Submitted:
21 January 2025
Posted:
22 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
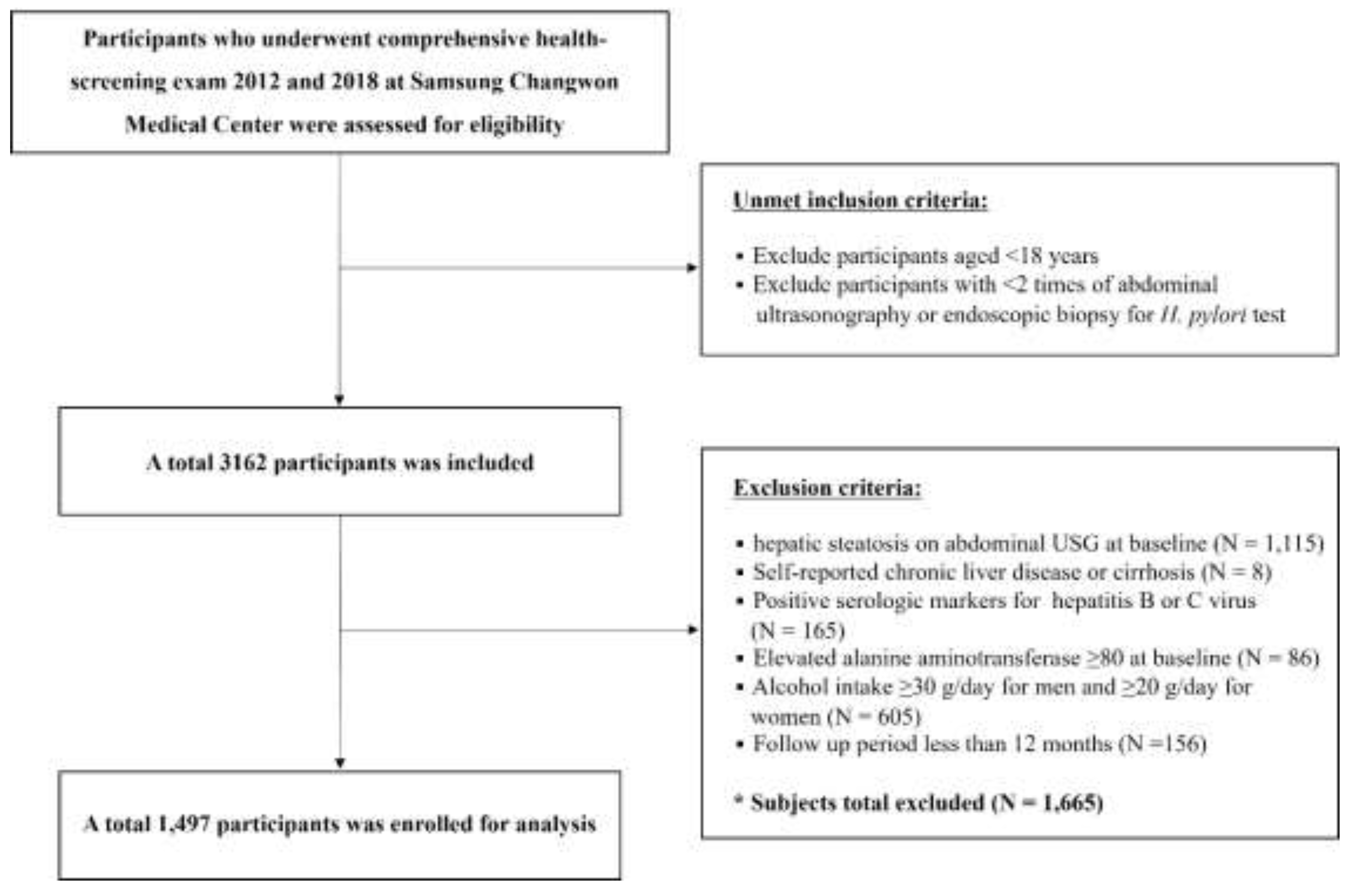
2.1. Database
2.2. Data Collection and Variables
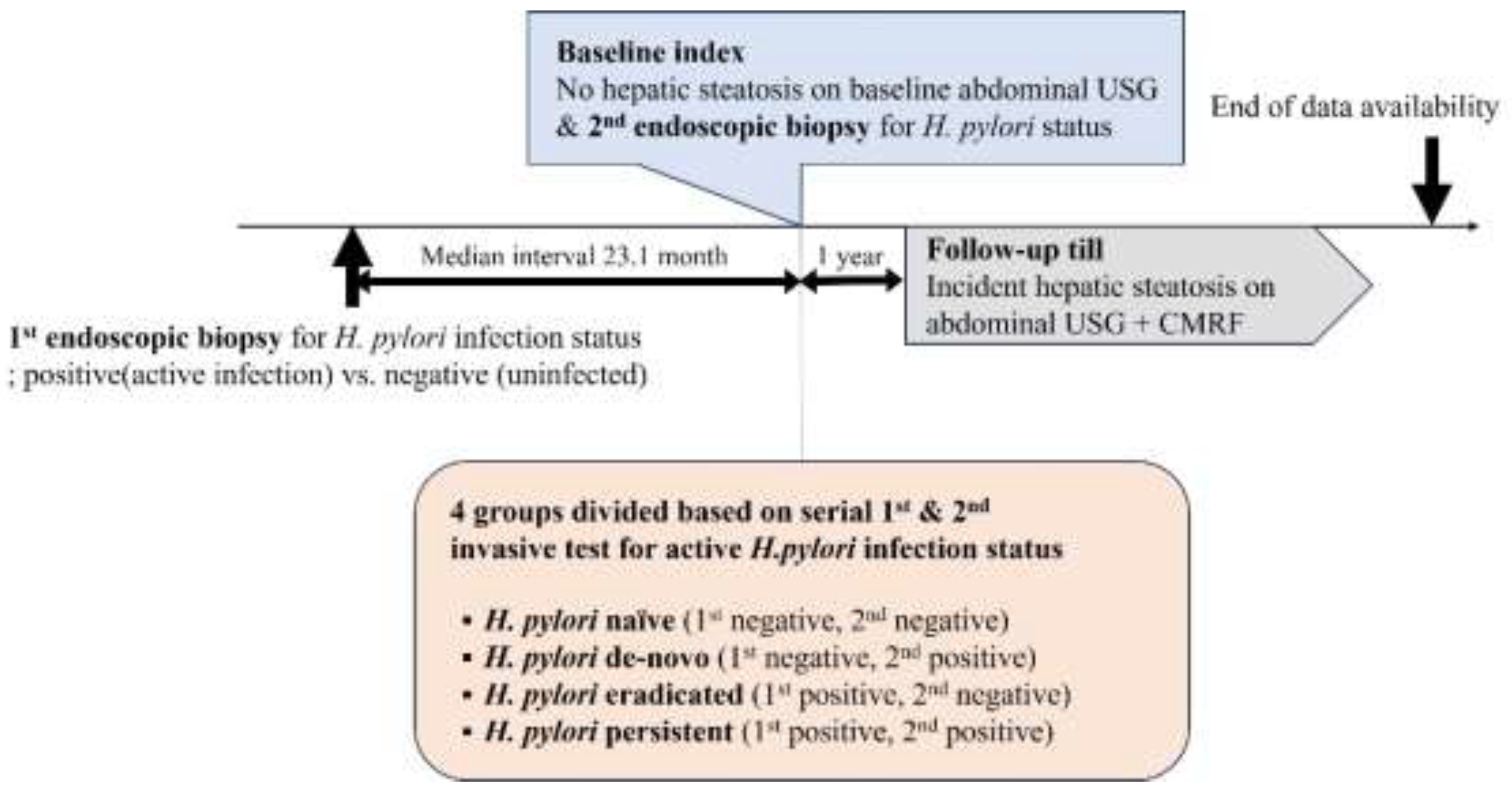
2.3. H. Pylori Diagnosis and Definition of Active H. pylori Infection Status
2.4. Definition of MASLD Development
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics of the Study Cohort
3.2. Factors Associated with MASLD Development
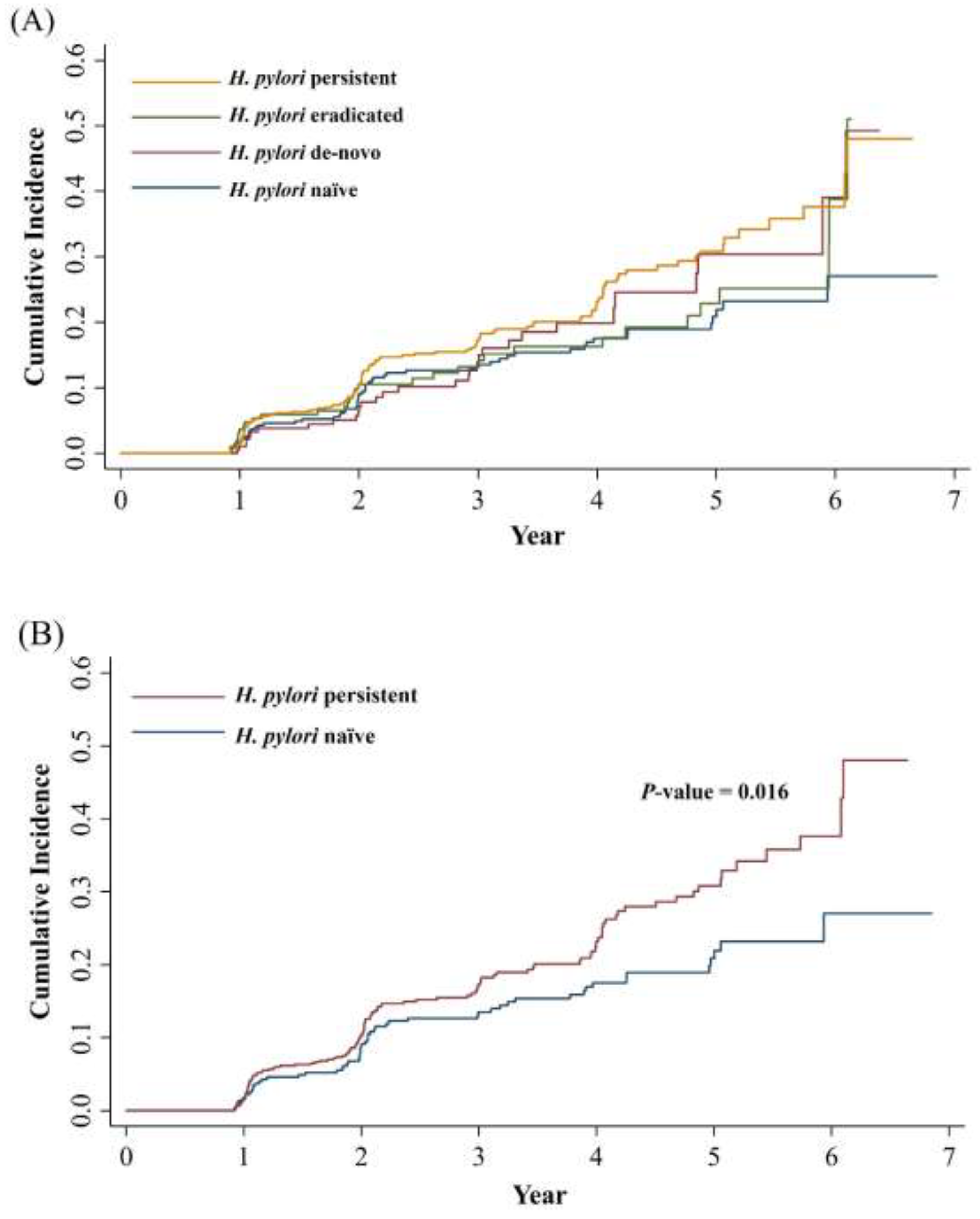
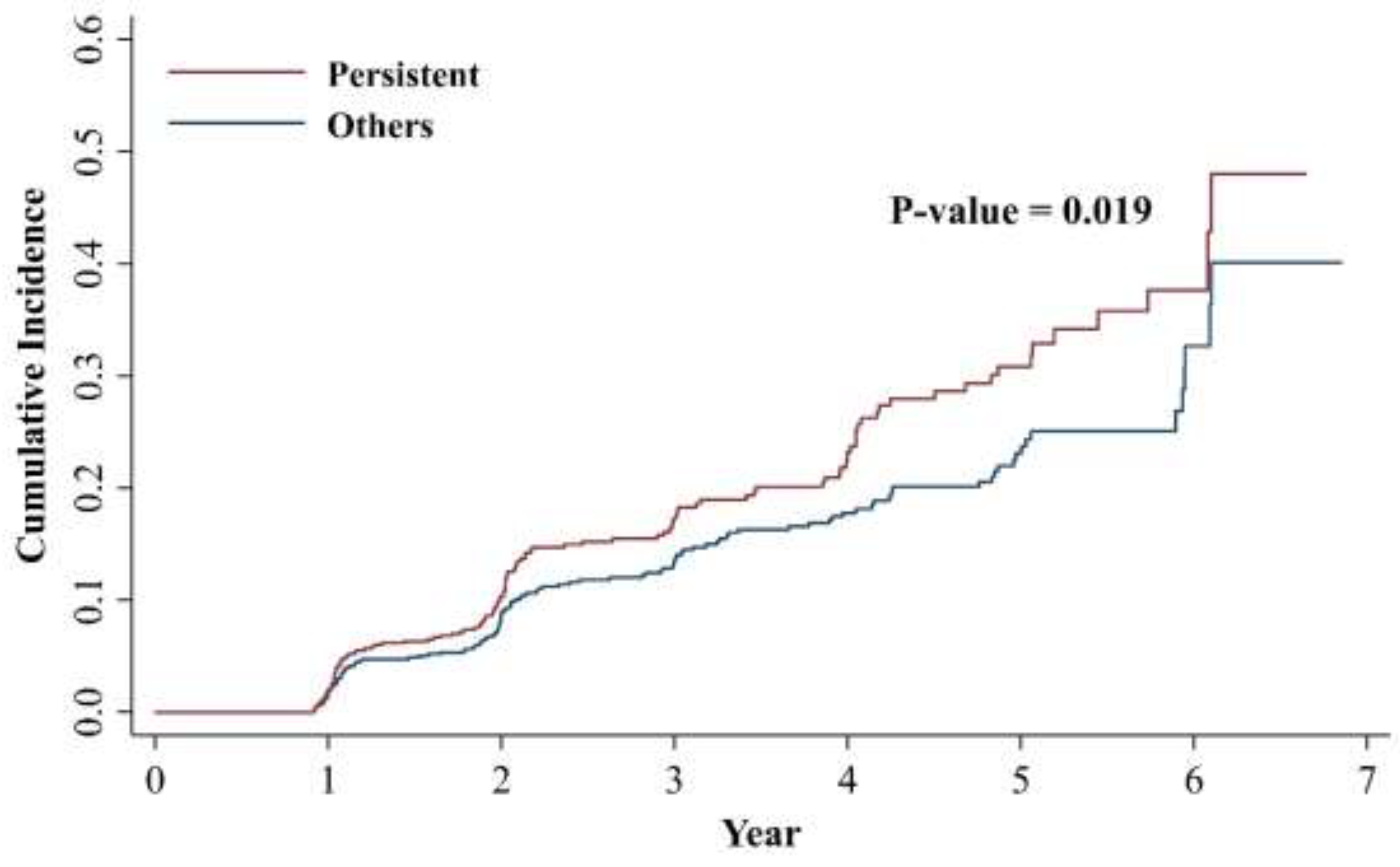
3.3. Active H. pylori Infection Status and the Development of MASLD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coelho, L.G.V.; Marinho, J.R.; Genta, R.; Ribeiro, L.T.; Passos, M.; Zaterka, S.; Assumpcao, P.P.; Barbosa, A.J.A.; Barbuti, R.; Braga, L.L.; et al. Ivth Brazilian Consensus Conference on Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Arq Gastroenterol 2018, 55, 97–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everhart, J.E. Recent developments in the epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2000, 29, 559–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leja, M.; Grinberga-Derica, I.; Bilgilier, C.; Steininger, C. Review: Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2019, 24 Suppl 1, e12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.L.C.; de Brito, B.B.; da Silva, F.A.F.; Sampaio, M.M.; Marques, H.S.; Oliveira, E.S.N.; de Magalhaes Queiroz, D.M.; de Melo, F.F. Helicobacter pylori infection: Beyond gastric manifestations. World J Gastroenterol 2020, 26, 4076–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenova, I.; Durazzo, M. Transmission of Helicobacter pylori. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 2018, 64, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Shi, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection Increase the Risk of Myocardial Infarction: A Meta-Analysis of 26 Studies Involving more than 20,000 Participants. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis of 39 studies involving more than 20,000 participants. Scand J Infect Dis 2013, 45, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunji, T.; Matsuhashi, N.; Sato, H.; Fujibayashi, K.; Okumura, M.; Sasabe, N.; Urabe, A. Helicobacter pylori infection is significantly associated with metabolic syndrome in the Japanese population. Am J Gastroenterol 2008, 103, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Ann Hepatol 2024, 29, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Sookoian, S. From NAFLD to MASLD: updated naming and diagnosis criteria for fatty liver disease. J Lipid Res 2024, 65, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Vessby, J.; Ekstedt, M.; Shang, Y. 99% of patients with NAFLD meet MASLD criteria and natural history is therefore identical. J Hepatol 2024, 80, e76–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Sinn, D.H.; Min, Y.W.; Son, H.J.; Kim, J.J.; Chang, Y.; Baek, S.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, H.; Ryu, S. A cohort study on Helicobacter pylori infection associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol 2017, 52, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Tong, Y.L.; Wu, L.Y.; Yu, X.Y. Helicobacter pylori infection eradication for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 19530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, Q.; He, Y.; Shi, W.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Lin, Q.; Li, B.; Ye, L.; Min, Y.; et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e17781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Lando, M.G.; Borella, N.; Scoccia, E.; Pecoraro, B.; Gobbi, F.; Bisoffi, Z.; Valenti, L.