1. Introduction
With the accelerated digitalization of the world, companies have been adapting by promoting their sales and marketing strategies online, expanding their range of products and services to reach a broader audience [
1]. In this context, it is crucial for companies to adopt effective strategies for digital communication and interaction, consistently monitoring their results to adjust actions according to consumer needs, thereby maximizing the impact of campaigns [
2]. This adaptation becomes even more relevant when considering that acquiring new customers is more expensive than retaining existing ones, making customer loyalty a critical strategy [
3], and [
4] emphasize that establishing long-term relationships requires creating value for consumers, with loyalty programs playing an essential role in this process, as highlighted by [
5].
Additionally, the intensification of competitiveness in the digital market has encouraged companies to invest in innovative strategies to differentiate themselves and retain customers. The adoption of innovations in digital marketing, such as artificial intelligence and big data, has proven effective in enhancing engagement, retention, and financial performance [
6,
7,
8], companies that prioritize digital innovation achieve significantly higher profit margins, creating sustainable competitive advantages.
Digital innovation also directly impacts customer experience, which has become a central factor in loyalty strategies. The usability and design of digital platforms enhance consumer satisfaction while simultaneously reinforcing trust and fostering loyalty bonds [
9]. Furthermore, personalizing interactions in an omnichannel environment plays a crucial role, as it improves perceived value, increases engagement, and strengthens long-term loyalty [
10]. Reward programs, such as discounts and freebies, are also effective loyalty strategies, encouraging repeat purchases and sustaining sales growth [
11].
With the growing importance of social media in digital transformation, companies have been using these platforms to segment their audiences and create targeted campaigns, leveraging their vast reach to connect brands with consumers based on characteristics such as age, gender, and location [
12,
13]. In this context, bibliometric analysis emerges as a valuable tool, as it allows the mapping of trends and gaps in the literature on loyalty in the digital environment, helping to identify methodological approaches and dynamics of international collaboration, [
14,
15], as well as understanding the most relevant factors in research.
Therefore, the main objective of this research is to analyze the determining factors for customer loyalty and retention in the digital environment, focusing on effective practices for retention on digital platforms. Through a bibliometric study, the research seeks to identify the most relevant factors and evaluate how new digital technologies impact this process. The central question is: What are the main factors contributing to customer loyalty and retention, and how can bibliometric analysis reveal trends and gaps in the literature on this topic?
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Impact of Customer Loyalty and Retention
According to [
16], customer loyalty goes beyond being a strategy; it is a central framework for guiding business objectives and evaluating their outcomes. It is based on the premise that a company's mission is to serve consumer interests, establishing relationships of mutual benefits and trust. This contrasts with the traditional profit-maximization approach, emphasizing the importance of relationships and value generation for both parties rather than focusing solely on financial analyses.
For [
17] states that companies often concentrate their strategies on acquiring new customers. However, the same author highlights that the costs of attracting new customers can be up to five times higher than the costs of retaining existing ones. In this context, customer loyalty can become a determining factor in a company's short- and medium-term growth or decline.
In a market study conducted in China, [
18] demonstrated a positive correlation between customer loyalty, technological innovation, and business continuity. The study revealed that companies capable of retaining customers have a greater capacity for business expansion, financial stability, and long-term planning.
In a study conducted in Brazil,) [
19] showed that brands capable of evoking emotions in their customers have a higher capacity for fostering loyalty. An essential factor in customer retention is the trust that the brand can instill in its customers, which becomes a critical element in loyalty-building. According to [
20], a customer is considered loyal when they repeatedly choose to purchase the same brand over others.
2.2. Innovation in Sales for the Digital Environment and Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is more than a mere platform shift; it represents a profound transformation in how companies connect with consumers. Rather than simply adapting traditional strategies for the online environment, organizations must rethink their marketing approaches, focusing on creating personalized and interactive experiences. This involves understanding consumer behavior in the digital world, leveraging tools like social media, data analytics, and relevant content to effectively engage and retain audiences in an increasingly interconnected and dynamic context, [
21] (p. 45). Kotler highlights the use of tools such as social media and data analytics to create interactive campaigns. Complementarily, [
21] emphasize that personalization is essential in the digital environment, strengthening loyalty and broadening companies' reach.
Perceived value also becomes a central goal in digital innovation, according to [
4]. They argue that the overall customer experience on digital platforms, including usability and consistency, is as important as product quality. These factors are crucial in attracting and retaining consumers, underscoring the importance of continuous adaptation to technological changes in the digital environment.
Recent studies reinforce the crucial role of innovation in digital marketing in driving business performance. According to [
6], companies integrating artificial intelligence and big data into their digital sales strategies improve audience segmentation and personalize offerings, increasing conversion rates. Additionally, the use of chatbots and virtual assistants has been identified as a practice that significantly enhances customer experience, offering 24/7 support and reducing response times. These innovations not only improve engagement but also strengthen loyalty by offering convenience and added value.
Another relevant study by [
7] examines the impact of "marketing affordances" in the digital environment, highlighting how technological tools enable new forms of consumer interaction. The authors note that using augmented reality platforms, for instance, provides immersive experiences that showcase companies' competitive advantages. They also emphasize the importance of an integrated omnichannel approach, where consumers experience consistency across all touchpoints, whether on the website, app, or physical store. This convergence of channels, combined with technological innovation, fosters both customer loyalty and the acquisition of new clients.
2.3. Digital Customer Experience and Its Relationship with Loyalty
Digital customer experience has emerged as an essential element for loyalty, reflecting the evolution of the relationship between companies and consumers. [
16] emphasize that loyalty transcends conventional strategies, representing a long-term commitment based on trust and mutual value. This classic perspective aligns with [
17] argument that customer retention is more economical and strategic than acquisition, given that the costs of attracting new consumers can be significantly higher. On the other hand, recent authors [
9], expand this view, highlighting the impact of digital technologies on the usability and design of platforms as critical factors for satisfaction and trust, elements that reinforce consumer loyalty.
Furthermore, [
21] address digital transformation as an opportunity to create more personalized interactions, [
12] highlight the relevance of social media in this process, arguing that targeted campaigns can strengthen emotional bonds between consumers and brands. These ideas converge in emphasizing personalization as a pillar of customer experience but diverge in focus: while classical authors emphasize the importance of retention strategies grounded in fundamental marketing principles, contemporary authors incorporate technological tools such as big data and artificial intelligence. Thus, integrating these perspectives provides a robust and multifaceted understanding of digital loyalty.
Standards and regulations also play a crucial role in building effective digital experiences and promoting loyalty. ISO 9001, for example, emphasizes the importance of quality management in services and products, which directly applies to the digital context by ensuring that platforms meet customer expectations. Similarly, 9241-210 on ergonomics in human-computer interaction provides guidelines for user-centered design, essential for creating intuitive and satisfying interfaces.
Moreover, associations such as the Brazilian Association of Electronic Commerce (ABComm) promote best practices in e-commerce, encouraging clear privacy policies and effective customer service tools to increase consumer trust. These initiatives, combined with reward programs and discounts, as suggested by [
11], are effective strategies for retaining customers and consolidating their loyalty. Companies adhering to these guidelines not only improve customer experience but also strengthen their reputation in the digital marketplace.
2.4. Interactive Marketing and Customer Loyalty
Marketing theory is conceived as the foundation that guides the practice of promoting voluntary changes, whether through the dissemination of ideas or by influencing lifestyles, aiming to benefit a specific audience or society as a whole [
22]. While marketing as a practice dates back to the origins of civilization, its formal scientific theory only emerged during the intense competition for customers in the 20th century.
