1. Introduction
Leukemia and lymphoma are common hematologic malignancies in children, young and adults which pose a huge threat to the lives of these patients worldwide despite the availability of efficient therapies. Finding ways to cure these diseases is of great importance in oncohematology.
In this study, we have showed that targeting the MST1/2 kinases, the key molecules in the Hippo signaling pathway may prove to be an effective way to treat hematologic tumors.
Hippo signaling pathway regulates the development of organs and their size, tissue regeneration, and apoptosis. The central role of this pathway in maintaining tissue homeostasis has been demonstrated [
1]. The disorders of this signaling pathway usually lead to tumor formation [
2,
3]. A detailed analysis of the Hippo signaling pathway is extremely hard to perform due to the multitude of its components and its ability to respond to a vast array of extracellular and intracellular signals [
4]. The key players in the Hippo signaling pathway include the MST1/2 and LATS1/2 kinases and their targets, YAP/TAZ transcription coactivators [
5,
6]. LATS1/2 is phosphorylated by the MST1/2–SAV1 complex [
7]. It gets thereby activated, and in its turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP and TAZ [
8,
9,
10]. If YAP/TAZ are not phosphorylated, they translocate to the nucleus and act via TEAD 1-4 and other transcription factors they interact with [
11,
12].
Disruption of this signaling pathway is observed in many human tumors. A recent systematic analysis of tumor samples revealed dysregulation of the Hippo signaling pathway components in many types of human cancers, including glioma, collateral cancer, endometrial cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma [
13,
14]. YAP/TAZ hyperactivation stimulates cancer cell proliferation [
15]. The cells stop responding to the negative regulators of proliferation, overcome internal death mechanisms, and acquire resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs or molecular targeted therapy, which contributes to cancer recurrence [
16,
17].
However, how the Hippo signaling pathway works depends on the cell type. For example, in hematopoietic cells, the Hippo signaling pathway works in a nontypical way, or its alternative variant is implemented. The recent data confirm the role of YAP1 as a suppressor gene in hematopoietic tumors. Unlike solid tumors, MST1 knockdown or high expression of YAP1 in hematopoietic tumors inhibits their growth and leads to apoptosis [
18].
In leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, low levels of YAP1 block the apoptosis induced by the nuclear ABL1 in these cells, while YAP1 activation causes the death of hematologic cancer cell. Genetic inactivation of MST1 restores the levels of unphosphorylated YAP1 triggering apoptosis in vitro and in vivo [
19]. These data demonstrate that MST1 can be a promising therapeutic target and provide a rationale for the development and clinical evaluation of novel MST1 inhibitors. The CN103429582A Patent describes the drug called XMU-MP-1. This compound is a reversible, potent and selective inhibitor of Mammalian sterile 20-like kinases 1/2 (MST1/2), the key molecules in the Hippo signaling pathway. This drug appears to have a similar effect on both solid and hematopoietic tumor cells at the initial steps of the Hippo signaling pathway. XMU-MP-1 blocks the activity of MST1 and MST2 kinases, which reduces the phosphorylation of endogenous LATS1/2 and YAP1 in human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells when applied in the concentrations from 0.1 to 10 μM in a dose-dependent way. This leads to the activation of YAP1 and TAZ and their nuclear translocation. Similar results have been obtained for other tumor cell lines [
20].
XMU-MP-1 was originally designed and used as a
“small molecule” to analyze the Hippo signaling pathway [
20,
21] and as a drug promoting liver regeneration, as well as for the prevention and treatment of hematopoietic system diseases caused by oxidative stress and ionizing radiation. XMU-MP-1 treatment restores hematopoietic stem cell and progenitor cell functions under the oxidative stress induced by ionizing radiation and also increased the survival rate of mice which received lethal radiation doses [
21].
At the same time, XMU-MP-1 antitumor activity towards hematologic tumors has not been yet described. The antitumor activity in combination with other drugs has not been investigated. In the present study, we have shown that XMU-MP-1 effectively inhibits the growth of hematologic tumor B- and T-cells. XMU-MP-1 blocking the cell cycle and inducing cell death by apoptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy. XMU-MP-1 enhances the effects of doxorubicin. Whole transcriptome analysis has revealed the key regulatory genes for these processes, which expression is changed in response to XMU-MP-1.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
B lymphoblastoid Burkitt lymphomas Namalwa, Daudi, and Ramos, Jurkat T-cell lymphoblastoma, myelomas HL-60, K-562, and breast adenocarcinomas MDA MB-231 and MCF-7 were used in the work. Human cell lines were obtained from the Russian Cell Culture Collection, Institute of Cytology, St. Petersburg, Russia. Cells were maintained in DMEM or RPMI (“GIBCO”, “Thermo Fisher Scientific”, United States) with 10% FCS (FBS; “HyClone”, United States), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin, in the 5% CO2 atmosphere.
2.2. Measuring Cell Proliferation Capacity
Cells were cultured at +37ºС in the humid atmosphere in the cultural plates manufactured by ТРР (Switzerland) in DMEM or RPMI (Life Technologies, United States) with the addition of 10% calf fetal serum (BioSera, France), in 5% СО2.
The cytotoxicity of XMU-MP-1 in Namalwa line was evaluated using the CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution kit (Promega, United States). Namalwa cells were inoculated into a 96-well plate at the density of 3x104 cells per well in the DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum 24 h prior to the addition of the studied compound. Antiproliferative activity of XMU-MP-1 was studied by treating Namalwa cells with the XMU-MP-1 reagent at the concentrations of 0.3; 0.6; 1.25, and 2.5 μM in DMSO. Cells with only DMSO and no reagent added served as the control. After 72 h of incubation, antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of XMU-MP-1 were analyzed using the CellTiter 96 suppresses the expression AQueous One Solution kit (Promega, United States) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Solutions' optical density was measured at 490 nm using the Chameleon V plate reader (Hydex Oy, Finland). The amount of the formazan product calculated based on the absorbance rate at 490 nm is in direct proportion to the live cells number in the culture. Cell viability was assessed relative to the control, and the concentration reducing cell viability by 50% (CD50) was determined.
2.3. Bioluminescence Caspase 3/7 Assay
Apoptosis caused by XMU-MP-1 in the cell lines was assessed using the Caspase 3/7-Glo kit (Promega, United States). Namalwa cells were inoculated into a 96-well plate at the density of 2x104 cells per well in the DMEM or RPMI medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum 24 h prior to the addition of the studied compound. Apoptotic activity of XMU-MP-1 was studied by treating Namalwa cells with the XMU-MP-1 reagent at the concentrations of 0.3; 0.6; 1.25, and 2.5 μM. The other cell lines were treated with XMU-MP-1 at the concentration of 2.5 μM. Cells with only DMSO and no reagent added served as the control. After 48 h of incubation, the apoptosis was assessed by measuring the activity of caspases 3 and 7 in accordance with the manufacturer's protocol. Towards this end, 20 µl of reagent was added to each well and cells were incubated for 30 min at room temperature. The luminescence of the solutions was then measured using the Chameleon V plate reader (Hydex Oy, Finland). Luminescence activity is directly proportional to the activity of the terminal capases 3 and 7 and to the cell apoptosis levels in the culture. Apoptosis level at different concentrations of XMU-MP-1 was estimated based on the luminescence levels relative to control.
