1. Introduction
The family Lecithoceridae is the sixth largest within the superfamily Gelechioidea, encompassing more than 1,430 species [
1,
2]. This family has a wide distribution across the Oriental, Ethiopian, Australian and Palaearctic regions. Members of Lecithoceridae are typically characterized by the antennae, which are as long as or longer than the forewing, and by the gnathos in the male genitalia, which usually features a median process that is consistently downturned, except in the subfamily Crocanthinae. Despite its remarkable diversity, Lecithoceridae has received very limited scientific attention. In certain regions, such as southern China, this family is a dominant group; however, the lack of research interest may persist due to the group's minimal economic significance and the shortage of specialists in this field. Interestingly, Lecithoceridae larvae have been reported to feed on non-living materials and organisms [
3,
4,
5,
6], highlighting their potentially significant role in environmental ecosystems.
Coproptilia is a small genus of Lecithoceridae, first established by Snellen, with
C. glebicolorella from Indonesia designated as the type species [
7]. Wu later described the second species,
C. diona from China [
8], followed by Park's description of a third species,
C. tawiensis from Philippines [
9]. Currently, only three species of the genus
Coproptilia are known worldwide. Wu initially classified the genus within the subfamily Torodorinae [
10], but Park et al. excluded it from the Torodorinae in their monograph on the subfamily [
2].
Nosphistica was established by Meyrick [
11], and currently comprises 22 species. The species within this genus are geographically restricted to the Oriental region, with 17 species recorded in China. Wu classified
Nosphistica within the subfamily Lecithocerinae [
10], but Park suggested that the genus represents an intermediate group between Lecithocerinae and Torodorinae [
12]. Furthermore, Park synonymized Philoptila Meyrick, 1918 with
Nosphistica [
12].
The genera
Coproptilia and
Nosphistica share several morphological characteristics, including the ventrally ciliate flagellum of the male antenna, a darkened area between vein 3A and the dorsum of the hindwing, and the costal bar of the valva, which is conspicuously free at the base but fused to the valva distally. The only distinguishing feature of
Coproptilia is the presence of the R1 vein in the forewing, which is absent in
Nosphistica, according to current criteria [
12,
13]. However, it is questionable whether the presence of the R1 vein alone is sufficient as the sole criterion for distinguishing these two genera, considering the significant intra-generic variation in wing vein patterns.
To date, the taxonomy of Lecithoceridae has primarily been based on morphological characteristics, with relatively few studies employing molecular methods. Sterling
et al. conducted the first phylogenetic analysis of Lecithoceridae based on multiple molecular markers, incorporating 17 multi-genetic exemplars [
14]. However, molecular data for the family remains limited, with only one dataset currently available for
Nosphistica. Therefore, a combined approach integrating both molecular data and morphological characteristics is crucial and meaningful to resolve the relationship between
Coproptilia and
Nosphistica.
The primary objectives of this study are twofold: first, to clarify the taxonomic relationship between the genera Coproptilia and Nosphistica, and second, to describe two new species and report one new record from China.
2. Materials and Methods
The examined specimens were collected using GYZ 450 W high-pressure mercury lamps (Yaming, China). Morphological terminology used in the descriptions follows Gozmány [
3]. Wingspan measurements were taken from the tips of the left and right forewings of fully well spread specimens. Genitalia slides were prepared following the methods introduced by Li [
15]. Photographs of adults were captured using an M205A stereomicroscope, and genitalia photographs were taken using a DM750 microscope with Leica Application Suite software version 4.6 (Leica, Germany). All images were processed with Photoshop CC (Adobe, USA). The type series of the new species are deposited at the Insect Collection of Nankai University (NKU), Tianjin, China (NKU), and at Liaocheng University (LCU), Liaocheng, China.
In this study, a total of 11 Lecithoceridae specimens were independently collected for molecular analysis. These included two specimens of Spatulignatha olaxana (Vouchers: LCU054 and LCU058), one of Frisilia cornualis (Voucher: LCU063), one of Tegenocharis tenebrans (Voucher: LCU063), one of Nosphistica eucalla (Voucher: YUS007), one of Nosphistica paramecola (Voucher: YUS010), one of Nosphistica grandiunca (Voucher: YUS011), one of Synesarga breviclavata (Voucher: YUS012) and three of Coproptilia tawinensis (Vouchers: YUS033, YUS038, and LCU369). Genomic DNA was extracted from the legs or partial body of dried specimens using Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China).
One mitochondrial marker (Cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 [COI]) and six nuclear markers (Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase domain protein [CAD], Elongation factor 1 alpha [EF-1α], Glyceraldhyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [GAPDH], Cytosolic malate dehydrogenase [MDH], Ribosomal protein S5 [RpS5] gene, and wingless) were amplified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The primers used were sourced from previous studies[
16,
17,
18,
19]. When the published primers failed to amplify sequences, newly designed primers were used to obtain shorter fragments of the target regions in this study (
Table 1). DNA amplification and sequencing protocols primarily followed those described by Wahlberg & Wheat [
19]. The purified PCR products were directly sequenced using Sanger sequencing by Qingke Biotech (Beijing, China).
