Submitted:
04 February 2025
Posted:
05 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
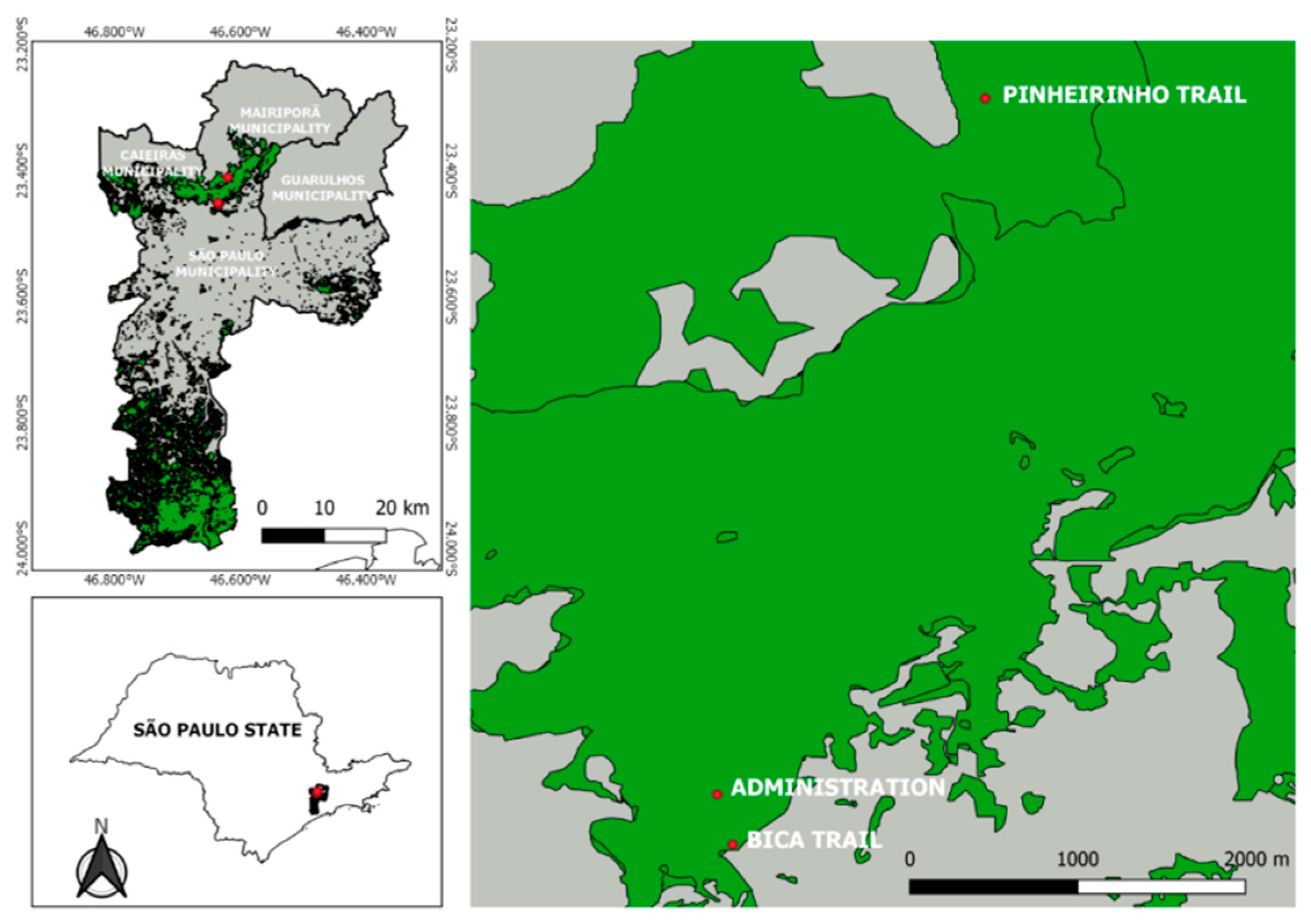
2.1. Characterization of the Study Area: Cantareira State Park
2.2. Mosquito Collection
2.3. Identification and Cataloging
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maguirre, B. Phytotelmata: Biota and community structure determination in plant-held waters. Annu. Ver. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1971, 2, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; OLiveira-Christe, R.; Camargo, A.A.; Milani, G.M.; Urbinatti, P.R.; Natal, D.; Ceretti-Junior, W.; Marrelli, M.T. Influence of water's physical and chemical parameters on mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) assemblages in larval habitats in urban parks of São Paulo, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 205, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Mei, T.; Röll, A.; Hölscher, D. Water transfer between bamboo culms in the period of sprouting. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos Raúl, E.; Spinelli, G.; Mogi, M. Culicidae and ceratopogonidae (diptera: nematocera) inhabiting phytotelmata in Iguazú National Park, Misiones Province, subtropical Argentina. Rev. Soc. Entomol. Argent. 2011, 70, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Noutcha, M.A.E.; Harry, O.T.; Isang, K.O.; Okiwelu, S.N. Arthropod communities in Phytotelmata of the Musacae, Lauraceae and Burseraceae. Public Health Res. 2018, 8, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, R.; Barták, M.; Borkent, A.; Courtney, G.; Goddeeris, B.; Haenni, J.; Knutson, L.; Pont, A.; Rotheray, G.E.; Roskosny, R.; Sinclair, B.; Woodley, N.; Zatwarnicki, T.; Zwick, P. Global diversity of dipteran families (Insecta Diptera) in freshwater (excluding Simulidae, Culicidae, Chironomidae, Tipulidae and Tabanidae). Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 489–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangudo, C.; Aparicio, J.P.; Rossi, G.C.; Gleiser, R.M. Tree hole mosquito species composition and relative abundances differ between urban and adjacent forest habitats in northwestern Argentina. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2018, 108, 203–212.
