Submitted:
23 January 2025
Posted:
23 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Overview of Different Biosensor Types
3.1. Electrochemical Sensors
3.2. Optical Sensors
3.3. FET-Based Sensors
3.4. Other Types of Sensors
3.4.1. Piezoelectric Biosensors
3.4.2. Surface Acoustic Wave Biosensors
3.4.3. Magnetic Relaxation Switching Biosensors
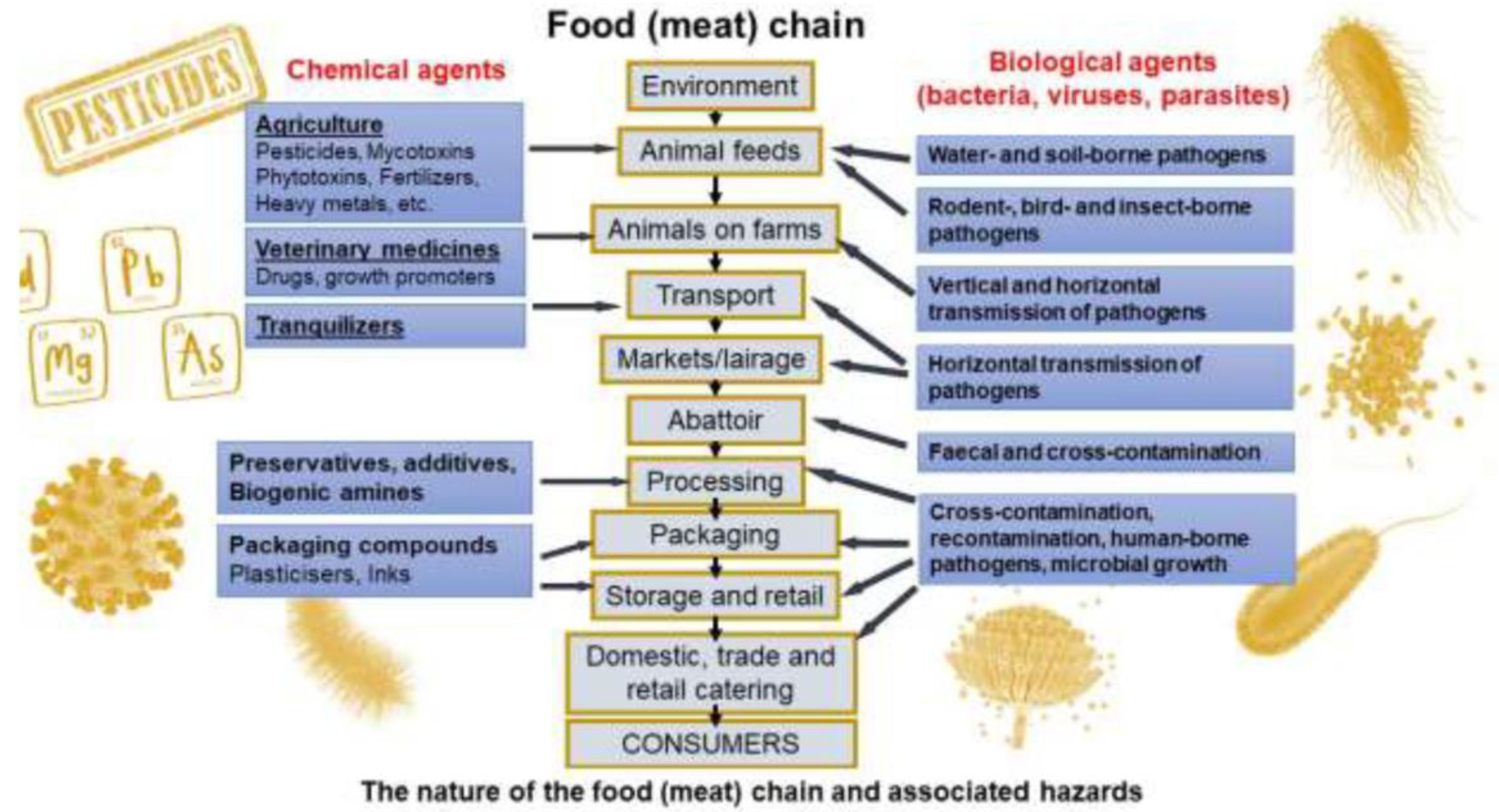
4. Application of Biosensors in the Meat Chain Continuum
4.1. Animal Health
4.1.1. Detection of Disease Markers
4.2. Animal Welfare
4.2.1. Behavioral, Physiological and Nutrition Status Monitoring
4.2.2. Transport and Handling
4.2.3. Pre-Slaughter Welfare Assessment
4.2.4. Application in Precision Livestock Farming
4.2.5. Slaughterhouse and Meat Processing
4.3. Meat Quality Traits
4.4. Food Fraud & Food Crime
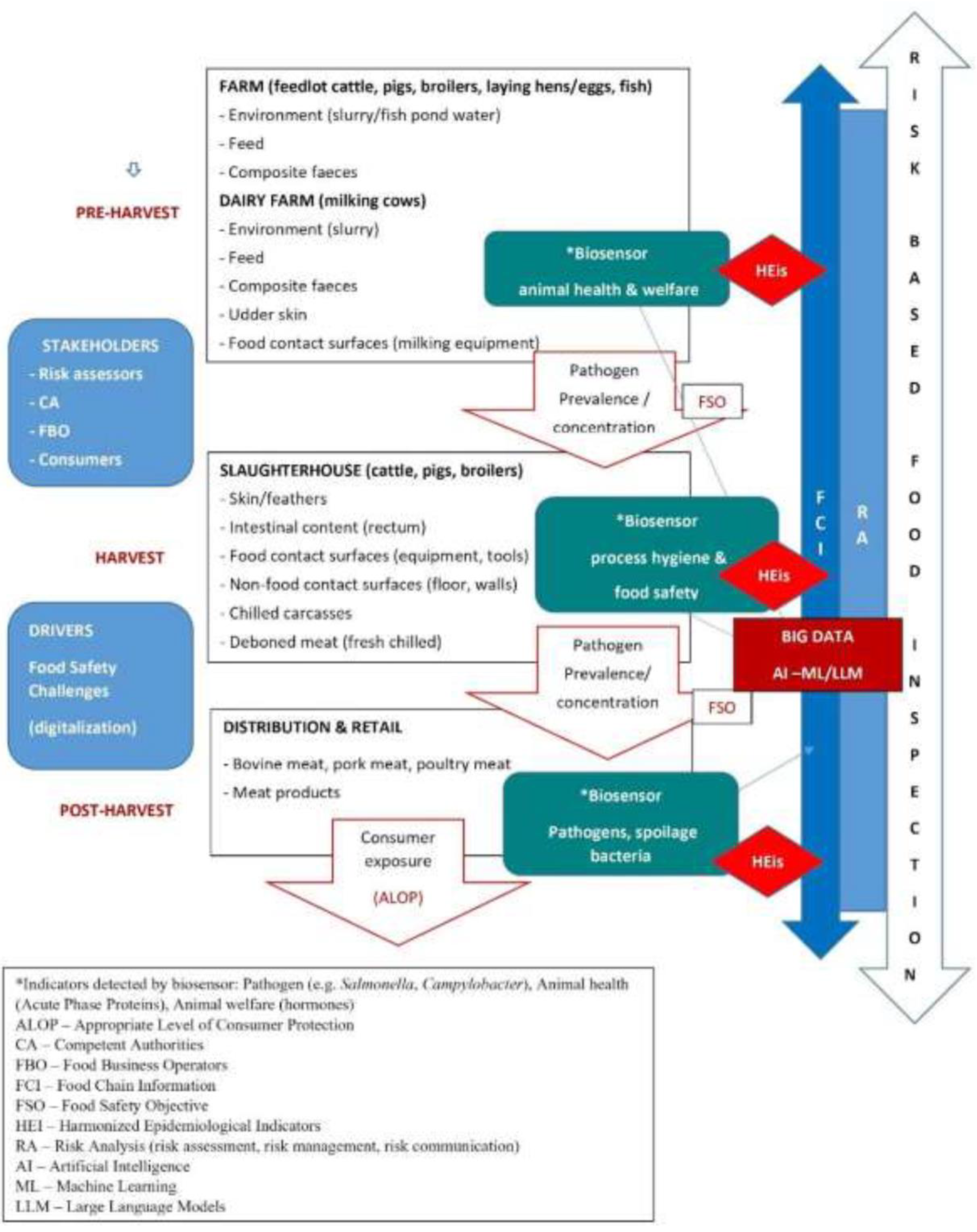
4.5. Risk-Based Meat Safety Assurance System
4.6. Opportunities and Challenges for Biosensors` Application in the Meat Production Chain
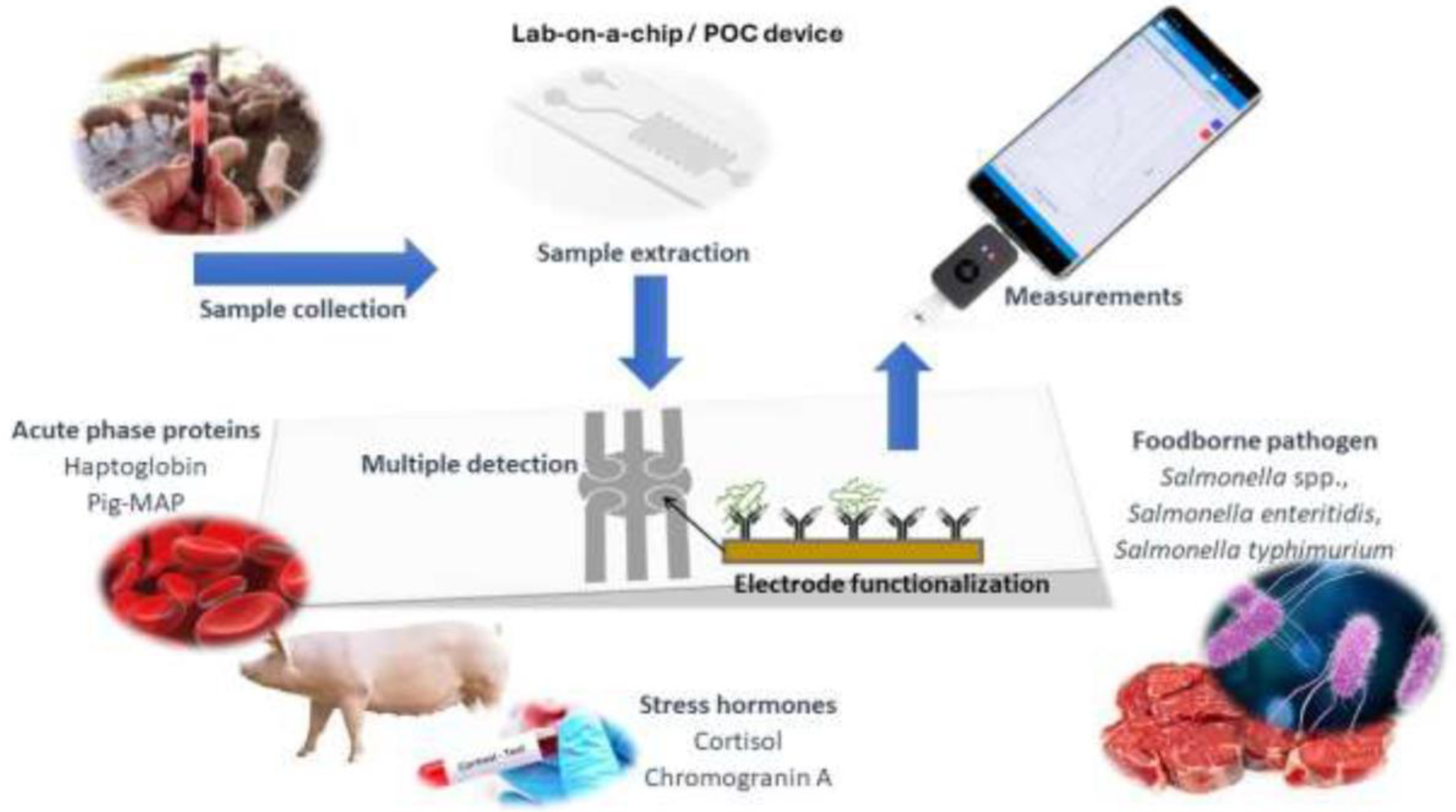
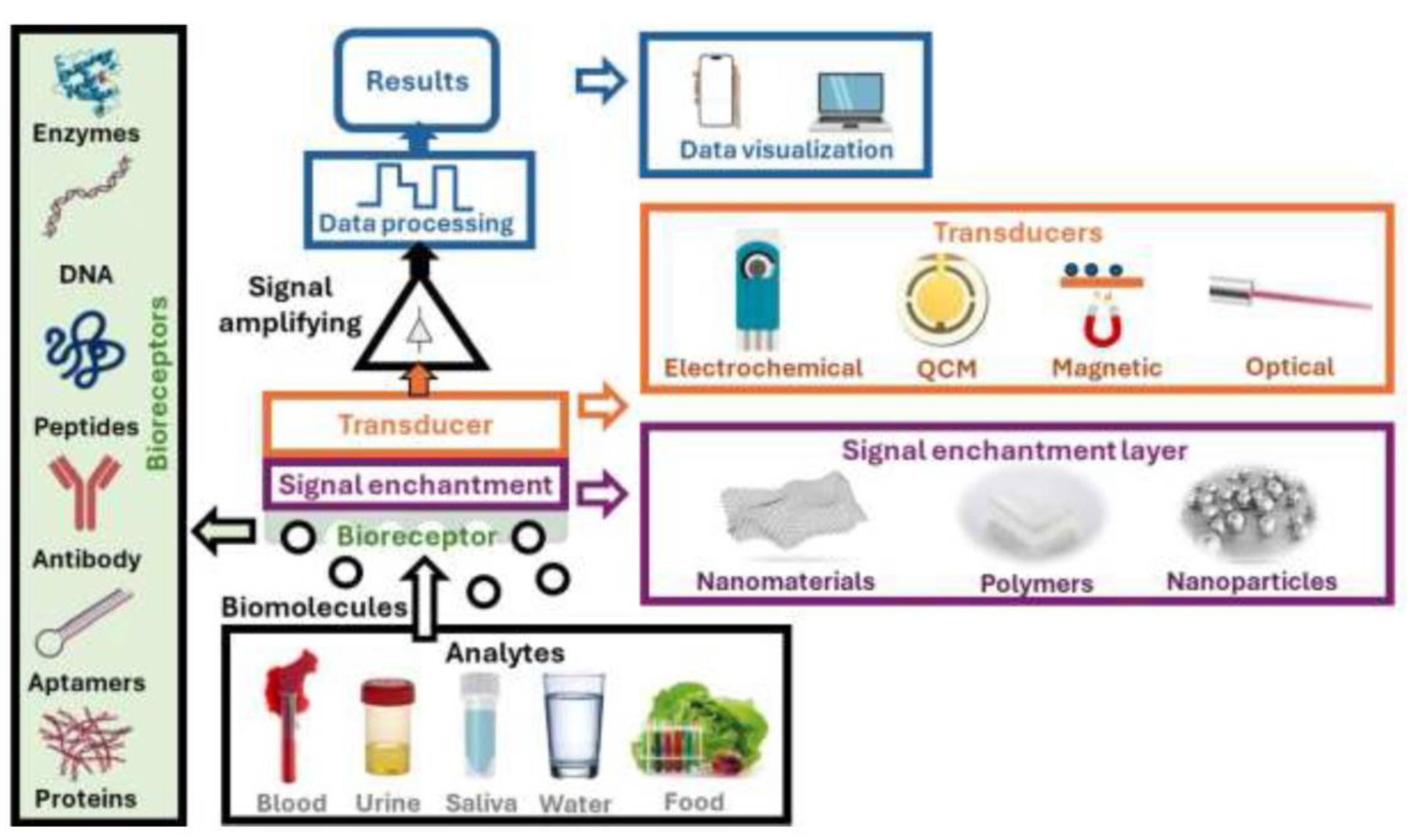
5. Conclusions
Declaration of interest statement
List of Abbreviations (in Alphabetical Order)
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AMR | Antimicrobial Resistance |
| ASFV | African Swine Fever virus |
| ASSURED | Affordable, Sensitive, Specific, User-friendly, Rapid and Robust, Equipment free, Deliverable |
| BHV | Bovine Herpes Virus |
| BRD | Bovine Respiratory Disease |
| BSE | Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy |
| BVD | Bovine Viral Diarrhoea |
| CIA | WHO Critically Important Antibiotics |
| CFU | Colony Forming Units |
| CgA | Chromagronin A |
| CGM | Continuous glucose monitors |
| CMT | California Mastitis Test |
| COVID-19 | Corona Virus Disease of 2019 |
| CRISPR | Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats |
| CSFV | Classical Swine Fever Virus |
| 2D | Two dimensional |
| DMBs | Driven magnetic beads |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| EBL | Enzootic Bovine Leucosis |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| EID | Egg infective dose |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| EMA | European Medicine Agency |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EPEC | Enteropathogenic E. coli |
| F2F | Farm-to-Fork |
| FCI | Food Chain Information |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FET | Field-effect transistor |
| FMD | Foot and Mouth Diseases |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gases |
| HACCP | Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points |