2.4. Sequencing Library Preparation
Human Namalwa cells treated with 0.3 or 2.5 µM of XMU-MP-1 for 72 h and control Namalwa cells to which only DMSO was added were obtained in triplicate. The NEBNext Poly(A) mRNA Magnetic Isolation Module (NEB#E7490) was used to isolate mRNA . NEBNext Ultra II Directional RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (NEB #E7760) was used with 3 ug of total RNA for sequencing library construction. Standard Illumina protocols were used to make RNA libraries. AgencourtAMPure XP beads were used to purify double-stranded cDNA, ligation reaction products, and PCR reaction products.
2.5. Illumina Sequencing and Bioinformatics Pre-Processing
the KAPA Library Quant qPCR kit (Kapa Biosystems) was used to measure molar library concentrations. Library size distribution was assessed after PCR (12 cycles) using Agilent BioAnalyzer. Human mRNA profiles of the Namalwa cells and Namalwa cells treated with 0.3 or 2.5 µM of XMU-MP-1 were obtained by new generation sequencing, in triplicate, in Illumina NovaSeq. The bcl2fastq v2.20 Conversion Software (Illumina) was utilized to obtain FASTQ files. Recording format for the quality data strings – Phred 33. The hisat software was used to map reads on the human genome (hg38) . In each library, about 89–90% of the obtained data on average were uniquely aligned. The htseq-count package was used to calculate the number of reads which were mapped to known genes (ncbi – entrezID). The obtained values (cpm – countpermillion) for each gene in each library were combined into a matrix for further analysis. Filtration, normalization by the TMM method, variance estimation, and assessment of differentially expressed genes were performed using the edgeR module. Genes in which cpm was lower that 1 in any of the three libraries were considered to be low-expressed. The following terms were used. GeneID: Gene name (gene symbol) obtained from the database – org. Hs.eg.db based on the entrezID. LogFC: Logarithm to the base 2 of fold change. FDR: p-value with multiple testing correction. Genes with positive LogFC values were considered as upregulated and with negative LogFC values, as downregulated.
2.6. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
Gene Ontology (GO) screening was performed using DAVID (david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp) including GOTERM_BP_FAT (biological process), GOTERM_ MF_FAT (molecular function), and GOTERM_CC_FAT (cellular component), and KEGG Pathway (www.genome. jp/kegg/pathway.html) resources. DAVID calculates modified Fisher’s Exact p-values to demonstrate GO or molecular pathway enrichment. The Paji <0.01 was chosen as a cut-off criterion.
2.7. Statistics
Statistical analysis was performed using the GraphPad software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). The unpaired Student’s t-test was used to generate P-values. Error bars represent S.E.M. (*P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01).
2.8. Accession Number
RNA-Seq data GSE279247.
3. Results
3.1. Hippo Pathway Inhibitor XMU-MP-1 Suppresses the Growth of B and T Tumor Cells
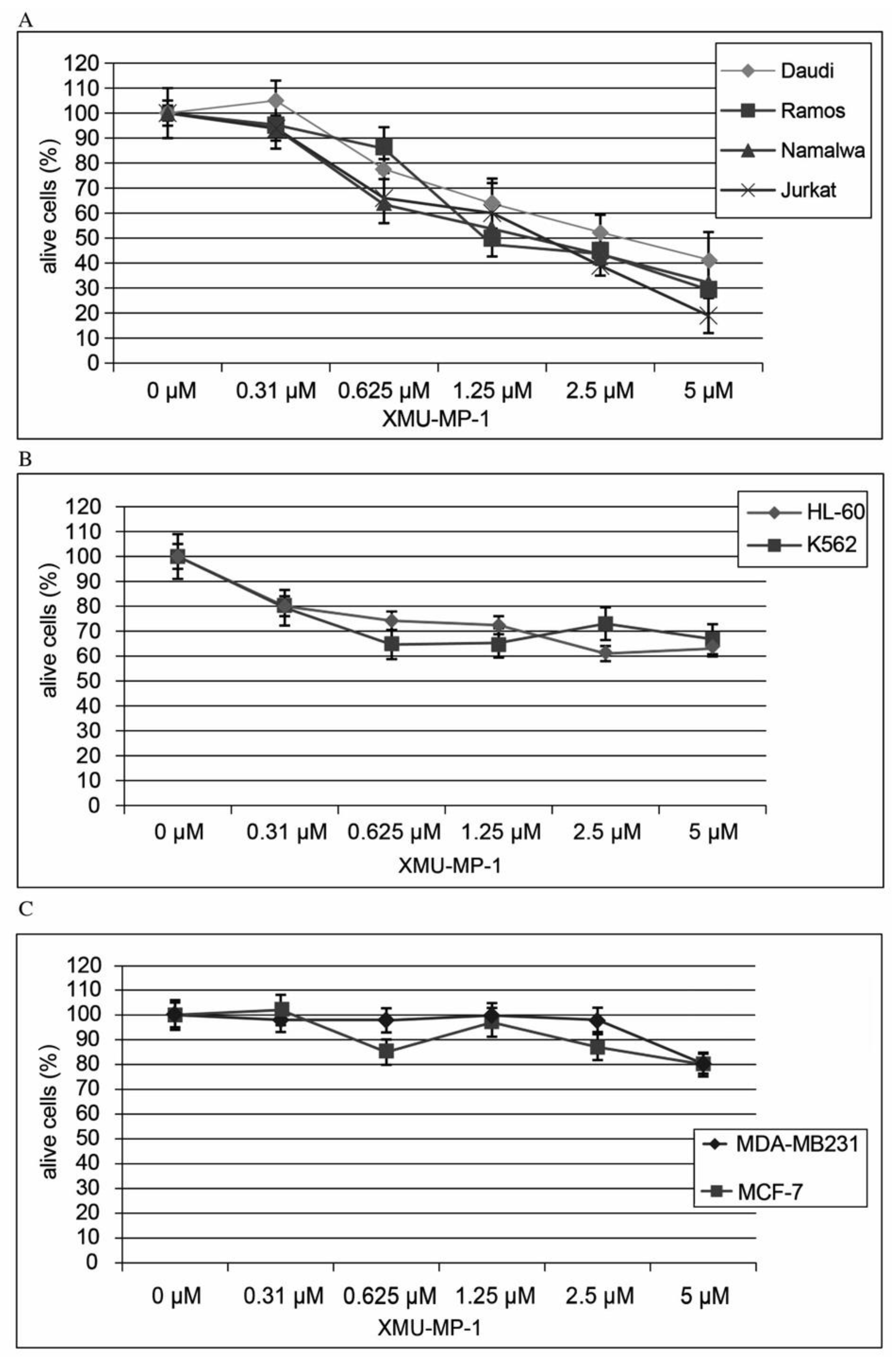
Using the CellTiter AQueous One Solution kit we have shown that treatment of hematopoietic cell lines with the MST1/2 inhibitor XMU-MP-1 causes a concentration- dependent inhibition of cell population growth (
Figure 1). This XMU-MP-1 effect was particularly strong in the B and T tumor cell lines (
Figure 1a). EC50 is achieved in the Namalwa, Raji, Ramos, Yurkat, and Daudi cell lines in 72 h at XMU-MP-1 concentrations ranging from 1.25 to 2.7 µM (
Figure 1a). At the same time, HL-60, and K562 cell lines show higher resistance to XMU-MP-1 (
Figure 1b). The triplet-negative and triplet-positive breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB231 and MCF-7 are resistant to XMU-MP-1 in the discussed concentration range (
Figure 1c).