To construct a more comprehensive phylogenetic tree for Lecithoceridae, a total of 5,350 bp dataset was downloaded from GenBank, which includes all available mixed COI and 6 nuclear gene sequences of 17 Lecithoceridae individuals. This dataset included 1,475 bp of COI, 850 bp of CAD, 691 bp of GAPDH, 925 bp of EF-1α, 600 bp of RpS5, 400 bp of wingless, and 407 bp of MDH (
Table S1).
The sequences were manually edited using BioEdit v.7.2.5 [
20] and analyzed with MEGA X software [
21]. Each gene (COI, CAD, GAPDH, EF-1α, RpS5, wingless, and MDH) was independently aligned and subsequently concatenated into a dataset with a total length of 5,350 bp using PhyloSuite v1.2.2 [
22]. Phylogenetic reconstructions of Lecithoceridae species were performed based on this concatenated dataset using Maximum Likelihood (ML) in IQ-TREE [
23] and Bayesian Inference (BI) in MrBayes 3.2 [
24]. The best-fit model of sequence evolution for each locus alignment was selected using the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) in PartitionFinder v2 [
25]. The selected models were as follows: GTR+I+G for COI, GTR+G for CAD, HKY+G for MDH, and SYM+I+G for wingless, RpS5, EF-1α, and GAPDH. Bootstrap support values were calculated using a rapid bootstrapping algorithm with 1,000 replicates in the ML analysis. For the BI analysis, four Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) runs with four chains were performed for 20,000,000 generations, sampling every 1,000 trees and discarding the first 20% as burn-in.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Analysis Results
We obtained a total of 3,438 bp of sequences for our specimen, which included 647 bp of COI for 11 individuals, 759 bp of CAD for 4 individuals, 345 bp of EF-1α for 11 individuals, 521 bp of GAPDH for 9 individuals, 335 bp of MDH for 3 individuals, 502 bp of RpS5 for 10 individuals, and 329 bp of wingless for 7 individuals. These gene sequences generated in this study have been deposited in GenBank under the following accession numbers: PQ820469-PQ820479 (COI), PQ819874-PQ8198777 (CAD), PQ819878-PQ819888 (EF-1α), PQ819889-PQ819897 (GAPDH), PQ819898-PQ819900 (MDH) PQ819901-PQ819909 (RpS5), and PQ819911-PQ819917 (wingless) (
