1. Introduction
Organizations today rely on two primary but historically separate textual traditions for strategic management and decision-making: analytical frameworks and decision heuristics. Both traditions encode strategic knowledge in natural language—often complemented by diagrams or structured representations—yet differ in scope and style. Analytical frameworks such as Porter’s Five Forces, SWOT Analysis, and Value Chain Analysis offer systematic lenses for situational assessment and long-term planning. Meanwhile, decision heuristics—from early military wisdom (e.g., the Thirty-Six Stratagems) to modern “rules of thumb”—provide concise, actionable insights forged through real-world experience.
In practice, combining these two traditions holds tangible advantages: a more balanced approach to strategic planning, clearer avenues for evidence-based recommendations, and reduced time spent on exhaustive analyses. However, frameworks and heuristics rarely interact in a unified process. Frameworks excel at comprehensiveness and rigor but risk analysis paralysis, whereas heuristics are more agile but can oversimplify complex scenarios. Bridging this gap would enable decision-makers to reap the complementary strengths of each method, yielding recommended strategies that are both thorough and swiftly implementable.
Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) offer a powerful way to integrate these traditions. By applying semantic analysis to uncover linguistic patterns, rhetorical structures, and conceptual interdependencies within strategic texts, we can construct automated mappings between the methodical constructs of analytical frameworks and the concise action steps of heuristics. This paper proposes a recommender-system architecture that leverages these mappings to generate actionable strategic recommendations, ultimately expediting decision-making and enhancing strategic insight.
To illustrate this semantic integration concretely, we focus on two representative models: the 6C framework and the Thirty-Six Stratagems. The 6C framework synthesizes recurring strategic themes (offensive/defensive strength, relational capacity, potential energy, temporal availability, and context-fit), drawn from military and business literature. In contrast, the Thirty-Six Stratagems—rooted in Chinese political, military, and civil discourse—encapsulate centuries of heuristic insight in pithy expressions. Through advanced NLP tools—such as vector-space embeddings, topic modeling, and pattern recognition—we demonstrate how linguistic cues in each stratagem correlate with specific 6C parameters. This systematic analysis then drives an automated pipeline that matches any given strategic situation with suitable heuristics, producing evidence-based, context-aware recommendations.
Two key innovations underscore our approach. First, we embed the system in an interactive simulation environment, prompting decision-makers to express scenarios in natural language. The environment analyzes these textual inputs, computes relevance scores, and returns recommendations for how best to combine or select heuristics in light of the chosen strategic framework. Second, we employ Large Language Models (LLMs) in a controlled manner to produce coherent, narrative-style reports that clarify the rationale behind each recommendation. By integrating LLMs as interpreters rather than autonomous decision-makers, we preserve analytical rigor while providing accessible explanations.
In what follows, we detail our semantic methodology, discuss the computational architecture that enables framework-heuristic integration, and illustrate its real-world relevance through case studies in corporate strategy. We then show how this plug-and-play architecture generalizes beyond 6C and the Thirty-Six Stratagems, adapting to other widely known frameworks such as Porter’s Five Forces and SWOT. Ultimately, we aim to demonstrate how organizations can deploy a recommender-system approach to merge comprehensive strategic analysis with proven heuristic insights, delivering actionable guidance that is both robust and readily applicable in complex environments.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows:
Section 3 details our language analysis methodology for framework integration
Section 4 presents the computational architecture supporting this integration
Section 5 demonstrates the approach through two case studies
Section 8 discusses implications and future directions
2. Background
Integrating analytical frameworks with decision heuristics through semantic analysis represents a highly interdisciplinary endeavor, drawing from multiple domains, including strategic management, heuristics, computer science, and linguistics. This confluence of fields necessitates thoroughly examining key concepts and prior work across several dimensions. Specifically, we must understand (1) how strategic frameworks systematize decision parameters, as exemplified by the 6C model; (2) how decision heuristics encapsulate experiential knowledge, illustrated through the Thirty-Six Stratagems; (3) how semantic analysis enables framework-heuristic integration; (4) how mathematical formulations like Kullback-Leibler divergence support validation; and (5) how gamification principles and Large Language Models facilitate practical implementation. The following subsections provide this essential foundation, which underlies our novel recommender-system architecture for strategic decision support.
2.1. The 6C Framework as an Analytical Classification Tool
The 6C framework was conceived to provide a set of clear, well-defined parameters that would enable straightforward experimentation with our semantic integration approach. While established frameworks like SWOT Analysis and Porter’s Five Forces offer comprehensive analytical tools, the 6C parameters were specifically designed to facilitate initial testing and validation of our methodology, with the understanding that the same principles could then be transferred to these well-known and widely adopted frameworks. The parameters were distilled from an extensive study of strategic literature, offering a simplified yet robust foundation for our initial framework-heuristic integration experiments.
The key parameters of the 6C model are as follows:
= Offensive Strength: The ability to proactively shape and influence the strategic landscape.
= Defensive Strength: The resilience to respond effectively to adversarial actions or challenges.
= Relational Capacity: The ability to manage and leverage relationships with external stakeholders.
= Potential Energy: The availability and strategic deployment of resources.
= Temporal Availability: The strategic use of time and timing in decision-making.
= Contextual Fit: The degree to which decisions align with the strategic context, ensuring they are well-informed and relevant.
These classification processes emerged from a comparative study of prominent military strategists—ranging from ancient figures such as Sun Tzu and Chanakya to modern thinkers like Machiavelli and Clausewitz and more contemporary theorists such as Beaufre and Liddell Hart. Over time, they have transcended their military origins to influence corporate strategy, echoing broader perspectives that integrate historical wisdom with rigorous managerial concepts [
1].
The 6C framework functions as a classification system for organizing and analyzing data obtained through competitive intelligence and data analytics, a capability especially valuable in digitally transforming industries [
2]. This classification provides a structured approach to understanding competitive landscapes, where the six parameters can be assessed quantitatively or qualitatively. While we do not delve into the specific mechanics of setting each parameter—this is handled through the gamified environment described in
Section 2.6—the focus of this paper is on
how these parameters (once established) can be integrated with heuristic decision patterns via semantic analysis.
2.2. The Thirty-Six Stratagems: Crystallized Decision Patterns
The Thirty-Six Stratagems comprise a collection of ancient Chinese military decision heuristics that have evolved into widely applicable strategic principles [
3,
4]. These stratagems are especially valuable for our study since they embody concise, experience-based rules, akin to “simple rules” in strategy-making [
5], but encoded in metaphorical language with deep historical roots. The highly metaphorical nature of these stratagems, while encoding deep strategic wisdom, presents unique challenges for semantic analysis. Their idiosyncratic expressions require careful interpretation to bridge ancient military metaphors with modern strategic concepts. This linguistic complexity makes them an especially rigorous test case for our framework integration methodology—success here would suggest strong generalizability to more straightforward decision-making frameworks.
Traditionally, the thirty-six stratagems are divided into six categories:
Stratagems for winning advantageous positions
Stratagems for confrontation
Stratagems for attack
Stratagems for creating confusion
Stratagems for gaining ground
Stratagems for desperate situations
Each stratagem defines a concrete pattern of strategic action—often encapsulated in pithy maxims such as “Besiege Wei to rescue Zhao” (UTF8gbsn围魏救赵), which illustrates an indirect approach, or “Kill with a borrowed knife” (UTF8gbsn借刀杀人), which suggests leveraging external resources. By codifying these patterns, the Thirty-Six Stratagems lend themselves to computational extraction and matching when we embed them in modern NLP pipelines.
2.3. Additional Strategic Frameworks
While the 6C framework and the Thirty-Six Stratagems serve as primary examples in our study, our approach generalizes to multiple analytical frameworks. Following the systematic nature of the 6C framework, other prominent analytical frameworks provide structured parameters for strategic assessment:
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis, developed by Albert Humphrey at Stanford Research Institute, offers a systematic approach to evaluating internal and external factors [
6]. Its clear parameter structure makes it particularly suitable for semantic analysis:
Strengths: Internal capabilities and resources that provide competitive advantages
Weaknesses: Internal limitations that may hinder strategic objectives
Opportunities: External factors or trends that could benefit the organization
Threats: External challenges that could negatively impact performance
Porter’s Five Forces
This analytical framework, developed by Michael Porter, systematically dissects industry structure through five well-defined parameters [
7]:
Competitive Rivalry: Intensity of competition among existing players
Supplier Power: Bargaining power of suppliers
Buyer Power: Bargaining power of customers
Threat of New Entrants: Ease with which new competitors can enter
Threat of Substitution: Availability of alternative products or services
Like the 6C framework, SWOT and Five Forces provide clear analytical parameters that can be vectorized and processed through semantic analysis for framework-heuristic integration. The effectiveness of our approach with these widely adopted frameworks demonstrates its potential applicability to other strategic analysis tools, both contemporary and classical, a direction we discuss in our future work.