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: An updated meta-analysis. Liver Int 2024, 44, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okushin, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamamichi, N.; Shimamoto, T.; Enooku, K.; Fujinaga, H.; Tsutsumi, T.; Shintani, Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Ono, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is not associated with fatty liver disease including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a large-scale cross-sectional study in Japan. BMC Gastroenterol 2015, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeg, M.K.; Yoon, S.K.; Ko, S.H.; Noh, Y.S.; Lee, I.S.; Choi, M.G. Helicobacter pylori infection is not associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016, 22, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, N.; Peng, L.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y. Helicobacter pylori Infection Is Not Associated with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernly, S.; Wernly, B.; Semmler, G.; Völkerer, A.; Rezar, R.; Semmler, L.; Stickel, F.; Aigner, E.; Niederseer, D.; Datz, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not independently associated with Helicobacter pylori in a central European screening cohort. Minerva Med 2022, 113, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, E.S.; Shim, J.S.; Kim, S.E.; Bae, J.H.; Kang, S.; Won, J.C.; Shin, M.J.; Jin, H.Y.; Moon, J.; Lee, H.; et al. Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022. Diabetes Metab J 2023, 47, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.-y.; Ahn, J.Y. Endoscopic Features According to Helicobacter pylori Infection Status. The Korean Journal of Medicine 2023, 98, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Soares Monteiro, L.B. Ultrasound-based techniques for the diagnosis of liver steatosis. World J Gastroenterol 2019, 25, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, K.; Yousefi, M.