Submitted:
30 January 2025
Posted:
30 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
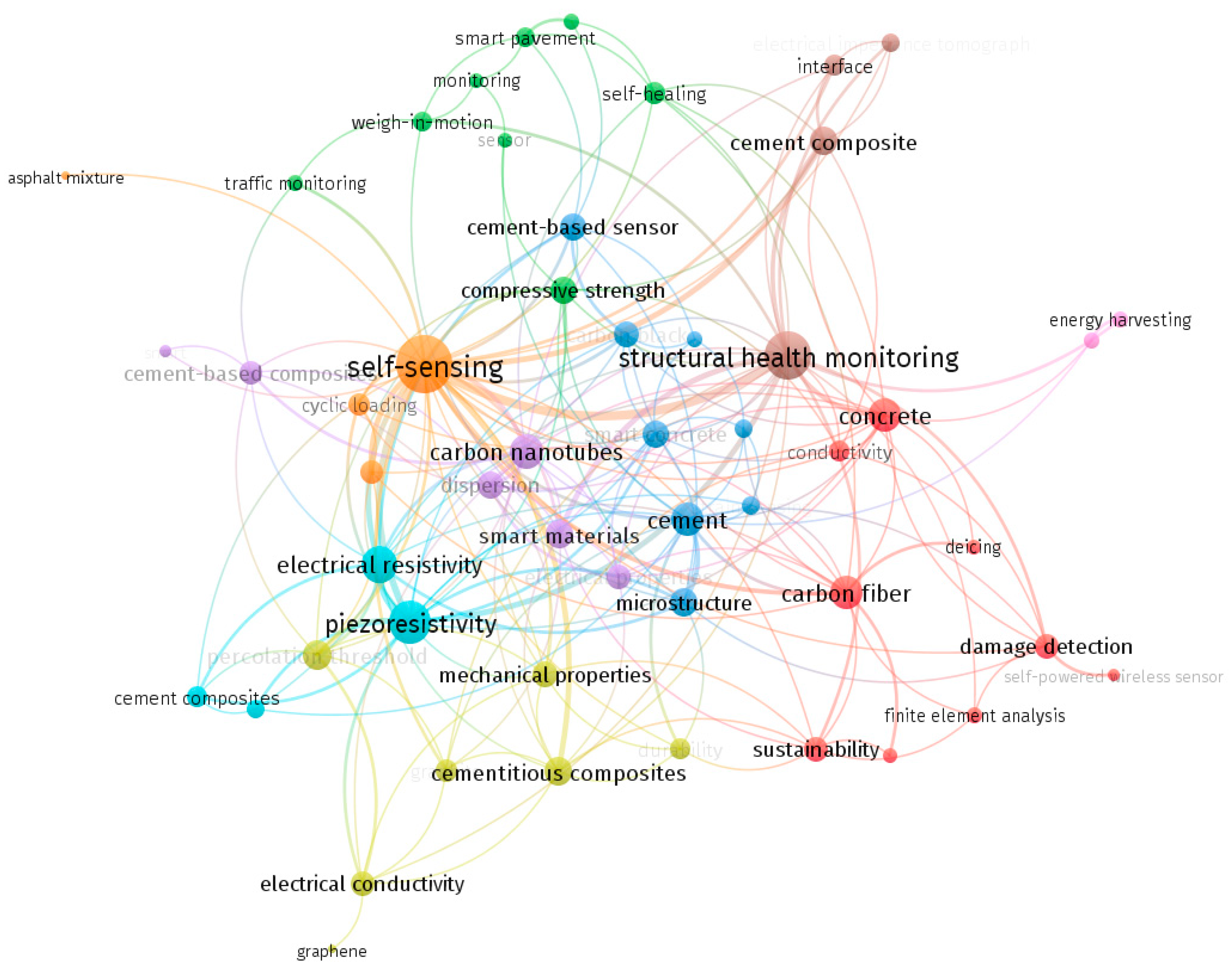
2. Methodology
3. Properties of Multifunctional Cementitious Composites
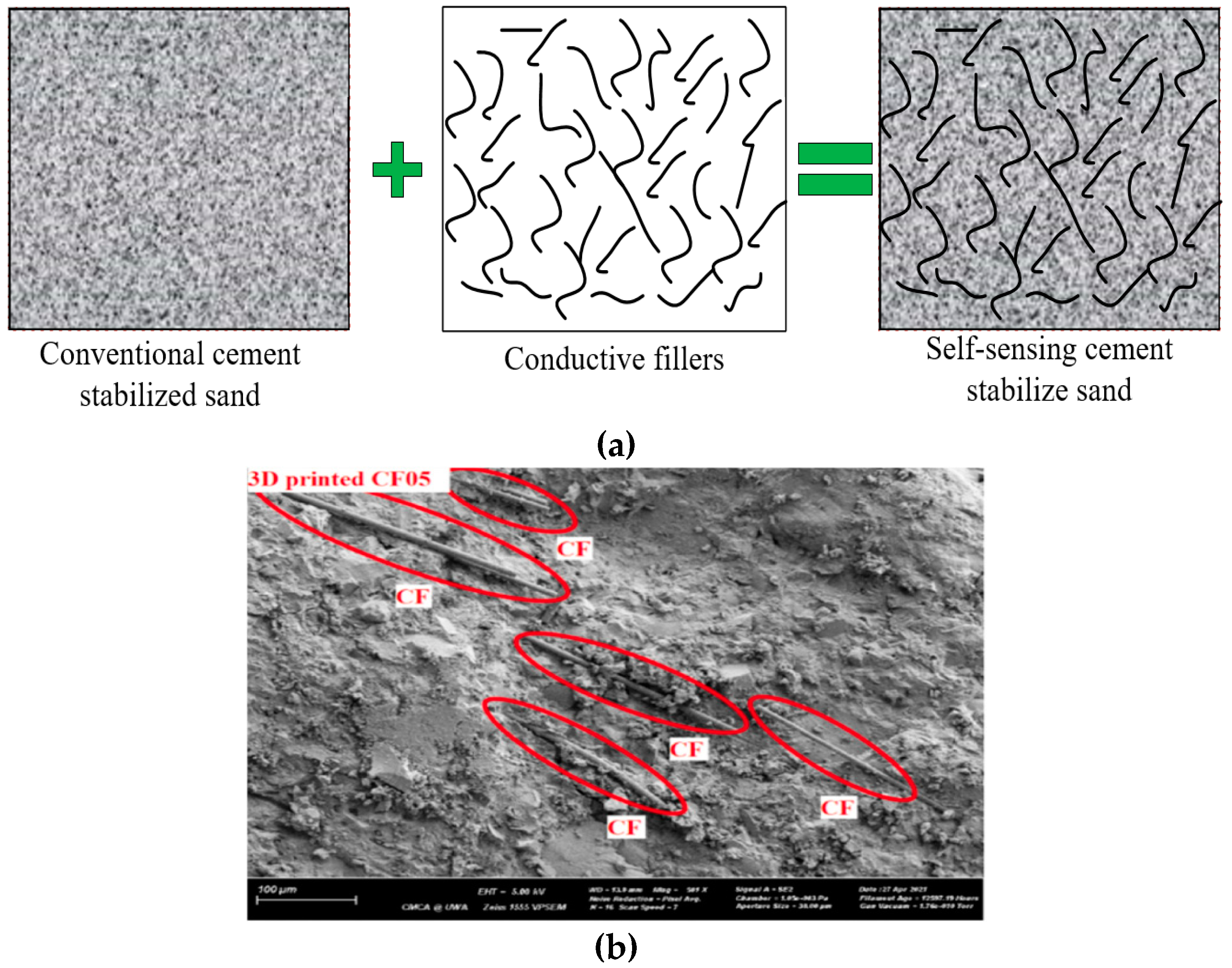
3.1. Conductive Fillers
3.2. Matrix Materials
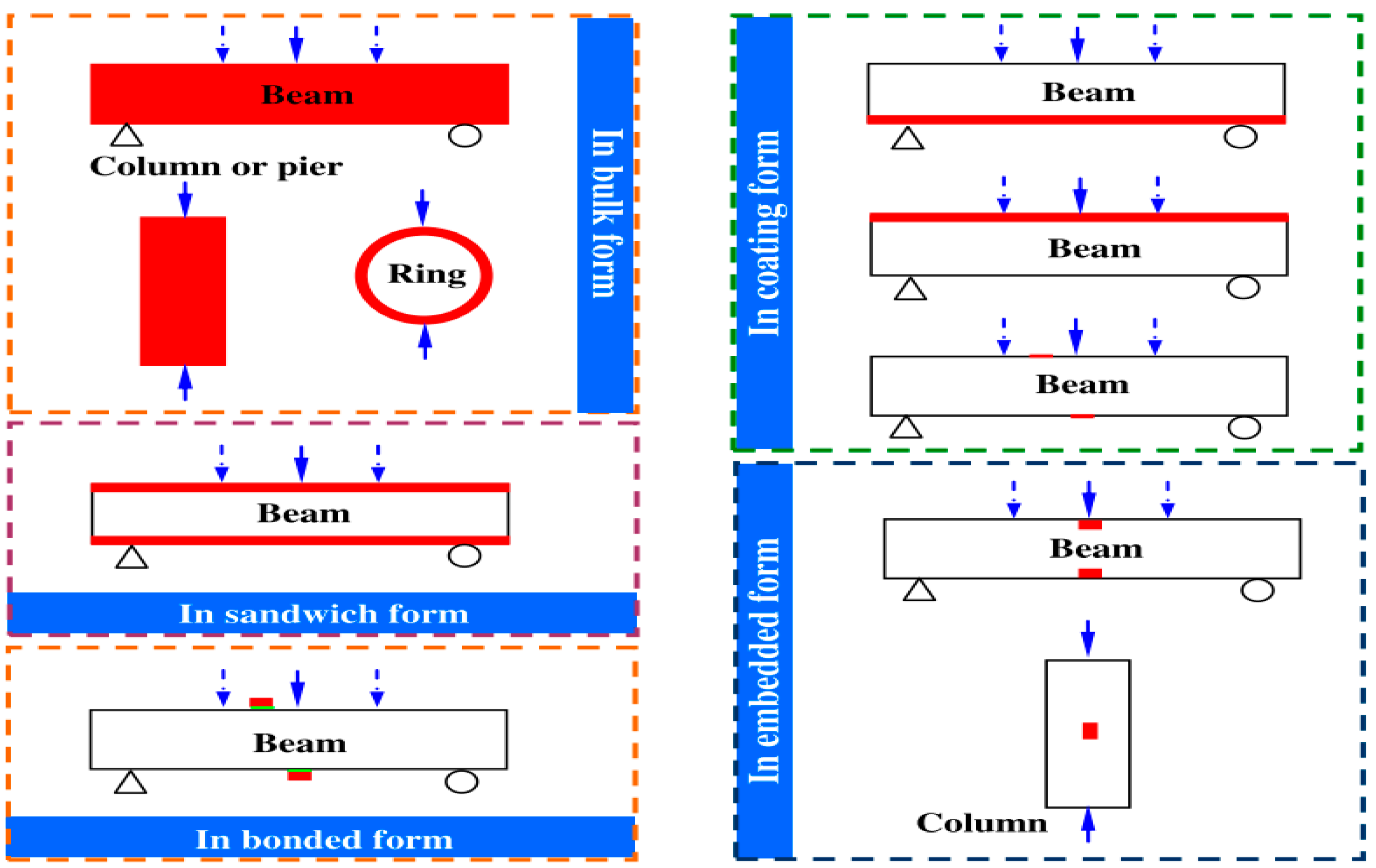
3.3. Electrodes Configurations
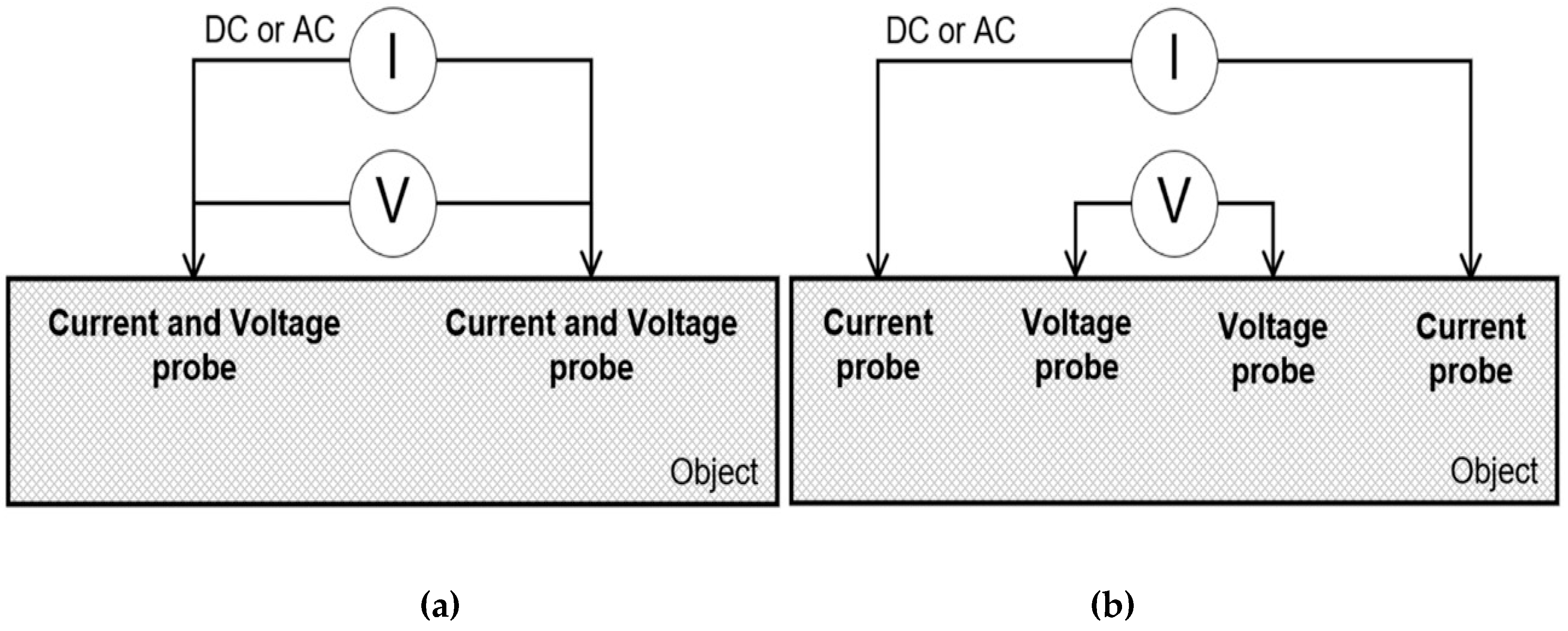
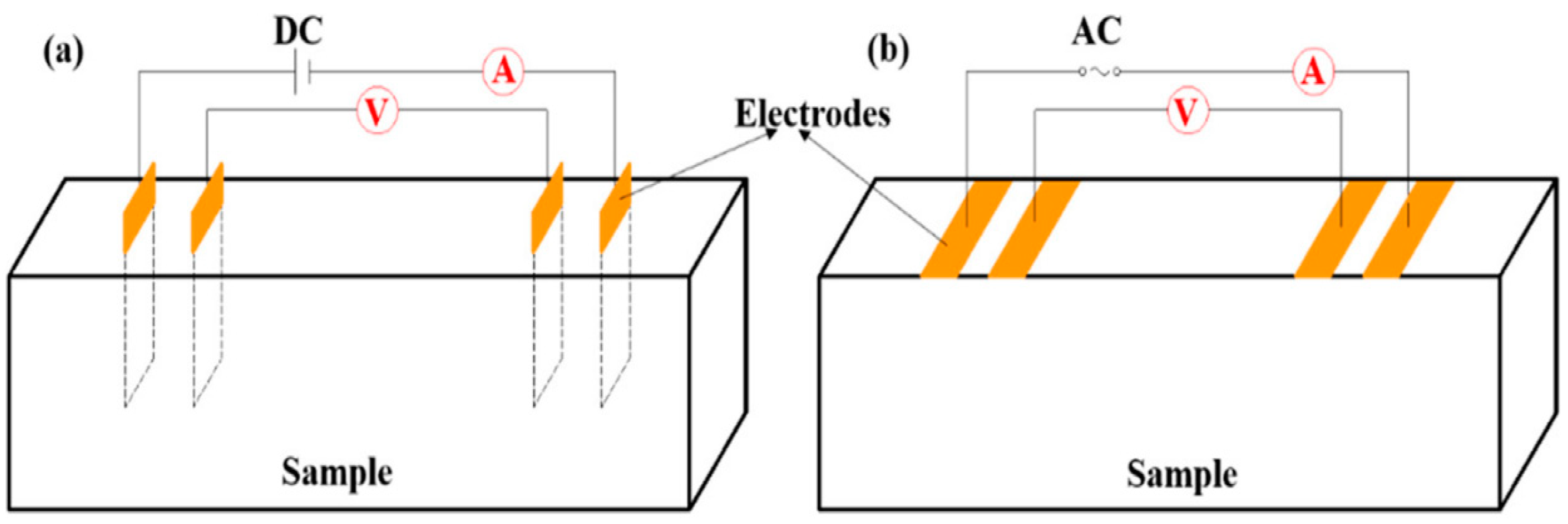
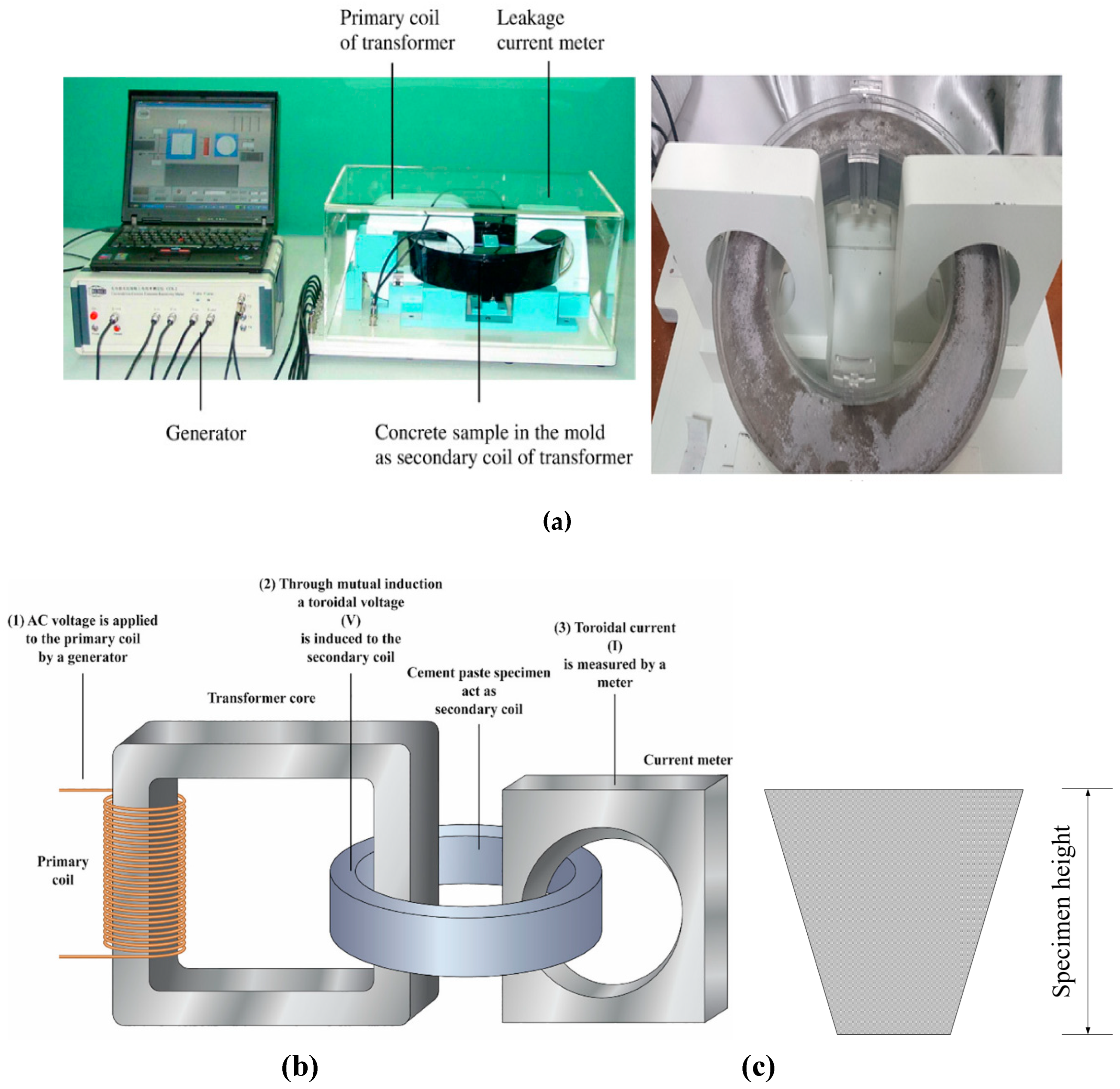
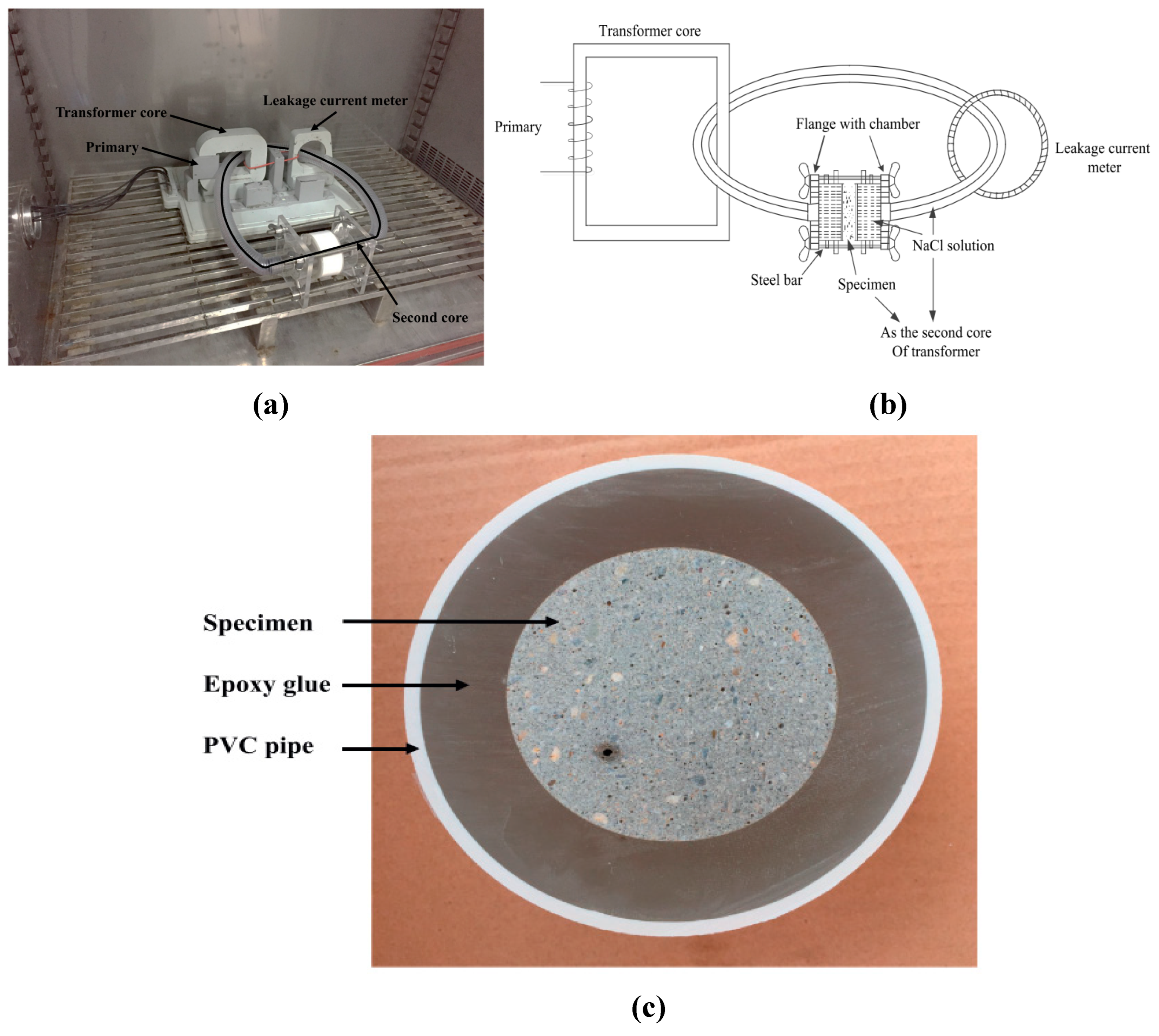
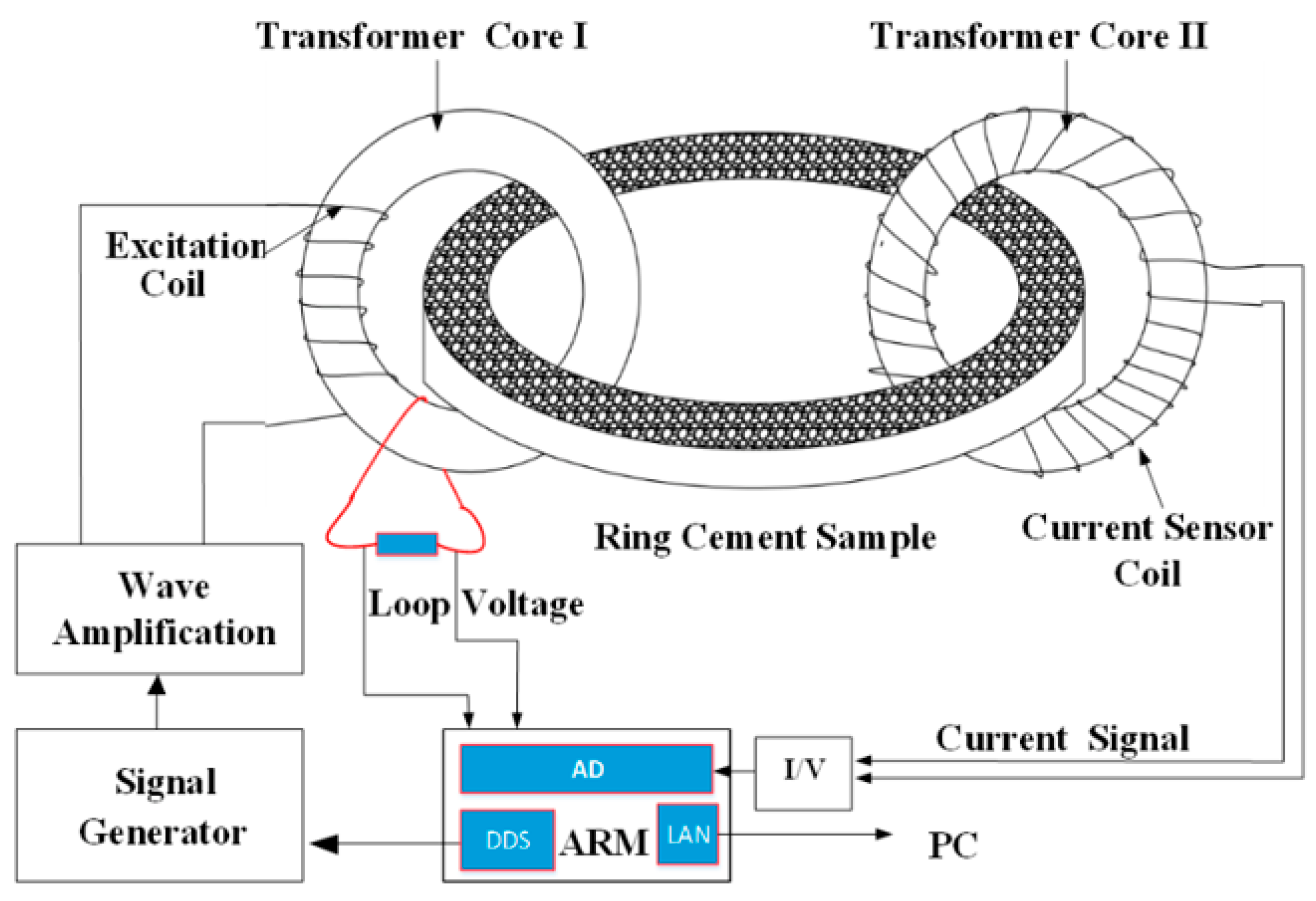
3.4. Contact and Non-Contact Electrical Measurement System
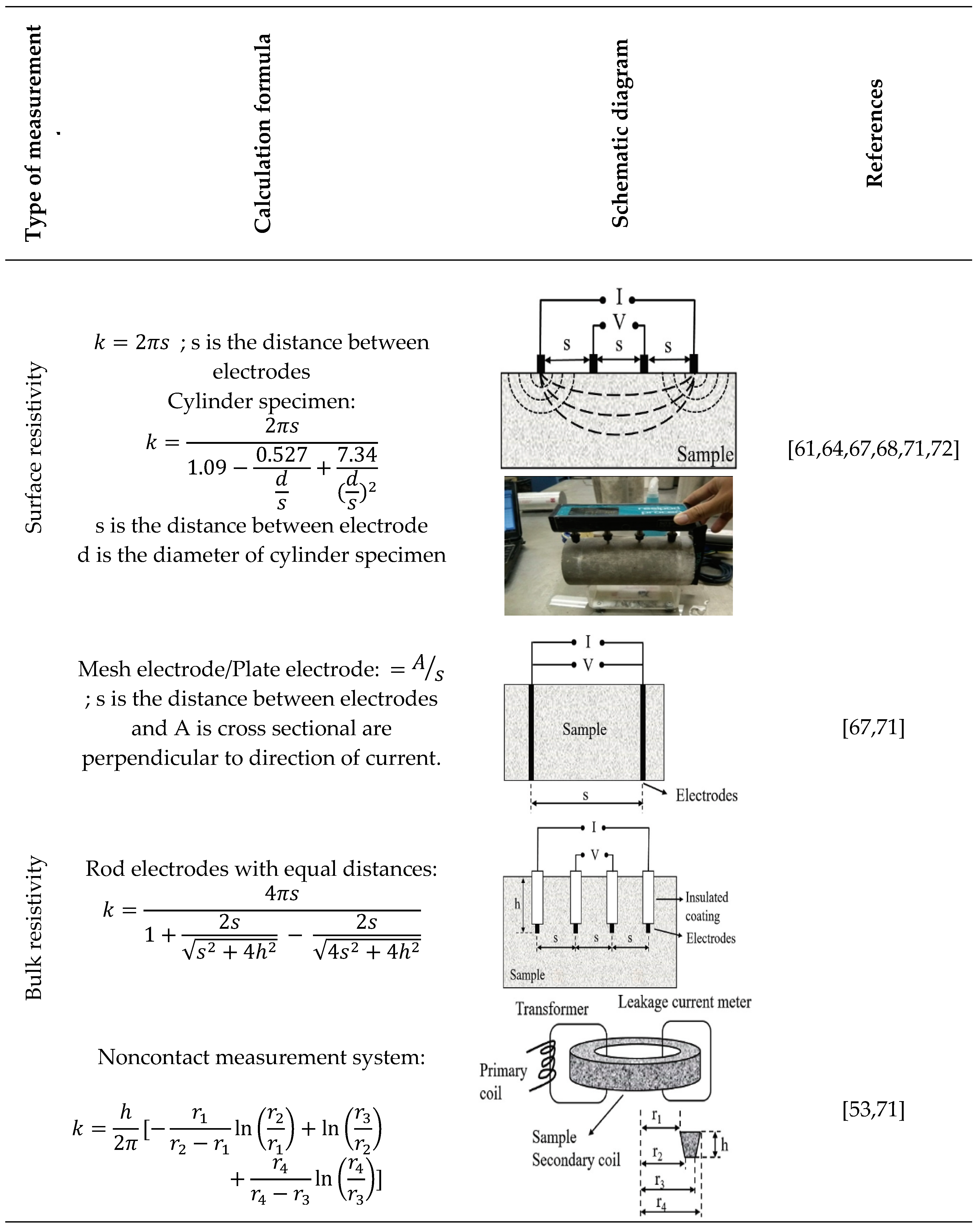
3.5. Surface and Bulk Electrical Resistivity
3.6. Electrical Conductivity
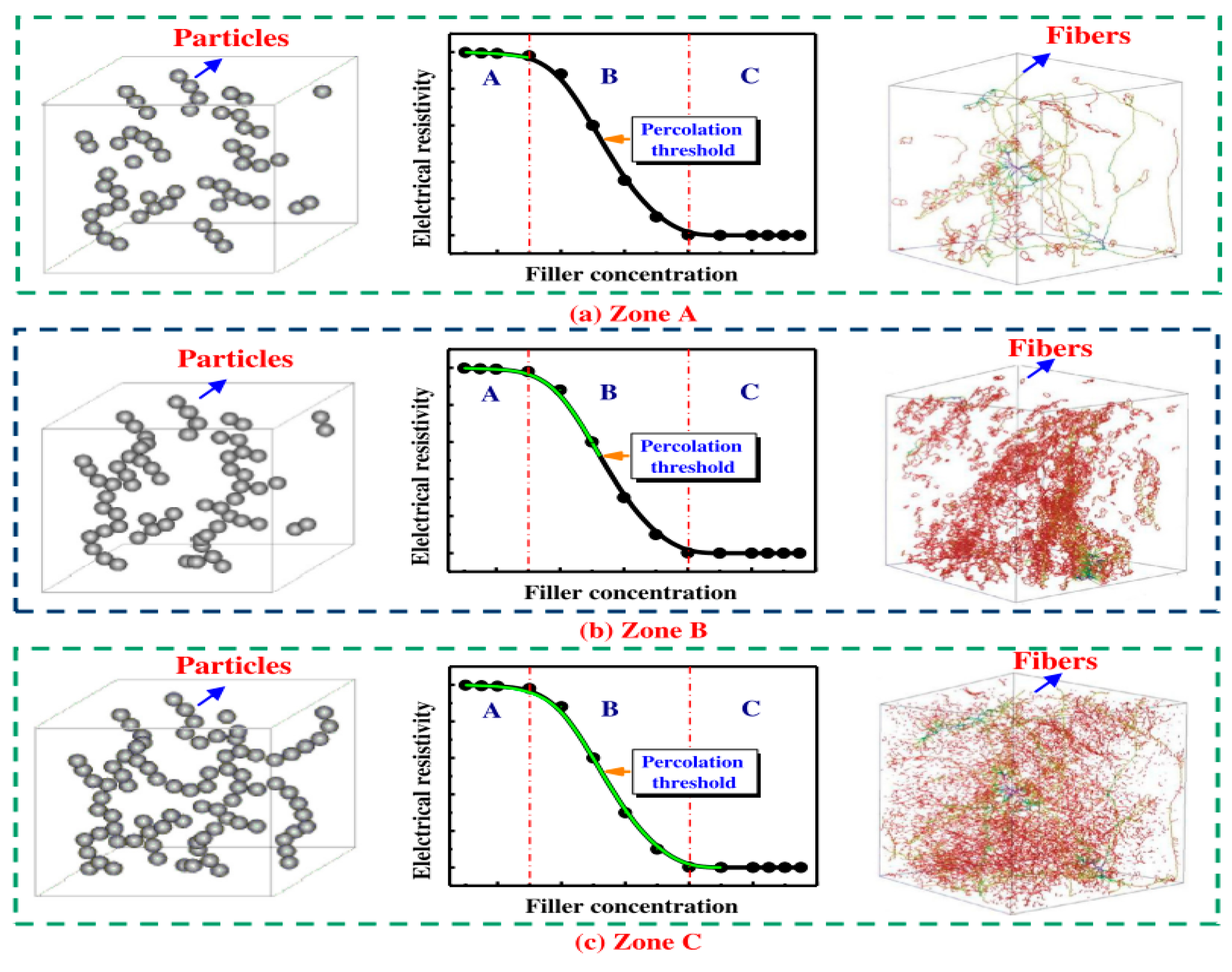
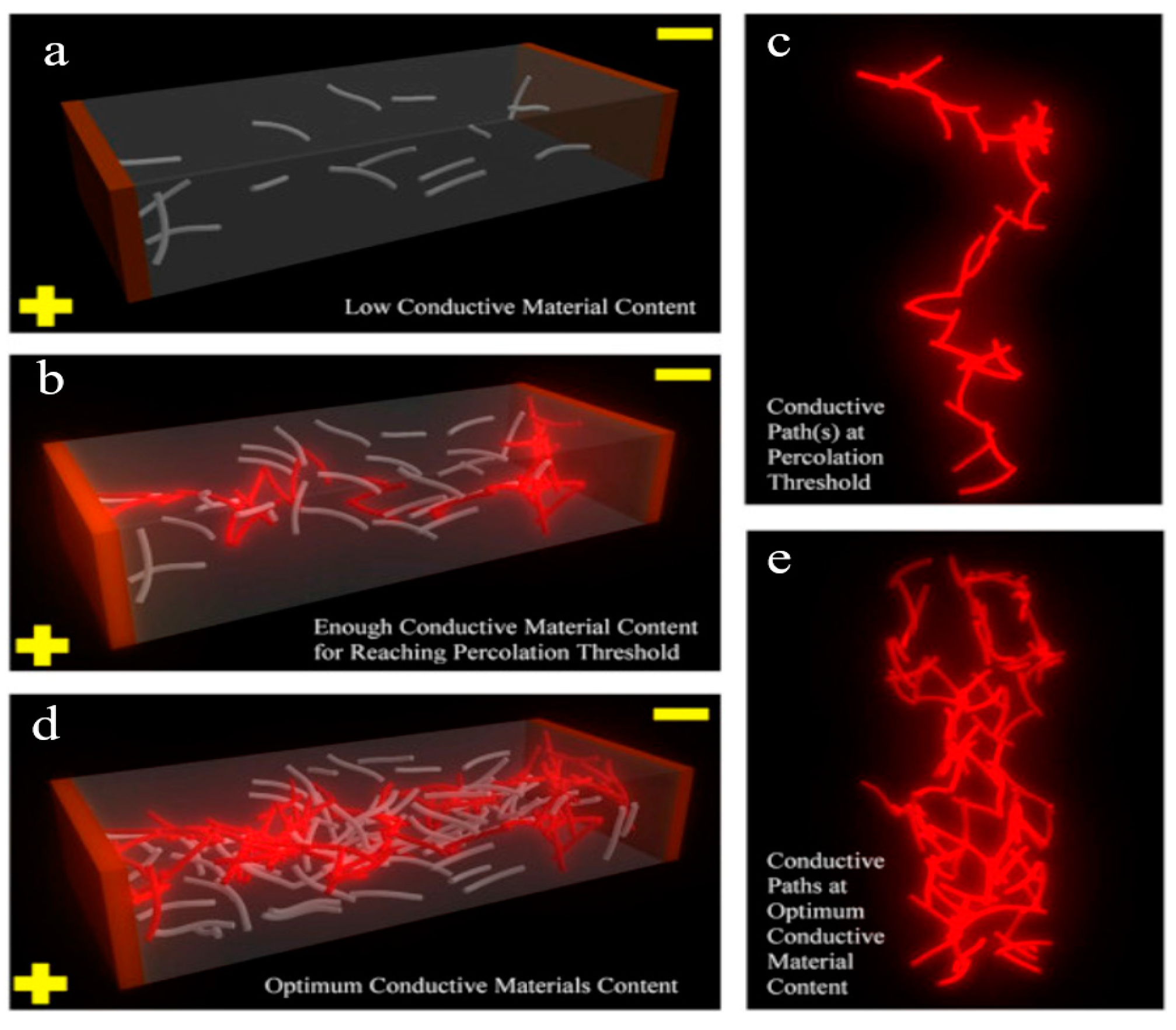
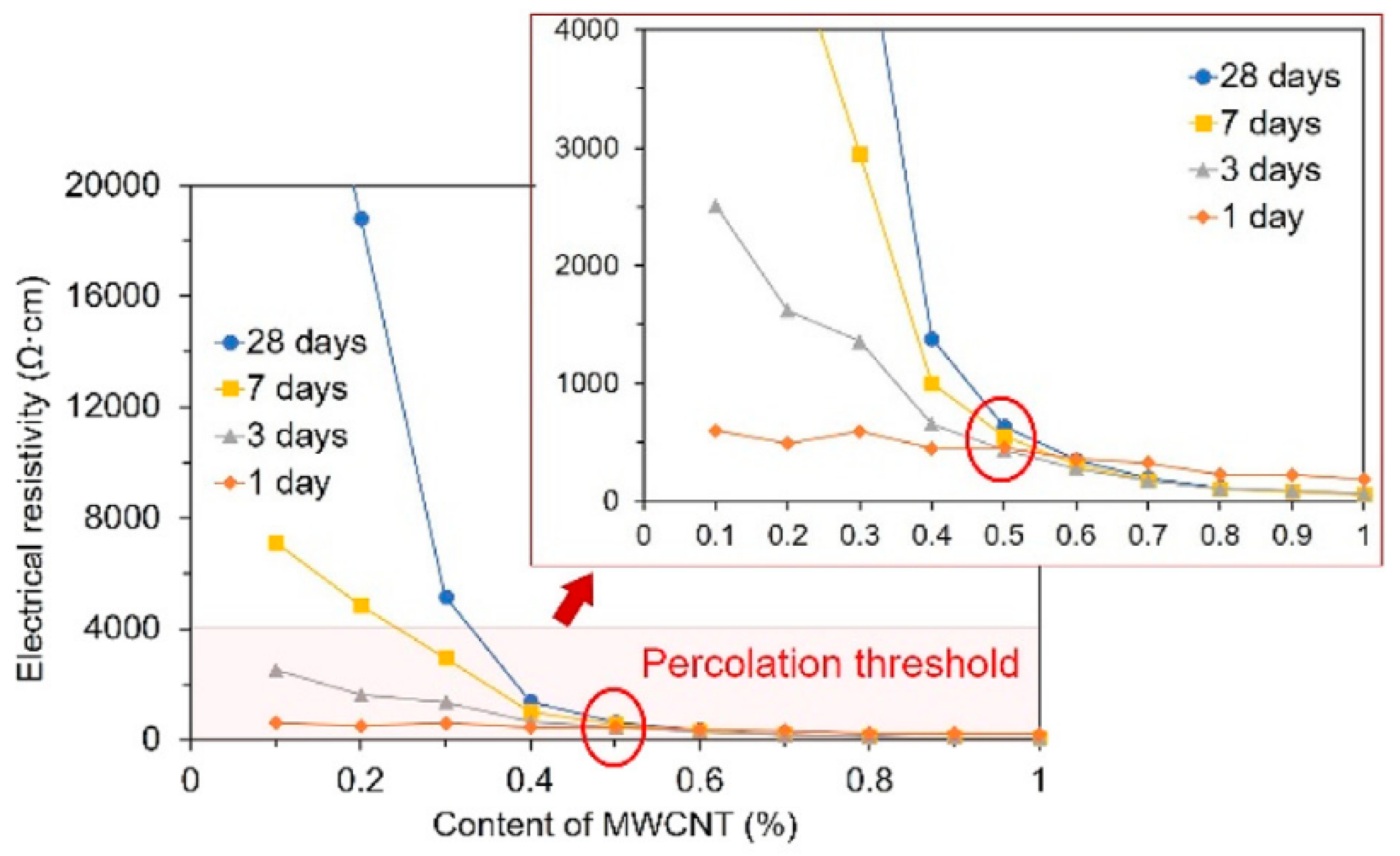
3.7. Percolation Threshold
3.8. Piezoresistivite Performance
3.9. Integrated Self-Sensing and Self-Healing
4. Challenges and Solutions
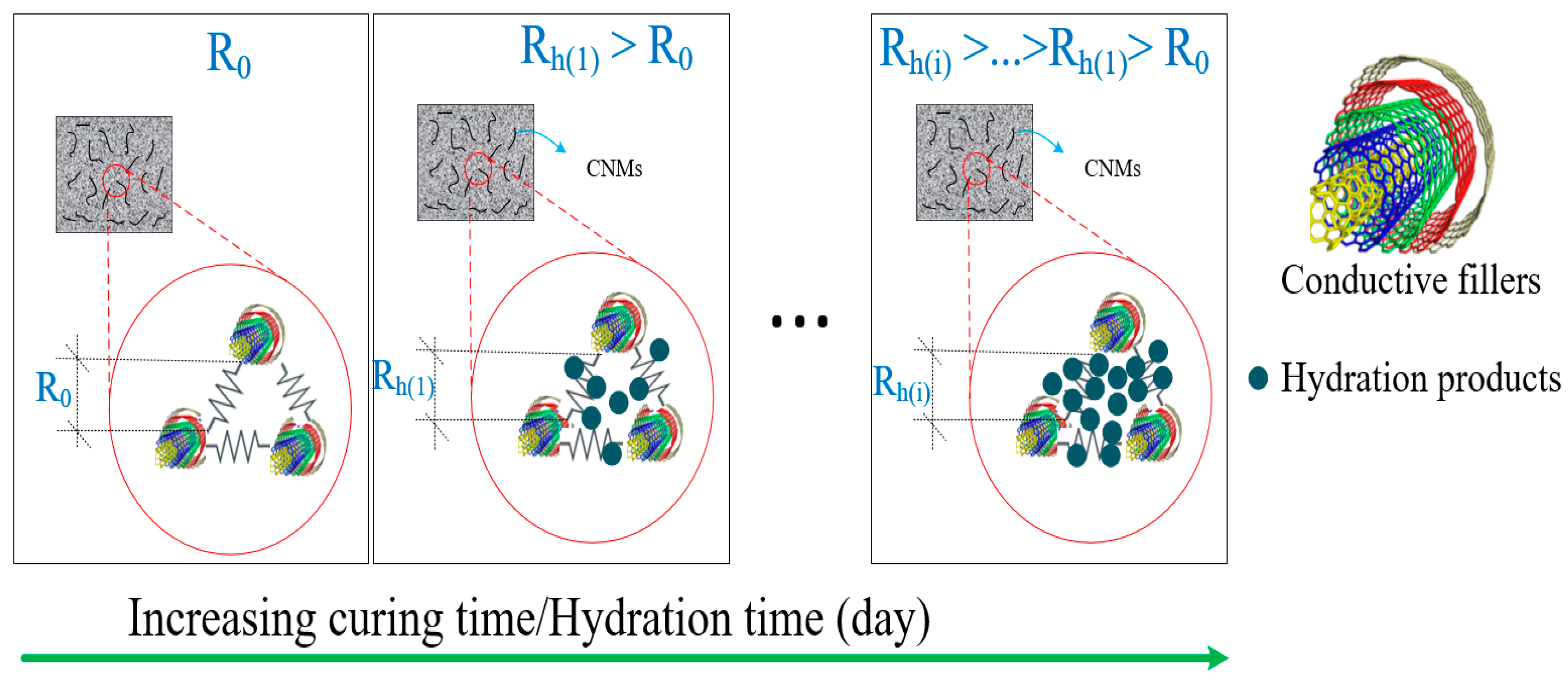
4.1. Agglomeration of Conductive Fillers
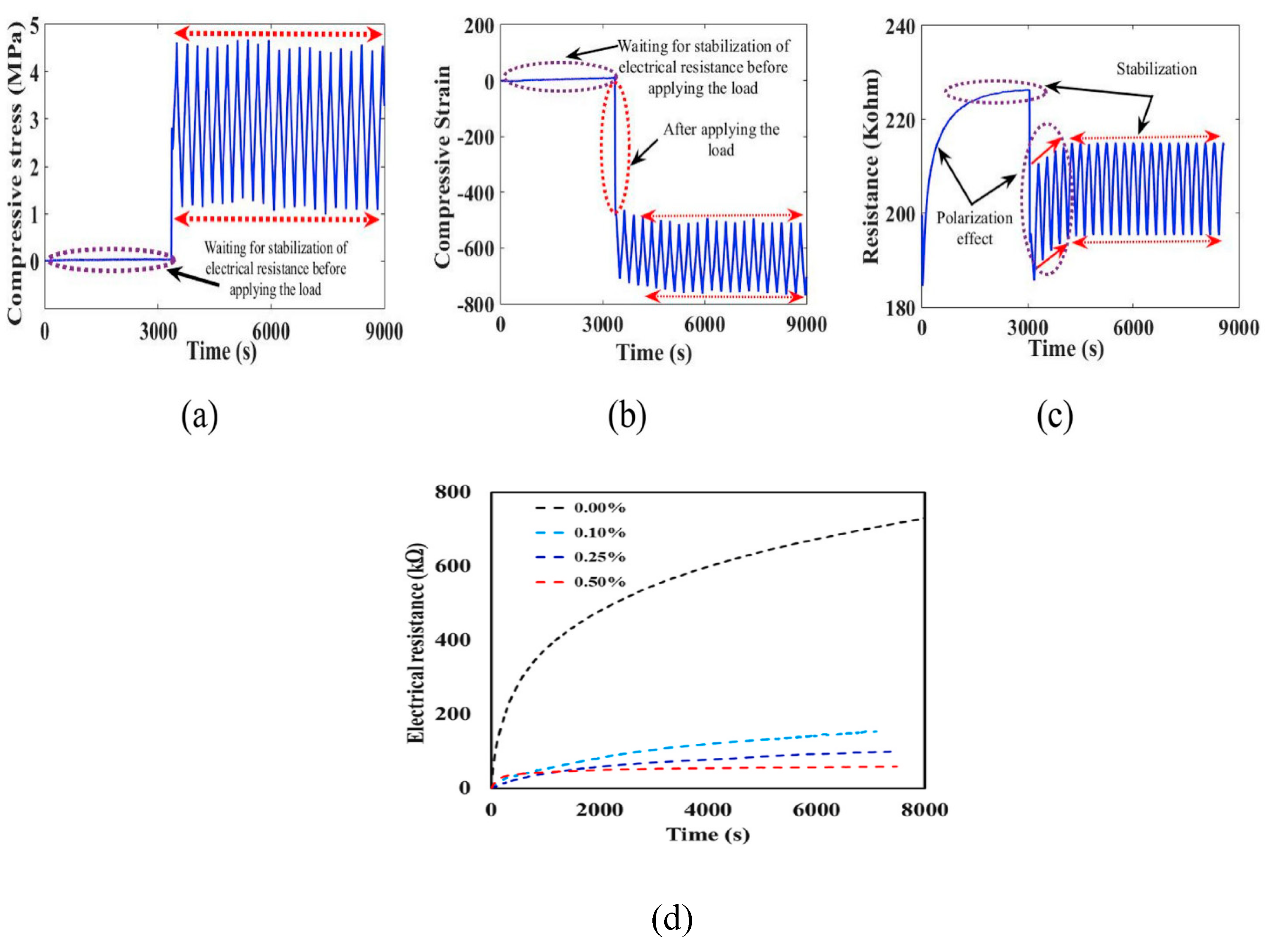
4.2. Polarization
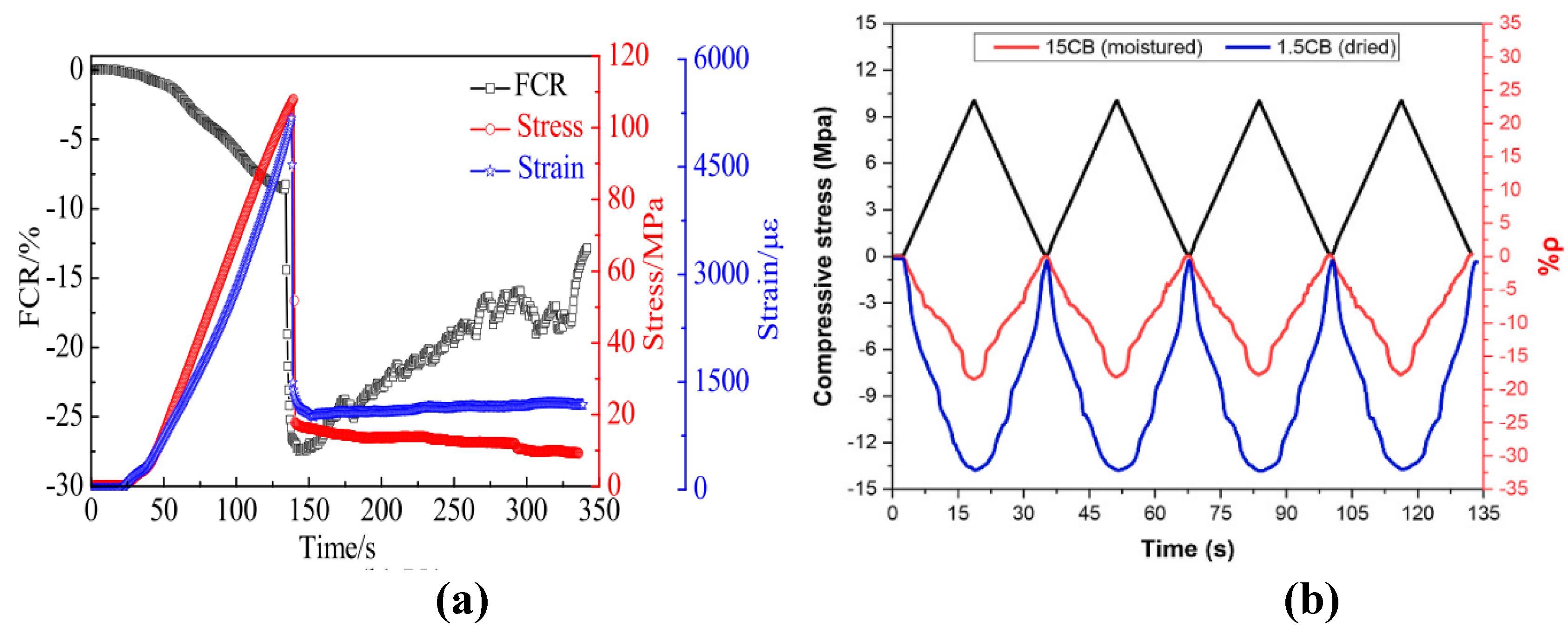
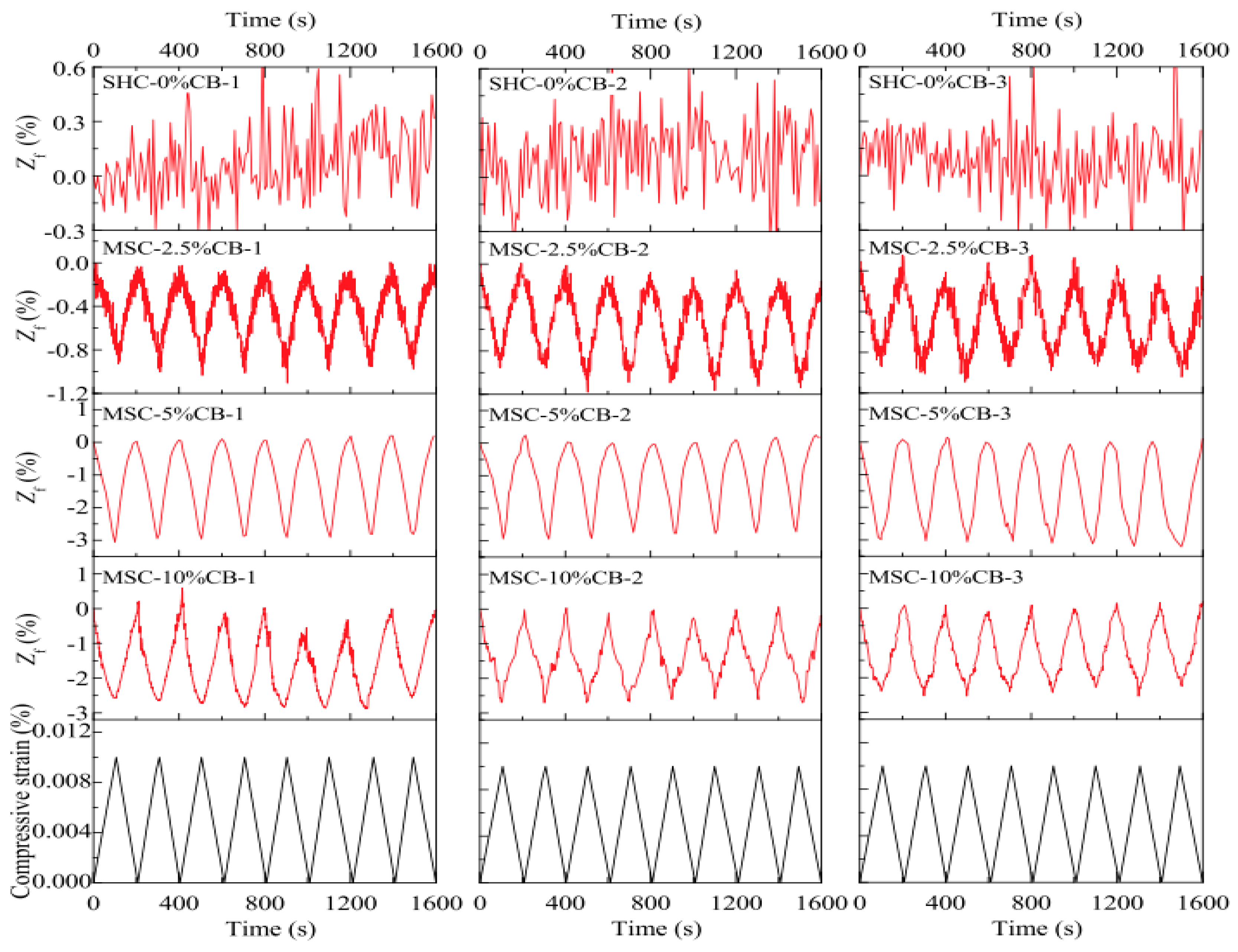
4.3. Temperature and Moisture Effects
4.4. Environmental and Cost Considerations
4.4.1. Cement
4.4.2. Aggregates
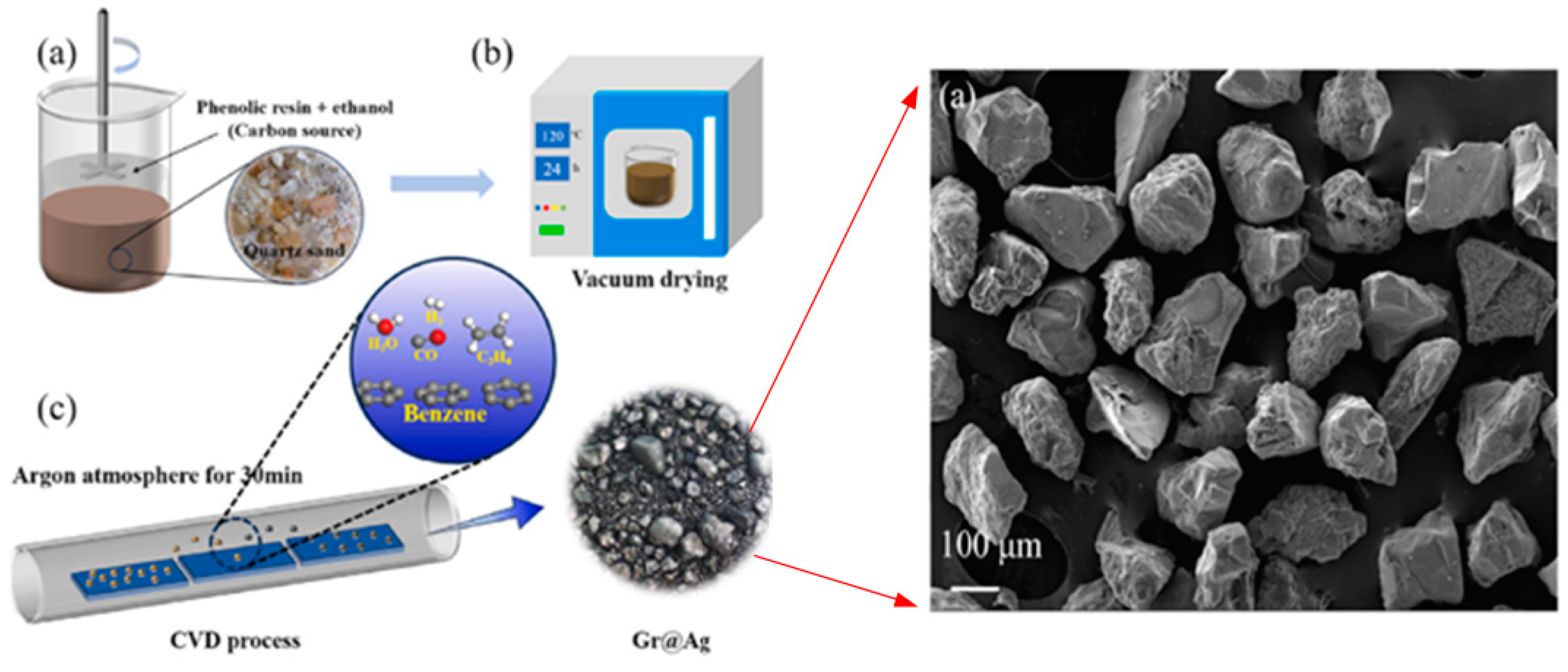
4.4.3. Conductive Fillers
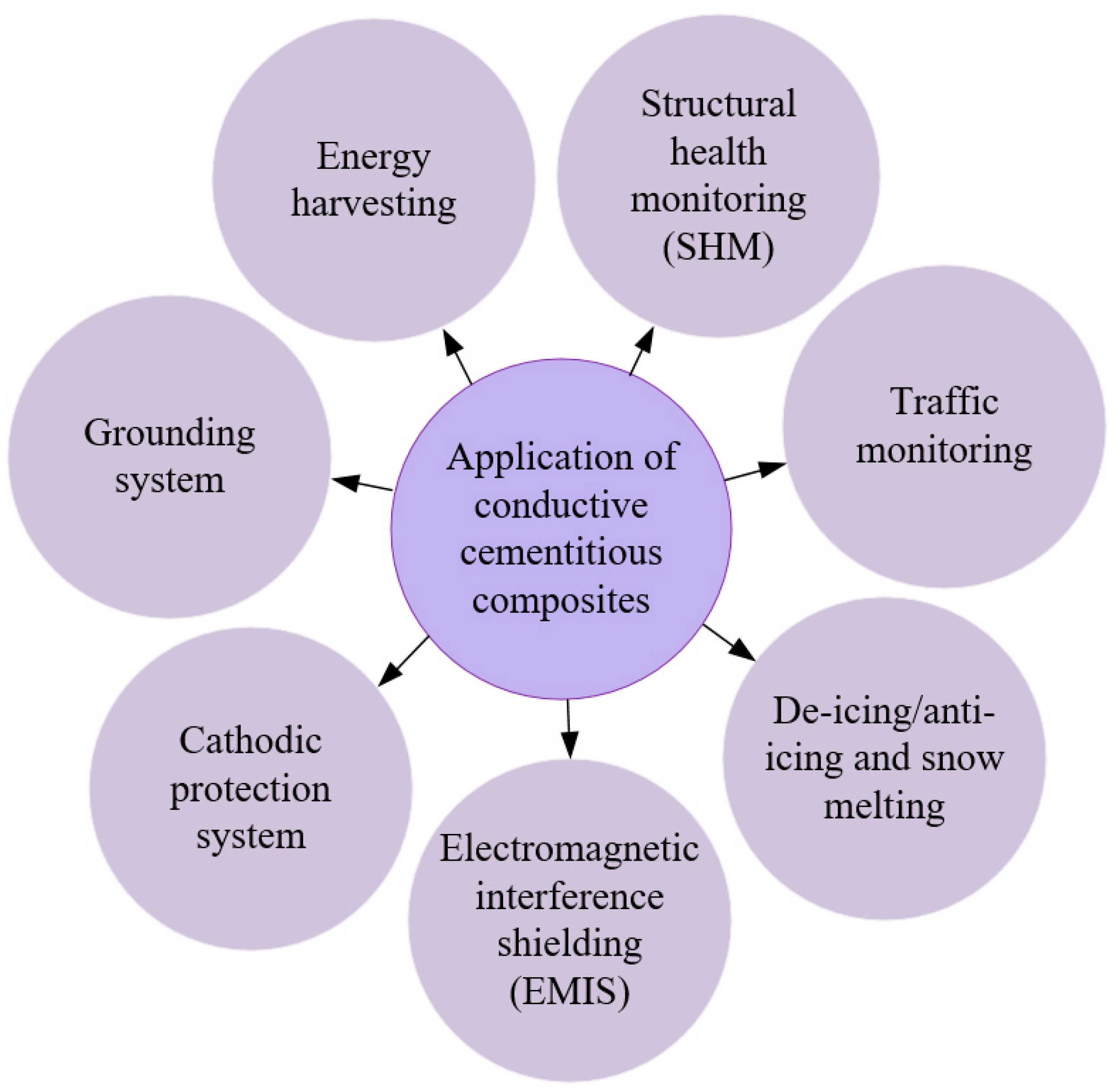
5. Application of Self-Sensing Materials for Transportation Infrastructures
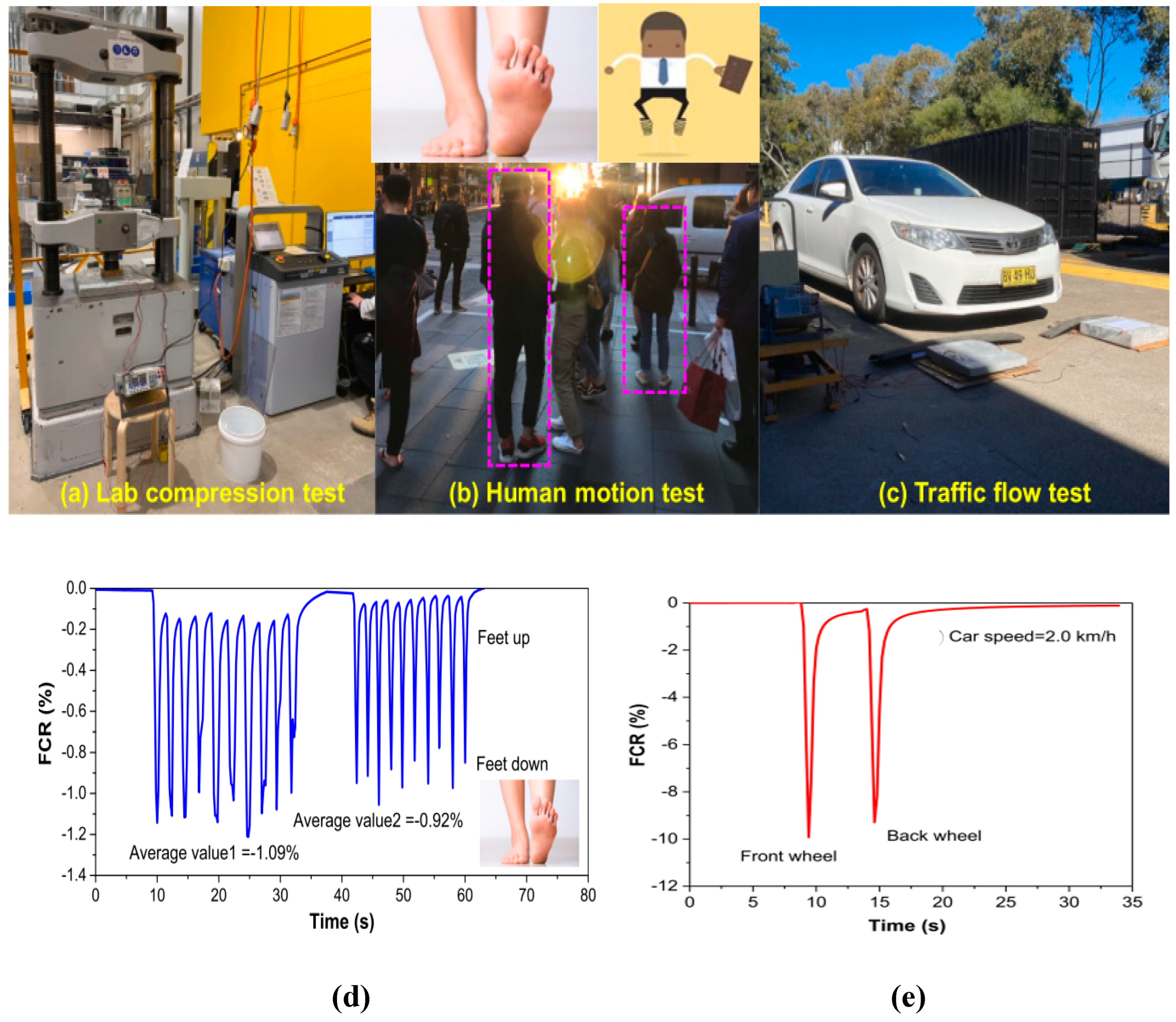
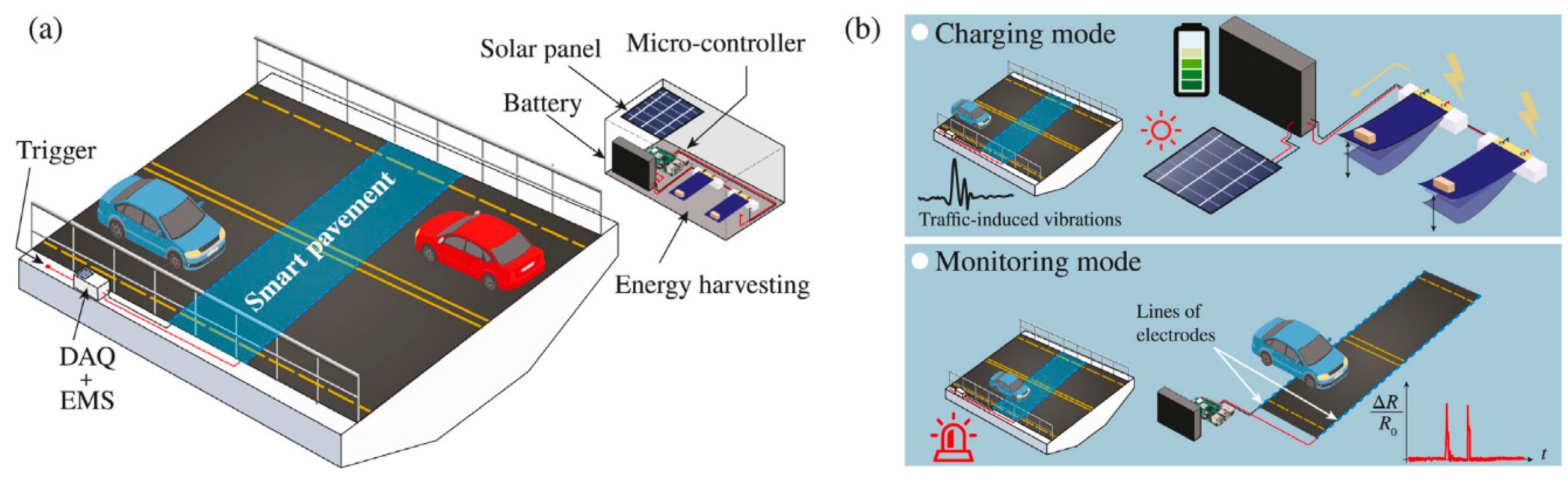
5.1. Traffic Monitoring
5.2. Structural Health Monitoring (SHM)
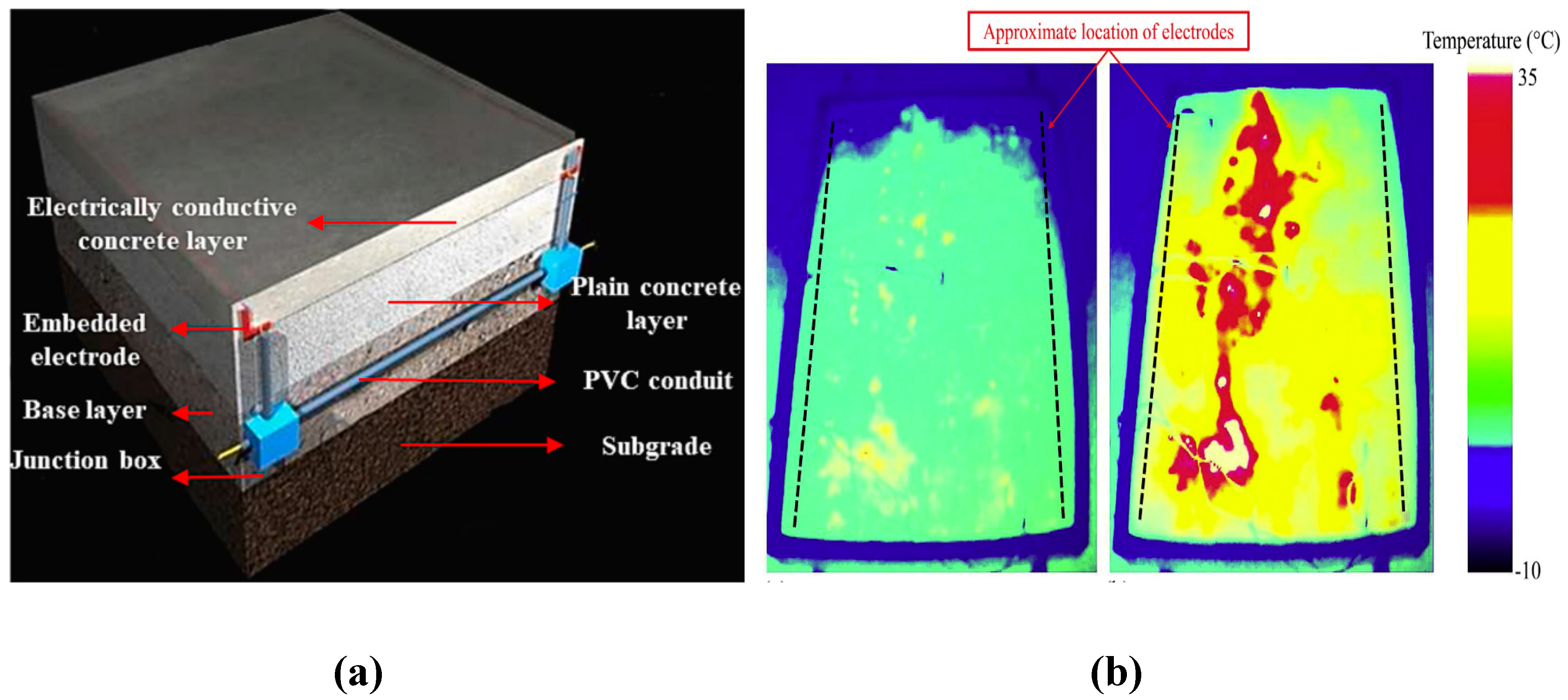
5.3. Deicing and Snow Melting
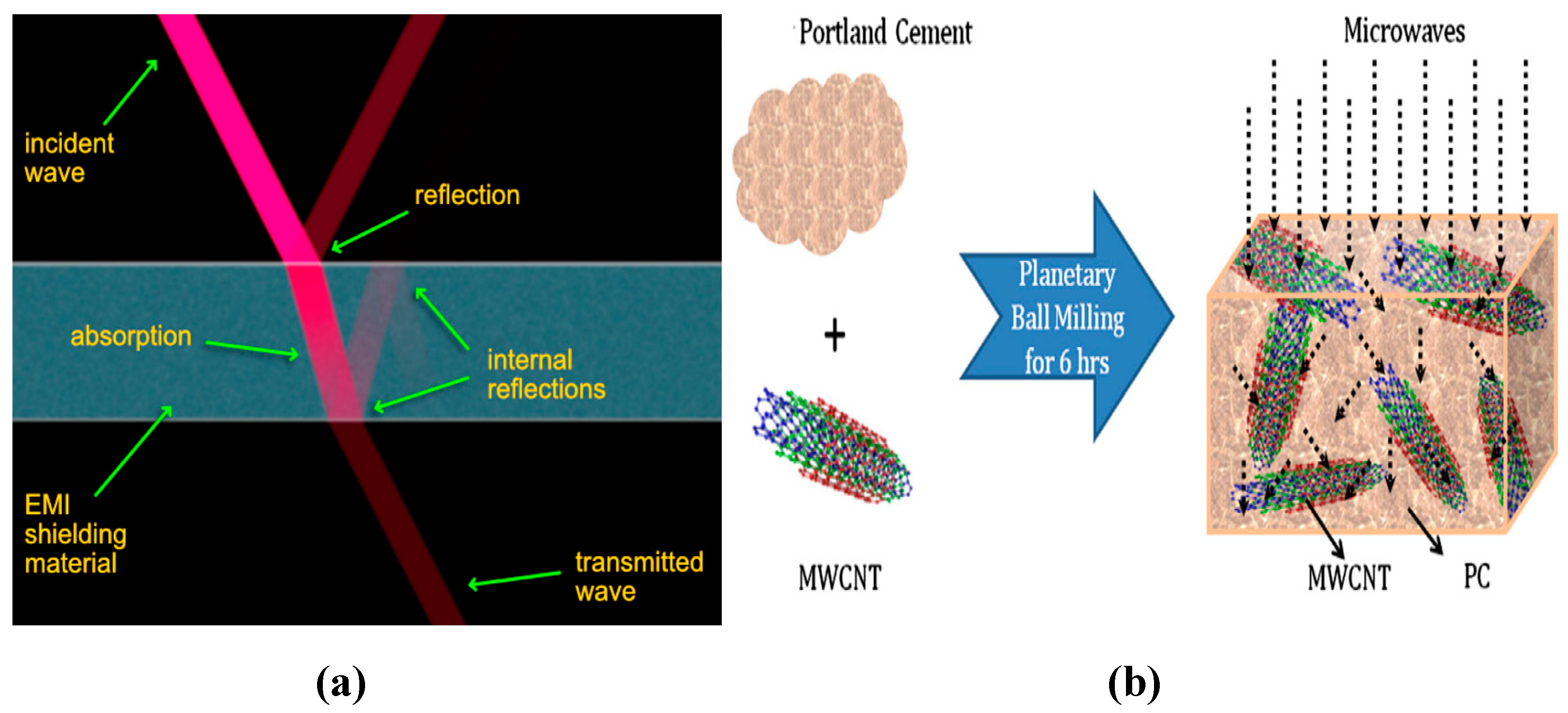
5.4. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding
5.5. Cathodic Protection System
5.6. Grounding System
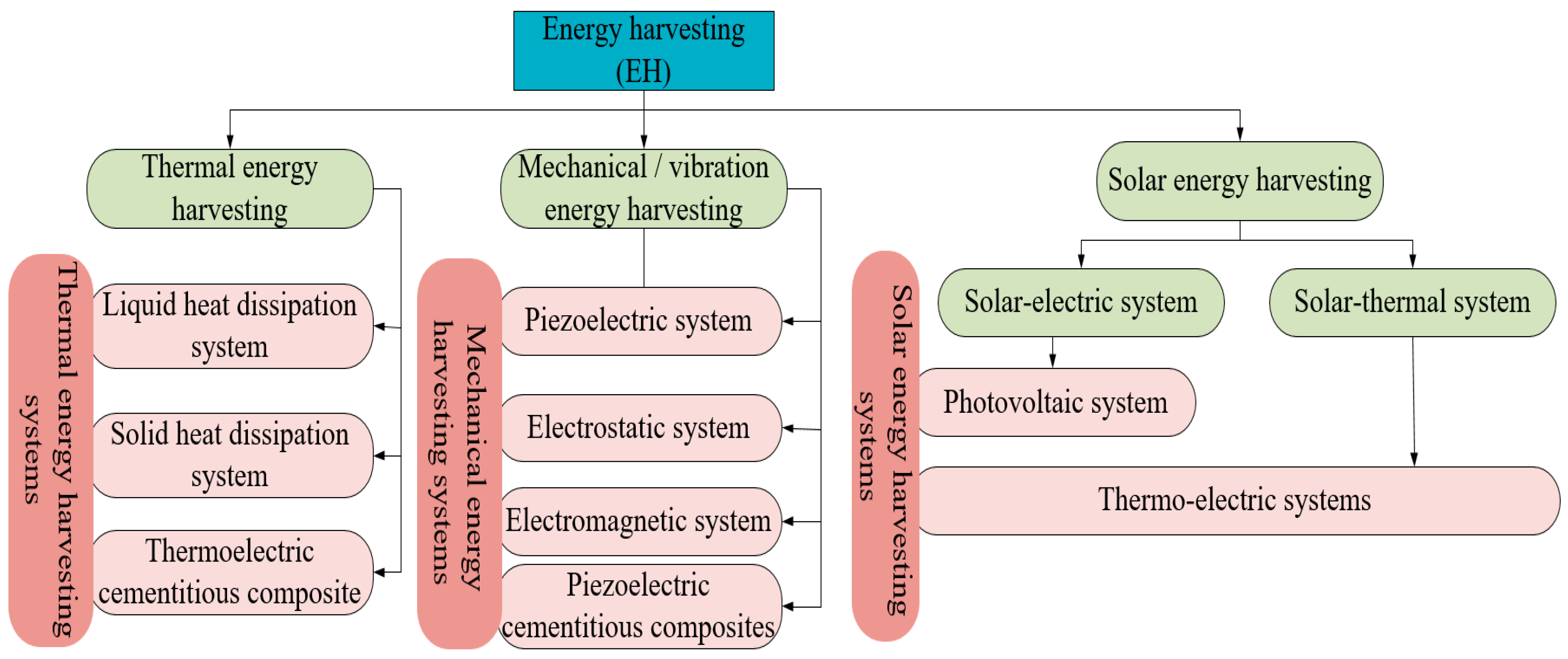
5.7. Energy Harvesting
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roshan, M.J.; A Rashid, A.S.; Abdul Wahab, N.; Tamassoki, S.; Jusoh, S.N.; Hezmi, M.A.; Nik Daud, N.N.; Mohd Apandi, N.; Azmi, M. Improved Methods to Prevent Railway Embankment Failure and Subgrade Degradation: A Review. Transp. Geotech. 2022, 37, 100834. [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, D.S.; Sivasuriyan, A.; Devarajan, P.; Krejsa, M.; Chalecki, M.; Żółtowski, M.; Kozarzewska, A.; Koda, E. Development of Intelligent Technologies in SHM on the Innovative Diagnosis in Civil Engineering—A Comprehensive Review. Buildings 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.Y.; Chen, W.Z.; Gao, H.; Qin, C.K.; Zhao, W.S. Overall Sensing Method for the Three-Dimensional Stress of Roadway via Machine Learning on SHM Data. Struct. Heal. Monit. 2024, 23, 175–186. [CrossRef]