- Frank, J.H., Lounibos. Insects and allies associated with bromeliads: a review. Terr. Arthropod. Rev. 2009, 1, 125–153. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, G.R.A.; ForattiniI, O.P. Culicidae in bromeliads: diversity of species by anthropic environments, coastal area of Southeastern Brazil. Rev. Saúde Pública 2008, 42, 979–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbach, R.E. Mosquito Taxonomic Inventory. 2024. https://mosquito-taxonomic-inventory.myspecies.info/valid-species-list (Access Feb 22 2024).
- Bastos, A.Q.; Mello, C.F.; Santos Silva, J.; Gil-Santana, H.R.; Silva, S.O.F.; Alencar, J. Diversity of Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Bom Retiro Private Natural Heritage Reserve, Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. J. Med. Entomol. 2022, 59, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounibos 2009.
- Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R.; Heyden, R.; Silva, T.F. Alguns aspectos da ecologia dos mosquitos (Diptera, Culicidae) de uma área de barreiras (granjas Calábria), em Jacarepaguá, Rio de Janeiro: V. Criadouros. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1986, 81, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zequi, J.A.; Lopes, J. Culicideofauna (Diptera) encontrada em entrenós de taquara de uma mata residual na área urbana de Londrina, Paraná, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2001, 18, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governo do Estado de São Paulo; Sistema Ambiental Paulista. Plano de manejo do Parque Estadual da Cantareira. 2009. Available at: http://www3.ambiente.sp.gov.br. (Access December 06 2024).
- Rares, C.D., Brandimarte. O desafio da conservação de ambientes aquáticos e manutenção de serviços ambientais em áreas verdes urbanas: o caso do Parque Estadual da Cantareira. Ambiente Soc. 2014, 17, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, L.M.; Deane, M.P.; Neto, J.A.; Almeida, F.B. On the transmission of simian malaria in Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med.Trop. 1971, 13, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, M.S.; Costa, A.C.; Fernandes, N.C.; Guerra, J.M.; Santos, F.C.; Nogueira, J.S.; D’Agostino, L.G.; Komninakis, S.V.; Witkin, S.S.; Ressio, R.A.; et al. Epizootics due to Yellow Fever Virus in São Paulo State, Brazil: viral dissemination to new areas (2016–2017). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buery, J.C.; Alencar, F.E.C.; Duarte, A.M.R.; Loss, A.C.; Vicente, C.R.; Ferreira, L.M.; Fux, B.; Medeiros, M.M.; Cravo, P.; Arez, A.P.; et al. Atlantic Forest Malaria: A Review of more than 20 years of epidemiological investigation. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, F.V.S., Ribeiro; et al. Haemagogus leucocelaenus and Haemagogus janthinomys are the primary vectors in the major yellow fever outbreak in Brazil, 2016–2018. Emerg. Microbes Infect 2019, 8, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governo do Estado de São Paulo. Secretaria de Estado da Saúde - Centro de Vigilância Epidemiológica Prof. Alexandre Vranjac. Boletim Epidemiológico Febre Amarela. 2018. Available at: http://www.saude.sp.gov.br/resources/cvecentro-de-vigilancia-epidemiologica/areas-de-vigilancia/doencas-de-transmissaopor-vetores-ezoonoses/doc/famarela/fa18_boletim_epid_0207.pdf (Access December 20 2024).