We have performed analysis of MST1 expression in the cell lines used in this work and have demonstrated high levels of MST1 expression in Namalwa, Daudi and Ramos В-cell lymphoblastomas and Jurkat Т-cell lymphoblastoma (
Supplementary Figure S1).
We showed time-dependent inhibitor effects after 24, 48 and 72 h of treatment in the Namalwa cell line (Supplementary Figure S2).
3.2. XMU-MP-1 Induces Apoptosis in Hematopoietic Tumor Cells
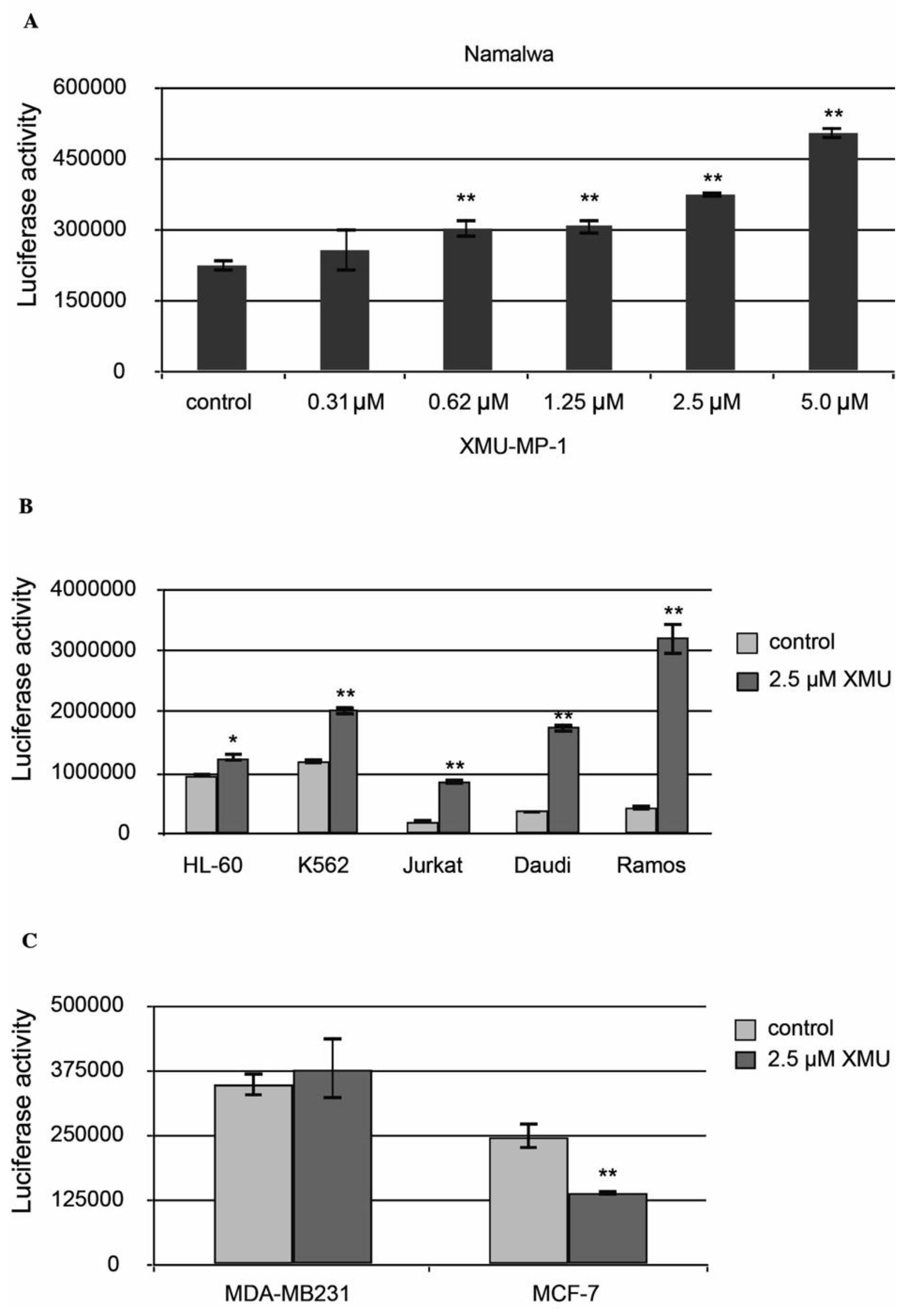
We have then demonstrated that XMU-MP-1 causes apoptosis in Namalwa cells. The Caspase-Glo 3/7 Assay protocol was used in this experiment. The analysis demonstrated a significant concentration-dependent increase in basic caspase 3/7 activity in XMU-MP-1–treated Namalwa cell line (
Figure 2a, b).
XMU-MP-1 also causes apoptosis in the Daudi, Ramos, Yurkat, K562, HL-60, and MP-1 cell lines. However, the XMU-MP-1-induced increase in caspase 3/7 activity may differ significantly between these tumor cell lines (
Figure 2b). It is important to mention that XMU-MP-1 doesn't induce caspase 3/7 activation and apoptosis in the breast cancer MDA-MB231 and MCF-7 cell lines. Suppression of the basic caspase 3/7 activity level can even be observed in the MCF-7 cells, which indicates the suppression of apoptosis as a result of XMU-MP-1 application (
Figure 2c).
To summarize, the results of our experiments have demonstrated that the response of cells to XMU-MP-1 being largely cell-specific. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic responses were found predominantly in the B- and T-cell lines.