| HEIs | Harmonized Epidemiological Indicators |
| HHSP | Heard Health Surveillance Programme |
| HPLC | Reaction - PCR, High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| ISF | Animal Intersticial Fluid |
| ISO | International Standard Organization |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography - mass spectrometry |
| LC-UV | Liquid chromatography and UV detector |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| LOC | Lab-on-a-Chip |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LLM | Large Language Models |
| MIA | WHO Medically Important Antibiotics |
| MIPs | Molecularly Imprinted Polymers |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MRS | Magnetic Relaxation Switching |
| POC | Point-of-Care |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PCV | Porcine circovirus |
| PCVAD | Porcine circovirus-associated disease |
| PDO | Protected Designation of Origin |
| PGI | Protected Geographical Indication |
| Pig-MAP | Pig Major Acute Proteins |
| PLF | Precision Livestock Farming |
| PMB | Portable multifunction biosensor |
| PrPc | Prion protein |
| PRRSV | Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus |
| PIC | Photonic integrated circuit |
| PPV | Porcine Parvovirus |
| QCM | Quartz Crystal Microbalance (Resonator) |
| RPA | Recombinase Polymerase Amplification |
| RB-MSAS | Risk-based meat safety assurance system |
| SAW | Surface Acoustic Wave |
| SERS | Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy |
| SIV | Swine Influenza Virus |
| SMEs | Small and medium-sized enterprises |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| STEC | Shiga toxin-producing E. coli |
| VOCs | Volatile Organic Compounds |
| WBE | Wastewater-based epidemiology |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Rios, T.B.; Maximiano, M.R.; Feitosa, G.C.; Malmsten, M.; Franco, O.L. Nanosensors for Animal Infectious Disease Detection. Sens Biosensing Res 2024, 43, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S. Recent Advances in Wearable Sensors for Animal Health Management. Sens Biosensing Res 2017, 12, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasijević, I.; Podunavac, I.; Janković, S.; Mitrović, R.; Radonić, V. Challenges in Agri-Food Chain: Biosensors in the Meat Production System. Meat Technology 2023, 64, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hao, X.; Wang, Z.; Le, T.; Zou, S.; Cao, X. Lab-on-a-Chip Analytical Devices. In Micro- and Nanotechnology Enabled Applications for Portable Miniaturized Analytical Systems; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 355–374.