- Deane, L.M. Monkey malaria in Brasil. A summary of studies performed in 1964–1966. Rev. Brasil. Biol. 1967, 27, 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Montes, J. Culicidae fauna of Serra da Cantareira, São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Saúde Pública 2005, 39, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, L.F.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Ceretti-Júnior, W.; Fernandes, A.; Camargo, A.A.; Evangelista, E.; Oliveira-Christe, R.; Montes, J.; Teixeira, R.S.; Marrelli, M.T. Haemagogus leucocelaenus and other mosquitoes potentially associated with sylvatic yellow fever in Cantareira State Park in the São Paulo metropolitan area, Brazil. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2016, 32, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceretti-Junior, W.; Oliveira-Christe, R.; Wilk-da-Silva, R.; Mucci, L.F.; Duarte, A.M.; Fernandes, A.; Barrio-Nuevo, K.M.; Carvalho, M.P.; Marrelli, M.T.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R. Diversity analysis and an updated list of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) found in Cantareira State Park, São Paulo, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 212, 105669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozovei, A.L.; Silva, M.A.N. Análise comparativa entre métodos alternativo e convencional para amostras de mosquitos obtidos a partir de habitats fitotélmicos (Bromeliaceae) na Floresta Atlântica, Serra do Mar, Paraná, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 1999, 16, 957–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J. Neotropical Culicidae. 1953. Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo. Vol 2.
- Galindo, P.; Blanton, F.S.; Peyton, E.L. A revision of the Uranotaenia of Panama with notes on other American species of the genus (Diptera, Culicidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1954, 47, 107–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, R.R., Ramalho. Revision of the Genus Phoniomyia. Folia Clin. Biol. 1956, 25, 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- Arnell, J.H. Mosquito Studies (Diptera: Culicidae). XXXIII. A revision of the Scapularis Group of Aedes (Ochlerotatus). Contr. Am. Ent. Inst. 1976, 13, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sirivanakarn, S. A review of the systematics and a proposed scheme of internal classification of the New World subgenus Melanoconion of Culex (Diptera, Culicidae). 1982. Smithsonian Institution, Dept of Entomology, Washington DC.
- Consoli, R.A. Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Principais mosquitos de importância sanitária do Brasil. 1994. FIOCRUZ, Rio de Janeiro Ed.
- Forattini, O.P. Culicidologia Médica: Identificação, Biologia, Epidemiologia 2. 2002. Edusp, São Paulo.
- Reinert, J.F. List of abbreviations for currently valid generic-level taxa in Family Culicidae (Diptera). Eur. Mosq. Bull. 2009, 27, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Hsieh, T.; Sander, E.L.; Ma, K.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Ellison, A.M. Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: a framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecol. Monogr. 2014, 84, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.O. Diversity and evenness: a unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology 1973, 54, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A. Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team, 2020. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Comput URL. https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed: Mar. 04 2024).
- Hsieh, T.C.; Ma, K.H.; Chao, A. iNEXT: an R package for rarefaction and extrapolation of species diversity (Hill numbers). Meth. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceretti-Junior, W.; Oliveira Christe, R.; Rizzo, M.; Strobel, R.C.; Matos Junior, M.O.; Mello, M.H.; Fernandes, A.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; de Carvalho, G.C.; Marrelli, M.T. Species composition and ecological aspects of immature mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in bromeliads in urban parks in the city of São Paulo, Brazil. J. Arthropod. Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Fernandes, A.; Ceretti-Junior, W.; Wilke, A.B.B.; Marrelli, M.T. Mosquitoes in urban green spaces: using an island biogeographic approach to identify drivers of species richness and composition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orta-Pineda, G.; Abella-Medrano, C.A.; Suzán, G.; Serrano-Villagrana, A.; Ojeda-Flores, R. Effects of landscape anthropization on sylvatic mosquito assemblages in a rainforest in Chiapas, Mexico. Acta Trop. 2021, 216, 105849.