- Gordan, M.; Ghaedi, K.; Ismail, Z.; Benisi, H.; Hashim, H.; Ghayeb, H.H. From Conventional to Sustainable SHM: Implementation of Artificial Intelligence in the Department of Civil Engineering, University of Malaya. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Engineering and Technology, IICAIET 2021; IEEE, September 13 2021; pp. 1–6.
- Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, F. Applications of Optical Fiber Sensor in Pavement Engineering: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132713. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.B.; Tewari, S.; Biswas, S.; Lohani, B.; Dwivedi, U.D.; Dwivedi, D.; Sharma, A.; Jung, J.P. Recent Advancements in Ai-Enabled Smart Electronics Packaging for Structural Health Monitoring. Metals (Basel). 2021, 11, 1537. [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Rallini, M.; Ubertini, F.; Materazzi, A.L.; Kenny, J.M. Investigations on Scalable Fabrication Procedures for Self-Sensing Carbon Nanotube Cement-Matrix Composites for SHM Applications. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 65, 200–213. [CrossRef]
- Siahkouhi, M.; Razaqpur, G.; Hoult, N.A.; Hajmohammadian Baghban, M.; Jing, G. Utilization of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) in Concrete for Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) Purposes: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125137. [CrossRef]
- Roshan, M.J.; Rashid, A.S.B.A. Geotechnical Characteristics of Cement Stabilized Soils from Various Aspects: A Comprehensive Review. Arab. J. Geosci. 2024, 17, 1. [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, K.; Burnham, T.; Kwon, E.; Yu, X. Integration and Road Tests of a Self-Sensing CNT Concrete Pavement System for Traffic Detection. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 015020. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pan, J.; Cai, J.; Li, X. A Review on Carbon-Based Self-Sensing Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120764. [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.; Xia, H.; Guo, R.; Yang, Y. Study on Self-Sensing Capabilities of Smart Cements Filled with Graphene Oxide under Dynamic Cyclic Loading. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 104775. [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Xiang, Y.; Ni, Y.-Q.; Thakur, V.K.; Wang, X.; Han, B.; Ou, J. In-Situ Synthesizing Carbon Nanotubes on Cement to Develop Self-Sensing Cementitious Composites for Smart High-Speed Rail Infrastructures. Nano Today 2022, 43, 101438. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Feng, J.; Pai, N.; Zequan, H.; Kaiyuan, L.; Cheng, Z.; Yazhen, Z. Effects of Filler Type and Aging on Self-Sensing Capacity of Cement Paste Using Eddy Current-Based Nondestructive Detection. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 182, 109708. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.W.; Chung, D.D.L. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Concrete for Smart Structures Capable of Non-Destructive Flaw Detection. Smart Mater. Struct. 1993, 2, 22–30. [CrossRef]