- Manessis, G.; Gelasakis, A.I.; Bossis, I. Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Farm Animal Diseases: From Biosensors to Integrated Lab-on-Chip Devices. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, Q. Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Based Microfluidic “Lab-on-a-Chip” for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria and Viruses in Agri-Foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 2024, 148, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buncic, S.; Nychas, G.-J.; Lee, M.R.F.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Hébraud, M.; Desvaux, M.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Bolton, D.; Blagojevic, B.; Antic, D. Microbial Pathogen Control in the Beef Chain: Recent Research Advances. Meat Sci 2014, 97, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; Lindqvist, R.; Nauta, M.; et al. Persistence of Microbiological Hazards in Food and Feed Production and Processing Environments. EFSA Journal 2024, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, L.; Tian, C.; Li, S.; Cao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G. A Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Six Foodborne Pathogens. Food Control 2012, 25, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, A.K. One Day to One Hour: How Quickly Can Foodborne Pathogens Be Detected? Future Microbiol 2014, 9, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, T.; Ramana, L.N.; Sharma, T.K. Current Advancements and Future Road Map to Develop ASSURED Microfluidic Biosensors for Infectious and Non-Infectious Diseases. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, K.J.; Boeras, D.I.; Chen, X.-S.; Ramsay, A.R.; Peeling, R.W. REASSURED Diagnostics to Inform Disease Control Strategies, Strengthen Health Systems and Improve Patient Outcomes. Nat Microbiol 2018, 4, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankole, O.E.; Verma, D.K.; Chávez González, M.L.; Ceferino, J.G.; Sandoval-Cortés, J.; Aguilar, C.N. Recent Trends and Technical Advancements in Biosensors and Their Emerging Applications in Food and Bioscience. Food Biosci 2022, 47, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, F.; Geng, P.; Guan, M. Recent Advancements in Microfluidic Chip Biosensor Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria: A Review. Anal Bioanal Chem 2022, 414, 2883–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araújo, P.D.; Araújo, W.M.C.; Patarata, L.; Fraqueza, M.J. Understanding the Main Factors That Influence Consumer Quality Perception and Attitude towards Meat and Processed Meat Products. Meat Sci 2022, 193, 108952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. United Nations, (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- FAO. 2022. Thinking about the future of food safety – A foresight report. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/acfc4e93-8702-47da-acd2-7bf064ea9b0b/content (accessed on 27 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.-Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.-K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia Coli. Microbiol Spectr 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Puyvelde, S.; Pickard, D.; Vandelannoote, K.; Heinz, E.; Barbé, B.; de Block, T.; Clare, S.; Coomber, E.L.; Harcourt, K.; Sridhar, S.; et al. An African Salmonella Typhimurium ST313 Sublineage with Extensive Drug-Resistance and Signatures of Host Adaptation. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine, 6th revision. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/312266/9789241515528-eng.pdf? (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- WHO's List of Medically Important Antimicrobials: a risk management tool for mitigating antimicrobial resistance due to non-human use. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/gcp/who-mia-list-2024-lv. (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Niloofar, P.; Francis, D.P.; Lazarova-Molnar, S.; Vulpe, A.; Vochin, M.-C.; Suciu, G.; Balanescu, M.; Anestis, V.; Bartzanas, T. Data-Driven Decision Support in Livestock Farming for Improved Animal Health, Welfare and Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Overview and Challenges. Comput Electron Agric 2021, 190, 106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep Trinh, T.N.; Trinh, K.T.L.; Lee, N.Y. Microfluidic Advances in Food Safety Control. Food Research International 2024, 176, 113799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ahmed, M.A.; Abubakar, A.A.; Hayat, M.N.; Kaka, U.; Ajat, M.; Goh, Y.M.; Sazili, A.Q. Improving Animal Welfare Status and Meat Quality through Assessment of Stress Biomarkers: A Critical Review. Meat Sci 2023, 197, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaswan, S.; Chandratre, G.A.; Upadhyay, D.; Sharma, A.; Sreekala, S.M.; Badgujar, P.C.; Panda, P.; Ruchay, A. Applications of Sensors in Livestock Management. In Engineering Applications in Livestock Production; Elsevier, 2024; pp. 63–92.
- Nanda, P.K.; Bhattacharya, D.; Das, J.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ekhlas, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Dandapat, P.; Alessandroni, L.; Das, A.K.; Gagaoua, M. Emerging Role of Biosensors and Chemical Indicators to Monitor the Quality and Safety of Meat and Meat Products. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrias, S.; Ibáñez, J.; Fernandes, J.R.; Martins-Lopes, P. The Role of DNA-Based Biosensors in Species Identification for Food Authenticity Assessment. Trends Food Sci Technol 2024, 145, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flauzino, J.M.R.; Alves, L.M.; Rodovalho, V.R.; Madurro, J.M.; Brito Madurro, A.G. Application of Biosensors for Detection of Meat Species: A Short Review. Food Control 2022, 142, 109214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, D.; Lo Presti, D.; Silvestri, S.; Schena, E.; Massaroni, C. Current and Future Technologies for Monitoring Cultured Meat: A Review. Food Research International 2023, 173, 113464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. 2022. Food safety aspects of cell-based food – Background document two: Generic production process. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/cc2502en/cc2502en.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Curulli, A. Electrochemical Biosensors in Food Safety: Challenges and Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesche, C.; Baeumner, A.J. Biosensors to Support Sustainable Agriculture and Food Safety. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 128, 115906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliana, C.; Liu, J.; Show, P.L.; Low, S.S. Biosensor in Smart Food Traceability System for Food Safety and Security. Bioengineered 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; He, J.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Xiao, S.; Huang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Yue, T. Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Sensing for Food Safety Analysis. Processes 2022, 10, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, N. Intelligent Biosensors Promise Smarter Solutions in Food Safety 4.0. Foods 2024, 13, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Jairath, G.; Ahlawat, S.S.; Pathera, A.; Singh, P. Biosensor: An Emerging Safety Tool for Meat Industry. J Food Sci Technol 2016, 53, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Mitea, V.; Howlader, M.M.R.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Deen, M.J. Analyzing Electrochemical Sensing Fundamentals for Health Applications. Advanced Sensor Research 2024, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gupta, R.; Bansal, D.; Bhateria, R.; Sharma, M. A Review on Recent Trends and Future Developments in Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Omega 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. The Future of Nanotechnology-Driven Electrochemical and Electrical Point-of-Care Devices and Diagnostic Tests. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry 2024, 17, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Aryal, N. Advances in Nano-Electrochemical Materials and Devices. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Covalent Organic Frameworks-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Food Safety Analysis. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Gautam, A.; Chauhan, T.; Kumar, D. Nanomaterial Based Sensors for Detection of Food Contaminants: A Prospect. Sensing Technology 2024, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Barfidokht, A.; Tehrani, F.; Mishra, R. Food Safety Analysis Using Electrochemical Biosensors. Foods 2018, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer-Baranyi, K.; Székács, A.; Adányi, N. Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for Determination of Food Spoilage. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhan, A.; Muthukumarappan, K.; Wei, L. Biosensors and Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposites for Smart Food Packaging: Challenges and Opportunities. Food Packag Shelf Life 2021, 30, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostufa, S.; Rezaei, B.; Ciannella, S.; Yari, P.; Gómez-Pastora, J.; He, R.; Wu, K. Advancements and Perspectives in Optical Biosensors. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 24181–24202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, J.; Salena, B.J.; Li, Y. Aptamer and DNAzyme Based Colorimetric Biosensors for Pathogen Detection. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, M.; Fan, Z. Current Trends in Colorimetric Biosensors Using Nanozymes for Detecting Biotoxins (Bacterial Food Toxins, Mycotoxins, and Marine Toxins). Analytical Methods 2024, 16, 6771–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mal, D.K.; Pal, H.; Chakraborty, G. A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances in Fluorescence-Based Bio-Analytes Sensing. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2024, 171, 117493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.A.; Kazanskiy, N.L.; Khonina, S.N.; Voronkov, G.S.; Grakhova, E.P.; Kutluyarov, R. V. A Review on Photonic Sensing Technologies: Status and Outlook. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.C.; Grajales García, D.; Maldonado, J.; Fernández-Gavela, A. Current Trends in Photonic Biosensors: Advances towards Multiplexed Integration. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, N.; Kumar, S.; M, Y.; S, R.; C A, M.; Thirunavookarasu S, N.; C K, S. Recent Advances in Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Biosensors for Food Analysis: A Review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2023, 63, 1055–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Qi, Q.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Biosensors for Food Allergen Detection in Food Matrices. Biosens Bioelectron 2019, 142, 111449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Lednev, I.K.; Jung, Y.M. Recent Trends in Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Biosensors: Label-Free Early Disease Diagnosis. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2024, 128, 8861–8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esther Jebakumari, K.A.; Murugasenapathi, N.K.; Peixoto, L.P.F.; Oliveira, G.P.; Andrade, G.F.S.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Tamilarasan, P. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering in Biosensing Technologies. In Health and Environmental Applications of Biosensing Technologies; Elsevier, 2024; pp. 355–391.
