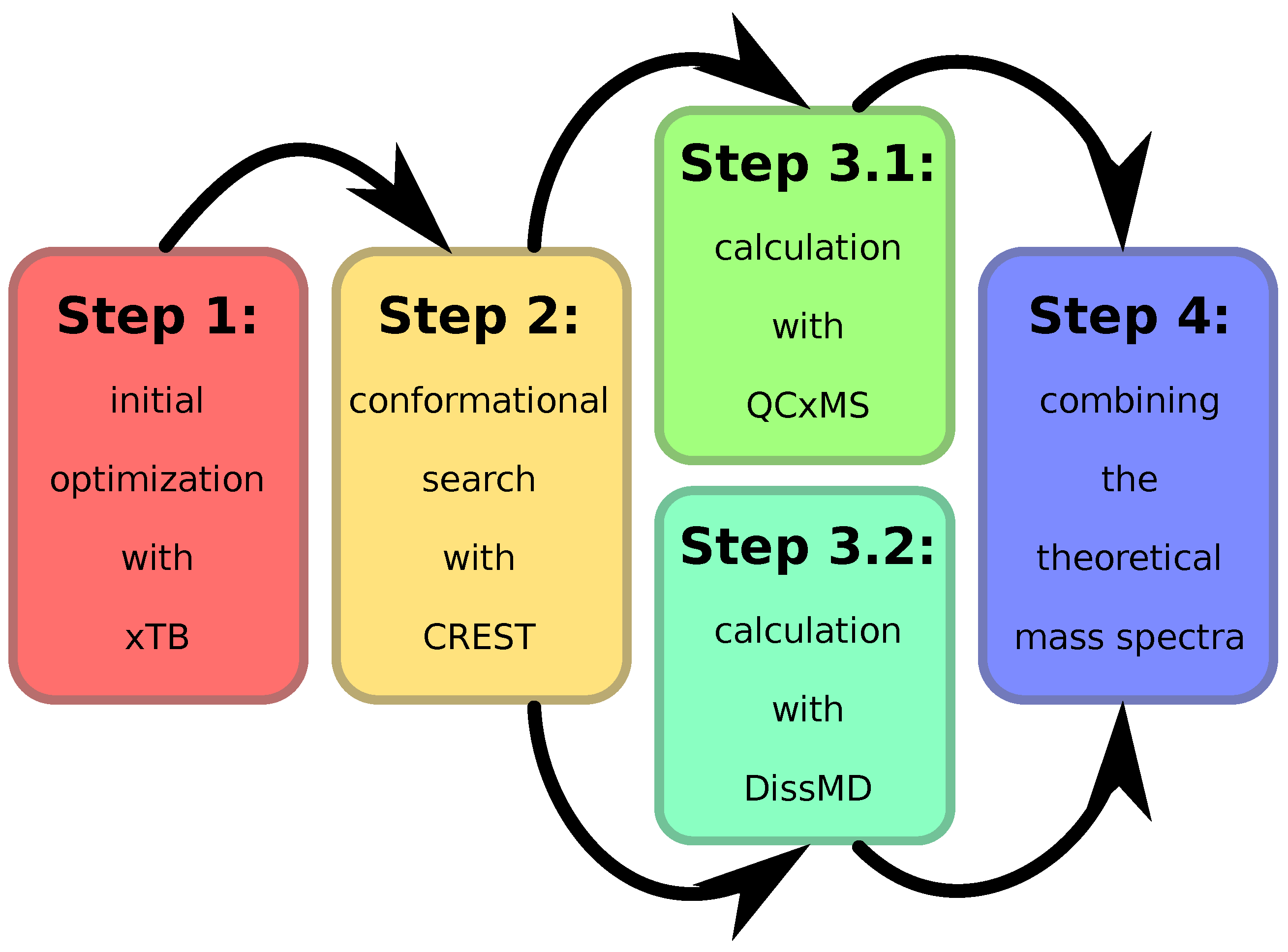
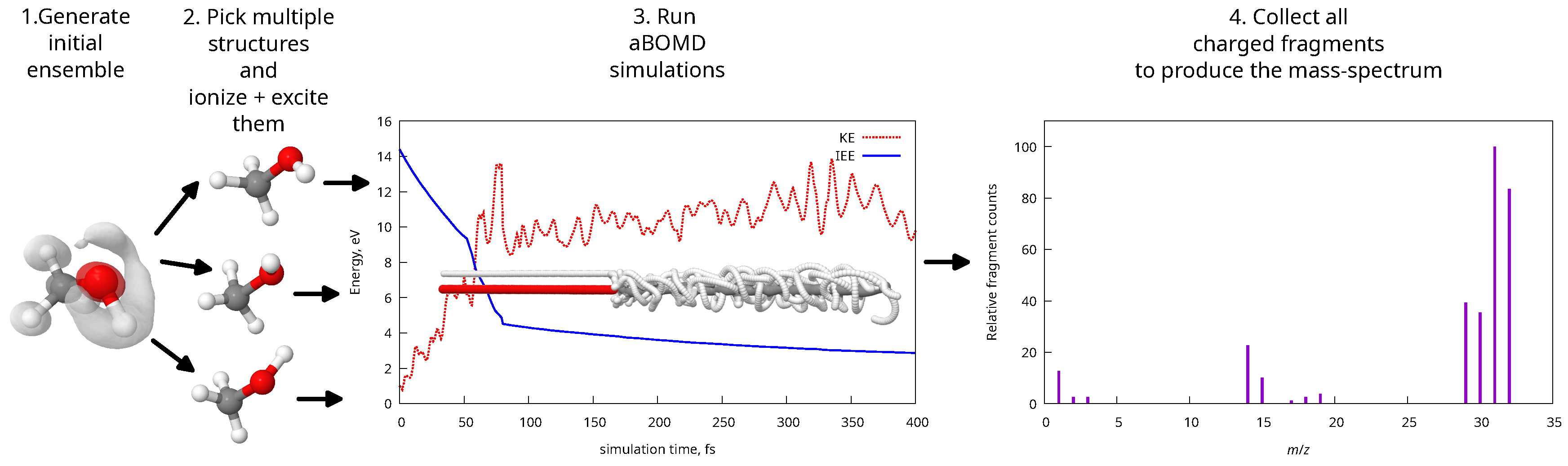
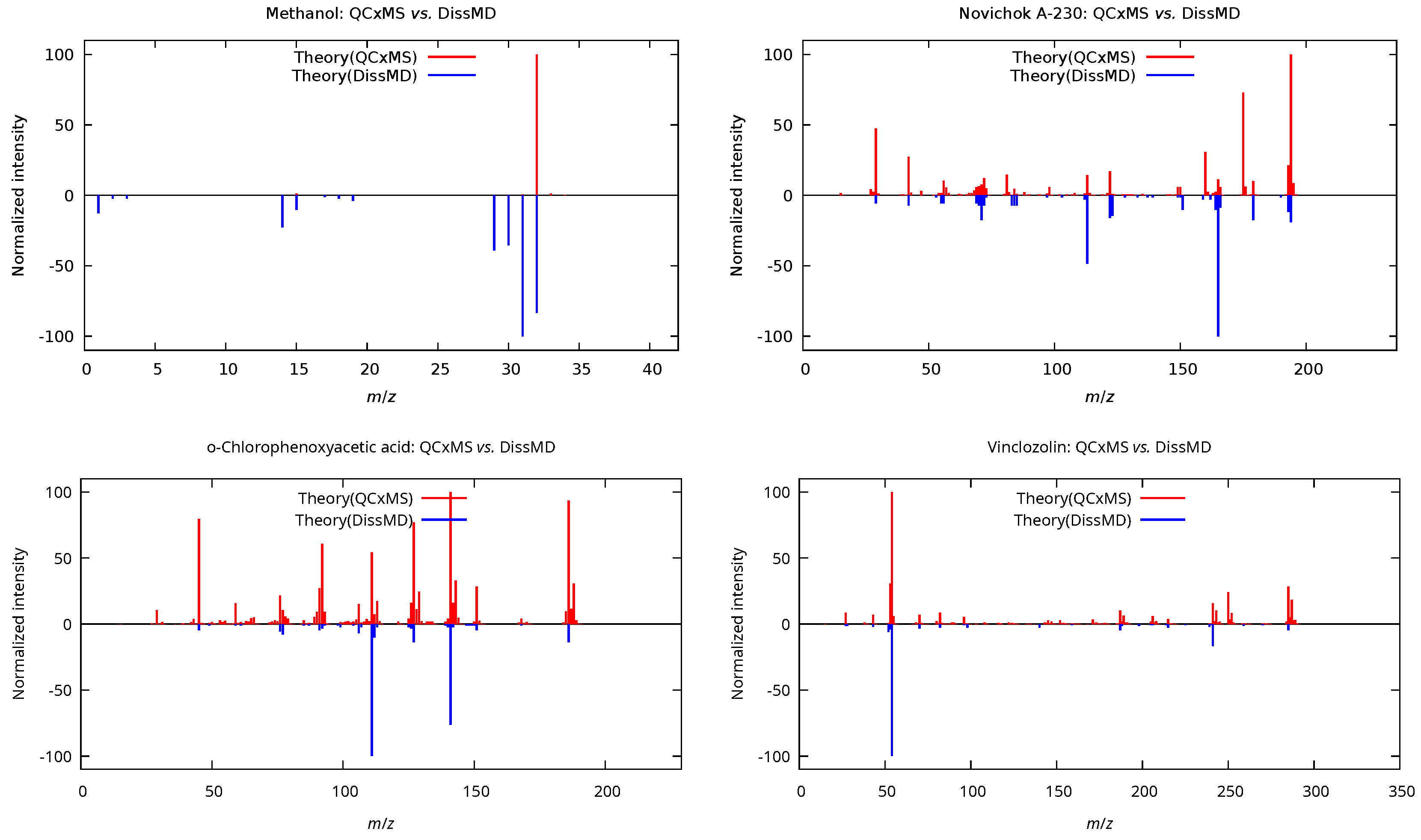
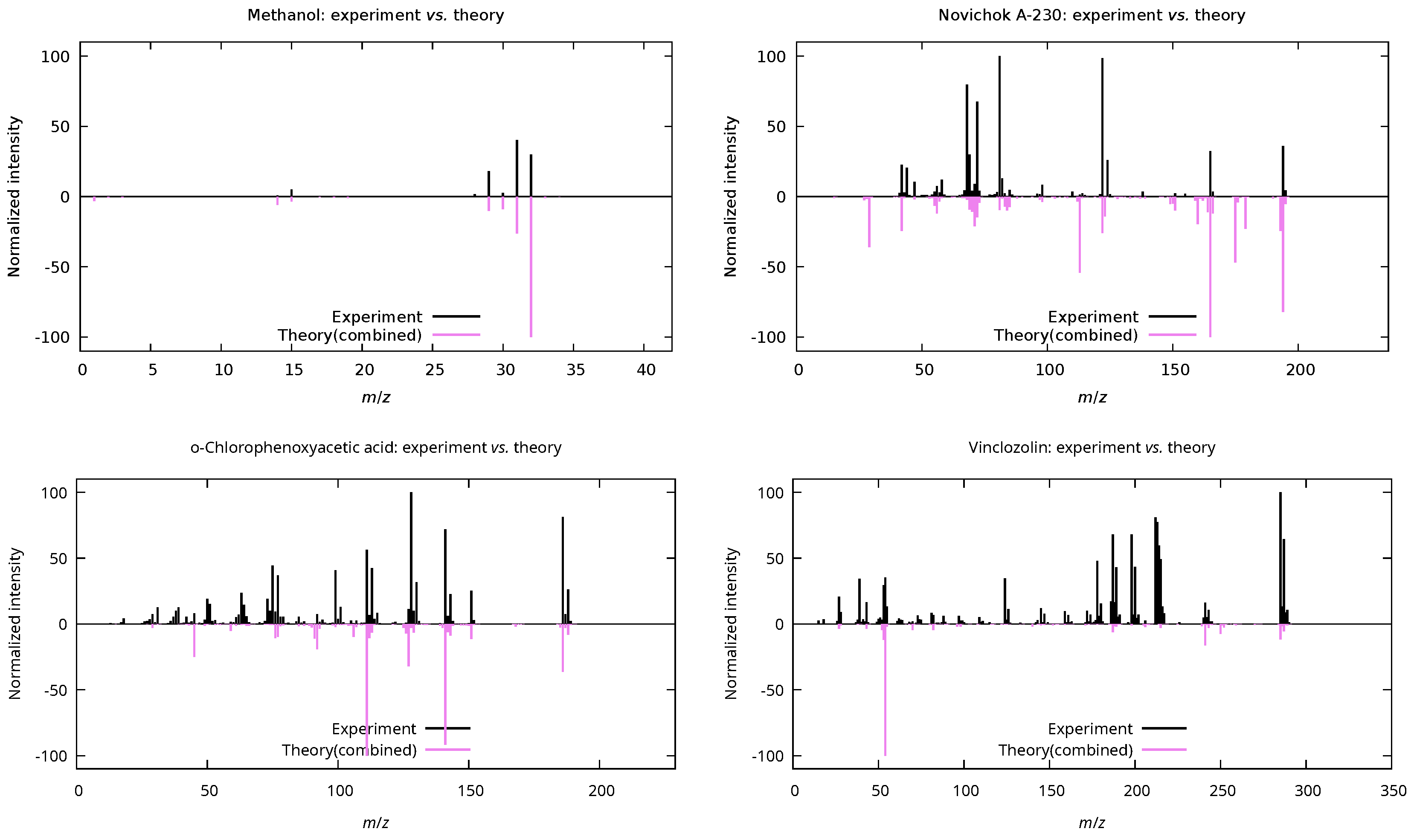
3.1. Mass-Spectra Prediction Workflow
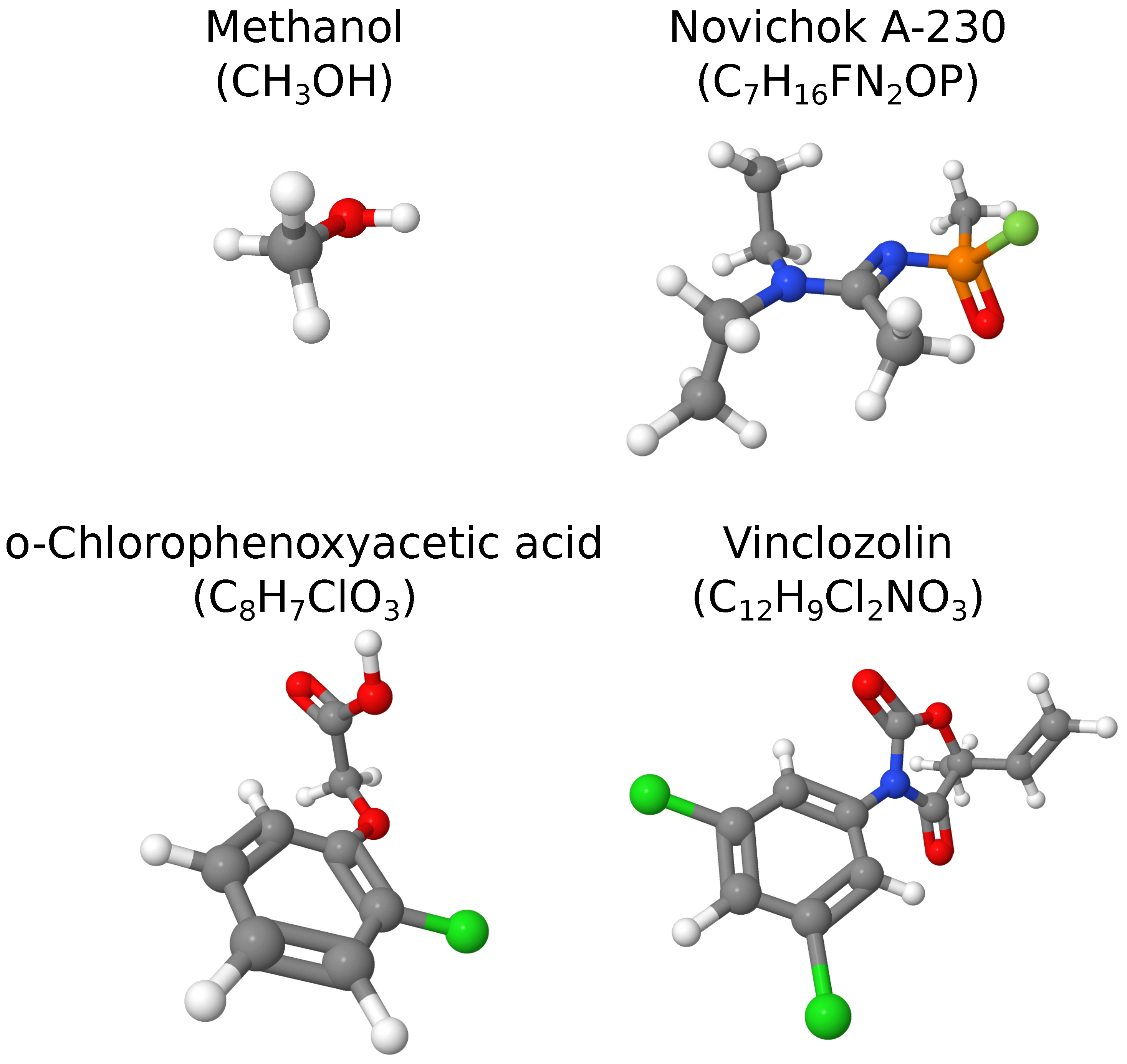
| Spectrum | P, % | , % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol () | ||||
| QCxMS | 9/16 | 56.2 | 109.90 | 0.47 |
| DissMD | 10/16 | 62.5 | 29.02 | 0.06 |
| Combined | 13/16 | 81.2 | 36.98 | 0.10 |
| Novichok A-230 () | ||||
| QCxMS | 46/52 | 88.5 | 90.34 | 0.24 |
| DissMD | 17/52 | 32.7 | 180.01 | 0.60 |
| Combined | 46/52 | 88.5 | 117.12 | 0.32 |
| o-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid () | ||||
| QCxMS | 118/129 | 91.5 | 104.03 | 0.28 |
| DissMD | 30/129 | 23.3 | 137.05 | 0.56 |
