Submitted:
29 January 2025
Posted:
30 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bio-Layer Interferometry Studies
| A + L |
ka1 → ← |
AL | AL + L |
ka2 → ← |
ALL | (1) | |
|
kd1 KD1 |
kd2 KD2 |
| A + L1 |
ka1 → ← |
AL1 | A + L2 |
ka2 → ← |
AL2 | (2) | |
|
kd1 KD1 |
kd2 KD2 |
2.3. ThT Fluorescence Assay
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.5. Structural Modeling of Aβ40-S100 Complexes
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering Measurements
2.7. Chemical Crosslinking of Proteins
3. Results
3.1. The Interaction of S100A8/S100A9 Proteins with Aβ Peptides
3.2. Modeling of Aβ40-S100A8/S100A9 Complexes
3.3. S100A8/S100A9 Prevent HSA Interaction with Monomeric Aβ
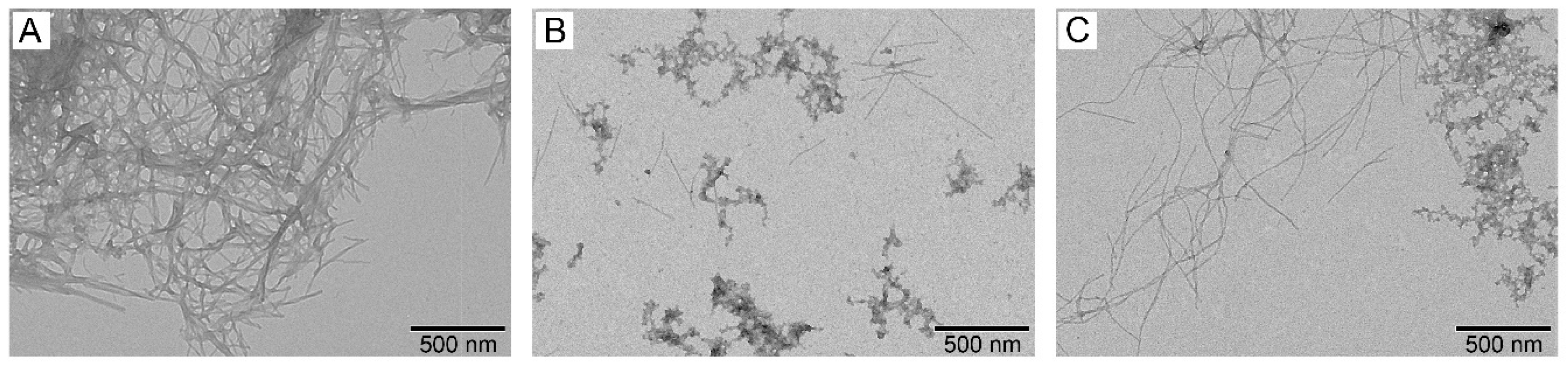
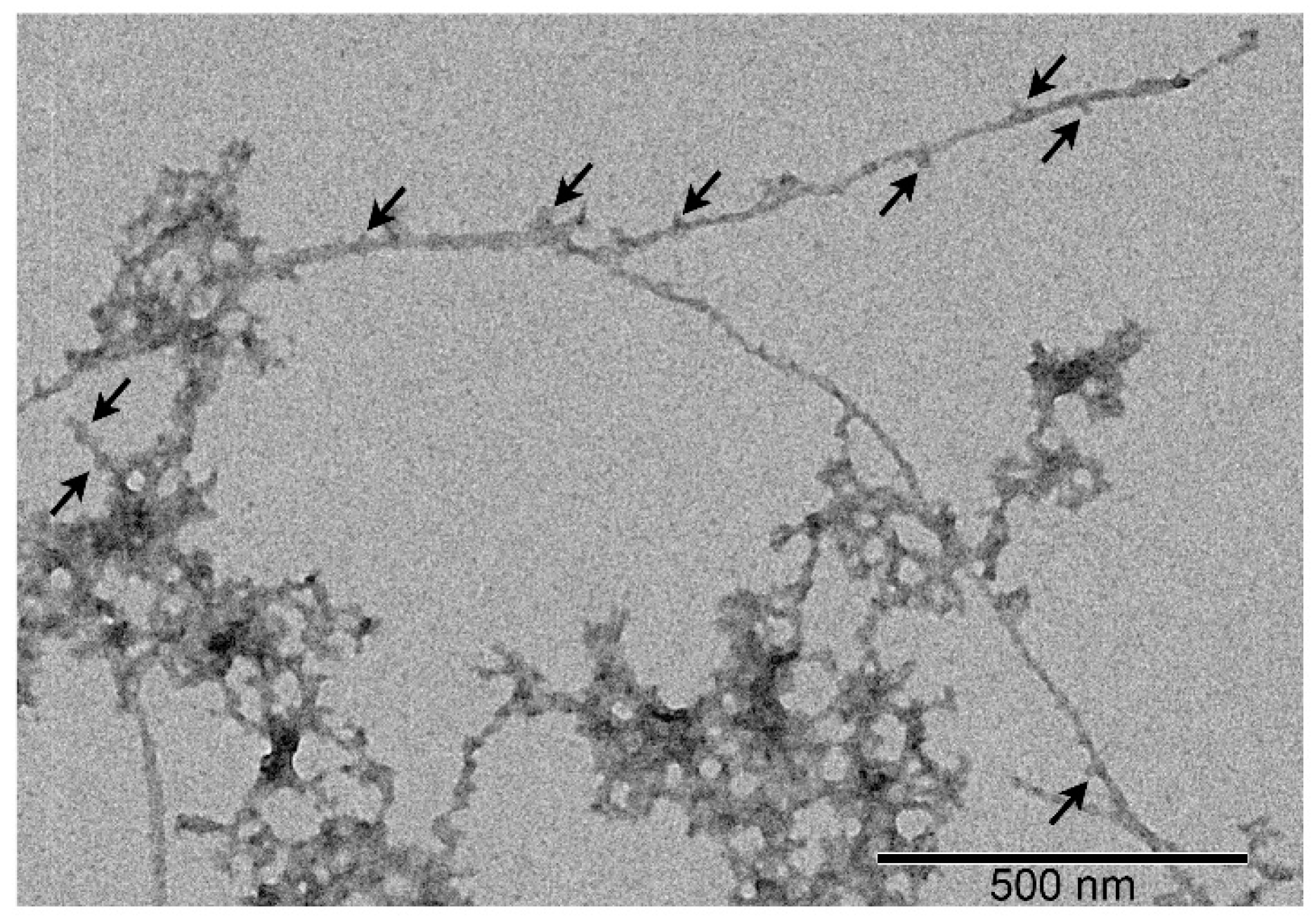
3.4. Effect of S100A8/S100A9 on Aβ Fibrillation In Vitro
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reitz, C.; Mayeux, R. Alzheimer disease: Epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochemical Pharmacology 2014, 88(4), 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C. R., Jr.; Bennett, D. A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M. C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S. B.; Holtzman, D. M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; Liu, E.; Molinuevo, J. L.; Montine, T.; Phelps, C.; Rankin, K. P.; Rowe, C. C.; Scheltens, P.; Siemers, E.; Snyder, H. M.; Sperling, R. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2018, 14(4), 535–562. [Google Scholar]
- DeTure, M. A.; Dickson, D. W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener 2019, 14(1), 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorszewska, J.; Prendecki, M.; Oczkowska, A.; Dezor, M.; Kozubski, W. Molecular Basis of Familial and Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2016, 13(9), 952–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseininasab, S. S. M.; Ebrahimi, R.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Kazemi, K.; Khakpour, Y.; Hajibeygi, R.; Mohamadkhani, A.; Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Tavasol, A.; Tutunchian, Z.; Fazel, T.; Fathi, M.; Hajiesmaeili, M. Alzheimer's disease and infectious agents: a comprehensive review of pathogenic mechanisms and microRNA roles. Front Neurosci 2024, 18, 1513095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinney, J. W.; Bemiller, S. M.; Murtishaw, A. S.; Leisgang, A. M.; Salazar, A. M.; Lamb, B. T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Wang, L. Neurotransmitters in Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawuenyega, K. G.; Sigurdson, W.; Ovod, V.; Munsell, L.; Kasten, T.; Morris, J. C.; Yarasheski, K. E.; Bateman, R. J. Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2010, 330(6012), 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, U.; Nilson, A. N.; Kayed, R. The Role of Amyloid-β Oligomers in Toxicity, Propagation, and Immunotherapy. eBioMedicine 2016, 6, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liang, Z. H.; Gong, C.-X. Hyperphosphorylation of tau and protein phosphatases in Alzheimer disease. Panminerva medica 2006, 48, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ba, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Jiang, J.; Huang, N.; Luo, Y. Comprehensive review on Alzheimer's disease: From the posttranslational modifications of Tau to corresponding treatments. Ibrain 2024, 10(4), 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G. P.; Clark, I. A.; Vissel, B. Questions concerning the role of amyloid-β in the definition, aetiology and diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica 2018, 136(5), 663–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroni, G.; Bisceglia, P.; Seripa, D. Understanding the Amyloid Hypothesis in Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2019, 68(2), 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karran, E.; De Strooper, B. The amyloid hypothesis in Alzheimer disease: new insights from new therapeutics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2022, 21(4), 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnsten, A. F. T.; Datta, D.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. Hypothesis: Tau pathology is an initiating factor in sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 2021, 17(1), 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Nizamutdinov, D.; Yi, S. S.; Wu, E.; Huang, J. H. Disease Modifying Monoclonal Antibodies and Symptomatic Pharmacological Treatment for Alzheimer's Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12(11). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. M.; Lendel, C. Extracellular protein components of amyloid plaques and their roles in Alzheimer's disease pathology. Mol Neurodegener 2021, 16(1), 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, M. A.; Robertson, J. D.; Teesdale, W. J.; Campbell, J. L.; Markesbery, W. R. Copper, iron and zinc in Alzheimer's disease senile plaques. J Neurol Sci 1998, 158(1), 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmeyer, S.; Romao, M. A.; Cristovao, J. S.; Vilella, A.; Zoli, M.; Gomes, C. M.; Grabrucker, A. M. Distribution and Relative Abundance of S100 Proteins in the Brain of the APP23 Alzheimer's Disease Model Mice. Front Neurosci 2019, 13, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, C. E.; Goyette, J.; Utter, V.; Rahimi, F.; Yang, Z.; Geczy, C. L.; Halliday, G. M. Inflammatory S100A9 and S100A12 proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2006, 27(11), 1554–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biere, A. L.; Ostaszewski, B.; Stimson, E. R.; Hyman, B. T.; Maggio, J. E.; Selkoe, D. J. Amyloid β-Peptide Is Transported on Lipoproteins and Albumin in Human Plasma*. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996, 271(51), 32916–32922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanyon, H. F.; Viles, J. H. Human serum albumin can regulate amyloid-β peptide fiber growth in the brain interstitium: implications for Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 2012, 287(33), 28163–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litus, E. A.; Kazakov, A. S.; Sokolov, A. S.; Nemashkalova, E. L.; Galushko, E. I.; Dzhus, U. F.; Marchenkov, V. V.; Galzitskaya, O. V.; Permyakov, E. A.; Permyakov, S. E. The binding of monomeric amyloid β peptide to serum albumin is affected by major plasma unsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019, 510(2), 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojevic, J.; Melacini, G. Stoichiometry and affinity of the human serum albumin-Alzheimer's Aβ peptide interactions. Biophysical journal 2011, 100(1), 183–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, F.; Xu, L.; Jia, L. HSA targets multiple Aβ42 species and inhibits the seeding-mediated aggregation and cytotoxicity of Aβ42 aggregates. RSC Advances 2016, 6(75), 71165–71175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezra, A.; Rabinovich-Nikitin, I.; Rabinovich-Toidman, P.; Solomon, B. Multifunctional Effect of Human Serum Albumin Reduces Alzheimer's Disease Related Pathologies in the 3xTg Mouse Model. J Alzheimers Dis 2016, 50(1), 175–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boada, M.; Ortiz, P.; Anaya, F.; Hernandez, I.; Munoz, J.; Nunez, L.; Olazaran, J.; Roca, I.; Cuberas, G.; Tarraga, L.; Buendia, M.; Pla, R. P.; Ferrer, I.; Paez, A. Amyloid-targeted therapeutics in Alzheimer's disease: use of human albumin in plasma exchange as a novel approach for Abeta mobilization. Drug News Perspect 2009, 22(6), 325–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boada, M.; López, O. L.; Olazarán, J.; Núñez, L.; Pfeffer, M.; Paricio, M.; Lorites, J.; Piñol-Ripoll, G.; Gámez, J. E.; Anaya, F.; Kiprov, D.; Lima, J.; Grifols, C.; Torres, M.; Costa, M.; Bozzo, J.; Szczepiorkowski, Z. M.; Hendrix, S.; Páez, A. A randomized, controlled clinical trial of plasma exchange with albumin replacement for Alzheimer's disease: Primary results of the AMBAR Study. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2020, 16(10), 1412–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Cristovao, J. S.; Gomes, C. M. S100 Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease. Front Neurosci 2019, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.; Cannon, B. R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Hsu, K.; Weber, D. J.; Geczy, C. L. Functions of S100 proteins. Curr Mol Med 2013, 13(1), 24–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Ali, S. A. Multifunctional Role of S100 Protein Family in the Immune System: An Update. Cells 2022, 11(15). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L. L.; Garrie, K.; Turner, M. D. Role of S100 proteins in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2020, 1867(6), 118677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreejit, G.; Flynn, M. C.; Patil, M.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Murphy, A. J.; Nagareddy, P. R. S100 family proteins in inflammation and beyond. Adv Clin Chem 2020, 98, 173–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Persechini, A.; Moncrief, N. D.; Kretsinger, R. H. The EF-hand family of calcium-modulated proteins. Trends Neurosci. 