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Lotfi, P.; Sheydaee, F.; Raei, M.; Vahdatinia, A.; Hessami, A.; Rafati, S.; Moosazadeh, M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Turk J Gastroenterol 2022, 33, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.G.; Yang, H.J.; Xu, W.; Wang, K.; Guo, P.; Ai, Y.W. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Turino, T.; Altomari, A.; Lonardo, A.; Zoppini, G.; Valenti, L.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An updated meta-analysis. Metabolism 2019, 96, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulberis, M.; Srivastava, S.; Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Klukowska-Rotzler, J.; Blank, A.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Srivastava, D.S. Active Helicobacter pylori Infection is Independently Associated with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. J Clin Med 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.Y.; Hu, K.C.; Liu, C.J.; Hung, C.L.; Bair, M.J.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Wu, M.S.; Shih, S.C.; Liu, C.C. Helicobacter pylori infection combined with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease increase the risk of atherosclerosis: Focus in carotid artery plaque. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e14672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecube, A.; Valladares, S.; López-Cano, C.; Gutiérrez, L.; Ciudin, A.; Fort, J.M.; Reñé, J.M.; Matias-Guiu, X.; de Torres, I.; Bueno, M.; et al. The Role of Morbid Obesity in the Promotion of Metabolic Disruptions and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Helicobacter Pylori. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0166741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Mascianà, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaté, J.M.; Jouët, P.; Harnois, F.; Mechler, C.; Msika, S.; Grossin, M.; Coffin, B. High prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with morbid obesity: a contributor to severe hepatic steatosis. Obes Surg 2008, 18, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C.; Deretzi, G. The association between Helicobacter pylori infection and insulin resistance: a systematic review. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waluga, M.; Kukla, M.; Żorniak, M.; Bacik, A.; Kotulski, R. From the stomach to other organs: Helicobacter pylori and the liver. World J Hepatol 2015, 7, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J. Novel Advances in the Association Between Helicobacter pylori Infection, Metabolic Syndrome, and Related Morbidity. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.W.; Kwon, H.T.; Kang, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.C.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.M.; Son, K.Y.; Cho, B. Association between metabolic syndrome and Helicobacter pylori infection diagnosed by histologic status and serological status. J Clin Gastroenterol 2012, 46, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upala, S.; Jaruvongvanich, V.; Riangwiwat, T.; Jaruvongvanich, S.; Sanguankeo, A. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dig Dis 2016, 17, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.; Rinella, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernaez, R.; Lazo, M.; Bonekamp, S.; Kamel, I.; Brancati, F.L.; Guallar, E.; Clark, J.M. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: a meta-analysis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 1,497) |
H. pylori naïve (n = 365) |
H. pylori de-novo (n = 203) |
H. pylori eradicated (n = 199) |
H. pylori persistent (n = 730) |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 46.71 ± 7.17 | 48.85 ± 7.67 | 47.83 ± 7.14 | 46.72 ± 7.29 | 45.32 ± 6.56 | <0.001 |