| Combined | 120/129 | 93.0 | 98.48 | 0.30 |
| Vinclozolin () | ||||
| QCxMS | 84/105 | 80.0 | 122.95 | 0.42 |
| DissMD | 19/105 | 18.1 | 235.75 | 0.85 |
| Combined | 86/105 | 81.9 | 166.31 | 0.50 |
3.2. Performance Tests with Simulated Data
| Top-1 | Top-3 | Top-5 | Top-10 | MRR | MR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 91 ± 1 | 98.6 ± 0.6 | 98.8 ± 0.4 | 99.0 ± 0.3 | 94.9 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | |
| 55 ± 2 | 87 ± 2 | 94 ± 1 | 96.9 ± 0.9 | 72 ± 2 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | |
| 61 ± 2 | 92 ± 1 | 97.0 ± 0.9 | 98.7 ± 0.7 | 77 ± 1 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | |
| 61 ± 2 | 92 ± 1 | 97.0 ± 0.9 | 98.7 ± 0.6 | 77 ± 1 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | |
| 30 ± 2 | 69 ± 2 | 84 ± 2 | 95 ± 1 | 53 ± 2 | 4.1 ± 0.5 |
3.3. Performance Test with Experimental Noisy Dataset
3.4. Performance Tests with an Experimental Dataset of Cleaned Spectra
| Substance class | Top-1 | Top-3 | Top-5 | Top-10 | MRR | MR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid contaminants | 9 | 44.4 | 55.6 | 55.6 | 66.7 | 52.8 | 17.0 |
| Dioxins | 4 | 75.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 87.5 | 1.2 |
| PAHs | 16 | 43.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 68.8 | 1.8 |
| Pesticides | 29 | 82.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 90.8 | 1.2 |
| Herbicides | 6 | 50.0 | 83.3 | 83.3 | 83.3 | 66.8 | 19.2 |
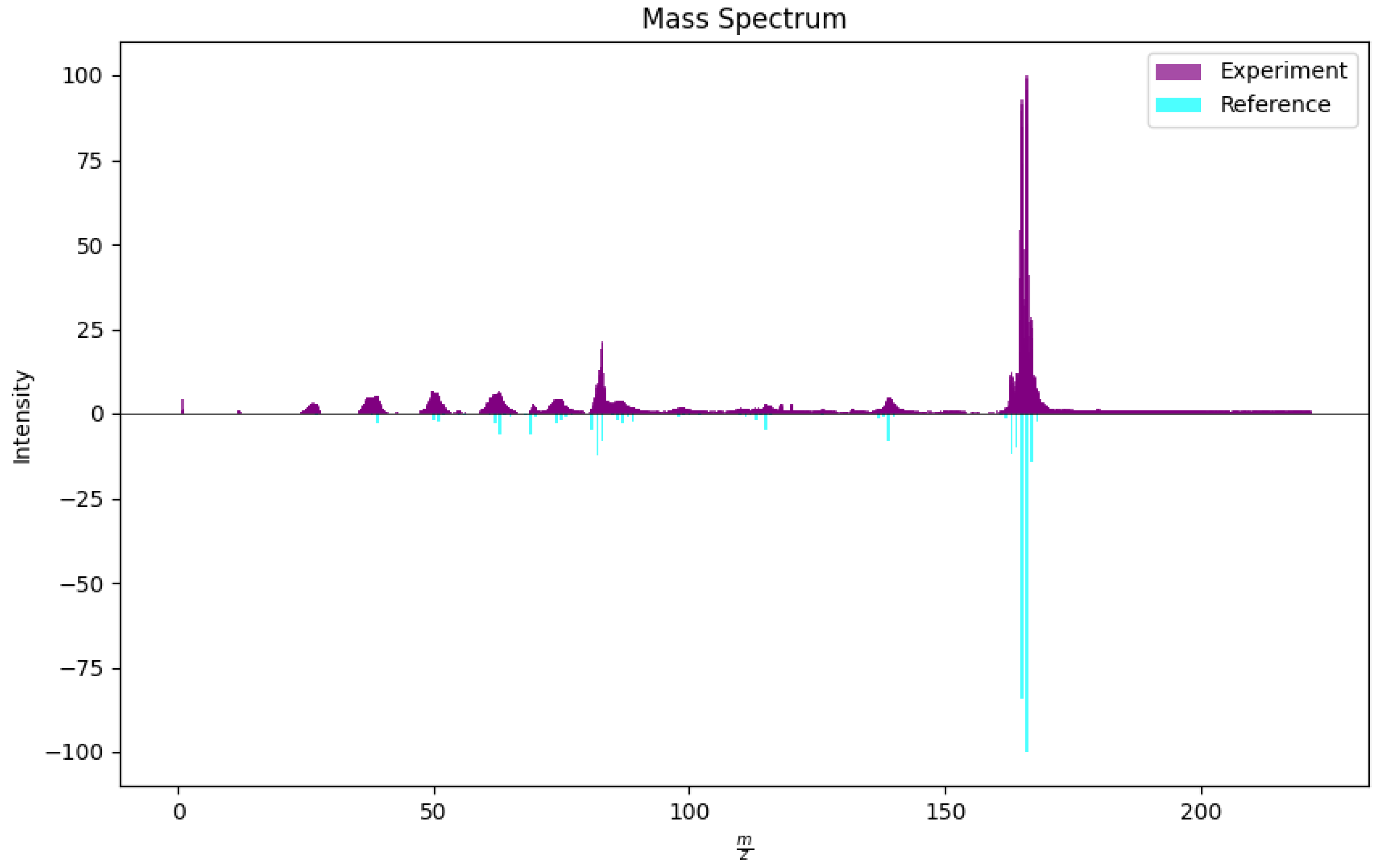