Table S1).
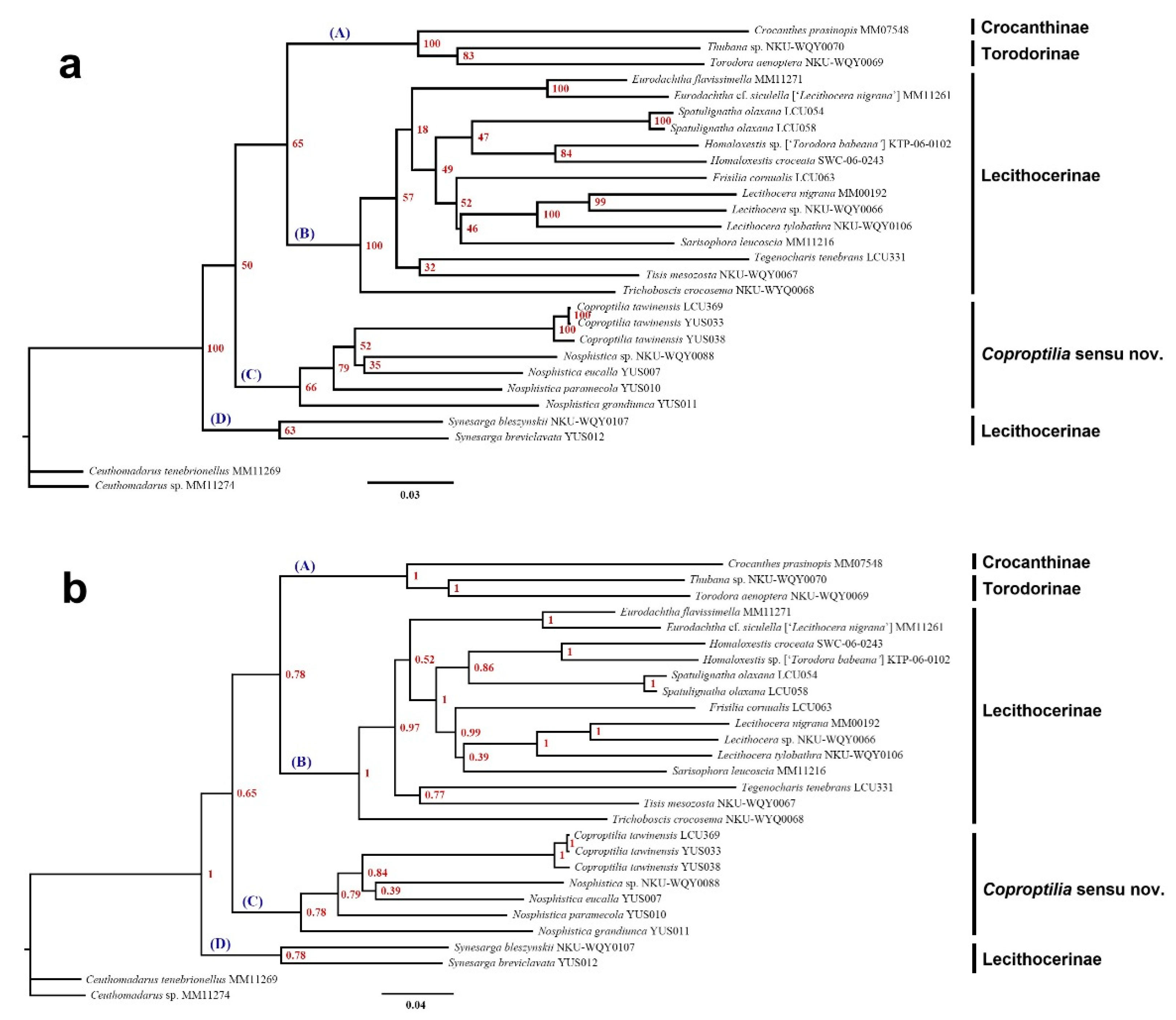
The Maximum Likelihood (ML) tree and Bayesian Inference (BI) tree were constructed based on 28 exemplars representing 25 Lecithoceridae species, and the topological results presented nearly identical results (
Figure 1). According to the phylogenetic tree topology, four major clades are recognized: A, B, C, and D. The clade A contains one species from the subfamily Crocanthinae and two species from the subfamily Torodorinae, with the two subfamilies forming a sister-branch relationship (BS=100%, PP=1.00). The clade B includes 13 species from 9 genera within the subfamily Lecithocerinae. The clade C is composed of one species from the genus
Coproptilia and four species from the genus
Nosphistica, with
Coproptilia embedded within
Nosphistica. The clade D includes two species of the genus
Synersaga. This clade is located at the base of the phylogenetic tree and forms a sister relationship with the other three clades (BS=100%, PP=1.00). Although our molecular phylogenetic tree did not fully resolve the relationships of three clades (A, B, C), most intra-genus (e.g.,
Eurodachtha,
Homaloxestis, and
Lecithocera) and intra-species (e.g.,
Spatulignatha olaxana and
Coproptilia tawinensis) relationships were strongly supported (BS=100%, PP=1.00). Notably, within the three individuals of
Coproptilia tawinensis, specimen YUS038 is a male from Hunan, while YUS033 and LCU369 are male and female specimens from Guangxi, respectively. While YUS033 and YUS038 exhibit consistent male morphological characteristics, YUS033 and LCU369 display a closer genetic relationship, likely due to their geographic proximity. Consequently, molecular results confirm the matching of males and females for this species with high confidence.
3.2. Morphological Results
Coproptilia Snellen, 1903
Coproptilia Snellen, 1903: 32 [
7]. Type species:
Coproptilia glebicolorella Snellen, 1903.
Nosphistica Meyrick, 1911: 733 syn. nov. [
11]. Type species:
Nosphistica erratica Meyrick, 1911.
Philoptila Meyrick, 1918: 111 syn. nov. [
26]. Type species:
Philoptila effrenata Meyrick, 1918.