- Flynn, C.D.; Chang, D. Artificial Intelligence in Point-of-Care Biosensing: Challenges and Opportunities. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wei, Q.; Park, H.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire Nanosensors for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Biological and Chemical Species. Science (1979) 2001, 293, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.; Lieber, C.M. Fabrication of Silicon Nanowire Devices for Ultrasensitive, Label-Free, Real-Time Detection of Biological and Chemical Species. Nat Protoc 2006, 1, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Liu, W.; Xie, X.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S.; Banerjee, K. MoS 2 Field-Effect Transistor for Next-Generation Label-Free Biosensors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3992–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wustoni, S.; Hideshima, S.; Kuroiwa, S.; Nakanishi, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Mori, Y.; Osaka, T. Sensitive Electrical Detection of Human Prion Proteins Using Field Effect Transistor Biosensor with Dual-Ligand Binding Amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 2015, 67, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhera, T.; Kakkar, D.; Wadhwa, G.; Raj, B. Recent Advances and Progress in Development of the Field Effect Transistor Biosensor: A Review. J Electron Mater 2019, 48, 7635–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syedmoradi, L.; Ahmadi, A.; Norton, M.L.; Omidfar, K. A Review on Nanomaterial-Based Field Effect Transistor Technology for Biomarker Detection. Microchimica Acta 2019, 186, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, D.; Koo, J. A Review of BioFET’s Basic Principles and Materials for Biomedical Applications. Biomed Eng Lett 2021, 11, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotsky, A.; Butler, D.; Dong, C.; Gerace, K.; Glavin, N.R.; Muratore, C.; Robinson, J.A.; Ebrahimi, A. Two-Dimensional Materials in Biosensing and Healthcare: From In Vitro Diagnostics to Optogenetics and Beyond. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9781–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, F.; Salimi, A. Advances in 2d Based Field Effect Transistors as Biosensing Platforms: From Principle to Biomedical Applications. Microchemical Journal 2023, 187, 108432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to Selecting a Biorecognition Element for Biosensors. Bioconjug Chem 2018, 29, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Feng, H.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X. Wearable Internet of Things Enabled Precision Livestock Farming in Smart Farms: A Review of Technical Solutions for Precise Perception, Biocompatibility, and Sustainability Monitoring. J Clean Prod 2021, 312, 127712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samota, S.; Rani, R.; Chakraverty, S.; Kaushik, A. Biosensors for simplistic detection of pathogenic bacteria: A review with special focus on field-effect transistors, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process.2022, 141, 106404, doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2021. 1064. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Chen, F.; Huang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Cho, Y.-K.; Fang, R. H.; Gao, W.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L. 2019; 13. [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, D. S.; Chekusova, V. P.; Trul, A.A. Abramov, A; Borshechev, O.; Agina, E. ; Ponomarenko. S. Fully integrated ultra-sensitive electronic nose based on organic field-effect transistors. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 10683, doi.org/10. 1038. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.J.; Saha, T.; Tey, B.T.; Tan, W.S.; Ooi, C.W. Quartz Crystal Microbalance-Based Biosensors as Rapid Diagnostic Devices for Infectious Diseases. Biosens Bioelectron 2020, 168, 112513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Sensing Materials in Biosensors Development. Int J Electrochem Sci 2021, 16, 211220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, N.; Almutairi, M.; Alodhayb, A.N. A Review of Quartz Crystal Microbalance for Chemical and Biological Sensing Applications. Sens Imaging 2023, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forinová, M.; Pilipenco, A.; Lynn, N.S.; Obořilová, R.; Šimečková, H.; Vrabcová, M.; Spasovová, M.; Jack, R.; Horák, P.; Houska, M.; et al. A Reusable QCM Biosensor with Stable Antifouling Nano-Coating for on-Site Reagent-Free Rapid Detection of E. Coli O157:H7 in Food Products. Food Control 2024, 165, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangprapan, S.; Choke-arpornchai, B.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Choowongkomon, K. Sensing the Classical Swine Fever Virus with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer on Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Hollow Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for Rapid Detection of Methimazole in Food Samples. Food Chem 2020, 309, 125787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheubong, C.; Yoshida, A.; Mizukawa, Y.; Hayakawa, N.; Takai, M.; Morishita, T.; Kitayama, Y.; Sunayama, H.; Takeuchi, T. Molecularly Imprinted Nanogels Capable of Porcine Serum Albumin Detection in Raw Meat Extract for Halal Food Control. Anal Chem 2020, 92, 6401–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wu, W.; Yang, P.; Luo, J.; Fu, C.; Han, J.-C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y. A Review of Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors: Mechanisms, Stability and Future Prospects. Sensor Review 2024, 44, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronewold, T.M.A. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors in the Bioanalytical Field: Recent Trends and Challenges. Anal Chim Acta 2007, 603, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Cho, B.-K.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, K.-B. Feasibility Study for the Evaluation of Chicken Meat Storage Time Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor. Journal of Biosystems Engineering 2020, 45, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauke, T.N.; Gronewold, T.M.A.; Perpeet, M.; Plattes, S.; Petersen, B. Measurement of Porcine Haptoglobin in Meat Juice Using Surface Acoustic Wave Biosensor Technology. Meat Sci 2013, 95, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yuan, R.; Fu, H.; Xu, Z.; Wei, S. Foodborne Pathogen Detection Using Surface Acoustic Wave Biosensors: A Review. RSC Adv 2024, 14, 37087–37103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, F.; Chen, Y. Recent Advances in Magnetic Relaxation Switching Biosensors for Animal-Derived Food Safety Detection. Trends Food Sci Technol 2024, 146, 104387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Xu, L.; Yan, W.; Wu, W.; Yu, Q.; Tian, X.; Dai, R.; Li, X. A Magnetic Relaxation Switch Aptasensor for the Rapid Detection of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Using Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles. Microchimica Acta 2017, 184, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, C.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Y. Gold Core @ Platinum Shell Nanozyme-Mediated Magnetic Relaxation Switching DNA Sensor for the Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes in Chicken Samples. Food Control 2022, 137, 108916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Xiao, R.; Li, L.; Cai, Z.; Ren, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y. Win-Win Cooperation: Magnetic Relaxation Switching Biosensor for Chloramphenicol Detection Based on the Pipet Platform and Antigen-Driven Enzyme-Free Dual Signal Amplification Strategy. Sens Actuators B Chem 2023, 385, 133686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, R.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ruan, S.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Magnetic Relaxation Switching Immunoassay Based on “Limited-Magnitude” Particles for Sensitive Quantification of Aflatoxin B1. Anal Chim Acta 2023, 1266, 341329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Baldo, F.; Fracassi, F. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Dogs and Cats. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice 2023, 53, 591–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brobst, M.N.; Abi-Nader, B.A.; Blasczynski, S.J.; Chigerwe, M. Evaluation of a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Healthy Dairy Calves and Adult Goats. Am J Vet Res 2024, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, P.U.; von Woedtke, T. Biosensors for in Vivo Glucose Measurement: Can We Cross the Experimental Stage. Biosens Bioelectron 2002, 17, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- https://universalbiosensors.
