Submitted:
02 January 2025
Posted:
06 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
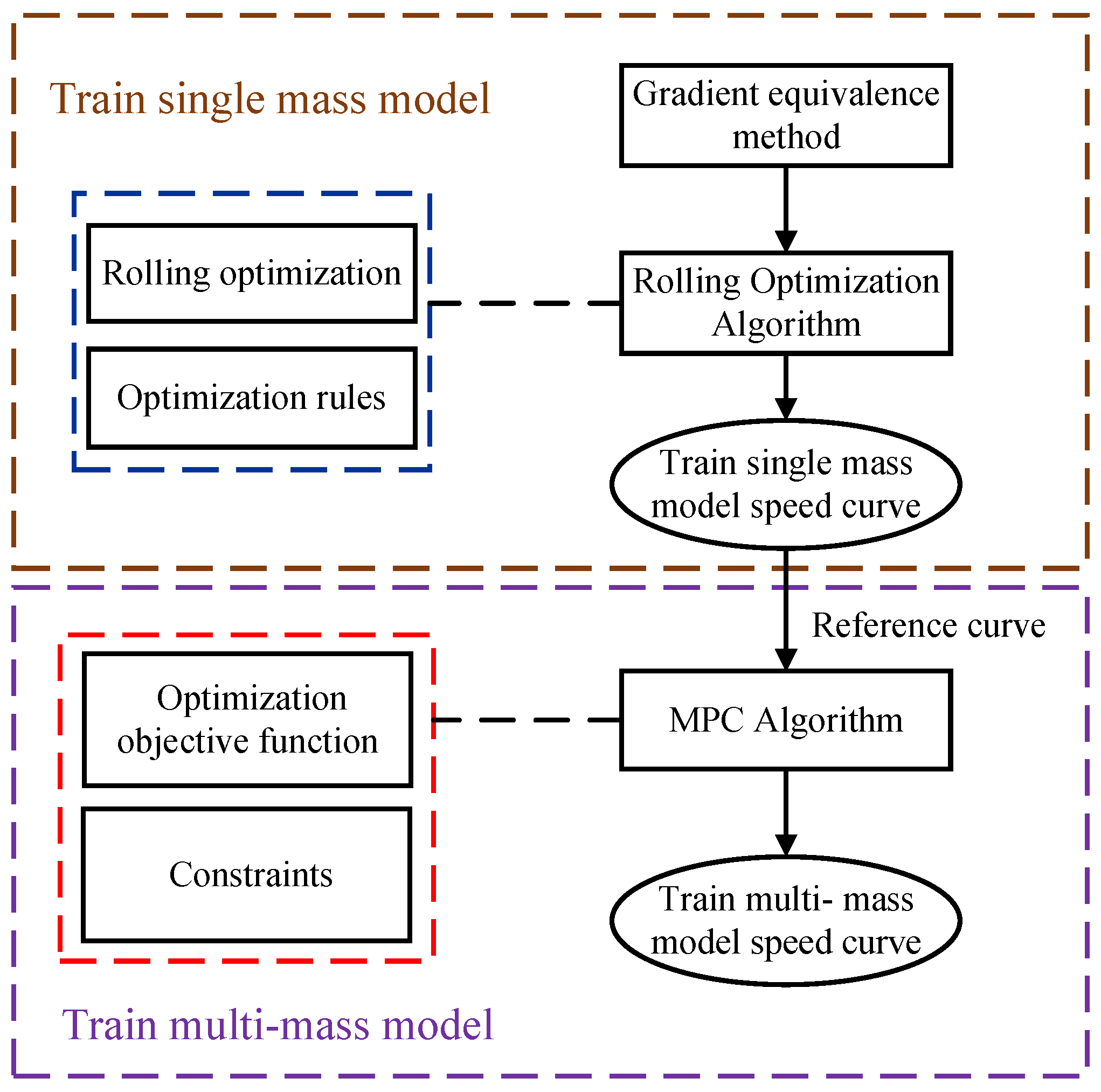
2. The Two-Step Optimization Method
2.1. Gradient Equivalent Method
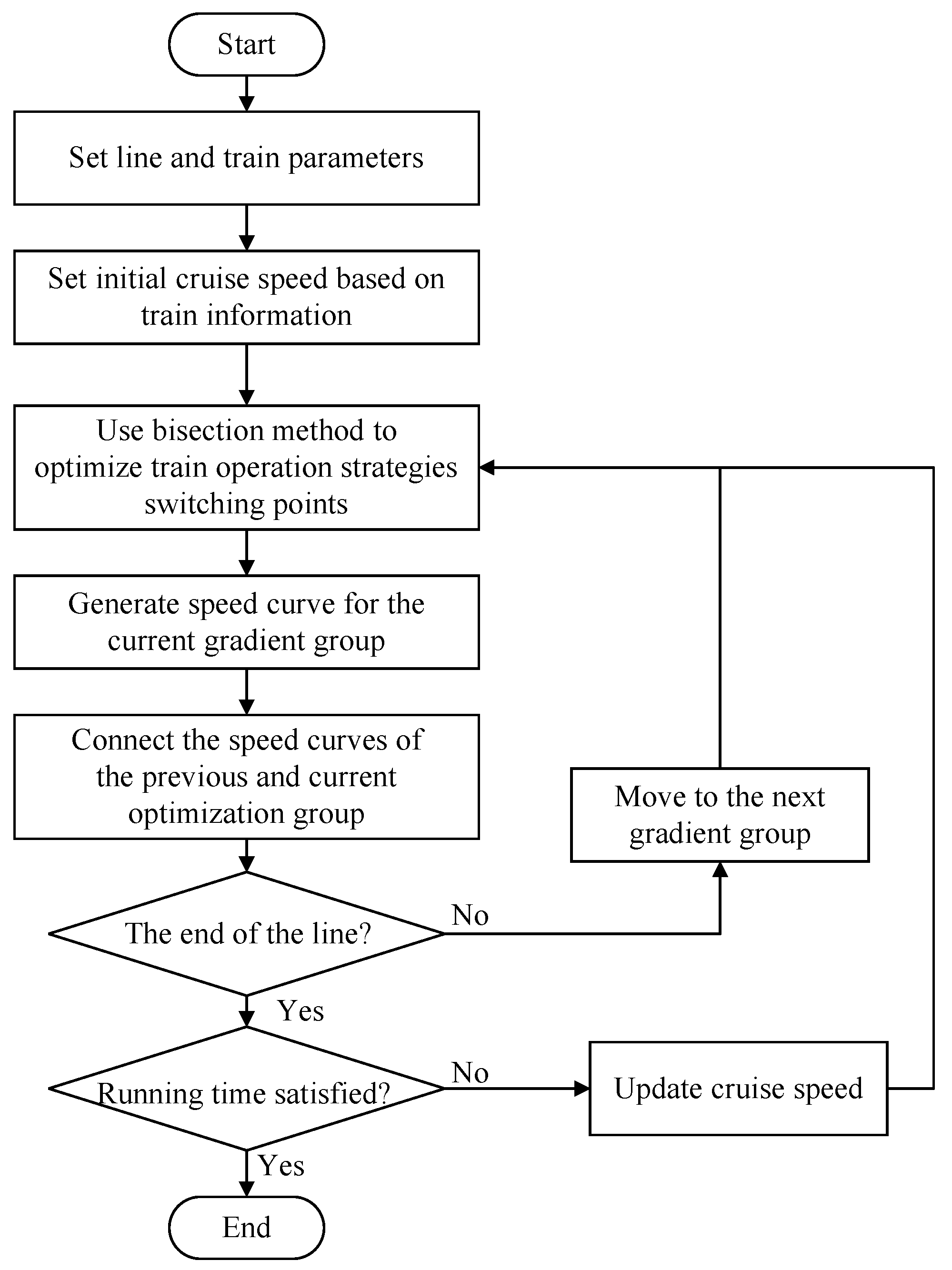
2.2. Rolling Optimization Algorithm (ROA) for Freight Train Speed Curve
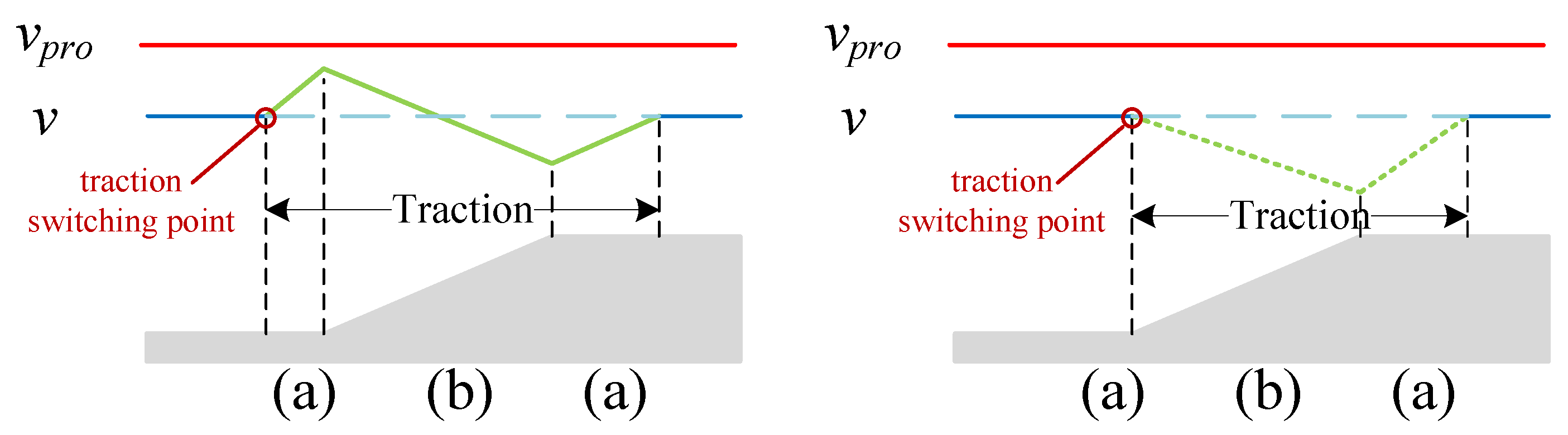
2.2.1. Train Speed Curve Optimization for Each Gradient Group
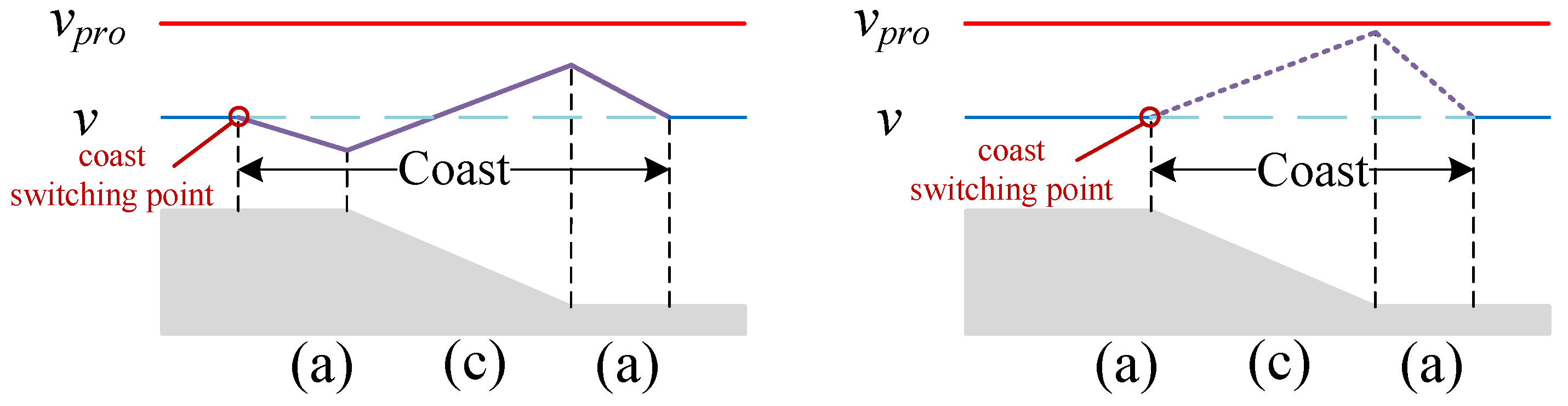
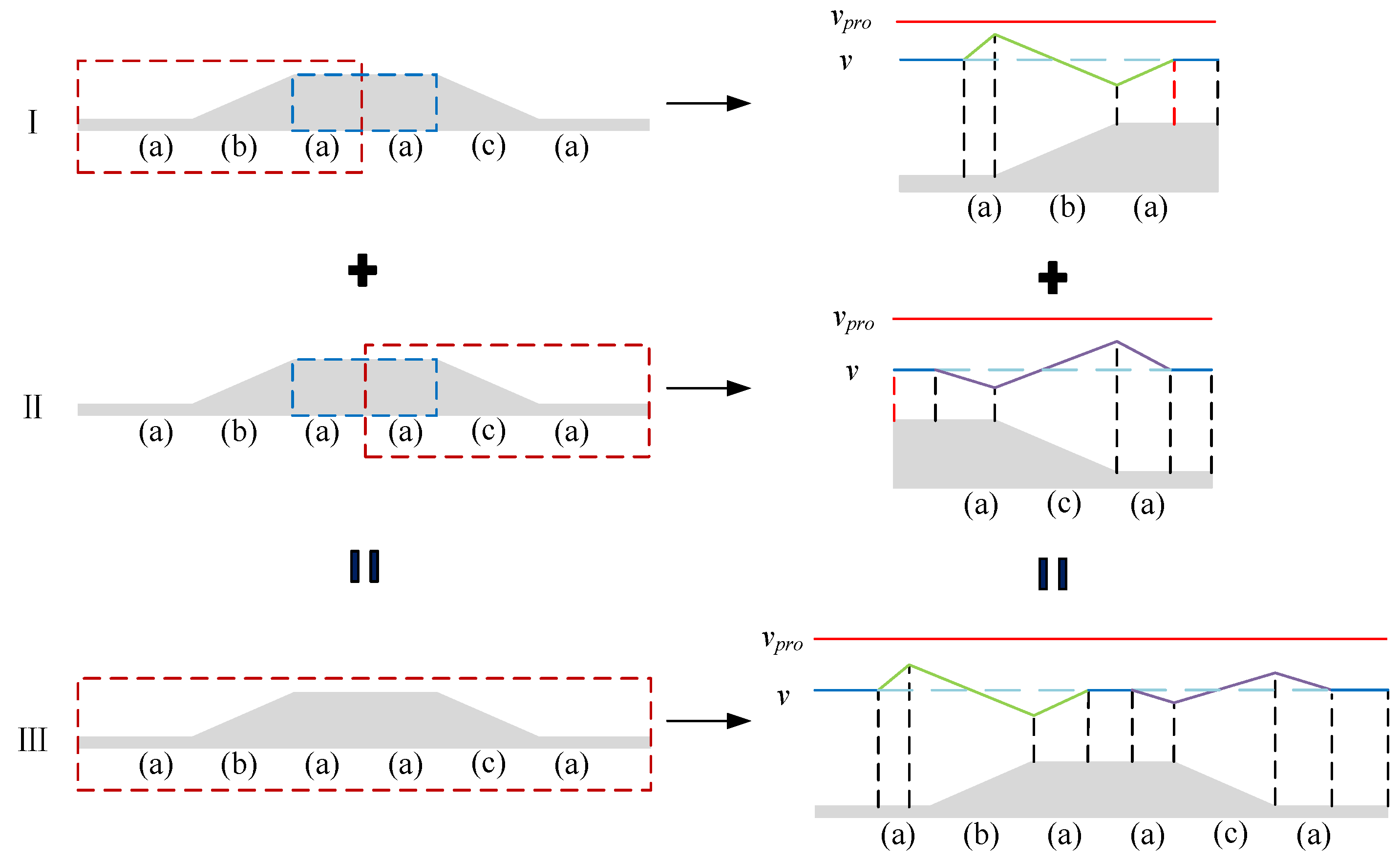
2.2.2. Speed Curves Connecting Method
2.2.3. Cruise Speed Updating Method
2.3. MPC Algorithm for Freight Train Speed Curve Re-Optimization
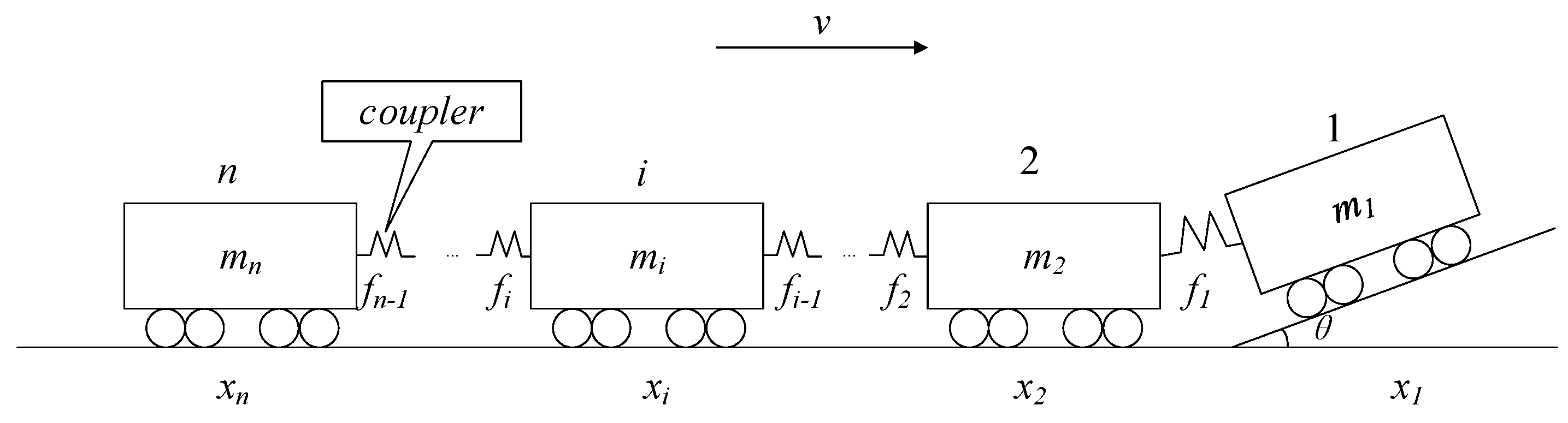
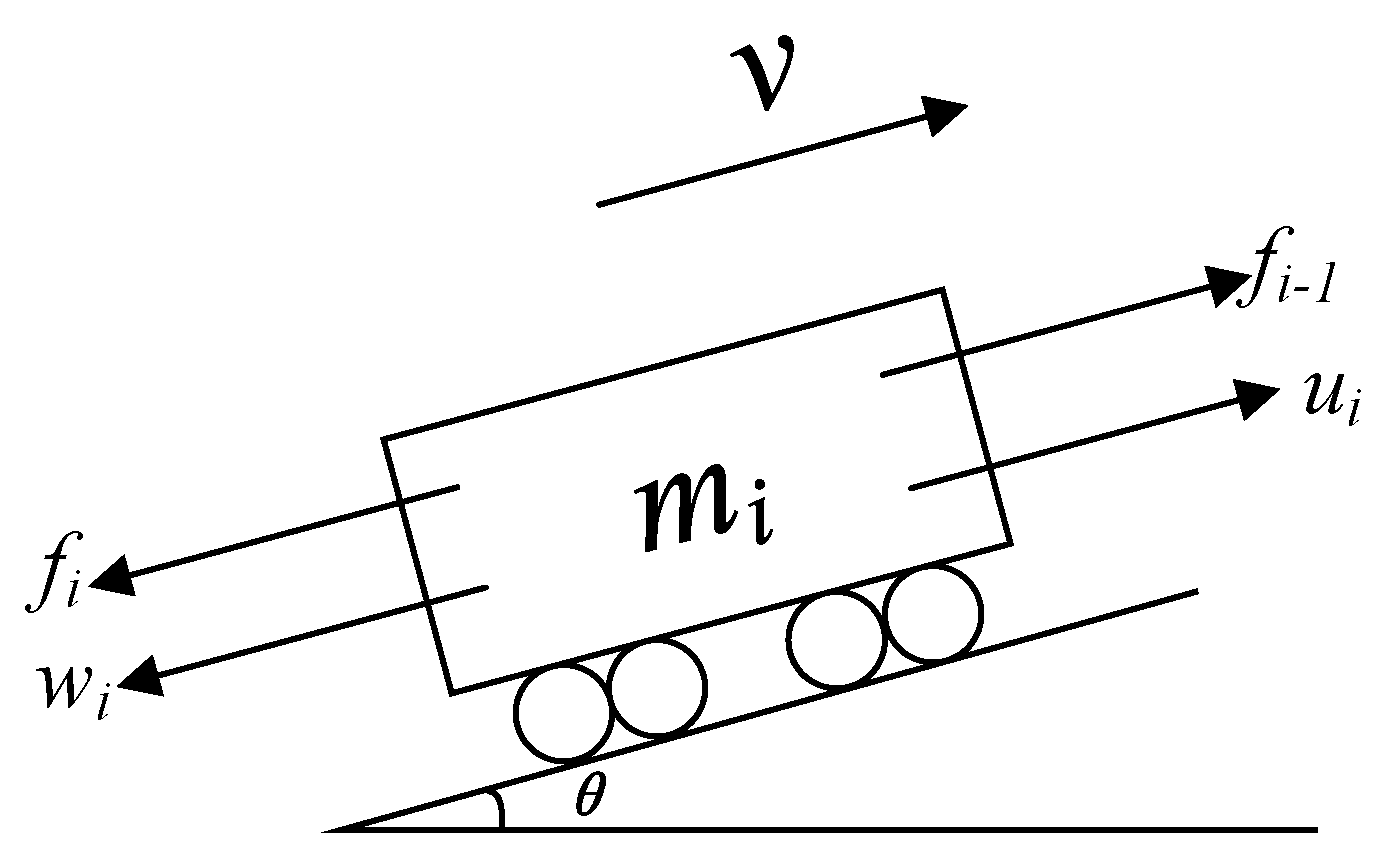
2.3.1. The Multi-Mass Train Model
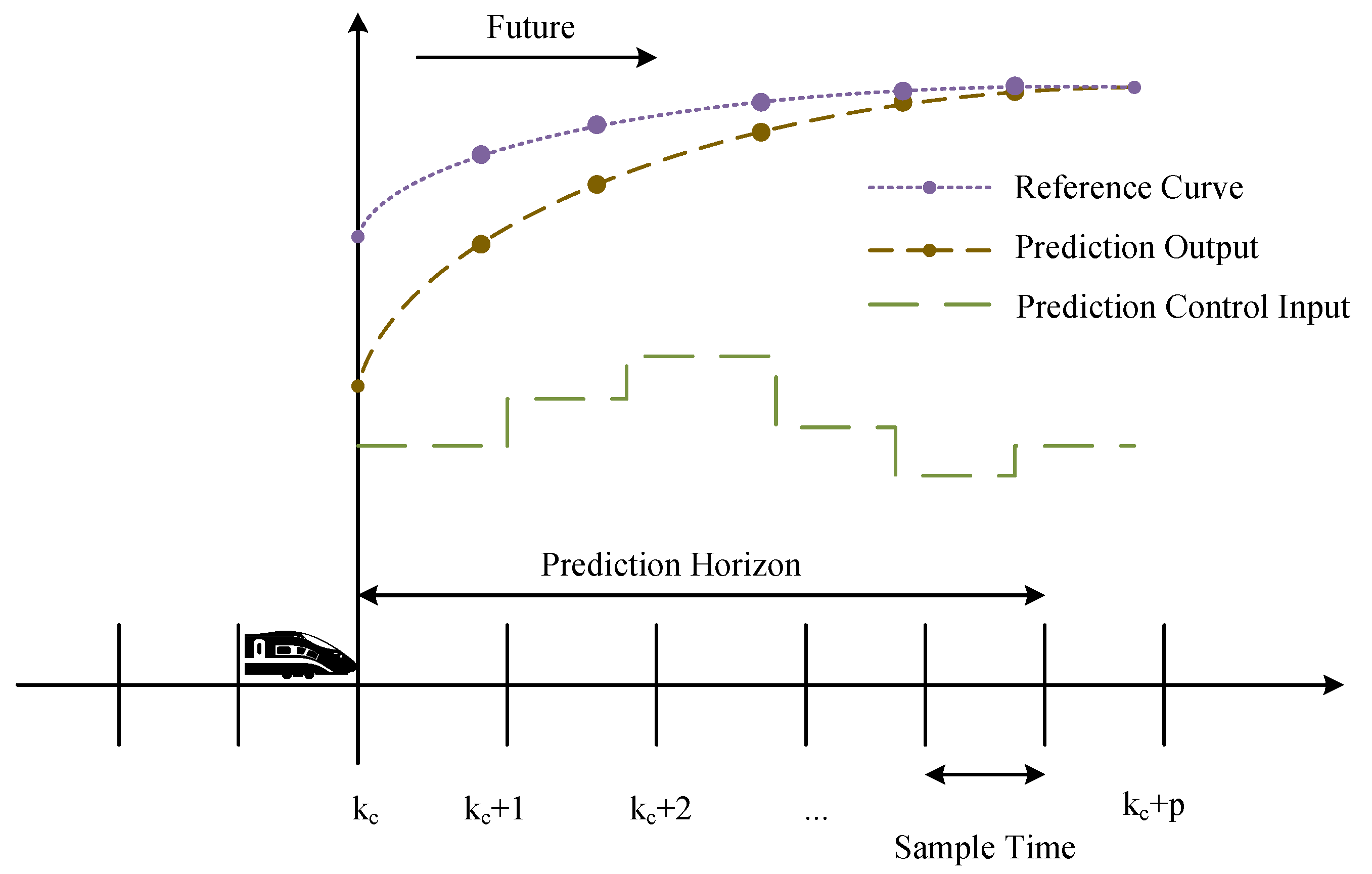
2.3.2. MPC Framework
2.3.3. Optimization Objective Function
2.3.4. Train Operational Constraints
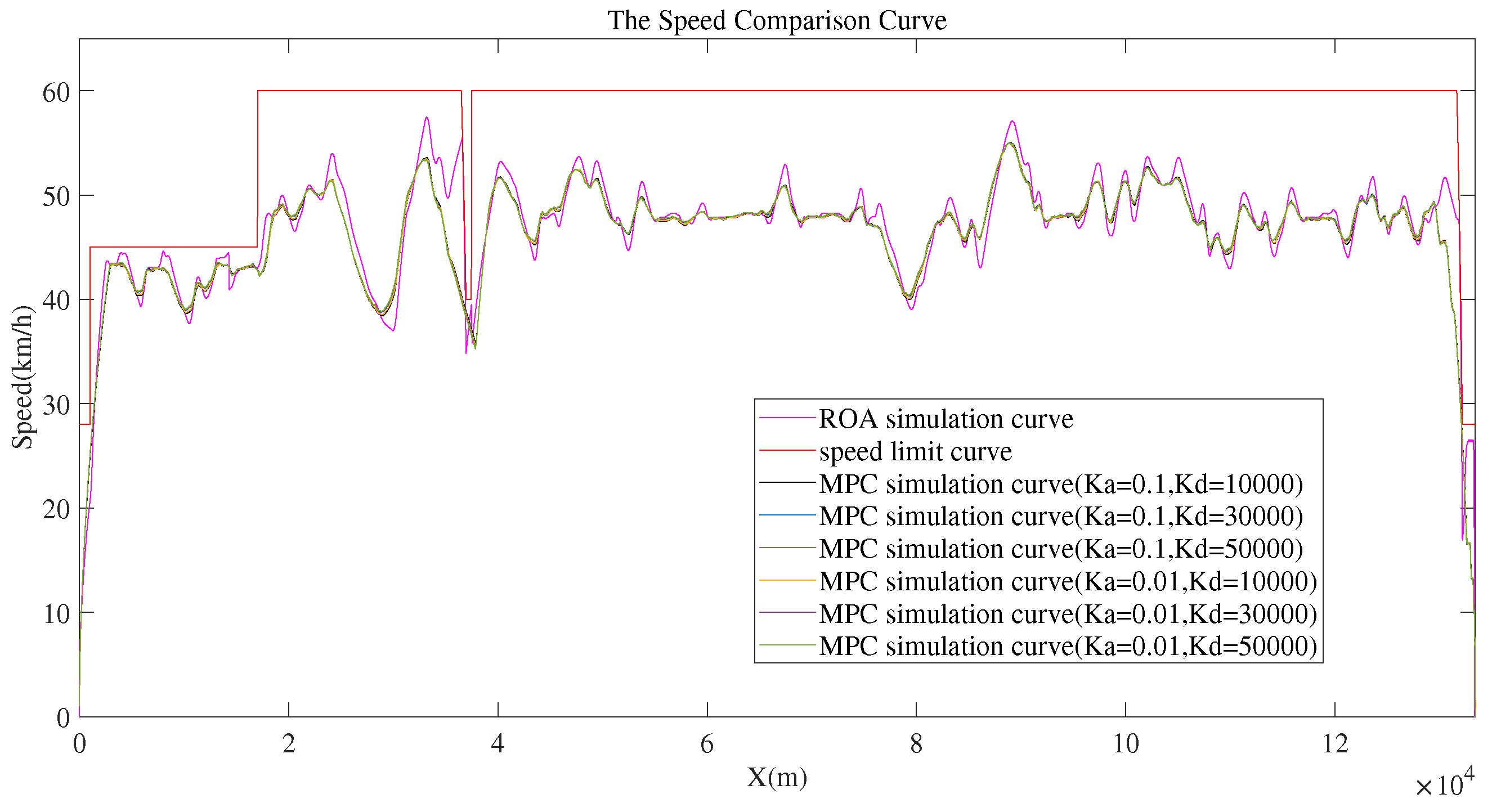
3. Simulation Results
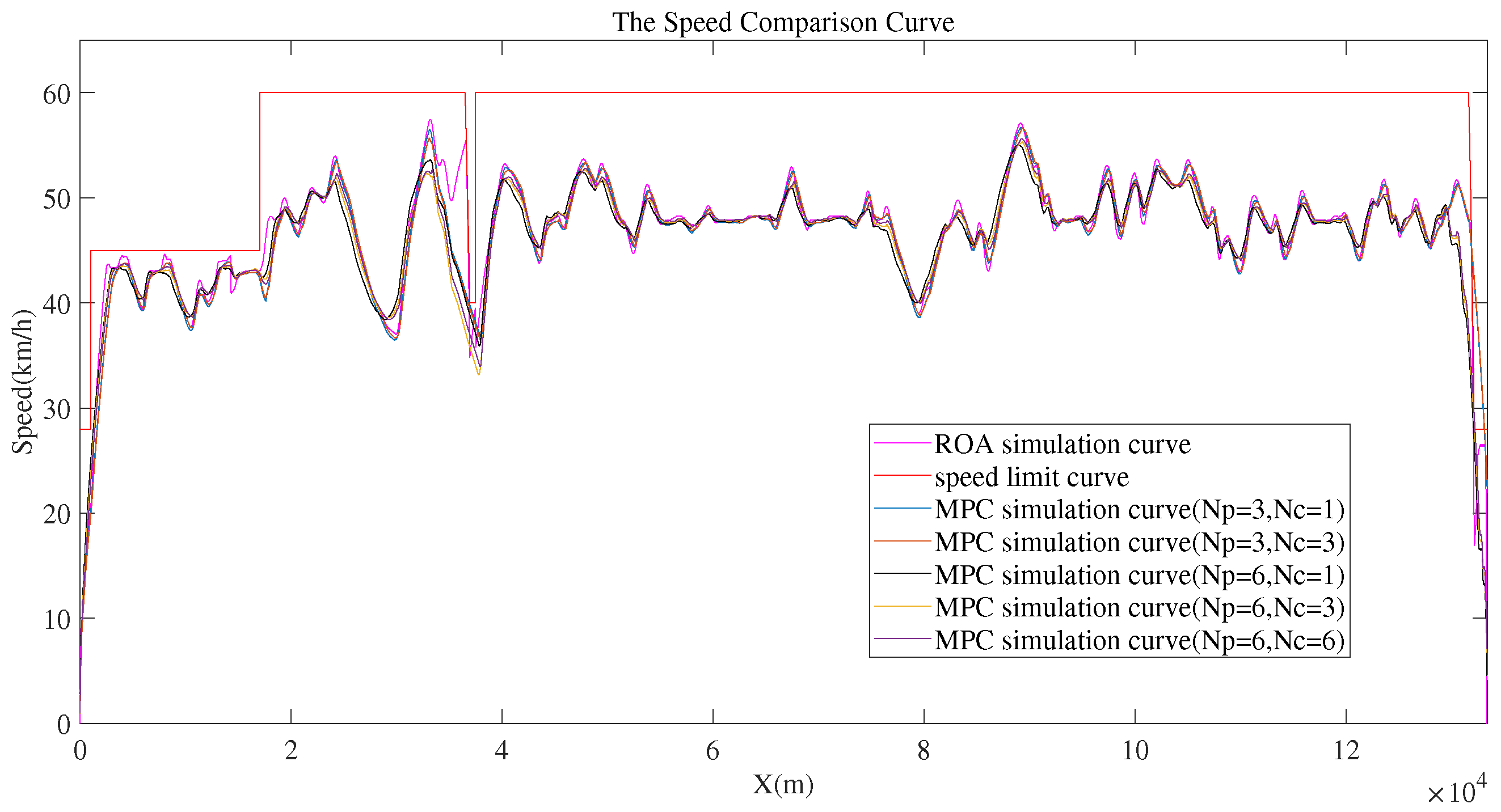