| Male (%) | 956 (63.9) | 218 (59.7) | 133 (65.5) | 133 (66.8) | 472 (64.7) | 0.272 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.14 ± 2.55 | 23.02 ± 2.42 | 23.18 ± 2.58 | 23.14 ± 2.40 | 23.20 ± 2.65 | 0.740 |
| <18.5 | 44 (2.94) | 10 (2.74) | 5 (2.46) | 5 (2.51) | 24 (3.29) | |
| 18.5-24.9 | 1110 (74.15) | 278 (76.16) | 145 (71.43) | 150 (75.38) | 537 (73.56) | |
| 25-29.9 | 305 (20.37) | 66 (18.08) | 46 (22.66) | 43 (21.61) | 150 (20.55) | |
| ≥30 | 17 (1.14) | 6 (1.64) | 1 (0.49) | 0 (0.00) | 10 (1.37) | |
| Smoking | 0.296 | |||||
| Never smoker | 533 (35.60) | 125 (34.25) | 68 (33.50) | 77 (38.69) | 263 (36.03) | |
| Current(<1pack/day) | 428 (28.59) | 97 (26.58) | 59 (29.06) | 56 (28.14) | 216 (29.59) | |
| Current(≥1pack/day) | 268 (17.90) | 59 (16.16) | 38 (18.72) | 37 (18.59) | 134 (18.36) | |
| Alcohol | 0.085 | |||||
| Mild (10g/day) | 442 (29.53) | 116 (31.78) | 53 (26.11) | 55 (27.64) | 218 (29.86) | |
| Modest (10g/day) | 690 (46.09) | 151 (41.37) | 89 (43.84) | 103 (51.76) | 347 (47.53) | |
| Regular exercise | 229 (19.97) | 74 (20.27) | 34 (16.75) | 44 (22.11) | 147 (20.14) | 0.021 |
| hsCRP (mg/dl) | 1.02 ± 3.29 | 0.96 ± 2.28 | 1.47 ± 5.72 | 1.02 ± 2.19 | 0.93 ± 3.04 | 0.222 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 116.66 ± 11.38 | 116.31 ± 11.65 | 118.79 ± 11.58 | 117.94 ± 10.98 | 115.90 ± 11.22 | 0.005 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl) | 89.46 ± 14.74 | 89.46 ± 11.69 | 89.58 ± 21.77 | 89.97 ± 18.96 | 89.28 ± 12.22 | 0.950 |
| AST (U/I) | 22.11 ± 8.37 | 23.30 ± 9.16 | 22.34 ± 8.73 | 22.98 ± 9.46 | 21.21 ± 7.41 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/I) | 20.29 ± 10.37 | 20.61 ± 10.46 | 20.79 ± 10.40 | 20.87 ± 10.96 | 19.83 ± 10.14 | 0.411 |