3.3. XMU-MP-1 Increases the Sensitivity of Tumor Cells to Doxorubicin
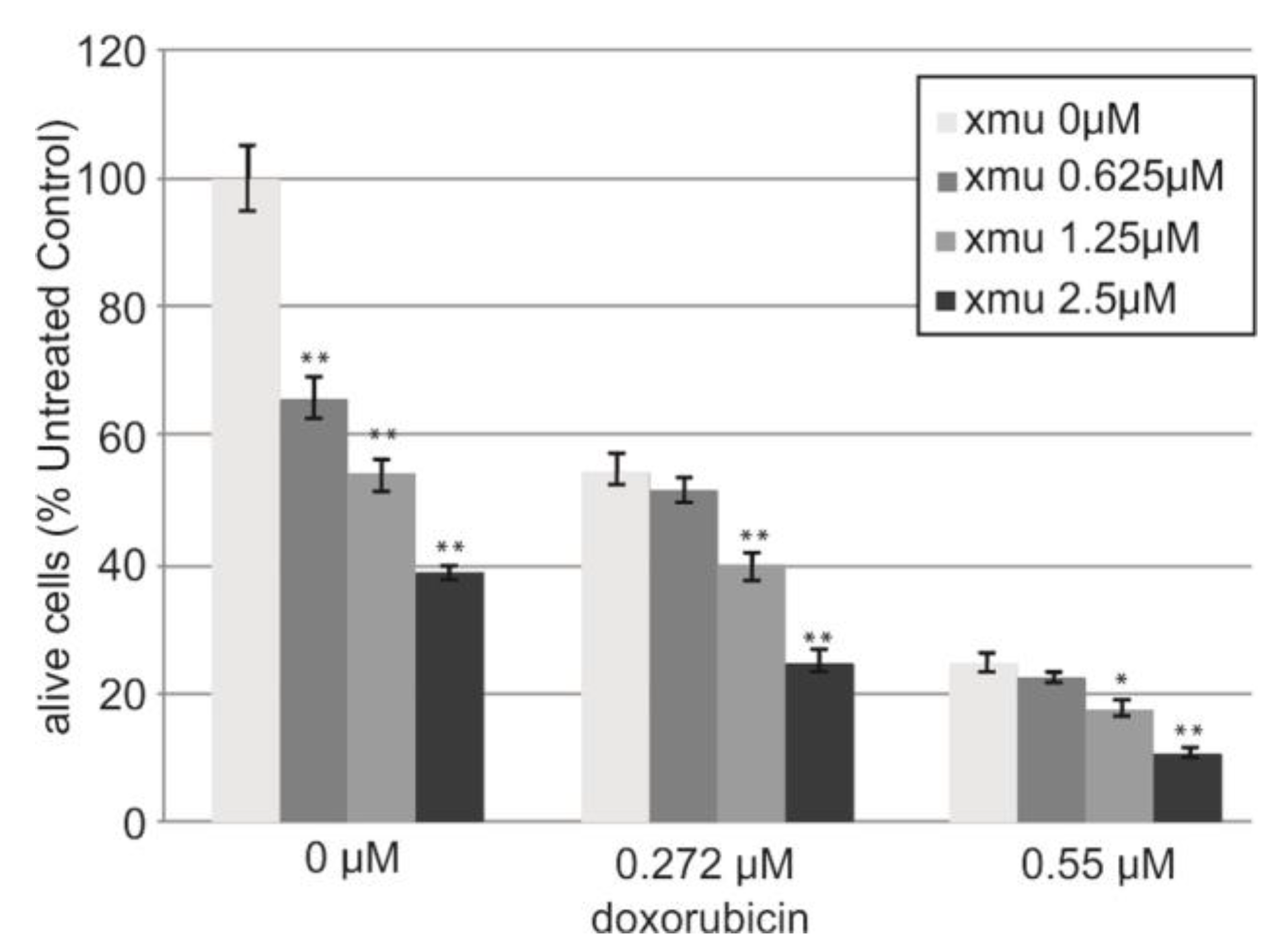
We performed in vitro analysis of the resistance of the B-cell lymphoma tumor cells Namalwa to the combined action of XMU-MP-1 and doxorubicin. The addition of XMU-MP-1 to the culture medium resulted in a dose-dependent enhancement of the chemotherapeutic action of doxorubicin (
Figure 3).
We observed the additive effect of combined XMU-MP-1 and doxorubicin resulting in their total effect being lower than the sum of effects, but higher than the effect of either compound used separately (Supplementary Table 1S). Doxorubicin is an antitumor anthracycline group antibiotic, the genotoxic drug which causes damage to genomic DNA. It is used to treat many different malignancies including lymphoblastic leukemias and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
3.4. RNA-Seq
Herein, for the better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the effects exerted by the Hippo signaling pathway inhibitor XMU-MP-1 on the B-cell lymphoma, we carried out a whole transcriptome analysis and identified genes which expression changes after cell line Namalwa treatment with XMU-MP-1. We have also determined their biological functions and the underlying mechanisms of XMU-MP-1 action in Namalwa cells. Towards this we have prepared cDNA libraries from the control Namalwa cell and Namalwa cells to which XMU-MP-1 was applied in the concentrations of 0.3 µМ and 2.5 µМ for 72 h.
RNA-Seq was used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the cells treated with XMU-MP-1 (GEO Database: GSE80287). Changes in gene transcription levels were considered significant based on a fold change of ≥2.0 and a Paji ≤ 0.01.
DEGs common for the 0.3 µM and 2.5 µM XMU-MP-1 treatments had a similar, unidirectional response (either up or down), response levels being different though. We also observed that at the higher concentration, the resulting change in gene activity was more pronounced and the effect could differ by several times (Tables S2-5). This shows that the action of XMU-MP-1 on gene expression is concentration dependent.
3.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
To identify biological processes and to determine more relevant groups of DEGs regulated by XMU-MP-1, we performed functional enrichment analysis by DAVID utilizing the GO (gene ontology) and KEGG pathways databases. Three gene ontology domains (biological process, cellular component, and molecular function) were analyzed for DEGs.