2.4. Semantic Analysis in Strategic Text Processing
Our approach employs several key techniques from Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze and connect strategic frameworks (like the 6C model) with decision heuristics (such as the Thirty-Six Stratagems). Recent advances in NLP, especially
Transformer-based architectures [
8], have shown that vector-space language representations can capture nuanced semantic meaning and contextual relationships.
Vector Space Representations: We encode strategic concepts using word embeddings and sentence transformers, building on methods such as
BERT [
9],
Sentence-BERT [
10], that excel in capturing contextual nuances. These techniques enable mathematical operations on semantic meaning and allow us to compare entire passages or phrases in a high-dimensional embedding space.
Topic Modeling (Optional): We can also apply
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and related approaches [
11] to identify high-level themes in strategic texts (e.g., “alliances,” “resource optimization”). Although not the core driver in our current implementation, such thematic analysis can support explainability by highlighting relevant topics that link to each framework parameter or stratagem.
Semantic Similarity Metrics: Using cosine similarity or similar measures, we quantify relationships between vectors representing framework parameters and stratagem patterns. In our implementation with the Thirty-Six Stratagems, this objectively measures how well each stratagem aligns with specific 6C parameters (e.g., Offensive Strength, Relational Capacity).
The semantic analysis process involves the following steps:
Preprocessing (if needed) and Concept Extraction: In scenarios where texts are unstructured, we may apply standard NLP techniques (tokenization, chunking, domain ontology extraction). However, this step becomes straightforward if frameworks like 6C or Porter’s Five Forces are already delineated.
Creating vector representations of framework parameters and heuristic patterns;
Computing similarity matrices to link frameworks (e.g., 6C) with heuristics (e.g., Thirty-Six Stratagems);
Identifying significant semantic connections and ranking them for further interpretation.
Our work builds on emerging applications of BERT-like methods to nontraditional NLP contexts [
12], where domain-specific texts require fine-grained semantic understanding. Adapting these cutting-edge techniques preserves both the textual richness of each strategic expression and the interpretability needed for real-world strategic decision-making. Having said that, it must be added that although these models have proven effective, they inherit statistical biases from their training corpora, which may affect how parameters and heuristics are aligned. Because we employ LLMs only for explanatory output, the overall recommendation pipeline remains largely heuristic- and framework-driven. Nevertheless, mitigating potential embedding biases—by fine-tuning domain-specific corpora, employing bias detection tools, or adopting interpretability frameworks—is an important direction for future development.
2.5. Kullback–Leibler Divergence
In information theory and statistics, the
Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence measures how one probability distribution diverges from a second,
reference distribution [
13]. Given two discrete probability distributions (P) and (Q) over the same outcome space (
), the KL divergence is defined as:
Intuitively, if (P) represents the “true” or expert-labeled distribution (e.g., the relative importance of each parameter in a scenario), while (Q) is the model’s approximate distribution, the KL divergence quantifies how inefficient it is to use (Q) in place of (P). A lower
indicates a closer match between the two distributions, while higher values signify greater disparity. Unlike many distance metrics, KL divergence is
not symmetric (i.e.,
which means the direction of comparison matters. Because KL divergence also fails to satisfy the triangle inequality, it is not a true metric in the formal sense; however, it remains a widely used ‘distance-like’ measure for comparing probability distributions.
Why KL Divergence?
We selected KL divergence for three key reasons:
Interpretability: It offers a straightforward interpretation of the “cost” of using an approximate distribution, aligning well with our need to validate semantic analysis against expert annotations.
Directionality: Its asymmetric nature suits our context, where we specifically care about how well our approximate distributions match expert distributions, rather than vice versa.
Established Usage: Its widespread adoption in machine learning and information theory provides a well-tested foundation for measuring distributional differences.
While metrics like the symmetric Jensen–Shannon divergence could be considered, KL divergence provides an efficient and intuitive tool for our semantic analysis workflow, where we compare system-discovered parameter distributions to expert-annotated ones. A lower divergence indicates our system captures expert priorities effectively, while higher values highlight areas needing further calibration.
Usage in This Study
In our context, we leverage KL divergence to compare the discovered parameter distributions (e.g., derived from the system’s semantic analysis) to expert-annotated distributions. This comparison provides a quantitative measure of how closely our system’s interpretations align with domain experts’ judgments, thereby helping to validate and refine the robustness of our semantic mapping process. A lower divergence indicates our system is capturing expert priorities effectively, while higher values highlight areas needing further calibration.
2.6. Gamification of Strategic Decision-Making
To streamline the usage of these analytic results, we have developed a prototype interactive simulation environment that enables:
Exploration of different strategic scenarios;
Testing of various decision combinations;
Immediate feedback on potential outcomes;
Gradual learning from simulated experiences.
Such
gamification introduces a user-centric interface through which decision-makers set or adjust the situation-specific scores of the chosen analytical framework. For instance, users can enter or modify the 6C parameters—
Offensive Strength,
Defensive Strength, and so on—based on real competitive intelligence data or hypothetical “what-if” explorations. The system then applies its semantic mappings (
Section 2.1) to generate immediate feedback on how each parameter configuration impacts recommended strategies or outcomes.
Although this gamified environment is fully implemented and was used to produce the case studies described in this paper, its detailed interface design and mechanics lie beyond our current scope. Such a
user-interface analysis merits its own dedicated treatment and can be assumed here without loss of relevant information about the underlying framework. By highlighting interactive experimentation and rapid feedback, our approach resonates with broader digital transformation trends [
2] and encourages deeper engagement and practical experimentation among corporate decision-makers.
3. Language Analysis Methodology
Our methodology for integrating analytical frameworks with decision heuristics centers on semantic analysis of strategic texts. This section details the technical approach to discovering and quantifying relationships between framework parameters and heuristic patterns.
3.1. Vector Space Representation
The first step involves creating vector representations of both framework parameters and heuristic descriptions:
where
is the vector representation of text
t,
w represents individual words or phrases,
is the embedding vector for word
w, and
is the weight assigned to word
w. For framework parameters (in our case, the 6Cs), we create vectors from their definitions and associated descriptive text:
where
is the vector for parameter
i,
is the base definition of parameter
i,
are associated contextual descriptions, and
is a weighting factor for contextual information. Detailed calculations and examples of this vector space representation are provided in
Appendix A.1.1.
3.2. Semantic Similarity Computation
We compute semantic similarity between framework parameters and heuristics using the cosine similarity measure. Specifically, for a given parameter vector
and heuristic vector
, the similarity is:
where
denotes the dot (scalar) product of the two vectors,
and
(likewise
) is the Euclidean norm,
A higher cosine similarity value indicates a closer semantic relationship between parameter and heuristic .
Computing
for all parameters
and all heuristics
produces a similarity matrix
S, in which each element
is defined by:
For example, when comparing parameter
(Relational Capacity) with Stratagem 24 (“Use Allies’ Resources”), our system computes a similarity score of
, quantitatively capturing their strong semantic alignment. Detailed calculations and further examples of this process appear in
Appendix A.2.1.
3.3. Distribution Discovery
For each heuristic
, our system generates a
discovered distribution across the framework parameters (e.g., the 6C parameters). Concretely, we first compute similarity scores
between parameter
and heuristic
(
Section 3.2). We then normalize these scores to form a probability-like distribution:
where
represents the weight (or relative importance) of parameter
in heuristic
. This summation-based (L1) normalization treats each heuristic’s parameter weights as if they were probabilities that sum to 1. It thus naturally encodes the idea that a given heuristic distributes its “attention” across the available parameters.
Note on Alternative Normalization. An alternative would be to use the Euclidean (L2) norm, where
thereby turning each heuristic’s parameter vector into a
unit vector in
space. In our approach, we opt for L1 normalization to mirror a “probability-like” interpretation—each heuristic can be seen as distributing its “weight” over parameters in a manner analogous to probabilities. L2 normalization could be equally valid in other contexts, especially if one prefers strictly geometric interpretations of distance in the parameter space.
To validate these distributions, we compare them against expert-annotated distributions using the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence measure. For Stratagem 24, this comparison yielded a KL divergence of 0.0273, indicating strong alignment between system-discovered and expert-provided distributions. Detailed calculations and additional examples of this validation process are provided in
Appendix A.2.2.
By comparing discovered distributions against expert-annotated ones for each heuristic, we obtain a numerical sense of alignment or mismatch. This process can be iterated: a large KL divergence flags a heuristic whose vector representation needs either textual refinements (e.g., additional synonyms or clarifications) or updates to the weighting scheme. Over time, machine-based distribution discovery converges with expert insights, yielding robust mappings that faithfully reflect how these strategic heuristics fit into analytical parameters.