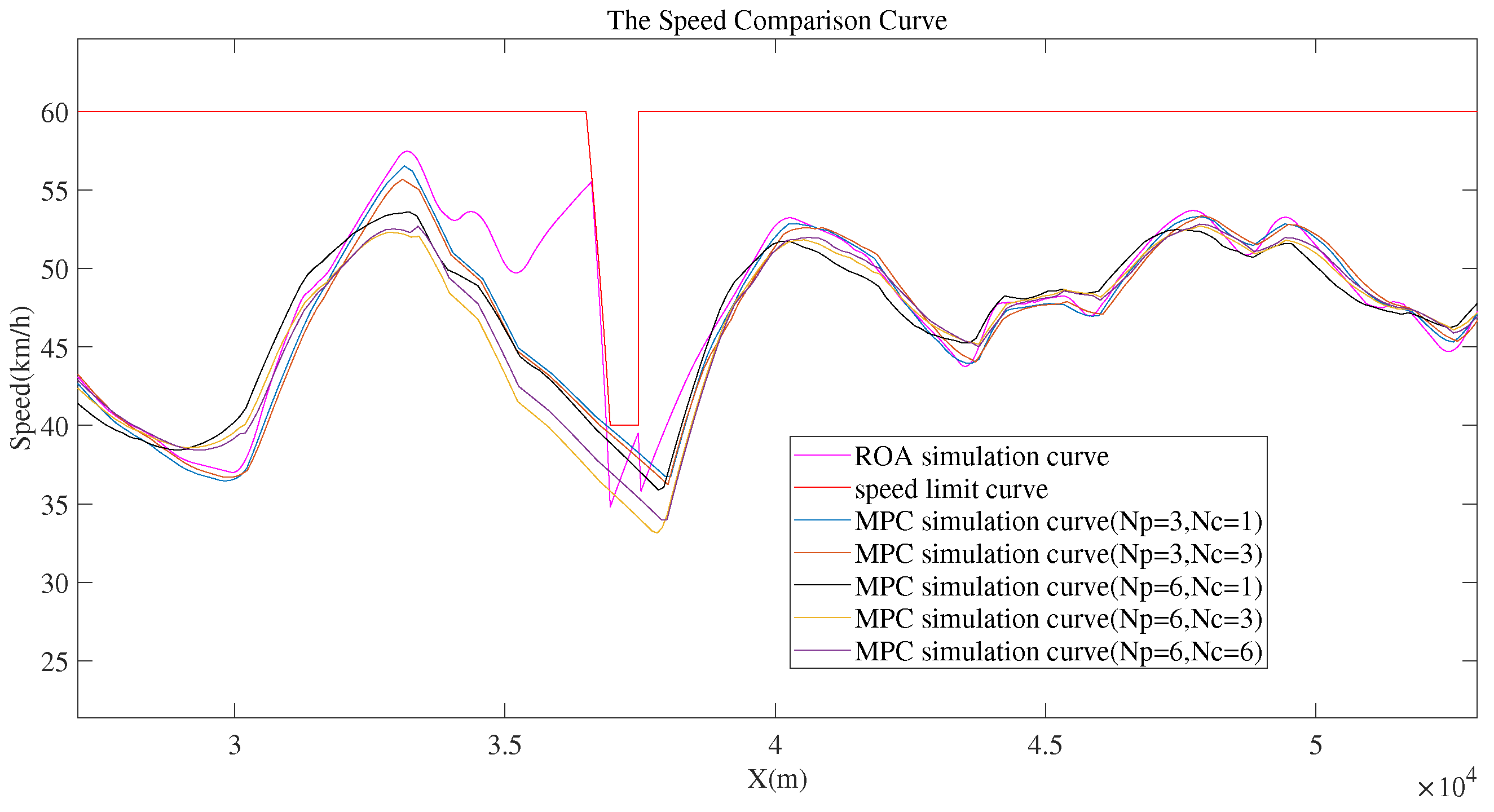
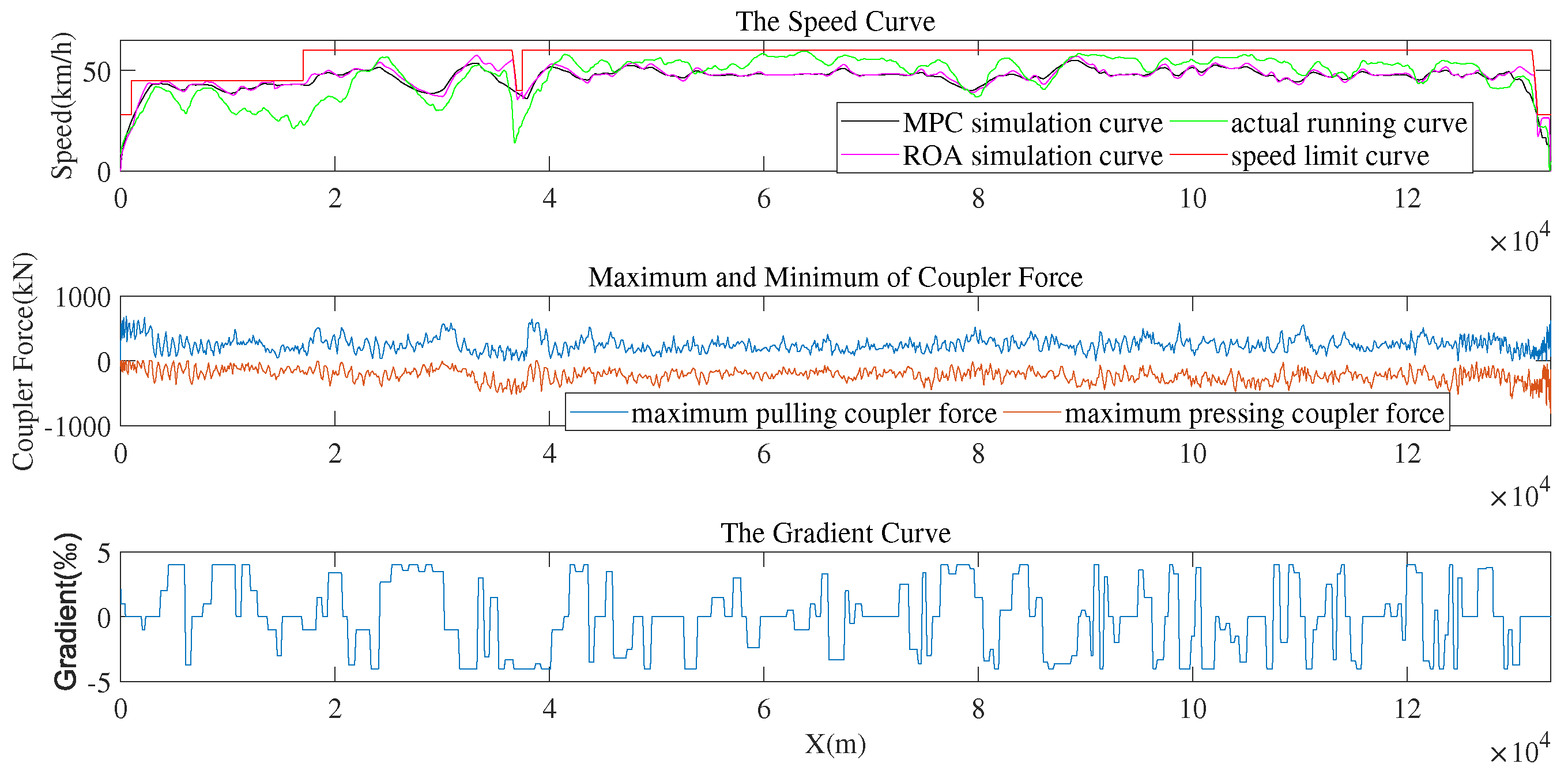

4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DAS | Driver Advisory System |
| ROA | Rolling Optimization Algorithm |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| ATO | Automatic Train Operation |
| LQR | Linear Quadratic Regulator |
| NSGA-II | Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II |
| FAGA | Fuzzy Adaptive Genetic Algorithm |
| PID | Proportion Integration Differentiation |
| LKJ | Train Operation Monitoring Equipment |
References
- National Railway Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Railway Statistics Bulletin 2023. Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Howlett, P.; Milroy, I.; Pudney, P. Energy-efficient train control. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 1993, 26, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, P.; Pudney, P.; Vu, X. Local energy minimization in optimal train control. Automatica 2009, 