Traditional marketing focuses on unidimensional strategies, where the brand delivers its message to consumers with minimal room for interaction or personalization [
33]. In contrast, interactive marketing fosters a continuous dialogue, enabling consumers to actively participate, contribute to brand co-creation, and directly influence marketing strategies, thereby establishing a deeper and more personalized connection [
24].
Customer loyalty is closely tied to interactive marketing, as this approach—combining elements of relationship marketing and service marketing—prioritizes building deeper, personalized connections with consumers [
25]. By emphasizing factors such as complaint resolution, commitment to relationships, trust, and service personalization, companies can enhance customer satisfaction, which in turn strengthens loyalty [
26]. Interactive marketing, by focusing on meeting and exceeding customer expectations, facilitates the creation of lasting bonds, leading to customer retention and increased loyalty [
27].
Interactive marketing stands out as one of the most dynamic and rapidly growing fields in the current business landscape. It embodies a strategy of shared value creation, where connection, engagement, active participation, and ongoing interaction with customers create a network of mutual influence and collaborative transformation [
28]. Rooted in the digital era and the growth of e-commerce [
29], interactive marketing has gained momentum with the rise of modern technologies and social media platforms, which have dramatically expanded its reach and impact [
30]. Grounded in bilateral communication, it places the consumer at the center, encouraging active participation at every stage of the marketing process.
Brand app personalization has been shown to foster brand co-creation, which is entirely mediated by consumer engagement, while also enhancing perceived quality and strengthening brand loyalty among app users [
31]. In a study on ride-hailing apps, [
32] found that transactional interactions play a critical role in boosting customer loyalty among DiDi users, partially mediated by functional, social-hedonic, and security benefits perceived by customers. Conversely, interpersonal interactions do not directly influence loyalty, with social-hedonic benefits being the only factors fully mediating the positive relationship between these interactions and loyalty.
3. Methods
The research follows the deductive scientific method, starting from general premises to test specific hypotheses, aiming to explore the topic and formulate hypotheses [
33]. The technical procedure employed is a bibliographic research approach, based on the analysis of published materials [
34]. Additionally, the chosen approach is quantitative, enabling the objective analysis of numerical data and the identification of patterns through statistical methods [
35].
To this end, the database selected for the bibliometric analysis was the Web of Science due to its extensive coverage of scientific sources and metrics such as citations and h-index, which assist in evaluating the impact of publications and collaboration networks. The search string used in Web of Science is defined as:
("customer loyalty" OR "customer retention" OR "repeat purchase" OR "repurchase intention") AND ("digital environment" OR "e-commerce" OR "online platforms" OR "digital marketing" OR "online shopping") AND ("factors" OR "determinants" OR "drivers") OR TS=(("customer satisfaction" OR "perceived value" OR "service quality") AND ("customer loyalty" OR "retention") AND ("digital environment" OR "e-commerce" OR "digital marketing")).
Moreover, the tool used for the analysis was Bibliometrix, developed in R, which facilitates the exploration of trends, collaboration networks, and keywords within research areas. Another significant advantage of this tool is its ability to process large datasets from sources like Scopus and Web of Science, providing detailed analyses of citations, scientific networks, and gaps in the literature.
Bibliometric analysis has emerged as a highly effective tool for identifying emerging trends and detecting knowledge gaps across various disciplines. The Biblioshiny tool, in particular, has been widely used in numerous studies exploring relevant topics across diverse knowledge areas. For [
36], consolidated two decades of research on mobile commerce using this tool, offering a comprehensive view of the subject. Similarly, [
37] conducted a robust review on the sustainable use of water in agriculture, employing bibliometric analysis to map progress and gaps in the field.
In another study, [
38] explored trends, emerging topics, and significant contributions in the field of sustainable and green entrepreneurship practices, highlighting the evolution of the field over time. [
39] investigated the correlation between children's excessive use of technology, home care, and parental education, bringing attention to critical discussions on the impacts of these interactions. Additionally, [
40] conducted an exhaustive analysis to identify studies adopting multi-criteria approaches and sensitivity analyses on a global scale, contributing to understanding challenges and advances in this area.
In their study, [
41] conducted a bibliometric analysis on sustainable product development in Brazil, emphasizing the need for targeted strategies to promote sustainability. Using a systemic approach [
42], analyzed how lean manufacturing and Industry 4.0 can be integrated into product development using a systemic approach. [
43] explored the use of this approach for decision-making in organizations. Continuing this line, [
44] assessed the impact of the organizational environment on the architecture of educational decisions, proposing solutions to enhance performance. [
45] highlighted the critical role of renewable energy in combating poverty in Brazil through a systematic review. Finally, [
46] discussed the interaction between sustainability, smart cities, and digital transformation, underscoring their implications for urban planning.
Regarding the research's analysis period, the years filtered were 2021 to 2024, considering that the pandemic caused a significant surge in digital commerce. The language filter was set to English, and the country analyzed was Brazil. The filtered categories included Business, Management, Economics, Environmental Studies, and Computer Science Information Systems. The meso citation topics were Management and Economics, while the micro citation topics included Customer Satisfaction, Knowledge Management, Corporate Social Responsibility, Sharing Economy, and Entrepreneurship. The selected research areas were Business Economics, Operations Research Management Science, Computer Science, and Information Science Library Science. This search returned 300 articles, which were assessed through a peer-review process to ensure the quality, accuracy, and relevance of the research.
4. Results
In the results section, the data collected from the bibliometric research were analyzed to identify connections among the selected articles and the main trends within the topic. Furthermore, graphs and tables were created to illustrate these relationships, such as author networks, keywords, and existing citations. These results provided a deeper understanding of how the subject has been developed and facilitated the identification of patterns.
4.1. Key Results of the Sample
At this stage, the main information about the sample is detailed. The analysis, presented in
Table 1, covers data collected between 2021 and 2024, sourced from 111 publications, totaling 300 documents. It exhibits an annual growth rate of 1.35 and an average of 6.803 citations per document, resulting in a total of 17,954 references. In terms of content, 671 global keywords and 1,115 author-specific keywords were identified. Regarding the authors, the table records 1,087 authors, with 20 responsible for single-authored documents and 280 involved in multi-authored works. The collaboration metrics reveal a collaborative academic environment, with 0.276 documents per author, 3.34 authors per document, 3.84 co-authors per document, and a collaboration index of 3.33.