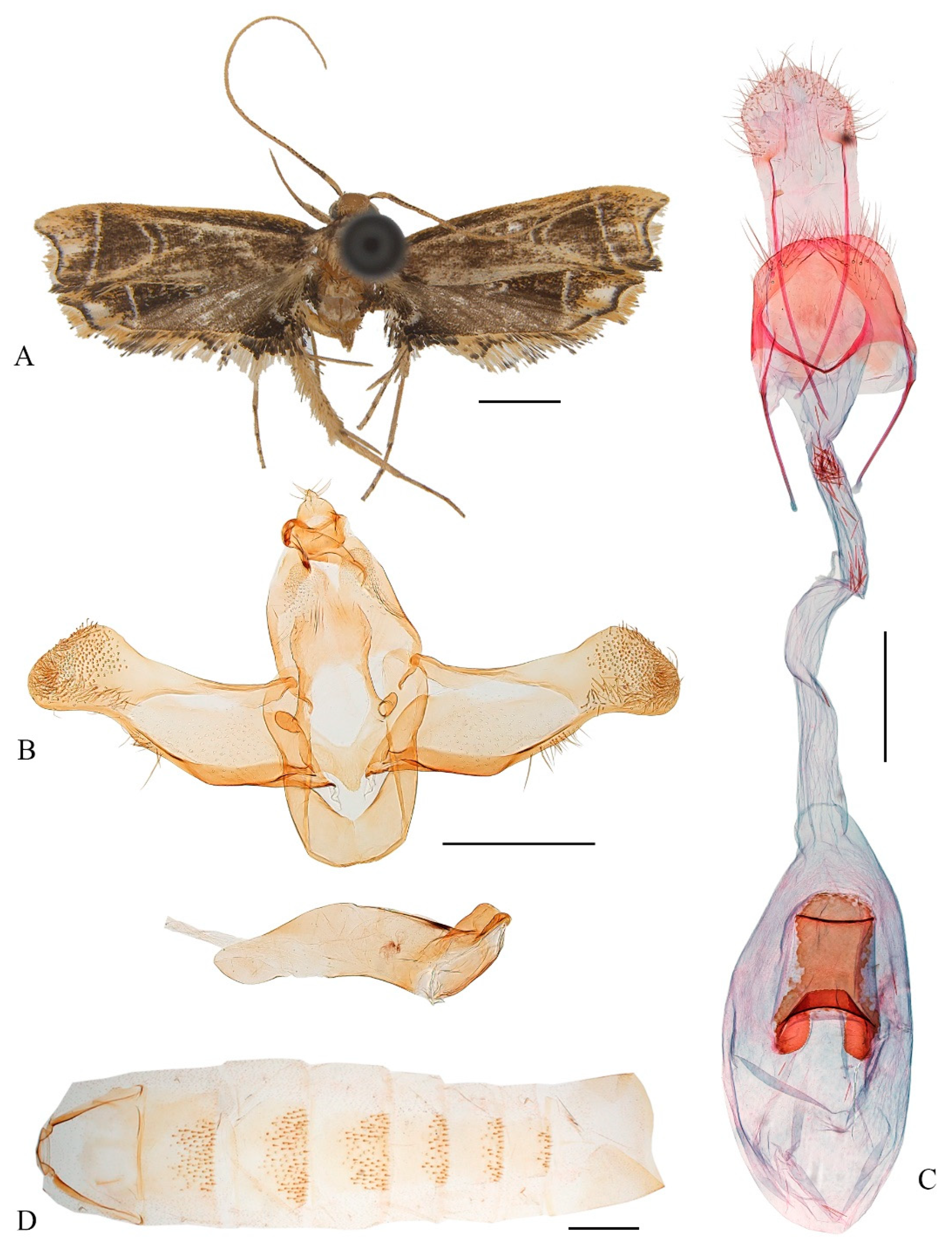
3.2.1. Coproptilia tawiensis Park, 2009
Coproptilia tawiensis Park, 2009: 241. Type locality: Philippines. (
Figure 2)
Material examined: China: 2♂♂, 1♀, Guangxi Prov., Lingui County, Huaping, 842 m, 4 Aug. 2022, leg. H. Sun et al., slide nos. YUS032♂, YUS033♂, WLCU369♀, deposited in NKU; 2♂♂, Guangxi Prov., Lingui County, Huaping, 789, 3 Aug. 2022, leg. H. Sun et al., slide no. LCU046, deposited in NKU; 1♂, Guangxi Prov., Lingui County, Huaping, 801 m, 2 Aug. 2022, leg. H. Sun et al., slide no. YUS130, deposited in NKU; 1♂, Hunan Prov., Yizhang County, Mt. Mang, 730 m, 27 Jul. 2020, leg. H. Sun et al. leg., slide no. YUS038, deposited in NKU; 1♂, Yunnan Prov., Pu’er City, Taiyanghe, 1450 m, Jul. 2023, leg. K.J. Teng, slide no. YUS076, deposited in LCU.
Female genitalia (
Figure 2C): Abdominal sternite VIII blunt on posterior margin. Apophyses anteriores about 2/3 the length of apophyses posteriores. Ostium bursae large, rounded. Antrum membranous, funnel-shaped. Ductus bursae narrow, nearly as long as corpus bursae; ductus seminalis slender, arising from posterior 1/3 of ductus bursae. Corpus bursae elliptical; signum nearly half length of corpus bursae, anterior part semicircular and heavily sclerotized, posterior part rectangular.
Distribution. China (Guangxi, Hunan, Yunnan, new record), Philippines.
Note. The female of the species is described for the first time.
