Submitted:
03 February 2025
Posted:
04 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of Photocatalytic Water Splitting
3. Advanced Engineering of TiO2 for Photocatalytic Water Splitting
3.1. Architectural Design and Crystal Phase Engineering
3.2. Surface Chemistry and Defect Engineering
3.3. Advanced Heterojunction Systems and Z-scheme Design
3.4. Cocatalyst Integration and Interface Optimization
3.5. Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
4. Hydrogen Production from Different Water Sources: Effects and Applications
4.1. Influence of Water Chemistry on Photocatalytic Performance
4.2. Impact of Dissolve Species and Impurities
4.3. Advanced Strategies for Seawater Splitting
4.4. Integration with Wastewater Treatment Systems
4.5. Future Prospectives and Challenges
5. Scale-Up and Engineering Challenges
5.1. Reactor Design Considerations and Optimization
5.2. Light Distribution and Mass Transfer Phenomena
5.3. Process Integration and System Optimization
5.4. Economic Feasibility and Sustainability Analysis
5.5. Future Direction and Research Needs
- The development of advanced reactor designs that integrate improved light delivery systems and enhanced mass transfer characteristics, aiming to maximize the system's overall performance.
- The incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches for the optimization of operational strategies, system control, and real-time monitoring [344].
- The implementation of sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing processes for catalyst production and system components, ensuring scalability and resource efficiency.
- The establishment of standardized methodologies for performance evaluation, including techno-economic and life cycle assessments, to streamline industry adoption and regulatory compliance.
6. Advanced Applications and System Integration of TiO2-Based Photocatalysts
6.1. Integration with Artificial Photosynthesis
- Improved photocatalytic efficiency and stability
- Enhanced charge separation and transfer
- Optimization of light harvesting capabilities
- Development of more cost-effective alternatives to noble metal co-catalysts
6.2. Coupling with CO2 Reduction Systems
6.3. Machine Learning Applications in Materials Discovery
7. Future Perspectives and Emerging Opportunities in Photocatalytic Water Splitting
- Quantum Computing for Materials Optimization: Quantum computing approaches are being explored for accelerated discovery and optimization of photocatalytic materials, offering potential breakthroughs in reaction efficiency and material design [382].
- Autonomous Systems for Real-Time Optimization: Autonomous systems equipped with real-time monitoring and adaptive control mechanisms are transforming operational efficiency and system reliability [383].
- Sustainable Manufacturing Processes: A focus on eco-friendly manufacturing of advanced photocatalytic materials ensures scalability and minimizes environmental impact [384].
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, F.Y.; Alharthi, M.; Bhatti, Z.; Sun, L.; Rasul, F.; Hanif, I.; Iqbal, W. The Dynamic Role of Energy Security, Energy Equity and Environmental Sustainability in the Dilemma of Emission Reduction and Economic Growth. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 280, 111828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Zakari, A.; Dagar, V.; Singh, S. World Energy Trilemma and Transformative Energy Developments as Determinants of Economic Growth amid Environmental Sustainability. Energy Econ. 2022, 108, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Khan, I.; Zakari, A.; Alharthi, M. Roles of Trilemma in the World Energy Sector and Transition towards Sustainable Energy: A Study of Economic Growth and the Environment. Energy Policy 2022, 170, 113238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yek, P.N.Y.; Cheng, Y.W.; Liew, R.K.; Wan Mahari, W.A.; Ong, H.C.; Chen, W.-H.; Peng, W.; Park, Y.-K.; Sonne, C.; Kong, S.H.; et al. Progress in the Torrefaction Technology for Upgrading Oil Palm Wastes to Energy-Dense Biochar: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Latif, S.N.; Chiong, M.S.; Rajoo, S.; Takada, A.; Chun, Y.-Y.; Tahara, K.; Ikegami, Y. The Trend and Status of Energy Resources and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Malaysia Power Generation Mix. Energies 2021, 14, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Msigwa, G.; Farghali, M.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.-S. Cost, Environmental Impact, and Resilience of Renewable Energy under a Changing Climate: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 741–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Ahmad, M.; Chen, J. Energy Transition, Ecological Governance, Globalization, and Environmental Sustainability: Insights from the Top Ten Emitting Countries. Energy 2024, 292, 130551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirat, Y.; Prodromou, T.; Suardi, S. Unveiling the Nexus: Climate Change, Green Innovation, and the Pendulum of Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions. Energy Econ. 2024, 138, 107727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.R.A. Overcome the Future Environmental Challenges through Sustainable and Renewable Energy Resources. Micro Nano Lett. 2022, 17, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkos, P. Global Energy System Transformations to 1.5 °C: The Impact of Revised Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Carbon Budgets. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 2000395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-T.; Zhai, P.-M. Achieving Paris Agreement Temperature Goals Requires Carbon Neutrality by Middle Century with Far-Reaching Transitions in the Whole Society. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogelj, J.; Lamboll, R.D. Substantial Reductions in Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reductions Implied by IPCC Estimates of the Remaining Carbon Budget. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, S.; Faheem, M.; Muqeet, H.A.; Waseem, M. Charting the UK’s Path to Net Zero Emissions by 2050: Challenges, Strategies, and Future Directions. IET Smart Grid n/a. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Bashir, S.; Sarker, T.; Shahzad, U. Sustainable Pathways for Attaining Net Zero Emissions in Selected South Asian Countries: Role of Green Energy Market and Pricing. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M, A.; V, M.K.; Hariharan, V.S.; Narahari, T.; P, A.K.; K, M.; G, P.K.; Prabakaran, R. Fuelling the Future: A Review of Non-Renewable Hydrogen Production and Storage Techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 188, 113791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikiru, S.; Oladosu, T.L.; Amosa, T.I.; Olutoki, J.O.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Abioye, K.J.; Rehman, Z.U.; Soleimani, H. Hydrogen-Powered Horizons: Transformative Technologies in Clean Energy Generation, Distribution, and Storage for Sustainable Innovation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 56, 1152–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, N.S.; Gbadamosi, A.O.; Epelle, E.I.; Abdulrasheed, A.A.; Haq, B.; Patil, S.; Al-Shehri, D.; Kamal, M.S. Hydrogen Production, Transportation, Utilization, and Storage: Recent Advances towards Sustainable Energy. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, U.Y. Future of Hydrogen as an Alternative Fuel for Next-Generation Industrial Applications; Challenges and Expected Opportunities. Energies 2022, 15, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, F.; Yusuf, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Pham, C.Q.; Vo, D.-V.N. Contemporary Avenues of the Hydrogen Industry: Opportunities and Challenges in the Eco-Friendly Approach. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Khan, M.H.; Daiyan, R.; Neal, P.; Haque, N.; MacGill, I.; Amal, R. A Framework for Assessing Economics of Blue Hydrogen Production from Steam Methane Reforming Using Carbon Capture Storage & Utilisation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 22685–22706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, M.; Teymouri, N.; Ashrafi, O.; Navarri, P.; Khojasteh-Salkuyeh, Y. Methane Pyrolysis as a Potential Game Changer for Hydrogen Economy: Techno-Economic Assessment and GHG Emissions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 66, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.; Hussain, M. Emerging Trends in Water Splitting Innovations for Solar Hydrogen Production: Analysis, Comparison, and Economical Insights. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 77, 975–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Li, R. Recent Advances and Perspectives for Solar-Driven Water Splitting Using Particulate Photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3561–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Mubashar, R.; Irshad, M.; Gillani, S.S.A.; Tahir, M.B.; Khalid, N.R.; Yasmin, A.; Shehzad, M.A. A Comprehensive Study on Methods and Materials for Photocatalytic Water Splitting and Hydrogen Production as a Renewable Energy Resource. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3837–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strizhenok, A.V.; Bykova, M.V.; Korotaeva, A.E. Extractive Industries as a Source of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and the Possibility of Its Natural Sequestration under the Climatic Conditions of Central and Northern Eurasia. J. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 25, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Li, R. Recent Advances and Perspectives for Solar-Driven Water Splitting Using Particulate Photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3561–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Toe, C.Y.; Scott, J.; Antonietti, M.; Guo, J.; Amal, R. Materials Advances in Photocatalytic Solar Hydrogen Production: Integrating Systems and Economics for a Sustainable Future. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2404618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Kaushal, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Thakur, N.; Thakur, N. Photocatalytic Water Splitting for Production of Green Hydrogen Using Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. In Towards Sustainable and Green Hydrogen Production by Photocatalysis: Insights into Design and Development of Efficient Materials (Volume 2); ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society, 2024; Vol. 1468, pp. 79–106.
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Yang, L.; Spadaro, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Guardia, P.; Arbiol, J.; Liu, T.; Fan, X.; Fernández-García, M.; Llorca, J.; et al. Controllable Synthesis of Defective TiO2 Nanorods for Efficient Hydrogen Production. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 5833–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamarpoor, R.; Fallah, A.; Jamshidi, M. A Review of Synthesis Methods, Modifications, and Mechanisms of ZnO/TiO2-Based Photocatalysts for Photodegradation of Contaminants. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 25457–25492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanos, F.; Razzouk, A.; Lesage, G.; Cretin, M.; Bechelany, M. A Comprehensive Review on Modification of Titanium Dioxide-Based Catalysts in Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202301139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatou, M.-A.; Syrrakou, A.; Lagopati, N.; Pavlatou, E.A. Photocatalytic TiO2-Based Nanostructures as a Promising Material for Diverse Environmental Applications: A Review. Reactions 2024, 5, 135–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Interfacial Charge Transport in 1D TiO2 Based Photoelectrodes for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Small 2021, 17, 1903378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahasan, T.; Xu, P.; Wang, H. Dual-Function Photocatalysis in the Visible Spectrum: Ag-G-TiO2 for Simultaneous Dye Wastewater Degradation and Hydrogen Production. Catalysts 2024, 14, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisooriya, E.M.N.T.; Senanayake, P.S.; Wang, H.B.; Talipov, M.R.; Xu, P.; Wang, H. Photo-Reforming and Degradation of Waste Plastics under UV and Visible Light for H2 Production Using Nanocomposite Photocatalysts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Betts, D.; Ghurye, G.L.; Wang, H. Au-TiO2 Nanoparticles Enabled Catalytic Treatment of Oil and Gas Produced Water in Slurry and Vacuum Membrane Distillation Systems. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 65, 105745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisooriya, E.M.N.T.; Senanayake, P.S.; Xu, P.; Talipov, M.R.; Wang, H. Optimization of Green Hydrogen Evolution from Low-Density Plastics Using TiO2-Based Nano-Photocatalysts with Techno-Economic and Carbon Footprint Assessment. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Jiang, W.; Nasr, M.; Bechelany, M.; Miele, P.; Wang, H.; Xu, P. Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalysis by TiO2–BN Enabled Electrospinning of Nanofibers for Pharmaceutical Degradation and Wastewater Treatment. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 2921–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilano-Camino, M.M.; García-González, A.; Olivo-Alanís, D.S.; García-Reyes, R.B. Photoreforming of Fermentation Byproducts by TiO2 and Pt/TiO2 to Enhance Hydrogen Production: Insight into a Real Perspective. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indla, N.R.; Shelake, S.P.; Sutar, D.N.; Mehmood, S.; Raghava Reddy, K.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Sainath, A.V.S.; Pal, U. Fluoro-Polymer/TiO2 Based Photocatalysts for High Efficiency Hydrogen Generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; Qin, R.; Zheng, N.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Nanoscale Engineering of Catalytic Materials for Sustainable Technologies. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, L.M.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Al-Azzawi, W.K. Nanomaterials: Paving the Way for the Hydrogen Energy Frontier. Discov. Nano 2024, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poerwoprajitno, A.R.; Cheong, S.; Gloag, L.; Gooding, J.J.; Tilley, R.D. Synthetic Strategies to Enhance the Electrocatalytic Properties of Branched Metal Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. D. Lund, P.; Kwan, J.; Edman Tsang, S.C. Black Titanium Oxide: Synthesis, Modification, Characterization, Physiochemical Properties, and Emerging Applications for Energy Conversion and Storage, and Environmental Sustainability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10660–10708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xue, J.; Shen, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Jia, H.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y. A Promoted Photocatalysis System Trade-off between Thermodynamic and Kinetic via Hierarchical Distribution Dual-Defects for Efficient H2 Evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-H.; Zhang, H.-R.; He, J.-G.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhou, Q.-B.; Cao, J.-L. Facile Construction Z-Scheme Anatase/Rutile TiO2/g-C3N4 Hybrid for Efficient Photocatalytic H2 Evolution under Visible-Light Irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 36644–36654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Ruan, X.; Xu, M.; Jiao, D.; Fang, G.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ravi, S.K.; Cui, X. An S-Scheme Artificial Photosynthetic System with H-TiO2/g-C3N4 Heterojunction Coupled with MXene Boosts Solar H2 Evolution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 211, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahar, K.U.; Rafiq, K.; Abid, M.Z.; Rehman, U.U.; Althomali, R.H.; Rauf, A.; Hussain, E. Sensitization of TiO2/g-C3N4 Heterostructures via Pd–Au Cocatalysts: A Rational Design of Water Splitting System for Green Fuel Production. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 17995–18009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, A.; Sarkar, S.; Nagappagari, L.R.; Bojja, S.; MuthukondaVenkatakrishnan, S.; Ghosh, S. Decoration of Graphene Quantum Dots on TiO2 Nanostructures: Photosensitizer and Cocatalyst Role for Enhanced Hydrogen Generation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 13060–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamukwaya, S.L.; Zhao, Z.; Hao, H.; Abo-Dief, H.M.; Abualnaja, K.M.; Alanazi, A.K.; Mashingaidze, M.M.; El-Bahy, S.M.; Huang, M.; Guo, Z. Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production and Carbon Dioxide Reduction by a Mesoporous Single-Crystal-like TiO2 Composite Catalyst. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 2620–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.R.; Bharagav, U.; Shankar, M.V.; Reddy, P.M.; Reddy, K.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Alonso-Marroquin, F.; Kumari, M.M.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Joo, S.W. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production by Ternary Heterojunction Composites of Silver Nanoparticles Doped FCNT-TiO2. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 286, 112130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Zuo, C.; Fang, X. Application of Nanostructured TiO2 in UV Photodetectors: A Review. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.Y.; Abdullah, O.Gh.; Mamand, S.M.; Aziz, S.B. Band Structure Study of Pure and Doped Anatase Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Using First-Principle-Calculations: Role of Atomic Mass of Transition Metal Elements (TME) on Band Gap Reduction. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen Ahmed, T.; Aziz, S.B.; Dannoun, E.M.A. Role of Outer Shell Electron-Nuclear Distant of Transition Metal Atoms (TMA) on Band Gap Reduction and Optical Properties of TiO2 Semiconductor. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Domen, K. Particulate Photocatalysts for Light-Driven Water Splitting: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Design Strategies. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 919–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasleem, S.; Tahir, M. Recent Progress in Structural Development and Band Engineering of Perovskites Materials for Photocatalytic Solar Hydrogen Production: A Review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 19078–19111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, D.; Wei, H.; Lin, Z.; Bai, X.; Ivan, M.N.A.S.; Tsang, Y.H.; Huang, H. The Role of Point Defects in Heterojunction Photocatalysts: Perspectives and Outlooks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Liang, G.; Hao, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. In Situ Synthesis of Chemically Bonded 2D/2D Covalent Organic Frameworks/O-Vacancy WO3 Z-Scheme Heterostructure for Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2303649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wudil, Y.S.; Ahmad, U.F.; Gondal, M.A.; Al-Osta, M.A.; Almohammedi, A.; Sa’id, R.S.; Hrahsheh, F.; Haruna, K.; Mohamed, M.J.S. Tuning of Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4) for Photocatalysis: A Critical Review. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jingyan Miao, T.; Tang, J. Charge Carrier Dynamics and Reaction Intermediates in Heterogeneous Photocatalysis by Time-Resolved Spectroscopies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5777–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, M.P.; Al-Ahmed, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; von Gratowski, S.; Iqbal, J. ; Inamuddin Photo-to-Chemical Energy Transformation: Pioneering Photocatalysts, Surface and Interface Engineering. Mater. Res. Bull. 2024, 180, 113046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, L.; Paramanik, L.; Sabnam, S.; Yoo, S.H. Advanced Strategies for Controlling Three-Phase Boundaries in Photocatalysis. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 22099–22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Q.; Wang, J.-J. Copper Sulfide Based Photocatalysts, Electrocatalysts and Photoelectrocatalysts: Innovations in Structural Modulation and Application. Small 2024, 20, 2404798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Jing, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J. Roles of Cocatalysts in Biomass Photo(Electro)Refining. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2401838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhao, X.; Hu, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, D.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sritharan, T. The Self-Passivation Mechanism in Degradation of BiVO4 Photoanode. iScience 2019, 19, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Liberto, G.; Maleki, F.; Pacchioni, G. pH Dependence of MgO, TiO2, and γ-Al2O3 Surface Chemistry from First Principles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 10216–10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liang, L.; Nie, T.; She, Y.; Tao, L.; Guo, L. Effect of Electrolyte pH on Oxygen Bubble Behavior in Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 5308–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Biswas, N.; Srivastav, A.; Saxena, S.; Verma, A.; Dutta, R.; Srivastava, M.; Rani Satsangi, V.; Shrivastav, R.; Dass, S. Role of Varying Ionic Strength on the Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Efficiency. Sol. Energy 2022, 247, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinque, B.; Escobedo, S.; de Lasa, H. Hydrogen Production via Pd-TiO2 Photocatalytic Water Splitting under Near-UV and Visible Light: Analysis of the Reaction Mechanism. Catalysts 2021, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.-H.; Nguyen, T.-A.; Le, M.-V.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, J.C.-S. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production from Seawater Splitting: Current Status, Challenges, Strategies and Prospective Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, A.K. Chemical Hardness-Driven Interpretable Machine Learning Approach for Rapid Search of Photocatalysts. Npj Comput. Mater. 2021, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, D.; Xu, P.; Xue, W.; Lei, L.; Cheng, M.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Deng, R. Semiconductor-Based Photocatalysts for Photocatalytic and Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting: Will We Stop with Photocorrosion? J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 2286–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Chen, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, L. C, N-Vacancies and Br Dopant Co-Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Evolution of g-C3N4 from Water and Simulated Seawater Splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-R.; Chang, Y.-C.; Ko, F.-H. One-Pot Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of In2S3/In2O3 Nanosheets as Highly Active Visible Light Photocatalysts for Seawater Splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 52, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imizcoz, M.; Puga, A.V. Assessment of Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production from Biomass or Wastewaters Depending on the Metal Co-Catalyst and Its Deposition Method on TiO2. Catalysts 2019, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa Reyes, M.; Camposeco, R.; Rodríguez González, V. Wastewater Contaminated with Hydrazine as Scavenger Agent for Hydrogen Production by Cu/Ti Nanostructures. Catalysts 2021, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpin, A.; Jones, G.; Jones, S.; Zheng, W.; Cookson, J.; York, A.P.E.; Collier, P.J.; Tsang, S.C.E. Quantitative Differences in Sulfur Poisoning Phenomena over Ruthenium and Palladium: An Attempt To Deconvolute Geometric and Electronic Poisoning Effects Using Model Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.-P. Renewable Feedstocks: The Problem of Catalyst Deactivation and Its Mitigation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13186–13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Luan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, Q.; Liu, W.; Yan, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, C. The Interference Mechanism of Na+ and Cl- on Photocatalytic Properties of Phosphate-Oxygen Co-Doped Graphite Carbon Nitride for Hydrogen Production from Water Splitting: Experimental and Theoretical Calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh-Afruzi, F. 12 - Synergistic Photocatalytic Effect. In Heterogeneous Micro and Nanoscale Composites for the Catalysis of Organic Reactions; Maleki, A., Ed.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 183–195 ISBN 978-0-12-824527-9.
- Hota, P.; Das, A.; Maiti, D.K. A Short Review on Generation of Green Fuel Hydrogen through Water Splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2023, 48, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Rauf, S.; Irfan, M.; Hayat, A.; M. Alghamdi, M.; A. El-Zahhar, A.; Ghernaout, D.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Lv, W. Recent Developments, Advances and Strategies in Heterogeneous Photocatalysts for Water Splitting. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 1286–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, M.; Hajra, S.; Irshad, M.; Usman, M.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A.; Ashraf, W.M. Hydrogen Production Using TiO2-Based Photocatalysts: A Comprehensive Review. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 25640–25648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldoni, A.; Altomare, M.; Zoppellaro, G.; Liu, N.; Kment, Š.; Zbořil, R.; Schmuki, P. Photocatalysis with Reduced TiO2: From Black TiO2 to Cocatalyst-Free Hydrogen Production. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.J. Semiconductor Band Structure, Symmetry, and Molecular Interface Hybridization for the Chemist. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 5735–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K. Photocatalytic Water Splitting Using Semiconductor Particles: History and Recent Developments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2011, 12, 237–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabasi Lee, S.; Lakhera, S.K.; Yong, K. Strategies to Enhance Interfacial Spatial Charge Separation for High-Efficiency Photocatalytic Overall Water-Splitting: A Review. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2023, 4, 2300130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Hasija, V.; Malhotra, M.; Verma, P.K.; Parwaz Khan, A.A.; Thakur, S.; Van Le, Q.; Phan Quang, H.H.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Singh, P.; et al. A Review of CdS-Based S-Scheme for Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Synthetic Strategy and Identification Techniques. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 52, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yates, J.T.Jr. Band Bending in Semiconductors: Chemical and Physical Consequences at Surfaces and Interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5520–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Antonietti, M. Polymeric Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Heterogeneous Organocatalyst: From Photochemistry to Multipurpose Catalysis to Sustainable Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Qi, Y.; Li, C.; Domen, K.; Zhang, F. Surface Strategies for Particulate Photocatalysts toward Artificial Photosynthesis. Joule 2018, 2, 2260–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lan, Z.-A.; Wang, X. Surface Engineering of Graphitic Carbon Nitride Polymers with Cocatalysts for Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 5261–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashina, K.; Iwase, A.; Ng, Y.H.; Amal, R.; Kudo, A. Z-Schematic Water Splitting into H2 and O2 Using Metal Sulfide as a Hydrogen-Evolving Photocatalyst and Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Solid-State Electron Mediator. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Ma, Y.; Zettsu, N.; Vequizo, J.J.M.; Gu, C.; Yamakata, A.; Hisatomi, T.; Takata, T.; Domen, K. Carbon Nanotubes as a Solid-State Electron Mediator for Visible-Light-Driven Z-Scheme Overall Water Splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 14829–14834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageshima, Y.; Gomyo, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Inuzuka, H.; Suzuki, H.; Abe, R.; Teshima, K.; Domen, K.; Nishikiori, H. Z-Scheme Overall Water Splitting Using ZnxCd1–xSe Particles Coated with Metal Cyanoferrates as Hydrogen Evolution Photocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 8004–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qi, Y.; Hisatomi, T.; Ding, Q.; Asai, T.; Li, Z.; Ma, S.S.K.; Zhang, F.; Domen, K.; Li, C. Efficient Visible-Light-Driven Z-Scheme Overall Water Splitting Using a MgTa2O6−N /TaON Heterostructure Photocatalyst for H2 Evolution. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 8618–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, N.; Ye, W.; Ju, H.; Shi, L.; Long, R.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, Y. Noble-Metal-Free Janus-like Structures by Cation Exchange for Z-Scheme Photocatalytic Water Splitting under Broadband Light Irradiation. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 4270–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Iwase, A.; Kudo, A. Role of Iron Ion Electron Mediator on Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting under Visible Light Irradiation Using Z-Scheme Systems. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, B.; Chu, J.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, P. Oxygen Vacancy-Induced Construction of CoO/h-TiO2 Z-Scheme Heterostructures for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 28945–28955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Shuaib, S.S.A.; Jiang, Y.; Bai, J.; Wei, Y.; Sun, S. Construction of SrTiO3/Ti3C2/TiO2 Z-Scheme Derived from Multilayer Ti3C2 MXene for Efficient Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hisatomi, T.; Ma, S.S.K.; Li, Y.; Domen, K. Core/Shell Structured La- and Rh-Codoped SrTiO3 as a Hydrogen Evolution Photocatalyst in Z-Scheme Overall Water Splitting under Visible Light Irradiation. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4144–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Nishioka, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Hirai, S.; Yanagisawa, K.; Eguchi, M.; Miseki, Y.; Yokoi, T.; Yui, T.; Kimoto, K.; et al. An Artificial Z-Scheme Constructed from Dye-Sensitized Metal Oxide Nanosheets for Visible Light-Driven Overall Water Splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 8412–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Hisatomi, T.; Vequizo, J.J.M.; Suzuki, S.; Chen, S.; Nakabayashi, M.; Lin, L.; Pan, Z.; Kariya, N.; et al. Sequential Cocatalyst Decoration on BaTaO2N towards Highly-Active Z-Scheme Water Splitting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Su, W. Simultaneous Enhancements in Photoactivity and Anti-Photocorrosion of Z-Scheme Mn0.25Cd0.75S/WO3 for Solar Water Splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 268, 118444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Kahng, S.; Hyeun Kim, J. Z-Scheme Assisted ZnO/Cu2O-CuO Photocatalysts to Increase Photoactive Electrons in Hydrogen Evolution by Water Splitting. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 204, 110211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X. 2D BiVO4/g-C3N4 Z-Scheme Photocatalyst for Enhanced Overall Water Splitting. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 10836–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Shi, R.; Wang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Che, C.-M.; Chen, Y. Direct Z-Scheme Hetero-Phase Junction of Black/Red Phosphorus for Photocatalytic Water Splitting. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11917–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.-J.; Putri, L.K.; Kong, X.Y.; Teh, Y.W.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Chai, S.-P. Z-Scheme Photocatalytic Systems for Solar Water Splitting. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Lin, L.; Takata, T.; Hisatomi, T.; Domen, K. A Perspective on Two Pathways of Photocatalytic Water Splitting and Their Practical Application Systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 6586–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.-F.; Wu, X.; Yang, J. Material Design for Photocatalytic Water Splitting from a Theoretical Perspective. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Meng, A.; Li, Z. Interfacial Chemical Bond and Internal Electric Field Modulated Z-Scheme Sv-ZnIn2S4/MoSe2 Photocatalyst for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwin Malefane, M.; John Mafa, P.; Thokozani Innocent Nkambule, T.; Elizabeth Managa, M.; Tawanda Kuvarega, A. Modulation of Z-Scheme Photocatalysts for Pharmaceuticals Remediation and Pathogen Inactivation: Design Devotion, Concept Examination, and Developments. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 138894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, W.; Jin, B.; Feng, Q.; Huang, J.; Jiao, Z. Advances in Z-Scheme Semiconductor Photocatalysts for the Photoelectrochemical Applications: A Review. Carbon Energy 2022, 4, 294–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Guan, X.; Zong, S.; Dai, A.; Qu, J. Cocatalysts for Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting: A Mini Review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Ueno, K.; Mori, Y.; Oshikiri, T.; Misawa, H. Cocatalyst Effects on Hydrogen Evolution in a Plasmon-Induced Water-Splitting System. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 8889–8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, M.; Cui, W.; Li, K.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F.; Sun, Y. Light-Induced Dynamic Stability of Oxygen Vacancies in BiSbO4 for Efficient Photocatalytic Formaldehyde Degradation. ENERGY Environ. Mater. 2022, 5, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Feng, W. Investigation on the Structural and Photocatalytic Performance of Oxygen-Vacancy-Enriched SnO2-CeO2 Heterostructures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanabe, K. Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Quantitative Approaches toward Photocatalyst by Design. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8006–8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, C.S.; Nalajala, N. A Scalable and Thin Film Approach for Solar Hydrogen Generation: A Review on Enhanced Photocatalytic Water Splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 1353–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.S.; Rajendran, S.; Nalajala, N.; Mathew, T.; Gopinath, C.S. Electronically Integrated Mesoporous Ag–TiO2 Nanocomposite Thin Films for Efficient Solar Hydrogen Production in Direct Sunlight. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo Camacho, S.Y.; Rey, A.; Hernández-Alonso, M.D.; Llorca, J.; Medina, F.; Contreras, S. Pd/TiO2-WO3 Photocatalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Water-Methanol Mixtures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Teng, F.; Tang, A.; Yin, Y. Fluorine-Assisted Structural Engineering of Colloidal Anatase TiO2 Hierarchical Nanocrystals for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 22575–22584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Huang, H.; Kubota, M.; He, Z.; Kobayashi, N.; Zhou, X.; Jin, B.; Luo, J. Synergetic Effect of MoS2 and G-C3N4 as Cocatalysts for Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Production Activity of TiO2. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 76, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-T.; Chan, A.; Al-Azri, Z.H.N.; Dosado, A.G.; Nadeem, M.A.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Idriss, H.; Waterhouse, G.I.N. Effect of TiO2 Polymorph and Alcohol Sacrificial Agent on the Activity of Au/TiO2 Photocatalysts for H2 Production in Alcohol–Water Mixtures. J. Catal. 2015, 329, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomani, F.; Shawaqfah, M.; Alkasrawi, M. Solar-Driven Hydrogen Production from a Water-Splitting Cycle Based on Carbon-TiO2 Nano-Tubes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 3294–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.G.; Sarkar, A.; Zade, S.S. The Type-II n-n Inorganic/Organic Nano-Heterojunction of Ti3+<math><msup Is="true"><mrow Is="true"></Mrow><mrow Is="true"><mn Is="true">3</Mn><mo Is="true">+</Mo></Mrow></Msup></Math> Self-Doped TiO2<math><msub Is="true"><mrow Is="true"></Mrow><mrow Is="true"><mn Is="true">2</Mn></Mrow></Msub></Math> Nanorods and Conjugated Co-Polymers for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting and Photocatalytic Dye Degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Varma, R.S. Selectivity Enhancement in Heterogeneous Photocatalytic Transformations. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 1445–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, P.; Hou, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Xi, X.; Hou, W. Ordered Layered N-Doped KTiNbO5/g-C3N4 Heterojunction with Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 228, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Warren, S.; Thimsen, E. Plasmonic Solar Water Splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5133–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, K.; Sk, S.; Chouti, S.; Gonuguntla, S.; Ega, S.P.; Tiwari, A.; Pal, U. Tailoring Hierarchical Porous TiO2 Based Ternary rGO/NiO/TiO2 Photocatalyst for Efficient Hydrogen Production and Degradation of Rhodamine B. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1235, 130222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navakoteswara Rao, V.; Kwon, H.; Lee, Y.; Ravi, P.; Won Ahn, C.; Kim, K.; Mo Yang, J.-. Synergistic Integration of MXene Nanosheets with CdS@TiO2 Core@shell S-Scheme Photocatalyst for Augmented Hydrogen Generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, I.M.; Kalimuthu, S.; P, G.P.; Sekar, K.; Rajendran, S. Hierarchical TiO2 Spheroids Decorated G-C3N4 Nanocomposite for Solar Driven Hydrogen Production and Water Depollution. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 3709–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, Z. Building Triple Shelled ZnO Hollow Microspheres Decorated TiO2 Nanotree to Boost Light Harvesting and Reduced Charges Recombination in Dye Sensitized Solar Cell. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 149, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowards, K.; Medina, H. Hierarchical Enhanced Surface Area Structures and Their Associated Applications with Titania. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 35, 101962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Diaz, M.-I.; Lecestre, A.; Salvagnac, L.; Bounor, B.; Pech, D.; Djafari-Rouhani, M.; Esteve, A.; Rossi, C. High Surface Area TiO2 Photocatalyst for H2 Production through Silicon Micromachining. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 588, 152919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Gautam, A.; Sk, S.; Gavali, D.S.; Thapa, R.; Pal, U. Controlled Loading of MoS2 on Hierarchical Porous TiO2 for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 11950–11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, M.; Pan, K.; Guo, L.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Lin, K.; Zhou, W. Surface Engineering of Mesoporous Anatase Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes for Rapid Spatial Charge Separation on Horizontal-Vertical Dimensions and Efficient Solar-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 586, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, J.; Ma, D.; Li, M. In-Situ Construction of S-Scheme (BiO)2CO3/TiO2 Heterojunctions with Enriched Oxygen Vacancies and Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance. Solid State Sci. 2023, 144, 107305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Cui, X.; Jin, M.; Xie, T.; Liu, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Interfacial Engineering of TiO2/Ti3C2 MXene/Carbon Nitride Hybrids Boosting Charge Transfer for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2102765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, D.K.; Chi, W.S.; Jeon, H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.H. High Efficiency Solid-State Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Assembled with Hierarchical Anatase Pine Tree-like TiO2 Nanotubes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J. Engineering of a N-Doped Anatase/Rutile TiO2 Heterophase Junction via In Situ Phase Growth for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 22806–22818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Song, W.; Li, W. Phase Transformation Strategies for the Construction of Heterojunction TiO2 Photocatalysts. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, e202301489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Xia, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, F.; et al. Two-Dimensional Lateral Anatase-Rutile TiO2 Phase Junctions with Oxygen Vacancies for Robust Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 648, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Wu, C.; Ma, J.; Chang, S.-H.; Liu, W. Interface Engineering of Ti3C2 MXene Assisted Anatase/Rutile TiO2 with Hetero-Phase Junction for Enhancing the Photocatalytic Activity of Tetracycline Hydrochloride Removal and H2 Production. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; You, W.; Tian, K.; Kong, E.; Ye, X.; Wang, Y.; Ye, J. Construction of TiO2(B)/Anatase Heterophase Junctions via a Water-Induced Phase Transformation Strategy for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Langmuir 2022, 38, 15282–15293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Niu, P.; Yang, Y.; Chen, R.; Yin, L.-C.; Fan, F.; Liu, G. Constructing Anatase–Brookite TiO2 Phase Junction by Thermal Topotactic Transition to Promote Charge Separation for Superior Photocatalytic H2 Generation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, Z.; Kang, Y.S. Facile Preparation of Hierarchical TiO2 Nano Structures: Growth Mechanism and Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Production from Water Splitting Using Methanol as a Sacrificial Reagent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 10342–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Qi, L.; Jaroniec, M. Hydrogen Production by Photocatalytic Water Splitting over Pt/TiO2 Nanosheets with Exposed (001) Facets. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 13118–13125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wang, G.; Tan, Y. Plasmonic Pt Nanoparticles—TiO2 Hierarchical Nano-Architecture as a Visible Light Photocatalyst for Water Splitting. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Chen, L. Controllable One-Step Synthesis of Mixed-Phase TiO2 Nanocrystals with Equivalent Anatase/Rutile Ratio for Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Ozkan, S.; Hwang, I.; Mazare, A.; Schmuki, P. TiO2 Nanotubes with Laterally Spaced Ordering Enable Optimized Hierarchical Structures with Significantly Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Generation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16868–16873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Xue, J.; Jia, S.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jia, H.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y. Self-Doping Surface Oxygen Vacancy-Induced Lattice Strains for Enhancing Visible Light-Driven Photocatalytic H2 Evolution over Black TiO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18758–18771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.-S.; Hong, M.; Kong, W.-L.; Zhao, Q.-C.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Oxygen Vacancy Defects and Cobalt Nanoparticle-Mediated Charge Separation in Black Ti3+ Self-Doped TiO2 Mesoporous Nanotubes for Enhanced Solar-Driven Hydrogen Evolution and Tetracycline Degradation. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 2885–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Xiong, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Z. Ultrathin 2D Photocatalysts: Electronic-Structure Tailoring, Hybridization, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldoni, A.; Allieta, M.; Santangelo, S.; Marelli, M.; Fabbri, F.; Cappelli, S.; Bianchi, C.L.; Psaro, R.; Dal Santo, V. Effect of Nature and Location of Defects on Bandgap Narrowing in Black TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7600–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Y.; Xiang, Q. Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Activity of Carbon and Nitrogen Self-Doped TiO2 Hollow Sphere with the Creation of Oxygen Vacancy and Ti3+. Mater. Today Energy 2018, 10, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.-J.; Tan, L.-L.; Chai, S.-P.; Yong, S.-T.; Mohamed, A.R. Self-Assembly of Nitrogen-Doped TiO2 with Exposed {001} Facets on a Graphene Scaffold as Photo-Active Hybrid Nanostructures for Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Methane. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1528–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O.; Li, Q. Halogen Element Modified Titanium Dioxide for Visible Light Photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, L.K.; Antony, R.P.; Mathews, T.; Walczak, L.; Gopinath, C.S. A Study on Doped Heterojunctions in TiO2 Nanotubes: An Efficient Photocatalyst for Solar Water Splitting. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Li, Z.; Yu, H.; Shang, L.; Zhou, C.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wu, L.-Z.; Zhang, T. Effect of Nitrogen Doping Level on the Performance of N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dot/TiO2 Composites for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4650–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Lv, C.; Meng, X.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z.; Huang, K. In Situ Characterization Techniques Applied in Photocatalysis: A Review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barawi, M.; A. Mesa, C.; Collado, L.; J. Villar-García, I.; Oropeza, F.; O’Shea, V.A. de la P.; García-Tecedor, M. Latest Advances in in Situ and Operando X-Ray-Based Techniques for the Characterisation of Photoelectrocatalytic Systems. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 23125–23146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermakov, A.Ye.; Galakhov, V.R.; Minin, A.S.; Mesilov, V.V.; Uimin, M.A.; Kuepper, K.; Bartkowski, S.; Molochnikov, L.S.; Konev, A.S.; Gaviko, V.S.; et al. Magnetic Properties, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance, and Photoelectron Spectroscopy Studies of Nanocrystalline TiO2 Co-Doped with Al and Fe. Phys. Status Solidi B 2021, 258, 2000399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Madanat, O.; Nunes, B.N.; AlSalka, Y.; Hakki, A.; Curti, M.; Patrocinio, A.O.T.; Bahnemann, D.W. Application of EPR Spectroscopy in TiO2 and Nb2O5 Photocatalysis. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, N.; Xiao, B.; Shen, Y.; Zi, B.; Qiu, Z.; Zhou, T.; Hu, R.; Zhan, W.; Qiu, G.; et al. C,N Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles with Abundant Surface Ti3+ and Oxygen Vacancies for Visible-Light Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 21842–21851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, S.M.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Ibrahim, S.A.; El-Bery, H.M. Boosting Photocatalytic Water Splitting of TiO2 Using Metal (Ru, Co, or Ni) Co-Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, D.; Namdeo, A.; Golder, A.K.; Peela, N.R. Ag-Doped TiO2 Photocatalysts with Effective Charge Transfer for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Production through Water Splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 2729–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bery, H.M.; Abdelhamid, H.N. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation via Water Splitting Using ZIF-67 Derived Co3O4@C/TiO2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; He, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Z. In Situ Loading CuO Quantum Dots on TiO2 Nanosheets as Cocatalyst for Improved Photocatalytic Water Splitting. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 813, 152184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ke, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Wang, S. Co3O4 Quantum Dots/TiO2 Nanobelt Hybrids for Highly Efficient Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 236, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. Enhanced Photocatalytic H2-Production Activity of Anatase TiO2 Nanosheet by Selectively Depositing Dual-Cocatalysts on {101} and {001} Facets. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, H.; Han, A.; Yu, X.; Du, P. Noble Metal-Free Cobalt Oxide (CoOx) Nanoparticles Loaded on Titanium Dioxide/Cadmium Sulfide Composite for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production from Water. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 13353–13360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, G.L.; Bernareggi, M.; Selli, E. Redox Dynamics of Pt and Cu Nanoparticles on TiO2 during the Photocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions Studied by In Situ Modulated Excitation X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 12879–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dholam, R.; Patel, N.; Adami, M.; Miotello, A. Hydrogen Production by Photocatalytic Water-Splitting Using Cr- or Fe-Doped TiO2 Composite Thin Films Photocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 5337–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, A.T.; Gillan, E.G. Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution from Transition-Metal Surface-Modified TiO2. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Xie, L.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, X. Direct Microwave–Hydrothermal Synthesis of Fe-Doped Titania with Extended Visible-Light Response and Enhanced H2-Production Performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero-Romero, M.J.; Santaclara, J.G.; Oar-Arteta, L.; van Koppen, L.; Osadchii, D.Y.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2 and Fe-Doped TiO2 Prepared by Metal Organic Framework-Mediated Synthesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Muñoz-Batista, M.J.; Kubacka, A.; Luque, R.; Fernández-García, M. Enhancing Photocatalytic Performance of TiO2 in H2 Evolution via Ru Co-Catalyst Deposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 238, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido Melián, E.; Nereida Suárez, M.; Jardiel, T.; Calatayud, D.G.; del Campo, A.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M.; Araña, J.; González Díaz, O.M. Highly Photoactive TiO2 Microspheres for Photocatalytic Production of Hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 24653–24666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Choi, K.; Schreck, M.; Liu, T.; Tervoort, E.; Niederberger, M. Gas-Phase Nitrogen Doping of Monolithic TiO2 Nanoparticle-Based Aerogels for Efficient Visible Light-Driven Photocatalytic H2 Production. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 53691–53701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Liu, E.; Liang, X.; Hu, X.; Fan, J. Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution from Water Splitting Using Fe-Ni Codoped and Ag Deposited Anatase TiO2 Synthesized by Solvothermal Method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Fu, G.; Hu, Y. Passivation of Defect States in Anatase TiO2 Hollow Spheres with Mg Doping: Realizing Efficient Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Song, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, C.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Q. Single-Atomic Pt Sites Anchored on Defective TiO2 Nanosheets as a Superior Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Shen, H.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, T. Synthesis of High Efficient Cu/TiO2 Photocatalysts by Grinding and Their Size-Dependent Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 409, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Luo, B.; Lyu, M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Du, A.; Wang, L. Molten-Salt-Mediated Synthesis of an Atomic Nickel Co-Catalyst on TiO2 for Improved Photocatalytic H2 Evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7230–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Wu, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Yu, H.; Yu, J. Simultaneous Realization of Direct Photoinduced Deposition and Improved H2-Evolution Performance of Sn-Nanoparticle-Modified TiO2 Photocatalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10084–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, V.J.; Kumar, M.K.; Nair, A.S.; Kheng, T.L.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Ramakrishna, S. Visible Light Photocatalytic Water Splitting for Hydrogen Production from N-TiO2 Rice Grain Shaped Electrospun Nanostructures. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 8897–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Tade, M.O.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Facile Synthesis of Carbon-Doped Mesoporous Anatase TiO2 for the Enhanced Visible-Light Driven Photocatalysis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13971–13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmat, M.; El-Hosainy, H.; Tahawy, R.; Jevasuwan, W.; Tsunoji, N.; Fukata, N.; Ide, Y. Nitrogen Doping-Mediated Oxygen Vacancies Enhancing Co-Catalyst-Free Solar Photocatalytic H2 Production Activity in Anatase TiO2 Nanosheet Assembly. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 285, 119755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, W. In-Situ S-Doped Porous Anatase TiO2 Nanopillars for High-Efficient Visible-Light Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Shen, X.; Yu, R.; Ma, M.; Liu, R. Porous Carbon-Doped TiO2 on TiC Nanostructures for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production under Visible Light. J. Catal. 2017, 347, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Shibata, K.; Xiao, Y.; Du, S.; Tanaka, T.; Qi, Y.; Ishitani, O.; Maeda, K.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, F. A Band-to-Band Transition Visible-Light-Responsive Anatase Titania Photocatalyst by N,F-Codoping for Water Splitting and CO 2 Reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, J.; Sheng, X.; Fang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W. Hierarchical Honeycomb Br-, N-Codoped TiO2 with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic H2 Production. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18796–18804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fiaz, M.; Kim, J.; Carl, N.; Kim, Y.K. Kinetic Evidence for Type-II Heterojunction and Z-Scheme Interactions in g-C3N4/TiO2 Nanotube-Based Photocatalysts in Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 5197–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Seyed Dorraji, M.S.; Rasoulifard, M.H. Boosting Photo-Charge Transfer in 3D/2D TiO2@Ti3C2 MXene/Bi2S3 Schottky/Z-Scheme Heterojunction for Photocatalytic Antibiotic Degradation and H2 Evolution. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 262, 110820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, M.; Wei, G.; Nie, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y. Synergistic Modulation on Atomic-Level 2D/2D Ti3C2/Svac-ZnIn2S4 Heterojunction for Photocatalytic H2 Production. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chen, W.; Hao, L.; Shen, R.; Zhang, P.; Li, N.; Li, X. Assembling Ti3C2 MXene into ZnIn2S4-NiSe2 S-Scheme Heterojunction with Multiple Charge Transfer Channels for Accelerated Photocatalytic H2 Generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 447, 137488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, L.; Nayak, S.; Parida, K. Rationally Designed Ti3C2/N, S-TiO2/g-C3N4 Ternary Heterostructure with Spatial Charge Separation for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 621, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Ye, H.; Xie, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, L. Strong Interaction between Sulfur Sites and Oxygen Vacancies in Z-Scheme ZnIn2S4/TiO2-x Heterojunction for Improved Photocatalytic Hydrogen Yield and Stability. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Hou, J.; Cao, D.; Wang, Q. Construction of Z-Scheme CdS/Ag/TiO2 NTs Photocatalysts for Photocatalytic Dye Degradation and Hydrogen Evolution. Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 276, 121215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chi, D.; Chen, R.; Ma, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, B. N-Doped C Layer Boost Z-Scheme Interfacial Charge Transfer in TiO2/ZnIn2S4 Heterojunctions for Enhance Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Renew. Energy 2023, 219, 119494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, R.; Zhang, T. Strain Engineering: A Boosting Strategy for Photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, T.; Rajendran, S.; Zeng, Z.; Qin, J.; Zhang, X. A Long-Standing Polarized Electric Field in TiO2@BaTiO3/CdS Nanocomposite for Effective Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Fuel 2022, 314, 122758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.K.; Majhi, S.M.; Jeong, K.-U.; Lee, I.-H.; Yu, Y.T. Nitrogen Doping on the Core-Shell Structured Au@TiO2 Nanoparticles and Its Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution under Visible Light Irradiation. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Yamashita, H.; Verma, P. Unveiling the Critical Role of High/Low-Index Facets in Nanostructured Energy Materials for Enhancing the Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. ChemCatChem n/a, e202401672. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Poyraz, A.S.; Kuo, C.-H.; Miao, R.; Meng, Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Jiang, T.; Wenos, C.; Suib, S.L. Crystalline Mixed Phase (Anatase/Rutile) Mesoporous Titanium Dioxides for Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarage, G.W.C.; Hakkoum, H.; Comini, E. Recent Advancements in TiO2 Nanostructures: Sustainable Synthesis and Gas Sensing. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; J. Desroches, G.; J. Macfarlane, R. Ordered Polymer Composite Materials: Challenges and Opportunities. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaor, D.A.H.; Sorrell, C.C. Review of the Anatase to Rutile Phase Transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, Z.; Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Yan, P.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Zong, X.; Han, H.; et al. Understanding the Anatase–Rutile Phase Junction in Charge Separation and Transfer in a TiO2 Electrode for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6076–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Afzal, N.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J. Structure-Activity Relationship of Defective Metal-Based Photocatalysts for Water Splitting: Experimental and Theoretical Perspectives. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.Z. Earth-Abundant Cocatalysts for Semiconductor-Based Photocatalytic Water Splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7787–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, B.; Han, K.; Mul, G. Driving Surface Redox Reactions in Heterogeneous Photocatalysis: The Active State of Illuminated Semiconductor-Supported Nanoparticles during Overall Water-Splitting. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9154–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Dong, F.; Lu, Z.; Lv, E.; Dong, X.; Li, H.; Yuan, Z.; Peng, X.; Yang, S.; et al. Dynamic Transformation of Active Sites in Energy and Environmental Catalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 6435–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Stam, W. The Necessity for Multiscale In Situ Characterization of Tailored Electrocatalyst Nanoparticle Stability. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salciccioli, M.; Stamatakis, M.; Caratzoulas, S.; Vlachos, D.G. A Review of Multiscale Modeling of Metal-Catalyzed Reactions: Mechanism Development for Complexity and Emergent Behavior. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 4319–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.M.O.; Kharissova, O.V.; González, L.T.; Méndez-Rojas, M.A.; Quezada, T.S.; Méndez, Y.P. Kharissova, O.V., Torres-Martínez, L.M., Kharisov, B.I., Eds.; Scalable Synthesis of Nanomaterials. In Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 899–921. ISBN 978-3-030-36268-3. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A Review of Synthesis Methods, Properties, Recent Progress, and Challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, N.; Schmuki, P. Photocatalysis with TiO2 Nanotubes: “Colorful” Reactivity and Designing Site-Specific Photocatalytic Centers into TiO2 Nanotubes. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3210–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakata, A.; Ishibashi, T.; Onishi, H. Kinetics of the Photocatalytic Water-Splitting Reaction on TiO2 and Pt/TiO2 Studied by Time-Resolved Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2003, 199, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, Y.-K.; Hu, L.; Zheng, J.; Prabhakaran, D.; Wu, S.; Puchtler, T.J.; Li, M.; Wong, K.-Y.; Taylor, R.A.; et al. Photocatalytic Water Splitting by N-TiO2 on MgO (111) with Exceptional Quantum Efficiencies at Elevated Temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lu, G.; Li, S. The Role of Cu(I) Species for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation Over CuOx/TiO2. Catal. Lett. 2009, 133, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Wang, T.; Gong, J. Multifunctional TiO2 Overlayer for P-Si/n-CdS Heterojunction Photocathode with Improved Efficiency and Stability. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K. Photocatalytic Properties of Rutile TiO2 Powder for Overall Water Splitting. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, B.; Sun, J.; Gong, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production from Seawater by TiO2/RuO2 Hybrid Nanofiber with Enhanced Light Absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 654, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, M.; Biriukov, D.; Předota, M.; Roke, S.; Marchioro, A. Surface Potential and Interfacial Water Order at the Amorphous TiO2 Nanoparticle/Aqueous Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 10961–10974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maghsoodi, M.; Jacquin, C.; Teychené, B.; Lesage, G.; Snow, S.D. Delineating the Effects of Molecular and Colloidal Interactions of Dissolved Organic Matter on Titania Photocatalysis. Langmuir 2023, 39, 3752–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, F.; Di Liberto, G.; Pacchioni, G. pH- and Facet-Dependent Surface Chemistry of TiO2 in Aqueous Environment from First Principles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 11216–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Y.; Ku, Y. Effect of Solution pH on the Adsorption and Photocatalytic Reaction Behaviors of Dyes Using TiO2 and Nafion-Coated TiO2. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, A.; Yao, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Shah, J.H.; Han, H. Strategies for Efficient Charge Separation and Transfer in Artificial Photosynthesis of Solar Fuels. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4277–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, T.; Schwanitz, K.; Kaiser, B.; Hajduk, A.; Lebedev, M.V.; Jaegermann, W. Semiconductor/Electrolyte Interfaces for Solar Energy Conversion: Interface Studies by Synchrotron Induced Photoelectron Spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2017, 221, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Gong, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, S.; Ye, J.; Wang, Z.; Dionysiou, D.D. Dissolved Organic Matter Promotes Photocatalytic Degradation of Refractory Organic Pollutants in Water by Forming Hydrogen Bonding with Photocatalyst. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nam, S.-N.; Kim, J.; Oh, J. Photocatalytic Degradation of Dissolved Organic Matter under ZnO-Catalyzed Artificial Sunlight Irradiation System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colón, G.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Macı́as, M.; Navı́o, J.A. Enhancement of TiO2/C Photocatalytic Activity by Sulfate Promotion. Appl. Catal. Gen. 2004, 259, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarmelina, M.; W. Dlamini, M.; Pattisson, S.; R. Davies, P.; J. Hutchings, G.; A. Catlow, C.R. The Effect of Dissolved Chlorides on the Photocatalytic Degradation Properties of Titania in Wastewater Treatment. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 4161–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Guo, Q.; Tang, G.; Peng, W.; Luo, Y.; He, D. Effects of Inorganic Ions on the Photocatalytic Degradation of Carbamazepine. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2019, 9, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Bahnemann, D.W. Undesired Role of Sacrificial Reagents in Photocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 3479–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, C.M.; Schneider, P.M.; Song, K.-T.; Yu, H.; Götz, R.; Haimerl, F.; Gubanova, E.; Zhou, J.; Schmidt, T.O.; Zhang, Q.; et al. How to Assess and Predict Electrical Double Layer Properties. Implications for Electrocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 12391–12462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsarskaia, O.; Roosen-Runge, F.; Schreiber, F. Multivalent Ions and Biomolecules: Attempting a Comprehensive Perspective. ChemPhysChem 2020, 21, 1742–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, B.; Abdullahi, A.S.; Fan, H. Understanding the Prototype Catalyst TiO Surface with the Help of Density Functional Theory Calculation. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2024, 14, e1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, S.; Pavone, M.; Fioravanti, A.; Santamaria Amato, L.; Maddalena, P. Charge Carrier Processes and Optical Properties in TiO2 and TiO2-Based Heterojunction Photocatalysts: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebre, S.T.; Kiefer, L.M.; Guo, F.; Yang, K.R.; Miller, C.; Liu, Y.; Kubiak, C.P.; Batista, V.S.; Lian, T. Amine Hole Scavengers Facilitate Both Electron and Hole Transfer in a Nanocrystal/Molecular Hybrid Photocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 3238–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSalka, Y.; Al-Madanat, O.; Hakki, A.; Bahnemann, D.W. Boosting the H2 Production Efficiency via Photocatalytic Organic Reforming: The Role of Additional Hole Scavenging System. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cherevan, A.S.; Hannecart, C.; Naghdi, S.; Nandan, S.P.; Gupta, T.; Eder, D. Ti-Based MOFs: New Insights on the Impact of Ligand Composition and Hole Scavengers on Stability, Charge Separation and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 283, 119626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, Y.; Cao, S.; Hu, W.; Piao, L.; Chen, X. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production from Seawater under Full Solar Spectrum without Sacrificial Reagents Using TiO2 Nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesupatham, M.S.; Augustin, A.; Agamendran, N.; Honnappa, B.; Shanmugam, M.; Sagayaraj, P.J.J.; Thennarasu, G.; Selvam, N.C.S.; Sekar, K. Photocatalytic Seawater Splitting for Hydrogen Fuel Production: Impact of Seawater Components and Accelerating Reagents on the Overall Performance. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 4727–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amore-Domenech, R.; Santiago, Ó.; Leo, T.J. Multicriteria Analysis of Seawater Electrolysis Technologies for Green Hydrogen Production at Sea. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, F. NiS Protective Layer for Repelling Chloride Ion Effectively for Water Oxidation on Photocatalytic Seawater Splitting. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 2618–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, C. Surface Passivation Engineering for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Catalysts 2023, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhera, S.K.; Kangeyan, K.P.; Yazhini S, C.; Golda A, S.; Bernaurdshaw, N. Advances in Hybrid Strategies for Enhanced Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Bridging Conventional and Emerging Methods. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2024, 11, 041305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, H.; Obata, K.; Wada, M.; Nishimoto, T.; Takanabe, K. Electrolyte Engineering Applying Concentrated Chloride Ions with Mixed Buffer Solutions for a Versatile High-Productivity Water-Splitting System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 12614–12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suguro, T.; Kishimoto, F.; Kariya, N.; Fukui, T.; Nakabayashi, M.; Shibata, N.; Takata, T.; Domen, K.; Takanabe, K. A Hygroscopic Nano-Membrane Coating Achieves Efficient Vapor-Fed Photocatalytic Water Splitting. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Qian, W.; Wang, X. Recent Advances in Phase-Engineered Photocatalysts: Classification and Diversified Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalothia, D.; Huang, T.-H.; Chang, C.-W.; Lin, T.-H.; Wu, S.-C.; Wang, K.-W.; Chen, T.-Y. High-Performance and Stable Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Achieved by Pt Trimer Decoration on Ultralow-Metal Loading Bimetallic PtPd Nanocatalysts. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 11142–11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Bo, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Piao, L. Precise Design of TiO2 Photocatalyst for Efficient Photocatalytic H2 Production from Seawater Splitting. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 55, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, Y.; Cao, S.; Hu, W.; Piao, L.; Chen, X. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production from Seawater under Full Solar Spectrum without Sacrificial Reagents Using TiO2 Nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Swain, G.; Dutta, S. Synthesis of Visible Light-Sensitive Photocatalysts for Hydrogen Production. Fuel 2024, 360, 130555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyub, M.M.; Chhetri, M.; Gupta, U.; Roy, A.; Rao, C.N.R. Photochemical and Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Generation by Splitting Seawater. Chem. – Eur. J. 2018, 24, 18455–18462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, H.; Kiuchi, M.; Jin, T. Pt/TiO2 Granular Photocatalysts for Hydrogen Production from Aqueous Glycerol Solution: Durability against Seawater Constituents and Dissolved Oxygen. Catal. Commun. 2018, 114, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Qin, J.; Rajendran, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R. WS2 and C-TiO2 Nanorods Acting as Effective Charge Separators on g-C3N4 to Boost Visible-Light Activated Hydrogen Production from Seawater. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 4077–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Z.; Marcus, K.; Li, Z.; Luo, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Yang, Y. MoS 2 /TiO 2 Heterostructures as Nonmetal Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Nuo Connor, P.K.; Wei Ho, G. Plasmonic Photothermic Directed Broadband Sunlight Harnessing for Seawater Catalysis and Desalination. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3151–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govinda raj, M.; Mahalingam, S.; Gnanarani, S.V.; Jayashree, C.; Ganeshraja, A.S.; Pugazhenthiran, N.; Rahaman, M.; Abinaya, S.; Senthil, B.; Kim, J. TiO2 Nanorod Decorated with MoS2 Nanospheres: An Efficient Dual-Functional Photocatalyst for Antibiotic Degradation and Hydrogen Production. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 142033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Abed, A.M.; Shaban, M.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Lei, G.; Abdullaev, S.; Mahariq, I. Superb Photocatalytic H2 Production/Tetracycline Pollutant Degradation by Synthesizing Novel and Recyclable Ternary g-C3N4-Based Photocatalyst: Characterization/Optimization/Mechanism/Toxicity Assessment. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 69, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yu, J.C.-C.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Wu, J.C.S.; Wang, X. A Dual-Function Photocatalytic System for Simultaneous Separating Hydrogen from Water Splitting and Photocatalytic Degradation of Phenol in a Twin-Reactor. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 239, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, S.; Al-Salem, S.M.; Manos, G.; Constantinou, A. Fuel Production Using Membrane Reactors: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.; Dai, Y. Progress on Simultaneous Photocatalytic Degradation of Pollutants and Production of Clean Energy: A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyle, M.D.; Bartholomew, C.H. Heterogeneous Catalyst Deactivation and Regeneration: A Review. Catalysts 2015, 5, 145–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Huo, W.; Li, G.; Choi, W.; An, T. Photocatalytic Mechanisms and Photocatalyst Deactivation during the Degradation of 5-Fluorouracil in Water. Catal. Today 2023, 410, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Shin, H.; Kang, M. Dual-Functional Cu-Fe Co-Doped TiO₂ Photocatalyst for Efficient Hydrogen Production and Phenol Degradation. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 55, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Rabboh, H.S.M.; Benaissa, M.; Hamdy, M.S.; Ahmed, M.A.; Glal, M. Synthesis of an Efficient, and Recyclable Mesoporous BiVO4/TiO2 Direct Z-Scheme Heterojunction by Sonochemical Route for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production and Photodegradation of Rhodamine B Dye in the Visible Region. Opt. Mater. 2021, 114, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshipour, S.; Mohammad-Alizadeh, S. Nickel Phthalocyanine@graphene Oxide/TiO2 as an Efficient Degradation Catalyst of Formic Acid toward Hydrogen Production. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elysabeth, T.; Dewi, E.L.; Ratnawati; Mulia, K. ; Slamet Simultaneous Photoelectrocatalytic Hydrogen Production and Ammonia Degradation Using Titania Nanotube-Based Photoanodes. Commun. Sci. Technol. 2024, 9, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, Y.; Azzi, H.; Sridharan, K.; Ji, S.; Choi, H.; Allan, M.G.; Benaissa, S.; Saidi-Bendahou, K.; Damptey, L.; Ribeiro, C.S.; et al. Facile Synthesis of Gram-Scale Mesoporous Ag/TiO2 Photocatalysts for Pharmaceutical Water Pollutant Removal and Green Hydrogen Generation. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Hu, Z.; Ao, Z.; Brudvig, G.W.; Tian, F.; Yu, J.C.; et al. Photocatalytically Recovering Hydrogen Energy from Wastewater Treatment Using MoS2 @TiO2 with Sulfur/Oxygen Dual-Defect. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 303, 120878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Zeng, G.; Li, C. Recovering Hydrogen Energy from Photocatalytic Treatment of Pharmaceutical-Contaminated Water Using Co3O4 Modified {001}/{101}-TiO2 Nanosheets. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, M. Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production and Degradation of Organic Pollutants from Fe (III) Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Shu, R.; Zhang, J.; Bu, E.; Liao, M.; Song, Q. A Novel Approach for Enhancing Hydrogen Production from Bio-Glycerol Photoreforming by Improving Colloidal Dispersion Stability. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlSalka, Y.; Hakki, A.; Fleisch, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding the Degradation Pathways of Oxalic Acid in Different Photocatalytic Systems: Towards Simultaneous Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2018, 366, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kuang, L.; Xiao, D.; Badireddy, A.R.; Hu, M.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, X.; Lee, E.S.; Marhaba, T.; Zhang, W. Hydrogen Production from Organic Fatty Acids Using Carbon-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles under Visible Light Irradiation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 4335–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-J.; Moon, G.; Kanazawa, T.; Maeda, K.; Choi, W. Selective Dual-Purpose Photocatalysis for Simultaneous H 2 Evolution and Mineralization of Organic Compounds Enabled by a Cr 2 O 3 Barrier Layer Coated on Rh/SrTiO 3. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9636–9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.I.; Ghaly, M.Y.; Ali, M.E.M. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production over Nanostructured Mesoporous Titania from Olive Mill Wastewater. Desalination 2011, 267, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Dong, N.; Yu, H.; Yin, W.; Zhu, F.; Gao, B.; Xu, S. Effective Inhibition of Chloride Ion Interference in Photocatalytic Process by Negatively Charged Molecularly Imprinted Photocatalyst: Behavior and Mechanism. Water Res. 2024, 262, 122040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-H.; Huang, C.-W.; Wu, J.C.S. Hydrogen Production from Semiconductor-Based Photocatalysis via Water Splitting. Catalysts 2012, 2, 490–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisnet, M.; Ribeiro, F.R. DEACTIVATION AND REGENERATION OF SOLID CATALYSTS. In Deactivation and Regeneration of Zeolite Catalysts; Catalytic Science Series; IMPERIAL COLLEGE PRESS, 2011; Vol. 9, pp. 3–18 ISBN 978-1-84816-637-0.