3.5. Testing Theoretical Reference Against Cleaned Experimental Data
| Substance | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | R | R | ||||||
| 1,2-DpD | 21 | 154 | 13 | 64 | 11 | 15 | ||
| 1,3-DpD | 37 | 135 | 20 | 64 | 31 | 15 | ||
| 1,4-DpD | 10 | 152 | 3 | 69 | 11 | 17 | ||
| o-CA | 5 | 140 | 3 | 45 | 3 | 19 | ||
| Vinclozolin | 2 | 201 | 14 | 26 | 36 | 7 | ||
| MR | 15.0 | 10.6 | 18.4 | |||||
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIST | National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology |
| EI | electron ionization |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| HPLC | high-pressure liquid chromatography |
| IC | internal conversion |
| IEE | internal excess energy |
| KE | kinetic energy |
| KER | kinetic energy release |
| MD | molecular dynamics |
| MR | mean rank |
| MRR | mean reciprocal rank |
| MS | mass-spectrometry |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PAHs | polycylcic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| XUV | extreme ultraviolet |
References
- Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons. Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on Their Destruction.
- UN Secretary-General.; UN Mission to Investigate Allegations of the Use of Chemical Weapons in the Syrian Arab Republic (2013). Report of the United Nations Mission to Investigate Allegations of the Use of Chemical Weapons in the Syrian Arab Republic on the Alleged Use of Chemical Weapons in the Ghouta Area of Damascus on :: Note /: By the Secretary-General 2013. 21 August.