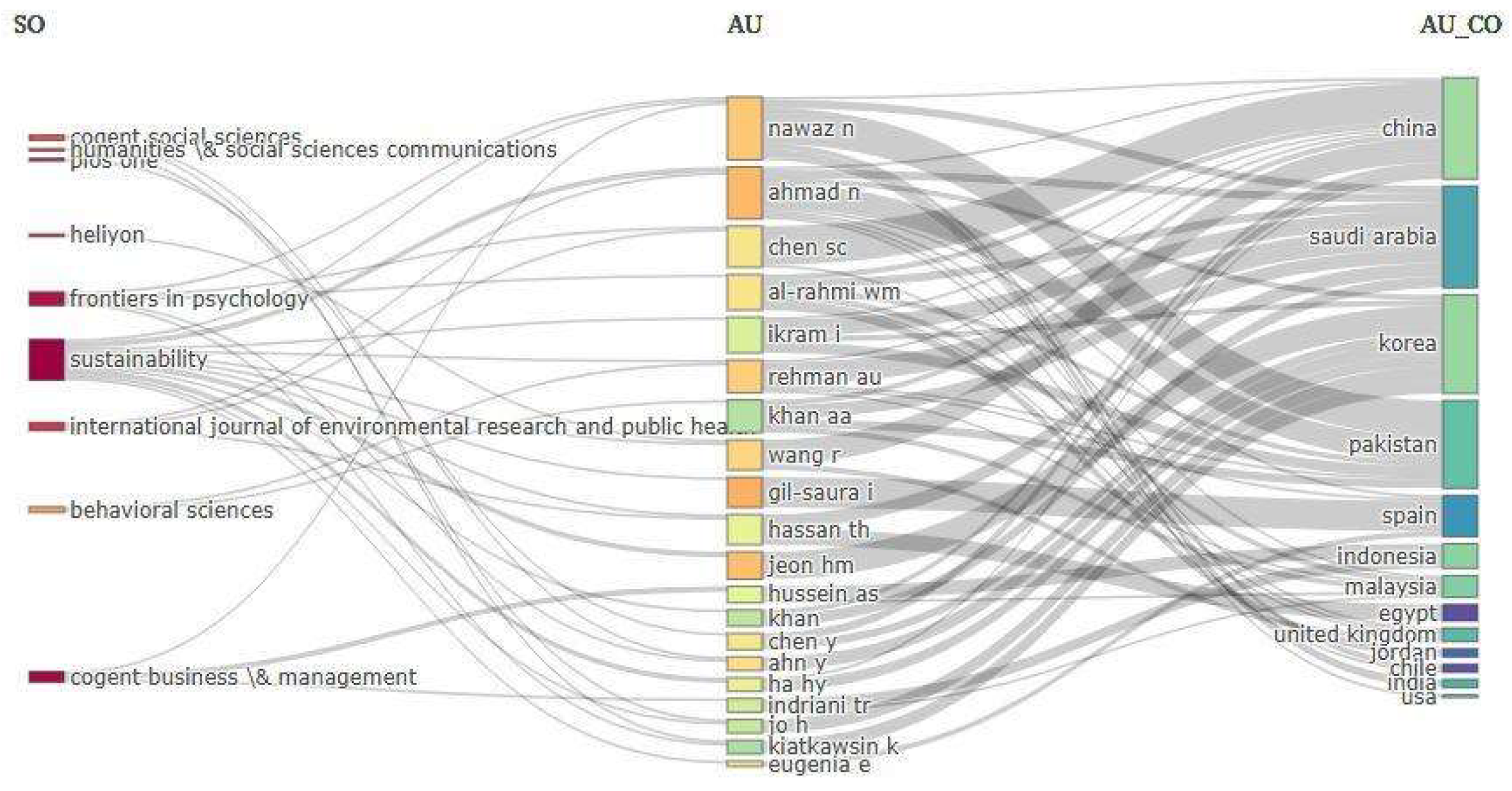
4.2. Sankey Diagram
According to [
47], the Sankey diagram is a graphical representation that illustrates data flows with arrows proportional to the magnitude of the flows. A three-category chart was created using the Sankey diagram, linking the most relevant journals, the most influential authors, and the most prominent countries in the study.
As shown in
Figure 1, the journal Sustainability from Switzerland absorbs a significant portion of the studies related to customer loyalty, with a high concentration of studies from countries such as China, Saudi Arabia, Korea, and Pakistan. Authors from China, such as Chen, and from Pakistan, such as Nawaz and Ahmad, stand out in the number of studies conducted.
4.3. Clustering by Bibliographic Coupling
According to [
48], two articles are considered bibliographically coupled if they share at least one source cited in both of their bibliographies. The degree of bibliographic coupling between two articles is measured by the number of references shared between them.
Different research topics are identified through a co-word analysis, [
49] highlights that different research topics are identified through a co-word analysis. [
50] mentions that the classification of keywords into topics is performed using a simple centrality algorithm that identifies subgroups of words with strong connections, reflecting research interests of high academic relevance.
As stated by [
51], the similarity between keywords is calculated by the equivalence index, as shown in Equation 1.
In which eij refers to the number of publications in which two keywords appear together, ci refers to the frequency with which the keyword appears in publications from theme i, and cj refers to the frequency in publications from theme j.
The bibliographic coupling analysis is conducted in a two-dimensional diagram, where the X-axis corresponds to the centrality index proposed by [
52]. This index assesses the level of interaction between the keyword networks. The equation used for the calculation is as follows (Equation 2):
Where k represents a keyword from one theme and h represents a keyword from another theme, and nn refers to the network in question.
The network density, as proposed by [
52], assesses the internal strength of the cluster. The equation used considers the Normalized Global Citation Score (MNGCS), which is calculated by dividing the actual count of global citations by its expected rate, taking into account the publication year. The Y-axis of the diagram represents this impact, reflecting the quality and relevance of the network.
Where i and j represent the analyzed themes, and w refers to the keyword count in each theme.
Based on the X and Y axes, it is possible to construct a graph in which the quadrants can be interpreted according to [
52]. The first quadrant represents the core and central themes, essential for structuring a research field. The second quadrant encompasses transversal and basic themes, which, although relevant, remain underdeveloped. The third quadrant includes underdeveloped and marginal themes, often emerging or in the process of disappearing. Finally, the fourth quadrant gathers themes of low relevance, with strong internal links (local citations) and weak external connections (global citations).
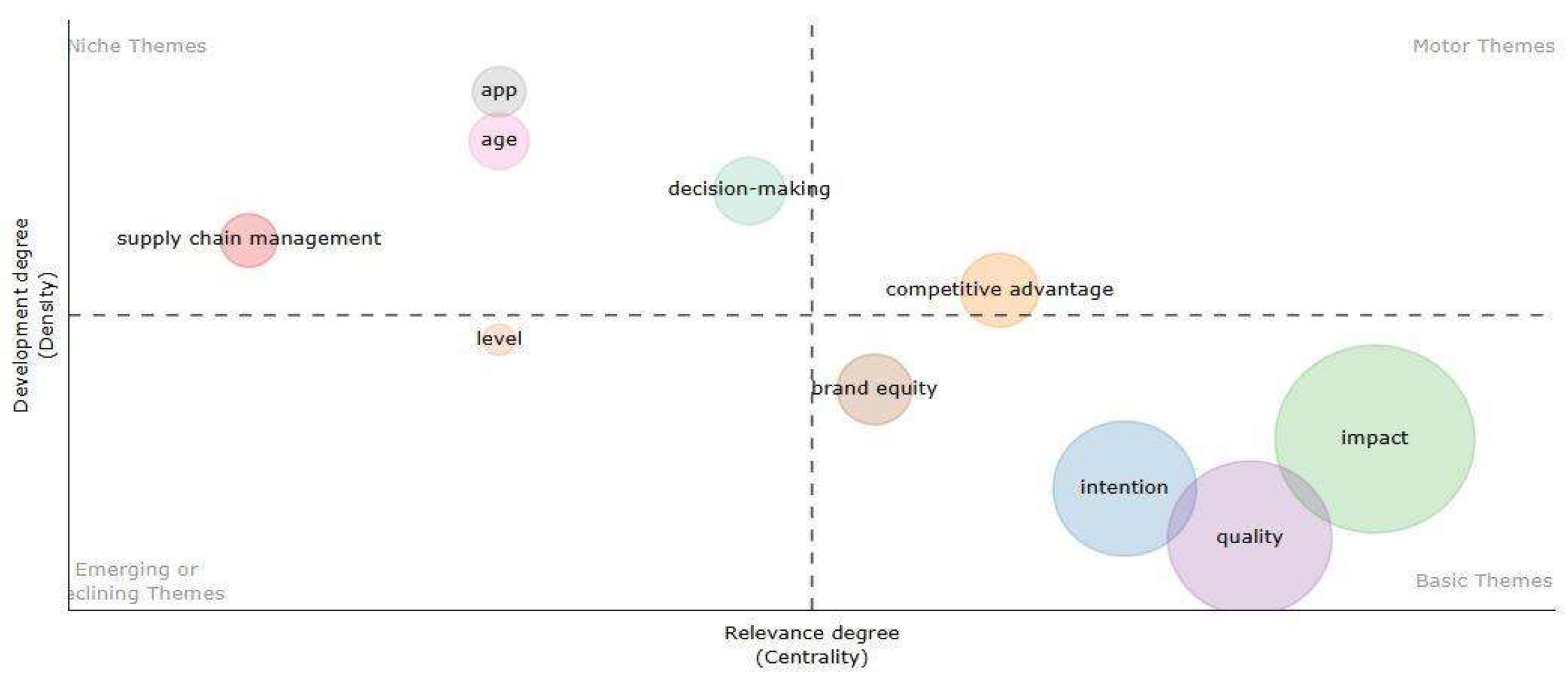
As shown in
Figure 2, bibliographic coupling was performed, organizing the clusters based on the articles. The coupling was measured by the shared references between documents, using three-word title terms to label the clusters. With this information, bibliographic coupling resulted in the formation of 6 clusters, differentiated by colors and labels.