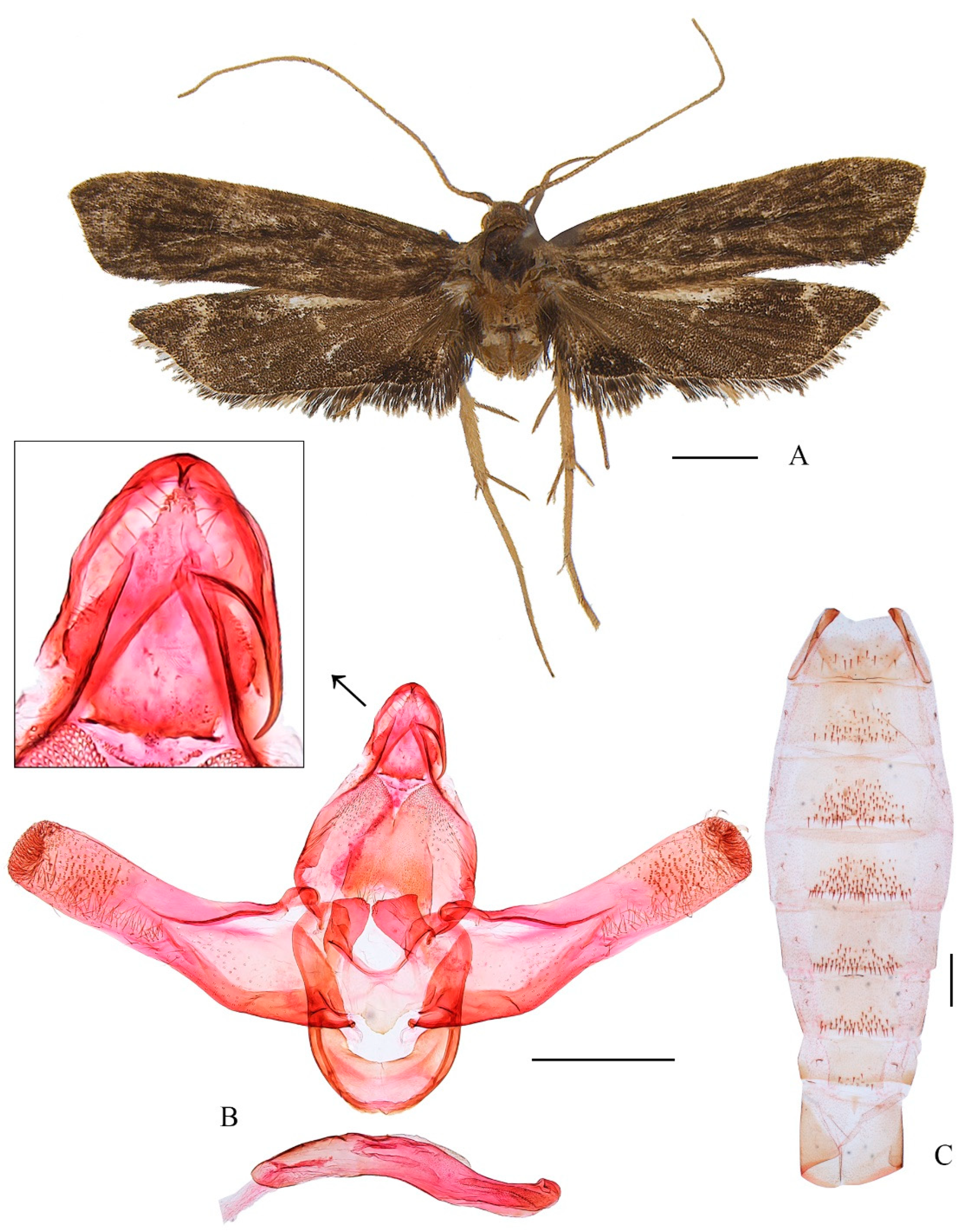
3.2.2. Coproptilia uniformis Yu, sp. nov. (Figure 3)
Material examined: Holotype: ♂, China, Sichuan Prov., Baoxing County, Fengtongzhai, 30.57ºN, 102.88ºE, 1565 m, 3 Aug. 2016, leg. Y. Fei, slide no. LCU214, deposited in LCU.
Diagnosis: The new species is externally similar to Nosphistica paramecola (Wu, 1996), but it can be distinguished by the uncus triangular on posterior margin, the posterolateral lobe of the juxta widened distally, the sacculus arched ventrally. Nosphistica paramecola has an uncus posteriorly blunt with a semiovate lobe, and has widely arm-shaped posterolateral lobes of the juxta, as well as the sacculus nearly straight.
Adult (
Figure 3A): Wingspan 20.5 mm. Head dark brown. Antenna yellow, dark brown basally. Labial palpus with second palpomere thickened, third palpomere slender, as long as the second. Forewing with costal margin nearly straight, slightly curved downward distally, apex blunt, termen oblique; ground color dark brown. Hindwing trapezoidal; dark brown, with a subterminal line running from distal 1/4 of costal margin sinuate to before tornus; area between 3A and dorsum black.