- Demir, M.E.; Chehade, G.; Dincer, I.; Yuzer, B.; Selcuk, H. Synergistic Effects of Advanced Oxidization Reactions in a Combination of TiO2 Photocatalysis for Hydrogen Production and Wastewater Treatment Applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 23856–23867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petala, A.; Mantzavinos, D.; Frontistis, Z. Impact of Water Matrix on the Photocatalytic Removal of Pharmaceuticals by Visible Light Active Materials. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, T.; Lin, L.; Hisatomi, T.; Domen, K. Best Practices for Assessing Performance of Photocatalytic Water Splitting Systems. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2406848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Domen, K. Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Recent Progress and Future Challenges. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beil, S.B.; Bonnet, S.; Casadevall, C.; Detz, R.J.; Eisenreich, F.; Glover, S.D.; Kerzig, C.; Næsborg, L.; Pullen, S.; Storch, G.; et al. Challenges and Future Perspectives in Photocatalysis: Conclusions from an Interdisciplinary Workshop. JACS Au 2024, 4, 2746–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Mou, T.; Pillai, H.S.; Wang, S.-H.; Huang, Y. Interpretable Machine Learning for Catalytic Materials Design toward Sustainability. Acc. Mater. Res. 2024, 5, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayo, D.D.K.; Goliatt, L.; Ganji, D. AI and Quantum Computing in Binary Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production 2024.
- Dmitrieva, A.P.; Fomkina, A.S.; Tracey, C.T.; Romanenko, E.A.; Ayati, A.; Krivoshapkin, P.V.; Krivoshapkina, E.F. AI and ML for Selecting Viable Electrocatalysts: Progress and Perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 31074–31102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X.; Tryk, D.A. TiO2 Photocatalysis and Related Surface Phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 515–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding TiO2 Photocatalysis: Mechanisms and Materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, S.; Ghaedi, M. Chapter 13 - Photocatalytic Reactors: Technological Status, Opportunities, and Challenges for Development and Industrial Upscaling. In Interface Science and Technology; Ghaedi, M., Ed.; Photocatalysis: Fundamental Processes and Applications; Elsevier, 2021; Vol. 32, pp. 761–790.
- Jamil, Q.; Rana, K.B.; Matoh, L. A CFD Study on Optimization of Mass Transfer and Light Distribution in a Photocatalytic Reactor with Immobilized Photocatalyst on Spheres. Water 2024, 16, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benefits of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs). Available online: https://www.energy.gov/ne/benefits-small-modular-reactors-smrs (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Nandy, S.; Ashok Savant, S.; Haussener, S. Prospects and Challenges in Designing Photocatalytic Particle Suspension Reactors for Solar Fuel Processing. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 9866–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Visioli, L.; Enzweiler, H. Photocatalytic Reactors and Their Scale up: Literature Review. Conjecturas 2022, 22, 509–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.S.O.; Santos, R.J.; Dias, M.M.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, C.G. Radiation Models for Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations of Photocatalytic Reactors. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 1059–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Hou, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L. Solar Concentrator with Uniform Irradiance for Particulate Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production System. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 16040–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.T.; Dai, Y.J.; Wang, R.Z.; Sumathy, K. Concentrated Solar Energy Applications Using Fresnel Lenses: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2588–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Le-The, H.; Karamanos, T.; Suryadharma, R.N.S.; van den Berg, A.; Pinkse, P.W.H.; Rockstuhl, C.; Shui, L.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Segerink, L.I. Plasmonic Nanocrystal Arrays on Photonic Crystals with Tailored Optical Resonances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 37657–37669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, A.; Lei, D.Y.; Fernández-Domínguez, A.I.; Sonnefraud, Y.; Maier, S.A.; Pendry, J.B. Plasmonic Light-Harvesting Devices over the Whole Visible Spectrum. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2574–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, Q.; Xia, Y. Plasmon-Induced Hot Electrons in Nanostructured Materials: Generation, Collection, and Application to Photochemistry. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 8597–8619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Canady, T.D.; Gupta, R.; Li, N.; Singamaneni, S.; Cunningham, B.T. Enhanced Plasmonic Photocatalysis through Synergistic Plasmonic–Photonic Hybridization. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 1994–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.; Lonergan, A.; McNulty, D.; Glynn, C.; Buckley, D.; Hu, C.; O’Dwyer, C. Semiconducting Metal Oxide Photonic Crystal Plasmonic Photocatalysts. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1901805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gu, Z.; Xu, W.; Tan, Y.; Fan, X.; Tan, D. Mixing Mass Transfer Mechanism and Dynamic Control of Gas-Liquid-Solid Multiphase Flow Based on VOF-DEM Coupling. Energy 2023, 272, 127015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ji, Y.-N.; Deng, W.-S.; Su, Y.-F. Process Intensification in Gas/Liquid/Solid Reaction in Trickle Bed Reactors: A Review. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1203–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.S.; Vitankar, V.S.; Dalvi, V.H.; Joshi, J.B. Solid Suspension and Solid-Liquid Mass Transfer in Stirred Reactors. In Handbook of Multiphase Flow Science and Technology; Yeoh, G.H., Joshi, J.B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 1491–1553. ISBN 978-981-287-092-6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Lyu, L.-M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lee, G.-C.; Hsiao, K.-Y.; Lu, M.-Y. Improved Mass-Transfer Enhances Photo-Driven Dye Degradation and H2 Evolution over a Few-Layer WS2/ZnO Heterostructure. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakachaka, V.M.; Tshangana, C.S.; Mamba, B.B.; Muleja, A.A. CFD-Assisted Process Optimization of an Integrated Photocatalytic Membrane System for Water Treatment. Membranes 2023, 13, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, A.; van Ommen, J.R.; Kreutzer, M.T.; Lammertink, R.G.H. Photocatalytic Reactor Design: Guidelines for Kinetic Investigation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 5349–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Gao, C.; Xie, Y.; Chen, J. Fluid Field Modulation in Mass Transfer for Efficient Photocatalysis. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H.; Ayati, B.; Ganjidoust, H. Mass Transfer Phenomenon in Photocatalytic Cascade Disc Reactor: Effects of Artificial Roughness and Flow Rate. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 116, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Tugaoen, H.; Brame, J.; Sinha, S.; Li, C.; Schoepf, J.; Hristovski, K.; Kim, J.-H.; Shang, C.; Westerhoff, P. Coupling Light Emitting Diodes with Photocatalyst-Coated Optical Fibers Improves Quantum Yield of Pollutant Oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13319–13326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Ling, L.; Westerhoff, P.; Shang, C. Evanescent Waves Modulate Energy Efficiency of Photocatalysis within TiO2 Coated Optical Fibers Illuminated Using LEDs. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Shang, C.; Westerhoff, P.; Ling, L. Novel Polymer Optical Fibers with High Mass-Loading g-C3N4 Embedded Metamaterial Porous Structures Achieve Rapid Micropollutant Degradation in Water. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, T.-H.; Doong, R.; Lai, Y.-J.S.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Zhao, Z.; Westerhoff, P. Boosting Hydrogen Production via Water Splitting: An ITO Plus g-C3N4 Nanomaterial Enabled Polymer Optical Fiber Design. ACS Mater. Lett. 2024, 6, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Javed, H.; Zhang, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Westerhoff, P.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Porous Electrospun Fibers Embedding TiO2 for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4285–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Rho, H.; Shapiro, N.; Ling, L.; Perreault, F.; Rittmann, B.; Westerhoff, P. Biofilm Inhibition on Surfaces by Ultraviolet Light Side-Emitted from Optical Fibres. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shapiro, N.D.; Mobasher, B.; Wang, T.-H.; Smith, D.; Sinha, S.; Ling, L.; Perreault, F.; Westerhoff, P. Subtractive Engineering of Polymer Cladding Induces Tunable UV-C Irradiation from Flexible Side-Emitting Optical Fibers for Biofilm Control in Curved Piping. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-H.; Chen, M.-J.; Lai, Y.S.; Doong, R.; Westerhoff, P.; Rittmann, B. High-Efficiency Photocatalytic H2O2 Production in a Dual Optical– and Membrane–Fiber System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6465–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-H.; Zhao, Z.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Ling, L.; Doong, R.; Westerhoff, P. Flexible Fiber Optoelectrodes Integrating Perovskite-Nafion-ITO Layers for Efficient Photoelectrocatalytic Water Purification. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 342, 123397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Si, Y.; Lu, K.; Liu, F.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Li, N.; et al. Energy and Mass Flow in Photocatalytic Water Splitting by Coupling Photothermal Effect. Chem. Phys. Rev. 2024, 5, 031301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornrungroj, C.; Mohamad Annuar, A.B.; Wang, Q.; Rahaman, M.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Andrei, V.; Reisner, E. Hybrid Photothermal–Photocatalyst Sheets for Solar-Driven Overall Water Splitting Coupled to Water Purification. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitapure, N.; Kwon, J.S.-I. Machine Learning Meets Process Control: Unveiling the Potential of LSTMc. AIChE J. 2024, 70, e18356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouhara, H.; Khordehgah, N.; Almahmoud, S.; Delpech, B.; Chauhan, A.; Tassou, S.A. Waste Heat Recovery Technologies and Applications. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 6, 268–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhom, F.; Isa, Y.M. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Using TiO2-Based Catalysts: A Review. Glob. Chall. 2024, 8, 2400134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattry, A.; Johnson, H.; Chatzikiriakou, D.; Haussener, S. Probabilistic Techno-Economic Assessment of Medium-Scale Photoelectrochemical Fuel Generation Plants. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 12058–12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisatomi, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ardo, S.; Reisner, E.; Nishiyama, H.; Kudo, A.; Yamada, T.; Domen, K. Photocatalytic Water Splitting for Large-Scale Solar-to-Chemical Energy Conversion and Storage. Front. Sci. 2024, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, P.; Noh, J. Photocatalytic Water Splitting: How Far Away Are We from Being Able to Industrially Produce Solar Hydrogen? Molecules 2022, 27, 7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keoleian, G.A. Life-Cycle Optimization Methods for Enhancing the Sustainability of Design and Policy Decisions. In Treatise on Sustainability Science and Engineering; Jawahir, I.S., Sikdar, S.K., Huang, Y., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2013; pp. 3–17. ISBN 978-94-007-6229-9. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Su, R. Environmental Impact of Waste Treatment and Synchronous Hydrogen Production: Based on Life Cycle Assessment Method. Toxics 2024, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sahu, P.; Champati, A.; Pradhan, A.; Naik, B. Design and Development of Nanostructured Photocatalysts for Large-Scale Solar Green Hydrogen Generation. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2024, 8, 1872–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballari, M. de los M.; Brandi, R.; Alfano, O.; Cassano, A. Mass Transfer Limitations in Photocatalytic Reactors Employing Titanium Dioxide Suspensions: II. External and Internal Particle Constrains for the Reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 136, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, R.; Severino, A.; Lavorato, C.; Argurio, P. Which Configuration of Photocatalytic Membrane Reactors Has a Major Potential to Be Used at an Industrial Level in Tertiary Sewage Wastewater Treatment? Catalysts 2023, 13, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhwani, L.; Soni, A.; Cuce, E.; Kumarasamy, S. Optical Fiber Technology for Efficient Daylighting and Thermal Control: A Sustainable Approach for Buildings. Eng 2024, 5, 2680–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Whang, A.J.-W. Development of Optical Fiber-Based Daylighting System and Its Comparison. Energies 2015, 8, 7185–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, S.; Allian, A. Scale-up of Mass Transfer-Limited Reactions. In Chemical Engineering in the Pharmaceutical Industry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2019; pp. 227–239 ISBN 978-1-119-60080-0.