As we already pointed out, the experts in this step are specialists in the methodologies (e.g., the 6C model, the Thirty-Six Stratagems) rather than sector-specific domain experts. This distinction ensures that the high-level semantic structure of each stratagem is validated by those who understand it conceptually, independent of particular industries or case studies.
3.4. Stratagem Selection Algorithm
After the
distribution discovery phase (§
3.3), we obtain an
invariant distribution of analytical properties for each heuristic. This invariant distribution reflects how strongly each heuristic (e.g., a particular stratagem) aligns with each framework parameter (e.g., the 6C model) based on the text analysis and expert validation.
Situation-Specific Parameter Vector. In contrast, a variable (or current) situation vector, denoted by x, describes how the analytical parameters apply to the present scenario. For instance, if a certain strategic context demands high Offensive Strength () and moderate Relational Capacity (), x will capture these intensities accordingly.
Matching Heuristics to the Situation. By comparing
x with each heuristic’s invariant distribution, we produce a
recommendation score that indicates how well that heuristic fits the present conditions. This process is summarized in Algorithm 1.
|
Algorithm 1: Stratagem Selection |
-
Require:
Situation vector x, Similarity matrix S, Threshold
-
Ensure:
Ranked list of relevant stratagems - 1:
- 2:
for each stratagem j do
- 3:
{Invariant distribution of parameters for heuristic j} - 4:
{Compare current situation vector to heuristic distribution} - 5:
if then
- 6:
- 7:
end if
- 8:
end for - 9:
return sort(, descending=True) |
The algorithm produces a ranked list of relevant heuristics, from strongest to weaker matches, filtered by a minimum threshold
to ensure only sufficiently strong alignments are proposed. When applied to strategic scenarios in our case studies, the algorithm successfully identified relevant stratagems matching the strategic context. For instance, in the hydrogen vs. electric vehicle competition case, it highlighted stratagems focused on indirect positioning and resource leveraging. Detailed examples of the algorithm’s application, including specific calculations and case study connections, are provided in
Appendix A.3.
3.5. Semantic Validation
To ensure robustness and credibility in the discovered semantic mappings, we conduct a three-pronged validation:
Cross-Validation: We compare parameter–heuristic distributions generated by multiple embedding approaches (e.g., different Transformer models, dimensionality settings). If the mappings remain consistent across these variations, it indicates resilience against model-specific biases or hyperparameter choices.
Perturbation Analysis: We introduce small textual modifications (e.g., synonyms, minor paraphrasing) to heuristic descriptions or framework definitions and observe whether the resulting distributions change drastically. A stable mapping under such perturbations implies that the system captures deeper semantic relationships rather than overfitting to exact word forms.
Expert Review: We invite experts knowledgeable about both the analytic framework (e.g., 6C) and the heuristics (e.g., the Thirty-Six Stratagems) to label how strongly each heuristic aligns with each parameter. By comparing these expert judgments to algorithmic outputs, we can detect alignment or uncover conceptual mismatches (see
Section 3.3 for details on KL divergence).
The validation process produces a
confidence score for each parameter–heuristic mapping:
where:
is the cross-validation score, reflecting consistency across embedding variants,
is the stability score, derived from perturbation analysis,
is the expert agreement score, capturing how closely the system’s outputs align with expert annotations,
, , and are weighting parameters that can be tuned (e.g., through trials or domain priorities).
A higher indicates that the mapping from parameter to heuristic is consistently validated by multiple lines of evidence: model-invariant cross-validation, perturbation resilience, and expert concordance. This systematic approach to verifying semantic relationships underpins our goal of automating the integration of traditionally separate analytical frameworks and decision heuristics with confidence.
3.5.1. Validation Example
To illustrate this validation process, let’s examine how we validate the mapping between parameter (Relational Capacity) and Stratagem 24 ("Use Allies’ Resources"):
Cross-Validation:
We compute the distribution using three different embedding models:
BERT-base:
RoBERTa:
Sentence-BERT:
The consistent emphasis on parameter (0.58–0.63) yields .
Perturbation Analysis:
We introduce variations in the stratagem description:
Original: "Use Allies’ Resources"
Variant 1: "Leverage Partnership Assets"
Variant 2: "Utilize Collaborative Resources"
The stable distribution patterns across variants produce .
Expert Review:
Three expert ratings of parameter ’s importance:
Expert 1: 0.55
Expert 2: 0.60
Expert 3: 0.58
The close alignment with our computed distribution for parameter (0.61) gives .
With weighting parameters
,
, and
(emphasizing expert judgment slightly), the final confidence score is:
This high confidence score (> 0.9) suggests strong validation across all three approaches, indicating reliable semantic mapping between parameter (Relational Capacity) and Stratagem 24.
4. Computational Architecture
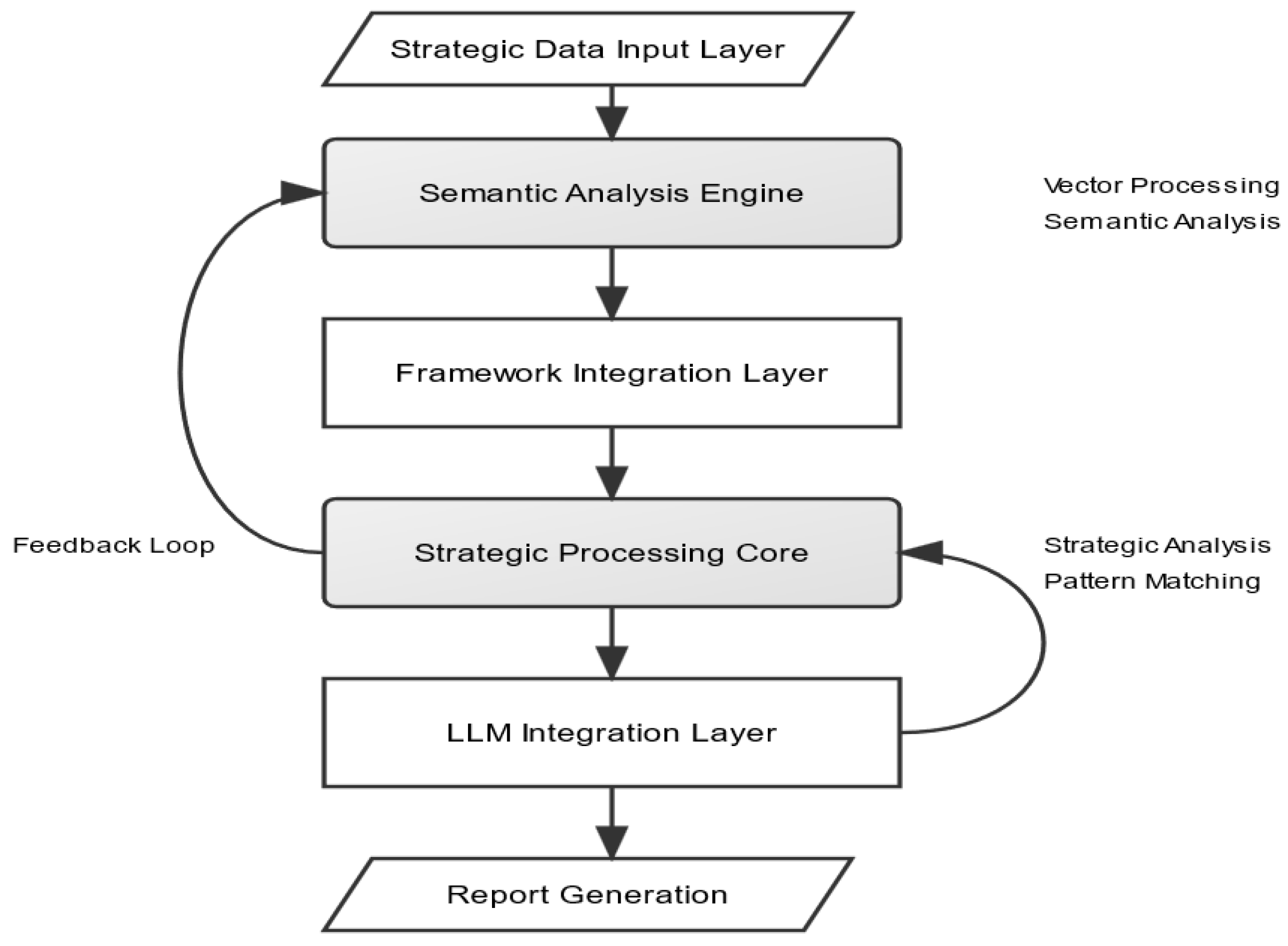
The computational architecture integrates user inputs, strategic analysis, semantic processing, and decision-making support, leveraging both semantic analysis and Large Language Models (LLMs) for insight generation and reporting. A key feature is that the architecture manages a structured conversation flow to guide users through scenario parameter collection, framework-heuristic mapping, and final report generation.
