Submitted:
07 January 2025
Posted:
07 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish
2.2. Isolation, Characterization, and Identification of Bacteria
2.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Experimental Infections
3. Results
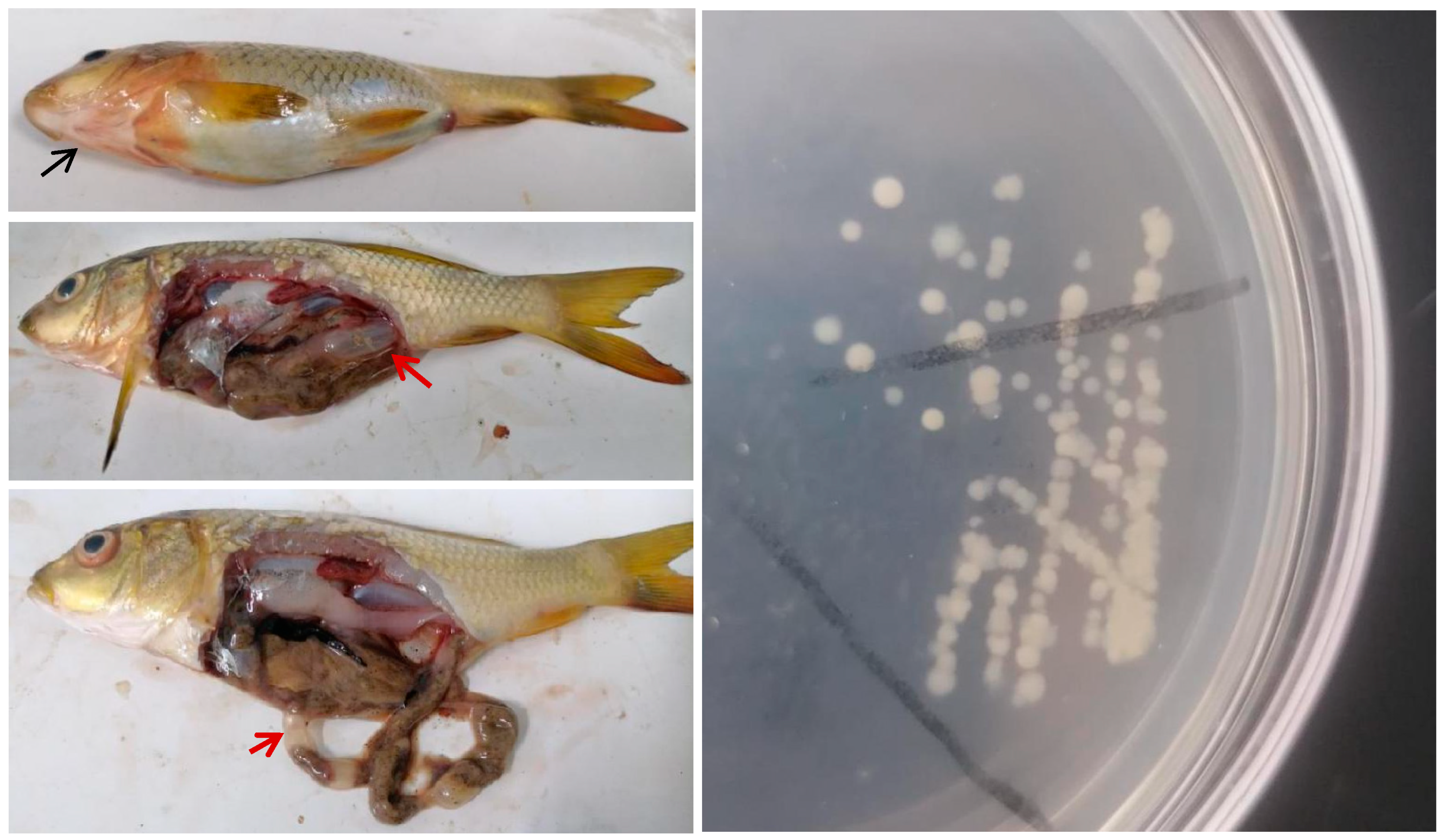
3.1. Clinical Signs and Isolation of Bacteria from Diseased Common Carp
3.2. Biochemical Characteristics
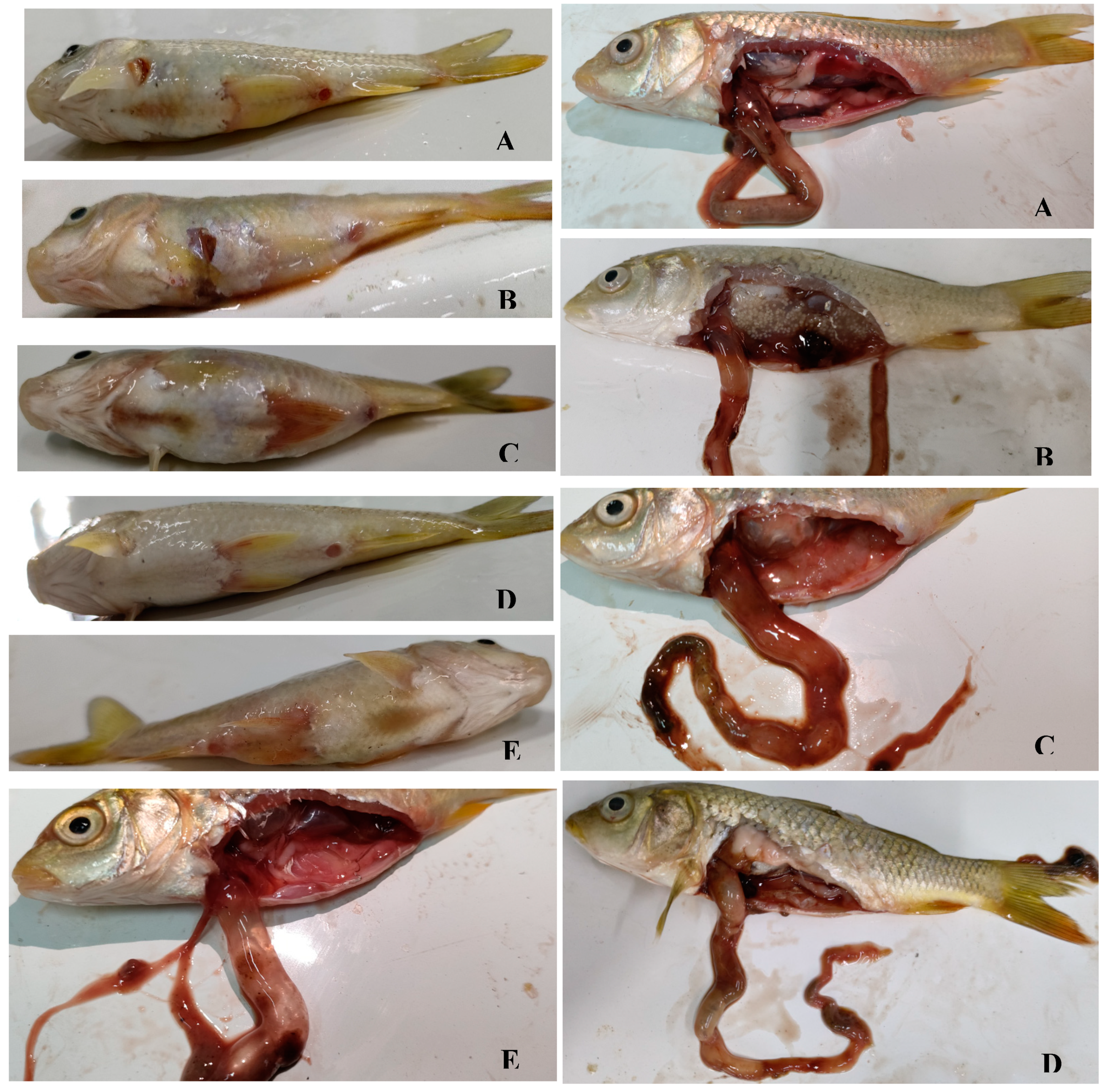
3.3. Experimental Infections
3.4. Determination of Antimicrobial Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, D.; Yun, Y.; He, Z.; Mi, J.; Wang, L.; Jin, M.; Zhou, Q.; Nie, G. Fillet texture, physicochemical indexes, muscle cellularity and molecular expression in muscle of Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus) in response to dietary hydroxyproline supplementation. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Yan, Y.; Pei, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Kong, X. Characterization of hepcidin gene and protection of recombinant hepcidin supplemented in feed against Aeromonas hydrophila infection in Yellow River carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Fish & Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.M.; Sherif, A.H.; Abdelsalam, M.; Elgendy, M.Y. Dactylogyrus extensus and Pseudomonas fluorescens dual infection in farmed common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Microb. Pathog. 2022, 173, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Huo, Y.; Hu, X.; Lu, A.; Sun, J. Characterization of pathogenic Pseudomonas alcaligenes isolated from Koi Carp in China. J. Aquat. Anim. Health. 2021, 33, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazdzior, E.; Pekala-Safinska, A.; Wasyl, D. Phenotypic diversity and potential virulence factors of the Shewanella putrefaciens group isolated from freshwater fish. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Jin, Z.; Di, G.; Li, L.; Kong, X. Molecular characteristics, pathogenicity and medication regimen of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, M.N.A.; Koh, C.B.; Nurliyana, M.; Suhaiba, M.; Nor-Amalina, Z.; Santha, S.; Diyana-Nadhirah, K.P.; Yusof, M.T.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M. A case of natural co-infection of Tilapia Lake Virus and Aeromonas veronii in a Malaysian red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus x O. mossambicus) farm experiencing high mortality. Aquaculture 2018, 485, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Sun, J.; Han, Z.; Yang, X.; Xian, J.-a.; Lv, A.; Hu, X.; Shi, H. Isolation, identification and characteristics of Aeromonas veronii from diseased Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.T.; Techatanakitarnan, C.; Jindakittikul, P.; Thaiprayoon, A.; Taengphu, S.; Charoensapsri, W.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.; Song, H.; Zhu, L.; Qiao, D.; Yan, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Kong, X. Identification of Aeromonas veronii isolated from largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and histopathological analysis. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.S.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Raja, S.A.; Ramraj, D.; Lal, K.K. Aeromonas veronii caused bilateral exophthalmia and mass mortality in cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) (L.) in India. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Lin, L. Characterization of virulence properties of Aeromonas veronii isolated from diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohai, T.D.; Trang, T. T.; Van, T.N.; Giang, N.T.H.; Van, K.V. Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in channel catfish in Vietnam. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Mo, Z. Identification and virulence properties of Aeromonas veronii bv.sobria isolates causing an ulcerative syndrome of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Qiao, D.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H. The molecular characterizations of Cu/ZnSOD and MnSOD and its responses of mRNA expression and enzyme activity to Aeromonas hydrophila or lipopolysaccharide challenge in Qihe crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 67, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachanawan, A.; Phumkhachorn, P.; Rattanachaikunsopon, P. Potential of Psidium guajava supplemented fish diets in controlling Aeromonas hydrophila infection in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 106, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peatman, E.; Mohammed, H.; Kirby, A.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Beck, B.H. Mechanisms of pathogen virulence and host susceptibility in virulent Aeromonas hydrophila infections of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2018, 482, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, X.; Kong, X.; Wang, L.; Jiao, D.; Zhang, H. Molecular characterization and expressing analysis of the c-type and g-type lysozymes in Qihe crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 52, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, B.; Feng, J.; Zhu, Z. Enhanced resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila infection and enhanced phagocytic activities in human lactoferrin-transgenic grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Aquaculture 2004, 242, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Bera, A.K.; Paria, P.; Das, A.; Parida, P.K.; Kumari, S.; Bhowmick, S.; Das, B.K. Identification and pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides in Silver Carp. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. Pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides causing mass mortalities of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and its induced host immune response. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2023, 132, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierralta Chichizola, V.; Mayta Huatuco, E.; León Quispe, J. Primer registro de Plesiomonas shigelloides como patógeno oportunista de Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) (Linnaeus, 1758) en una piscigranja de Lima, Perú. Rev. Investig. Vet. Perú 2016, 27, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S. Effects of dietary blackberry syrup supplement on growth performance, antioxidant, and immunological responses, and resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus to Plesiomonas shigelloides. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 84, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, S.; Hu, S.; Yan, F.; Xia, L.; Zhang, Y. Screening of a Plesiomonas shigelloides phage and study of the activity of its lysis system. Virus Res. 2021, 306, 198581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira Junior, G.; dos Santos, A.C.; Souza, C. d. F.; Baldissera, M.D.; dos Santos Moreira, K.L.; da Veiga, M.L.; de Ugalde Marques da Rocha, M.I.; Castagna de Vargas, A.P.; da Cunha, M.A.; Baldisserotto, B. Citrobacter freundii infection in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen): Hematological and histological alterations. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Guo, M.; Lou, J.; Zhang, L.; An, Z.; Vakharia, V.N.; Kong, W.; Liu, X. Identification and characterization of a highly virulent Citrobacter freundii isolate and its activation on immune responses in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2023, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, A.; Hu, X.; Xue, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G. Gene expression profiling in the skin of zebrafish infected with Citrobacter freundii. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2012, 32, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, A.; Hu, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, A.; Cao, C.; Jiang, J. Isolation and characterization of Citrobacter spp. from the intestine of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Aquaculture 2011, 313, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, D.; Khan, T.A.; Chen, P.; Yan, L.; Hu, S.; Ding, X.; Sun, Y.; Xia, L.; Yi, G. The novel pathogenic Citrobacter freundii (CFC202) isolated from diseased crucian carp (Carassius auratus) and its ghost vaccine as a new prophylactic strategy against infection. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanigaivel, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Gopinath, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Thomas, J. In vivo and in vitro antimicrobial activity of Azadirachta indica (Lin) against Citrobacter freundii isolated from naturally infected Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Aquaculture 2015, 437, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Valencia, M.A.; Osornio-Esquivel, J.L.; Martinez Palacios, C.A.; Contreras-Avila, J.L.; Barriga-Tovar, E.; Ingle-de la Mora, G.; Arellano-Torres, A.; Baizabal-Aguirre, V.M.; Bravo-Patino, A.; Cajero-Juarez, M.; Valdez Alarcon, J.J. Bacterial and parasite co-infection in Mexican golden trout (Oncorhynchus chrysogaster) by Aeromonas bestiarum, Aeromonas sobria, Plesiomonas shigelloides and Ichthyobodo necator. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallani, S.U.; Sebastiao, F. d. A.; Valladao, G.M.R.; Boaratti, A.Z.; Pilarski, F. Pathogenesis of mixed infection by Spironucleus sp and Citrobacter freundii in freshwater angelfish (Pterophyllum scalare). Microb. Pathog. 2016, 100, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1966, 36, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REED, L.J.; MUENCH, H. A simple method for estimating fifty percent end points. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, X.; Jiang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L. Pseudomonas alcaligenes infection and mortality in cultured Chinese Sturgeon Acipenser sinensis. Aquaculture 2015, 446, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Mu, Z.; Lv, X. Pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides and Citrobacter freundii isolated from the endangered Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Microb. Pathog. 2022, 173, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, J.P. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd Ed. vol. 2, Part B; Springer: Michigan, MI, USA, 2005; pp. 497–546. [Google Scholar]