- Mani, P.; Shenoy, S.; Sagayaraj, P.J.J.; Agamendran, N.; Son, S.; Bernaurdshaw, N.; Kim, H.; Sekar, K. Scaling up of Photocatalytic Systems for Large-Scale Hydrogen Generation. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2025, 12, 011303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bbumba, S.; Kigozi, M.; Karume, I.; Arum, C.T.; Murungi, M.; Babirye, P.M.; Kirabo, S. Prediction and Optimization of Process Parameters Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Models. Asian J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2025, 16, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockenstedt, J.; Vidwans, N.A.; Gentry, T.; Vaddiraju, S. Catalyst Recovery, Regeneration and Reuse during Large-Scale Disinfection of Water Using Photocatalysis. Water 2021, 13, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanka, S.; Zeng, G.; Deutsch, T.G.; Toma, F.M.; Mi, Z. Long-Term Stability Metrics of Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Li, G.; Guo, S.; Wang, W.; Hou, Q.; Li, Y.; Ma, W.; He, G.; Fei, Q. A De Novo Auto-Activated Solar-Driven Biohybrid System for Hydrogen Production in Methanotrophic Cells. Angew. Chem. n/a, e202419973. [CrossRef]
- Lubner, C.E.; Applegate, A.M.; Knörzer, P.; Ganago, A.; Bryant, D.A.; Happe, T.; Golbeck, J.H. Solar Hydrogen-Producing Bionanodevice Outperforms Natural Photosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011, 108, 20988–20991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X. Whole-Cell-Based Photosynthetic Biohybrid Systems for Energy and Environmental Applications. ChemPlusChem 2021, 86, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Lee, I.; Kim, G.-M.; Kim, J.; Panpranot, J.; Lee, D.C. Light-Driven Chemical Production with Quantum Dot-Biohybrid System: A Review. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2024, 57, 2419109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, A.; Han, J.; Wang, X.-F. Biohybrid Molecule-Based Photocatalysts for Water Splitting Hydrogen Evolution. ChemPlusChem 2023, 88, e202200424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Photosynthesis-Inspired Biohybrid and Biomimetic Systems (Special Issue). Available online: https://link.springer.com/collections/cfbfgbhiha (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Ortiz-Torres, M.; Fernández-Niño, M.; Cruz, J.C.; Capasso, A.; Matteocci, F.; Patiño, E.J.; Hernández, Y.; Barrios, A.F.G. Rational Design of Photo-Electrochemical Hybrid Devices Based on Graphene and Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Light-Harvesting Proteins 2020.
- Britz, A.; Bokarev, S.I.; Assefa, T.A.; Bajnóczi, É.G.; Németh, Z.; Vankó, G.; Rockstroh, N.; Junge, H.; Beller, M.; Doumy, G. ; et al. Site-Selective and Real-Time Observation of Bimolecular Electron Transfer during Photocatalytic Water Splitting 2020.
- Zou, Q.; Liu, K.; Abbas, M.; Yan, X. Peptide-Modulated Self-Assembly of Chromophores toward Biomimetic Light-Harvesting Nanoarchitectonics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihssen, J.; Braun, A.; Faccio, G.; Gajda-Schrantz, K.; Thony-Meyer, L. Light Harvesting Proteins for Solar Fuel Generation in Bioengineered Photoelectrochemical Cells. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.S.; Shin, T.; Park, H.; Magyar, A.P.; Choi, K.; Fantner, G.; Nelson, K.A.; Belcher, A.M. Virus-Templated Assembly of Porphyrins into Light-Harvesting Nanoantennae. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1462–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R. Soltau, S.; D. Dahlberg, P.; Niklas, J.; G. Poluektov, O.; L. Mulfort, K.; M. Utschig, L. Ru–Protein–Co Biohybrids Designed for Solar Hydrogen Production: Understanding Electron Transfer Pathways Related to Photocatalytic Function. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 7068–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lin, H.; Zhao, G.; Huang, X. Photocatalytic Material-Microorganism Hybrid System and Its Application—A Review. Micromachines 2022, 13, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.A.; Li, G.; Liang, H.; Ali, M. Recent Advances in Hybrid Photocatalysts for Efficient Solar Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2025, 97, 920–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, A.; Chuaicham, C.; Shanmugam, M.; Vellaichamy, B.; Rajendran, S.; Hoang, T.K.A.; Sasaki, K.; Sekar, K. Recent Development of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Photocatalysts for Biomass Conversion into Hydrogen Production. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 2561–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.A.; Yoo, S.; Shuler, E.W.; Sherman, B.D.; Lee, S.; Leem, G. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution from Biomass Conversion. Nano Converg. 2021, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udry, G.A.O.; Tiessler-Sala, L.; Pugliese, E.; Urvoas, A.; Halime, Z.; Maréchal, J.-D.; Mahy, J.-P.; Ricoux, R. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production and Carbon Dioxide Reduction Catalyzed by an Artificial Cobalt Hemoprotein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-K.; Li, Y.-H.; Qi, M.-Y.; Lin, Q.; Xu, Y.-J. Enhanced Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with Suppressing H2 Evolution via Pt Cocatalyst and Surface SiO2 Coating. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 278, 119267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, S.; Iwase, A.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Suzuki, T.M.; Morikawa, T.; Kudo, A. Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Using Water as an Electron Donor under Visible Light Irradiation by Z-Scheme and Photoelectrochemical Systems over (CuGa)0.5ZnS2 in the Presence of Basic Additives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezendam, S.; Herran, M.; Nan, L.; Gruber, C.; Kang, Y.; Gröbmeyer, F.; Lin, R.; Gargiulo, J.; Sousa-Castillo, A.; Cortés, E. Hybrid Plasmonic Nanomaterials for Hydrogen Generation and Carbon Dioxide Reduction. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 778–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, M.; You, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, L. Defect Engineering in Photocatalysts and Photoelectrodes: From Small to Big. Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanga, G.S.; Pransu, G.; Krishna, H.; Thomas, T. Discovery of Novel Photocatalysts Using Machine Learning Approach. In Machine Learning for Advanced Functional Materials; Joshi, N., Kushvaha, V., Madhushri, P., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 233–261. ISBN 978-981-99-0393-1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liang, L.; Su, B.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Fu, C. Transformative Strategies in Photocatalyst Design: Merging Computational Methods and Deep Learning. J. Mater. Inform. 2024, 4, N/A-N/A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyzer-Knapp, E.O.; Pitera, J.W.; Staar, P.W.J.; Takeda, S.; Laino, T.; Sanders, D.P.; Sexton, J.; Smith, J.R.; Curioni, A. Accelerating Materials Discovery Using Artificial Intelligence, High Performance Computing and Robotics. Npj Comput. Mater. 2022, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; McCullough, K.; Lauterbach, J.A. Enabling Catalyst Discovery through Machine Learning and High-Throughput Experimentation. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, K.; Williams, T.; Mingle, K.; Jamshidi, P.; Lauterbach, J. High-Throughput Experimentation Meets Artificial Intelligence: A New Pathway to Catalyst Discovery. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 11174–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Hu, J.; Samia, A.; Yu, X. (Bill) Predicting Active Sites in Photocatalytic Degradation Process Using an Interpretable Molecular-Image Combined Convolutional Neural Network. Catalysts 2022, 12, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, F. Predicting and Understanding Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction with IR Spectroscopy-Based Interpretable Machine Learning Framework. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Cui, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Wen, C.; Sa, B.; Sun, Z. Interpretable Machine Learning for Stability and Electronic Structure Prediction of Janus III–VI van Der Waals Heterostructures. Mater. Genome Eng. Adv. 2024, 2, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, H.; Yamada, T.; Nakabayashi, M.; Maehara, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kuromiya, Y.; Nagatsuma, Y.; Tokudome, H.; Akiyama, S.; Watanabe, T.; et al. Photocatalytic Solar Hydrogen Production from Water on a 100-M2 Scale. Nature 2021, 598, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Wang, Z.; Maeda, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, L. Addressing the Stability Challenge of Photo(Electro)Catalysts towards Solar Water Splitting. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 3415–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-J. Promises and Challenges in Photocatalysis. Front. Catal. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, S.A.; Kim, K.-H. Heterogeneous Photocatalysis Scalability for Environmental Remediation: Opportunities and Challenges. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.S.; Ardo, S.; Wu, R.Q. Hybrid Density Functional Study of Band Gap Engineering of SrTiO3 Photocatalyst via Doping for Water Splitting. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2021, 5, 065801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Ren, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Du, Y.; Hao, W. Band-Gap Engineering of BiOCl with Oxygen Vacancies for Efficient Photooxidation Properties under Visible-Light Irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, S.; Kinge, S.; Visscher, L. Modeling Heterogeneous Catalysis Using Quantum Computers: An Academic and Industry Perspective. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blessing, M.; Surisetti, S. Real-Time Control and Optimization in Machine Learning for Dynamic Systems. 2024.