45, 2692–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudovikov, O.E.; Bespał’Ko, S.V.; Kiselev, M.D.; Serdobintsev, E.V. Application of a reference train model in an automatic control system of freight-train speed. Russ. Electr. Engin. 2017, 88, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, P.; Bayoumi, M.M. Suboptimal control strategies for multilocomotive powered trains. In Proceedings of the 19th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control including the Symposium on Adaptive Processes, Albuquerque, NM, USA; 1980; pp. 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.; Xia, X.; Kayser, C. Modelling and model validation of heavy-haul trains equipped with electronically controlled pneumatic brake systems. Control Engineering Practice 2007, 15, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuan, X.; Xia, X. Speed regulation with measured output feedback in the control of heavy haul trains. Autom 2008, 44, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, P.G.; Cheng, J. Optimal driving strategies for a train on a line with continuously varying gradient. The Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series B. Applied Mathematics 1997, 38, 388–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmelnitsky, E. On an optimal control problem of train operation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2000, 45, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, V.D.; Weidmann, U.A. Improving energy efficiency for freight trains during operation: The use of simulation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC); Florence, Italy, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Koseki, T.; Miyatake, M. Application of dynamic programming to optimization of running profile of a train. Computers in Railways IX 2004, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, T.; WGassel, C.; Binder, A.; van Luipen, J. Dealing with operational constraints in energy efficient driving. In