In
Figure 2, the graph is divided into four quadrants, representing the density (development of the theme) and centrality (relevance of the theme). In the first quadrant, the term "competitive advantage" stands out. This term is central and has a high degree of development, indicating that it is a fundamental and widely explored topic in the field of study.
In the second quadrant (niche themes), the terms "app", "age", "decision-making", and "supply chain management" appear. These topics, while well-developed, are less central in terms of relevance. This suggests that they are specific topics, relevant to more specialized areas of study, but have not yet become central.
The third quadrant presents the term "level", indicating that, although it is a relevant topic, it has a lower degree of development and may be in an ascending or declining phase, depending on the analysis.
Finally, in the fourth quadrant, terms such as "impact", "quality", "intention", and "brand equity" are found. These themes have high centrality but less development compared to the other quadrants. The presence of these terms suggests that they are essential concepts in the study, but need further depth and exploration to achieve a higher level of development.
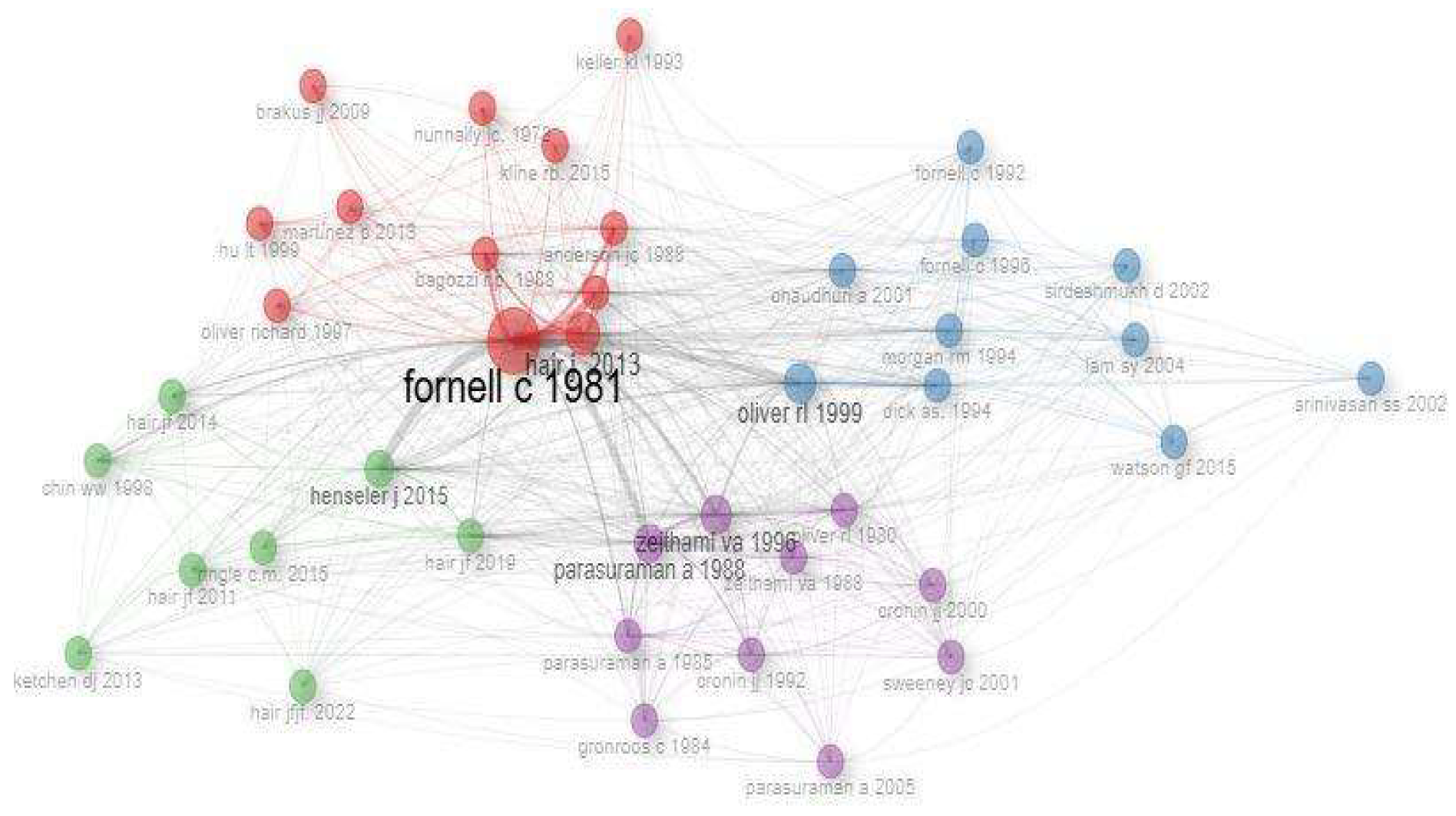
4.4. Clustering by Bibliographic Co-Citation
According to [
53], bibliographic co-citation occurs when two articles are cited by a third article. In Figure X, each cluster is composed of groups of articles, separated by colors. The larger the node radius, the more co-cited the article is. To perform the clustering, the Louvain algorithm was used, which is a heuristic method aimed at maximizing modularity in networks. This agglomerative algorithm operates on weighted networks composed of n vertices, as described [
51]. To facilitate the visualization of the results, the number of nodes was limited to 40, providing a clearer and more organized representation of the network.
In
Figure 3, it is possible to identify four distinct clusters of co-cited articles, organized by color. The red cluster (central upper part) is the most expressive, containing the highest number of co-cited articles and presenting dense connections around “Fornell C. (1981)”, who is the most central. The blue cluster (located on the right) appears as the second most relevant, composed of a significant set of well-connected articles. The green cluster (positioned on the left) has a moderate number of articles, with fewer connections compared to the previous two. Finally, the purple cluster (at the bottom central) is the smallest group, with a lower density of connections and fewer articles represented. The organization and connection between the clusters suggest different theoretical currents or research groups within the analyzed field.