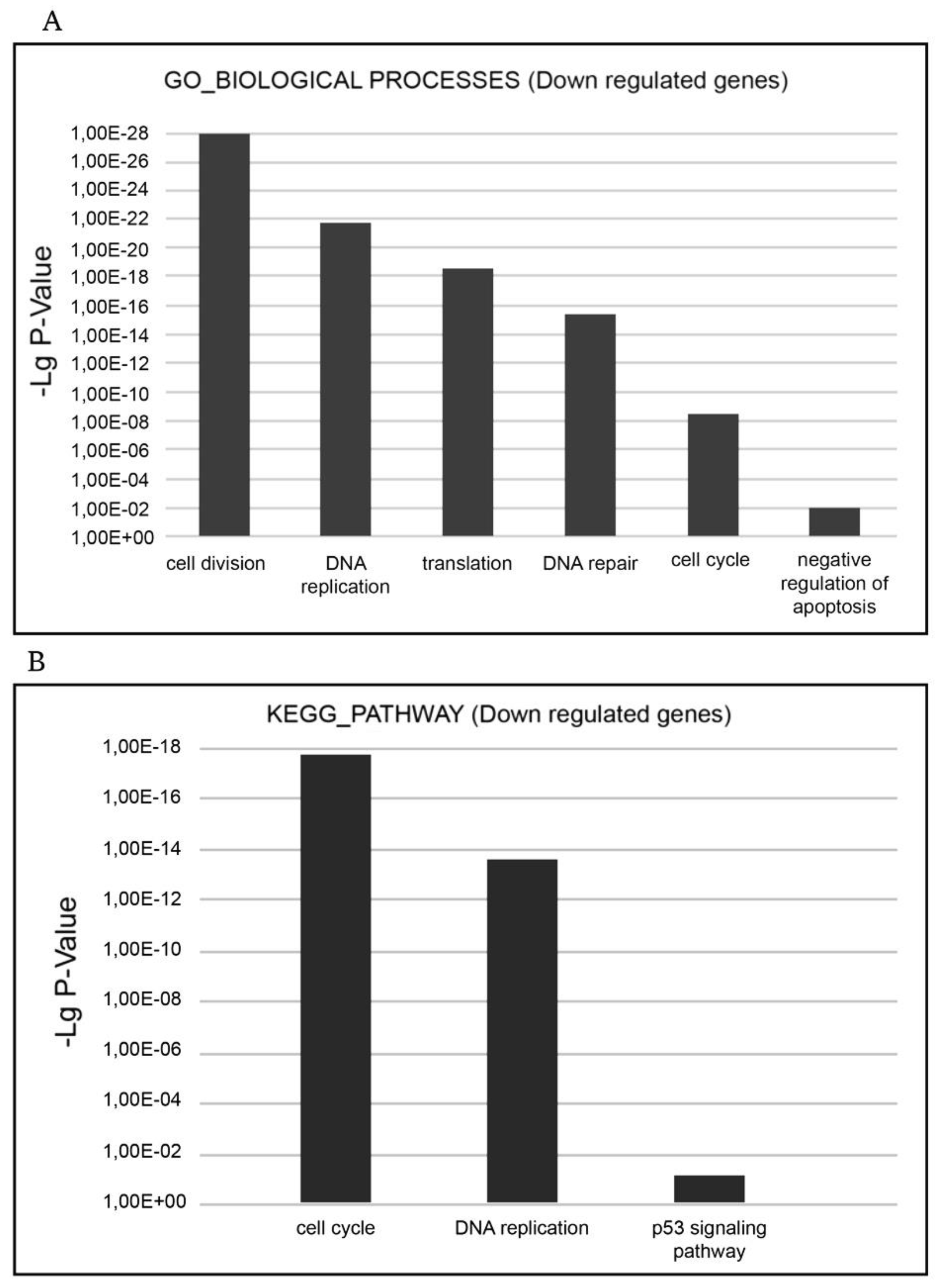
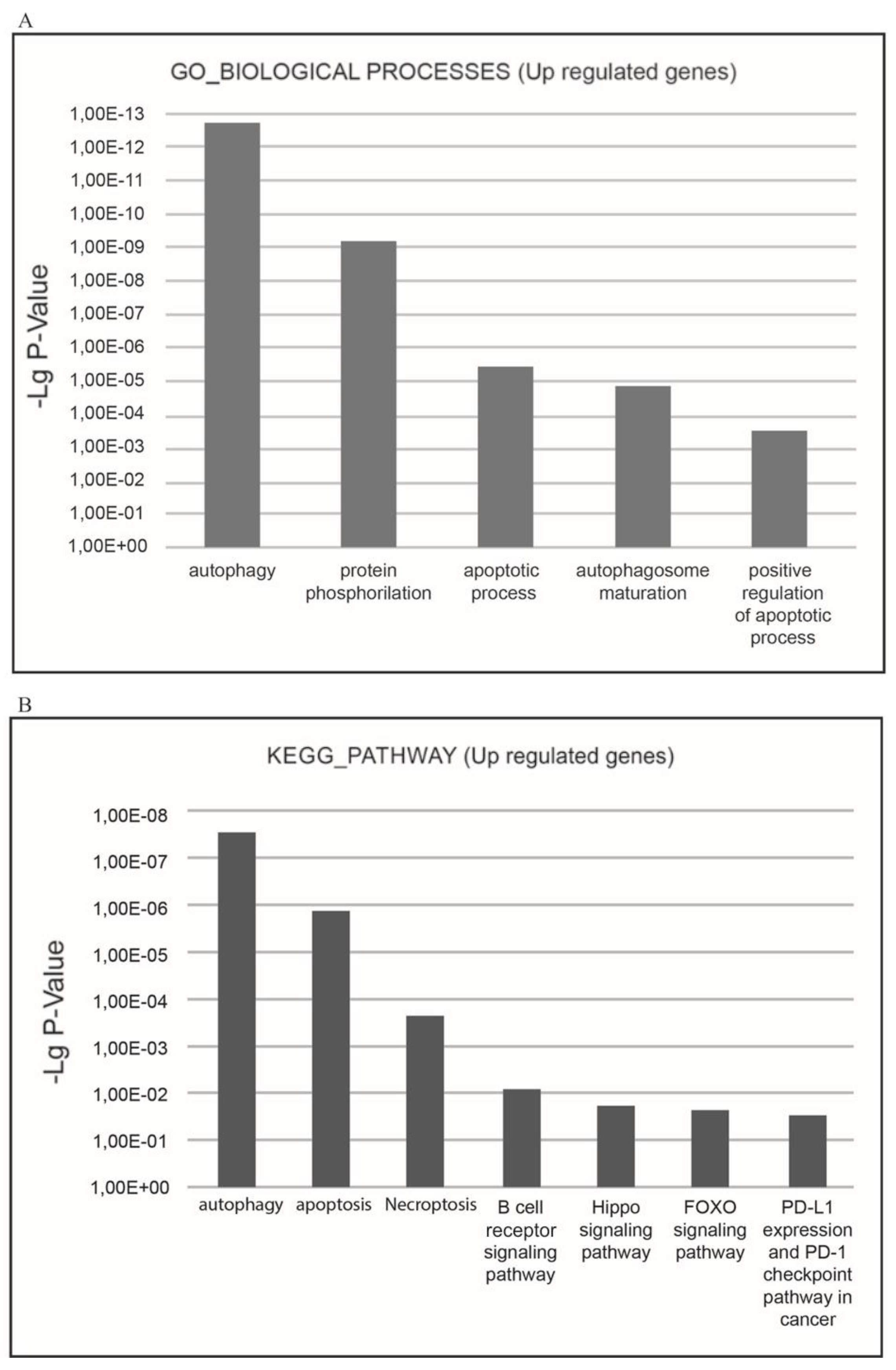
The functional enrichment analysis demonstrated XMU-MP-1 to be a negative regulator of cell cycle and a positive regulator of programmed cell death in hematopoietic tumor cells. The most relevant strongly up- and down-regulated biological processes are shown in
Figure 4a, b and
Figure 5a, b. The downregulated genes are related to such GO terms as ‘cell cycle’, ‘cell division’, ‘mitosis’, ‘DNA replication’, ‘DNA repair’, ‘DNA damage’, ‘mRNA splicing’, and ‘stress response’. The most relevant down-regulated KEGG pathways are ‘cell cycle’, ‘DNA replication’, and ‘p53 signaling pathway’ implying that negative cell cycle regulation is the XMU-MP-1 function in Namalwa cells (
Figure 4a and b).