Male genitalia (
Figure 3B). Uncus pentagonal, triangular on posterior margin. Gnathos with basal plate rounded on posterior margin; median process arched, wide at base, narrowed to middle, thereafter slender to pointed apex. Valva wide at base, narrowed slightly to middle; distal half straight and parallel-sided, apex blunt; costal bar free basally; sacculus uniformly wide, arched ventrally. Juxta wide, concave widely on posterior margin, with a semi-ovate extension at middle on anterior margin; posterolateral lobe stout, widened distally, with a nearly straight apical margin. Vinculum U-shaped; saccus region not developed. Aedeagus uniformly narrow, more or less S-shaped; cornute absent.
Female unknown.
Distribution: China (Sichuan).
Etymology: The specific epithet is derived from the Latin uniformis, referring to the uniformly wide phallus.
3.2.3. Coproptilia funiuensis Yu, sp. nov. (Figure 4)
Material examined: Holotype: ♀, China, Henan Prov., Mt. Fu’niu, 33.61ºN, 111.68ºE, 1236 m, 22 Jul. 2023, leg. M.J. Qi & Y.T. Fu, genitalia slide no. LCU373, deposited in LCU.
Diagnosis: The new species can be easily identified by the large size with wingspan 26.0 mm and the diversified signa. It is externally similar to Coproptilia orientana (Park, 2005) comb. nov., but it can be distinguished by the female genitalia with eight signa varied in shape, and the eighth abdomen sternite shallowly concave on anterior margin; Coproptilia orientana has two signa rounded or elliptical, and has an eighth abdomen sternite anteriorly deeply concaved in U-shape.
Adult (
Figure 4A): Wingspan 26.0 mm. Head dark brown. Antenna dark brown, paler toward apex. Labial palpus yellowish brown, second palpomere thickened, third palpomere slender, as long as the second. Forewing with costal margin slightly arched, apex bluntly rounded, termen shallowly concave medially; ground color dark brown except brownish yellow on apical area; terminal line pale yellow, arising from distal 1/4 of costal margin to distal 1/5 of dorsum, arched outward medially. Hindwing trapezoidal; ground color dark brown except brownish yellow on apical area; terminal line pale yellow, arising from distal 1/4 of costal margin to before tornus; area between 3A and dorsum black.
Female genitalia (
Figure 4C): Abdominal sternite VIII shallowly concave on anterior margin, deeply incised at middle on posterior margin forming two lateral lobes. Apophyses anteriores slightly shorter than apophyses posteriores, with a furcation at middle. Ductus bursae narrowed posteriorly, shorter than corpus bursae; ductus seminalis slender, arising from about posterior 1/5 of ductus bursae. Corpus bursae ovate; with eight signa: two large, dentate, two plate-shaped, as well as four small discs.
Male unknown.
Distribution: China (Henan).
Etymology: The specific epithet is derived from the type locality.
4. Discussion
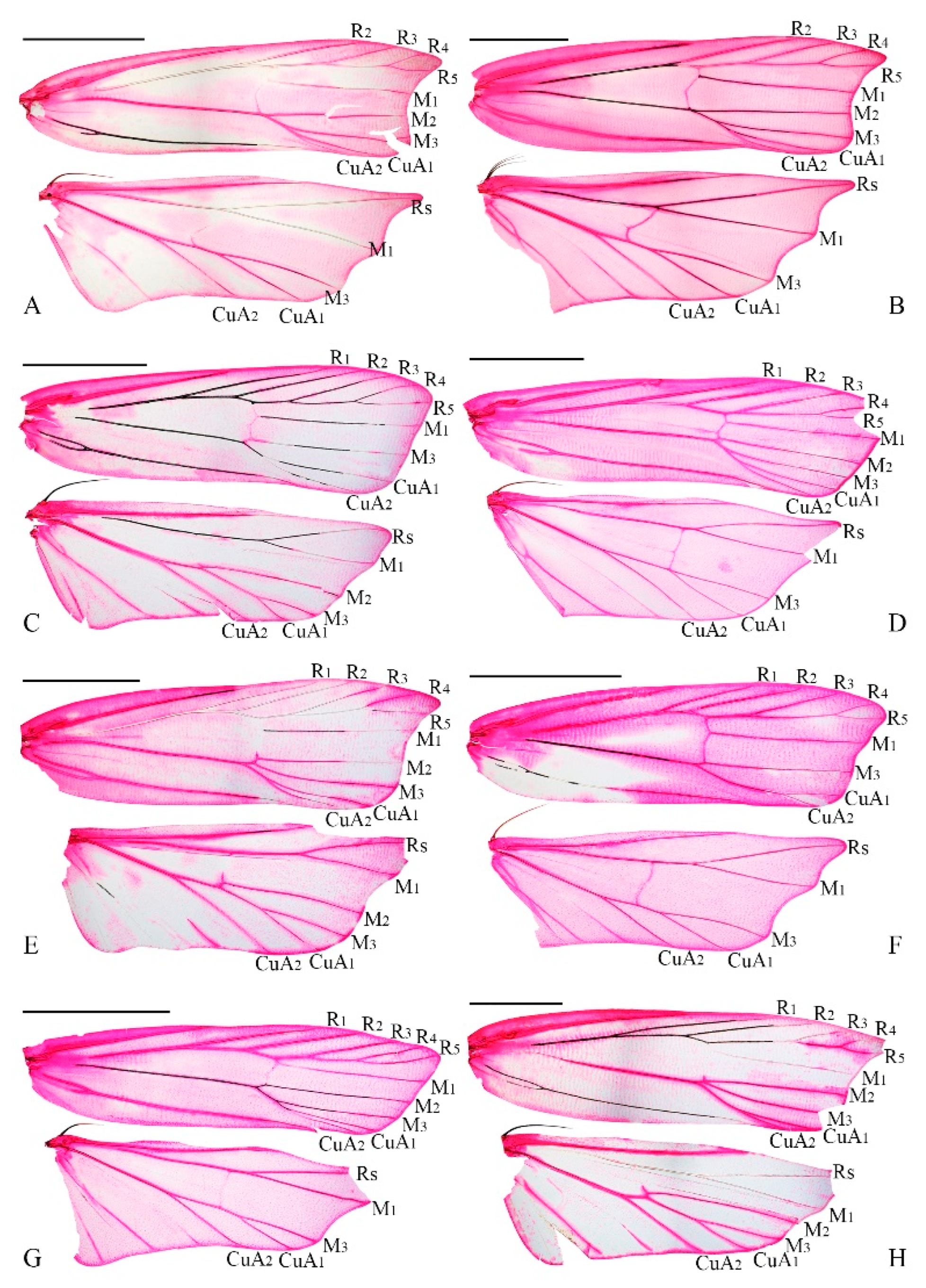