1989, 12(11), 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, J. L.; Walsh, M. P.; Vogel, H. J. Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix-loop-helix EF-hand motifs. Biochem J 2007, 405(2), 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Klechikov, A. G.; Gharibyan, A. L.; Warmlander, S. K.; Jarvet, J.; Zhao, L.; Jia, X.; Narayana, V. K.; Shankar, S. K.; Olofsson, A.; Brannstrom, T.; Mu, Y.; Graslund, A.; Morozova-Roche, L. A. The role of pro-inflammatory S100A9 in Alzheimer's disease amyloid-neuroinflammatory cascade. Acta Neuropathol 2014, 127(4), 507–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boom, A.; Pochet, R.; Authelet, M.; Pradier, L.; Borghgraef, P.; Van Leuven, F.; Heizmann, C. W.; Brion, J. P. Astrocytic calcium/zinc binding protein S100A6 over expression in Alzheimer's disease and in PS1/APP transgenic mice models. Biochim Biophys Acta 2004, 1742(1-3), 161-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z. Y.; Wang, C. Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. C.; Wang, Z. Y. Glial S100A6 Degrades beta-amyloid Aggregation through Targeting Competition with Zinc Ions. Aging Dis 2019, 10(4), 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J. C.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, S. L. Proinflammatory effects of S100A8/A9 via TLR4 and RAGE signaling pathways in BV-2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Med 2017, 40(1), 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, C.; Heneka, M. T. Danger-associated molecular patterns in Alzheimer's disease. Journal of leukocyte biology 2017, 101(1), 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M. T.; Carson, M. J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G. E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D. L.; Jacobs, A. H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R. M.; Herrup, K.; Frautschy, S. A.; Finsen, B.; Brown, G. C.; Verkhratsky, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Koistinaho, J.; Latz, E.; Halle, A.; Petzold, G. C.; Town, T.; Morgan, D.; Shinohara, M. L.; Perry, V. H.; Holmes, C.; Bazan, N. G.; Brooks, D. J.; Hunot, S.; Joseph, B.; Deigendesch, N.; Garaschuk, O.; Boddeke, E.; Dinarello, C. A.; Breitner, J. C.; Cole, G. M.; Golenbock, D. T.; Kummer, M. P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol 2015, 14(4), 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummer, M. P.; Vogl, T.; Axt, D.; Griep, A.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Jessen, F.; Gelpi, E.; Roth, J.; Heneka, M. T. Mrp14 deficiency ameliorates amyloid beta burden by increasing microglial phagocytosis and modulation of amyloid precursor protein processing. J Neurosci 2012, 32(49), 17824–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T. Y.; Chang, K. A.; Kim, J.; Kim, H. S.; Kim, S.; Chong, Y. H.; Suh, Y. H. S100a9 knockdown decreases the memory impairment and the neuropathology in Tg2576 mice, AD animal model. PLoS One 2010, 5(1), e8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Yin, Q.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Morozova-Roche, L. A. Proinflammatory S100A9 stimulates TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathways causing enhanced phagocytic capacity of microglial cells. Immunol Lett 2023, 255, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Gilthorpe, J.; van der Maarel, J. R. MRP14 (S100A9) protein interacts with Alzheimer beta-amyloid peptide and induces its fibrillization. PLoS One 2012, 7(3), e32953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Iashchishyn, I. A.; Pansieri, J.; Nystrom, S.; Klementieva, O.; Kara, J.; Horvath, I.; Moskalenko, R.; Rofougaran, R.; Gouras, G.; Kovacs, G. G.; Shankar, S. K.; Morozova-Roche, L. A. S100A9-Driven Amyloid-Neuroinflammatory Cascade in Traumatic Brain Injury as a Precursor State for Alzheimer's Disease. Sci Rep 8 1), 12836. [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M. M.; Ransom, J. E.; Mandrekar, J.; Turcano, P.; Savica, R.; Brown, A. W. Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias in the Population. J Alzheimers Dis 2022, 88(3), 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, M.; Puerta, E.; Ismail, M. A.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, P.; Ronnback, A.; Codita, A.; Parrado-Fernandez, C.; Maioli, S.; Gil-Bea, F.; Merino-Serrais, P.; Cedazo-Minguez, A. Aggregation of the Inflammatory S100A8 Precedes Abeta Plaque Formation in Transgenic APP Mice: Positive Feedback for S100A8 and Abeta Productions. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2016, 72(3), 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Litus, E.; Shevelyova, M.; Vologzhannikova, A.; Deryusheva, E.; Nemashkalova, E.; Machulin, A.; Nazipova, A.; Permyakova, M.; Permyakov, S. S100A8 Interaction with Amyloid-β Peptide Suppresses Its Fibrillation Proceedings [Online], 2024.