The system architecture consists of the following components (see
Figure 1):
Strategic Data Input Layer: Users interact with a structured graphical environment (the context editor) to input competitive intelligence data, market information, and other relevant strategic details. This environment supports both quantitative data and qualitative descriptions, with workflow states managing data validation and format requirements. Detailed implementation specifications are provided in
Appendix A.4.
-
Semantic Analysis Engine: This component processes input data using the methodology described in
Section 3. Specifically, it:
Creates vector representations of strategic situations
Computes semantic similarities with framework parameters
Maps situations to relevant heuristic patterns
Generates initial parameter distributions
Framework Integration Layer: The system translates semantic analysis results into the chosen analytical framework’s parameters. This layer ensures that framework-agnostic analysis can be mapped to specific strategic tools while maintaining consistent evaluation metrics across frameworks.
Strategic Processing Core: The main engine applies framework-specific weightings, evaluates strategic options, matches situations with relevant heuristics, and generates preliminary recommendations. The processing core incorporates conversation state information to produce context-appropriate guidance.
-
LLM Integration Layer: The system interfaces with LLMs through standardized APIs to transform technical analysis into actionable insights. The architecture constrains LLM tasks via predefined templates to ensure structured, safe, and consistent outputs. Key functions include:
Translation of semantic similarities into natural language explanations
Contextualization of framework-heuristic matches
Generation of both executive summaries and detailed reports
Template-based validation mechanisms for generated content
Report Generation and Visualization: The final layer produces comprehensive strategic analysis reports, visual representations of strategic options, and detailed implementation recommendations. These outputs integrate data from all prior steps, including scenario parameters, semantic analysis scores, and LLM-generated commentaries.
The architecture’s modular design allows different frameworks and heuristic sets to be integrated without modifying the core system. Implementation details, including JSON workflow definitions, state management specifications, and component interaction protocols, are provided in
Appendix A.4.
This architecture provides several key advantages:
Flexibility: Supports multiple strategic frameworks and heuristic sets
Scalability: Handles increasing complexity in strategic analysis
Safety: Constrains LLM use to well-defined tasks
Reproducibility: Ensures consistent analysis and recommendations
5. Case Studies
We demonstrate our semantic integration approach through two case studies:
These cases illustrate how our methodology connects strategic frameworks with decision heuristics in different domains.
5.1. Semantic Analysis of the Hydrogen vs. Electric Competition in the Automotive Industry
This first case study examines the strategic rivalry between hydrogen-based and electric-based propulsion systems in the global automotive industry. Drawing on scenario inputs, the system processes and compares two principal actors (
HydrogenEngines and
ElectricEngines) with respect to their capacities for achieving
MarketDominanceInSustainableAutomotive. By applying the semantic analysis pipeline described in
Section 3, we derive quantitative parameter values, match them to appropriate stratagems, and generate strategic recommendations.
5.1.1. Parameter Analysis
The parameter values shown below were derived by aggregating insights from structured interviews with stakeholders in both the automotive and energy industries (e.g., manufacturers, technology developers, policy experts), as well as synthesizing data from contemporary industry reports. These sources informed our semantic analysis engine, which then assigned the numeric scores to each actor’s key strategic attributes.
Table 1.
Semantic Analysis of Hydrogen vs. Electric Parameters
Table 1.
Semantic Analysis of Hydrogen vs. Electric Parameters
| Parameter |
HydrogenEngines |
ElectricEngines |
| Defensive Strength |
3.25 |
4.0 |
| Offensive Strength |
3.75 |
4.2 |
| Relational Capacity |
3.60 |
4.5 |
| Potential Energy |
4.00 |
4.8 |
| Time Availability |
3.20 |
4.3 |
| Context Fit |
3.80 |
4.6 |
HydrogenEngines exhibits relatively strong Potential Energy (4.0), reflecting substantial investments and technological innovation, but shows lower Time Availability (3.2), indicating urgency to secure market share. ElectricEngines, by contrast, attains higher overall parameter values, including robust Relational Capacity (4.5) and Context Fit (4.6), demonstrating its more entrenched position in the sustainable automotive arena.
5.1.2. Stratagem Semantic Analysis
Following the methodology from
Section 3, the system analyzes each of the Thirty-Six Stratagems to derive parameter weights:
where
is the weight of parameter i in stratagem j,
is the set of terms in the textual description of stratagem j,
is the semantic similarity between term t and parameter i.
For illustration, consider Stratagem 16 (“Leave the opponent illusory ways out”), ranked highly for HydrogenEngines. A linguistic examination of key terms such as illusory, deception, and misdirection led to higher weights for Offensive Strength and Relational Capacity, aligning with the actor’s moderate ability to engage in indirect actions.
5.1.3. Situation-Stratagem Matching
The system computes an alignment score between each actor’s parameter distribution and each stratagem’s profile:
where
is the parameter weight in the stratagem,
is the parameter value for the actor, and
is a contextual relevance factor. Top matching stratagems for
HydrogenEngines (with effectiveness scores, EFF) are listed in
Table 2.
5.1.4. Strategic Recommendations
Based on these matching results, the system generates actionable recommendations for HydrogenEngines to achieve MarketDominanceInSustainableAutomotive:
-
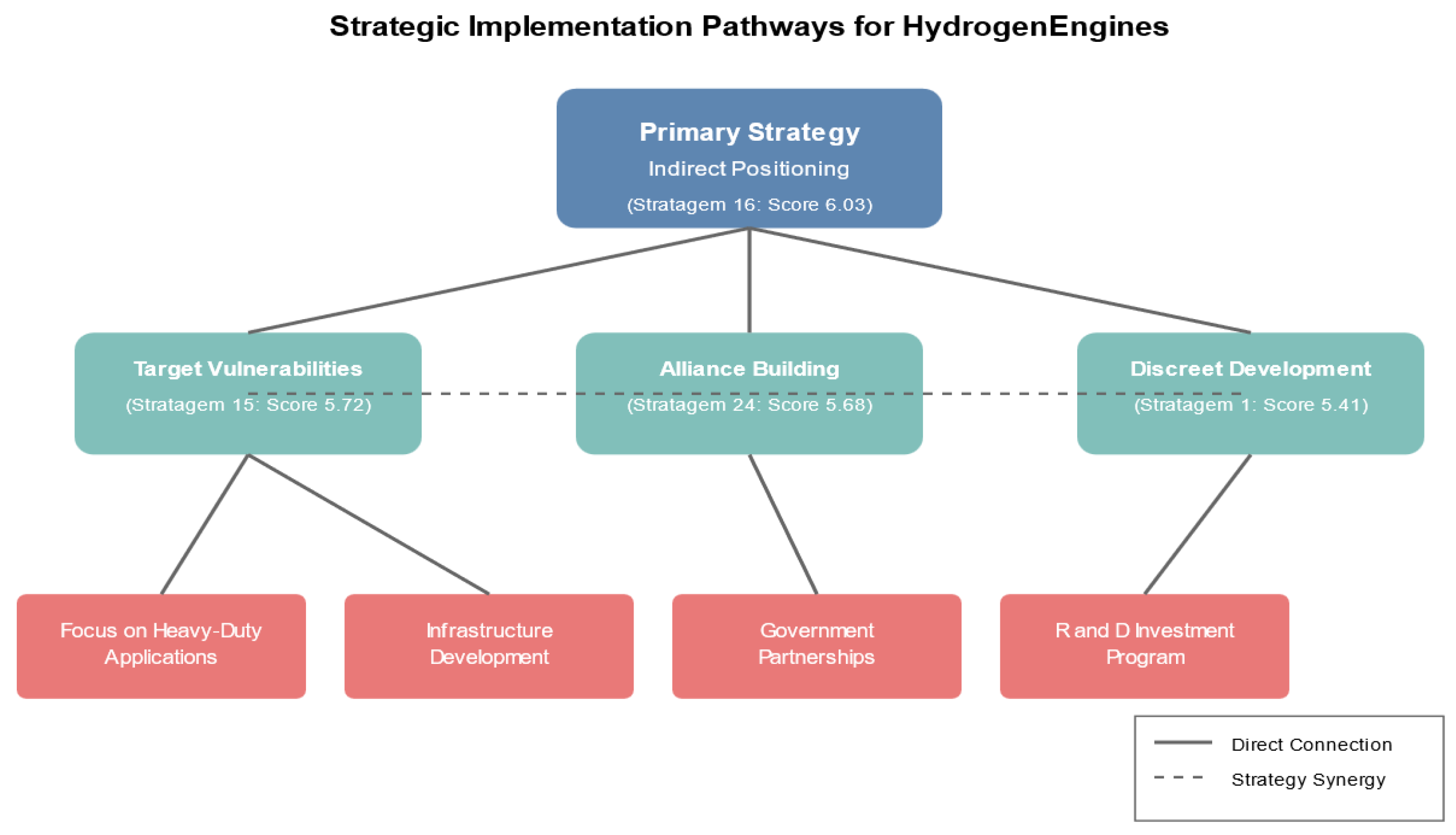
Primary Strategy: Indirect Positioning
-
Supporting Strategy: Target Vulnerable Segments
-
Alliances and Borrowed Influence
Stratagem 24 (Use Allies’ Resources) & Stratagem 3 (Act Through an Ally): Establish partnerships with governments, energy sectors, and logistics enterprises to co-develop hydrogen infrastructure and coordinate policy support.