- United Nations. `Reasonable Grounds to Believe’ Syrian Government Used Chlorine Gas on Douma Residents in 2018, Head of Chemical Weapons Monitoring Organization Tells Security Council, 2023.
- United Press International. 1988 Kurdish Massacre Labeled Genocide. https://www.upi.com/Top_News/Special/2010/03/08/1988-Kurdish-massacre-labeled-genocide/93471268062566/.
- Ogawa, Y.; Yamamura, Y.; Ando, H.; Kadokura, M.; Agata, T.; Fukumoto, M.; Satake, T.; Machida, K.; Sakai, O.; Miyata, Y.; et al. , An Attack with Sarin Nerve Gas on the Tokyo Subway System and Its Effects on Victims. In Natural and Selected Synthetic Toxins; chapter 22, pp. 333–355, [https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/bk-2000-0745.ch022]. [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Matsuoka, T.; Sakamune, K.; Akita, T.; Makita, R.; Kimura, S.; Kuroiwa, Y.; Nagao, M.; Tanaka, J. The Tokyo subway sarin attack has long-term effects on survivors: A 10-year study started 5 years after the terrorist incident. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GURIEV, S.; TREISMAN, D. , FEAR AND SPIN. In Spin Dictators: The Changing Face of Tyranny in the 21st Century; Princeton University Press, 2022; pp. 3–30.
- Schulmann, E. The Russian political system in transition: Scenarios for power transfer. NUPI Working Paper 2018, 883. [Google Scholar]
- Brunka, Z.; Ryl, J.; Brushtulli, P.; Gromala, D.; Walczak, G.; Zięba, S.; Pieśniak, D.; Sein Anand, J.; Wiergowski, M. Selected Political Criminal Poisonings in the Years 1978–2020: Detection and Treatment. Toxics 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunka, Z.; Ryl, J.; Brushtulli, P.; Gromala, D.; Walczak, G.; Zięba, S.; Pieśniak, D.; Sein Anand, J.; Wiergowski, M. Selected Political Criminal Poisonings in the Years 1978–2020: Detection and Treatment. Toxics 2022, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, K. Poisonous Affairs: Russia’s Evolving Use of Poison in Covert Operations. The Nonproliferation Review 2022, 29, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellingcat Investigation Team. FSB Team of Chemical Weapon Experts Implicated in Alexey Navalny Novichok Poisoning, 2020.
- Steindl, D.; Boehmerle, W.; Körner, R.; Praeger, D.; Haug, M.; Nee, J.; Schreiber, A.; Scheibe, F.; Demin, K.; Jacoby, P.; et al. Novichok nerve agent poisoning. The Lancet 2021, 397, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, T. ; Prime Minister’s Office, 10 Downing Street. PM Commons Statement on Salisbury Incident: , 2018. 12 March.
- Sorg, O.; Zennegg, M.; Schmid, P.; Fedosyuk, R.; Valikhnovskyi, R.; Gaide, O.; Kniazevych, V.; Saurat, J.H. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) poisoning in Victor Yushchenko: identification and measurement of TCDD metabolites. The Lancet 2009, 374, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E. Post-Mortem: VX Poison Killed Brother of North Korean Leader. https://apnews.com/general-news-90e425dbaf1e44d1ba77e2eea890fc67, 2017.
- Amesbury Novichok Poisoning: Couple Exposed to Nerve Agent 2018.
- Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin. Pyotr Verzilov Receiving Treatment at Charité, 2018.
- Bellingcat Investigation Team. Russian Poet Dmitry Bykov Targeted by Navalny Poisoners, 2021.
- Countersanctions. How FSB Officers Tried to Poison Vladimir Kara-Murza. https://theins.ru/en/politics/253146.
- Weiss, M. Blood Simple. Several Russian Journalists and Activists Were Poisoned in Europe. https://theins.ru/en/politics/264280, 2023.
- Amend, N.; Niessen, K.V.; Seeger, T.; Wille, T.; Worek, F.; Thiermann, H. Diagnostics and Treatment of Nerve Agent Poisoning—Current Status and Future Developments. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2020, 1479, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybal’chenko, I.V.; Baigil’diev, T.M.; Rodin, I.A. Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis for the Determination of the Markers and Biomarkers of Chemical Warfare Agents. Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2021, 76, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygildiev, T.; Vokuev, M.; Braun, A.; Rybalchenko, I.; Rodin, I. Monitoring of hydrolysis products of mustard gas, some sesqui- and oxy-mustards and other chemical warfare agents in a plant material by HPLC-MS/MS. Journal of Chromatography B 2021, 1162, 122452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokuev, M.F.; Baygildiev, T.M.; Plyushchenko, I.V.; Ikhalaynen, Y.A.; Ogorodnikov, R.L.; Solontsov, I.K.; Braun, A.V.; Savelieva, E.I.; Rybalchenko, I.V.; Rodin, I.A. Untargeted and targeted analysis of sarin poisoning biomarkers in rat urine by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2021, 413, 6973–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vokuev, M.; Baygildiev, T.; Braun, A.; Frolova, A.; Rybalchenko, I.; Rodin, I. Monitoring of hydrolysis products of organophosphorus nerve agents in plant material and soil by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A 2022, 1685, 463604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Tsay, O.G.; Atwood, D.A.; Churchill, D.G. Destruction and Detection of Chemical Warfare Agents. Chemical Reviews 2011, 111, 5345–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agilent Masshunter Quantitative Analysis software (RRID:SCR_015040).