- Horvath, I.; Jia, X.; Johansson, P.; Wang, C.; Moskalenko, R.; Steinau, A.; Forsgren, L.; Wagberg, T.; Svensson, J.; Zetterberg, H.; Morozova-Roche, L. A. Pro-inflammatory S100A9 Protein as a Robust Biomarker Differentiating Early Stages of Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer's Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 2016, 7(1), 34–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litus, E. A.; Kazakov, A. S.; Sokolov, A. S.; Nemashkalova, E. L.; Galushko, E. I.; Dzhus, U. F.; Marchenkov, V. V.; Galzitskaya, O. V.; Permyakov, E. A.; Permyakov, S. E. The binding of monomeric amyloid beta peptide to serum albumin is affected by major plasma unsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019, 510(2), 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryusheva, E. I.; Shevelyova, M. P.; Rastrygina, V. A.; Nemashkalova, E. L.; Vologzhannikova, A. A.; Machulin, A. V.; Nazipova, A. A.; Permyakova, M. E.; Permyakov, S. E.; Litus, E. A. In Search for Low-Molecular-Weight Ligands of Human Serum Albumin That Affect Its Affinity for Monomeric Amyloid beta Peptide. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25(9). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, J.; Pannell, R. Selective removal of albumin from plasma by affinity chromatography. Clin Chim Acta 1973, 49(1), 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litus, E. A.; Kazakov, A. S.; Deryusheva, E. I.; Nemashkalova, E. L.; Shevelyova, M. P.; Machulin, A. V.; Nazipova, A. A.; Permyakova, M. E.; Uversky, V. N.; Permyakov, S. E. Ibuprofen Favors Binding of Amyloid-beta Peptide to Its Depot, Serum Albumin. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(11). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakov, A. S.; Sofin, A. D.; Avkhacheva, N. V.; Denesyuk, A. I.; Deryusheva, E. I.; Rastrygina, V. A.; Sokolov, A. S.; Permyakova, M. E.; Litus, E. A.; Uversky, V. N.; Permyakov, E. A.; Permyakov, S. E. Interferon Beta Activity Is Modulated via Binding of Specific S100 Proteins. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21(24). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzariti, A. M.; Soboleva, T. A.; Jans, D. A.; Board, P. G.; Baker, R. T. An efficient system for high-level expression and easy purification of authentic recombinant proteins. Protein Sci 2004, 13(5), 1331–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, C. N.; Vajdos, F.; Fee, L.; Grimsley, G.; Gray, T. How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci 1995, 4(11), 2411–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ferrari, G. V.; Mallender, W. D.; Inestrosa, N. C.; Rosenberry, T. L. Thioflavin T is a fluorescent probe of the acetylcholinesterase peripheral site that reveals conformational interactions between the peripheral and acylation sites. J Biol Chem 2001, 276(26), 23282–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litus, E. A.; Kazakov, A. S.; Deryusheva, E. I.; Nemashkalova, E. L.; Shevelyova, M. P.; Nazipova, A. A.; Permyakova, M. E.; Raznikova, E. V.; Uversky, V. N.; Permyakov, S. E. Serotonin Promotes Serum Albumin Interaction with the Monomeric Amyloid beta Peptide. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22(11). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiiman, A.; Krishtal, J.; Palumaa, P.; Tougu, V. In vitro fibrillization of Alzheimers amyloid-b peptide (1-42). AIP Advances 2015, 5(092401). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H. M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T. N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I. N.; Bourne, P. E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28(1), 235–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desta, I. T.; Porter, K. A.; Xia, B.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S. Performance and Its Limits in Rigid Body Protein-Protein Docking. Structure 2020, 28(9), 1071–1081 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakov, A. S.; Deryusheva, E. I.; Sokolov, A. S.; Permyakova, M. E.; Litus, E. A.; Rastrygina, V. A.; Uversky, V. N.; Permyakov, E. A.; Permyakov, S. E. Erythropoietin Interacts with Specific S100 Proteins. Biomolecules 12 1). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrodinger, LLC, The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8. 2015.