4.5. Clustering by Scientific Collaboration
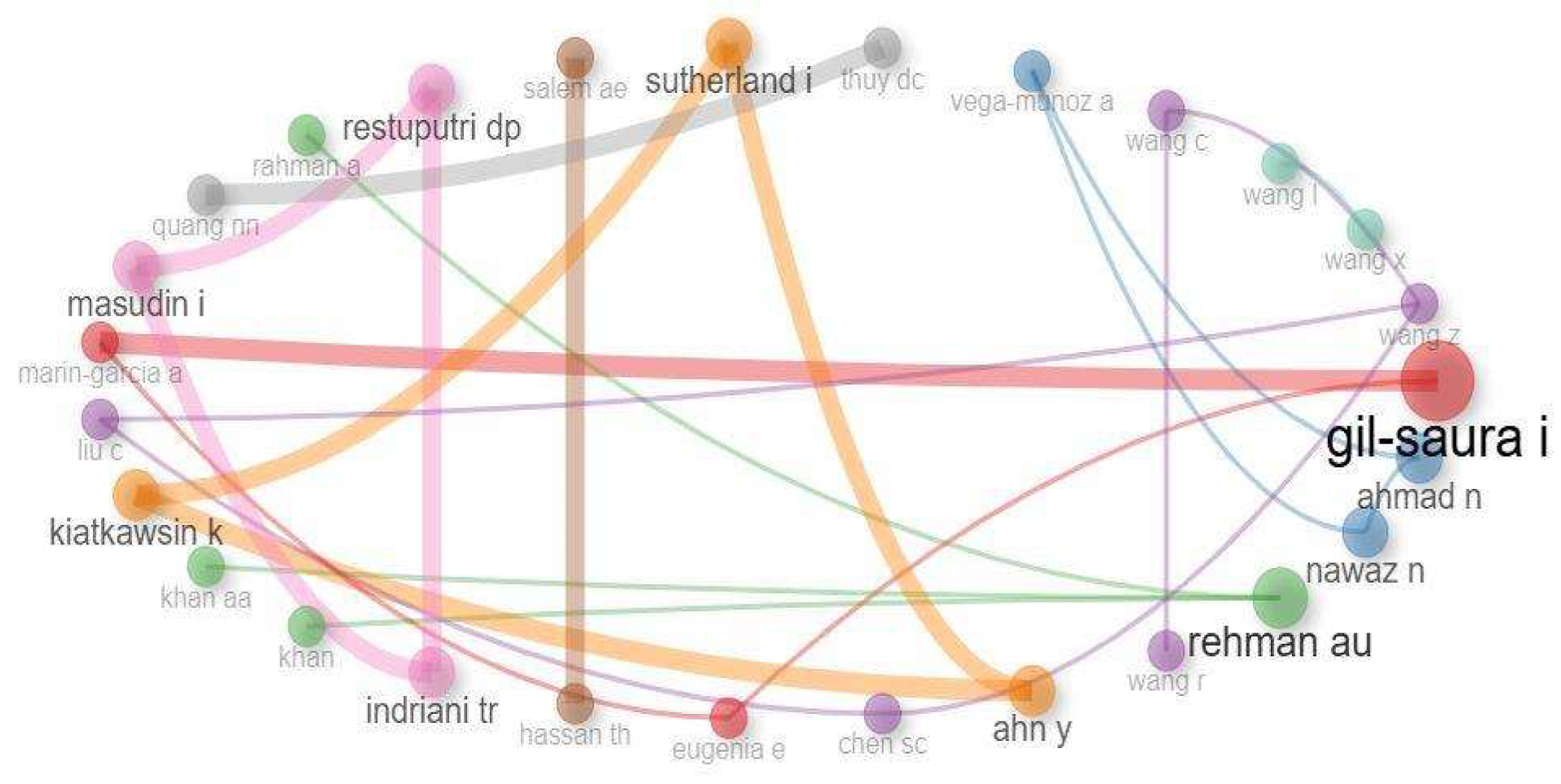
According to [
54], the scientific collaboration network is represented by nodes, which correspond to authors, and edges, which indicate co-authorship relations, one of the most recognized forms of academic collaboration. To construct this network, author clusters were formed using the Louvain algorithm to maximize modularity. The layout chosen was circular, utilizing the association normalization method. The visualization was limited to 50 nodes to ensure greater clarity in the graphical representation. The result of this configuration can be observed in
Figure 4, which illustrates the network generated from these parameters.
Figure 4 presents a scientific collaboration network composed of 27 authors. It is possible to identify four clusters of higher intensity, represented by different colors. The first cluster (in red) has Gil-Saura I as the central author, with strong connections to Masudin I. and Eugenia E. The second cluster (in orange) groups authors like Ajn Y, Kiatkawsin K, and Sutherland I, forming a cohesive network with multiple interactions. The third cluster (in pink) stands out with authors like Restuputri DP, Masudin I, and Idriani Tr. The fourth cluster (in brown) consists of authors like Salem Se, Hassan Th, and Liu C, demonstrating moderate interactions among them.
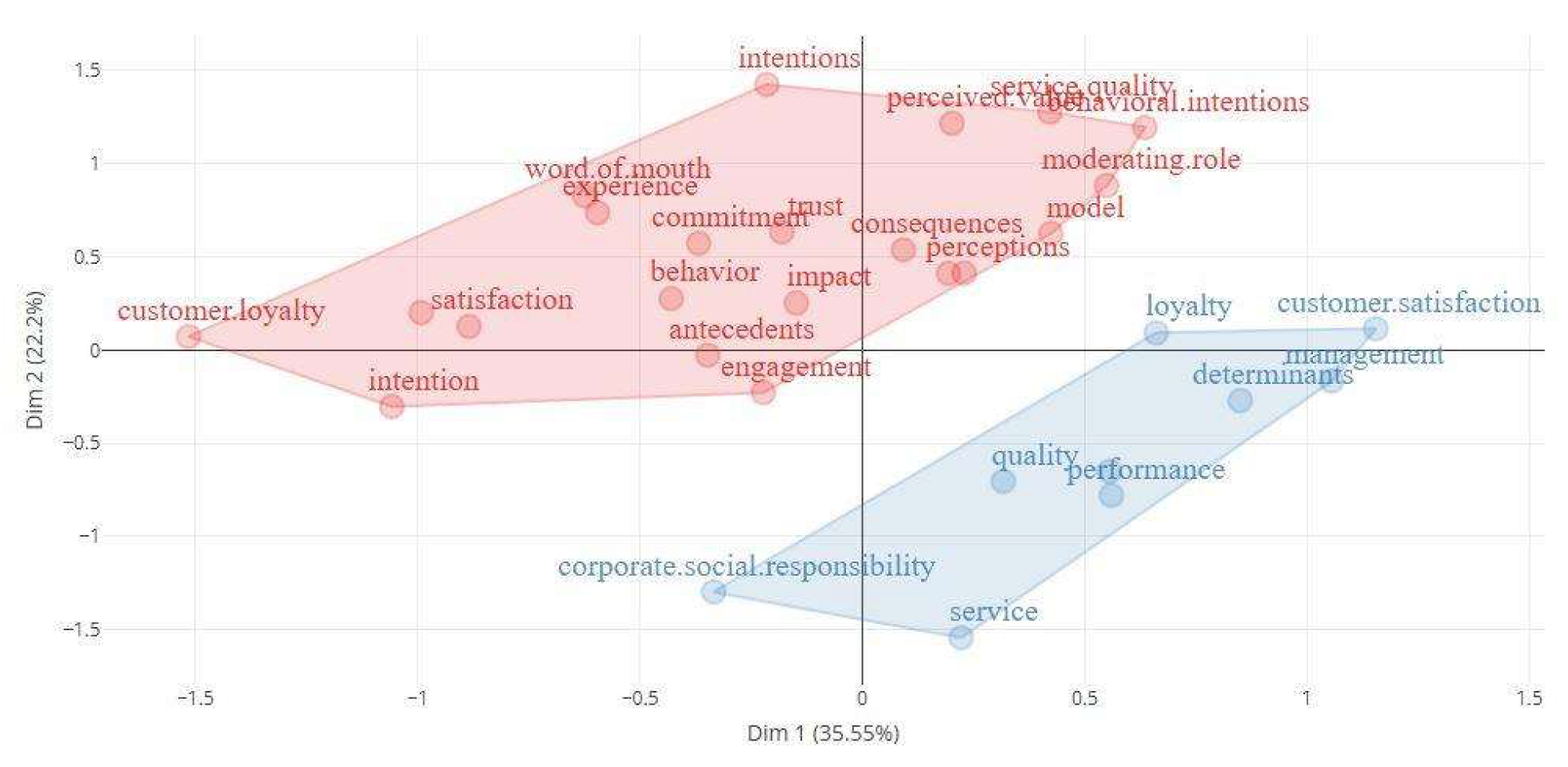
4.6. Conceptual Structure Map via Factor Analysis
The purpose of the Conceptual Structure Map is to identify and represent the conceptual structure of a given construct through the co-occurrence of words in a dataset. This mapping is often performed using dimensionality reduction techniques, such as Multiple Correspondence Analysis (MCA), Multidimensional Scaling (MDS), or Correspondence Analysis (CA).