- Stein, S.E.; Scott, D.R. Optimization and testing of mass spectral library search algorithms for compound identification. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 1994, 5, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.E. An integrated method for spectrum extraction and compound identification from gas chromatography/mass spectrometry data. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 1999, 10, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, B.J. Development of a Data Analysis Tool to Determine the Measurement Variability of Consensus Mass Spectra. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2021, 32, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, W.E.; Moorthy, A.S. NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center standard reference libraries and software tools: Application to seized drug analysis. Journal of Forensic Sciences 2023, 68, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.E. Estimating probabilities of correct identification from results of mass spectral library searches. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 1994, 5, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nature Biotechnology 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Verhoeven, S.; Meijer, C.; Spreeuw, H.; Castilla, E.M.V.; Geng, C.; j. van der Hooft, J.J.; Rogers, S.; Belloum, A.; Diblen, F.; et al. matchms - processing and similarity evaluation of mass spectrometry data. Journal of Open Source Software 2020, 5, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, N.F.; Hecht, H.; Strobel, M.; Wang, M.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Huber, F. Reproducible MS/MS library cleaning pipeline in matchms. Journal of Cheminformatics 2024, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R"ost, H.L.; Sachsenberg, T.; Aiche, S.; Bielow, C.; Weisser, H.; Aicheler, F.; Andreotti, S.; Ehrlich, H.C.; Gutenbrunner, P.; Kenar, E.; et al. OpenMS: a flexible open-source software platform for mass spectrometry data analysis. Nature methods 2016, 13, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röst, H.L.; Schmitt, U.; Aebersold, R.; Malmström, L. pyOpenMS: A Python-based interface to the OpenMS mass-spectrometry algorithm library. PROTEOMICS 2014, 14, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Ji, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Sun, J.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Z. Ultra-fast and accurate electron ionization mass spectrum matching for compound identification with million-scale in-silico library. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- "Mass Spectra" by NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center, William E. Wallace, director in NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, Eds. P.J. Linstrom and W.G. 2089; 9, (retrieved January 11, 2025). [CrossRef]
- sdbs : https://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp/Disclaimer.aspx (National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, 05.01. sdbs : https://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp/Disclaimer.aspx (National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, 05.01.2025).
- Mirzayanov, V.S. State Secrets: An Insider’s Chronicle of the Russian Chemical Weapons Program; Outskirts Press, Inc.: Denver, Colorado, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Grimme, S. Towards First Principles Calculation of Electron Impact Mass Spectra of Molecules. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2013, 52, 6306–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicharo, F.C.; Modesto-Costa, L.; Borges Jr, I. Molecular dynamics simulation of the electron ionization mass spectrum of tabun. Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2020, 55, e4513–e4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicharo, F.C.S.; Modesto-Costa, L.; Borges Jr., I. Simulation of the electron ionization mass spectra of the Novichok nerve agent. Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2021, 56, e4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Chauhan, S.; D’Cruz, R.; Faruqi, S.; Singh, K.; Varma, S.; Singh, M.; Karthik, V. Chemical warfare agents. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 2008, 26, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srogi, K. Monitoring of environmental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2007, 5, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Låg, M.; vrevik, J.; Refsnes, M.; Holme, J.A. Potential role of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in air pollution-induced non-malignant respiratory diseases. Respiratory Research 2020, 21, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hites, R.A. Dioxins: An Overview and History. Environmental Science & Technology 2011, 45, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkok, S.K.; Kibet, J.K.; Kinyanjui, T.K.; Okanga, F.I. A review of persistent organic pollutants: dioxins, furans, and their associated nitrogenated analogues. SN Applied Sciences 2020, 2, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Rhode Island Explosives Database : http://expdb.chm.uri.edu (accessed on 01.11.2024). (accessed on 01.11.2024).
- Eskandari, M.; Faraz, S.M.; Hosseini, S.E.; Moradi, S.; Saeidian, H. Fragmentation pathways of chemical weapons convention-related organophosphorus Novichok agents: The electron ionization and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectroscopy and DFT calculation studies. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2022, 473, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, A. Webplotdigitizer: Version 4.6, 2022.
- Bannwarth, C.; Ehlert, S.; Grimme, S. GFN2-xTB—An Accurate and Broadly Parametrized Self-Consistent Tight-Binding Quantum Chemical Method with Multipole Electrostatics and Density-Dependent Dispersion Contributions. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 2019, 15, 1652–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannwarth, C.; Caldeweyher, E.; Ehlert, S.; Hansen, A.; Pracht, P.; Seibert, J.; Spicher, S.; Grimme, S. Extended tight-binding quantum chemistry methods. WIREs Computational Molecular Science 2021, 11, e1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmol: an open-source Java viewer for chemical structures in 3D.