- Charanpahari, A.; Gupta, N.; Devthade, V.; Ghugal, S.; Bhatt, J. Ecofriendly Nanomaterials for Sustainable Photocatalytic Decontamination of Organics and Bacteria. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L.M.T., Kharissova, O.V., Kharisov, B.I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 1–29. ISBN 978-3-319-48281-1. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wei, B. Boosting Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production from Water by Photothermally Induced Biphase Systems. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
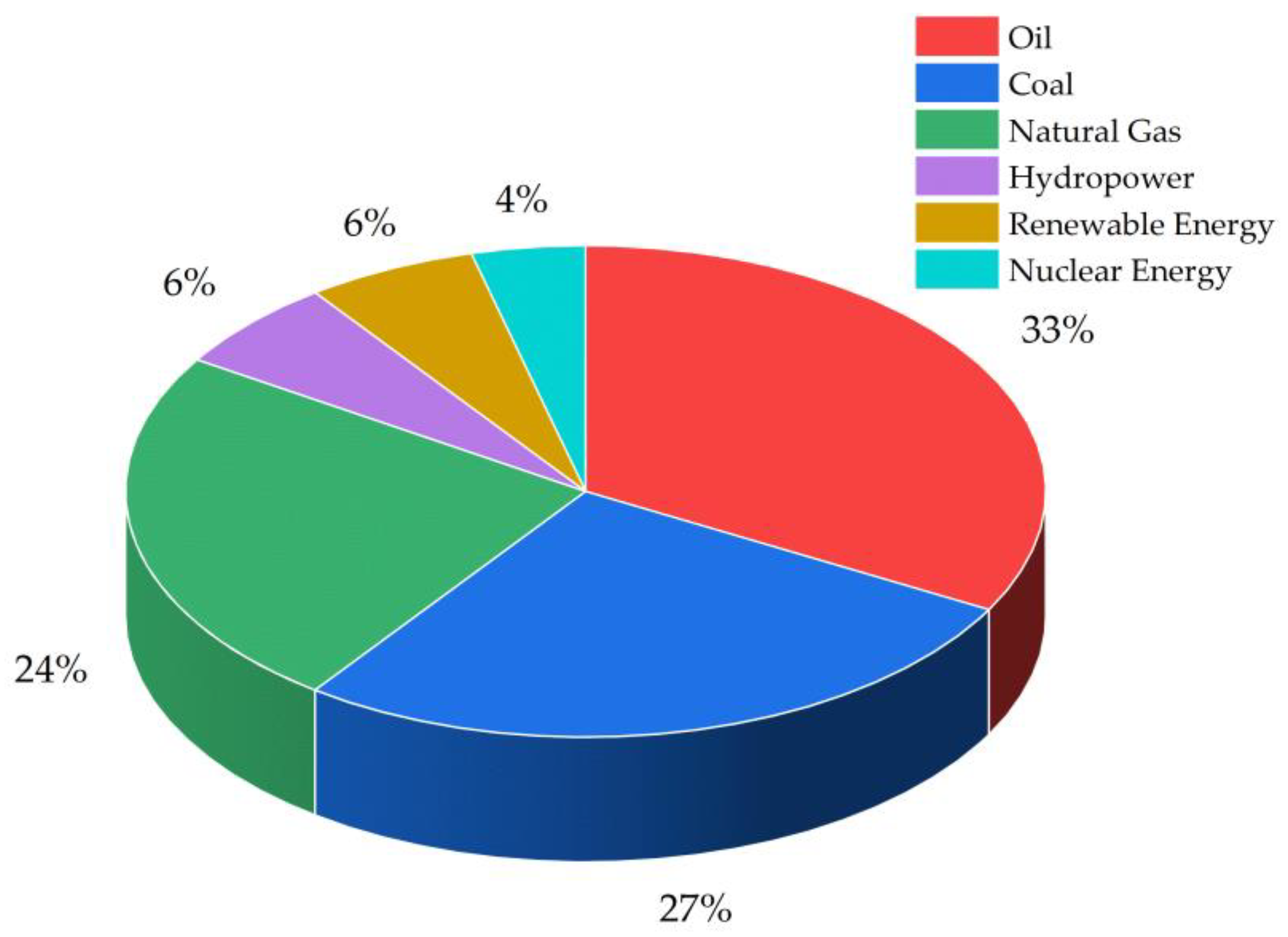
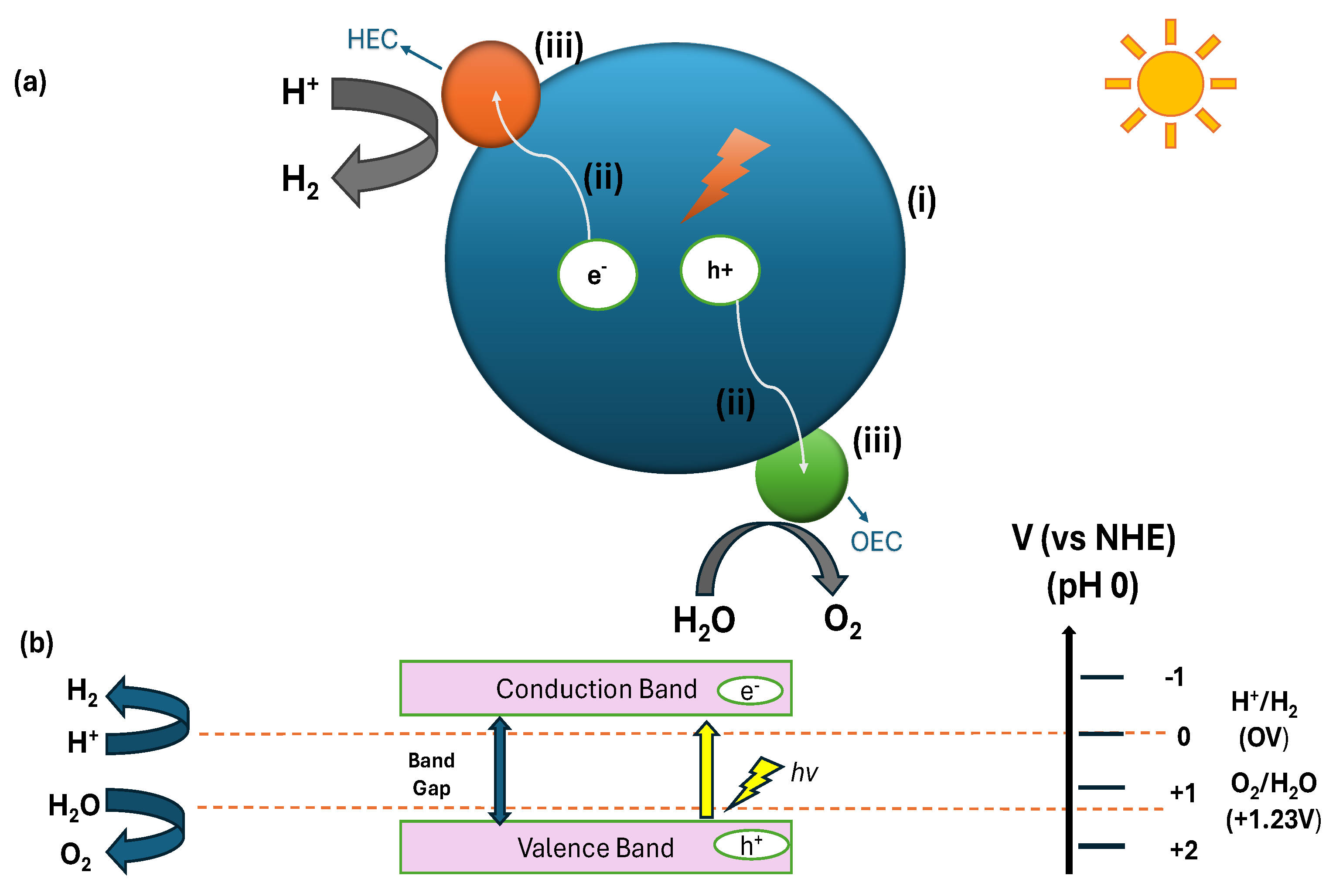
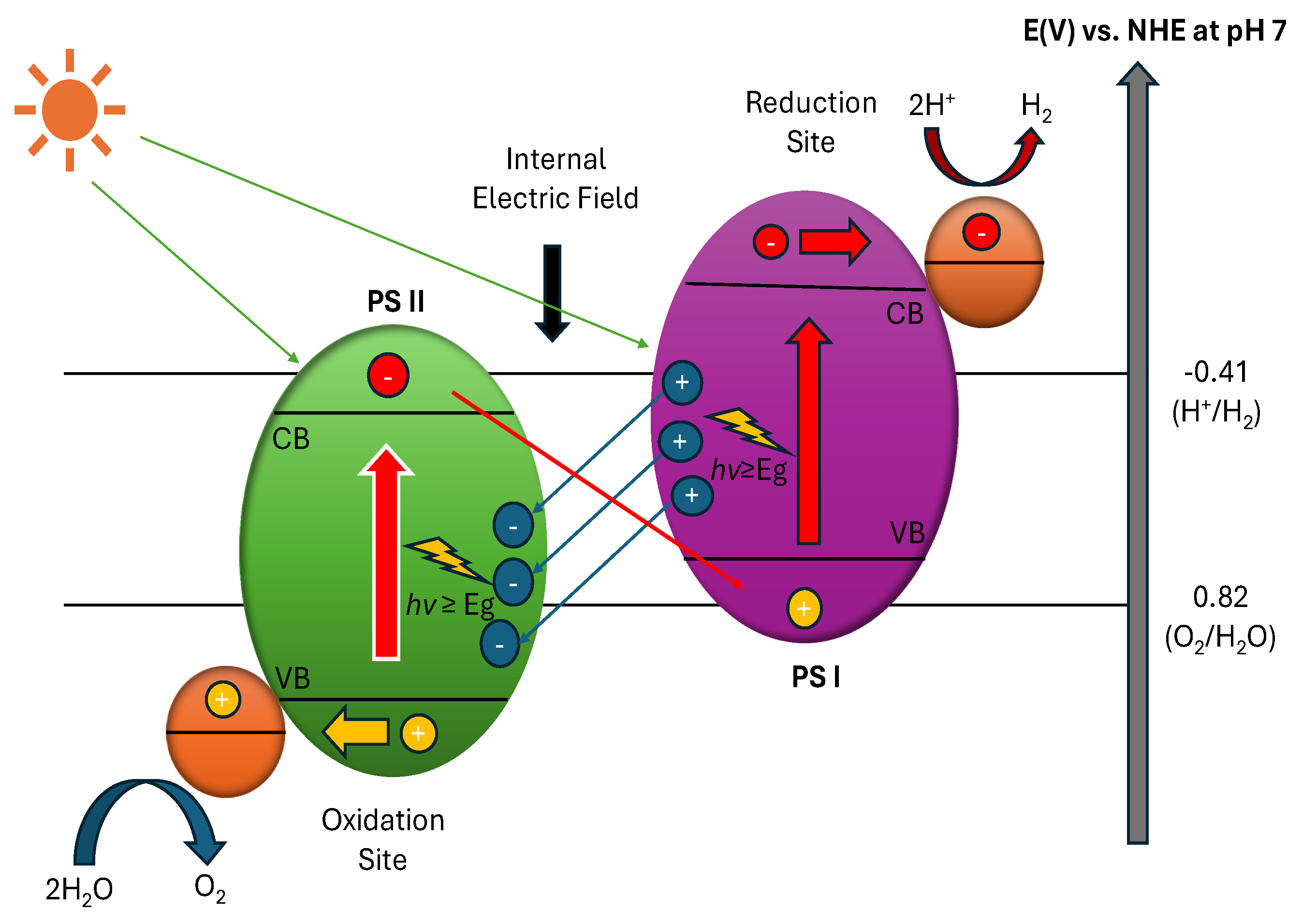
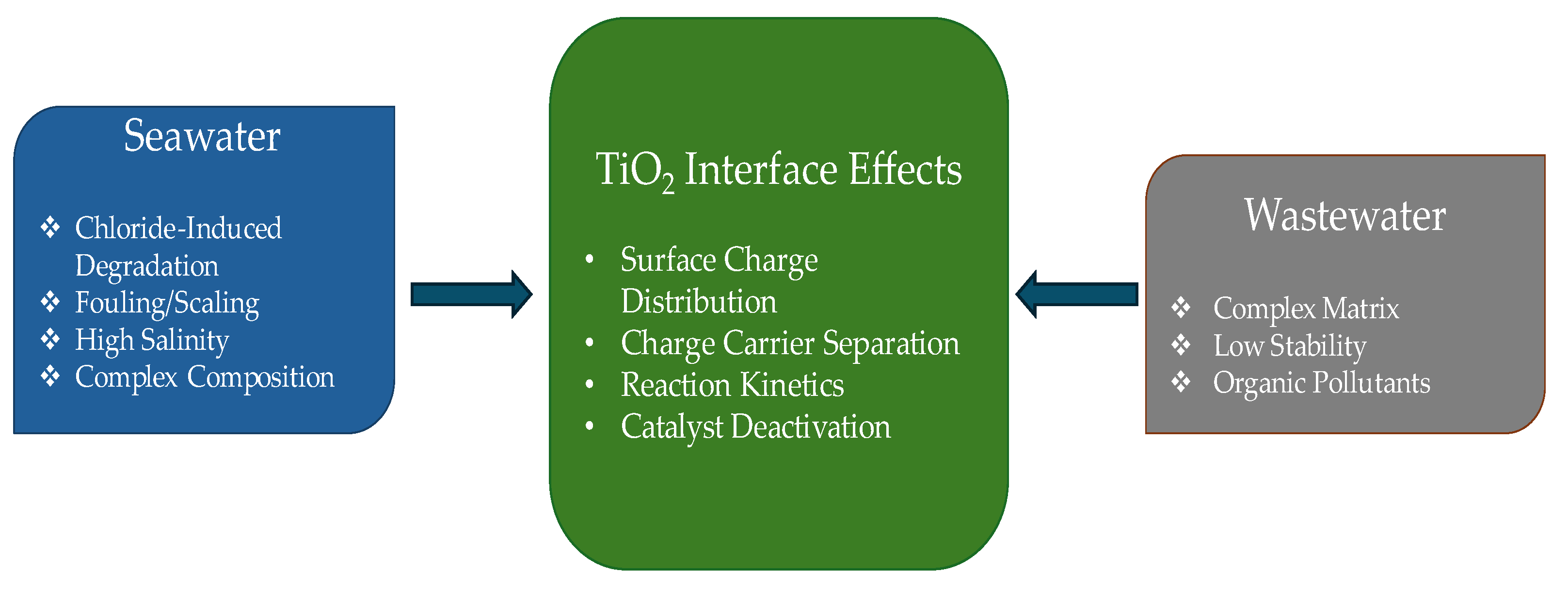
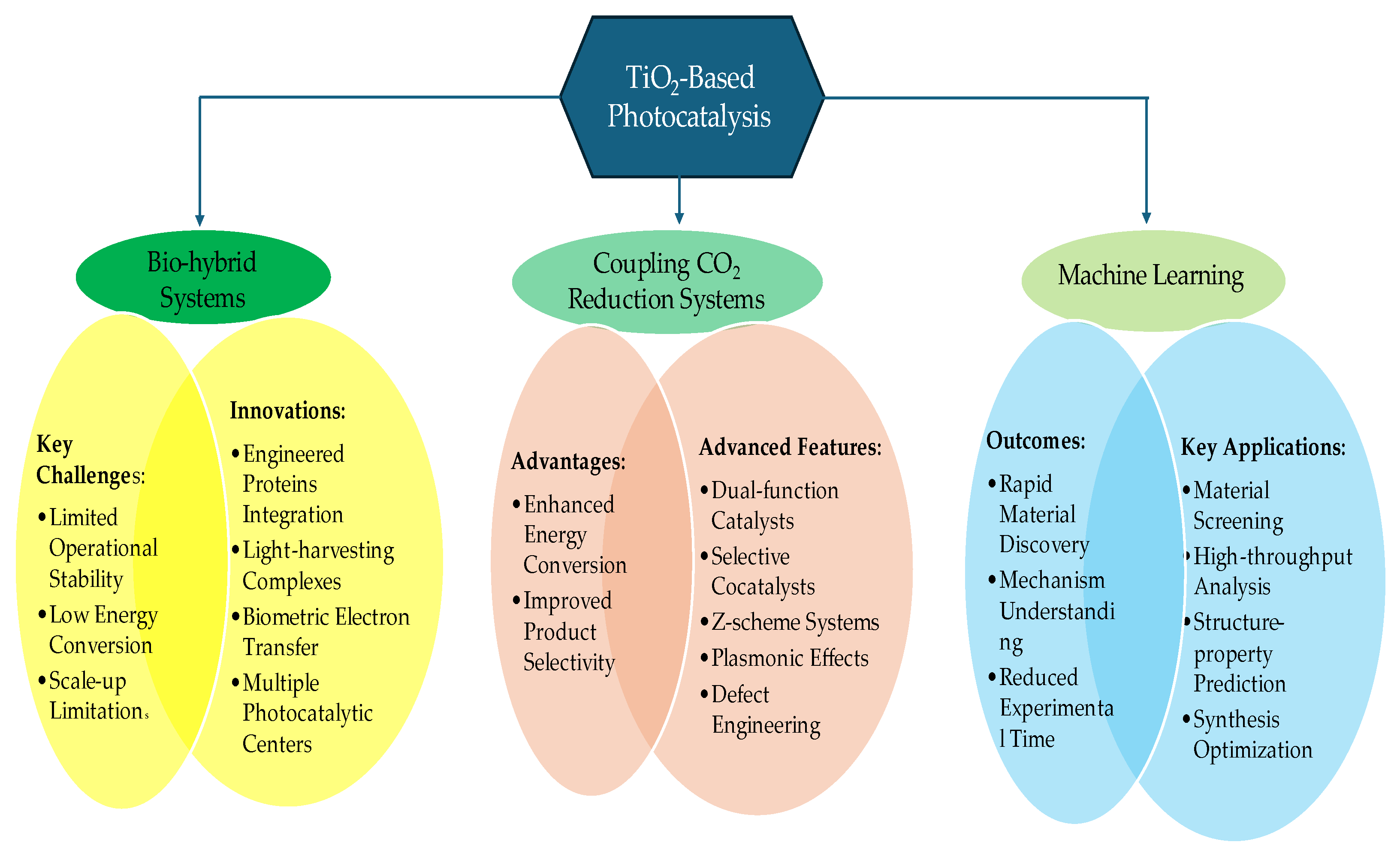
| Advancement | Key Features | Impact on Efficiency | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical Nanostructures | Integration of nanotubes, nanosheets, and nanoparticles into cohesive architectures. | Enhanced light scattering and trapping mechanisms, leading to improved photocatalytic hydrogen production. | [148] |
| Macro/Mesoporous Structures | Engineered pores facilitating superior mass transport and maximizing reactive surface area. | Significant improvements in photocatalytic hydrogen production due to enhanced surface area and reaction kinetics. | [149] |
| Ordered Arrays and Self-Assembly | Formation of ordered arrays and self-assembled structures for directional charge transport. | Addressed limitations in traditional designs by enhancing charge separation and reducing recombination rates, leading to improved hydrogen evolution. | [150] |
| Crystal Phase Engineering | Controlled synthesis of mixed-phase TiO2 (anatase/rutile) junctions. | Exceptional charge separation properties, significantly reducing recombination rates and enhancing hydrogen production efficiency. | [151] |
| Nanoscale Engineering | Precise control over TiO2 nanostructures, including size, shape, and surface properties. | Enhanced light absorption, charge separation, and surface reaction kinetics, leading to improved hydrogen production efficiency. | [152] |
| Advancement | Key Features | Impact on Efficiency | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black TiO2 via Oxygen Vacancy Engineering | Controlled introduction of oxygen vacancies to create black TiO2 with enhanced visible light absorption. | Extends photocatalytic activity into the visible spectrum, significantly improving hydrogen production rates. | [153] |
| Surface Modification and Defect Engineering | Atomic-level control over surface defects, including Ti3+ states and non-metal doping. | Improves charge separation and extends light absorption, leading to higher hydrogen evolution rates. | [166] |
| Co-doping with Transition Metals and Non-Metals | Incorporation of both metal and non-metal dopants into TiO2 lattice. | Synergistic effect leading to enhanced visible light absorption and improved hydrogen production rates. | [167] |
| Photocatalyst Composition | Fabrication Method | Hydrogen Production Rate | Light Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/TiO2 | Chemical Reduction | 23.5 mmol g−1 h−1 | UV lamp (254 nm Wavelength) | [168] |
| Co3O4@C/TiO2 | Carbonization | 11,400 µmol g−1 h−1 | UV-LED lamp (365 nm Wavelength) | [169] |
| CuO/TiO2 | Hydrothermal | 2,000 µmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [170] |
| Co3O4 QDs/TiO2 | Hydrothermal | 1735 µmol g−1 h−1 | Solar light | [171] |
| Co3O4@TiO2/ Pt | Hydrothermal | 5280 µmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [172] |
| CoOx-TiO2/ CdS | Solvothermal | 660 µmol g−1 h−1 | Visible light (> 400 nm Wavelength) | [173] |
| Pt/TiO2 | Hydrothermal | 334 µmol h−1 | 350 W Xe lamp | [149] |
| FP-Pt/TiO2 | Pyrolysis | 19.25 mmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [174] |
| FP-Cu/TiO2 | Pyrolysis | 5.02 mmol g−1 h−1 | 300W Xenon lamp | [174] |
| Cr-TiO2 | Magnetron sputtering and Sol–gel | 5.3 µmol h−1 | Visible light | [175] |
| Fe-TiO2 | Magnetron sputtering and Sol–gel | 15.5 µmol h−1 | Visible light | [175] |
| Cu-TiO2 (P25) | Photoassisted Deposition | 8.47 mmol g−1 h−1 | 450 W Hg lamp | [176] |
| Co-TiO2 | Photoassisted Deposition | 2.48 mmol g−1 h−1 | 450 W Hg lamp | [176] |
| Fe-TiO2 | Microwave-Hydrothermal | 11 µmol g−1 h−1 | Xe lamp | [177] |
| Fe-TiO2 | Impregnation | 230 µmol g−1 h−1 | UV light | [178] |
| Ru-TiO2 | Micro-emulsion | 0.80 mmol g−1 h−1 | 500 W Xe lamp | [179] |
| Au-TiO2 | Photodeposition | 1.1 mmol g−1 h−1 | UV lamp | [180] |
| Pd/N-TiO2 | Chemical vapor deposition | 6.3 mmol g−1 h−1 | White LED | [181] |
| Fe-Ni-/Ag/TiO2 | Solvothermal | 794 µmol g−1 h−1 | 500 W Xe lamp | [182] |
| Pt/Mg-TiO2 | Hydrothermal | 850 µmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [183] |
| Pt SA/Def-s-TiO2 | Deposition-Precipitation | 13.5 mmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [184] |
| Cu-TiO2 | Ball Milling | 9.5 mmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [185] |
| Ni-TiO2 | Molten Salt | 1.9 mmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [186] |
| Sn/TiO2 | Photoinduced Deposition | 553 µmol g−1 h−1 | 3 W UV lamp | [187] |
| N-TiO2 | Sol-gel and Electrospinning | 28 µmol h−1 | 150 W Xe lamp | [188] |
| N-TiO2 | RF Magnetron Sputtering Deposition | 4.5 mmol cm-2 h-1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [189] |
| N-TiO2 with VO | Solvothermal | 1.04 mmol g−1 h−1 | Solar Simulator | [190] |
| S-TiO2 | Thermal Protection | 164 µmol g−1 h−1 | Visible light | [191] |
| TiC@C-TiO2 | Situ Thermal Growth | 558 µmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [192] |
| N/F-TiO2 | Calcination | 11.5 µmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [193] |
| C/N self-doped TiO2 | Hydrothermal | 332.3 µmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [157] |
| Br/N-TiO2 | Hydrothermal | 2.3 mmol g−1 h−1 | 300 W Xe lamp | [194] |
| Factors | Effect of Photocatalytic Performance | References |
|---|---|---|
| pH | Modulates band edge positions, surface charge, and adsorption/desorption equilibrium of reactive species. Affects hydrogen evolution rates depending on the pH range. | [229,230] |
| Ionic Strength | Influences the electric double layer and charge carrier separation. High ionic strength can improve conductivity but may increase recombination. | [69,239] |
| DOM | Acts as electron donors and acceptors; competing pathways can either enhance or inhibit hydrogen evolution rates. | [233] |
| Common Ions (e.g., Na+, Cl-, SO42-) | Alters the electric field at the semiconductor-electrolyte interface and influences charge carrier separation. Some ions stabilize the catalyst, while others lead to degradation. | [235,236] |
| Dissolved Oxygen | Competes with hydrogen evolution by capturing electrons, reducing overall photocatalytic efficiency. | [238] |
| Photocatalyst | Hydrogen Production Rate | Key Strategy/Condition Addressed | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesoporous brookite/anatase TiO2 | 6.59 mmolg-1h-1 | Mitigated chloride-induced degradation | [256] |
| Brookite TiO2 | 1,476 µmolg-1h-1 | Improved stability in saline environments | [257] |
| Phosphorus and Nickel co-doped TiO2 | 149 µmolg-1h-1 | Improved stability by preventing photo-corrosion | [258] |
| TiO2(NT)/Pt/ Cd0.8Zn0.2S | 21.7 mmolg-1h-1 | Increased active sites and hydrogen production rate | [259] |
| Granular Pt/TiO2 | 23.6 µmolh-1 | Catalyst deflocculation and oxygen inhibition | [260] |
| WS2/C-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 986 µmolg-1h-1 | Enhanced electron-hole pair separation | [261] |
| MoS2@TiO2 | 580 mmolg-1h-1 | Enhanced plasmonic effect | [262] |
| SiO2/Ag@TiO2 | 816 µmolg-1h-1 | Photothermic interfacial heating synergy | [263] |