- Jawed Roshan, M.; Abedi, M.; Gomes Correia, A.; Fangueiro, R. Application of Self-Sensing Cement-Stabilized Sand for Damage Detection. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 403, 133080. [CrossRef]
- Roshan, M.J.; Abedi, M.; Gomes Correia, A.; Fangueiro, R.; Mendes, P.M. A Multifunctional Cementitious Composite for Pavement Subgrade. Materials (Basel). 2024, 17, 621. [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, A.; Suji, D.; Pichumani, M. Real-Time Implication of Hybrid Carbonaceous Fibre and Powder Integrated Self-Sensing Cement Composite in Health Monitoring of Beams and Columns. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2023, 27, 4563–4580. [CrossRef]
- Le, H.V.; Dao, P.L.; Nguyen, S.D.; Ngo, T.T.; Tran, N.T.; Nguyen, D.L.; Kim, D.J. Improvement of the Stress Sensing Ability of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete Using Short Steel Fibers and Steel Slag Aggregates under High Compression. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2023, 362, 114616. [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Das, S. Spatial Damage Sensing Ability of Metallic Particulate-Reinforced Cementitious Composites: Insights from Electrical Resistance Tomography. Mater. Des. 2019, 175, 107817. [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Neithalath, N. Strain Sensing Ability of Metallic Particulate Reinforced Cementitious Composites: Experiments and Microstructure-Guided Finite Element Modeling. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 90, 225–234. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qu, F.; Dong, W.; Mishra, G.; Shah, S.P. A Comprehensive Review on Self-Sensing Graphene/Cementitious Composites: A Pathway toward next-Generation Smart Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127284. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, J.; Im, S.; Cho, S.; Bae, S. Graphene Nanoribbons as a Novel Nanofiller for Enhancing the Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133273. [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Chung, D.D.L. Spatially Resolved Self-Sensing of Strain and Damage in Carbon Fiber Cement. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 4823–4831. [CrossRef]
- Esawi, A.M.K.; Farag, M.M. Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Potential and Current Challenges. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 2394–2401. [CrossRef]