Wing venation has traditionally been regarded as one of the key characters for defining genera in Lecithoceridae, with particular emphasis on features such as the presence of R1 and M2 in the forewing and M2 in the hindwing [
3,
9,
10,
27]. In some cases, it has even been used as the sole character to distinguish genera. For instance, separating
Torodora from
Deltoplastis,
Halolaguna from
Antiochtha, and
Lecithocera from
Sarisophora based on the presence or absence of M2 in the hindwing. Similarly, in this study,
Coproptilia was distinguished from
Nosphistica based on the presence of R1 in the forewing. However, such classifications often rely on the researcher's experience and subjective judgment. Moreover, substantial interspecific variation in wing venation is frequently observed within certain Lecithoceridae genera. For example,
Nosphistica exhibits notable variability in wing venation (
Figure 5):
N. metalychna and
N. fusoidea possess M2 in both the forewing and hindwing;
N. bisinuata lacks M2 in both the forewing and hindwing;
N. fenestrata and
N. fusoidea have M2 in the forewing but lack it in the hindwing;
N. paramecola lacks M2 in the forewing but has it in the hindwing. Given these inconsistencies, using the presence of R1 in the forewing as the sole criterion to distinguish
Coproptilia from
Nosphistica appears unreliable.
The phylogenetic analysis conducted in this study includes three exemplars of Coproptilia tawiensis and four exemplars representing four Nosphistica species. The topological results of both Maximum Likelihood (ML) and Bayesian Inference (BI) trees reveal that the Coproptilia branch is embedded within the Nosphistica branch. This strongly supports the conclusion that Coproptilia and Nosphistica should be regarded as a single genus. Consequently, we propose synonymizing Nosphistica Meyrick with Coproptilia Snellen.
Currently,
Coproptilia Snellen has not been assigned to any subfamily, while
Nosphistica Meyrick is classified under the subfamily Lecithocerinae [
3,
10,
13]. However, Park suggested that
Nosphistica might represent an intermediate group between Lecithocerinae and Torodorinae [
12]. Our phylogenetic analysis suggests that
Coproptilia sensu nov. may belong to an unrecognized or yet-to-be-defined subfamily. This conclusion is supported by the placement of clade C, which is distinct from clades A and B in the phylogenetic tree. Morphological evidence further supports this hypothesis. For instance,
Coproptilia sensu nov. exhibits a polygonal uncus (typically posteriorly bilobed in Lecithocerinae and thorn-like in Torodorinae) and a partially free costal bar in the male genitalia (completely free in Lecithocerinae and absent in Torodorinae). These findings suggest that
Coproptilia sensu nov. is distantly related to other subfamily within Lecithocerinae. The current scarcity of representative species and the limited availability of molecular data contribute to instability in phylogenetic trees interpretation. Therefore, additional evidence is required to formally establish it as a valid subfamily.