- Lozovei, A.L. Microhabitats de mosquitos (Diptera, Culicidae) em internódios de taquara na mata atlântica, Paraná, Brasil [Microhabitats of mosquitoes (Diptera, Culicidae) in internodes of bamboo in the rainforest, Paraná, Brazil]. Iheringia Sér. Zool. 2001, 90, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.A.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R.; Codeço, C.T.; Motta, M.A. Mosquitoes in bromeliads at ground level of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest: the relationship between mosquito fauna, water volume, and plant type. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2015, 108, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marteis, L.S.; Natal, D.; Sallum, M.A.M.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; La Corte, R. Mosquitos da Caatinga: 2. Species from periodic sampling of bromeliads and tree holes in a dry Brazilian forest. Acta Trop. 2017, 171, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuka, W.; Sulin, C.; Sommitr, W.; Rattanarithikul, R.; Aupalee, K.; Harbach, R. Mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) diversity and community in Doi Inthanon National Park, Northern Thailand. Insects 2022, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbach, R.E. Classification within the cosmopolitan genus Culex (Diptera: Culicidae): The foundation for molecular systematics and phylogenetic research. Acta Trop. 2011, 120, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Christe, R.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Fernandes, A.; Ceretti-Junior, W.; Marrelli, M.T. Distribution of Culex (Microculex) (Diptera: Culicidae) in forest cover gradients. Acta Trop. 2020, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, J.D. Mosquito studies (Diptera, Culicidae) XXXI. A revision of the subgenus Carrollia of Culex. Contrib. Am. Entomol. Inst. 1973, 9, 1–173. [Google Scholar]
- Pecor, J.E.; Jones, J.; Turell, J.; Fernández, R. Annotated checklist of the mosquito species encountered during arboviral studies in Iquitos, Peru (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 2000, 16, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayala-Sulca, Y.; Carrasco-Badajoz, C.; Huicho-Yanasupo, N.; Zamalloa-Vilca, C.; Arque-Chunga, W.; Ortega-Morales, A.I.; Ramírez, R.; Fernadez-Salas, I. First National Record for Culex iridescens in Peru. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2021, 37, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, G.A.; Marcondes, C.B. Bromeliad-associated mosquitoes from Atlantic forest in Santa Catarina Island, southern Brazil (Diptera, Culicidae), with new records for the State of Santa Catarina. Iheringia Sér. Zool. 2006, 96, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, T.C.; Bourke, B.P.; Laporta, G.Z.; Sallum, M.A.M. Mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) assemblages associated with Nidularium and Vriesea bromeliads in Serra do Mar, Atlantic Forest, Brazil. Parasites & vectors 5, 1–9.
- Mocellin, M.G.; Simões, T.C.; Silva-do-Nascimento, T.F.; Teixeira, M.L.F.; Lounibos, L.P.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Bromeliad-inhabiting mosquitoes in an urban botanical garden of dengue endemic Rio de Janeiro - Are bromeliads productive habitats for the invasive vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus? Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forattini, O.P.; Kakitani, I.; Massad, E.; Marucci, D. Studies on mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) and anthropic environment: 11-Biting activity and blood-seeking parity of Anopheles (Kerteszia) in South-Eastern Brazil. Rev. Saúde Pública 1996, 30, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branquinho, M.S.; Marrelli, M.T.; Curado, I.; Natal, D.; Barata, J.M.S.; Tubaki, R.M.; Carréri-Bruno, G.C.; Menezes, R.T.; Kloetzel, J.K. Infecção do Anopheles (Kerteszia) cruzii por Plasmodium vivax e Plasmodium vivax variante VK247 nos municípios de São Vicente e Juquitiba, São Paulo. Pan. Am. J. Public Health 1997, 2, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, A.C.; Navarro-Silva, M.A. A. Diversidade de Culicidae durante os períodos crepusculares em bioma de Floresta Atlântica e paridade de Anopheles cruzii (Diptera: Culicidae). Rev. Bras. Zool. 2008, 25, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorvillé, L.F.M. Mosquitoes as bioindicators of forest degradation in southeastern Brazil, a statistical evaluation of published data in the literature. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environm. 1996, 31, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forattini, O.P.; Kakitani, I.; Santos, R.L.; Ueno, H.M.; Kobayashi, K.M. Role of Anopheles (Kerteszia) bellator as malaria vector in Southern Brazil (Diptera: Culicidae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1999, 94, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.E.; Mello, R.P.D.; Lopes, C.M.; Gentile, C. Ecology of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in areas of Serra do Mar State Park, State of São Paulo, Brazil. I-monthly frequency and climatic factors. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2000, 95, 01–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterno, U., Marcondes. Mosquitos antropofílicos de atividade matutina em Mata Atlântica, Florianópolis, SC. Rev. Saúde Pública 2004, 38, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceretti-Júnior, W.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Multini, L.C; Urbinatti, P.R.; Vendrami, D.P.; Natal, D.; Marques, S.; Fernandes, A.; Ogata, H.; Marrelli, M.T. Immature mosquitoes in bamboo internodes in municipal parks, city of São Paulo, Brazil. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2014, 30, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros-Sousa, A.R., Ceretti-Júnior, W., de Carvalho, G.C., Nardi, M.S., Araujo, A.B., Vendrami, D.P., Marrelli, M.T. Diversity and abundance of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in an urban park: Larval habitats and temporal variation. Acta Trop. 2015, 150, 200–209. [CrossRef]
- Natal, D. Bioecologia do Aedes aegypti. Biológico 2002, 64, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, C.M.R., Melo-Santos, M.A.V., Bezerra, M.A.S., Barbosa, R.M.R., Silva, D.F., Silva, E. Primeiro registro de Aedes albopictus em área de Mata Atlântica, Recife, PE, Brasil. Rev. Saúde Pública 2000, 34, 314–315. [CrossRef]
- Fouque, F., Garinci, R., Gaborit, P. Epidemiological and entomological surveillance of the co-circulation of DEN-1, DEN-2 and DEN-4 viruses in French Guiana. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2004, 9, 41–46. [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.P., Carreira Alves, J R., Lima, M.M., Duarte, J.R., Barros, L.C., Silva, J.L., Gammaro, A.T., Monteiro Filho, O.S., Wanzeler, A.R. Presença de Aedes aegypti em Bromeliaceae e depósitos com plantas no município do Rio de Janeiro, RJ. Rev. Saúde Pública 2002, 6.
- Maciel-de-Freitas, R., Marques, W.A., Peres, R.C., Cunha, S.P., Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Variation in Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) container productivity in a slum and a suburban district of Rio de Janeiro during dry and wet seasons. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2007, 102, 489–496. [CrossRef]
- Wilk-da-Silva, R., Mucci, L.F., Ceretti-Junior, W., Duarte, A.M.R., Marrelli, M.T., Medeiros-Sousa, A.R. Influence of landscape composition and configuration on the richness and abundance of potential sylvatic yellow fever vectors in a remnant of Atlantic Forest in the city of São Paulo, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 204, 105385.
- Wilk-da-Silva, R. Wilk-da-Silva, R., Medeiros-Sousa, A.R., Mucci, L.F., Alonso, D.P., Alvarez, M.V., Ribolla, P.E.M., Marrelli, M.T. Genetic structuring of one of the main vectors of sylvatic yellow fever: Haemagogus (Conopostegus) leucocelaenus (Diptera: Culicidae). Genes 2023, 14, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J. Ecologia de mosquitos (Diptera: Culicidae) em criadouros naturais e artificiais de área rural do Norte do Estado do Paraná, Brasil. V. Coleta de larvas em recipientes artificiais instalados em mata ciliar. Rev. Saúde Pública 1997, 31, 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas-Silva, S.O., Mello, C.F., Machado, S.L., Leite, P.J., Alencar, J. Interaction of Haemagogus leucocelaenus (Diptera: Culicidae) and other mosquito vectors in a Forested Area, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Trop. Med. Infect Dis. 2022, 7, 94. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.O., Ferreira de Mello, C., Figueiró, R., Aguiar Maia, D., Alencar, J. Distribution of the mosquito communities (Diptera: Culicidae) in oviposition traps introduced into the Atlantic Forest in the State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 214–221. [CrossRef]
- Crovello, T.J.; Hacker, C.S. Evolutionary strategies in life table characteristics among feral and urban strains of Aedes aegypti (L.). Evolution 1972, 26, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, R. Competition and resistance to starvation in larvae of container-inhabiting Aedes mosquitoes. Ecol. Entomol. 1996, 21, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, S.A. Species introduction and replacement among mosquitoes: interspecific resource competition or apparent competition? Ecology 1998, 79, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.C., Almeida, M.A.B., Santos, E., Fonseca, D.F., Sallum, M.A., Noll, C.A., Monteiro, H.A., Cruz, A.C., Carvalho, V.L., Pinto, E.V., Castro, F.C., Nunes Neto, J. P., Segura, M.N., Vasconcelos, P.F.C. Yellow fever virus in Haemagogus leucocelaenus and Aedes serratus mosquitoes, southern Brazil, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1918.
- Donalisio, M.R.; Freitas, A.R.R.; Zuben, A.P. Arboviroses emergentes no Brasil: desafios para a clínica e implicações para a saúde pública. Rev. Saúde Pública 2017, 51, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Drumond, P.M., Wiedman, G., Patrícia Maria Drumond, C.P., Wiedman, G. Bambus no Brasil: da biologia à tecnologia. 2017. Rio de Janeiro: Instituto Ciência Hoje, 2017. 655 p.