The results obtained by RNA-Seq are in a perfect agreement with the results of the experiments which demonstrated the suppression of B and T tumor cells growth.
The ‘cell cycle’ term encompasses a significant group of downregulated DEGs which participate in cell cycle regulation (Supplementary Table 2S). This group includes the E2F family transcription factors (E2F1, E2F2, E2F7, and E2F8), which expression is 7-15 times decreased. The E2F family of transcription factors play a key role in cell cycle control. As transcription activators they interact with the promoters of the genes which products are engaged in cell cycle regulation or DNA replication and control cell cycle progression from the G1 to S phase. Along with the downregulation of the E2F family transcription factors expression, the expression of other key cell cycle regulators is significantly downregulated too; the expression of many of them is under E2F control. These include cell division cycle genes (CDC6; CDC7; CDC20; CDC25A; CDC25B; CDC25C, and CDC45), which regulate the cell cycle at its different stages, cyclins including А2, which controls both the G1/S and the G2/M transition phases of the cell cycle, and cyclin B1(CCNB1) and cyclin B2(CCNB2), which are indispensable in the control of cell cycle at the G2/M (mitosis) transition, kinases – the regulators of the cell cycles including cyclin dependent kinase 1(CDK1), Checkpoint kinase 1(CHEK1), polo-like kinase 1(PLK1) and others, мinichromosome maintenance complex components (MCM2-7), Origin recognition complex subunits 1 and 6 (ORC1 and PRC6) and others. Thus, XMU-MP-1 triggers a cascade of transcription repression of the key cell cycle regulators in Namalwa cells.
The most relevant upregulated processes, which are present in the KEGG pathways and BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES databases are
‘autophagy,
‘apoptosis
’,
‘necroptosis
’, which confirms the suppressive effect of XMU-MP-1 on cell population growth and demonstrates the mechanisms by which XMU-MP-1 regulates the programmed cell death (
Figure 5a, b).
The processes which are connected with the following GO terms: ‘apoptosis’, ‘autophagy’, and ‘necroptosis’ are among the upregulated ones. These are three most common form of the programmed cell death. Their molecular mechanisms are different in principle. For example, unlike apoptosis, which is induced by caspase 8 activation, necroptosis may occur only when this enzyme is inactivated. Therefore, these processes are induced in different cells within the Namalwa line cell population.
XMU-MP-1 causes changes in the activity of many key apoptotic regulatory genes (Supplementary Table 3S). The ‘apoptosis’ term includes a significant group of upregulated DEGs involved in the development and regulation of apoptosis: CASP6 и CASP7 caspases; BBC3; BCL2A1; BLCAP; FAS (Fas cell surface death receptor); TRAF1; TRAF4; TNFSF10; TRADD; XAF1; APAF1; BIRC3 and other.
XMU-MP-1 activates key genes involved in the initiation and development of necroptosis (Supplementary Table 4S). Necroptosis is the programmed necrotic cell death which may be triggered when apoptosis is for some reasons impossible. The ‘necroptosis’ term includes a significant group of upregulated DEGs: RIPK1 receptor interacting serine/threonine kinase 1 which is the key regulator of TNF-mediated necroptosis, apoptosis, and inflammatory pathways; FAS (Fas cell surface death receptor); TNF (tumor necrosis factor); TNFSF10 (TNF superfamily member 10), the protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family; TRADD (TNFRSF1A associated via death domain), the receptor for tumor necrosis factor 1 mediates programmed cell death signaling and is engaged in the Fas-induced cell death pathway.
XMU-MP-1 considerably increases the expression of the key gene participating in autophagy activation and autophagosomes maturation (Supplementary Table 5S). The ‘autophagy’ term includes a significant group of upregulated DEGs involved in autophagy regulation and autophagosome membrane formation including beclin 1(BECN1); DEPP autophagy regulator 1(DEPP1); DNA damage regulated autophagy modulator 2(DRAM2); autophagy related 2A(ATG2A); autophagy related 4B cysteine peptidase(ATG4B); death associated protein(DAP); VPS18 core subunit of CORVET and HOPS complexes(VPS18); VPS39 subunit of HOPS complex(VPS39); autophagy and beclin 1 regulator 1(AMBRA1); ectopic P-granules 5 autophagy tethering factor(EPG5), and unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1(ULK1).
We hypothesize that this cascade of changes begins with the activation of the Hippo signaling pathway and leads to the death of Namalwa cells. Under the influence of XMU-MP-1, expression of some key genes of the Hippo signaling pathway is changed. This change in expression conceivably shows that the Hippo signaling pathway may be regulated via a feedback mechanism. XMU-MP-1 causes an increase in the following gene expression: MST1 serine/threonine kinase 4; LIMD1 (LIM domain containing 1); MOB1A and MOB1B; NF2; RASSF2 and others.
4. Discussion
MST1/2 regulates the development of Т and В cells via the «noncanonical» Hippo signaling pathway hematopoiesis and in hematopoietic tumor cells [
22,
23]. We have investigated how XMU-MP-1, the inhibitor of the STE20-like serine/threonine kinases MST1/2, the key components of the Hippo pathway, affects hematologic tumors and have demonstrated that treatment of several hematopoietic tumor cell lines with XMU-MP-1 causes suppression of their growth and induces programmed cell death.
When the MST1 and MST2 kinases are inhibited, the canonical Hippo signaling pathway leads to increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis in many somatic cells. However, we observe the opposite effect in hematopoietic tumor cells. This suggests that in these cells, the Hippo signaling pathway activates and represses alternative transcription regulation pathways. In particular, RNA-Seq results show that the expression of such “canonical” Hippo signaling pathway target genes as Cyr61(CCN1) and CTGF(CCN2) is not altered in the Namalwa cells under MST1/2 inhibition.