In the process, Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods are applied to extract relevant terms, especially from titles and abstracts. One of the steps involves the use of the Porter lemmatization algorithm, which simplifies inflected or derived words, reducing them to their root or base form.
For constructing the conceptual map, the extracted terms were obtained from the abstracts, using two-word combinations and the MCA technique. The number of terms was limited to 30 to optimize the visualization.
Figure 5 illustrates the final result, presenting the conceptual map generated through multiple correspondence analysis.
Figure 5 shows that the concepts in red are associated with themes such as customer loyalty, experience, satisfaction, and engagement, highlighting a strong relationship between these factors and the customer experience. On the other hand, the concepts in blue cluster around corporate social responsibility (CSR), quality, and performance, emphasizing their impact on leadership and customer satisfaction. The map reveals two distinct conceptual groups, with possible differences or complements between the analyzed factors.
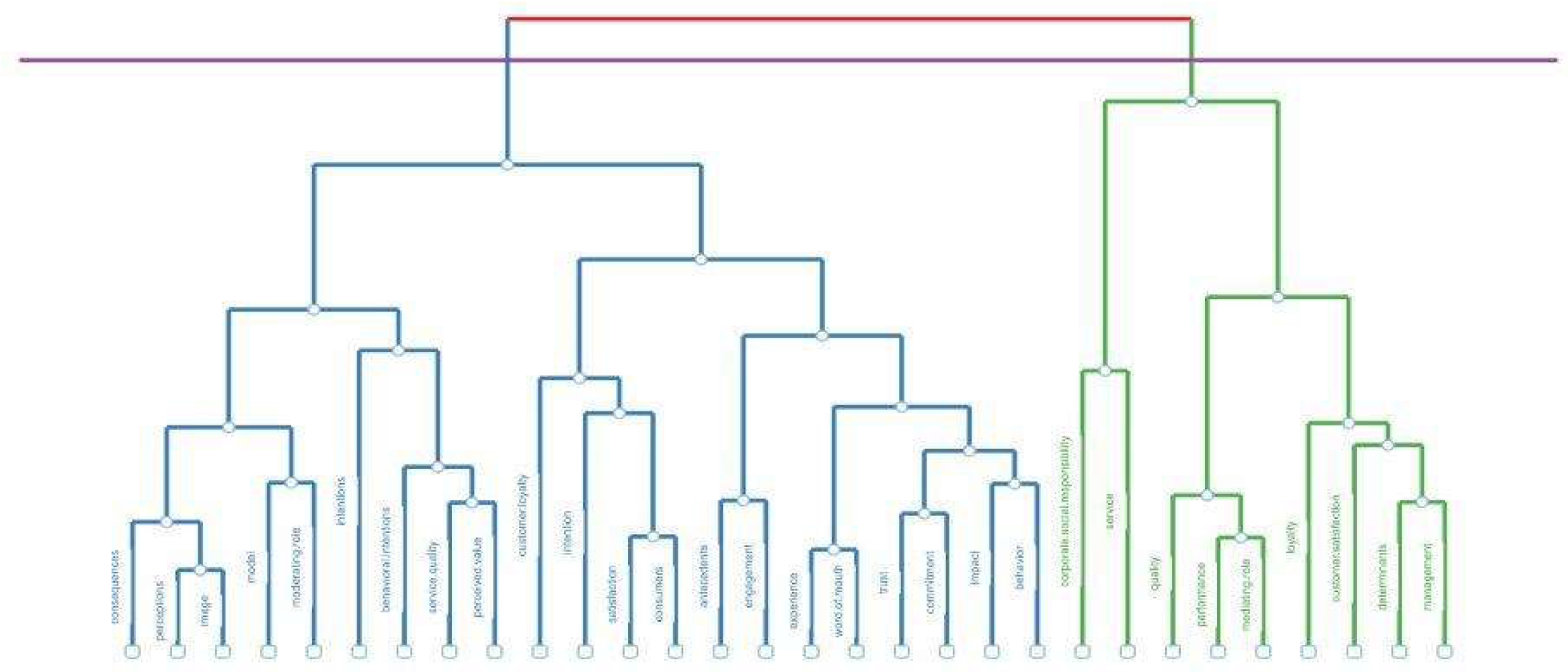
4.7. Dendrogram
A dendrogram is a hierarchical graph used to visualize relationships of similarity or clustering between elements. It organizes data in a tree-like structure, where the branches indicate higher similarity between the items.
5. Discussion
It is noticeable that there are two groups separated by the blue and green colors, indicating similarity between the terms belonging to each group.
This research highlights the importance of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, big data, and augmented reality, in strengthening customer loyalty in the digital environment. These tools create personalized experiences, optimize engagement, and promote sustainable retention by reducing acquisition costs and increasing consumer trust. An example of such a tool would be using artificial intelligence on an e-commerce platform to recommend personalized products based on the user’s purchase history and preferences, significantly increasing repurchase intent. Additionally, the bibliometric analysis identifies central trends, such as "competitive advantage," and emerging gaps in the literature, reinforcing personalization as one of the pillars of loyalty and demonstrating its direct connection with consumer trust and repurchase intention.
The study's findings provide practical guidelines for companies seeking competitive advantages in the digital market. The study emphasizes that personalization is a pillar of loyalty, directly connected to consumer trust and increasing repurchase intent. The application of innovative technologies not only meets the demand for personalization but also consolidates consumer trust and loyalty, optimizing costs and improving overall performance. Companies can adopt these strategies to enhance customer experience and strengthen their operations, expanding retention and generating a sustainable competitive advantage, such as implementing chatbots to offer 24/7 support, quickly answering product and delivery questions, improving satisfaction and promoting customer loyalty.
