Submitted:
18 January 2025
Posted:
20 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
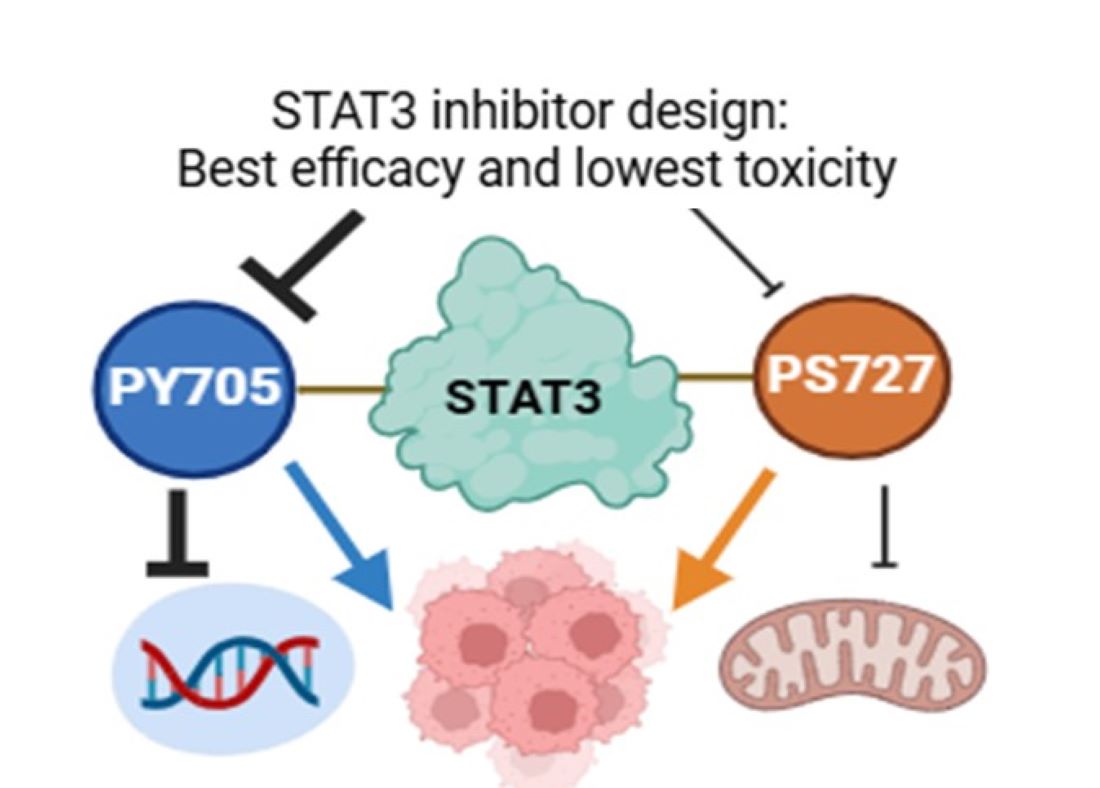
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. STAT3 Signaling Mechanisms
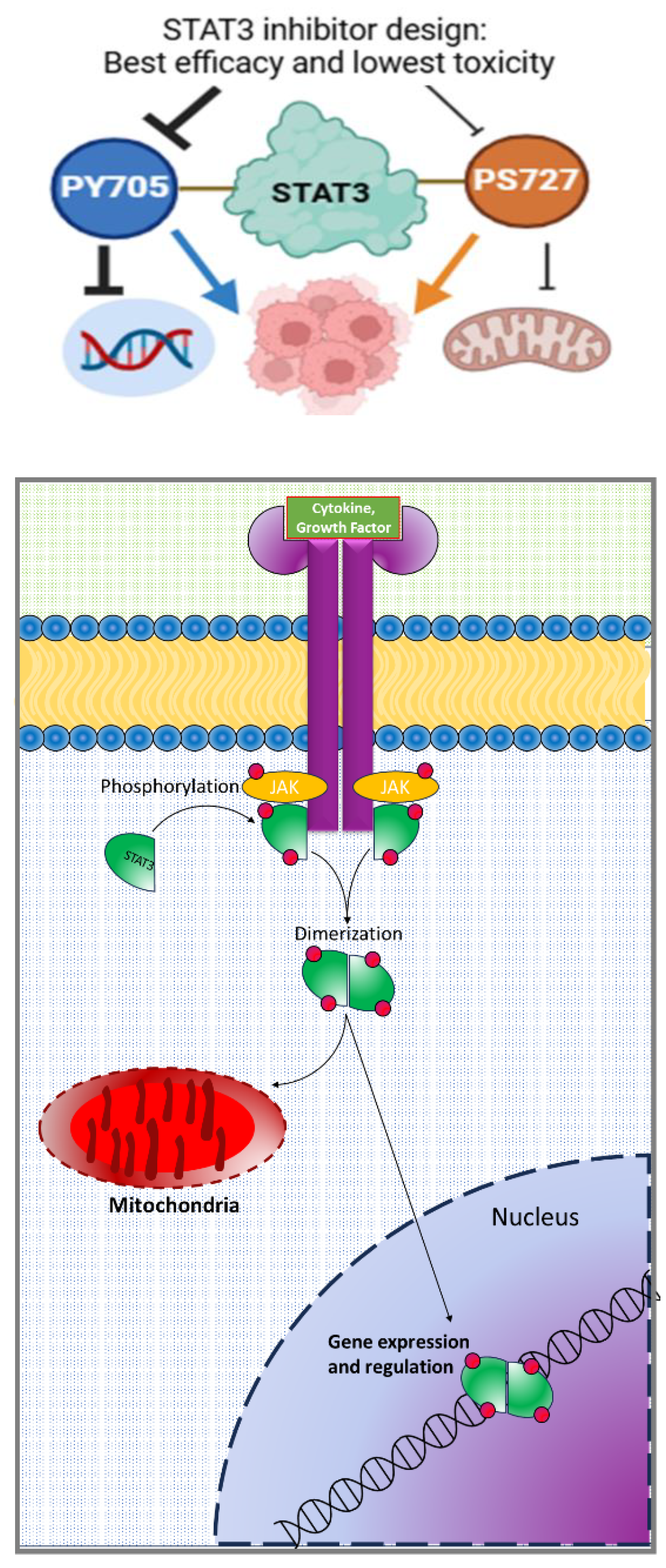
2.1. Canonical STAT3 Signaling and the Role of Y705 Phosphorylation
2.2. Noncanonical STAT3 Signaling and the Role of S727 Phosphorylation
2.3. Interplay Between pY705 and pS727 in Cancer
3. Clinical Relevance of STAT3 in Cancer and Rational for Therapeutic Development
3.1. STAT3 Hyperactivation in Various Cancers Is Associated with Poor Prognosis
3.2. Rationale for Targeting STAT3 in Cancer
4. Evaluation of STAT3 Inhibitors of Y705 and/or S727 in Clinical Development
5. Comparative Analysis: Targeting Y705 vs. S727 in STAT3 Inhibitor Design
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EMT | Epithelieal-to-mesenchymal transition |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| EMT | Epithelieal-to-mesenchymal transition |
References
- Huang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Dong, H.; Zheng, Q.; Shi, S.; Zhu, K.; Qu, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Revisiting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) as an Anticancer Target and Its Inhibitor Discovery: Where Are We and Where Should We Go? European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 187, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Zhang, C.; Martincuks, A.; Herrmann, A.; Yu, H. STAT Proteins in Cancer: Orchestration of Metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 2023, 23, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, K.; Resat, H. Constitutive Activation of STAT3 in Breast Cancer Cells: A Review: Constitutive STAT3 Activation in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinakar, Y.H.; Kumar, H.; Mudavath, S.L.; Jain, R.; Ajmeer, R.; Jain, V. Role of STAT3 in the Initiation, Progression, Proliferation and Metastasis of Breast Cancer and Strategies to Deliver JAK and STAT3 Inhibitors. Life Sciences 2022, 309, 120996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.-D. STAT3 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibi, T.; Babaloo, Z.; Hosseini, A.; Abdollahpour-alitappeh, M.; Hashemi, V.; Marofi, F.; Nejati, K.; Baradaran, B. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases. European Journal of Pharmacology 2020, 878, 173107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Noguchi, K.; Shi, W.; Tanaka, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Yoshida, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Targeted Disruption of the Mouse Stat3 Gene Leads to Early Embryonic Lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997, 94, 3801–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Robinson, P.; Tweardy, D.J. Targeting Janus Kinases and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 to Treat Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cancer: Rationale, Progress, and Caution. Pharmacol Rev 2020, 72, 486–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-Q.; Man, Q.-W.; Huo, F.-Y.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Li, S.-R.; Wang, J.; Su, F.-C.; Cai, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. STAT3 Pathway in Cancers: Past, Present, and Future. MedComm 2022, 3, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-C.; Shi, L.-H.; Wang, X.-J.; Wang, S.-X.; Wan, X.-Q.; Liu, S.-R.; Wang, Y.-F.; Lu, Z.; Wang, L.