- Nastasijevic, I.; Glisic, M.; Milijasevic, M.; Jankovic, S.; Mitrovic, R.; Milijasevic, J.B.; Boskovic Cabrol, M. Biosecurity and Lairage Time versus Pork Meat Quality Traits in a Farm–Abattoir Continuum. Animals 2022, 12, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, R. Monitoring Stress Hormone Metabolites as a Useful, Non-Invasive Tool for Welfare Assessment in Farm Animals. Animal Welfare 2012, 21, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Kannan, P.; Natarajan, B.; Maiyalagan, T.; Subramanian, P.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, S. MnO2 Cacti-like Nanostructured Platform Powers the Enhanced Electrochemical Immunobiosensing of Cortisol. Sens Actuators B Chem 2020, 317, 128134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Ye, H.; Chen, Z.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Guo, Z. An Ultrasensitive Aptamer-Antibody Sandwich Cortisol Sensor for the Noninvasive Monitoring of Stress State. Biosens Bioelectron 2021, 190, 113451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Liu, W.-C.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Liu, B.-D.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, H.-Y. A Multichannel System Integrating Molecularly Imprinted Conductive Polymers for Ultrasensitive Voltammetric Determination of Four Steroid Hormones in Urine. Microchimica Acta 2019, 186, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachaliou, C.-E.; Koukouvinos, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.; Petrou, P.; Livaniou, E. Cortisol Immunosensors: A Literature Review. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Jing, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J. Ultrasensitive Indirect Competitive ELISA and Strip Sensor for Detection of Furazolidone Metabolite in Animal Tissues. Food Agric Immunol 2017, 28, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelis, J.L.D.; Bose, U.; Broadbent, J.A.; Hughes, J.; Sikes, A.; Anderson, A.; Caron, K.; Schmoelzl, S.; Colgrave, M.L. Biomarkers and Biosensors for the Diagnosis of Noncompliant PH, Dark Cutting Beef Predisposition, and Welfare in Cattle. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2022, 21, 2391–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckelkamp, E.A. Invited Review: Current State of Wearable Precision Dairy Technologies in Disease Detection. Applied Animal Science 2019, 35, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Moreddu, R.; Seifi, S.; Jiang, N.; Vega, K.; Dong, X.; Dong, J.; Butt, H.; Jakobi, M.; Elsner, M.; et al. Dermal Tattoo Biosensors for Colorimetric Metabolite Detection. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2019, 58, 10506–10513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro, M.; Morales, J.; Vizcaíno, E.; Murillo, J.A.; Klauke, T.; Petersen, B.; Piñeiro, C. The Use of Acute Phase Proteins for Monitoring Animal Health and Welfare in the Pig Production Chain: The Validation of an Immunochromatographic Method for the Detection of Elevated Levels of Pig-MAP. Meat Sci 2013, 95, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Lassiter, K.; Li, Y.; Hargis, B.; Tung, S.; Berghman, L.; Bottje, W. Interdigitated Array Microelectrode Based Impedance Immunosensor for Detection of Avian Influenza Virus H5N1. Talanta 2009, 79, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niamh, A.M.; Ryona Sayers, C.; Alan O’riordan, S.B. Novel Single Gold Nanowire-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Antibodies in Serum. J Biosens Bioelectron 2015, 06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Gray, D.W.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Shields, N.; Montrose, A.; Creedon, N.; Lovera, P.; O’Riordan, A.; Mooney, M.H.; Vogel, E.M. A Potentiometric Biosensor for Rapid On-Site Disease Diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 2016, 79, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirala, N.R.; Pinker, N.; Desitti, C.; Shtenberg, G. Milk Haptoglobin Detection Based on Enhanced Chemiluminescence of Gold Nanoparticles. Talanta 2019, 197, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Ahmed, S.R.; Neethirajan, S. A Nanocomposite-Based Biosensor for Bovine Haptoglobin on a 3D Paper-Based Analytical Device. Sens Actuators B Chem 2018, 265, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomorska-Mól, M.; Krzysztof, K.; Pejsak, Z.; Markowska-Daniel, I. Analysis of the Acute-phase Protein Response in Pigs to Clinical and Subclinical Infection with <scp>H</Scp> 3 <scp>N</Scp> 2 Swine Influenza Virus. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2014, 8, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saco, Y.; Bassols, A. Acute Phase Proteins in Cattle and Swine: A Review. Vet Clin Pathol 2023, 52, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, J.H.; van Hooijdonk, R.T.; Sterk, P.J.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Schultz, M.J.; Bos, L.D. Glucose Prediction by Analysis of Exhaled Metabolites – a Systematic Review. BMC Anesthesiol 2014, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burciaga-Robles, L.O.; Holland, B.P.; Step, D.L.; Krehbiel, C.R.; McMillen, G.L.; Richards, C.J.; Sims, L.E.; Jeffers, J.D.; Namjou, K.; McCann, P.J. Evaluation of Breath Biomarkers and Serum Haptoglobin Concentration for Diagnosis of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Heifers Newly Arrived at a Feedlot. Am J Vet Res 2009, 70, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, H.; Köhler, H.; Commander, N.; Reinhold, P.; Turner, C.; Chambers, M.; Pardo, M.; Sberveglieri, G. Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Analysis For Disease Detection: Proof Of Principle For Field Studies Detecting Paratuberculosis And Brucellosis. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP; 2009; 195–197. [Google Scholar]
- Fend, R.; Geddes, R.; Lesellier, S.; Vordermeier, H.-M.; Corner, L.A.L.; Gormley, E.; Costello, E.; Hewinson, R.G.; Marlin, D.J.; Woodman, A.C.; et al. Use of an Electronic Nose To Diagnose Mycobacterium Bovis Infection in Badgers and Cattle. J Clin Microbiol 2005, 43, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanan, V.; Nugen, S.R.; Baeumner, A.J.; Chang, Y.-F. A Biosensor Assay for the Detection of Mycobacterium Avium Subsp. Paratuberculosis in Fecal Samples. J Vet Sci 2009, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottram, T.T.; Dobbelaar, P.; Schukken, Y.H.; Hobbs, P.J.; Bartlett, P.N. An Experiment to Determine the Feasibility of Automatically Detecting Hyperketonaemia in Dairy Cows. Livest Prod Sci 1999, 61, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.S.; Brehm, K.E.; Skov, J.; Harlow, K.W.; Christensen, J.; Haas, B. Detection of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus in the Breath of Infected Cattle Using a Hand-Held Device to Collect Aerosols. J Virol Methods 2011, 177, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Sasaki, M.; Kadoma, Y.; Imai, Y.; Niwa, D.; Shetty, V. Immunosensor with Fluid Control Mechanism for Salivary Cortisol Analysis. Biosens Bioelectron 2013, 41, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schazmann, B.; Morris, D.; Slater, C.; Beirne, S.; Fay, C.; Reuveny, R.; Moyna, N.; Diamond, D. A Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for the Real-Time Measurement of Sweat Sodium Concentration. Analytical Methods 2010, 2, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, A.; Kundu, R.S.; Ahlawat, S.; Singh, K.P.; Karki, K.; Lather, A.S.; Poonia, K.; Budania, S.; Kumar, V. Current Trends in Biosensors for the Detection of Cattle Diseases Worldwide. Biosens Bioelectron X 2023, 14, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klestova, Z.S. Diagnostics of Cattle Leucosis by Using an Biosensor Based on Surface Plasmon Resonance Phenomenon. Semiconductor Physics, Quantum Electronics & Optoelectronics 2019, 22, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Sun, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Jiang, F.; Chen, H.; Wu, W. Enzyme Linked Aptamer Assay: Based on a Competition Format for Sensitive Detection of Antibodies to Mycoplasma Bovis in Serum. Anal Chem 2014, 86, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitzel, A.-C.; Stamer, E.; Junge, W.; Thaller, G. Calibration of an Automated California Mastitis Test with Focus on the Device-Dependent Variation. Springerplus 2014, 3, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.A.M.; Martins, V.C.; Cardoso, F.A.; Germano, J.; Rodrigues, M.; Duarte, C.; Bexiga, R.; Cardoso, S.; Freitas, P.P. Biosensors for On-Farm Diagnosis of Mastitis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, D.; Hasegawa, H.; Kaneko, K.