- Sevim, O.; Jiang, Z.; Ozbulut, O.E. Effects of Graphene Nanoplatelets Type on Self-Sensing Properties of Cement Mortar Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129488. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Development of Self-Sensing Cementitious Composite Incorporating Hybrid Graphene Nanoplates and Carbon Nanotubes for Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2022, 336, 113367. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Aslani, F.; Mukherjee, A. Development of 3D Printable Self-Sensing Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 337, 127601. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Aslani, F. A Review on Material Design, Performance, and Practical Application of Electrically Conductive Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116892. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L. Self-Sensing Cementitious Composites Incorporating Hybrid NGPs/CNTs/NCBs for Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2023, 357, 114365. [CrossRef]
- Wahab, N.A.; Roshan, M.J.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Hezmi, M.A.; Jusoh, S.N.; Nik Norsyahariati, N.D.; Tamassoki, S.; Norsyahariati, N.D.N.; Tamassoki, S. Strength and Durability of Cement-Treated Lateritic Soil. Sustain. 2021, 13, 6430. [CrossRef]
- Tamassoki, S.; Nik Daud, N.N.; Nejabi, M.N.; Roshan, M.J. Fibre-Reinforced Soil Mixed Lime/Cement Additives: A Review. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 217–235. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Du, T.; Zhang, A.; Cao, P.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Shi, F.; He, Z. Relationship between Electrical Resistance and Rheological Parameters of Fresh Cement Slurry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119479. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Qian, S. Self-Sensing Properties of Engineered Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 253–262. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lin, S.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Morsy, A.M.; Wang, X. The Effect of Graphite and Slag on Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Electrically Conductive Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122606. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Al-Tabbaa, A.; Haigh, S.K. Measurement Techniques for Self-Sensing Cementitious Composites under Flexure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 142, 105215. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, D.J. Electromechanical Response of Strain-Hardening Fiber-Reinforced Cementitious Composites (SH-FRCCs) under Direct Tension: A Review. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2023, 349, 114096. [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. Self-Sensing Concrete: From Resistance-Based Sensing to Capacitance-Based Sensing. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2021, 12, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. A Critical Review of Electrical-Resistance-Based Self-Sensing in Conductive Cement-Based Materials. Carbon N. Y. 2023, 203, 311–325. [CrossRef]