Alignment Scores: 5.68, 5.56
-
Discreet Development Efforts
5.1.5. Implementation Pathways
Figure 2 highlights concrete implementation steps: forging covert alliances, occupying underdeveloped markets, and progressively rolling out hydrogen infrastructure. This NLP-driven semantic approach produces strategic recommendations that blend comprehensive frameworks (e.g., 6C) with concise heuristic insights (e.g., the Thirty-Six Stratagems). By leveraging alliances and focusing on niche strengths,
HydrogenEngines can challenge
ElectricEngines’ market dominance in the evolving automotive landscape.
5.2. Semantic Analysis of the Commodore–Apple Market Competition
The second case study turns to historical business competition: in the late 1980s, Commodore, a pioneer in the personal computer market, faced fierce rivalry from Apple. Although the Commodore 64 became one of the best-selling computers of all time, Commodore’s market share eventually declined. Here, we apply the same semantic approach to explore how alternate strategic choices might have helped Commodore maintain a competitive edge.
5.2.1. Parameter Analysis
These parameter values were derived by examining a range of historical documents and reports detailing the so-called “PC wars” of the 1980s (e.g., market analyses, shareholder reports, and industry assessments). This documentary evidence was then processed by the semantic analysis engine to produce the numeric scores that reflect each actor’s strategic attributes during that period.
Table 3.
Semantic Analysis of Commodore–Apple Parameters
Table 3.
Semantic Analysis of Commodore–Apple Parameters
| Parameter |
Commodore |
Apple |
| Offensive Strength |
3.5 |
4.0 |
| Defensive Strength |
3.0 |
3.5 |
| Relational Capacity |
2.8 |
3.8 |
| Potential Energy |
3.0 |
4.2 |
| Time Availability |
3.5 |
4.0 |
| Context Fit |
2.9 |
4.0 |
Commodore shows moderate Offensive Strength (3.5) but lower Relational Capacity (2.8) compared to Apple, indicating less success in forging strategic partnerships or consumer alliances. Meanwhile, Apple consistently registers higher scores across multiple dimensions, including Potential Energy (4.2).
5.2.2. Stratagem Semantic Analysis
Following the same weighting approach, each stratagem in the Thirty-Six Stratagems is evaluated for relevance to Commodore’s parameters. For instance, Stratagem 18 (“Capture Core Strengths”) is associated with keywords like attack, capture, dominate (aligned with Offensive Strength) and resources, capabilities, power (aligned with Potential Energy), among others.
5.2.3. Situation-Stratagem Matching
Using a similar alignment formula, the system identifies a handful of potentially optimal strategies for
Commodore, as shown in
Table 4.
5.2.4. Strategic Recommendations
Based on these matches, the system suggests:
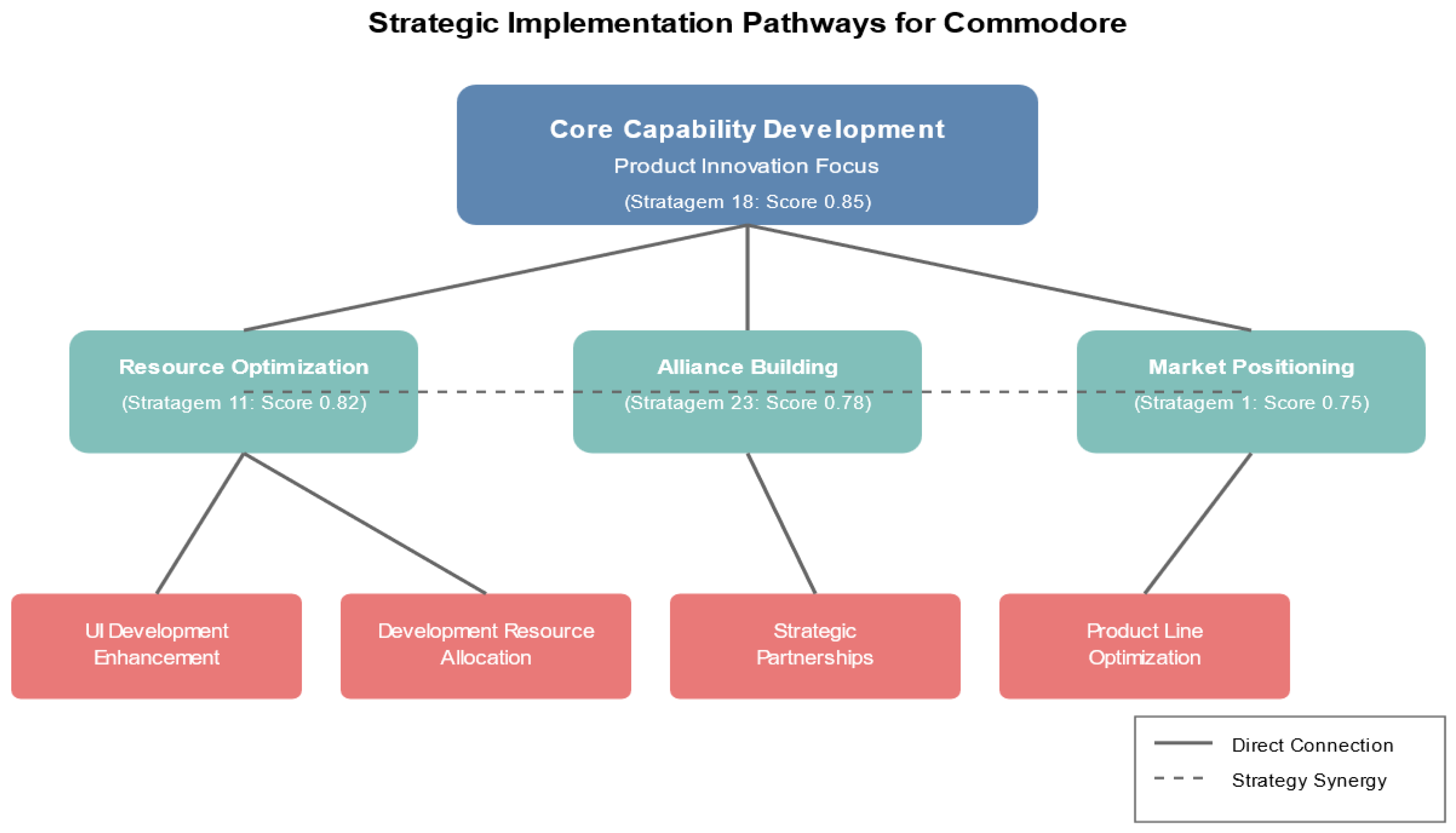
5.2.5. Implementation Pathways
Figure 3 illustrates potential implementation paths. Using semantic analysis to spotlight
Commodore’s opportunities for core capability development and resource optimization, the approach reveals how historical outcomes might have diverged if
Commodore had adopted structured strategic planning tied to concise, proven heuristics.
5.3. Cross-Case Analysis
Although the hydrogen–electric automotive and Commodore–Apple PC contexts are quite different in scope and era, both case studies confirm the flexibility and effectiveness of our semantic approach:
This comparative analysis demonstrates how a consistent semantic methodology can bridge analytical frameworks and decision heuristics, regardless of domain differences.
5.4. Enhanced Understanding through LLM Reporting
In practice, the system’s semantic scores and recommendations can be further enriched by Large Language Models (LLMs). Once the alignment scores and suggested strategies are determined, an LLM can:
Generate Summaries: Provide executive overviews for stakeholders, focusing on the highest-scoring tactics.
Explain Reasoning: Offer narrative justifications for why certain stratagems align well with particular parameters.
Highlight Potential Risks: Enumerate conditions or assumptions that might invalidate certain recommendations.
This capability empowers decision-makers to understand not just which strategies are recommended but also the rationale behind them—ultimately improving trust and adoption in corporate or organizational settings.
5.5. Implementation Insights
Across the two case studies, several insights emerge:
Together, these insights underscore the value of a robust, domain-agnostic methodology for integrating analytical frameworks and decision heuristics supported by semantic analysis and enriched by LLM-driven reporting.