| GGT (U/I) | 26.55 ± 28.65 | 24.57 ± 22.89 | 27.71 ± 28.58 | 24.68 ± 21.93 | 27.74 ± 32.58 | 0.247 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 27.5 | 26.8 | 29.1 | 25.1 | 28.1 | 0.798 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.94 ± 0.61 | 0.92 ± 0.57 | 0.92 ± 0.66 | 0.95 ± 0.59 | 0.95 ± 0.62 | 0.925 |
| MASLD (%) | 247 (16.5) | 57 (15.6) | 31 (15.3) | 32 (16.1) | 127 (17.4) | |
| Follow up (month) | 31.1 (12, 83.3) | 39.0 (12, 83.3) | 33.8 (12, 77.5) | 31.9 (12, 74.6) | 25.5 (12, 80.8) | |
| Interval between serial biopsy (months) | 23.1 (5.0, 77.5) | 21.6 (5.0, 73.1) | 24.6 (7.4, 70.3) | 22.4 (5.2, 73.7) | 23.2 (5.8, 77.5) |
| Univariable analysis | Multivariable analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-value | HR (95% CI) | p-value | |||
| Age | 1.02 (1.00, 1.04) | 0.019 | 1.02 (1.00, 1.04) | 0.033 | ||
| Male sex | 3.00 (2.14, 4.21) | <0.001 | 1.89 (1.18, 3.01) | 0.008 | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ||||||
| <18.5 | - | - | ||||
| 18.5-24.9 | reference | Reference | ||||
| 25-29.9 | 2.87 (2.20, 3.74) | <0.001 | 1.99 (1.49, 2.66) | <0.001 | ||
| ≥30 | 6.70 (3.52, 12.75) | <0.001 | 6.48 (3.31, 12.69) | <0.001 | ||
| Smoking | ||||||
| Never smoker | reference | Reference | ||||
| Current(<1pack/day) | 2.50 (1.76, 3.56) | <0.001 | 1.40 (0.92, 2.13) | 0.115 | ||
| Current(≥1pack/day) | 2.47 (1.67, 3.65) | <0.001 | 1.17 (0.75, 1.84) | 0.487 | ||
| Alcohol | ||||||
| Mild (10g/day) | reference | Reference | ||||
| Modest (10g/day) | 1.64 (1.19, 2.26) | 0.002 | 0.91 (0.64, 1.29) | 0.598 | ||
| Regular exercise | 0.84 (0.61, 1.17) | 0.315 | 0.83 (0.59, 1.17) | 0.288 | ||
| hsCRP (mg/dl) | 1.02 (1.00, 1.05) | 0.074 | ||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 1.02 (1.01, 1.03) | 0.001 | 1.00 (0.99, 1.01) | 0.726 | ||
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl) | 1.01 (1.01, 1.02) | <0.001 | 1.01 (1.00, 1.01) | 0.022 | ||
| AST (U/I) | 1.02 (1.01, 1.04) | <0.001 | 0.99 (0.97, 1.01) | 0.406 | ||