- A., D.; D., S.; Pichumani, M. Electro-Mechanical Investigations of Steel Fiber Reinforced Self-Sensing Cement Composite and Their Implications for Real-Time Structural Health Monitoring. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104343. [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Yang, B.; Cho, G. Effects of Electrodes Type and Design on Electrical Stability of Conductive Cement as Exposed to Various Weathering Conditions. Carbon Lett. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Sindu, B.S.; Sasmal, S. Synthesis, Design and Piezo-Resistive Characteristics of Cementitious Smart Nanocomposites with Different Types of Functionalized MWCNTs under Long Cyclic Loading. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 108, 103517. [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, G.; Sarwary, M.H.; Al-Dahawi, A.; Öztürk, O.; Anıl, Ö.; Şahmaran, M. Piezoresistive Behavior of CF- and CNT-Based Reinforced Concrete Beams Subjected to Static Flexural Loading: Shear Failure Investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 266–279. [CrossRef]
- Henrique Nalon, G.; Carlos Lopes Ribeiro, J.; Nery Duarte de Araújo, E.; Marcio da Silva, R.; Gonçalves Pedroti, L.; Emilio Soares de Lima, G. Concrete Units for Strain-Monitoring in Civil Structures: Installation of Cement-Based Sensors Using Different Approaches. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132169. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pan, J.; Ma, X.; Cai, J. Sensing Performance of Engineered Cementitious Composites in Different Application Forms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 355, 129223. [CrossRef]
- Vlachakis, C.; Su, Y.-F.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Investigation of the Interfacial Bonding Effect on Self-Sensing Cementitious Coatings for Infrastructure Monitoring. MATEC Web Conf. 2023, 378, 05006. [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Roshan, M.J.; Gulisano, F.; Shayanfar, J.; Adresi, M.; Fangueiro, R.; Correia, A.G. An Advanced Cement-Based Geocomposite with Autonomous Sensing and Heating Capabilities for Enhanced Intelligent Transportation Infrastructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134577. [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ding, S.; Yu, X. Intrinsic Self-Sensing Concrete and Structures: A Review. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2015, 59, 110–128. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, T.; Tang, S.; She, J.; Wang, F.; Zhao, J. Non-Contact Multiple-Frequency AC Impedance Instrument for Cement Hydration Based on a High-Frequency Weak Current Sensor. Actuators 2023, 12, 26. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, W. Contactless, Transformer-Based Measurement of the Resistivity of Materials 2003, 2, 0–5.