As [
55] emphasize, bibliometry enables the development of indicators for analyzing scientific production in a specific area of knowledge. This study contributes to the academic literature by presenting a bibliometric analysis approach to identify and understand the factors of customer loyalty and return in the digital environment. The results obtained can serve as a basis for future research and further developments on the subject.
Identifying the factors of customer loyalty and return in the digital environment allows for the identification of new technologies and tools being researched, developed, and used, contributing to innovation in both the service and industrial sectors. This bibliometric study is therefore directly related to SDG (Sustainable Development Goal) 9, which addresses industry, innovation, and infrastructure for the 2030 agenda. SDG 9 highlights, among other factors, the importance of technological modernization and innovation as drivers of sustainable development [
56].
Finally, the hypotheses of this study were confirmed through bibliometric analysis. The results showed that factors such as personalization, trust, and technological innovation are crucial in increasing customer engagement in the digital environment. Moreover, the use of tools such as artificial intelligence and big data emphasizes the importance of creating more personalized and efficient experiences. Thus, the results support the hypotheses and help understand which strategies can improve customer loyalty and retention.
6. Conclusions
This research achieved its primary objective by analyzing the determining factors for customer loyalty and return in the digital environment, focusing on effective practices to promote this retention. Through a bibliometric study, key elements that directly influence consumer loyalty were identified, and the most relevant aspects of this audience were understood to meet expectations in the digital context. The analysis mapped trends and gaps in the literature, providing a broader view of strategies that drive customer satisfaction.
To assess the fulfillment of the study's main objective, data collected in the bibliometric research were analyzed to identify connections between the selected articles and the main trends of the subject. Some graphs were generated to aid in better understanding the topic. Tables were also created to illustrate the relationship of key information about the sample. The Sankey diagram showed the concentration by countries concerning customer loyalty. Bibliographic coupling clustering illustrated, through four quadrants, the development and relevance of the topic, niche themes, and term analysis in relation to ascension or decline within the analysis.
References
- ARAÚJO, Jackson Bruno Feitosa; ALBUQUERQUE, Joyce da Silva. Marketing Digital: Um Estudo Multicasos em Bares e Restaurantes de Crato-CE. Id on Line Rev.Mult. Psic.,2018, vol.12, n.42, p.719-742.ISSN: 1981-1179.
- Torres, C. A Bíblia do Marketing Digital, 2nd ed.; Novatec Editora: São Paulo, Brasil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR, S. Council Post: Customer Retention Versus Customer Acquisition. Forbes, 12 ago. 2024.
- CHURCHILL J., G.; PETER, J. P. Marketing - Criando Valor Para o Cliente.3. ed. São Paulo: Saraiva, 2013.
- Invesp (Instituto de Investimentos de São Paulo). Available online: https://www.invespcro.com/blog/customer-acquisition-retention/ (accessed on 02 January 2025).
- JUNG, S.-U.; SHEGAI, V. The impact of digital marketing innovation on firm performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.M.; Herhausen, D.; Troilo, G.; Rossi, A. How and when do big data investments pay off? The role of marketing affordances and service innovation. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. in press. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DI VAIO, A.; PALLADINO, R.; PEZZI, A.; KALISZ, D. E. The role of digital innovation in knowledge management systems: A systematic literature review. Journal of Business Research 2021, 123, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wenqian, Z.; Xia, T. Impact of Shopping Website Design on Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: The Mediating Role of Usability and the Moderating Role of Trust. Sustainability in press. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerea, C.; Gonzalez-Lopez, F.; Herskovic, V. Omnichannel Customer Experience and Management: An Integrative Review and Research Agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13(5), in press. [CrossRef]
- Khairawati, S. Effect of Customer Loyalty Program on Customer Satisfaction and Its Impact on Customer Loyalty. Int. J. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2019, 9(1), in press. [CrossRef]
- SINGH, Roopa; KHAN, Imran Akhtar. An approach to increase customer retention and loyalty in B2C world. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, v. 2, n. 11, p. 1-6, nov. 2012. ISSN 2250-3153.
- LI, F.; LARIMO, J.; LEONIDOU, L. C. Social media in marketing research: Theoretical bases, methodological aspects, and thematic focus. Psychology & Marketing 2023, 40, 124–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BASHIR, Muhammad Adnan; SARAIH, Ummi Naiemah Binti; GUNDALA, Raghava; ANSARI, Junaid; QURESHI, Muhammad Azeem; AHMED, Shiraz. Digital influence: examining social media marketing dynamics and how they affect consumer brand loyalty. WSEAS Transactions on Business and Economics, v. 21, p. 128-135, 2024. [CrossRef]
- GÜMÜŞ, Rafika; GÖK, E. E.; ESEN, M. A review of research on international student mobility: science mapping the existing knowledge base. Journal of Studies in International Education, v. 24, n. 5, p. 495-517, 2020. [CrossRef]
- FINNIE, William; RANDALL, Robert. Loyalty as a philosophy and strategy: An interview with Frederick F. Reichheld. Strategy & Leadership, v. 30, p. 25–31, 2002. [CrossRef]
- Philip. Marketing management: analysis, lanning, implementation, and control. 11. ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 2002.
- LI, Biao; MOUSA, Saeed; REYES REINOSO, Johanna Rosali; ALZOUBI, Haitham M.; ALI, Anis; HOANG, Anh Duong. The role of technology innovation, customer retention and business continuity on firm performance after post-pandemic era in China’s SMEs. Economic Analysis and Policy, 2023; 78, 1209–1220. [CrossRef]
- CARDOSO, António; GABRIEL, Marx; FIGUEIREDO, Jorge; OLIVEIRA, Isabel; RÊGO, Reiville; SILVA, Rui; OLIVEIRA, Márcio; MEIRINHOS, Galvão. Confiança e lealdade na construção do relacionamento da marca com o cliente: análise empírica em uma rede varejista do Norte do Brasil. Revista de Inovação Aberta: Tecnologia, Mercado e Complexidade , v. 3, pág. 109, conjunto. 2022. [CrossRef]
- ZEREN, Deniz; KARA, Ali. Efeitos da herança da marca nas intenções de compra de serviços de companhias aéreas: os papéis mediadores da confiança e da lealdade à marca. Sustainability , v. 13, n. 1, p. 303, 2021. [CrossRef]
- KOTLER, Philip; KARTAJAYA, Hermawan; SETIAWAN, Iwan. Marketing 4.0: Moving from Traditional to Digital. 1. ed. Nova Jersey: Wiley, 2016. p. 45.
- LIM, Weng Marc. Transformative marketing in the new normal: A novel practice-scholarly integrative review of business-to-business marketing mix challenges, opportunities, and solutions. Journal of Business Research, 2023; 160, 113638. [CrossRef]
- XU, Zhenning; FRANKWICK, Gary L.; RAMIREZ, Edward. Effects of big data analytics and traditional marketing analytics on new product success: A knowledge fusion perspective. Journal of Business Research, v. 69, n. 5, p. 1562-1566, mai. 2016. [CrossRef]
- KRISHEN, Anjala S.; DWIVEDI, Yogesh K.; BINDU, N.; KUMAR, K. Satheesh. A broad overview of interactive digital marketing: A bibliometric network analysis. Journal of Business Research, v. 131, p. 183-195, jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- ASLAM, Tanveer; HAMID, Kashif; ARSHAD, Salman. The effects of interactive marketing, customer satisfaction and flashes on customer loyalty. EuroEconomica, issue 1(34), 2015. ISSN 1582-8859.