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Screening of DNA Aptamer Against Mouse Prion Protein by Competitive Selection. Prion 2007, 1, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, R.; Yu, L.; Du, Q.; Ge, A.; Liu, C.; Chi, Z. Improved Triple-Module Fluorescent Biosensor for the Rapid and Ultrasensitive Detection of Campylobacter Jejuni in Livestock and Dairy. Food Control 2022, 137, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttenthaler, E.; Kößlinger, C.; Drost, S. Quartz Crystal Biosensor for Detection of the African Swine Fever Disease. Anal Chim Acta 1998, 362, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Lv, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xia, X.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. One-Step Rapid and Sensitive ASFV P30 Antibody Detection via Nanoplasmonic Biosensors. Microbiol Spectr 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Fu, S.; Li, J.; Yi, X.; Qu, Z.; Li, Y.; Miao, J.; Miao, P.; Xu, Y. A Smartphone-Based Portable Biosensor for Colorimetric Detection of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Sens Actuators B Chem 2023, 396, 134617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuitio, C.; Rasri, N.; Kiriwan, D.; Unajak, S.; Choowongkomon, K. Development of a Biosensor from Aptamers for Detection of the Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. J Vet Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnese, C.; Barattini, P.; Giusti, A.; Balka, G.; Bruno, U.; Bossis, I.; Gelasakis, A.; Bonasso, M.; Philmis, P.; Dénes, L.; et al. A Diagnostic Device for In-Situ Detection of Swine Viral Diseases: The SWINOSTICS Project. Sensors 2019, 19, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gómez, M.; Sánchez, C.; Peransi, S.; Zurita, D.; Bellieres, L.; Recuero, S.; Rodrigo, M.; Simón, S.; Camarca, A.; Capo, A.; et al. Photonic Label-Free Biosensors for Fast and Multiplex Detection of Swine Viral Diseases. Sensors 2022, 22, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griol, A.; Peransi, S.; Rodrigo, M.; Hurtado, J.; Bellieres, L.; Ivanova, T.; Zurita, D.; Sánchez, C.; Recuero, S.; Hernández, A.; et al. Design and Development of Photonic Biosensors for Swine Viral Diseases Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hideshima, S.; Hinou, H.; Ebihara, D.; Sato, R.; Kuroiwa, S.; Nakanishi, T.; Nishimura, S.-I.; Osaka, T. Attomolar Detection of Influenza A Virus Hemagglutinin Human H1 and Avian H5 Using Glycan-Blotted Field Effect Transistor Biosensor. Anal Chem 2013, 85, 5641–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Bhunia, A.K. Cell-Based Biosensor for Rapid Screening of Pathogens and Toxins. Biosens Bioelectron 2010, 26, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, W.; Lin, T.; Sun, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Liu, F. Three-Mode Ratiometric Biosensor Based on Integrated DNA-Driven Magnetic Beads for Clostridium Perfringens Detection. Food Chem 2025, 463, 141228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mungroo, N.; Neethirajan, S. Biosensors for the Detection of Antibiotics in Poultry Industry—A Review. Biosensors (Basel) 2014, 4, 472–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cháfer-Pericás, C.; Maquieira, Á.; Puchades, R. Fast Screening Methods to Detect Antibiotic Residues in Food Samples. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2010, 29, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claycomb, R.W.; Delwiche, M.J. Biosensor for On-Line Measurement of Bovine Progesterone during Milking. Biosens Bioelectron 1998, 13, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Dupaty, J.; Baer, R.C.; Kuzmanovic, U.; Fan, A.; Grinstaff, M.W.; Galagan, J.E.; Klapperich, C.M. Paper-Based Progesterone Sensor Using an Allosteric Transcription Factor. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 5804–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazon, C.; Baer, R.C.; Kuzmanović, U.; Nguyen, T.; Chen, M.; Zamani, M.; Chern, M.; Aquino, P.; Zhang, X.; Lecommandoux, S.; et al. A Progesterone Biosensor Derived from Microbial Screening. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zutz, C.; Wagener, K.; Yankova, D.; Eder, S.; Möstl, E.; Drillich, M.; Rychli, K.; Wagner, M.; Strauss, J. A Robust High-Throughput Fungal Biosensor Assay for the Detection of Estrogen Activity. Steroids 2017, 126, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Välimaa, A.-L.; Kivistö, A.T.; Leskinen, P.I.; Karp, M.T. A Novel Biosensor for the Detection of Zearalenone Family Mycotoxins in Milk. J Microbiol Methods 2010, 80, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.A.; Abu Hanifah, S.; Heng, L.Y.; Al-badaii, F.; Ulianas, A. Systematic Review on Biosensors for the Early Detection of Mycotoxins as Endocrine Disruptors. Food Control 2024, 157, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.M.; Zhao, S.; Niazi, S.; Mohsin, A.; Shoaib, M.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Silver Nanoclusters Based FRET Aptasensor for Sensitive and Selective Fluorescent Detection of T-2 Toxin. Sens Actuators B Chem 2018, 277, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bai, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Mu, Z. An Electrochemical Aptasensor for Highly Sensitive Detection of Zearalenone Based on PEI-MoS2-MWCNTs Nanocomposite for Signal Enhancement. Anal Chim Acta 2019, 1060, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Han, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhai, B.; Xu, Y. A Portable Multifunctional Biosensor Based on a Newly Screened Endogenous Reference Gene for Pork Adulteration Detection. Microchemical Journal 2024, 206, 111445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee Sadi, B.; Bayat, M.; Tajik, P.; Hashemi, S.J. Citrinin Detection by Intensified Fluorescence Signal of a FRET-Based Immunosensor Using Magnetic/Silica Core–Shell. Saudi J Biol Sci 2018, 25, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, G.I.; Voulgarakis, N.; Terzidou, G.; Fotos, L.; Giamouri, E.; Papatsiros, V.G. Precision Livestock Farming Technology: Applications and Challenges of Animal Welfare and Climate Change. Agriculture 2024, 14, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Jacinto, J.G.P.; Mϋnchemyer, W.; Walte, A.; Gentile, A.; Formigoni, A.; Mammi, L.M.E.; Csaba Bajcsy, Á.; Abdu, M.S.; Kamel, M.M.; et al. Estrus Detection in a Dairy Herd Using an Electronic Nose by Direct Sampling on the Perineal Region. Vet Sci 2022, 9, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Delwiche; X. Tang; R. BonDurant; C. Munro ESTRUS DETECTION WITH A PROGESTERONE BIOSENSOR. Transactions of the ASAE 2001, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kwon, W.-S.; Ha, J.; Moon, J.; Yi, J. Increased Accuracy of Estrus Prediction Using Ruminoreticular Biocapsule Sensors in Hanwoo (Bos Taurus Coreanae) Cows. J Anim Sci Technol 2023, 65, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Gao, K.; Yang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shao, L.; Zhai, P.; Qin, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; et al. A Sperm Quality Detection System Based on Microfluidic Chip and Micro-Imaging System. Front Vet Sci 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordas-Perpinyà, M.; Yánez-Ortiz, I.; Sergeant, N.; Mevel, V.; Catalán, J.; Bruyas, J.-F.; Miró, J.; Briand-Amirat, L. ProAKAP4 as Indicator of Long-Lasting Motility Marker in Post-Thaw Conditions in Stallions. Animals 2024, 14, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, I.; Verplanck, C.; Thomas, Y.R.J. Electrochemical Sensors for Animal Welfare. In Proceedings of the Eurosensors 2023; MDPI: Basel Switzerland, March 18, 2023; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Neethirajan, S.; Tuteja, S.K.; Huang, S.-T.; Kelton, D. Recent Advancement in Biosensors Technology for Animal and Livestock Health Management. Biosens Bioelectron 2017, 98, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerón, J.J.; Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Escribano, D.; Martínez-Miró, S.; López-Martínez, M.J.; Ortín-Bustillo, A.; Franco-Martínez, L.; Rubio, C.P.; Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; et al. Basics for the Potential Use of Saliva to Evaluate Stress, Inflammation, Immune System, and Redox Homeostasis in Pigs. BMC Vet Res 2022, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suba-Bokodi, É.; Nagy, I.; Molnár, M. The Impact of Transportation on the Cortisol Level of Dwarf Rabbits Bred to Animal-Assisted Interventions. Animals 2024, 14, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Escribano, D.; Martínez-Miró, S.; López-Arjona, M.; Rubio, C.P.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J.; Tecles, F. Application of a Score for Evaluation of Pain, Distress and Discomfort in Pigs with Lameness and Prolapses: Correlation with Saliva Biomarkers and Severity of the Disease. Res Vet Sci 2019, 126, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, D.; Soler, L.; Gutiérrez, A.M.