| ALT (U/I) | 1.04 (1.03, 1.05) | <0.001 | 1.02 (1.01, 1.04) | 0.004 | ||
| GGT (U/I) | 1.01 (1.01, 1.01) | <0.001 | 1.01 (1.00, 1.01) | 0.003 | ||
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 2.23 (1.73, 2.86) | <0.001 | 1.51 (1.15, 1.97) | 0.003 | ||
| H. pylori activity status | ||||||
| H. pylori naïve | reference | Reference | ||||
| H. pylori de-novo | 1.21 (0.78, 1.88) | 0.388 | 1.04 (0.65, 1.65) | 0.884 | ||
| H. pylori Eradicated | 1.18 (0.77, 1.82) | 0.446 | 1.18 (0.75, 1.85) | 0.472 | ||
| H. pylori Persistent | 1.48 (1.08, 2.02) | 0.015 | 1.41 (1.01, 1.96) | 0.045 | ||
| Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-value | HR (95% CI) | p-value | HR (95% CI) | p-value | HR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Active H. pylori infection status divided by 4 groups | ||||||||
| Naïve (-/-) | Reference | Reference | Reference | reference | ||||
| De-novo (-/+) | 1.21 (0.78, 1.88) | 0.388 | 1.13 (0.73, 1.76) | 0.573 | 1.11 (0.70, 1.76) | 0.659 | 1.04 (0.65, 1.65) | 0.884 |
| Eradicated (+/-) | 1.18 (0.77, 1.82) | 0.446 | 1.16 (0.75, 1.79) | 0.516 | 1.13 (0.72, 1.76) | 0.596 | 1.18 (0.75, 1.85) | 0.472 |
| Persistent (+/+) | 1.48 (1.08, 2.02) | 0.015 | 1.48 (1.07, 2.04) | 0.017 | 1.39 (1.00, 1.92) | 0.051 | 1.41 (1.01, 1.96) | 0.045 |
| Last active H. pylori infection (Baseline H. pylori activity) | ||||||||
| H. pylori (-) | Reference | Reference | Reference | reference | ||||
| H. pylori (+) | 1.34 (1.03, 1.74) | 0.029 | 1.32 (1.02, 1.73) | 0.038 | 1.27 (0.97, 1.66) | 0.086 | 1.24 (0.94, 1.63) | 0.122 |
| Persistently active H. pylori infection | ||||||||
| Others | Reference | Reference | Reference | reference | ||||
| Persistent | 1.35 (1.05, 1.73) | 0.019 | 1.38 (1.07, 1.78) | 0.014 | 1.31 (1.01, 1.69) | 0.043 | 1.33 (1.02, 1.73) | 0.033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