- Xiao, L.; Ren, Z.; Shi, W.; Wei, X. Experimental Study on Chloride Permeability in Concrete by Non-Contact Electrical Resistivity Measurement and RCM. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 27–34. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Z. Early-Age Hydration of Fresh Concrete Monitored by Non-Contact Electrical Resistivity Measurement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 312–319. [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, F.; Xiaosheng, W. Early Strength Development and Hydration of Cement Pastes at Different Temperatures or with Superplasticiser Characterised by Electrical Resistivity. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00911. [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, F.; Wei, X.; Zhou, J. Monitoring the Setting and Hardening Behaviour of Cement Paste by Electrical Resistivity Measurement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 118941. [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ma, H.; Hafiz, R.B.; Fu, C.; Jin, X.; He, J. Determining Porosity and Pore Network Connectivity of Cement-Based Materials by a Modified Non-Contact Electrical Resistivity Measurement: Experiment and Theory. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 82–92. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Borg, R.P. Improved Non-Contact Variable-Frequency AC Impedance Instrument for Cement Hydration and Pore Structure Based on SVM Calibration Method. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 179, 109402. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Study on Hydration Process of Early-Age Concrete Using Embedded Active Acoustic and Non-Contact Complex Resistivity Methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 183–192. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, S.; Lu, Y. Pore Structure Analyzer Based on Non-Contact Impedance Measurement for Cement-Based Materials 2011, US Patent 20,120,158,333,.
- Tang, S.W.; Cai, X.H.; He, Z.; Zhou, W.; Shao, H.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Wu, T.; Chen, E. The Review of Pore Structure Evaluation in Cementitious Materials by Electrical Methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 117, 273–284. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Tran, Q. Influence of Parameters on Surface Resistivity of Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 62, 134–145. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Tran, Q. Correlation Between Bulk and Surface Resistivity of Concrete. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2015, 9, 119–132. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Sasamoto, A.; Iwata, M. Wenner Method of Impedance Measurement for Health Evaluation of Reinforced Concrete Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 576–586. [CrossRef]
- Cheytani, M.; Chan, S.L.I. The Applicability of the Wenner Method for Resistivity Measurement of Concrete in Atmospheric Conditions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00663. [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Ahmed, H.; Kuusela, P.; Seppänen, A.; Punkki, J. Monitoring of Concrete Segregation Using AC Impedance Spectroscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 384, 131453. [CrossRef]
- Azarsa, P.; Gupta, R. Electrical Resistivity of Concrete for Durability Evaluation: A Review. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Spragg, R.; Villani, C.; Snyder, K.; Bentz, D.; Bullard, J.; Weiss, J. Factors That Influence Electrical Resistivity Measurements in Cementitious Systems. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2342, 90–98. [CrossRef]
- Cunha Araújo, E.; Macioski, G.; Henrique Farias de Medeiros, M. Concrete Surface Electrical Resistivity: Effects of Sample Size, Geometry, Probe Spacing and SCMs. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126659. [CrossRef]
- Piro, N.S.; Mohammed, A.S.; Hamad, S.M. Electrical Resistivity Measurement, Piezoresistivity Behavior and Compressive Strength of Concrete: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106573. [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Kurashige, I.; Hisada, M. Appropriate Geometrical Factors for Four-Probe Method to Evaluate Electrical Resistivity of Concrete Specimens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 374, 130784. [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q. Electrical Resistivity of Plain Cement-Based Materials Based on Ionic Conductivity: A Review of Applications and Conductive Models. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103642. [CrossRef]
- Daniyal, M.; Akhtar, S. Corrosion Assessment and Control Techniques for Reinforced Concrete Structures: A Review. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabil. 2020, 5, 1. [CrossRef]
- García-Macías, E.; D’Alessandro, A.; Castro-Triguero, R.; Pérez-Mira, D.; Ubertini, F. Micromechanics Modeling of the Uniaxial Strain-Sensing Property of Carbon Nanotube Cement-Matrix Composites for SHM Applications. Compos. Struct. 2017, 163, 195–215. [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Elchalakani, M.; Boussaid, F.; Yehia, S.; Sadakkathulla, M.A.; Yang, B. Development and Evaluation of Conductive Ultra-Lightweight Cementitious Composites for Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure Applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 375, 131017. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Heath, A.; Abdalgadir, H.M.T.; Ball, R.J.; Paine, K. Electrical Impedance Behaviour of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Cement-Based Sensors at Different Moisture Contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 353, 129049. [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, E.; Sousa, I.; Vieira, M.; Matos, A.M.; Santos, L.P.M.; Silvestro, L.; Salvador, R.; D’Alessandro, A.; Ubertini, F. Investigation of the Electrical Sensing Properties of Cementitious Composites Produced with Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in NaOH. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107496. [CrossRef]
- Baeza, F.J.; Galao, O.; Zornoza, E.; Garcés, P. Effect of Aspect Ratio on Strain Sensing Capacity of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement Composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 1085–1094. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-Y.; You, I.; Lee, S.-J. Electrical and Piezoresistive Sensing Capacities of Cement Paste with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 371–384. [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Min, Y.K.; Chung, W.; Lee, S.-E.E.; Kang, S.-W.W. Effects of Dispersants and Defoamers on the Enhanced Electrical Performance by Carbon Nanotube Networks Embedded in Cement-Matrix Composites. Compos. Struct. 2020, 243, 112193. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ni, Z.; Mu, S.; Hang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Su, Y.; Weng, G.J. Hybrid Micromechanical Modelling and Experiments on Electrical Conductivity of Graphene Reinforced Porous and Saturated Cement Composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 141. [CrossRef]
- Le, H.V.; Nguyen, V.M.; Pham, T.N.; Tang, V.L.; Pham, X.N.; Nguyen, D.L.; Kim, D.J. Self-Sensing Characteristics of Smart High-Performance Cementitious Composites Containing Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes, Steel Fibers, and Steel Slag Aggregates under Compression. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2024, 365, 114920. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.N.; Kavyateja, B.V.; Jindal, B.B. Structural Health Monitoring Methods, Dispersion of Fibers, Micro and Macro Structural Properties, Sensing, and Mechanical Properties of Self-Sensing Concrete—A Review. Struct. Concr. 2021, 22, 793–805. [CrossRef]
- Al-Dahawi, A.; Sarwary, M.H.; Öztürk, O.; Yildirim, G.; Akin, A.; Şahmaran, M.; Lachemi, M. Electrical Percolation Threshold of Cementitious Composites Possessing Self-Sensing Functionality Incorporating Different Carbon-Based Materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105005. [CrossRef]
- Pichór, W.; Frąc, M.; Radecka, M. Determination of Percolation Threshold in Cement Composites with Expanded Graphite by Impedance Spectroscopy. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104328. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, F.; Shen, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Jin, K.; Feng, L.; Tang, Z. Research on the Self-Sensing and Mechanical Properties of Aligned Stainless Steel Fiber-Reinforced Reactive Powder Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 119, 104001. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S. A State-of-the-Art on Self-Sensing Concrete: Materials, Fabrication and Properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 177, 107437. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhong, W.; Yao, W. Modeling of Conductivity in Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Cement-Based Composite. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 3538–3546. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Sun, J.; Tang, W.; Zeng, X.; Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Mechanical and Electrical Properties Investigation for Electrically Conductive Cementitious Composite Containing Nano-Graphite Activated Magnetite. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104847. [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Wang, Q.; Fang, Z. Effect of Graphite on the Self-Sensing Properties of Cement and Alkali-Activated Fly Ash/Slag Based Composite Cementitious Materials. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107493. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, K.; Shah, S.P. Advances in Multifunctional Cementitious Composites with Conductive Carbon Nanomaterials for Smart Infrastructure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 128, 104454. [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Chung, D.D.L. The Role of Electronic and Ionic Conduction in the Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement. Carbon N. Y. 2006, 44, 2130–2138. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pan, J.; Cai, J. Self-Sensing Properties and Piezoresistive Effect of High Ductility Cementitious Composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126390. [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Liang, M.; Yao, Z.; Su, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Sun, C.; Jiang, H. Self-Sensing Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes/Epoxy Resin Composite for Asphalt Pavement Strain Monitoring. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119404. [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z.; Huo, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J. Electrically Conductive Asphalt Concrete for Smart and Sustainable Pavement Construction: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133433. [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, A.; Notani, M.A.; Kazemiyan Zadeh, A.; Nahvi, A.; Sassani, A.; Ceylan, H. Electrically Conductive Asphalt Concrete: An Alternative for Automating the Winter Maintenance Operations of Transportation Infrastructure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 173, 106985. [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Q. A Comparative Study on the Influences of CNT and GNP on the Piezoresistivity of Cement Composites. Mater. Lett. 2020, 259, 126858. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; He, X.; Sheng, D. Effects of Silica Fume on Physicochemical Properties and Piezoresistivity of Intelligent Carbon Black-Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 120399. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Lu, N.; Qu, F.; Vessalas, K.; Sheng, D. Piezoresistive Behaviours of Cement-Based Sensor with Carbon Black Subjected to Various Temperature and Water Content. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 178, 107488. [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Han, B. Modifying Self-Sensing Cement-Based Composites through Multiscale Composition. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 074002. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Dong, W.; Luo, Z.; Qu, F.; Yang, F.; Wang, K. Self-Sensing Performance of Cement-Based Sensor with Carbon Black and Polypropylene Fibre Subjected to Different Loading Conditions. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 59, 105003. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xie, N.; Cheng, X.; Feng, L.; Hou, P.; Huang, S.; Zhou, Z. Electrical Properties of Low Dosage Carbon Nanofiber/Cement Composite: Percolation Behavior and Polarization Effect. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 109, 103539. [CrossRef]
- Al-Dahawi, A.; Yıldırım, G.; Öztürk, O.; Şahmaran, M. Assessment of Self-Sensing Capability of Engineered Cementitious Composites within the Elastic and Plastic Ranges of Cyclic Flexural Loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.K.; Sindu, B.S.; Sasmal, S. Real-Time Monitoring of Structures under Extreme Loading Using Smart Composite-Based Embeddable Sensors. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2022, 34, 1073–1096. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, B.; Sun, S.; Qin, Y.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Li, M.; Fan, X.; Peng, W. Advances in Self-Sensing Cement-Based Composites Containing Nano Materials for Smart Civil Infrastructures. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2024, 230, 114514. [CrossRef]
- Baeza, F.J.; Galao, O.; Zornoza, E.; Garcés, P. Effect of Aspect Ratio on Strain Sensing Capacity of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement Composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 1085–1094. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M. Multifunctional Self-Sensing and Ductile Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 123, 105714. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; You, I.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.O.; Yoo, D.Y. Self-Sensing Capacity of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Containing Conductive Powders in Tension. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104331. [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Georgaklis, J.; Ams, M.; Patabendigedara, S.; Belford, A.; Wu, S. Smart Self-Sensing Concrete: The Use of Multiscale Carbon Fillers. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 2667–2682. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Aslani, F. Self-Sensing Performance of Cementitious Composites with Functional Fillers at Macro, Micro and Nano Scales. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125679. [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Bang, J.; Yoon, H.N.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, H.; Cheon, S.H.; Yang, B. Directionally Sensitive Cement-Based Sensor Using Carbon Nanotube and Carbonyl Iron Powder (CNT@CIP)-Based Nanohybrid Clusters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134116. [CrossRef]
- Gharehbaghi, V.R.; Noroozinejad Farsangi, E.; Noori, M.; Yang, T.Y.; Li, S.; Nguyen, A.; Málaga-Chuquitaype, C.; Gardoni, P.; Mirjalili, S. A Critical Review on Structural Health Monitoring: Definitions, Methods, and Perspectives. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 2209–2235. [CrossRef]
- Rytter, A. Vibrational Based Inspection of Civil Engineering Structures, Aalborg Universitet, 1993.