- Uversky, V. N. Natively unfolded proteins: a point where biology waits for physics. Protein Sci 2002, 11(4), 739–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemashkalova, E. L.; Permyakov, E. A.; Permyakov, S. E.; Litus, E. A. Modulation of linoleic acid-binding properties of human serum albumin by divalent metal cations. Biometals 2017, 30(3), 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streicher, W. W.; Lopez, M. M.; Makhatadze, G. I. Modulation of quaternary structure of S100 proteins by calcium ions. Biophys Chem 2010, 151(3), 181–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C. C.; Khan, I.; Tsai, K. L.; Li, H.; Yang, L. W.; Chou, R. H.; Yu, C. Blocking the interaction between S100A9 and RAGE V domain using CHAPS molecule: A novel route to drug development against cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, 1864(11), 1558–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katte, R.; Yu, C. Blocking the interaction between S100A9 protein and RAGE V domain using S100A12 protein. PLoS One 2018, 13(6), e0198767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramasivam, S.; Murugesan, J.; Vedagiri, H.; Perumal, S. S.; Ekambaram, S. P. Virtual Probing on the Influence of Ca(2+) and Zn(2+) Bound S100A8 and S100A9 Proteins Towards their Interaction Against Pattern Recognition Receptors Aggravating Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cell Biochem Biophys 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakov, A. S.; Deryusheva, E. I.; Rastrygina, V. A.; Sokolov, A. S.; Permyakova, M. E.; Litus, E. A.; Uversky, V. N.; Permyakov, E. A.; Permyakov, S. E. Interaction of S100A6 Protein with the Four-Helical Cytokines. Biomolecules 13 9). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakov, A. S.; Deryusheva, E. I.; Permyakova, M. E.; Sokolov, A. S.; Rastrygina, V. A.; Uversky, V. N.; Permyakov, E. A.; Permyakov, S. E. Calcium-Bound S100P Protein Is a Promiscuous Binding Partner of the Four-Helical Cytokines. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(19). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permyakov, S. E.; Ismailov, R. G.; Xue, B.; Denesyuk, A. I.; Uversky, V. N.; Permyakov, E. A. Intrinsic disorder in S100 proteins. Mol Biosyst 2011, 7(7), 2164–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewski, H. M.; Kozlowski, P. B. Evidence for blood-brain barrier changes in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (SDAT). Ann N Y Acad Sci 1982, 396, 119–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. J.; Park, K. W.; Kim, T. E.; Im, J. Y.; Shin, H. S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D. H.; Ye, B. S.; Kim, J. H.; Kim, E. J.; Park, K. H.; Han, H. J.; Jeong, J. H.; Choi, S. H.; Park, S. A. Elevation of the Plasma Abeta40/Abeta42 Ratio as a Diagnostic Marker of Sporadic Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2015, 48(4), 1043–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeux, R.; Honig, L. S.; Tang, M. X.; Manly, J.; Stern, Y.; Schupf, N.; Mehta, P. D. Plasma A[beta]40 and A[beta]42 and Alzheimer's disease: relation to age, mortality, and risk. Neurology 2003, 61(9), 1185–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Steenoven, I.; van der Flier, W. M.; Scheltens, P.; Teunissen, C. E.; Lemstra, A. W. Amyloid-beta peptides in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Alzheimers Res Ther 2019, 11(1), 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P. D.; Pirttila, T.; Mehta, S. P.; Sersen, E. A.; Aisen, P. S.; Wisniewski, H. M. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid beta proteins 1-40 and 1-42 in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 2000, 57(1), 100–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, T.; Gingele, S.; Guzeloglu, Y. E.; Heitmann, L.; Luling, B.; Kohle, F.; Pressler, H.; Stascheit, F.; Motte, J.; Fisse, A. L.; Gruter, T.; Pitarokoili, K.; Skripuletz, T. Comparative analysis of albumin quotient and total CSF protein in immune-mediated neuropathies: a multicenter study on diagnostic implications. Front Neurol 2023, 14, 1330484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srsen, S.; Held, M.; Sestan, M.; Kifer, N.; Kozmar, A.; Supe Domic, D.; Benzon, B.; Gagro, A.; Frkovic, M.; Jelusic, M. Serum Levels of S100A8/A9 as a Biomarker of Disease Activity in Patients with IgA Vasculitis. Biomedicines 2024, 12(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosch, M.; Strey, A.; Vogl, T.; Wulffraat, N. M.; Kuis, W.; Sunderkotter, C.; Harms, E.; Sorg, C.; Roth, J. Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 are specifically secreted during interaction of phagocytes and activated endothelium and are useful markers for monitoring disease activity in pauciarticular-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2000, 43(3), 628–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S. M.; Byun, K.; Cho, K.; Kim, J. Y.; Yoo, J. S.; Kim, D.; Paek, S. H.; Kim, S. U.; Simpson, R. J.; Lee, B. Human microglial cells synthesize albumin in brain. PLoS One 2008, 3(7), e2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskatov, J. A. What Is the "Relevant" Amyloid β42 Concentration? Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2019, 20(13), 1725–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronaite, I.; Sulskis, D.; Kopu Stas, A.; Tutkus, M.; Smirnovas, V. Formation of Calprotectin Inhibits Amyloid Aggregation of S100A8 and S100A9 Proteins. ACS Chem Neurosci 2024, 15(9), 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansieri, J.; Iashchishyn, I. A.; Fakhouri, H.; Ostojic, L.; Malisauskas, M.; Musteikyte, G.; Smirnovas, V.; Schneider, M. M.; Scheidt, T.; Xu, C. K.; Meisl, G.; Knowles, T. P. J.; Gazit, E.; Antoine, R.; Morozova-Roche, L. A. Templating S100A9 amyloids on Abeta fibrillar surfaces revealed by charge detection mass spectrometry, microscopy, kinetic and microfluidic analyses. Chem Sci 2020, 11(27), 7031–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
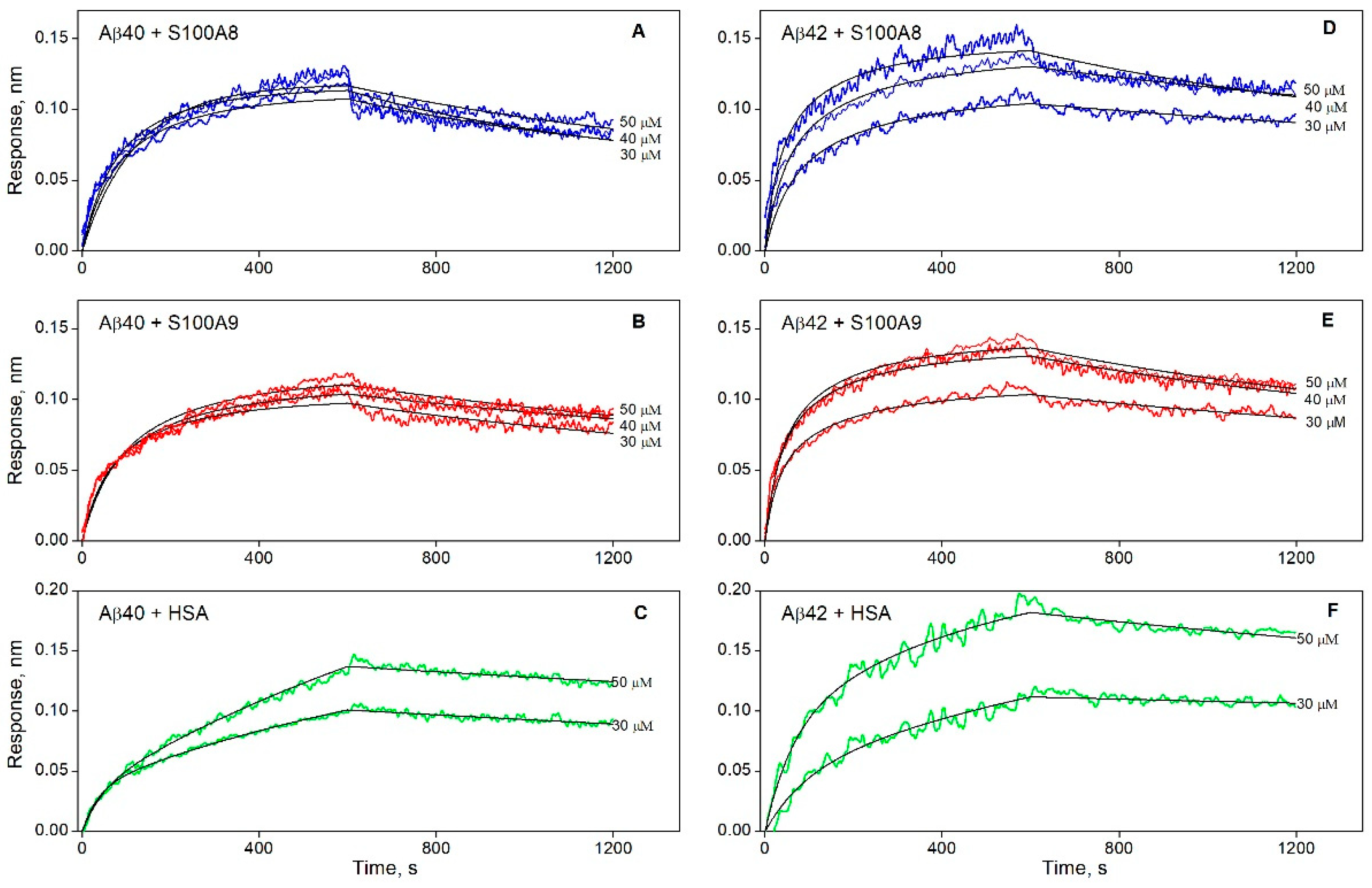
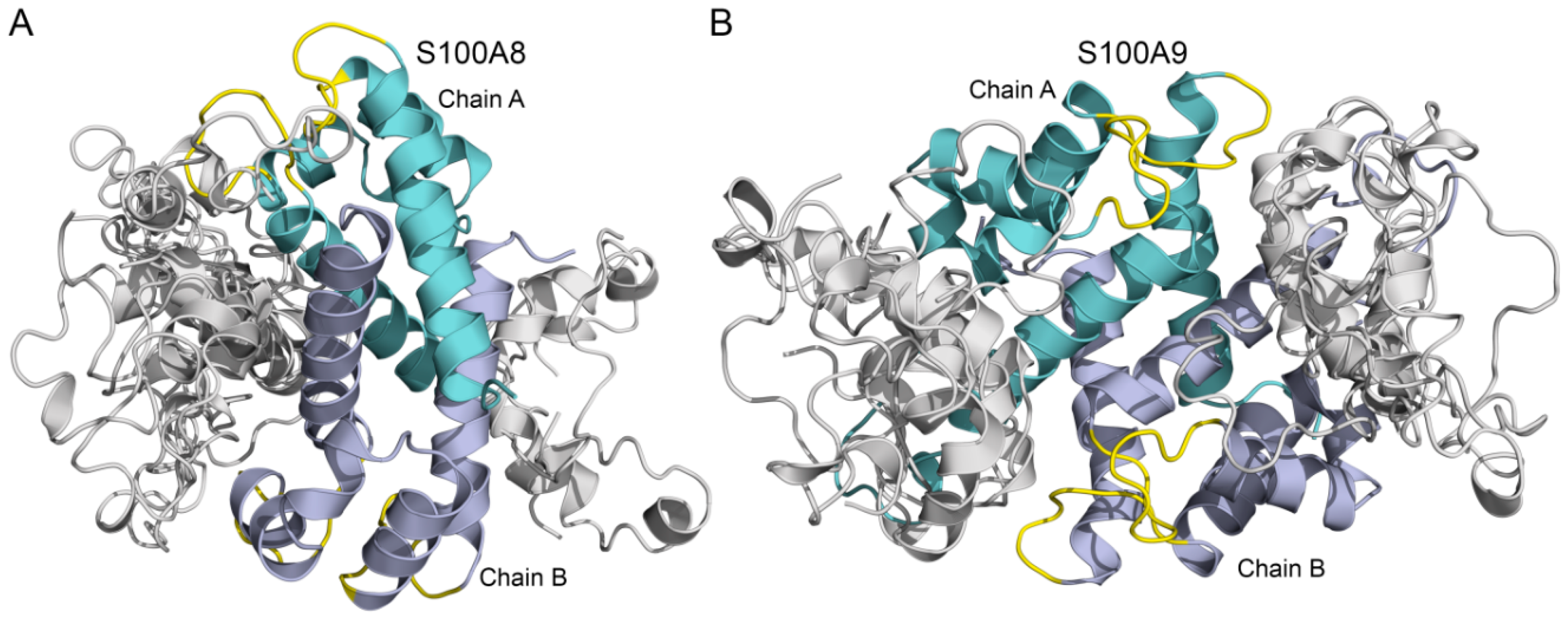
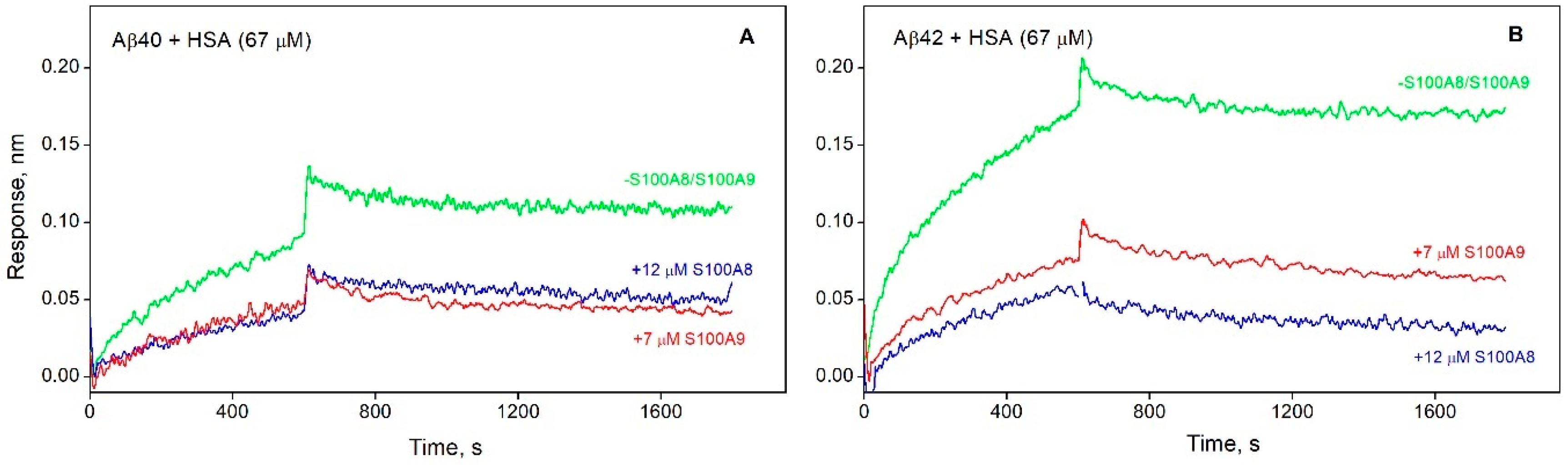
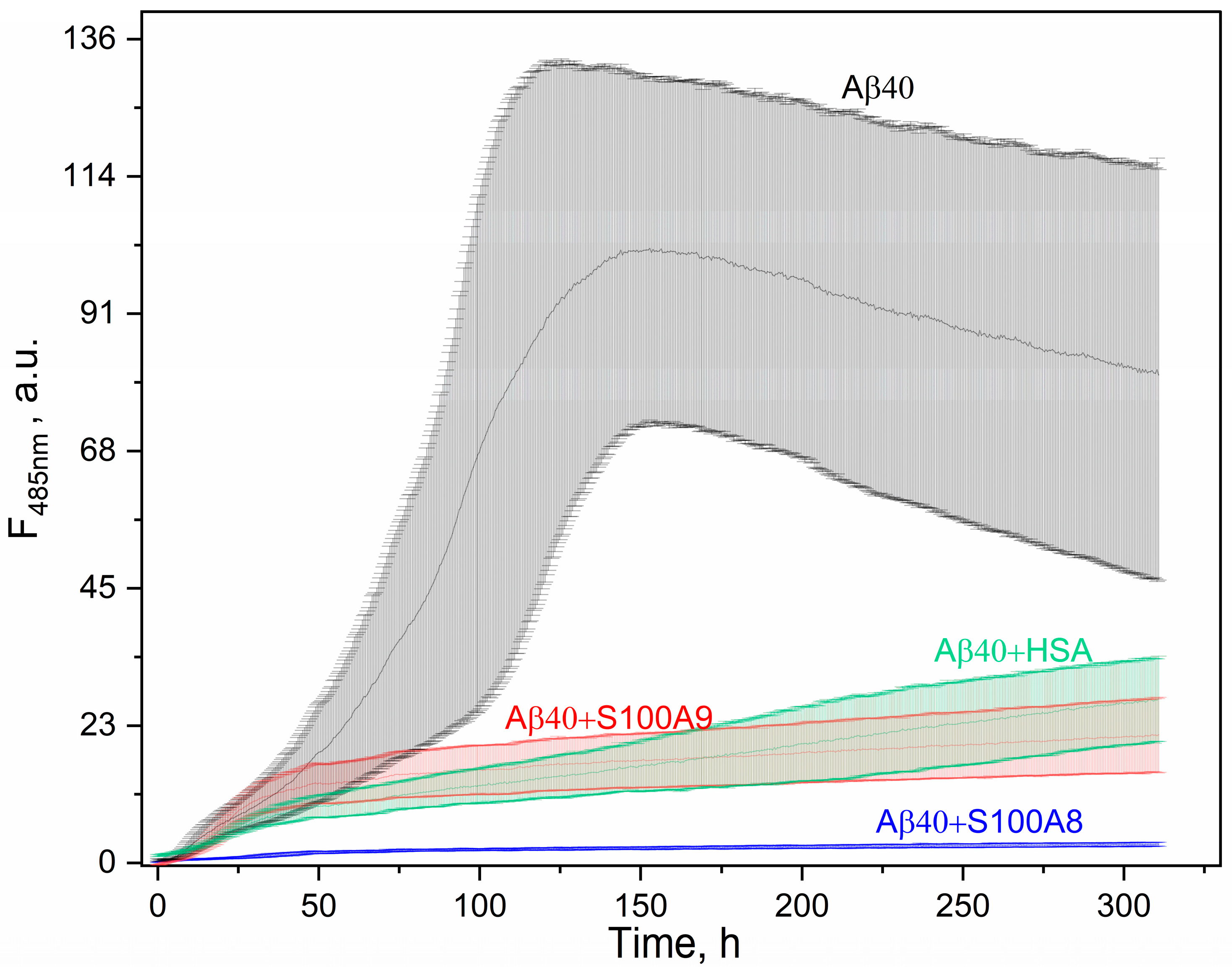
| KD×106, M | ka×10-2, M-1s-1 | kd×104, s-1 | |
| Aβ40 | |||
| S100A8 | 5.1 ± 2.3 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 10.9 ± 1.5 |
| S100A9 | 2.1 ± 1.3 | 2.6 ± 1.0 | 5.4 ± 1.0 |
| Aβ42 | |||
| S100A8 | 1.3 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.9 | 4.6 ± 1.9 |
| S100A9 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 4.5 ± 1.3 | 5.1 ± 1.1 |
| KD1×106, M | ka1×10-2, M-1s-1 | kd1×104, s-1 | KD2×106, M | ka2×10-2, M-1s-1 | kd2×104, s-1 |
| Aβ40 | |||||
| 0.22±0.12 | 7.9 ± 4.4 | 1.72 ± 0.04 | 6.7 ± 4.5 | 0.36 ± 0.24 | 2.38 ± 0.06 |
| Aβ42 | |||||
| 0.48±0.09 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 1.66 ± 0.10 | 5.6 ± 4.6 | 0.28 ± 0.18 | 1.58 ± 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