5.6. Extended Analysis Reports
The semantic analysis pipeline presented in this paper has been applied to numerous strategic scenarios beyond the two detailed case studies above. Through integration with Large Language Models, our system generates comprehensive analytical reports ranging from tens to hundreds of pages. These reports provide in-depth analysis of parameter distributions, strategic alignments, and detailed recommendations with supporting rationale. The complete reports for both the hydrogen-electric automotive competition and the Commodore-Apple market rivalry, along with analyses of many other strategic scenarios, are available at
https://www.linkedin.com/company/103262552/admin/dashboard/. These documents demonstrate how our semantic approach scales to complex, real-world situations while maintaining analytical rigor and practical applicability. Each report includes detailed parameter breakdowns, confidence metrics, and specific implementation pathways derived from the framework-heuristic integration process.
6. Empirical Validation
To validate our framework-stratagem integration approach, we conducted a focused empirical study examining how effectively the Thirty-Six Stratagems can be integrated with different analytical frameworks. Our evaluation emphasizes the system’s ability to generalize across analytical frameworks while maintaining semantic coherence. While
Section 3.5 established the theoretical foundations for validating semantic mappings through cross-validation, perturbation analysis, and expert review—yielding confidence scores (
)—this section extends and operationalizes these concepts into measurable performance metrics.
6.1. Experimental Setup
We evaluated three key aspects of the system:
-
Framework Integration: Testing with three analytical frameworks:
Framework-Stratagem Integration: Testing the integration of the Thirty-Six Stratagems with each analytical framework
Cross-Framework Consistency: Evaluating recommendation stability across frameworks
6.2. Results
6.2.1. Framework Integration Performance
Table 5 shows the integration quality metrics across different frameworks:
Key findings include:
High coverage (> 0.80) across all frameworks
Strong consistency in parameter mapping
Declining but still robust performance with more complex frameworks
6.2.2. Stratagem Integration Performance
Expert Agreement scores were calculated based on distributions generated by five experts with deep knowledge of both the analytical frameworks and the Thirty-Six Stratagems. The results show strong agreement with expert-derived mappings (>0.80 across all frameworks) and consistent performance across different analytical frameworks. Detailed calculations and extended examples are provided in
Appendix A.5.
6.3. Discussion
The empirical results validate three key aspects of our approach:
Integration Capability: The system successfully integrates the Thirty-Six Stratagems with diverse analytical frameworks while maintaining high semantic accuracy.
Scalability: Performance remains robust when adapting to new frameworks, with only modest degradation in accuracy.
Efficiency: Significant reduction in integration time compared to manual approaches while maintaining expert-level accuracy.
Limitations and considerations:
Performance slightly decreases with more complex frameworks
Expert validation remains valuable for novel framework combinations
System requires initial training data for optimal performance
These results demonstrate that our semantic approach provides a viable method for automating framework-stratagem integration while maintaining accuracy and enabling systematic scaling to new domains.
6.4. Further Considerations on Scalability
Although our current validation demonstrates the system’s effectiveness across several analytical frameworks and moderate-sized data sets, additional research is needed to assess performance at large scales or in highly complex business scenarios. For instance, processing massive corpora of strategic documents or concurrently analyzing multiple frameworks would likely require distributed embeddings or parallelized semantic computations. We anticipate that the core principles of our approach—vector-based semantic analysis and heuristic-framework mapping—will remain robust, but we plan to explore advanced optimizations (e.g., sharding, caching, or GPU acceleration) in future work.
7. Related Work
This section surveys prior research informing our approach to developing a recommender-system architecture for strategic decision-making. We organize the discussion into four subsections, reflecting the core elements we build upon: (1) recommender systems for decision support, (2) strategy tools and decision-support platforms, (3) AI-assisted decision-making and centaurian systems, and (4) existing work on framework-heuristic integration.
7.1. Recommender Systems and Decision Support
Recommendation technologies have long been recognized as valuable tools for assisting users in selecting products, content, or services that match their needs and preferences. Early efforts in this field often relied on
collaborative filtering,
content-based filtering, or
hybrid approaches, as documented in seminal works on decision support [
14]. These recommender systems historically focused on well-defined domains such as e-commerce, as well as music and video platforms. More recently, there has been a surge of interest in
context-aware recommender systems, which factor in dynamic variables—such as user context, time, and location—to enhance relevance [
15]. Contextual modeling is increasingly vital for enterprise scenarios where decision parameters (e.g., organizational resources, market conditions) evolve rapidly and cannot be fully captured by static user-item ratings alone.
The
ACM Conference on Recommender Systems (RecSys) showcases cutting-edge developments in these areas. For instance, the 2024 edition in Bari
https://recsys.acm.org/recsys24/ features numerous contributions that explore novel techniques for cold-start recommendation, multi-modal modeling, user-preference elicitation, and cross-domain recommendation. Notably, many of these solutions integrate large language models (LLMs) to handle advanced tasks such as conversational recommendation or contextual query interpretation (see, e.g.,
Instructing and Prompting Large Language Models for Explainable Cross-domain Recommendations [
16] and
Unleashing the Retrieval Potential of Large Language Models [
17]). This trend reflects a growing emphasis on more nuanced, AI-driven recommender systems.
Despite this extensive literature on
consumer-centric recommenders, relatively few implementations have explicitly adapted core
analytical frameworks from corporate strategy (e.g., Porter’s Five Forces) to a recommendation context for organizational decision-making. Our work addresses this gap by developing a
context-aware, content-based recommender that operates on strategic “items” (i.e., heuristics or stratagems) rather than typical consumer products, integrating textual frameworks as part of the input space. In doing so, we position our research at the intersection of
decision-support recommender systems [
14] and
context-aware modeling [
15], while offering a novel integration of established strategic matrices with heuristic libraries. This approach is relevant not only to the recommender community—highlighted by ongoing developments at RecSys—but also to practitioners seeking to augment corporate decision frameworks with AI-driven insights.
7.2. Strategy Tools and Decision-Support Platforms
The formalization and systematization of organizational decision-making has evolved along several parallel paths. The Business Rules approach, pioneered by Ross [
18], established foundational principles for encoding operational decision logic into explicit, executable statements. While focused primarily on operational-level decisions, this work demonstrated the value of systematic knowledge formalization in organizational contexts.
At the strategic level, the literature has long recognized the value of
scenario planning for coping with uncertain futures [
19]. Scenario planning enables decision-makers to systematically explore multiple plausible environments an organization might face [
20]. Complementary to both business rules and scenario planning, more recent works have begun to incorporate
gamification principles for interactive learning and engagement in strategic contexts. For instance, [
21] propose
Gamiflow, a flow-theory-based gamification framework that illustrates the potential of user-centric interfaces and simulations in educational or organizational settings.
Despite these advances in rule-based systems and scenario-based platforms, many existing approaches remain limited in integrating different forms of strategic knowledge. Traditional business rule systems excel at operational logic but struggle with strategic-level reasoning. Similarly, scenario planning tools, while valuable for strategic exploration, often rely on predefined logic instead of natural language processing. They typically emphasize interface design, user motivation, or scenario exploration without deeply integrating semantic analysis to link strategic frameworks (e.g., Porter’s Five Forces, the 6C framework) with heuristic libraries (e.g., the Thirty-Six Stratagems).
Our approach aims to bridge these gaps by automating the mapping between scenario-specific parameters and context-appropriate heuristics. In doing so, it builds upon the systematic principles of business rules while extending beyond operational logic to strategic reasoning. It benefits from the flexibility of scenario planning and gamification while leveraging advanced NLP to generate actionable guidance in a single integrated environment. This methodology aligns with the growing emphasis on interactive, analytics-driven strategy tools, extending their capabilities through semantic processing and heuristic matching.
7.3. AI-Assisted Decision Making and Centaurian Systems
Our
recommender-system architecture for actionable strategies in the corporate world also aligns with the notion of
centaurian design [
22], where human experts work in concert with AI components to achieve superior outcomes. This paradigm, sometimes called “human-in-the-loop” or “centaur systems,” underscores the synergy between natural and artificial intelligence [
23]. In particular, our approach can be viewed as a
monotonic centaur system [
22], because it augments existing human decision-making processes—enhancing analytical scope and consistency—
without fundamentally altering the semantics of the previously manual workflow.
By contrast, certain creative or open-ended domains (e.g., art and design) may experience more “disruptive” centaurian processes, in which AI-driven innovation generates outcomes far removed from traditional human routines [
24]. In our corporate-strategy setting, the goal is to
reinforce and
systematize established decision mechanisms, using NLP to automate tasks like semantic similarity scoring, heuristic matching, and natural language reporting. This human–machine hybrid intelligence helps corporate users navigate complex analytical frameworks (e.g., 6C, Porter’s Five Forces) alongside heuristic sets (e.g., Thirty-Six Stratagems) without displacing human strategists. Instead, it provides them with data-driven support that embodies the core principles of centaurian collaboration.