- Lozovei, A.L. Mosquitos dendrícolas (Diptera, Culicidae) em internódios de taquara da Floresta Atlântica, serra do mar e do primeiro planalto, Paraná, Brasil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 1998, 41, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.A., Mello, C.F., Bueno, A.S., de Alcantara Azevedo, W., Alencar, J. Little noticed, but very important: The role of breeding sites formed by bamboos in maintaining the diversity of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Atlantic Forest biome. PloS one 2022, 17, e0273774.
- Bastos, A.Q., Leite, P.J., Mello, C.F., Maia, D.A., Machado, S.L., Gil-Santana, H.R., Silva, S.O.F., Santos-Mallet, J.R., Alencar, J. Bionomy of Mosquitoes in Bamboo Internodes in an Atlantic Forest Remnant of the State of Rio De Janeiro, Brazil. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2021, 37, 208–215. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givnish, T.J., Barffus, M.H.J., Van, E.B., Riina, R., Schulte, K., Horres, R., Gonsiska, P.A., Jabaily, R.S., Crayn, D. M., Smith, J.A.C., Inverno, K., Brown, G.K., Evans, T.M., Holst, B.K., Luther, H., Até, W., Zizka, G., Barry, P.E., Sytsma, K.J. Phylogeny, adaptative radiation, and historical biogeography in bromeliaceae: insights from an eight-locus plastid phylogeny. Am. J. Bothany 2011, 98, 872–895.
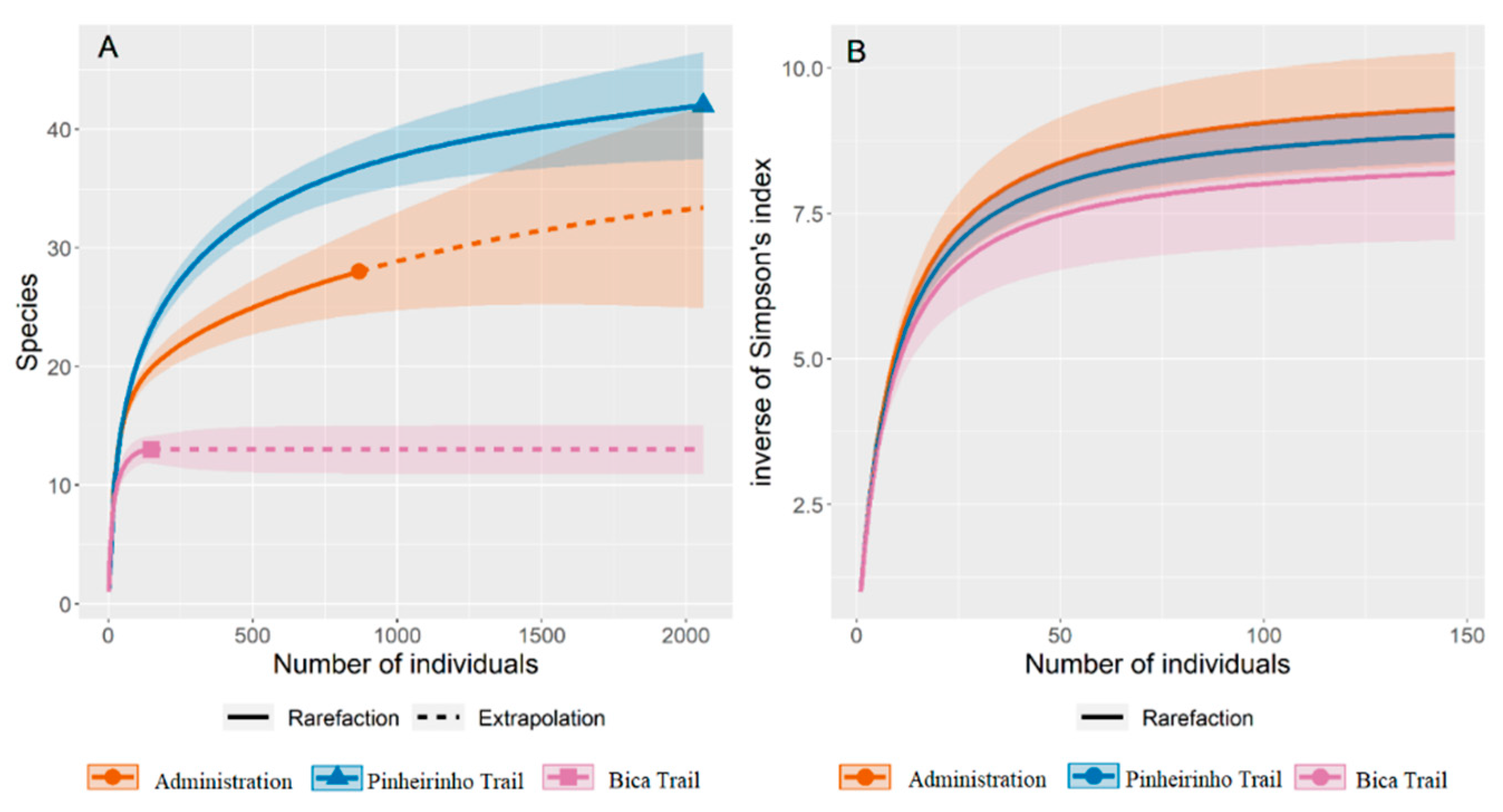
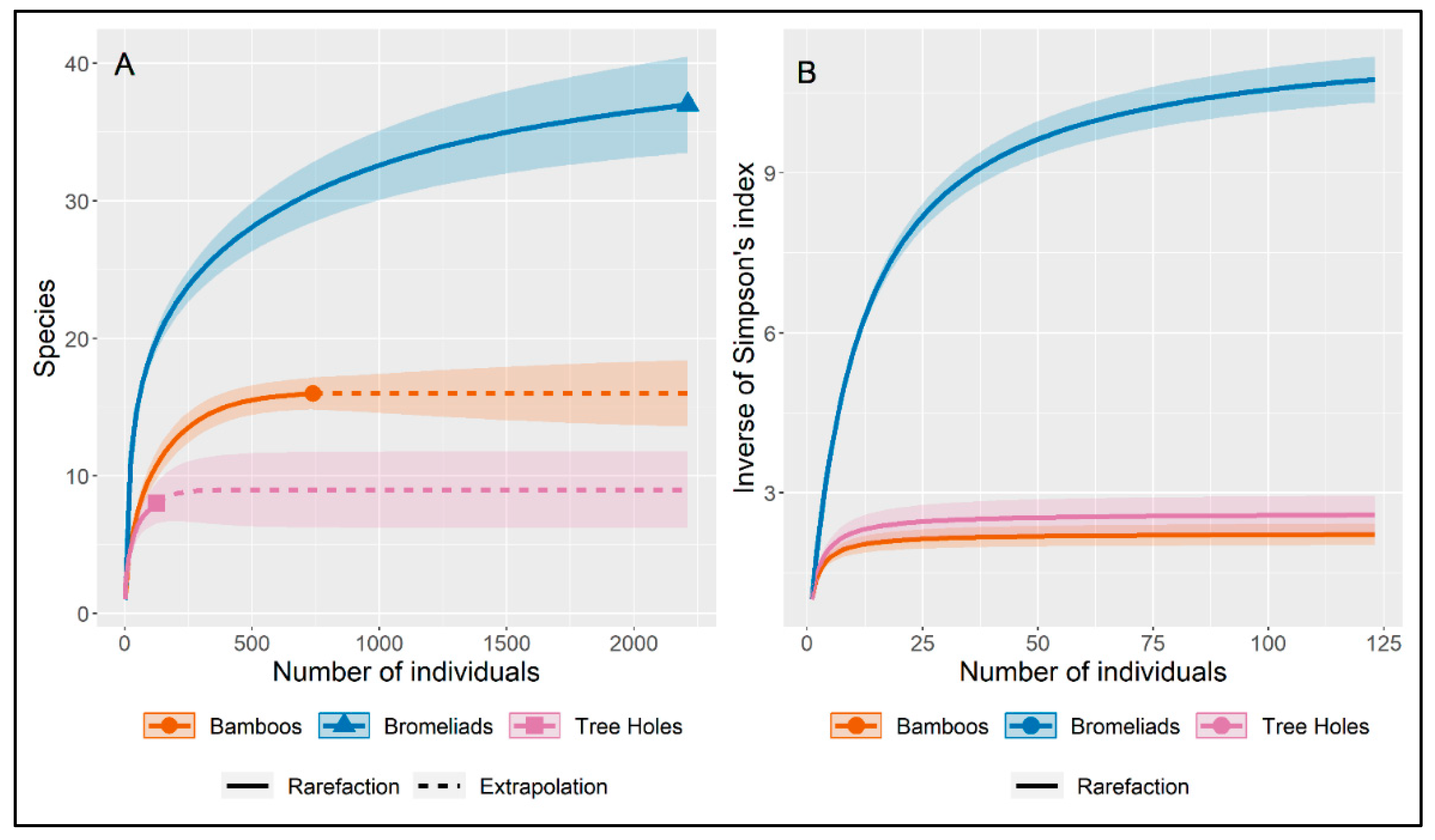
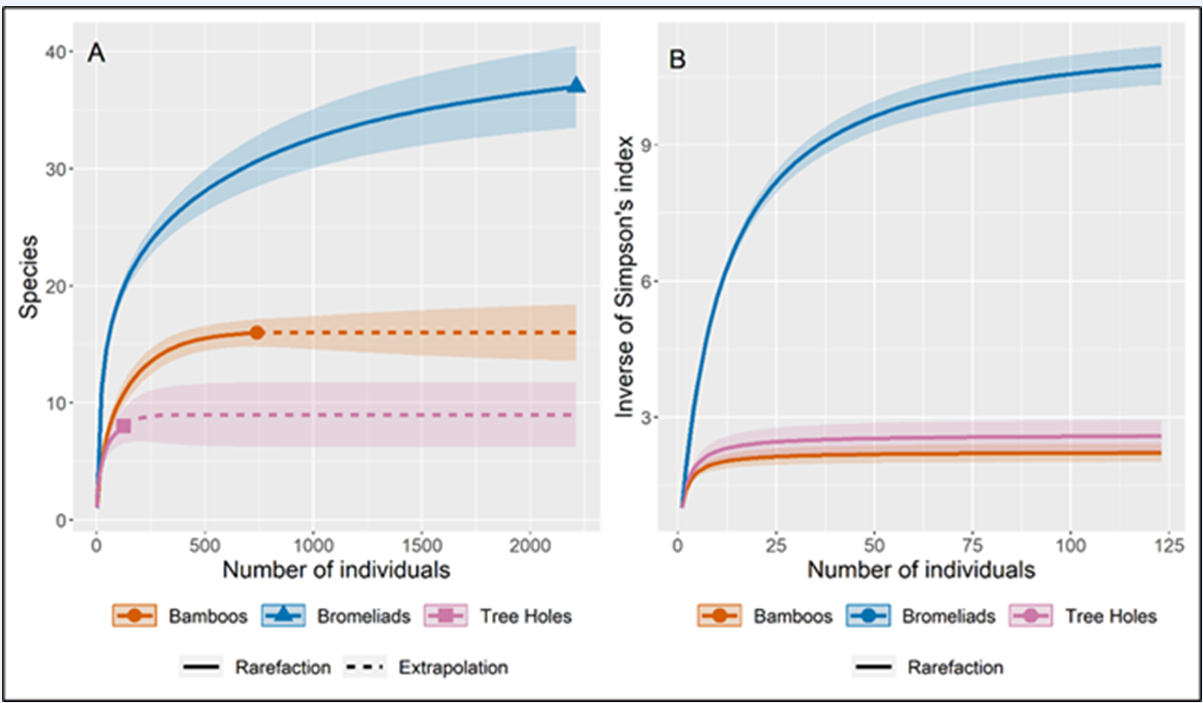
| Diversity index | CSP Collection Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Administration Area | Pinheirinho Trail | Bica Trail | |
| Individuals | 868 | 2059 | 148 |
| Observed richness | 28 | 42 | 13 |
| Estimated richness | 37 | 60 | 13 |
| Upper Est_richness | 58 | 82 | 15 |
| Lower Est_richness | 28 | 42 | 13 |
| Observed Simpson | 9.76 | 9.31 | 8.20 |
| Estimated Simpson | 9.86 | 9.34 | 8.62 |
| Upper Est_Simpson | 10.81 | 9.92 | 9.83 |
| Lower Est_Simpson | 8.91 | 8.77 | 7.41 |
| Diversity index | Breeding-site type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bamboo | Bromeliads | Tree Holes | |
| Individuals | 739 | 2212 | 124 |
| Observed richness | 16 | 37 | 8 |
| Estimated richness | 16 | 43 | 9 |
| Upper Est_richness | 20 | 57 | 12 |
| Lower Est_richness | 16 | 37 | 8 |
| Observed Simpson | 2.24 | 11.63 | 2.59 |
| Estimated Simpson | 2.24 | 11.69 | 2.62 |
| Upper Est_Simpson | 2.43 | 12.18 | 3.07 |
| Lower Est-Simpson | 2.06 | 11.19 | 2.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