| Test | P. shigelloides | C. freundii | Test | A. veronii | A.hydropha |
| H2S production | - | + | Glucose (gas production) | + | + |
| Phenylalanine deaminase | - | - | Sucrose | + | + |
| Gluconate | - | - | Mannose | + | + |
| Indole reaction | + | - | Indole reaction | + | + |
| Voges–Proskauer | - | - | Voges–Proskauer | + | + |
| Citrate | - | + | Arabinose | - | + |
| Motility | + | + | Arginine dihydrolase | + | + |
| Glucose (gas production) | - | + | Inositol | - | - |
| Lysine decarboxylase | + | - | Lysine | + | + |
| Ornithine decarboxylase | + | - | Unsalted peptone water | + | + |
| Raffinose | - | + | 3% NaCI peptone water | + | + |
| Sorbitol | - | + | 6% NaCI peptone water | + | + |
| Adonitol | - | - | 8% NaCI peptone water | - | - |
| Xylose | - | + | 10% NaCI peptone water | - | - |
| Urease | - | + |
| Group | Concentration (CFU) | Fish | Dead fish number on day after challenge | Accumulative mortality | LD50 value (CFU) | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |||||
| Control | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0% | |
| P. shigelloides | 1.0×107 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | 4.74×104 |
| 1.0×106 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 90% | ||
| 1.0×105 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 70% | ||
| 1.0×104 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20% | ||
| C. freundii | 1.0×107 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | 1.95×104 |
| 1.0×106 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | ||
| 1.0×105 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90% | ||
| 1.0×104 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30% | ||
| A. veronii | 1.0×107 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90% | 5.12×104 |
| 1.0×106 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90% | ||
| 1.0×105 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 70% | ||
| 1.0×104 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20% | ||
| A. hydrophila | 1.0×107 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | 1.53×105 |
| 1.0×106 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80% | ||
| 1.0×105 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40% | ||
| 1.0×104 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10% | ||
| Mixed infection | 1.0×107 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | 5.41×104 |
| 1.0×106 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 90% | ||
| 1.0×105 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 50% | ||
| 1.0×104 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30% | ||
| Antibiotic | Drug concentration (μg/ disc) | Inhibition zone diameter (mm) | |||
| A.veronii | A.hydrophila | C. freundii | P.shigelloides | ||
| Streptomycin | 10 | 19S | 15S | 15S | 15S |
| Enrofloxacin | 10 | 40S | 23S | 10R | 30S |
| Florfenicol | 30 | 30S | 32S | 0R | 28S |
| Gentamicin | 10 | 21S | 19S | 20S | 19S |
| Kanamycin | 30 | 20S | 20S | 15I | 18S |
| Neomycin | 30 | 17S | 18S | 17I | 18S |
| Tetracycline | 30 | 11R | 25S | 0R | 21S |
| Norfloxacin | 10 | 34S | 23S | 14I | 27S |
| Co-trimoxazole | 23.75/1.25 | 19S | 20S | 0R | 13I |
| Ceftizoxime | 30 | 44S | 40S | 32S | 37S |
| Ampicillin | 10 | 10R | 10R | 14I | 0R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