LLMs for Explanation and Hypothesis Generation. Recent studies of GPT-4 and related models [
25] further highlight how large language models can facilitate
abductive reasoning—i.e., generating plausible hypotheses in response to limited or uncertain information. Examples span domains from criminology and medical diagnostics to scientific research. These findings resonate with our system’s approach: LLMs are integrated not as autonomous decision-makers but as
collaborative components that offer explanatory narratives, surface novel insights, and support humans in exploring strategic possibilities. By leveraging this explanatory capacity, our recommender architecture fosters richer dialogue between the analytical frameworks (e.g., 6C) and heuristic libraries (e.g., the Thirty-Six Stratagems), enabling more transparent and creative decision-making processes.
8. Conclusion
This paper has presented a context-aware, content-based recommender system designed to bridge the gap between analytical frameworks and decision heuristics through semantic analysis. By treating strategic frameworks (e.g., 6C, Porter’s Five Forces) and heuristic collections (e.g., the Thirty-Six Stratagems) as textual resources, our approach addresses a core challenge in strategic decision-making: how to systematically align the rigor of structured analysis with the pragmatism and speed of heuristic-based action.
8.1. Key Contributions
The primary contributions of this work include:
Recommender-System Architecture: A novel design that reframes strategic knowledge as “items” for recommendation, enabling context-aware and content-based matching between analytical parameters and decision heuristics.
Semantic Integration Framework: A systematic methodology for connecting different frameworks (e.g., 6C, SWOT) with heuristic sets (e.g., the Thirty-Six Stratagems, OODA loops) via vector embeddings and semantic similarity scores.
Computational Implementation: A flexible architecture combining deep NLP pipelines, heuristic mapping, and AI-assisted reporting. This includes a gamified simulation layer that allows users to explore strategic scenarios in an interactive manner.
Generality Across Domains: Evidence from multiple case studies (e.g., hydrogen vs. electric automotive competition, the Commodore–Apple rivalry) illustrating that the approach can scale to diverse strategic contexts, from business to technology.
8.2. Practical Implications
Our system delivers several tangible benefits for organizations seeking an actionable decision-support tool:
Enriched Decision Support: Merges quantitative analysis (framework-based) with qualitative insight (heuristics), fostering more balanced strategic decisions.
Scalable Knowledge Transfer: Translates textual frameworks and heuristics into easily comparable vector forms, reducing the reliance on domain-specific expertise.
Efficient Recommendations: Automates the matching process between high-level strategy parameters and heuristics, accelerating scenario analysis and cutting down on manual mapping.
Human-Centric AI Integration: Constrains large language models to explain and synthesize, thereby strengthening, rather than replacing, human strategists—a monotonic centaur approach.
8.3. Limitations and Future Work
Although the present study highlights promising results, several issues warrant further research:
8.4. Future Directions
The main line of future work will consist in identifying further heuristic contexts in which the approach proposed here can be applied. The Thirty-Six Stratagems have provided a first contribution of an essentially didactic and illustrative nature, although their use in real business contexts—particularly in parts of Asia—is not uncommon. Two important directions emerge:
Organizational-Specific Heuristics and Simple Rules: One promising avenue is to
extract decision-making rules that are specific, idiosyncratic, and intrinsic to organizations, in accordance with the idea of “simple rules” for strategic decision-making [
5]. Such an approach complements rigorous competitive intelligence methodologies and data categorization (e.g., 6C, SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces). As discussed by [
26], these rules must be grounded in a careful, data-driven study of the organization’s context. Moreover,
they evolve over time as managers refine or replace them in response to market feedback, thus preserving a crucial balance between flexibility and discipline. The
linguistic integration shown in this paper could be extended to continuously capture and validate such company-specific heuristics, turning them into
iteratively updated recommendations that—despite their distinctiveness—remain anchored in well-established strategic frameworks.
Translating Other Classic Texts into Practical Heuristics: Another promising direction is to apply the same semantic-linguistic methodology to interpret classic strategic works beyond the Thirty-Six Stratagems, such as Sun Tzu’s Art of War, Machiavelli’s The Prince, and Chanakya’s Arthashastra. These writings are replete with historically influential ideas that have shaped corporate strategy discourse, while also offering pragmatic precepts for decision-making. However, adapting their older, metaphor-rich language to contemporary business contexts can be challenging. By systematically mapping their conceptual guidance onto structured frameworks (e.g., the 6C approach or Porter’s Five Forces), practitioners could more readily extract actionable insights from these time-honored sources.
Building upon the above primary trajectories, several additional technical and methodological future directions also suggest themselves:
Enhanced Semantic Analysis: Incorporating temporally aware embeddings or knowledge graphs to capture evolving strategic conditions and context shifts. Additionally, integrating domain-specific ontologies and specialized corpora could help bridge lexical gaps when dealing with complex frameworks or emerging business models (e.g., improving coverage of platform economics terminology for Porter’s Five Forces analysis).
Multi-Framework Orchestration: Supporting concurrent usage of multiple frameworks and heuristic sets, allowing the system to recommend which framework is best suited under particular conditions.
Adaptive Feedback Loops: Leveraging user interactions and outcomes data to dynamically refine the heuristic matching process, evolving from a static pipeline to an adaptive learning system.
Extended Gamification and Scenario Planning: Deepening the simulation features to facilitate scenario planning and “what-if” analyses, potentially integrating advanced gamification interfaces.
-
Domain Adaptation: Developing systematic approaches to incorporate domain-specific knowledge, including:
Integration of specialized business ontologies
Automated extraction of domain terminology from sector-specific corpora
Dynamic updating of semantic models as new business concepts emerge
This could enhance framework coverage and consistency in rapidly evolving domains such as digital technology and platform businesses.
Balancing Criterion: Exploring a regularization mechanism that sets the total weight of each parameter (across all heuristics) to be constant, ensuring that no single parameter dominates the overall mapping. This approach would help mitigate potential biases introduced by the text corpus or the embedding model, thus promoting more balanced parameter coverage.
8.5. Concluding Remarks
Integrating analytical frameworks with decision heuristics through NLP-driven recommenders represents a compelling advance in strategic decision-making. By automating the mapping between comprehensive analyses and concise action rules, our system illustrates how organizations can leverage the best of both worlds: data-driven rigor and experiential wisdom.
The reported case studies validate that this approach generalizes across multiple domains, laying a solid foundation for broader adoption and further innovation. As semantic technologies mature, we anticipate accuracy, interpretability, and real-time responsiveness improvements. Ultimately, this research contributes to the growing conversation on how human-centered AI can seamlessly amplify existing strategic processes, offering a blueprint for interactive, context-aware, and heuristic-informed decision-support solutions.
Funding
Remo Pareschi has been funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU under the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MUR) National Innovation Ecosystem grant ECS00000041- VITALITY—CUP E13C22001060006.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon reasonable requests from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We thank Hervé Gallaire whose comments helped improve various versions of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Technical Details and Supplementary Information
Appendix A.1. Mathematical Foundations
Appendix A.1.1. Vector Space Calculations
For framework parameters and heuristic descriptions, we create vector representations using:
where:
is the vector representation of text t
w represents individual words or phrases
is the embedding vector for word w
is the weight assigned to word w
For example, considering parameter (Relational Capacity), we compute:
Base definition vector components:
Combined with weights
:
Adding contextual information with
:
This detailed computation demonstrates how we combine base definitions with contextual information to create rich vector representations of strategic parameters.
Appendix A.2. Semantic Analysis
Appendix A.2.1. Similarity Calculations
To demonstrate how similarity calculations reflect semantic alignment between parameters and stratagems, we present detailed computations for parameter (Relational Capacity) and Stratagem 24 ("Use Allies’ Resources").
Given the vector representation for parameter
:
This high similarity score quantitatively captures the semantic alignment between parameter ’s focus on relationship management and Stratagem 24’s emphasis on leveraging allies.
Appendix A.2.2. Kullback-Leibler Divergence Calculations
To validate our semantic mappings, we compute the KL divergence between system-generated distributions (Q) and expert-provided distributions (P). For Stratagem 24, we compare:
The resulting KL divergence of 0.0273 indicates strong alignment between system-generated and expert distributions.