- Taheri, S. A Review on Five Key Sensors for Monitoring of Concrete Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 492–509. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, M.; Li, P.; Chang, Q.; Guo, J. An Alkali-Responsive Mineral Self-Healing Agent with Mechanical Property Enhancement for Cementitious Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 266, 110986. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Haider, M.Z.; Cui, Y.; Jang, J.G.; Kim, Y.J.; Fang, G.; Hu, J.W. Development of Nanomodified Self-Healing Mortar and a U-Net Model Based on Semantic Segmentation for Crack Detection and Evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 129985. [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, X.; Li, M. The Effects of Damage and Self-Healing on Impedance Spectroscopy of Strain-Hardening Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 106, 77–90. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Shen, L.; Zhang, S.; Vessalas, K. Integrated Self-Sensing and Self-Healing Cementitious Composite with Microencapsulation of Nano-Carbon Black and Slaked Lime. Mater. Lett. 2021, 282, 128834. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, W.; Castel, A.; Sheng, D. Self-Sensing Cement-Based Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring toward Smart Infrastructure. J. Proc. R. Soc. New South Wales 2021, 154, 24–32. [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Du, H.; Zou, N.Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Measurement and Simulation of Electrical Resistivity of Cement-Based Materials by Using Embedded Four-Probe Method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 357. [CrossRef]
- Canbek, O.; Washburn, N.R.; Kurtis, K.E. Relating LC3 Microstructure, Surface Resistivity and Compressive Strength Development. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 160, 106920. [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lu, L.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, S. Hydration Monitoring and Strength Prediction of Cement-Based Materials Based on the Dielectric Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 179–189. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Shi, F. Electrical and Piezoresistive Properties of Carbon Nanofiber Cement Mortar under Different Temperatures and Water Contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120740. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Han, B.; Yu, X.; Ni, Y.-Q. Effect of Water Content on the Piezoresistive Property of Smart Cement-Based Materials with Carbon Nanotube/Nanocarbon Black Composite Filler. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 119, 8–20. [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Cao, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, C. Effects of Microstructure and Pore Water on Electrical Conductivity of Cement Slurry during Early Hydration. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 177, 107435. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, L.; Li, Z. Hydration Monitoring of Cement-Based Materials with Resistivity and Ultrasonic Methods. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2009, 42, 15–24. [CrossRef]
- Le, H.V.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, D.J.; Park, J. Electrical Properties of Smart Ultra-High Performance Concrete under Various Temperatures, Humidities, and Age of Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 118, 103979. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.N.; Jang, D.; Kil, T.; Lee, H.K. Influence of Various Deterioration Factors on the Electrical Properties of Conductive Cement Paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130289. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Nam, I.W.; Tafesse, M.; Kim, H.K. Fluctuation of Electrical Properties of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials/Cement Composites: Case Studies and Parametric Modeling. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 102, 55–70. [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Tiecco, M.; Meoni, A.; Ubertini, F. Improved Strain Sensing Properties of Cement-Based Sensors through Enhanced Carbon Nanotube Dispersion. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 115, 103842. [CrossRef]
- Sobolkina, A.; Mechtcherine, V.; Khavrus, V.; Maier, D.; Mende, M.; Ritschel, M.; Leonhardt, A. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes and Its Influence on the Mechanical Properties of the Cement Matrix. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 1104–1113. [CrossRef]
- Thomoglou, A.K.; Falara, M.G.; Gkountakou, F.I.; Elenas, A.; Chalioris, C.E. Influence of Different Surfactants on Carbon Fiber Dispersion and the Mechanical Performance of Smart Piezoresistive Cementitious Composites. Fibers 2022, 10, 49. [CrossRef]
- Siahkouhi, M.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Aela, P.; Ni, Y.Q.; Jing, G. Railway Ballast Track Hanging Sleeper Defect Detection Using a Smart CNT Self-Sensing Concrete Railway Sleeper. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 399, 132487. [CrossRef]
- Triana-Camacho, D.A.; Quintero-Orozco, J.H.; Mejía-Ospino, E.; Castillo-López, G.; García-Macías, E. Piezoelectric Composite Cements: Towards the Development of Self-Powered and Self-Diagnostic Materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 139, 105063. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.M.; Fattah, K.P.; Tamimi, A.K. Modelling Mechanical Behavior of Cementitious Material Incorporating CNTs Using Design of Experiments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 763–770. [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiak, B.; Greer, H.F.; Dzido, G.; Kolanowska, A.; Jędrysiak, R.; Dziadosz, J.; Dzida, M.; Boncel, S. Effect of Ultrasonication Time on Microstructure, Thermal Conductivity, and Viscosity of Ionanofluids with Originally Ultra-Long Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 77, 105681. [CrossRef]
- Blanch, A.J.; Lenehan, C.E.; Quinton, J.S. Parametric Analysis of Sonication and Centrifugation Variables for Dispersion of Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Aqueous Solutions of Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate. Carbon N. Y. 2011, 49, 5213–5228. [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Rana, S.; Fangueiro, R.; Paiva, M.C. Characterizing Dispersion and Long Term Stability of Concentrated Carbon Nanotube Aqueous Suspensions for Fabricating Ductile Cementitious Composites. Powder Technol. 2017, 307, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Liang, Y.; Yin, H.; Long, W.; Pu, P.; Liu, J. PDMS/CNB-Impregnation Treatment for Improving the Electrical and Piezoresistive Properties of Recycled Fine Aggregate Mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106253. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yao, J.; Zhong, J.; Ruan, W.; Xiao, H.; Sun, Y. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Performance and Piezoresistivity of Multifunctional Cement Composites by Adopting Conductive Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 153, 105697. [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Choi, S.; Yoo, D.Y.; Oh, T.; Song, Y.; Yeon, J.H. Moisture Dependence of Electrical Resistivity in Under-Percolated Cement-Based Composites with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 47–58. [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.K.; Sasmal, S. Nanoengineered Smart Cement Composite for Electrical Impedance-Based Monitoring of Corrosion Progression in Structures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 126, 104348. [CrossRef]
- Siad, H.; Lachemi, M.; Sahmaran, M.; Mesbah, H.A.; Hossain, K.A. Advanced Engineered Cementitious Composites with Combined Self-Sensing and Self-Healing Functionalities. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 313–322. [CrossRef]
- Chi, V.M.; Hai, N.M.; Lan, N.; Huong, N. Van An Empirical Model for Electrical Resistivity of Mortar Considering the Synergistic Effects of Carbon Fillers, Current Intensity, and Environmental Factors. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02685. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, D.; Zhao, Z.; Tan, S.; Wang, M.; Ma, Q.; Wu, J.; Cai, G. Smart Cement for Fire Alarms and Indoor Climate Control. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 148298. [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Yoon, H.N.; Farooq, S.Z.; Lee, H.K.; Nam, I.W. Influence of Water Ingress on the Electrical Properties and Electromechanical Sensing Capabilities of CNT/Cement Composites. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 42, 103065. [CrossRef]
- Rovnaník, P.; Kusák, I.; Bayer, P. Effect of Water Saturation on the Electrical Properties of Cement and Alkali-Activated Slag Composites with Graphite Conductive Admixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129699. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, J. Coupling Effect of Salt Freeze-Thaw Cycles and Cyclic Loading on Performance Degradation of Carbon Nanofiber Mortar. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 95–102. [CrossRef]
- Jawed Roshan, M.; Safuan A. Rashid, A.; Abdul Wahab, N.; Azril Hezmi, M.; Norafida Jusoh, S.; Daud Nik Norsyahariati, N.; Tamasoki, S.; Zurairahetty Mohd Yunus, N.; Razali, R. Effects of Ordinary Portland Cement on the Soil-Water Characteristics Curve of Lateritic Soil. Suranaree J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 30, 010183(1-10). [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.M. Global CO2 Emissions from Cement Production. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 195–217. [CrossRef]
- Tamassoki, S.; Nik Daud, N.N.; Jakarni, F.M.; Mohd Kusin, F.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Roshan, M.J. Performance Evaluation of Lateritic Subgrade Soil Treated with Lime and Coir Fibre-Activated Carbon. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8279. [CrossRef]
- Tamassoki, S.; Daud, N.N.N.; Jakarni, F.M.; Kusin, F.M.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Roshan, M.J. Compressive and Shear Strengths of Coir Fibre Reinforced Activated Carbon Stabilised Lateritic Soil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9100. [CrossRef]
- Tamassoki, S.; Daud, N.N.N.; Wang, S.; Roshan, M.J. CBR of Stabilized and Reinforced Residual Soils Using Experimental, Numerical, and Machine-Learning Approaches. Transp. Geotech. 2023, 42, 101080. [CrossRef]
- Birgin, H.B.; D’Alessandro, A.; Corradini, A.; Laflamme, S.; Ubertini, F. Self-Sensing Asphalt Composite with Carbon Microfibers for Smart Weigh-in-Motion. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2022, 55, 138. [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.I.; Khan, R.I.; Ashraf, W.; Pendse, H. Production of Sustainable, Low-Permeable and Self-Sensing Cementitious Composites Using Biochar. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 28, e00279. [CrossRef]
- Vlachakis, C.; Wang, X.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Investigation of the Compressive Self-Sensing Response of Filler-Free Metakaolin Geopolymer Binders and Coatings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131682. [CrossRef]
- Payakaniti, P.; Pinitsoontorn, S.; Thongbai, P.; Amornkitbamrung, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Electrical Conductivity and Compressive Strength of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Fly Ash Geopolymeric Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 164–176. [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, K.J.D.; Bolton, M.J. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Aluminosilicate Inorganic Polymer Composites with Carbon Nanotubes. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 2851–2857. [CrossRef]
- Rovnaník, P.; Kusák, I.; Bayer, P.; Schmid, P.; Fiala, L. Electrical and Self-Sensing Properties of Alkali-Activated Slag Composite with Graphite Filler. Materials (Basel). 2019, 12, 1616. [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Yin, S.; Ouyang, X.; Fu, J.; Liu, A.; Zhang, Z. Preparation and Piezoresistive Properties of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Alkali-Activated Fly Ash/Slag Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 738–749. [CrossRef]
- Saafi, M.; Andrew, K.; Tang, P.L.; McGhon, D.; Taylor, S.; Rahman, M.; Yang, S.; Zhou, X. Multifunctional Properties of Carbon Nanotube/Fly Ash Geopolymeric Nanocomposites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 46–55. [CrossRef]
- Saafi, M.; Tang, L.; Fung, J.; Rahman, M.; Sillars, F.; Liggat, J.; Zhou, X. Graphene/Fly Ash Geopolymeric Composites as Self-Sensing Structural Materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 065006. [CrossRef]
- Baeza, F.J.; Galao, O.; Vegas, I.J.; Cano, M.; Garcés, P. Influence of Recycled Slag Aggregates on the Conductivity and Strain Sensing Capacity of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Cement Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 311–319. [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, T.; Sangoju, B.; Muthuramalingam, G. A Study on Copper Slag as Fine Aggregate in Improving the Electrical Conductivity of Cement Mortar. Sadhana - Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 2022, 47, 141. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Tao, Z.; Li, W. Development of Piezoresistive Cement-Based Sensor Using Recycled Waste Glass Cullets Coated with Carbon Nanotubes. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127968. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Vessalas, K.; Zhang, S. Mechanical Strength and Self-Sensing Capacity of Smart Cementitious Composite Containing Conductive Rubber Crumbs. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2020, 31, 1325–1340. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Ling, T.-C.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z. Investigation on Electrically Conductive Aggregates Produced by Incorporating Carbon Fiber and Carbon Black. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 106–114. [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Ma, L.P.; Zhong, J.; Tong, J.; Liu, Z.; Ren, W.; Cheng, H.M. Growing Nanocrystalline Graphene on Aggregates for Conductive and Strong Smart Cement Composites. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 3587–3597. [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Huo, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhong, J. Carbon Nanotube Polymer Nanocomposites Coated Aggregate Enabled Highly Conductive Concrete for Structural Health Monitoring. Carbon N. Y. 2023, 206, 340–350. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gonzalez, J.G.; Loh, K.J. Self-Sensing Concrete Enabled by Nano-Engineered Cement-Aggregate Interfaces. Struct. Heal. Monit. 2017, 16, 309–323. [CrossRef]
- Irshidat, M.R.; Al-Nuaimi, N.; Ahmed, W.; Rabie, M. Feasibility of Recycling Waste Carbon Black in Cement Mortar Production: Environmental Life Cycle Assessment and Performance Evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123740. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Wu, T.; Jin, B.; Yang, L.; Qiu, J. Synthesis, Modification Strategies and Applications of Coal-Based Carbon Materials. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 230, 107203. [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.B.; Chen, S.E. Assessment of an Axially Loaded Self-Sensing Concrete Element with Recycled Steel Residuals. CivilEng 2022, 3, 643–668. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Luo, Z.; Sheng, D. Self-Sensing Capabilities of Cement-Based Sensor with Layer-Distributed Conductive Rubber Fibres. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2020, 301, 111763. [CrossRef]
- Frąc, M.; Szudek, W.; Szołdra, P.; Pichór, W. The Applicability of Shungite as an Electrically Conductive Additive in Cement Composites. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103469. [CrossRef]
- Yaghobian, M.; Whittleston, G. A Critical Review of Carbon Nanomaterials Applied in Cementitious Composites – A Focus on Mechanical Properties and Dispersion Techniques. Alexandria Eng. J. 2022, 61, 3417–3433. [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.F.; Tutumluer, E.; Mechitov, K.A.; Qamhia, I.I.A.; Spencer, B.; Riley Edwards, J. Towards a Wireless Sensing Infrastructure for Smart Mobility. Transp. Geotech. 2023, 40, 100985. [CrossRef]
- Birgin, H.B.; Laflamme, S.; D’alessandro, A.; Garcia-Macias, E.; Ubertini, F. A Weigh-in-Motion Characterization Algorithm for Smart Pavements Based on Conductive Cementitious Materials. Sensors (Switzerland) 2020, 20, 659. [CrossRef]