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J. Measurement of Chromogranin A in Porcine Saliva: Validation of a Time-Resolved Immunofluorometric Assay and Evaluation of Its Application as a Marker of Acute Stress. Animal 2013, 7, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecles, F.; Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Martínez-Miró, S.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Escribano, D.; Cerón, J.J. Total Esterase Measurement in Saliva of Pigs: Validation of an Automated Assay, Characterization and Changes in Stress and Disease Conditions. Res Vet Sci 2017, 114, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Baltic, M.Z.; Duric, J.; Ivanovic, J.; Popovic, L.; Todorovic, M.; Markovic, R.; Pantic, S. Correlations among Stress Parameters, Meat and Carcass Quality Parameters in Pigs. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2015, 28, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.; Berends, B.; Lipman, L. The Value of Current Ante Mortem Meat Inspection and Food Chain Information of Dairy Cows in Relation to Post Mortem Findings and the Protection of Public Health: A Case for a More Risk-Based Meat Inspection. Foods 2023, 12, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Rodríguez, M.G.; Silva-Lance, F.; Parra-Arroyo, L.; Medina-Salazar, D.A.; Martínez-Ruiz, M.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Martínez-Prado, M.A.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Barceló, D.; et al. Biosensors for the Detection of Disease Outbreaks through Wastewater-Based Epidemiology. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2022, 155, 116585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossettini, A.; Vidic, J.; Maifreni, M.; Marino, M.; Pinamonti, D.; Manzano, M. Rapid Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes, Salmonella, Campylobacter Spp., and Escherichia Coli in Food Using Biosensors. Food Control 2022, 137, 108962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicle, Y.; Karamese, M. Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Future Microbiol 2024, 19, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banakar, M.; Hamidi, M.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Sapkota, J.; Azizian, R.; Rokaya, D. Electrochemical Biosensors for Pathogen Detection: An Updated Review. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Ramírez, A.Y.; González-Estrada, R.R.; Chacón-López, M.A.; García-Magaña, M. de L.; Montalvo-González, E.; Álvarez-López, A.; Rodríguez-López, A.; López-García, U.M. Detection of Foodborne Pathogens in Contaminated Food Using Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Anal Biochem 2024, 693, 115600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslan, S.N.H.; Yusof, N.Y.; Lim, S.J.; Ahmad, N.H. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella in Agro-Food and Environmental Samples: A Review of Advances in Rapid Tests and Biosensors. J Microbiol Methods 2024, 219, 106897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Wang, S.; Cai, G.; Xue, L.; Li, Y.; Liao, M.; Lin, J. A Microfluidic Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Based on Magnetic Separation, Enzymatic Catalysis and Electrochemical Impedance Analysis. Chinese Chemical Letters 2022, 33, 3156–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Dai, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Impedimetric Salmonella Aptasensor Using a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with an Electrodeposited Composite Consisting of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Carbon Nanotubes. Microchimica Acta 2016, 183, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, D.L.; Melo, A.M.A.; Furtado, R.F.; Borges, M.F.; Figueiredo, E.A.T.; Biswas, A.; Cheng, H.N.; Alves, C.R. A Rapid and Specific Biosensor for Salmonella Typhimurium Detection in Milk. Food Bioproc Tech 2018, 11, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podunavac, I.; Kukkar, M.; Léguillier, V.; Rizzotto, F.; Pavlovic, Z.; Janjušević, L.; Costache, V.; Radonic, V.; Vidic, J. Low-Cost Goldleaf Electrode as a Platform for Escherichia Coli Immunodetection. Talanta 2023, 259, 124557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinay, M.; Franche, N.; Grégori, G.; Fantino, J.-R.; Pouillot, F.; Ansaldi, M. Phage-Based Fluorescent Biosensor Prototypes to Specifically Detect Enteric Bacteria Such as E. Coli and Salmonella Enterica Typhimurium. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0131466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Li, S.; Horikawa, S.; Park, M.-K.; Vodyanoy, V.; Chin, B.A. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium on Eggshells by Using Wireless Biosensors. J Food Prot 2012, 75, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvano, F.; Pilloton, R.; Albanese, D. A Novel Impedimetric Biosensor Based on the Antimicrobial Activity of the Peptide Nisin for the Detection of Salmonella Spp. Food Chem 2020, 325, 126868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Song, D.; Zhuo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, A.; Long, F. Simultaneous and Sensitive Determination of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium Using Evanescent Wave Dual-Color Fluorescence Aptasensor Based on Micro/Nano Size Effect. Biosens Bioelectron 2021, 185, 113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pebdeni, A.B.; Roshani, A.; Mirsadoughi, E.; Behzadifar, S.; Hosseini, M. Recent Advances in Optical Biosensors for Specific Detection of E. Coli Bacteria in Food and Water. Food Control 2022, 135, 108822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Cai, M.; Liu, S.; Sun, C.; Chi, Y.; Xu, K. A Colorimetric Biosensor with Infrared Sterilization Based on CuSe Nanoparticles for the Detection of E. Coli O157:H7 in Food Samples. Microbiol Spectr 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forinová, M.; Pilipenco, A.; Lynn, N. S.; Obořilová, R.; Šimečková, H.; Vrabcová, M.; Spasovová, M.; Jack, R.; Horák, P.; Houska, M.; Skládal, P.; Šedivák, P.; Farka, Z.; Vaisocherová-Lísalová, H. A reusable QCM biosensor with stable antifouling nano-coating for on-site reagent-free rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7 in food products. Food Control. [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Singh, A.; Dutta, D.; Ghosh, S.S.; Iyer, P.K. Rapid and Label-Free Bacteria Detection Using a Hybrid Tri-Layer Dielectric Integrated n-Type Organic Field Effect Transistor. J Mater Chem A Mater 2019, 7, 18330–18337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, C.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Y. Gold Core @ Platinum Shell Nanozyme-Mediated Magnetic Relaxation Switching DNA Sensor for the Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes in Chicken Samples. Food Control 2022, 137, 108916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsène, M.M.J.; Davares, A.K.L.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Andreevna, S.L.; Sarra, S.; Khelifi, I.; Sergueïevna, D.M. The Public Health Issue of Antibiotic Residues in Food and Feed: Causes, Consequences, and Potential Solutions. Vet World 2022, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.H. Recent Biosensors for Detection of Antibiotics in Animal Derived Food. Crit Rev Anal Chem 2022, 52, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavadharini, B.; Kavimughil, M.; Malini, B.; Vallath, A.; Prajapati, H.K.; Sunil, C.K. Recent Advances in Biosensors for Detection of Chemical Contaminants in Food — a Review. Food Anal Methods 2022, 15, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehru, R.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. A Review of Smart Electrochemical Devices for Pesticide Detection in Agricultural Food and Runoff Contaminants. Science of The Total Environment 2024, 935, 173360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkrishna, A.; Kumari, A.; Kumar, A.; Arya, V.; Chauhan, A.; Upadhyay, N.K.; Guleria, I.; Amarowicz, R.; Kumar, D.; Kuca, K. Biosensors for Detection of Pesticide Residue, Mycotoxins and Heavy Metals in Fruits and Vegetables: A Concise Review. Microchemical Journal 2024, 205, 111292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, X. Recent Advances in Biosensors for the Detection of Estrogens in the Environment and Food. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2020, 127, 115882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoleli, G.-P.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Siontorou, C.G.; Karapetis, S.; Varzakas, T. Novel Biosensors for the Rapid Detection of Toxicants in Foods. In; 2018; pp. 57–102.