The results of whole transcriptome analysis showed that XMU-MP-1 suppresses the expression of proliferation activator genes in the Burkitt lymphoma cells Namalwa. In particular, decreased expression levels are observed for the E2F1 and E2F2 transcription factors (by 4 and 15 times, respectively), which play a key role in cell cycle control and regulate the genes, the products of which play roles in cell cycle regulation or DNA replication; the expression of cell division cycle genes (CDC6; CDC7; CDC20; CDC25A,B,C, and CDC45) and the cyclin А1, В1, and В2 genes is also reduced as well as the expression of the kinases regulating the cell cycle including CDK1, CHEK1; PLK1; TTK; CDKN1C; WEE1, BUB1 and BUB1B; DBF4B-CDC7 kinase regulatory subunit (DBF4B); Minichromosome maintenance complex components (MCM2-7) - acts as a component of the MCM2-7 complex (MCM complex) which is the replicative helicase essential for “once per cell cycle” DNA replication initiation and elongation in eukaryotic cells, and Origin recognition complex subunits 1 and 6 (ORC1 and PRC6) key for the initiation of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Thus, XMU-MP-1 suppresses the expression of many molecular components of the cell cycle machinery in the B cell lymphoma.
At the same time, XMU-MP-1 triggers the activation of genes regulating three types of programmed cell death - apoptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy. The activation of these three processes suggests that XMU-MP-1 exerts a profound effect on the cell death of hematopoietic tumor cells, while it doesn't have such effect on triplet-negative and triplet-positive breast cancer cells and does not cause their death.
One of the most important properties of neoplastic cells is suppression of apoptosis in them. The ability to escape apoptosis dramatically increases the viability of neoplastic cells, hence the activation of apoptosis in them is necessary for effective antitumor therapy. The treatment with XMU-MP-1 triggers an increase in apoptotic activator genes expression in Namalwa cells, these genes including APAF1, the cytoplasmic protein which activates apoptosis via binding to cytochrome c and dATP. This protein forms an oligomeric apoptosome that activates caspase and stimulates the subsequent caspase cascade. Increased expression is also observed for caspases 6 and 7, Fas cell surface death receptor, pro-apoptotic proteins of the BCL2 cascade (BBC3, BCL2A1), as well as apoptosis regulator proteins such as MOAP1, which interacts with BAX and activates caspase-dependent apoptosis, XAF1, which binds and inactivates the apoptosis inhibitor IAP, and other important apoptosis regulators, leading to the apoptotic death of Namalwa cells.
Resistance to apoptosis often occurs in cancer cells during anticancer chemotherapy. Necroptosis is known to be an important mechanism for increasing the sensitivity of tumor cells to anticancer drugs. Necroptosis and apoptosis are two mutually exclusive processes, since apoptosis activation requires the activation of caspase 8 while necroptosis is blocked in the presence of the active caspase 8. Necroptosis like apoptosis is induced by several death receptors, with FAS, TNFR1, and TNFR2 being among them, which may induce necroptosis in those cases when apoptosis is not possible with the involvement of RIPK1. We have demonstrated in our work that in the presence of XMU-MP-1, the expression of necroptosis activator genes FAS, TNFSF10, TRADD, and RIPK1, as well as the expression of PEA15, the caspase 8 inhibitor, increases in the Namalwa cell population. Activation of necroptosis is an important therapeutic tool to target tumors that are especially resistant to apoptosis. For example, the anticancer drug shikonin exerts an antitumor effect on osteosarcoma by triggering RIPK1 and RIPK3-dependent necroptosis [
24]. Resibufogenin triggers necroptosis in colon cancer cells thereby inhibiting tumor growth [
25]. Rasfonin triggers apoptosis, autophagy, and necroptosis in kidney cancer cells [
26]. In our work, we have shown that the expression of RIPK1 was significantly increased and necroptosis regulator genes were activated in the presence of XMU-MP-1.
We have also demonstrated that XMU-MP-1 activates autophagy. It is known that autophagy is necessary for maintaining the balance between proliferation and cell death of B and T lymphocytes. XMU-MP-1 significantly increases the expression of the key autophagosome assembly activator genes in Namalwa cells including beclin 1, DEPP autophagy regulator 1(DEPP1), death associated protein (DAP), VPS18, VPS39, and autophagy and beclin 1 regulator 1(AMBRA1). There is ample evidence that autophagy is one of the suppressors of neoplasm development. For example, expression of exogenous Beclin-1 (one of the main regulators of the molecular mechanisms of autophagy) reduces the in vitro proliferation ability of tumor cells and their carcinogenic potential in vivo [
27,
28]. The anticarcinogenic effect of autophagy is observed not only at the stage of cell transformation, but also during tumor progression, namely, during invasion and metastasis.
A cytotoxic role of autophagy has been shown in many hematologic cancers. For example, the antitumor activity of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in acute promyelocytic leukemia relies on the activation of autophagy leading to tumor cell death [
29,
30]. The mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) also blocks cell survival by inducing autophagy in the childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia model [
31,
32]. Another drug that induces the death of chronic myeloid leukemia cells via autophagy is resveratrol [
33]. All the data mentioned above emphasize the crucial role of autophagy in hematologic cancers. Our study shows that XMU-MP-1 induces the activation cascade of autophagy activator gene expression.
In our work, we have shown that the activation of several types of programmed cell death leads to both a substantial reduction of the tumor cell population and an increase in efficiency of antitumor therapy.
XMU-MP-1 treatment also decreases the resistance of Namalwa cells to such antitumor drug as doxorubicin, which causes DNA damage and is used to treat hematologic malignancies. In hematologic tumors, DNA damage leads to the activation of proapoptotic system based on nuclear relocation of ABL1 kinase. It was previously shown that low levels of YAP1 block ABL1-induced apoptosis in hematologic malignancies, while genetic inactivation of MST1 restores the YAP1 levels causing cell death in vitro and in vivo [
19]. By decreasing MST1 activity, XMU-MP-1 increases YAP1 activity, and doxorubicin causes DNA damage. As a consequence, the simultaneous action of these two substances leads to an increased death rate of Namalwa cells. XMU-MP-1 enhances the chemotherapeutic effect of doxorubicin. It is possible that the combined use of doxorubicin and XMU-MP-1 may allow to reduce the effective therapeutic dose of doxorubicin used in the treatment of hematologic cancers. The use of doxorubicin results in free radical formation, which underlies its cardiotoxic effects, and also causes thrombocytopenia and leukopenia, and necrotizing colitis. Including XMU-MP-1 into the doxorubicin-based treatment regimen may significantly reduce these life-threatening toxic effects of doxorubicin, firstly, through the reduction of the effective dose of doxorubicin and secondly, through the XMU-MP-1 ability to activate the regenerative systems of the organism. XMU-MP-1 has earlier been shown to stimulate platelet recovery after immune thrombocytopenia and to promote the migration of mature megakaryocytes from the bone marrow and platelet generation [
35]. The MST1/2 kinase inhibitor XMU-MP-1 promotes regeneration of hematopoietic stem cells and hematopoietic progenitor cells and markedly reduced the damage caused to the small intestine by whole body exposure to radiation in the dose of 9 Gy and increased the average survival time of mice exposed to lethal radiation doses [
21].