In addition, the genus Synesarga forms a distinct branch located at the base of the phylogenetic tree and exhibits a sister relationship with the other subfamilies (Crocanthnae, Torodorinae, Lecithocerinae and Coproptilia sensu nov.). This suggests that further research is needed to determine whether the genus Synesarga should be classified within the subfamily Lecithocerinae.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have revised Nosphistica Meyrick as a synonym of Coproptilia Snellen based on molecular and morphological evidence, and described two new species as well as a new record of Coproptilia from China. To better understand the phylogenetic relationships and subfamily taxonomic affiliations within Lecithocerinae, it is crucial to increase sampling and acquire more molecular data.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1: List of specimen information used for this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Y. and H.L.; methodology, S.Y. and H.L.; software, S.Y. and H.L.; investigation, S.Y.; resources, S.Y. and H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Y. and H.L; writing—review and editing, H.L.; funding acquisition, S.Y. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This study is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (no. ZR2022QD130, ZR2023QC255).
Data Availability Statement
All the sequences used in this study were accessed through the GenBank database and the accession numbers are listed in
Table S1. Morphological specimens were deposited at the Insect Collection of Nankai University (NKU), Tianjin, China (NKU), and at Liaocheng University (LCU), Liaocheng, China.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. Shuxia Wang (Nankai University, China) for providing some of the specimens used in this study. We also thank all the team members for their participating in the field collection. .
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wang, Q.Y.; Li, H.H. Phylogeny of the superfamily Gelechioidea (Lepidoptera: Obtectomera), with an exploratory application on geometric morphometrics. Zoologica Scripta 2019, 00, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.T.; Cho, S.; Koo, J.M. The subfamily Torodorinae of the world (Lepidoptera: Lecithoceridae); National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, South Korea, 2022; pp. 1–584. [Google Scholar]
- Gozmány, L. Lecithoceridae. In Microlepidoptera Palaearctica; Amsel, H.G., Reisser, H., Gregor, F., Eds.; Georg Fromme & Co.: Vienna, Austria, 1978; Volume 5, pp. 1–306. [Google Scholar]
- Common, I.F.B. Moths of Australia; Melbourne University Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1990; pp. 1–544. [Google Scholar]
- Komai, F.; Yoshiyasu, Y.; Nasu, Y.; Saito, T. A guide to the Lepidoptera of Japan; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2011; pp. 1–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.T.; Mey, W. A review of the genus Lecithocera Herrich-Schäffer, 1853 in the Philippines, with descriptions of seven new species (Lepidoptera: Lecithoceridae). SHILAP Revista Lepidopterolog 2016, 33, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellen, P.C.T. Beschrjvingen van nieuwe exotische Tortricinen, Tincinen, en Pterophorinen benevens aanteekeningen over reeds bekend gemaakte soorten. Tikdschrift vorr Rntomologie 1903, 46, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.S. The Lecithoeridae (Lepidoptera) of China, with descriptions of new taxa. Sinzoologica 1994, 11, 123–154. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.T. Revision of the genus Coproptilia Snellen, with description of a new species from the Philippines (Lepidoptera: Lecithoceridae). Entomological Research 2009, 39, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S. Fauna Sinica, Insecta, Lepidoptera, Lecithoceridae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 1–306. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Descriptions of Indian Micro-lepidoptera. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 1911, 20, 706–736. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.T. A revision of the genus Nosphistica Meyrick (Lepidoptera, Lecithoceridae). Zoological Studies 2002, 4, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Wang, S.X. Taxonomic study of the genus Nosphistica Meyrick, 1911 (Lepidoptera: Lecithoceridae) from China, with descriptions of seven new species. Zootaxa 2019, 4664, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, M.J.; Lees, D.C.; Grundy, D. Xenotorodor stygioxanthus gen. nov., sp. nov. (Lepidoptera, Lecithoceridae, Torodorinae), described from an established population in Spain with discussion of taxonomic placement. Nota Lepidopterologica 2023, 46, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H. The Gelechiidae of China (I) (Lepidoptera: Gelechioidea); Nankai University Press: Tianjin, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.B.; Hoch, W.; Lutz, R.A.; Vrijehock, R.C. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.W.; Mitchell, A.; Regier, J.C.; Mitter, C.; Poole, R.W.; Friedlander, T.P.; Zhao, S.W. A highly conserved nuclear gene for low-level phylogenetics: Elongation factor-1α recovers morphology-based tree for heliothine moths. Molecular Biology and Evolution 1995, 12, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brower, A.V.Z.; DeSalle, R. Patterns of mitochondrial versus nuclear DNA sequence divergence among nymphalid butterflies: the utility of wingless as a source of characters for phylogenetic inference. Insect Molecular Biology 1998, 7, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlberg, N.; Wheat, C.H. Genomic outposts serve the phylogenetic pioneers: designing novel nuclear markers for genomic DNA extractions of Lepidoptera. Systematic Biology 2008, 57, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular Ecology Resources 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Systematic Biology 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: new methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyrick, E. s. n. Exotic Microlepidoptera II; Thornhanger: Marlborough, Wilts, 1918; pp. 97–224. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhu, Y.M.; Wang, S.X. Eighteen new species and fifteen new records of the genus Torodora Meyrick (Lepidoptera: Lecithoceridae) from China. Zootaxa 2022, 5133, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).