- Pracht, P.; Bohle, F.; Grimme, S. Automated exploration of the low-energy chemical space with fast quantum chemical methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 7169–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracht, P.; Grimme, S.; Bannwarth, C.; Bohle, F.; Ehlert, S.; Feldmann, G.; Gorges, J.; Müller, M.; Neudecker, T.; Plett, C.; et al. CREST—A program for the exploration of low-energy molecular chemical space. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2024, 160, 114110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ásgeirsson, V.; Bauer, C.A.; Grimme, S. Quantum chemical calculation of electron ionization mass spectra for general organic and inorganic molecules. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4879–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.A.; Grimme, S. How to Compute Electron Ionization Mass Spectra from First Principles. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2016, 120, 3755–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonov, D.S. PyRAMD. https://gitlab.desy.de/denis.tikhonov/pyramd, 2024.
- Tikhonov, D.S.; Datta, A.; Chopra, P.; Steber, A.L.; Manschwetus, B.; Schnell, M. Approaching black-box calculations of pump-probe fragmentation dynamics of polyatomic molecules. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie 2020, 234, 1507–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.L.; Tikhonov, D.S.; Allum, F.; Boll, R.; Chopra, P.; Erk, B.; Gruet, S.; He, L.; Heathcote, D.; Kazemi, M.M.; et al. The kinetic energy of PAH dication and trication dissociation determined by recoil-frame covariance map imaging. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 23096–23105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopman, J.; Grimme, S. Calculation of Electron Ionization Mass Spectra with Semiempirical GFNn-xTB Methods. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15120–15133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On Information and Sufficiency. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A. On a measure of divergence between two statistical populations defined by their probability distributions. Bull. Calcutta Math. Soc.
- Hellinger, E. Neue Begründung der Theorie quadratischer Formen von unendlichvielen Veränderlichen. Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik 1909, 1909, 210–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, N.; Håkansson, B.; Ortiz-Catalan, M. Classification complexity in myoelectric pattern recognition. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2017, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailath, T. The Divergence and Bhattacharyya Distance Measures in Signal Selection. IEEE Transactions on Communication Technology 1967, 15, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A. On a Measure of Divergence between Two Multinomial Populations. Sankhyā: The Indian Journal of Statistics (1933-1960) 1946, 7, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Potemkin, A.A.; Proskurnin, M.A.; Volkov, D.S. Noise Filtering Algorithm Using Gaussian Mixture Models for High-Resolution Mass Spectra of Natural Organic Matter. Analytical Chemistry 2024, 96, 5455–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apache License Version 2.0, 04. https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0, Access date: January 5, 2025. 20 January.
- Git Source Control Management Tool. https://git-scm.com, Access date: , 2025. 5 January.
- GitLab. https://about.gitlab.com, Access date: , 2025. 5 January.
- Toxic Mass Sceptic (TMS): Release 0.0.1, 2025. https://gitlab.com/madschumacher/toxicmasssceptic, Access date: , 2025. 5 January.
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Computing in Science & Engineering 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heesch, D. Doxygen. http://www.doxygen.org, Access date: , 2025. 5 January.
- Package installer for Python PIP. https://pypi.org/project/pip/, Access date: , 2025. 5 January.
- Unittest — Unit testing framework. https://docs.python.org/3/library/unittest.html, Access date: , 2025. 5 January.
- Tikhonov, D.S. Metadynamics simulations with Bohmian-style bias potential. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2023, 44, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonov, D.S. PyRAMD Scheme: A Protocol for Computing the Infrared Spectra of Polyatomic Molecules Using ab Initio Molecular Dynamics. Spectroscopy Journal 2024, 2, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.S.; Vishnevskiy, Y.V. Describing nuclear quantum effects in vibrational properties using molecular dynamics with Wigner sampling. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 18406–18423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, T.E.; Ceriotti, M. Nuclear quantum effects enter the mainstream. Nature Reviews Chemistry 2018, 2, 0109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.A.; Grimme, S. Automated Quantum Chemistry Based Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Electron Ionization Induced Fragmentations of the Nucleobases Uracil, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine. European Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2015, 21, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, N.; Li, Z.; Tkachenko, V.; Ziaja, B. Electron-ion coupling in semiconductors beyond Fermi’s golden rule. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 014309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, N.; Milov, I. Electron-phonon coupling in metals at high electronic temperatures. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 064302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.S.; Lee, J.W.L.; Schnell, M. On the thermodynamic stability of polycations. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2024, 160, 244110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Chopra, P.; Lee, J.W.L.; Tikhonov, D.S.; Kumar, S.; Akcaalan, O.; Allum, F.; Boll, R.; Butler, A.A.; Erk, B.; et al. Ultrafast dynamics of fluorene initiated by highly intense laser fields. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 20261–20272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.S.; Sueyoshi, C.J.; Sun, W.; Xie, F.; Khon, M.; Gougoula, E.; Li, J.; Berggötz, F.; Singh, H.; Tonauer, C.M.; et al. Scaling of Rotational Constants. Molecules 2024, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class of substances | |
|---|---|
| Acid Contaminants | 9 |
| Blister Agents | 15 |
| Blood Agents | 6 |
| Chlorophenols | 7 |
| Choking Agents | 9 |
| Dioxines | 15 |
| Explosives | 59 |
| Herbicides | 7 |
| Lachrymators | 5 |
| Nerve Agents | 43 |
| PAHs | 16 |
| Pesticydes | 31 |
| Miscellaneous | 172 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