5. Conclusions
Thus, XMU-MP-1 may become an effective component in the combination therapy of hematologic tumors& Taking into account the results obtained in our work, we consider the investigation of the possibility of using the MST1/2 kinase inhibitors in the treatment of hematologic tumors extremely promising.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1; Figure S2; Table S1; S2; S3; S4; S5.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.V.P. and A.G.S, methodology, E.V.P. and A.G.S, validation, E.V.P., A.G.S, formal analysis, E.V.P., A.G.S, investigation, E.V.P., A.G.S, data curation, E.V.P., S.G.G, writing—original draft preparation, E.V.P, writing—review and editing, E.V.P., A.G.S., S.G.G; project administration, E.V.P.
Funding
This research and APC was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (Agreement No. 075-15-2019-1660) Center for Precision Genome Editing and Genetic Technologies for Biomedicine Engelhardt Institute of Molecular Biology.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and provided by GEO Database GSE279247.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
References
- Meng, Z.; Moroishi, T.; Mottier-Pavie, V.; Plouffe, S. W.; Hansen, C. G.; Hong, A. W.; Park, H. W.; Mo, J. S.; Lu, W.; Lu, S.; Flores, F.; Yu, F. X.; Halder, G.; Guan, K. L. MAP4K family kinases act in parallel to MST1/2 to activate LATS1/2 in the Hippo pathway. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Pan, D. The Hippo Signaling Pathway in Development and Disease. Dev Cell 2019, 50, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lan, T.; Guan, K.L.; Luo, T.; Luo, M. The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggiano, J.C.; Vanderzalm, P.J.; Fehon, R.G. Tao-1 phosphorylates Hippo/MST kinases to regulate the Hippo-Salvador-Warts tumor suppressor pathway. Dev Cell 2011, 21, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praskova, M.; Khoklatchev, A.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Avruch, J. Regulation of the MST1 kinase by autophosphorylation, by the growth inhibitory proteins, RASSF1 and NORE1, and by Ras. Biochem J 2004, 381, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glantschnig, H.; Rodan, G.A.; Reszka, A.A. Mapping of MST1 kinase sites of phosphorylation. Activation and autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 42987–42996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.L.; Lin, J.I.; Zhang, X.; Harvey, K.F. The sterile 20-like kinase Tao-1 controls tissue growth by regulating the Salvador-Warts-Hippo pathway. Dev Cell 2011, 21, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergovich, A.; Schmitz, D.; Hemmings, B.A. The human tumour suppressor LATS1 is activated by human MOB1 at the membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 345, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, N.; Pan, D. Spatial organization of Hippo signaling at the plasma membrane mediated by the tumor suppressor Merlin/NF2. Cell 2013, 154, 1342–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Lei, Q.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo-YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: an updated version. Genes Dev 2010, 24, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, P.; Chen, F.; Dong, Z.; Yang, H.; Guan, K. L.; Xu, Y. Structural insights into the YAP and TEAD complex. Genes Dev 2010, 24, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.G.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.L. YAP and TAZ: a nexus for Hippo signaling and beyond. Trends Cell Biol 2015, 25, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.L.; Guan, K.L. The two sides of Hippo pathway in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 2022, 85, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lan, T.; Guan, K.L.; Luo, T.; Luo, M. The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, S.; Lei, T.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Tong, R.; Wang, Y. Multifaceted regulation and functions of YAP/TAZ in tumors. Oncol Rep 2018, 40, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroja, I.; Kyriakidis, N.C.; Halder, G.; Moya, I.M. Expected and unexpected effects after systemic inhibition of Hippo transcriptional output in cancer. Nat Commun. 2024, 15, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology. Annu Rev Biochem 2019, 88, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottini, F.; Hideshima, T.; Xu, C.; Sattler, M.; Dori, M.; Agnelli, L.; ten Hacken, E.; Bertilaccio, M. T.; Antonini, E.; Neri, A.; et al. Rescue of Hippo coactivator YAP1 triggers DNA damage-induced apoptosis in hematological cancers. Nat Med 2014, 20, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; He, Z.; Kong, L. L.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ye, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Geng, J.; et al. Pharmacological targeting of kinases MST1 and MST2 augments tissue repair and regeneration. Sci Transl Med 2016, 8, 352ra108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Song, N.; Yang, F.; Xu, W. MST1/2 inhibitor XMU-MP-1 alleviates the injury induced by ionizing radiation in haematopoietic and intestinal system. J Cell Mol Med 2022, 26, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Jing, Y.; Kang, D.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Gong, Q.; et al. The Role of Mst1 in Lymphocyte Homeostasis and Function. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Du, X. The role of non-canonical Hippo pathway in regulating immune homeostasis. Eur J Med Res 2023, 28, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Park, T.; Noh, J.Y.; Kim, W. Emerging role of Hippo pathway in the regulation of hematopoiesis. BMB Rep 2023, 56, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Deng, B.; Liao, Y.; Shan, L.; Yin, F.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, H.; Zuo, D.; Hua, Y.; Cai, Z. The anti-tumor effect of shikonin on osteosarcoma by inducing RIP1 and RIP3 dependent necroptosis. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Jing, L.; Sun, X. Resibufogenin suppresses colorectal cancer growth and metastasis through RIP3-mediated necroptosis. J Transl Med 2018, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang,W. ; Sun, H.; Che, Y,.; Jiang, X. Rasfonin promotes autophagy and apoptosis via upregulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS)/JNK pathway. Mycology 2016, 7, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.H.; Jackson, S.; Seaman, M.; Brown, K.; Kempkes, B.; Hibshoosh, H.; Levine, B. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature 1999, 402, 672–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Jin, S.; Yang, C.; Levine, A.J.; Heintz, N. Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 15077–15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goussetis, D.J.; Altman, J.K.; Glaser, H.; McNeer, J.L.; Tallman MS, Platanias LC. Autophagy is a critical mechanism for the induction of the antileukemic effects of arsenic trioxide. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 29989–29997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarini, F.; Grimaldi, C.; Ricci, F.; Tazzari, P. L.; Evangelisti, C.; Ognibene, A.; Battistelli, M.; Falcieri, E.; Melchionda, F.; Pession, A.; et al. Activity of the novel dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 8097–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crazzolara, R.; Bradstock, K.F.; Bendall, L.J. RAD001 (Everolimus) induces autophagy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Autophagy 2009, 5, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crazzolara, R.; Cisterne, A.; Thien, M.; Hewson, J.; Baraz, R.; Bradstock, K. F.; Bendall, L. J. Potentiating effects of RAD001 (Everolimus) on vincristine therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puissant, A.; Robert, G.; Fenouille, N.; Luciano, F.; Cassuto, J. P.; Raynaud, S.; Auberger, P. Resveratrol promotes autophagic cell death in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells via JNK-mediated p62/SQSTM1 expression and AMPK activation. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patent CN114366750B. Application of XMU-MP-1 in preparation of medicine for preventing and/or treating immune thrombocytopenia ITP. Publication 2022-11-25.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).