| Photocatalyst | Hydrogen Production Rate | Pollutant Treated | Light Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO/TiO2 NT | 3.43 µmolg-1h-1 | Phenol | Visible light | [271] |
| Ag-G-TiO2 | 191 µmolg-1h-1 | Methylene Blue | Visible light | [35] |
| BiVO4/TiO2 | 14.3 mmolg-1h-1 | Rhodamine B | Visible light | [272] |
| NiPc@GO/TiO2 | 1.38 mmolh-1 | Formic Acid | Visible light | [273] |
| 7CuO-TiNTA | 910 mmol/m2 | Ammonia | UV light | [274] |
| Ag/TiO2 | 1729 µmolg-1h-1 | Paracetamol | Natural sunlight | [275] |
| MoS2−x @TiO2-OV | 42 µmolg-1h-1 | Pharmaceutical Wastewater | 300W Xenon lamp | [276] |
| MoS2−x @TiO2-OV | 103 µmolg-1h-1 | Coking wastewater | 300W Xenon lamp | [276] |
| PtCo3O4TiO2 | 2200 µmolg-1h-1 | Enrofloxacin | 300W Xenon lamp | [277] |
| Fe-doped TiO2 | 2423 µmolh-1 | Methyl Orange | Visible light | [278] |
| Mixed TiO2 nanosphere and nanosheet | 19.4 µmolg-1h-1 | Glycerol | 300W Xenon arc lamp | [279] |
| Pt/TiO2 | 101 µmolg-1h-1 | Oxalic Acid | 450W Xenon Arc lamp | [280] |
| Carbon-doped TiO2 | 374 µmolg-1h-1 | Lactic Acid | Visible light | [281] |
| Cr2O3/Rh/SrTiO3 | 590 µmolg-1h-1 | 4-chlorophenol | 300W Xe Arc lamp | [282] |
| Nanostructure mesoporous TiO2 | 19 mmolh-1 | Olive mill wastewater | UV light | [283] |
| Reactor Type | Key Features | Scalability Challenges | Engineering Solutions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suspended Particle | High light absorption, dynamic particle flow | Potential clogging, complex design | Optimization of particle dispersion and flow dynamics | [300] |
| Fixed-Bed Reactor | Stable, large-scale suitability | Low light utilization, heat management | Reactor designed for improved light penetration and mass transfer | [301] |
| Optical Fiber Reactor | Efficient light delivery through fibers, compact | Cost, complexity in large-scale integration | Optimization of fiber configuration for large-scale light distribution | [302] |
| Aspect | Challenges | Solutions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Distribution | - Non-uniform illumination in scaled reactors leading to efficiency loss. | - Advanced light delivery systems (e.g., internal illumination, solar concentrators). - Integration of plasmonic materials and photonic crystals to enhance light harvesting and uniformity |
[298,315] |
| Mass Transfer | - Limitation in gas-liquid-solid interactions affecting reaction rates. - Poor mixing leading to concentration gradients |
- Enhanced mixing strategies to improve contact between phases. - Structured catalysts and membrane-integrated systems to facilitate better mass transfer. |
[316,317] |
| Scaling-Up Factor | Challenges | Quantitative Metrics | Proposed Solutions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light Delivery Efficiency | - Light Scattering. - Poor penetration in slurries. - Limited light absorption by photocatalyst. |
- Single LED to optical fiber efficiency: ~91% evanescent wave utilization. - TiO2-coated optical fibers enhance degradation by 32%. |
- Optical fibers with reduced TiO2 patchiness (0.034 cm2/cm2). -Optimized interspace distance (114.3 nm) for evanescent waves. |
[318,319] |
| Reactor Design and Photocatalyst Loading | - Low photocatalyst mass-loading. - Reactor inefficiencies. - Catalyst detachment. |
- Mass-loading of g-C3N4-POFs up to 100-1000× higher than conventional reactors. - Photocatalyst coated optical fibers improved micropollutant degradation by 4×. |
Bundled 150 optical fibers for higher quantum efficiency and scalable production. | [320,321] |
| Surface Area Utilization | - Limited catalyst loading. - Light scattering losses. - Inefficient pollutant degradation. - Catalyst leaching. - High energy consumption. |
- High mass-loading g-C3N4 embedded in metamaterial porous polymer fibers (100-1000× higher than traditional coatings). - 4× higher degradation rates compared to slurry reactors. - Maintains photocatalytic activity for 20+ cycles. - No catalyst leaching. - Reduced energy-per-order (EEO) compared to slurry reactors |
- Metamaterial porous polymer fibers for efficient light delivery and increased reaction sites. - Photocatalyst immobilization for long-term stability. - Energy-efficient fiber-based reactor designs |
[320,322] |
| Biofouling and Catalyst Stability | - Biofilm accumulation on photocatalytic surfaces reduces efficiency and leads to fouling. - Controlling biofilm growth in enclosed water systems is challenging due to light delivery limitations. |
- UV-C SEOFs (side-emitting optical fibers) inhibited biofilm formation at ≥10 µW/cm² (265-275 nm). - UV-A and UV-B SEOFs were ineffective and even increased EPS (Extracellular Polymeric Substances) accumulation, leading to more fouling. |
- Low-fluence UV-C SEOFs enable continuous surface disinfection, preventing biofilm accumulation. - Subtractive engineering approach enhances UV-C side-emission, improving biofilm control in confined spaces. |
[323,324] |
| Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER) Efficiency | - Electron-hole recombination losses reduce reaction efficiency. - Conventional systems suffer from low quantum yield due to inefficient light absorption. |
- Quantum yield increased by nearly 2× when reactor length was doubled. - Photocatalytic H₂O₂ production improved by 60× compared to slurries, demonstrating superior light utilization. - HER efficiency increased significantly using g-C3N4 and ITO-modified polymer optical fibers. |
- Evanescent wave enhancement using optical fibers improves light utilization. - Dual optical-membrane fiber systems enable stable photocatalysis with enhanced oxygen delivery and light absorption. |
[319,321,325] |
| Water Source and Impurities | - Organic pollutants act as reactive species scavengers, reducing oxidation efficiency. - Background organic matter (e.g., WWTP effluent) significantly decreases photocatalytic degradation rates. |
- Organic matter in secondary wastewater effluent (17 mg TOC/L) inhibited photocatalysis. - In the presence of WWTP effluent, BPA removal rates decreased by 52% for electrospun TiO₂ fibers, compared to 91% for suspended TiO₂. |
- Coupled adsorption-photocatalysis systems enhance contaminant capture and oxidation efficiency. - Porous electrospun fibers increase surface area, improving pollutant access to photocatalytic sites. - TiO₂ immobilization mitigates organic interference, enhancing stability and reusability. |
[322] |
| Chemical Stability of Photocatalysts | Potential long-term performance degradation | Photocatalytic performance sustained over 20 cycles, with no structural loss of optical fibers. | - High-mass-loading photocatalysts. - Roll-to-roll fabrication for scalable and stable production. |
[320] |
| Photoelectrochemical (PEC) Integration | High energy cost due to inefficient PEC designs. | - Geometric space capacity: 2670 m²/m³ (>25× higher than flat PEC electrodes). - Photocurrent density: 0.2 mA/cm². - Hydrogen production rate: 15× higher than standard reactors. |
ITO and g-C₃N₄ coated polymer optical fiber optoelectrode improves electron transfer and efficiency. | [321] |
| Flexible Fiber-Based Reactor Designs | - Need for scalable and adaptable configurations for industrial applications. - Current reactor designs suffer from low energy efficiencies due to light attenuation. |
- >6000% larger surface area than flat glass electrodes. - >300% better incident photon-to-current efficiency. |
Flexible Perovskite-Nafion-ITO fiber optoelectrodes for efficient light-driven PEC water purification and hydrogen production. | [326] |
| Category | Innovation | Significance | Example Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Integration | Combination of photocatalysts with engineered proteins and synthetic biological components | Enhanced synergy between biological selectivity and inorganic stability | Large-scale hydrogen production systems. | [353] |
| Hybrid System Design | Bio-hybrid architectures incorporating light-harvesting complexes with multiple catalytic sites | Increased efficiency and robustness under visible light conditions. | Artificial photosynthesis setups for clean energy. | [354] |
| Electron Transfer Pathways | Biomimetic electron transfer mechanisms inspired by natural processes | Improved quantum efficiency and system longevity | Sustainable solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion | [355] |
| Performance Optimization | Development of systems with high solar-to-hydrogen conversion rates and operational stability | Breakthrough in achieving industrial scale feasibility. | Scaled-up photocatalytic energy production plants. | [356] |
| Advanced Architectures | Architectures combining multiple photocatalytic centers for distributed light utilization. | Uniform energy conversion and improved system durability. | Decentralized renewable energy systems. | [357] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