- Sun, Y.; He, J.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. A Selective Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor with GO@COF Signal Amplification for the Simultaneous Determination of Sulfadiazine and Acetaminophen. Sens Actuators B Chem 2019, 300, 126993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anchidin-Norocel, L.; Gutt, G.; Tătăranu, E.; Amariei, S. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors: Effective Tools for Detecting Heavy Metals in Water and Food with Possible Implications for Children’s Health. Int J Electrochem Sci 2024, 19, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szelenberger, R.; Cichoń, N.; Zajaczkowski, W.; Bijak, M. Application of Biosensors for the Detection of Mycotoxins for the Improvement of Food Safety. Toxins (Basel) 2024, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Iordache, F.; Stanca, L.; Mitranescu, E.; Bader Stoica, L.; Geicu, O.I.; Bilteanu, L.; Serban, A.I. Biosensors for Food Mycotoxin Determination: A Comparative and Critical Review. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.F.; Zankari, E.; Hasman, H. Molecular Methods for Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance. Microbiol Spectr 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, W.C.; Woodruff, E.S.; Weed, D.; Ward, D.C.; Jenison, R.D. Development of a Rapid Diagnostic Assay for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2008, 61, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, H.; Wilson, H.; Cara, I.; Carter, S.; Dyson, E.N.; Elangovan, R.; Rimmer, S.; Bachmann, T.T. Label-Free Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid Bacterial Pathogen Detection Using Vancomycin-Modified Highly Branched Polymers. Sensors 2021, 21, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, D.; Rostovsky, I.; Taussig, D.; Bar-Am, T.; Wine, Y.; Sal-Man, N.; Vernick, S. A Dual-Channel Electrochemical Biosensor Enables Concurrent Detection of Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance. Biosens Bioelectron 2024, 257, 116314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnano San Lio, R.; Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; La Rosa, M.C.; Favara, G.; Agodi, A. Updates on Developing and Applying Biosensors for the Detection of Microorganisms, Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Antibiotics: A Scoping Review. Front Public Health 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felicia, W.X.L.; Rovina, K.; ‘Aqilah, N.M.N.; Vonnie, J.M.; Yin, K.W.; Huda, N. Assessing Meat Freshness via Nanotechnology Biosensors: Is the World Prepared for Lightning-Fast Pace Methods? Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, P.F.M.; de Sousa Picciani, P.H.; Calado, V.; Tonon, R. V. Electrical Gas Sensors for Meat Freshness Assessment and Quality Monitoring: A Review. Trends Food Sci Technol 2021, 118, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, D.; Fu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Biogenic Amines Detection in Meat and Meat Products: The Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Trends. Journal of Future Foods 2024, 4, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Luo, F.; Lin, C.; Wang, J.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z. Multicolor Hydrogen Sulfide Sensor for Meat Freshness Assessment Based on Cu2+-Modified Boron Nitride Nanosheets-Supported Subnanometer Gold Nanoparticles. Food Chem 2022, 381, 132278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Shrivastava, A.; Saini, A. Biosensors for Food Spoilage Detection: A Comprehensive Review of Current Advances. Journal of Food Chemistry & Nanotechnology 2024, 10, S73–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionek, B.; Przybylski, W.; Tambor, K. Biosensors in Evaluation of Quality of Meat and Meat Products – A Review. Annals of Animal Science 2020, 20, 1151–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Lim, N.-R.; Kang, B.-S.; Park, H.-J. Prediction of Warmed-over Flavour Development in Cooked Chicken by Colorimetric Sensor Array. Food Chem 2016, 211, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, R.; Bi, Y.; Qu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L. Identification of Frozen/Thawed Beef Based on Label-Free Detection of Hemin (Iron Porphyrin) with Solution-Gated Graphene Transistor Sensors. Sens Actuators B Chem 2020, 305, 127167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Moon, D.; An, J.E.; Park, S.J.; Seo, S.E.; Ha, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Phyo, S.; Lee, J.; et al. Wireless Portable Bioelectronic Nose Device for Multiplex Monitoring toward Food Freshness/Spoilage. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 215, 114551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, C.S.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.; Seo, S.E.; An, J.E.; Ha, S.; Bae, J.; Phyo, S.; Lee, J.; et al. In-Situ Food Spoilage Monitoring Using a Wireless Chemical Receptor-Conjugated Graphene Electronic Nose. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 200, 113908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biosensor Technology to Detect Chemical Contamination in Food. In <i>Advanced Food Analysis, Tools</i>; Kobun, R. (Eds.) Biosensor Technology to Detect Chemical Contamination in Food. In Advanced Food Analysis Tools; Kobun, R., Ed.; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 127–146.
- Flauzino, J.M.R.; Nguyen, E.P.; Yang, Q.; Rosati, G.; Panáček, D.; Brito-Madurro, A.G.; Madurro, J.M.; Bakandritsos, A.; Otyepka, M.; Merkoçi, A. Label-Free and Reagentless Electrochemical Genosensor Based on Graphene Acid for Meat Adulteration Detection. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 195, 113628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fengou, L.-C.; Lianou, A.; Tsakanikas, P.; Mohareb, F.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Detection of Meat Adulteration Using Spectroscopy-Based Sensors. Foods 2021, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, D.; Rao, R. DNA Markers for Food Products Authentication. Diversity (Basel) 2014, 6, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- aKhalil, I.; Yehye, W.A.; Muhd Julkapli, N.; Sina, A.A.I.; Rahmati, S.; Basirun, W.J.; Seyfoddin, A. Dual Platform Based Sandwich Assay Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering DNA Biosensor for the Sensitive Detection of Food Adulteration. Analyst 2020, 145, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-Based Biosensors for Portable Food Evaluation. Curr Opin Food Sci 2019, 28, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S. Advancements in Food Quality Monitoring: Integrating Biosensors for Precision Detection. Sustainable Food Technology 2024, 2, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Blagojevic, B.; Maurer, P.; Hengl, B.; Guldimann, C.; Mojsova, S.; Sakaridis, I.; Antunovic, B.; Gomes-Neves, E.; Zdolec, N.; et al. Risk Based Meat Safety Assurance System – An Introduction to Key Concepts for Future Training of Official Veterinarians. Food Control 2023, 146, 109552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasijević, I.; Vesković-Moračanin, S. Digitalization in the Meat Chain. Acta agriculturae Serbica 2021, 26, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, H. Recent Advances and Trends in Aptasensors for Sensitive Detection of Foodborne Pathogens in Various Foods. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2023, 167, 117268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulahoum, H.; Ghorbanizamani, F. The LOD Paradox: When Lower Isn’t Always Better in Biosensor Research and Development. Biosens Bioelectron 2024, 264, 116670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rani, K. ; Ambika; Singh, S.; Singh, Y. Cost-Effectiveness, Reliability, Selectivity, and Sensitivity of Biosensors for Foodborne Pathogens. In Biosensors for Foodborne Pathogens Detection; Elsevier, 2024; pp. 247–263.
- Karim, M.E. Biosensors: Ethical, Regulatory, and Legal Issues. Handbook of Cell Biosensors.

| Biosensor | Applicability in the meat production chain |
Reference | |||
| F | S | MP | R | ||
| Stress detection sensors (hormones) | x | [2]; [155] | |||
| Breath sensors (VOCs for detection of metabolic and pathological processes) |
x | ||||
| Perspiration sensors (metabolites in sweat) | x | ||||
| Tears sensor (glucose monitoring) | x | ||||
| Salivary sensor (uric acid - metabolic syndrome, renal syndrome, and abnormalities in purine metabolism) | x | ||||
| Progesterone sensor (detection of ovulation) | x | ||||
| Food and feed sensors (dietary inputs/nutrition, bioactive compounds, microbiological and chemical contamination) | x | ||||
| Infectious diseases detection sensors (BRD, AIV, FMD, BVD, PRRSV, Avian Influenza, mastitis) | x | ||||
| Sensor for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in dairy calves | x | (89) | |||
| Sensor for monitoring of stress and animal welfare (hormonal levels) in pigs` blood | x | x | (92) | ||
| Glucocorticoid sensor (saliva, excreta, fecal samples, milk, hair/feathers and eggs) | x | (93) | |||
| Sensors for inflammatory markers (acute phase proteins) | x | x | (102); (5); (92); (109); (106); (107) | ||
| Sensors for metabolic markers (breath, blood, faeces, skin, urine and vaginal fluids) | x | x | (115); (111); (112); (113); (114); (118); (116); (117); (110); | ||
| Sensors for infectious diseases detection Bovine. BRD (serum), BVD (serum; LOD of 103 CCID/ml), EBL, FMD, bovine mycoplasma, mastitis (Hp in serum), Campylobacter in dairy cattle (LOD of 3 CFU/ml) Pigs. AFSV, PRRSV, SIV, PCVAD |
x x |
(119); (123); (125); (127); (128); (131); (132); |
|||
|
Poultry. H5N1 (LOD of 103 EID50/ml), Clostridium perfringens (LOD of 0.26 - 0.27 lg/CFU), audio-based sensor detection system (Newcastle Disease, Infectious Bronchitis, Infectious Laryngotracheitis, AI, MG, CRD, infectious sinusitis, mycoplasmosis), antibiotic residues Early disease detection *WBE |
x x |
(103); (134); (135); (136); (163) |
|||
| Sensors for monitoring reproductive health Hormonal levels (progesterone and estrogen in milk, urine, feces) in dairy herds Estrus detection Sperm quality (in livestock) |
x x x |
(138); (141); (139); (140); (149); (150); (151) (152); (153); (154); |
|||
| Animal welfare monitoring sensors Behavioral, physiological and nutrition status Animal Intersticial Fluid (ISF) Saliva |
x x |
(154); (156); (159); (160) |
|||
| Transport and Handling Stress Monitoring |
x | (155); (156); (157); (158); (159); (160); (161) | |||
| Pre-slaughter welfare assessment | x | (93); (162); | |||
| Slaughterhouse and meat processing Post-slaughter indicators (animal health, animal welfare) Pathogen detection (Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shiga toxin- producing E. coli (STEC), Listeria monocytogenes; viruses) Antibiotic residues AMR Pesticides Growth promoters Dioxins |
x x |
x x x x x x x |
x x x x x x |
x x x x x x |
(92); (164); (165); (166); (167); (168); (169); (170); (171); (172); (173); (174); (175); (176); (177); (178); (179); (180); (181); (182); (183); (194); (195); (196); (184); (185); (186); (187); (188); |
| Mycotoxins Meat quality traits Freshness and spoilage (purine derivatives, ammonia, VOCs) Sensory and nutritional attributes (color, texture, visible fat, aroma, flavor) |
x | x x x |
x x x |
(191); (192); (198); (199); (200); (201); (202): (203); (204); (205); (206); (207); (208); |
|
| Food fraud Food adulteration Species and origin authentication |
x x |
x x |
(209); (210); (211); (212); (213); (214); |
||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