- GILANINIA, S.; ALMANI, A. M.; POURNASERANI, A.; JAVAD, S. Relationship Marketing: a New Approach to Marketing in the Third Millennium. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, v. 5, n. 5, p. 787-799, 2011.
- MERISAVO, Marko. The interaction between digital marketing communication and customer loyalty. 2008. 122 p. Doctoral thesis (article-based)—School of Business, Aalto University, 2008. Acta Universitatis oeconomicae Helsingiensis. A, 333.
- WANG, Cheng Lu. Editorial – What is an interactive marketing perspective and what are emerging research areas? Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, v. 18, n. 2, p. 161-165, mar. 2024. [CrossRef]
- DEIGHTON, John. The future of interactive marketing. Harvard Business Review, v. 74, n. 6, p. 151-160, nov./dez. 1996.
- VERMA, D.; KUMAR, V. S.; KUMAR, D. Evolution of research in interactive marketing: a bibliometric and thematic review.
- TRAN, Trang P.; TAYLOR, David G.; WEN, Chao. Value co-creation through branded apps: enhancing perceived quality and brand loyalty. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, v. 17, n. 4, p. 1-19, out. 2022. [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, Jing; ZHANG, Jing; ZHANG, Linghua; MA, Bei. Ride-sharing platforms: the effects of online social interactions on loyalty, mediated by perceived benefits. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, v. 17, n. 5, p. 698-713, 2 fev. 2023. [CrossRef]
- GIL, Antônio Carlos. Métodos e técnicas de pesquisa social. 6. ed. São Paulo: Atlas, 2008.
- LAKATOS, Eva Maria; MARCONI, Marina de Andrade. Fundamentos de metodologia científica. 7. ed. São Paulo: Atlas, 2003.
- CRESWELL, John W. Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. 4. ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
- THANGAVEL, Packiaraj; CHANDRA, Bibhas. Two decades of M-commerce consumer research: a bibliometric analysis using R Biblioshiny. Sustainability, Basel, v. 15, n. 15, p. 11835, 2023. [CrossRef]
- ABAFE, Ejovi Akpojevwe; BAHTA, Yonas T.; JORDAAN, Henry. Exploring Biblioshiny for historical assessment of global research on sustainable use of water in agriculture. Sustainability, Basel, v. 14, n. 17, p. 10651, 2022. [CrossRef]
- MANOHARAN, Ajay Adithya et al. Green entrepreneurship for sustainable business: a bibliometric analysis. Journal of Lifestyle and SDG'S Review , [Sl], v. 5, n. 2, p. e03204, 2023. [CrossRef]
- AZİZOĞLU, Fatma; TERZİ, Banu; SÖNMEZ DÜZKAYA, Duygu. Global trends in technology-dependent children, home care, and parental discharge education: A bibliometric analysis using Biblioshiny. Journal of Pediatric Nursing, [S.l.], v. 79, p. e213-e222, nov.-dez. 2024. [CrossRef]
- DEMIR, Gülay; CHATTERJEE, Prasenjit; PAMUCAR, Dragan. Sensitivity analysis in multi-criteria decision making: A state-of-the-art research perspective using bibliometric analysis. Expert Systems with Applications, [S.l.], v. 237, Part C, p. 121660, 1 mar. 2024. [CrossRef]
- LOURENÇO, F.; NARA, E. O. B.; GONÇALVES, M. C.; CANCIGLIERI JUNIOR, O. Preliminary construct of sustainable product development with a focus on the Brazilian reality: A review and bibliometric analysis. In: World Sustainability Series (Part F1432, p. 197–220). Springer, 2023. [CrossRef]
- TARDIO, P. R.; SCHAEFER, J. L.; NARA, E. O. B.; BENITEZ, G. B.; CASTRO E SILVA, A. The link between lean manufacturing and Industry 4.0 for product development process: A systemic approach. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 2023; 34, 1404–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SERRA, F. N. T.; NARA, E. O. B.; GONÇALVES, M. C.; DA COSTA, S. E. G.; BORTOLUZZI, S. C. Preliminary construct for decision making in organizations: A systemic approach. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Production Research – Americas: ICPR Americas 2022 (p. 639–646). Springer, 2023. [CrossRef]
- SERRA, F. N. T.; GONÇALVES, M. C.; BORTOLUZZI, S. C.; BENITEZ, L. B.; NARA, E. O. B. The link between environment and organizational architecture for decision-making in educational institutions: A systemic approach. Sustainability (Switzerland), v. 16, n. 10, p. 4309, 2024. [CrossRef]
- DA SILVA, E. C. M.; LIRA, M. A. T.; GONÇALVES, M. C.; JEAN, W.; DOS SANTOS JÚNIOR, R. B. The role of renewable energies in combating poverty in Brazil: A systematic review. Sustainability (Switzerland), v. 16, n. 13, p. 5584, 2024. [CrossRef]
- DE CASTRO E SILVA, A.; NARA, E. O. B.; GONÇALVES, M. C.; PIOVESAN, C. V.; DOS SANTOS DOMINGOS, G. A preliminary reflection framework of sustainability, smart cities, and digital transformation with effects on urban planning: A review and bibliometric analysis. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, v. 702, p. 107–118, 2024. [CrossRef]
- ROMÁN-COLLADO, R.; CASADO RUÍZ, V. Key effects contributing to changes in energy imports in the EU-27 between 2000 and 2020: A decomposition analysis based on the Sankey diagram. Energy Economics, v. 140, 108009, 2024. [CrossRef]
- MAS-TUR, A.; ROIG-TIERNO, N.; SARIN, S.; HAON, C.; SEGO, T.; BELKHOUJA, M.; PORTER, A.; MERIGÓ, J. M. Co-citation, bibliographic coupling and leading authors, institutions and countries in the 50 years of Technological Forecasting and Social Change. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, v. 165, 120487, 2021. [CrossRef]
- CALLON, M.; COURTIAL, J. P.; TURNER, W. A.; BAUIN, S. From translations to problematic networks: An introduction to co-word analysis. Social Science Information, v. 22, n. 2, p. 191–235, 1983. [CrossRef]
- CRONIN, B. Bibliometrics and Beyond: Applying Citation Analysis to Research Management. 1. ed. New York: Garland, 1984.
- Callon M, Courtial JP, Laville F. Co-word analysis as a tool for describing the network of interactions between basic and technological research: the case of polymer chemistry. Scientometrics. 1991;22(1):155–205.
- Yesilbudak, M., Karaman, H. T., & Karacan, H. U. (2011). Object Oriented Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering Model in Data Mining. Gazi Üniversitesi Mühendislik-Mimarlık Fakültesi Dergisi, 26(1), 27–39.
- ARIA, Massimo; CUCCURULLO, Corrado. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, v. 11, n. 4, p. 959-975, nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- JANSSENS, F.; GLÄNZEL, W.; DE MOOR, B. Dynamic hybrid clustering of bioinformatics by incorporating text mining and citation analysis. In: Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (p. 360–369). 2007. [CrossRef]
- SILVA, Márcia Regina da; HAYASHI, Carlos Roberto Massao; HAYASHI, Maria Cristina Piumbato Innocentini. Bibliometric and scientometric analyses: challenges for specialists working in the field. Brazilian Journal of Information Science: Research Trends, v. 2, n. 1, p. 110-129, 2011. [CrossRef]
- United Nations. (2015). The Global Goals for Sustainable Development. Retrieved from https://www.globalgoals.org/.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).