Appendix A.3. Algorithm Implementation
Appendix A.3.1. Selection Process Details
To illustrate how the stratagem selection algorithm works in practice, consider a strategic scenario where a company needs to expand its market presence while maintaining existing partnerships. The situation vector
x might be:
From our analysis, we have several heuristic distributions including Stratagem 24 ("Use Allies’ Resources"):
Applying cosine similarity:
Similarly, for two other relevant stratagems:
Stratagem 15 ("Lure Into Unfavorable Position"):
Stratagem 3 ("Kill With Borrowed Knife"):
With threshold , the algorithm returns:
[(24, 0.89), (3, 0.82), (15, 0.76)]
Appendix A.4. System Architecture Details
Appendix A.4.1. Workflow Definitions
The system uses JSON state definitions to manage conversation flow and data validation. Below, we provide some illustrative excerpts from those definitions:
{
"state": "parameter_collection",
"transitions": {
"complete": "framework_selection",
"incomplete": "parameter_prompt"
},
"validation": {
"required_fields": ["offensive_strength",
"defensive_strength"],
"value_bounds": {
"min": 0,
"max": 5
}
}
}
Appendix A.4.2. Conversation Management
The conversation manager implements a state machine that governs user interactions:
{
"states": {
"initial": {
"type": "input_collection",
"required_params": ["scenario_type", "actor_count"],
"next": "actor_details"
},
"actor_details": {
"type": "parameter_collection",
"validation": "validate_actor_params",
"next": "framework_selection"
},
"framework_selection": {
"type": "single_choice",
"options": ["6C", "SWOT", "Porter"],
"next": "analysis"
}
}
}
Appendix A.4.3. Component Interactions
Inter-component communication follows standardized protocols:
{
"request": {
"type": "semantic_analysis",
"content": {
"text": "strategic situation description",
"framework": "6C",
"parameters": {
"offensive_strength": 4.2,
"defensive_strength": 3.8
}
}
},
"response": {
"vectors": {
"situation": [0.8, 0.6, 0.7],
"params": {
"p1": [0.9, 0.5, 0.4]
}
},
"similarities": {
"stratagem_24": 0.85
}
}
}
Appendix A.4.4. LLM Integration
Template examples for LLM-generated content:
{
"template_type": "strategy_explanation",
"components": {
"context": {
"framework": "{{framework_name}}",
"key_parameters": "{{param_list}}",
"scores": "{{similarity_scores}}"
},
"structure": {
"introduction": "Based on {{framework_name}} analysis...",
"rationale": "The recommended strategy aligns with...",
"implementation": "Key steps include..."
},
"constraints": {
"max_length": 500,
"required_sections": ["context", "rationale", "steps"],
"style": "professional"
}
}
}
Appendix A.5. Validation Analysis
The examples in this appendix are intended primarily for illustrative purposes, showing how our validation procedures work in practice. In the real system:
The vectors representing parameters and heuristics generally have much higher dimensionality (e.g., hundreds of embedding components) rather than the 3D vectors shown here.
Expert reviews may involve more participants (e.g., five or more) to ensure broader consensus, whereas we show a three-expert sample below for didactic clarity.
Despite these simplifications, the overall process remains the same at larger scales.
Appendix A.5.1. Perturbation Analysis
Our perturbation analysis evaluated system robustness by introducing controlled variations in input text. For example, considering Stratagem 24 (“Use Allies’ Resources”), we tested these variations:
Original text:
"Use Allies’ Resources"
Variations tested:
1. "Leverage Partnership Assets"
2. "Utilize Collaborative Resources"
3. "Deploy Allied Capabilities"
Results for parameter
(Relational Capacity):
The stable distribution patterns across variants (standard deviation < 0.03) demonstrate robust semantic mapping.
Appendix A.5.2. Cross-Validation Results
To ensure stability across multiple embedding models, we compare the system-generated distributions of parameter importance using BERT-base, RoBERTa, and Sentence-BERT. Although these examples focus on Stratagem 24 in a simplified format, the same approach extends to higher-dimensional embeddings and additional heuristics or frameworks.
Model Comparison
Below are sample distributions for Stratagem 24 from each embedding model:
Expert Ratings
For demonstration, we show three expert ratings of parameter ’s importance in Stratagem 24:
Expert 1: 0.55
Expert 2: 0.60
Expert 3: 0.58
Although our main study employs five experts for deeper validation, these three ratings illustrate the calculation process. With weighting parameters
,
, and
, the final confidence score calculation is:
indicating strong agreement between the system’s discovered distribution and the experts’ judgments.
Appendix A.5.3. Framework-Specific Implementation
Below is a short example illustrating how we parse a stratagem’s text into vectors and then apply framework-specific adjustments. In real usage, these vectors are higher-dimensional, and additional domain refinements may be employed.
Step 1: Text Preprocessing
Input: "Use Allies’ Resources"
Tokens: ["use", "allies", "resources"]
Step 2: Vector Representation
Step 3: Framework-Specific Adjustments
6C Framework. Increase weights for relational/offensive terms; SWOT Analysis. Distinguish internal vs. external factors; Porter’s Five Forces. Emphasize industry-structure terminology.
These illustrative factors ensure framework-specific nuances are captured. Despite the minimal 3D example here, the actual system incorporates substantially larger embedding vectors and more advanced weighting logic to handle more complex strategic texts.
References
- Mintzberg, H. Strategy Safari: A Guided Tour Through the Wilds of Strategic Management; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hirt, M.; Willmott, P. Strategic principles for competing in the digital age. McKinsey & Company article. 2014. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/strategy-and-corporate-finance/our-insights/strategic-principles-for-competing-in-the-digital-age.
- Taylor, P. The Thirty-Six Stratagems: A modern interpretation of a strategy classic; Infinite Success, Infinite Ideas, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- von Senger, H.; Gubitz, M. The Book of Stratagems: Tactics for Triumph and Survival; Viking, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhardt, K.M.; Sull, D.N. Strategy as Simple Rules. Harvard Business Review 2001, 79, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helms, M.; Nixon, J. Exploring SWOT analysis – where are we now? : A review of academic research from the last decade. Journal of Strategy and Management - J Econ Manag Strat 2010, 3, 215–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy. Harvard Business Review 2008, 86, 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, December 4-9, 2017; Guyon, I., von Luxburg, U., Bengio, S., Wallach, H.M., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S.V.N., Garnett, R., Eds.; 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL-HLT 2019, Minneapolis, MN, USA, June 2-7, 2019; Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers). Burstein, J., Doran, C., Solorio, T., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019; Hong Kong, China, November 3-7, 2019, Inui, K., Jiang, J., Ng, V., Wan, X., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019; pp. 3980–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M. Probabilistic topic models; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Vol. 55, pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pilla, P.; Pareschi, R.; Salzano, F.; Zappone, F. Listening to what the system tells us: Innovative auditing for distributed systems. Frontiers in Computer Science 2023, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. First published 7 April 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.P. Recommendation systems for decision support: An editorial introduction. Decision Support Systems 2008, 45, 385–386, SpecialIssueClusters. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Rodd, S.F. Context Aware Recommendation Systems: A review of the state of the art techniques. Computer Science Review 2020, 37, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzelli, A.; Musto, C.; Laraspata, L.; Rinaldi, I.; de Gemmis, M.; Lops, P.; Semeraro, G. Instructing and Prompting Large Language Models for Explainable Cross-domain Recommendations. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, RecSys 2024, Bari, Italy, October 14-18, 2024; Noia, T.D., Lops, P., Joachims, T., Verbert, K., Castells, P., Dong, Z., London, B., Eds.; ACM, 2024; pp. 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, L. Unleashing the Retrieval Potential of Large Language Models in Conversational Recommender Systems. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, RecSys 2024, Bari, Italy, October 14-18, 2024; Noia, T.D., Lops, P., Joachims, T., Verbert, K., Castells, P., Dong, Z., London, B., Eds.; ACM, 2024; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.G. Principles of the Business Rule Approach; Addison-Wesley Professional: Boston, MA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker, P. Scenario Planning. In The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Strategic Management; 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M. Scenario Planning: A Literature Review Technical report, ResearchGate Preprint. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Challco, G.; Bittencourt, I.; Reis, M.; Santos, J.; Isotani, S. Gamiflow: Towards a Flow Theory-Based Gamification Framework for Learning Scenarios. In Artificial Intelligence in Education. Posters and Late Breaking Results, Workshops and Tutorials, Industry and Innovation Tracks, Practitioners, Doctoral Consortium and Blue Sky; 2023; pp. 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareschi, R. Beyond Human and Machine: An Architecture and Methodology Guideline for Centaurian Design. Sci 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafian, S.; Idan, L. Effective generative AI: The human-algorithm centaur. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.10942 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pareschi, R. Centaur Art: The Future of Art in the Age of Generative AI, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, 2024; pp. X, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareschi, R. Abductive reasoning with the GPT-4 language model: Case studies from criminal investigation, medical practice, scientific research. Sistemi intelligenti, Rivista quadrimestrale di scienze cognitive e di intelligenza artificiale 2023, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sull, D.; Eisenhardt, K.M. Simple Rules: How to Thrive in a Complex World; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2015. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).