- Sujon, M.; Dai, F. Application of Weigh-in-Motion Technologies for Pavement and Bridge Response Monitoring: State-of-the-Art Review. Autom. Constr. 2021, 130, 103844. [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, X.; Kwon, E. A Self-Sensing Carbon Nanotube/Cement Composite for Traffic Monitoring. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 445501. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Zhu, H.H.; Wu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, T.X.; Shi, B. Artificial Intelligence-Based Fiber Optic Sensing for Soil Moisture Measurement with Different Cover Conditions. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2023, 206, 112312. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Qu, F.; Liang, R.; Shah, S.P. Application of Intrinsic Cement-Based Sensor for Traffic Detections of Human Motion and Vehicle Speed. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 355, 129130. [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, K.; Yu, X.; Kwon, E.; Ou, J. Nickel Particle-Based Self-Sensing Pavement for Vehicle Detection. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2011, 44, 1645–1650. [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.T.; Daniyal, M.; Alzara, M.; Elkady, M.; Armghan, A. Self-Sensing Cement Composite for Traffic Monitoring in Intelligent Transport System. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2021, 105. [CrossRef]
- Borke Birgin, H.; D’Alessandro, A.; Favaro, M.; Sangiorgi, C.; Laflamme, S.; Ubertini, F. Field Investigation of Novel Self-Sensing Asphalt Pavement for Weigh-in-Motion Sensing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 085004. [CrossRef]
- Nalon, G.H.; Santos, R.F.; Lima, G.E.S. de; Andrade, I.K.R.; Pedroti, L.G.; Ribeiro, J.C.L.; Franco de Carvalho, J.M. Recycling Waste Materials to Produce Self-Sensing Concretes for Smart and Sustainable Structures: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126658. [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.T.; Al-Dahawi, A. Electro-Mechanical Properties of Functional Fiber-Based Rigid Pavement under Various Loads Applied on a Large-Scale in-Situ Section. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 427, 22–26. [CrossRef]
- Birgin, H.B.; D’alessandro, A.; Laflamme, S.; Ubertini, F. Innovative Carbon-Doped Composite Pavements with Sensing Capability and Low Environmental Impact for Multifunctional Infrastructures. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 192. [CrossRef]
- Barri, K.; Zhang, Q.; Kline, J.; Lu, W.; Luo, J.; Sun, Z.; Taylor, B.E.; Sachs, S.G.; Khazanovich, L.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Multifunctional Nanogenerator-Integrated Metamaterial Concrete Systems for Smart Civil Infrastructure. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; He, J.; Xing, X.; Cao, D.; Gao, X.; Hao, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, Z. Functionality Enhancement of Industrialized Optical Fiber Sensors and System Developed for Full-Scale Pavement Monitoring. Sensors (Switzerland) 2014, 14, 8829–8850. [CrossRef]
- Lajnef, N.; Rhimi, M.; Chatti, K.; Mhamdi, L.; Faridazar, F. Toward an Integrated Smart Sensing System and Data Interpretation Techniques for Pavement Fatigue Monitoring. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 26, 513–523. [CrossRef]
- Lau, F.D.H.; Butler, L.J.; Adams, N.M.; Elshafie, M.Z.E.B.; Girolami, M.A. Real-Time Statistical Modelling of Data Generated from Self-Sensing Bridges. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Smart Infrastruct. Constr. 2018, 171, 3–13. [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, A.; Suji, D.; Pichumani, M. Self-Sensing Cementitious Composite Sensor with Integrated Steel Fiber and Carbonaceous Powder for Real-Time Application in Large-Scale Infrastructures. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2023, 353, 114209. [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Fu, J.; Sun, L.; Masuya, H.; Zhang, L. Fatigue Damage Self-Sensing of Bridge Deck Component with Built-in Giant Piezoresistive Cementitious Carbon Fiber Composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 276, 114459. [CrossRef]
- Chen, R. Preparation, Property Determination and Bridge Health Monitoring Applications of Self-Sensing Cement Nanocomposites. Alexandria Eng. J. 2023, 66, 891–900. [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.C.; Lynch, J.P. Electrical Impedance Tomographic Methods for Sensing Strain Fields and Crack Damage in Cementitious Structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 1363–1379. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Tallman, T.N. Precise Damage Shaping in Self-Sensing Composites Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Genetic Algorithms. Struct. Heal. Monit. 2023, 22, 372–387. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Lin, Y.-A.; Lee, H.-J.; Buscheck, J.; Wu, R.; Lynch, J.P.; Garg, N.; Loh, K.J. In Situ Crack Mapping of Large-Scale Self-Sensing Concrete Pavements Using Electrical Resistance Tomography. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 122, 104154. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, W. Effect of Coarse Aggregate and Carbon Fiber Content on Ohmic Heating Curing of Concrete Slab in Realistic Severely Cold Weather. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 211, 103861. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Che, G. Concrete Pavement Deicing with Carbon Fiber Heating Wires. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 65, 413–420. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, L.; Shu, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, P.; Ran, Q. Recent Advancements in Photothermal Anti-Icing/Deicing Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 143924. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, H. Self-Deicing Road System with a CNFP High-Efficiency Thermal Source and MWCNT/Cement-Based High-Thermal Conductive Composites. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 86, 22–35. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kong, G.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Shen, Y. Field Tests on the Prediction of Heating Power Requirements for Deicing in Jiangyin, China. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2022, 32, 100293. [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Ma, T.; Chen, F.; Han, C.; Li, H.; Xu, F. Co-Modifying Geopolymer Composite by Nano Carbon Black and Carbon Fibers to Reduce CO2 Emissions in Airport Pavement Induction Heating. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 177, 107951. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.G.; Ozgur, G.; Sevkat, E. Electrical Resistance Heating for Deicing and Snow Melting Applications: Experimental Study. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 160, 128–138. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, D.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Tan, S.; Wu, J.; Ding, Q. Construction of New Conductive Networks for Expandable Graphite-Based Cement Composites via a Facile Heat Treatment Process. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 141, 105142. [CrossRef]
- Sassani, A.; Arabzadeh, A.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Sadati, S.M.S.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Taylor, P.C.; Abdualla, H. Carbon Fiber-Based Electrically Conductive Concrete for Salt-Free Deicing of Pavements. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 799–809. [CrossRef]
- Sassani, A.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Arabzadeh, A.; Taylor, P.C.; Gopalakrishnan, K. Development of Carbon Fiber-Modified Electrically Conductive Concrete for Implementation in Des Moines International Airport. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2018, 8, 277–291. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Ban, H.; Park, W.J. Deicing Concrete Pavements and Roads with Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) as Heating Elements. Materials (Basel). 2020, 13, 2504. [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Ding, S.; Han, B.; Ou, J. Self-Heating Ultra-High Performance Concrete with Stainless Steel Wires for Active Deicing and Snow-Melting of Transportation Infrastructures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 138, 105005. [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Fu, J.; Chan, Y.; Tuan, C.Y.; Liu, C. Steel Fiber Confined Graphite Concrete for Pavement Deicing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 155, 187–196. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Taylor, P.C. Influence of Electrode Placement Depth on Thermal Performance of Electrically Conductive Concrete: Significance of Threshold Voltage for Long-Term Stability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134883. [CrossRef]
- Abdualla, H.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Taylor, P.C.; Turkan, Y. System Requirements for Electrically Conductive Concrete Heated Pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2569, 70–79. [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Tuan, C.Y.; Ye, M. Models for Estimating the Thermal Properties of Electric Heating Concrete Containing Steel Fiber and Graphite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 164, 116–120. [CrossRef]
- Malakooti, A.; Abdualla, H.; Sadati, S.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Cetin, K. Experimental and Theoretical Characterization of Electrodes on Electrical and Thermal Performance of Electrically Conductive Concrete. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 222, 109003. [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Dutta, S.; Kurup, P.; Yu, T.; Wang, X. A Review of Railway Infrastructure Monitoring Using Fiber Optic Sensors. Sensors Actuators, A Phys. 2020, 303, 111728. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.N.; Jang, D.; Lee, H.K.; Nam, I.W. Influence of Carbon Fiber Additions on the Electromagnetic Wave Shielding Characteristics of CNT-Cement Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121238. [CrossRef]
- Nam, I.W.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, H.K. Influence of Silica Fume Additions on Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube / Cement Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 480–487. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, D.; Yu, X.; Han, B. Electromagnetic Properties and Mechanisms of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Modified Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 427–443. [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kim, S.; Park, G.-K.; Lee, N. Influence of Carbon Fiber on the Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Cementitious Composites. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 101982. [CrossRef]
- Wanasinghe, D.; Aslani, F.; Ma, G. Electromagnetic Shielding Properties of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120439. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, H.; Shin, B.G.; Song, Y.J. Cement Composites with Carbon Fiber for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Applications. Carbon N. Y. 2024, 220. [CrossRef]
- Nam, I.W.; Lee, H.K. Synergistic Effect of MWNT/Fly Ash Incorporation on the EMI Shielding/Absorbing Characteristics of Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 651–661. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, S.; Liu, X. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Multifunctional Cementitious Composites Incorporating Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Fibers and Fly Ash: Effects of Microstructure and Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 143. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.; Joanni, E.; Singh, R.K.; Tan, W.K.; Kar, K.K.; Matsuda, A. Recent Progress on Carbon-Based Composite Materials for Microwave Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Carbon N. Y. 2021, 177, 304–331. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Gupta, B.K.; Mishra, M.; Govind; Chandra, A.; Mathur, R.B.; Dhawan, S.K. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Cement Composites with Exceptional Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 56, 86–96. [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, H.; Hadigheh, S.A.; Tao, Y.; Adam, G. Development of a Novel and Specialised Cementitious Matrix Overlay for Anode Embedment in Impressed Current Cathodic Protection ( ICCP ) Systems for Reinforced Concrete Bridges. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02908. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Chen, E.; Li, W.G. A Review on Corrosion Detection and Protection of Existing Reinforced Concrete (RC) Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325. [CrossRef]
- Thanh Tran, D.; Lee, H.S.; Kumar Singh, J.; Lee, D.E. Corrosion Prevention of Steel Rebar Embedded in the Cement Mortar under Accelerated Conditions: Combined Effects of Phosphate and Chloride Ions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130042. [CrossRef]
- Koleva, D.A.; de Wit, J.H.W.; van Breugel, K.; Veleva, L.P.; van Westing, E.; Copuroglu, O.; Fraaij, A.L.A. Correlation of Microstructure, Electrical Properties and Electrochemical Phenomena in Reinforced Mortar. Breakdown to Multi-Phase Interface Structures. Part II: Pore Network, Electrical Properties and Electrochemical Response. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 801–815. [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Wu, Y. Electrochemical Studies on the Performance of Conductive Overlay Material in Cathodic Protection of Reinforced Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2655–2662. [CrossRef]
- Jansson, H.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L.; Tang, L.; Mohammadi, A.S.; Babaahmadi, A. Carbon Enhanced Cementitious Coatings: Alternative Anode Materials for Impressed Current Cathodic Protection Systems Intended for Reinforced Concrete. Mater. Corros. 2024, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Jeong, J.; Jin, C. Development of Conductive Mortar for Efficient Sacrificial Anode Cathodic Protection of Reinforced Concrete Structures—Part 2: Four-Year Performance Evaluation in Bridges. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1797. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Q. Investigation of Carbon Fillers Modified Electrically Conductive Concrete as Grounding Electrodes for Transmission Towers: Computational Model and Case Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 347–353. [CrossRef]
- Lun, L.; Tian, X.; Pei, F.; Liu, X.; Jia, L.; Deng, C.; Wang, X.; Lan, F.; Cheng, H. Resistance Reduction Scheme for Tower Grounding with Conductive Cement. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 1731–1742. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, T. Experimental Study on the Road Energy Harvesting of Piezoelectric Ceramic in Unbound Granular Materials Based on a Large-Scale Triaxial Apparatus. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 4599–4625. [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Kong, L.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Lu, L.; Li, D. An Electromagnetic Energy Harvester for Applications in a High-Speed Rail Pavement System. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 243, 108018. [CrossRef]
- Birgin, H.B.; García-Macías, E.; D’Alessandro, A.; Ubertini, F. Self-Powered Weigh-in-Motion System Combining Vibration Energy Harvesting and Self-Sensing Composite Pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130538. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Z. A Large-Sized Thermoelectric Module Composed of Cement-Based Composite Blocks for Pavement Energy Harvesting and Surface Temperature Reducing. Energy 2023, 265, 126398. [CrossRef]
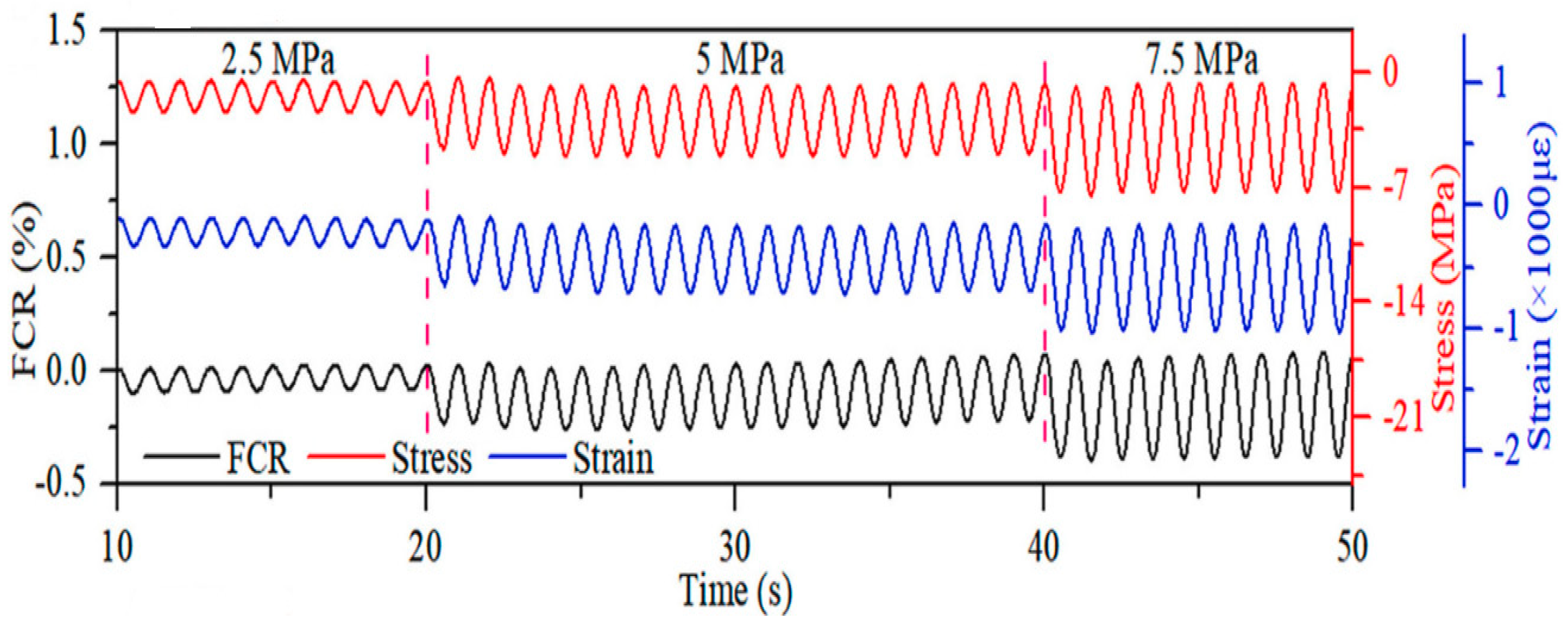
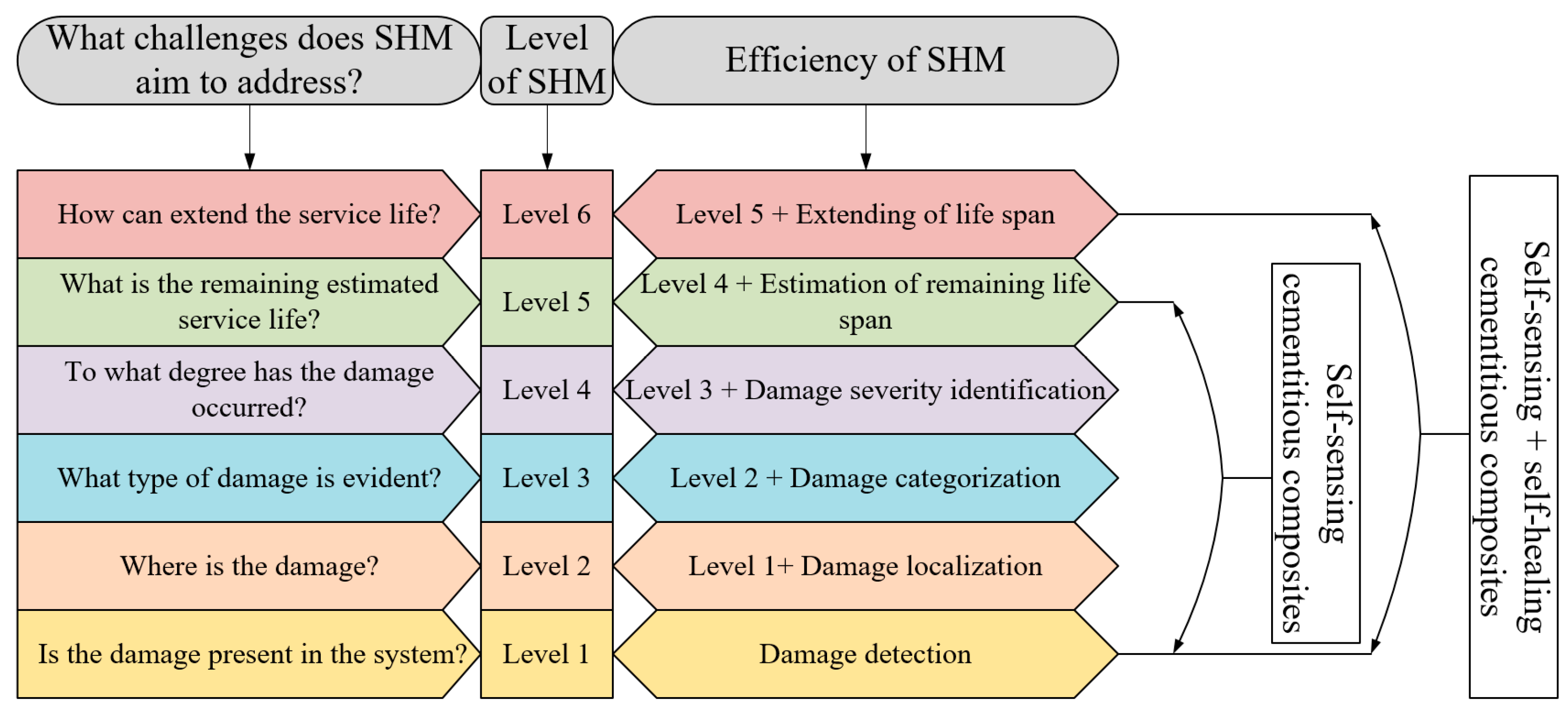
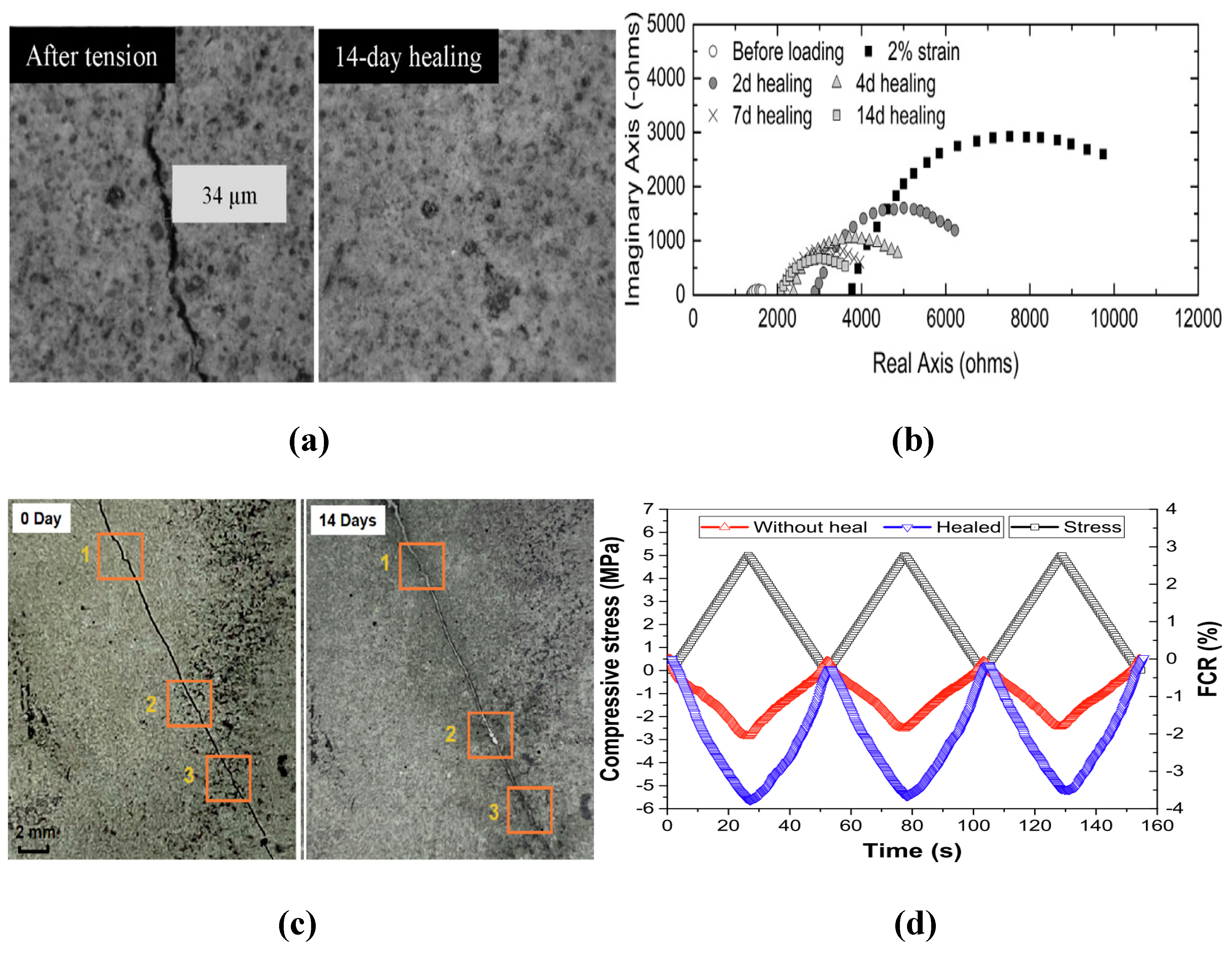
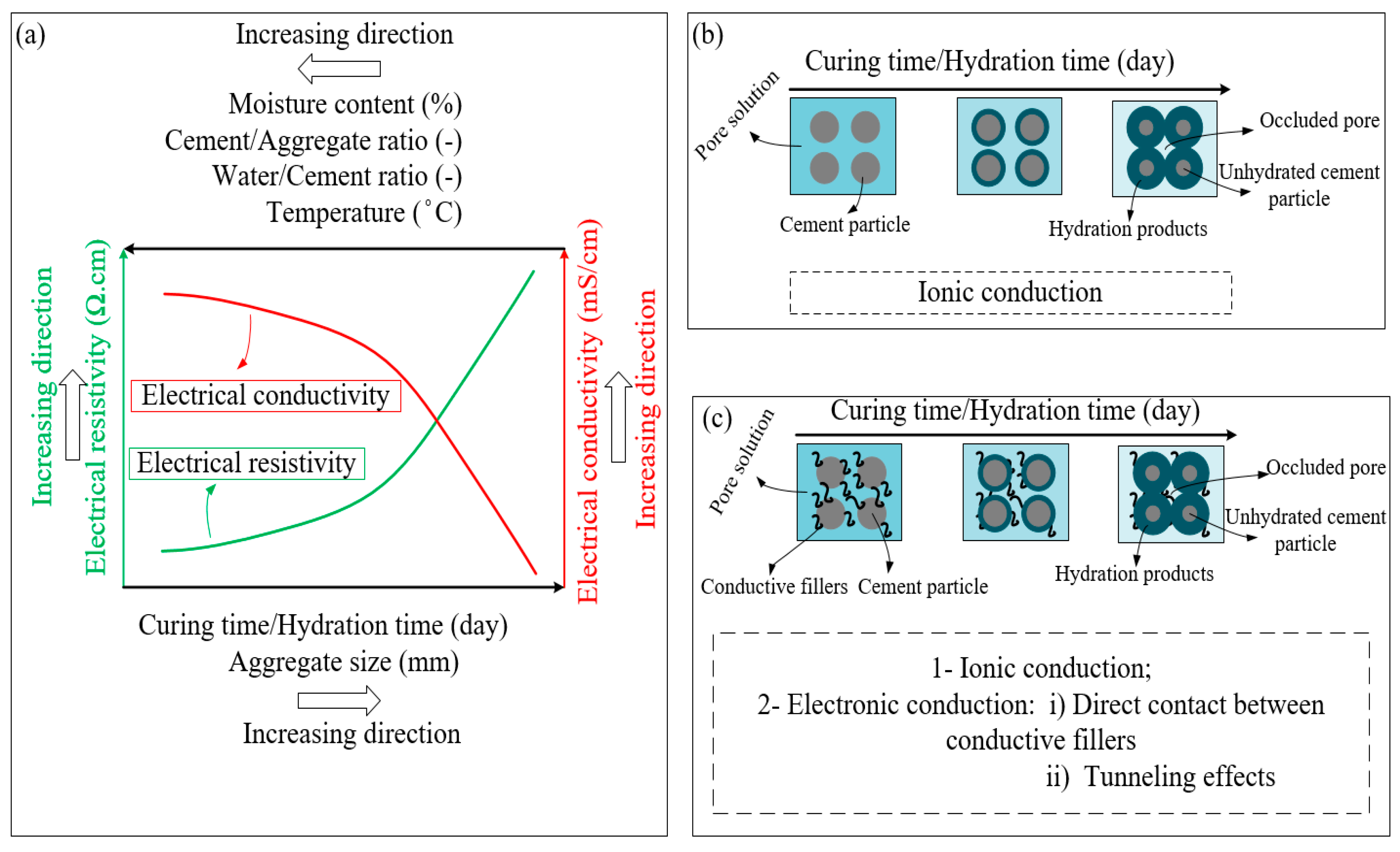
| Reference | Material Type | Activator | Precursor | Conductive filler |
| [156] | Paste | Na2SiO3+NaOH | Fly ash class C | Carbon fiber (0.5wt%) |
| [157] | Paste | K2SiO3+KOH | GGBFS | SWCNTs (0.2wt%) |
| [158] | Mortar | Na2SiO3 | GGBFS | Graphite powder (30wt%) |
| [159] | Mortar | Na2SiO3+NaOH | Fly ash class C +GGBFS | Carbon fiber (0.5% volume) |
| [160] | Mortar | Na2SiO3+NaOH | Fly ash Class F | MWCNTs (1wt%) |
| [161] | Paste | Na2SiO3+NaOH | Fly ash Class F | Graphene oxide (0.35wt%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