-H.; Ding, Y. Stat3/Oct-4/c-Myc Signal Circuit for Regulating Stemness-Mediated Doxorubicin Resistance of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells and Inhibitory Effects of WP1066. Int J Oncol 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Role of STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer. Cell Commun Signal 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, D.J.; Koetz, L.; Levy, D.E. The MEK-ERK Pathway Is Necessary for Serine Phosphorylation of Mitochondrial STAT3 and Ras-Mediated Transformation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Schwartz, D.M.; Villarino, A.V.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT Pathway: Impact on Human Disease and Therapeutic Intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.A.; Grandis, J.R. STAT3 SIGNALING: Anticancer Strategies and Challenges. Mol Interv 2011, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, S.; Malhotra, R.; Shet, T.; Mokal, S.; Gupta, S.; De, A. Noncanonical pS727 Post Translational Modification Dictates Major STAT3 Activation and Downstream Functions in Breast Cancer. Experimental Cell Research 2020, 396, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, J.; Campoy, I.; Durán, M.; Nemours, S.; Areny, A.; Vall-Palomar, M.; Martínez, C.; Cantero-Recasens, G.; Meseguer, A. STAT3 Phosphorylation at Serine 727 Activates Specific Genetic Programs and Promotes Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) Aggressiveness. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 19552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, M.; Dinarello, A.; Meneghetti, G.; Martorano, L.; Betto, R.M.; Facchinello, N.; Tesoriere, A.; Tiso, N.; Martello, G.; Argenton, F. Y705 and S727 Are Required for the Mitochondrial Import and Transcriptional Activities of STAT3, and for Regulation of Stem Cell Proliferation. Development 2021, 148, dev199477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Deng, L.; Shi, S.; Huang, Q.; Ou-Yang, S.; Mo, J.; Zhu, K.; Qu, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. The Novel STAT3 Inhibitor WZ-2-033 Causes Regression of Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Gastric Cancer Xenografts. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022, 43, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.L.; Soo, R.A.; Tan, D.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lim, J.S.; Marban, P.C.; Kong, L.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Thuya, W.L.; et al. Phase I and Biomarker Study of OPB-51602, a Novel Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) 3 Inhibitor, in Patients with Refractory Solid Malignancies. Annals of Oncology 2015, 26, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Guan, X.; Qin, J.-J. Inhibiting STAT3 Signaling Pathway by Natural Products for Cancer Prevention and Therapy: In Vitro and in Vivo Activity and Mechanisms of Action. Pharmacological Research 2022, 182, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beebe, J.D.; Liu, J.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T. Two Decades of Research in Discovery of Anticancer Drugs Targeting STAT3, How Close Are We? Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2018, 191, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genini, D.; Brambilla, L.; Laurini, E.; Merulla, J.; Civenni, G.; Pandit, S.; D’Antuono, R.; Perez, L.; Levy, D.E.; Pricl, S.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by a SH2 Domain-Targeting STAT3 Inhibitor Leads to Metabolic Synthetic Lethality in Cancer Cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2017, 114, E4924–E4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 Signalling in Cancer: New and Unexpected Biological Functions. Nat Rev Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stat3: A STAT Family Member Activated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Response to Epidermal Growth Factor and Interleukin-6 | Science Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.8140422 (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Agashe, R.P.; Lippman, S.M.; Kurzrock, R. JAK: Not Just Another Kinase. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2022, 21, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putoczki, T.L.; Thiem, S.; Loving, A.; Busuttil, R.A.; Wilson, N.J.; Ziegler, P.K.; Nguyen, P.M.; Preaudet, A.; Farid, R.; Edwards, K.M.; et al. Interleukin-11 Is the Dominant IL-6 Family Cytokine during Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis and Can Be Targeted Therapeutically. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The Molecular Details of Cytokine Signaling via the JAK/STAT Pathway. Protein Sci 2018, 27, 1984–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Diab, I.; Zhang, X.; Izmailova, E.S.; Zehner, Z.E. Stat3 Enhances Vimentin Gene Expression by Binding to the Antisilencer Element and Interacting with the Repressor Protein, ZBP-89. Oncogene 2004, 23, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Lo, H.-W. STAT3 Target Genes Relevant to Human Cancers. Cancers 2014, 6, 897–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Byun, W.S.; Lee, S.; Han, Y.T.; Jeong, Y.-S.; Jang, K.; Chung, S.-J.; Lee, J.; Suh, Y.-G.; Lee, S.K. A Novel Small Molecule STAT3 Inhibitor SLSI-1216 Suppresses Proliferation and Tumor Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through Apoptotic Induction. Biochemical Pharmacology 2020, 178, 114053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garama, D.J.; White, C.L.; Balic, J.J.; Gough, D.J. Mitochondrial STAT3: Powering up a Potent Factor. Cytokine 2016, 87, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberti, M.V.; Locasale, J.W. The Warburg Effect: How Does It Benefit Cancer Cells? Trends in biochemical sciences 2016, 41, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Darnell, J.E. Maximal Activation of Transcription by Statl and Stat3 Requires Both Tyrosine and Serine Phosphorylation. Cell 1995, 82, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, D.J.; Corlett, A.; Schlessinger, K.; Wegrzyn, J.; Larner, A.C.; Levy, D.E. Mitochondrial STAT3 Supports Ras-Dependent Oncogenic Transformation. Science 2009, 324, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Weng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Zhu, T. PKCι Induces Differential Phosphorylation of STAT3 to Modify STAT3-Related Signaling Pathways in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. J Cell Commun Signal 2023, 17, 1417–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Dong, H.; Zheng, Q.; Shi, S.; Zhu, K.; Qu, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Revisiting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) as an Anticancer Target and Its Inhibitor Discovery: Where Are We and Where Should We Go? European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 187, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, W.S.; Bae, E.S.; Cui, J.; Park, H.J.; Oh, D.-C.; Lee, S.K. Antitumor Activity of Pulvomycin via Targeting Activated-STAT3 Signaling in Docetaxel-Resistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, E.; Pennel, K.; Hatthakarnkul, P.; Leslie, H.; Mallon, E.; Andersen, D.; Jamieson, N.; McMillan, D.; Roseweir, A.; Edwards, J. High Expression of STAT3 within the Tumour-Associated Stroma Predicts Poor Outcome in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancer Medicine 2023, 12, 13225–13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X. STAT3: Key Targets of Growth-Promoting Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell International 2024, 24, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, K. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Enhance Metastatic Potential of Lung Cancer Cells through IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 76116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parakh, S.; Ernst, M.; Poh, A.R. Multicellular Effects of STAT3 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Patel, M.; Ruzevick, J.; Jackson, C.M.; Lim, M. STAT3 Activation in Glioblastoma: Biochemical and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2014, 6, 376–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Hou, X.; Dong, L.; Hou, W. Roles of STAT3 in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Glioblastoma. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11, 1098482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Li, S.-Y.; Gong, H.-Z.; Wang, L.-X.; Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Gu, N. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Roles of STAT3 and Its Phosphorylation in Glioma. Dis Markers 2020, 2020, 8833885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M.; Sabouni, E.; Rahmanian, P.; Entezari, M.; Mojtabavi, M.; Raei, B.; Zandieh, M.A.; Behroozaghdam, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Hushmandi, K.; et al. Deciphering STAT3 Signaling Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Tumorigenesis, Treatment Resistance, and Pharmacological Significance. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters 2023, 28, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Cheung, S.T. STAT3: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, A.; Wang, S.C.; Morris, J.P.; Folias, A.E.; Liou, A.; Kim, G.E.; Akira, S.; Boucher, K.M.; Firpo, M.A.; Mulvihill, S.J.; et al. Stat3 and MMP7 Contribute to Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Initiation and Progression. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagathihalli, N.S.; Castellanos, J.A.; Shi, C.; Beesetty, Y.; Reyzer, M.L.; Caprioli, R.; Chen, X.; Walsh, A.J.; Skala, M.C.; Moses, H.L.; et al. STAT3 Mediated Remodeling of the Tumor Microenvironment Results in Enhanced Tumor Drug Delivery in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1932–1943.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrkhanloo, M.; Paskeh, M.D.A.; Hashemi, M.; Raesi, R.; Motahhary, M.; Saghari, S.; Sharifi, L.; Bokaie, S.; Mirzaei, S.; Entezari, M.; et al. STAT3 Signaling in Prostate Cancer Progression and Therapy Resistance: An Oncogenic Pathway with Diverse Functions. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 158, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Baba, Y.; Yamauchi, M.; Kuchiba, A.; Nosho, K.; Shima, K.; Tanaka, N.; Huttenhower, C.; Frank, D.A.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. STAT3 Expression, Molecular Features, Inflammation Patterns and Prognosis in a Database of 724 Colorectal Cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2011, 17, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.-J.; Ma, C.; Hu, K.; Zhao, M.-M.; Zhang, N.; Sun, Z.-G. Molecular Mechanism, Regulation, and Therapeutic Targeting of the STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Esophageal Cancer (Review). Int J Oncol 2022, 61, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-Y.; Chu, M.-Y.; Lin, W.; Zheng, Y.-Q.; Xu, X.-E.; Chen, Y.; Liao, L.-D.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Li, E.-M.; et al. Blocking STAT3 Signaling Augments MEK/ERK Inhibitor Efficacy in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Song, B.; Zhu, M.; Liu, J. Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis of STAT3 as a Prognostic and Immunological Biomarker. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Transduction Pathway and Targeted Therapies in Cancer. Mol Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerma, K.; Piacentini, F.; Moscetti, L.; Barbolini, M.; Canino, F.; Tornincasa, A.; Caggia, F.; Cerri, S.; Molinaro, A.; Dominici, M.; et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Breast Cancer: From Biology to Clinical Challenges. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capivasertib. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB12218 (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- Truqap (Capivasertib) plus Faslodex Approved in the US for Patients with Advanced HR-Positive Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2023/truqap-approved-in-us-for-hr-plus-breast-cancer.html (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- Liu, D.; Weintraub, M.A.; Garcia, C.; Goncalves, M.D.; Sisk, A.E.; Casas, A.; Harding, J.J.; Harnicar, S.; Drilon, A.; Jhaveri, K.; et al. Characterization, Management, and Risk Factors of Hyperglycemia during PI3K or AKT Inhibitor Treatment. Cancer Med 2022, 11, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.G.; Barrios, D.M.; Blinder, V.S.; Bromberg, J.F.; Drullinsky, P.R.; Funt, S.A.; Jhaveri, K.L.; Lake, D.E.; Lyons, T.; Modi, S.; et al. Dermatologic Adverse Events Related to the PI3Kα Inhibitor Alpelisib (BYL719) in Patients with Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2020, 183, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, A.; Roubaud, G.; Dariane, C.; Barret, E.; Beauval, J.-B.; Brureau, L.; Créhange, G.; Fiard, G.; Fromont, G.; Gauthé, M.; et al. Overview of the Development and Use of Akt Inhibitors in Prostate Cancer. J Clin Med 2021, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, W.H.; Steelman, L.S.; Long, J.M.; Kempf, R.C.; Abrams, S.L.; Franklin, R.A.; Bäsecke, J.; Stivala, F.; Donia, M.; Fagone, P.; et al. Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR Inhibitors: Rationale and Importance to Inhibiting These Pathways in Human Health. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 135–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Rohweder, P.J.; Ongpipattanakul, C.; Basu, K.; Bohn, M.-F.; Dugan, E.J.; Steri, V.; Hann, B.; Shokat, K.M.; Craik, C.S. A Covalent Inhibitor of K-Ras(G12C) Induces MHC Class I Presentation of Haptenated Peptide Neoepitopes Targetable by Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1060–1069.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, M.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.R. Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK Pathway for Cancer Therapy: From Mechanism to Clinical Studies. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-L.; Liu, L.-X.; Li, E.-M.; Xu, L.-Y. STAT3, the Challenge for Chemotherapeutic and Radiotherapeutic Efficacy. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, J.L.; Grandis, J.R.; Bauman, J.E. The STAT3 Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Head and Neck Cancer: Barriers and Innovations. Oral Oncol 2016, 56, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortylewski, M.; Yu, H. Role of Stat3 in Suppressing Anti-Tumor Immunity. Current Opinion in Immunology 2008, 20, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fu, S.; Wu, J. Coordinated Regulation of Immune Contexture: Crosstalk between STAT3 and Immune Cells during Breast Cancer Progression. Cell Commun Signal 2021, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doheny, D.; Sirkisoon, S.; Carpenter, R.L.; Aguayo, N.R.; Regua, A.T.; Anguelov, M.; Manore, S.G.; Arrigo, A.; Jalboush, S.A.; Wong, G.L.; et al. Combined Inhibition of JAK2-STAT3 and SMO-GLI1/tGLI1 Pathways Suppresses Breast Cancer Stem Cells, Tumor Growth, and Metastasis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6589–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Yu, T.; Dong, N.; Wang, B.; Sun, F.; Jiang, D. Napabucasin, a Novel STAT3 Inhibitor Suppresses Proliferation, Invasion and Stemness of Glioblastoma Cells. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 2019, 38, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-S.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-A.; Shen, P.-C.; Al Haq, A.T.; Chen, L.-M.; Tung, Y.-C.; Hsu, H.-L. MCT-1/miR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R Signaling Axis Promotes EMT Progression, Cancer Stemness and M2 Macrophage Polarization in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol Cancer 2019, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Lou, J. Napabucasin Attenuates Resistance of Breast Cancer Cells to Tamoxifen by Reducing Stem Cell-Like Properties. Medical Science Monitor : International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research 2019, 25, 8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, H.-W.; Cole, B.; Rao, S.A.M.; Podolak, J.; Van Gaest, A.; King, C.; Eide, C.A.; Wilmot, B.; Xue, C.; Spellman, P.T.; et al. Src and STAT3 Inhibitors Synergize to Promote Tumor Inhibition in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44675–44687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtek, S.L.; Backos, D.S.; Matheson, C.J.; Reigan, P. Strategies and Approaches of Targeting STAT3 for Cancer Treatment. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Tong, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 2020, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 Activation and Dimerization. Chemistry & Biology 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.-X.; Zhang, H.-Y. C188-9, a Small-Molecule STAT3 Inhibitor, Exerts an Antitumor Effect on Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2019, 30, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yue, P.; Page, B.D.G.; Li, T.; Zhao, W.; Namanja, A.T.; Paladino, D.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Gunning, P.T.; et al. Orally Bioavailable Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Transcription Factor Stat3 Regresses Human Breast and Lung Cancer Xenografts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2012, 109, 9623–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poria, D.K.; Sheshadri, N.; Balamurugan, K.; Sharan, S.; Sterneck, E. The STAT3 Inhibitor Stattic Acts Independently of STAT3 to Decrease Histone Acetylation and Modulate Gene Expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2021, 296, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Duan, L.; He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Pan, J.; Pei, D.; Ding, K. Identification of Niclosamide as a New Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the STAT3 Signaling Pathway. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Wang, H.; Ren, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X. The Anticancer Effect of Napabucasin (BBI608), a Natural Naphthoquinone. Molecules 2023, 28, 5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, C.; Braiteh, F.S.; Spira, A.I.; Langleben, A.; Panasci, L.C.; Vukelja, S.J.; Hinshaw, I.M.; Goodwin, R.A.; Panella, T.J.; Edenfield, W.J.; et al. A Phase Ib/II Study of Cancer Stemness Inhibitor Napabucasin (BB608) Combined with Weekly Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple Negative Breast Cancer. JCO 2016, 34, 1094–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cheng, X.-D.; Zhang, W.-D.; Qin, J.-J. Recent Update on Development of Small-Molecule STAT3 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: From Phosphorylation Inhibition to Protein Degradation. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8884–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Grants Napabucasin Orphan Status for Gastric Cancer | Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center. Available online: https://meyercancer.weill.cornell.edu/news/2016-06-29/fda-grants-napabucasin-orphan-status-gastric-cancer (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Napabucasin Phase III Trial Discontinued in Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: https://www.onclive.com/view/napabucasin-phase-iii-trial-discontinued-in-pancreatic-cancer (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Kong, R.; Sun, G.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Xuan, P.; Yang, S.; Sun, B.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibitor C188-9 Synergistically Enhances the Demethylated Activity of Low-Dose 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine Against Pancreatic Cancer. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redell, M.S.; Ruiz, M.J.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Tweardy, D.J. Stat3 Signaling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Ligand-Dependent and -Independent Activation and Induction of Apoptosis by a Novel Small-Molecule Stat3 Inhibitor. Blood 2011, 117, 5701–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayyani, F.; Baretti, M.; Lee, S.S.; He, A.R.; Kim, R.D.; Lin, B.S.-L.; Enzler, T.; Al Hallak, M.N.; Ulahannan, S.V.; Davis, S.L.; et al. A Phase 1b/2 Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of TTI-101 as Monotherapy and in Combination in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JCO 2024, 42, TPS577–TPS577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Dong, Z.; Wang, F.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T. A Small Molecule Compound Targeting STAT3 DNA-Binding Domain Inhibits Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Bian, A.; Yang, L.; Yin, X.; Wang, J.; Ti, C.; Miao, Y.; Peng, S.; Xu, S.; Liu, M.; et al. Targeting STAT3 by a Small Molecule Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Progression. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1440–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bian, A.; Zhou, W.; Miao, Y.; Ye, J.; Li, J.; He, P.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. Discovery of the Highly Selective and Potent STAT3 Inhibitor for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment. ACS Cent. Sci. 2024, 10, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Chen, X.; Fu, S.; Yu, W.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Lo, H.-W.; Lin, J. LLY17, a Novel Small Molecule STAT3 Inhibitor Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses Cell Migration and Tumor Growth in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2020, 181, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, L.; Genini, D.; Laurini, E.; Merulla, J.; Perez, L.; Fermeglia, M.; Carbone, G.M.; Pricl, S.; Catapano, C.V. Hitting the Right Spot: Mechanism of Action of OPB-31121, a Novel and Potent Inhibitor of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Mol Oncol 2015, 9, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendell, J.C.; Hong, D.S.; Burris, H.A.; Naing, A.; Jones, S.F.; Falchook, G.; Bricmont, P.; Elekes, A.; Rock, E.P.; Kurzrock, R. Phase 1, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation, and Pharmacokinetic Study of STAT3 Inhibitor OPB-31121 in Subjects with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2014, 74, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, L.; Lahiri, T.; Cammer, M.; Levy, D.E. STAT3 Inhibitor OPB-51602 Is Cytotoxic to Tumor Cells Through Inhibition of Complex I and ROS Induction. iScience 2020, 23, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Uchida, T.; Terui, Y.; Hayakawa, F.; Kobayashi, Y.; Taniwaki, M.; Takamatsu, Y.; Naoe, T.; Tobinai, K.; Munakata, W.; et al. Phase I Study of OPB-51602, an Oral Inhibitor of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Hematological Malignancies. Cancer Sci 2015, 106, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vividion Therapeutics, Inc. A Phase 1, Open-Label, 2-Part, Multicenter, First-in-Human Dose Escalation and Dose Expansion Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Preliminary Anti-Tumor Activity of the STAT3 Inhibitor VVD-130850 as Single Agent and in Combination With Checkpoint Inhibition in Participants With Advanced Solid and Hematologic Tumors, 2024.
- Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a Novo Nordisk company An Open-Label, Phase 1, Dose-Ranging Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Intravenous DCR-STAT3 in Adults With Refractory Solid Tumors; clinicaltrials. 2024.
- Yang, J.; Liao, X.; Agarwal, M.K.; Barnes, L.; Auron, P.E.; Stark, G.R. Unphosphorylated STAT3 Accumulates in Response to IL-6 and Activates Transcription by Binding to NFκB. Genes Dev 2007, 21, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, O.A.; Chasovskikh, S.; Lonskaya, I.; Tarasova, N.I.; Khavrutskii, L.; Tarasov, S.G.; Zhang, X.; Korostyshevskiy, V.R.; Cheema, A.; Zhang, L.; et al. Mechanisms of Unphosphorylated STAT3 Transcription Factor Binding to DNA. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 14192–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkansah, E.; Shah, R.; Collie, G.W.; Parkinson, G.N.; Palmer, J.; Rahman, K.M.; Bui, T.T.; Drake, A.F.; Husby, J.; Neidle, S.; et al. Observation of Unphosphorylated STAT3 Core Protein Binding to Target dsDNA by PEMSA and X-Ray Crystallography. FEBS Letters 2013, 587, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Harris, D.M.; Li, P.; Ferrajoli, A.; Faderl, S.; Keating, M.J.; Estrov, Z. STAT-3 Activates NF-κB in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Molecular Cancer Research 2011, 9, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Cui, D.; Chen, X.; Xiong, X.; Zhao, Y. PROTACs: An Emerging Targeting Technique for Protein Degradation in Drug Discovery. BioEssays 2018, 40, 1700247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkley, K.; Zalejski, J.; Sharma, N.; Sharma, A. Journey of PROTAC: From Bench to Clinical Trial and Beyond. Biochemistry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Li, S.; Han, S.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y. Antibody Drug Conjugate: The “Biological Missile” for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Man, Q.; Huo, F.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Su, F.; Cai, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. STAT3 Pathway in Cancers: Past, Present, and Future. MedComm (2020) 2022, 3, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
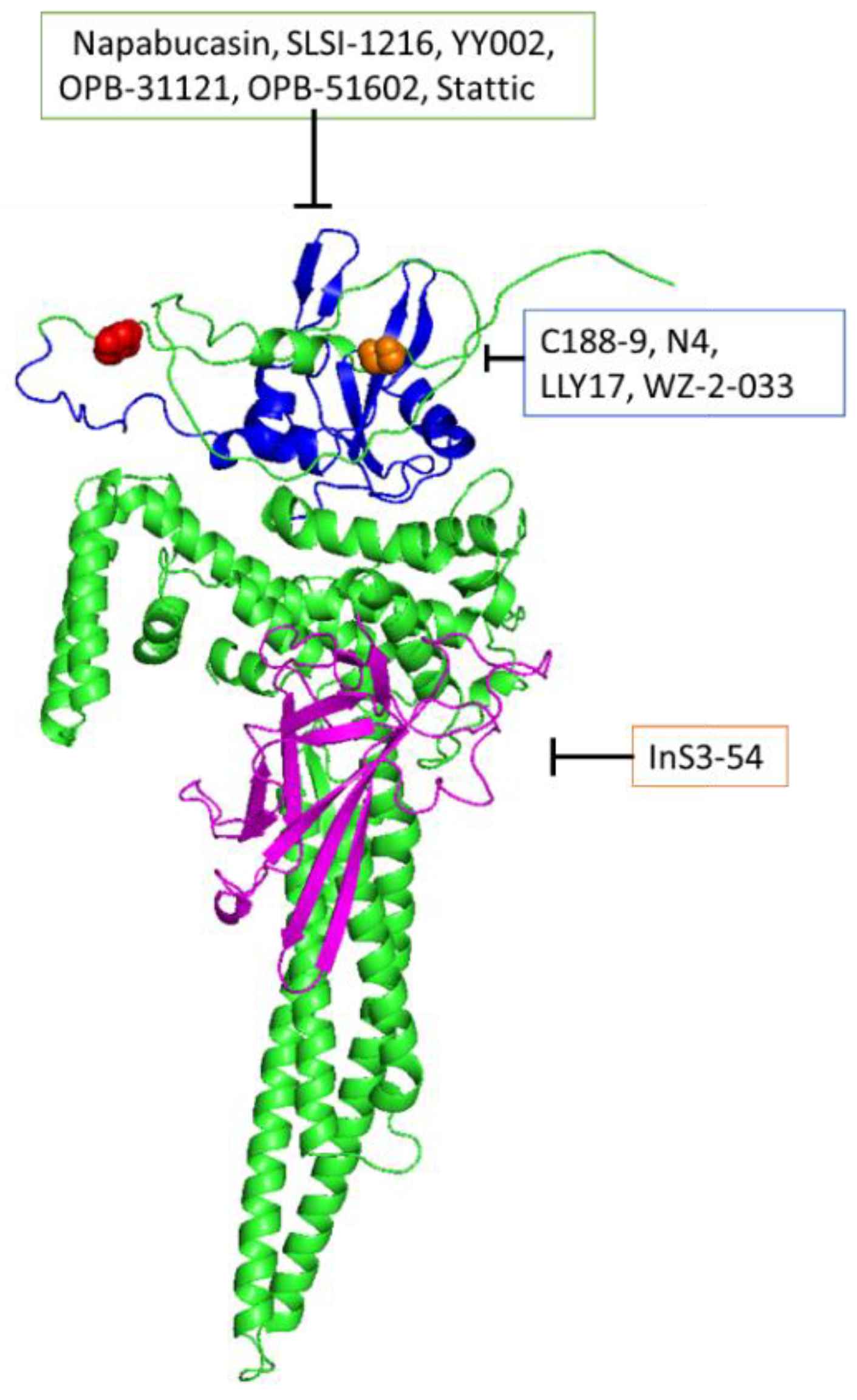
| Compound | Target Domain | pY705 | pS727 | Clinical Efficacy | Toxicity |
| Stattic | SH2 | Yes | Yes | N/A | High |
| Napabucasin (BBI608) | SH2 | Yes | Yes | Low | Low |
| SLSI-1216 | SH2 | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A |
| C188-9 (TTI-101) |
SH2 | Yes | N/A | High | Low |
| InS3-54 | DNA-binding | No | No | N/A | N/A |
| N4 | SH2 | Yes | No | N/A | Low |
| YY002 | SH2 | Yes | Yes | N/A | Low |
| LLY17 | SH2 | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| WZ-2-033 | SH2 | Yes | No | N/A | Low |
| OPB-31121 | SH2 | Yes | Yes | Low | High |
| OPB-51602 | SH2 | N/A | N/A | High | High |
| VVD-130850 | Allosteric | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| DCR-STAT3 | RNA | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