Proceedings of the IET Conference on Railway Traction Systems (RTS 2010), Birmingham; 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qiu, L.; Ma, J.E. Multi-objective optimization of high-speed train running speed trajectory based on particle swarm and NSGA-II fusion algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific); Haining, China, 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.Z.; hang, D.K.; Li, W. Research on multi-objective optimization of freight train operation process based on improved bald eagle search algorithm. Journal of Computers 2022, 33, 135–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Xu, K.X.; Fu, Y.T. Research on multi-objective optimal control of heavy haul train based on iImproved genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI); Shenyang, China, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isna, S.S.; Ari, S. Application of model predictive control on metro train scheduling problems. International Journal of Vehicle Information and Communication Systems 2023, 8, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.X. Research on train automatic operation control algorithm for heavy-hual trains based on model predictive control. M.S. thesis, Southwest Jiaotong Univ., Chengdu, Sichuan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Jiang, F. Research on model predictive control method of heavy-haul trains based on multi-point model. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC); Milan, Italy, 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Wang, S.; Alanamu, B.B. Research on optimal train adhesion control based on nonlinear model predictive control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Transportation and City Engineering (STCE 2023), Chongqing, China; 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Li, Q.; Zhuan, X.T. Energy-efficient operation of heavy haul trains in an MPC framework. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Rail Transportation Proceedings, Beijing, China; 2013; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Zhuan, X.T.; Xia, X.H. Optimal operation of heavy haul trains using model predictive control methodology. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations, Logistics and Informatics, Beijing, China; 2011; pp. 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Zhuan, X.T. Optimal operation of heavy-haul trains equipped with electronically controlled pneumatic brake systems using model predictive control methodology. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology 2014, 22, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Zhuan, X.T. Development of an Optimal Operation Approach in the MPC Framework for Heavy-Haul Trains. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2015, 16, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Research on receding optimization of energy-saving speed curve of freight trains. M.S. thesis, Beijng Jiaotong Univ., Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bujarbaruah, M.; Zhang, X.J.; Borrelli, F. Adaptive MPC with Chance Constraints for FIR Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC), Milwaukee, WI, USA; 2018; pp. 2312–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.M. Research on the dynamics performance evaluation standard for freight trains and the suggested schemes(last part continued)—evaluation standard for vertical wheel rail force and coupler force. Rolling Stock 2002, 03, 10–13+1. [Google Scholar]
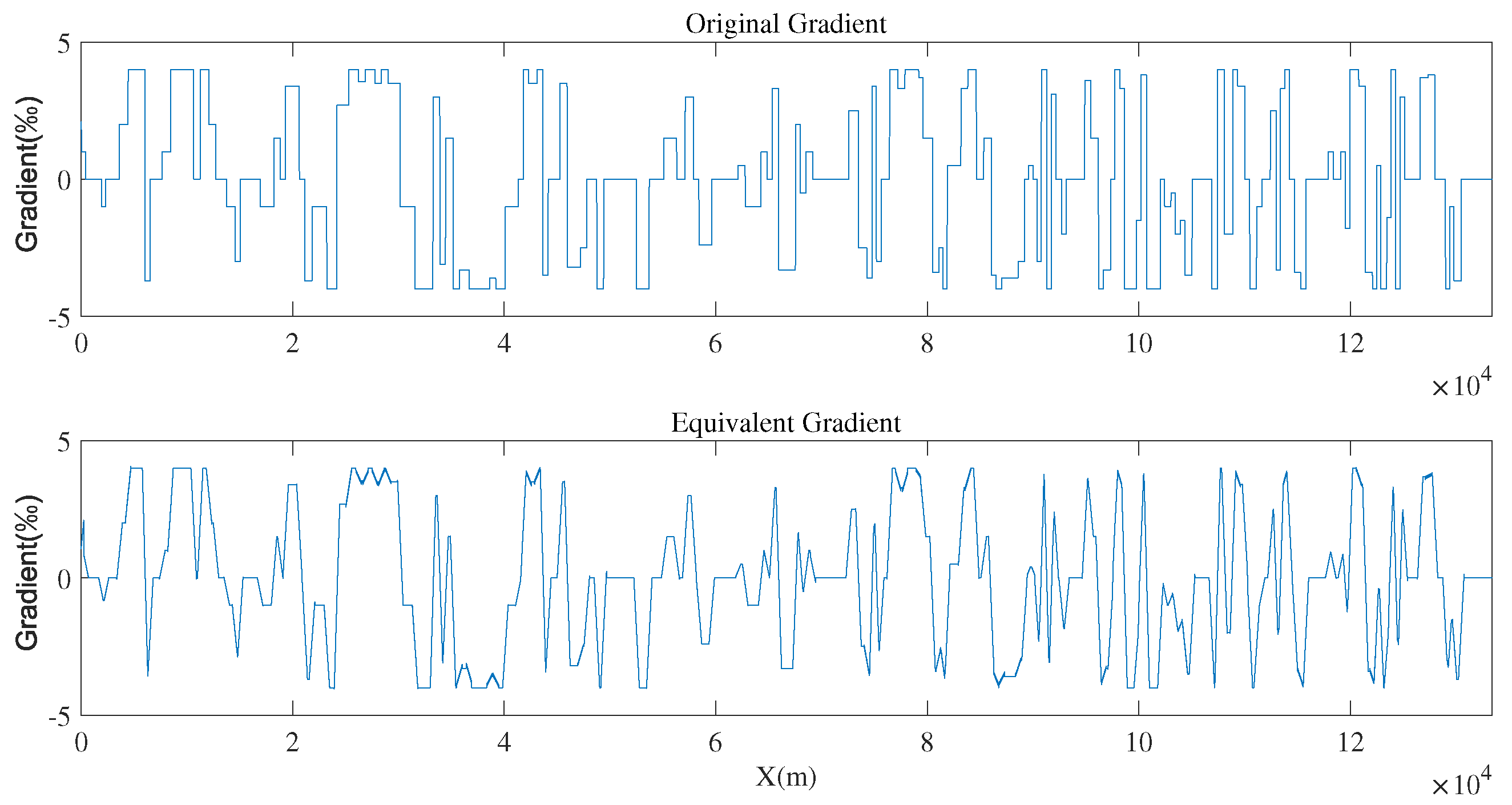
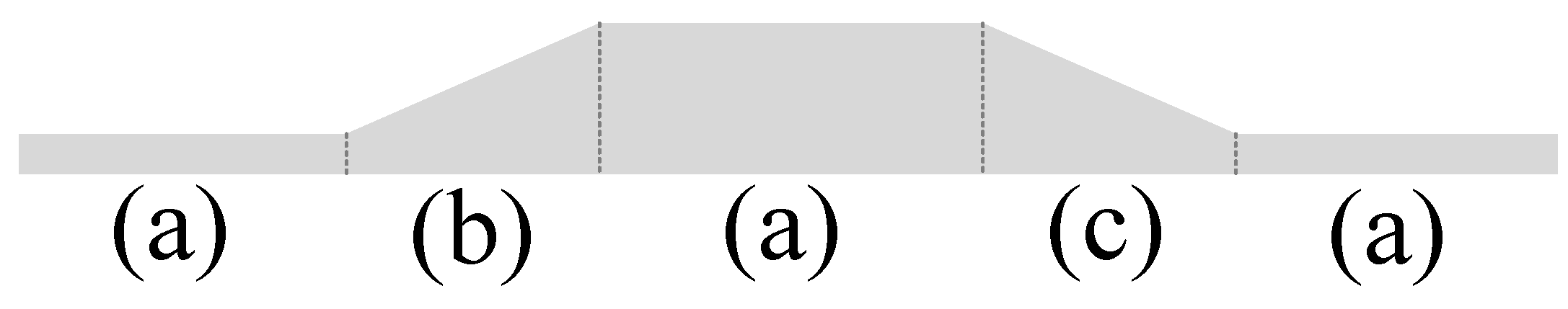
| Gradient Types | Gradient Values | Type Symbols |
|---|---|---|
| General section | a | |
| Steep uphill section | b | |
| Downhill section | c | |
| Steep downhill section | d |
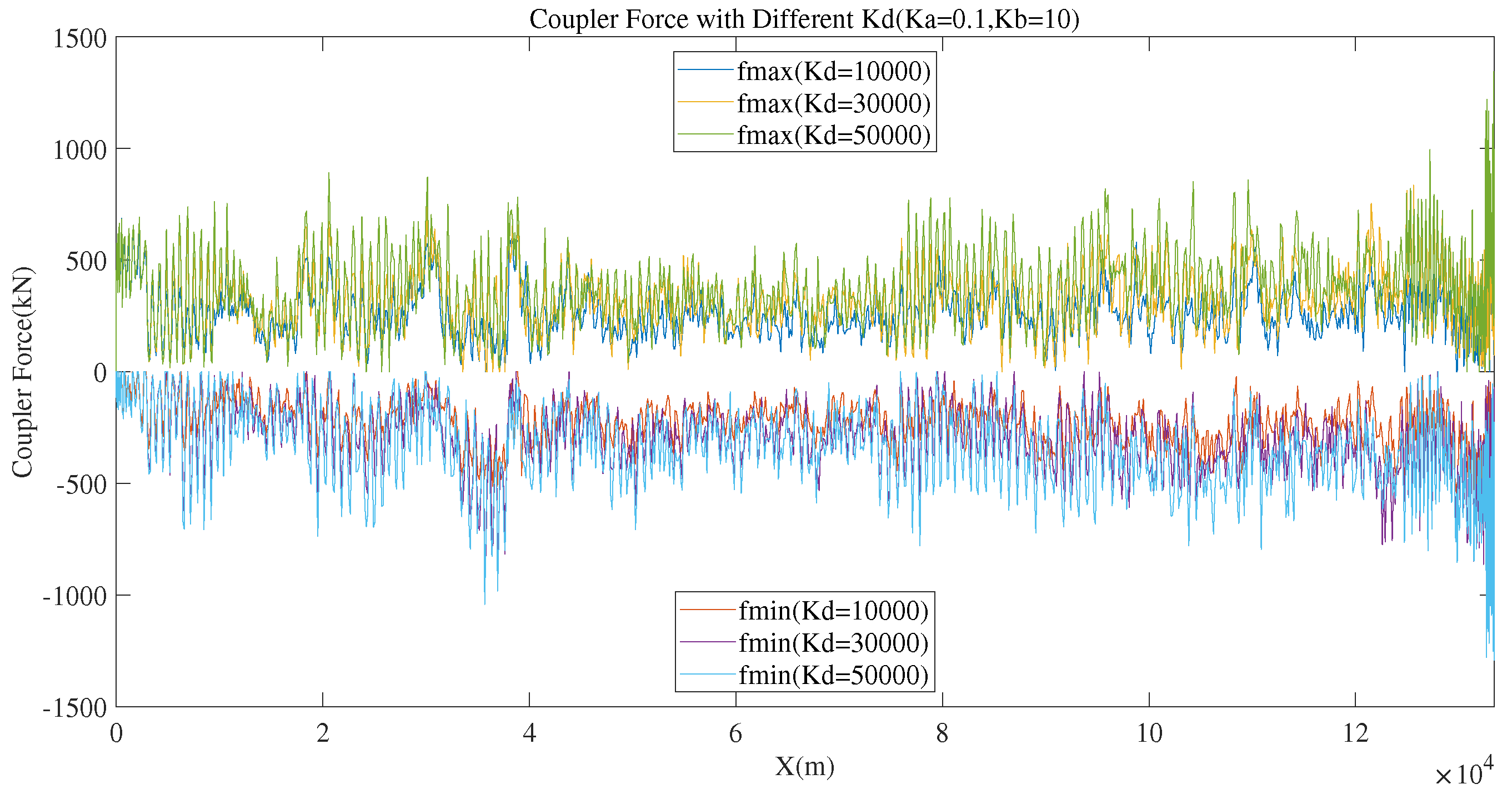
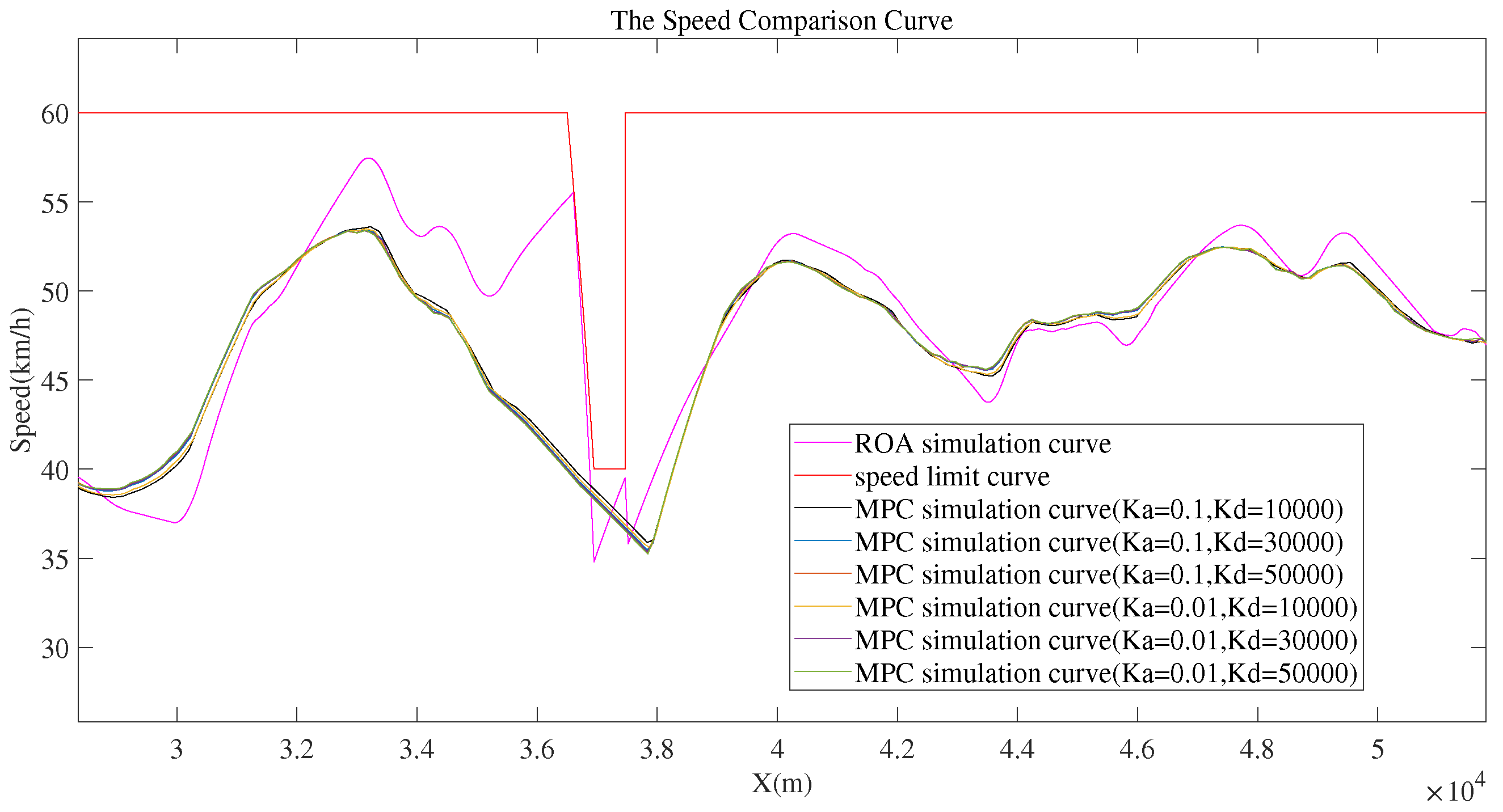
| 0.1 | 10 | 10000 | 687.2 | -804.2 | 20 |
| 0.1 | 10 | 30000 | 838.9 | -983.5 | 15 |
| 0.1 | 10 | 50000 | 1343.6 | -1292.4 | 25 |
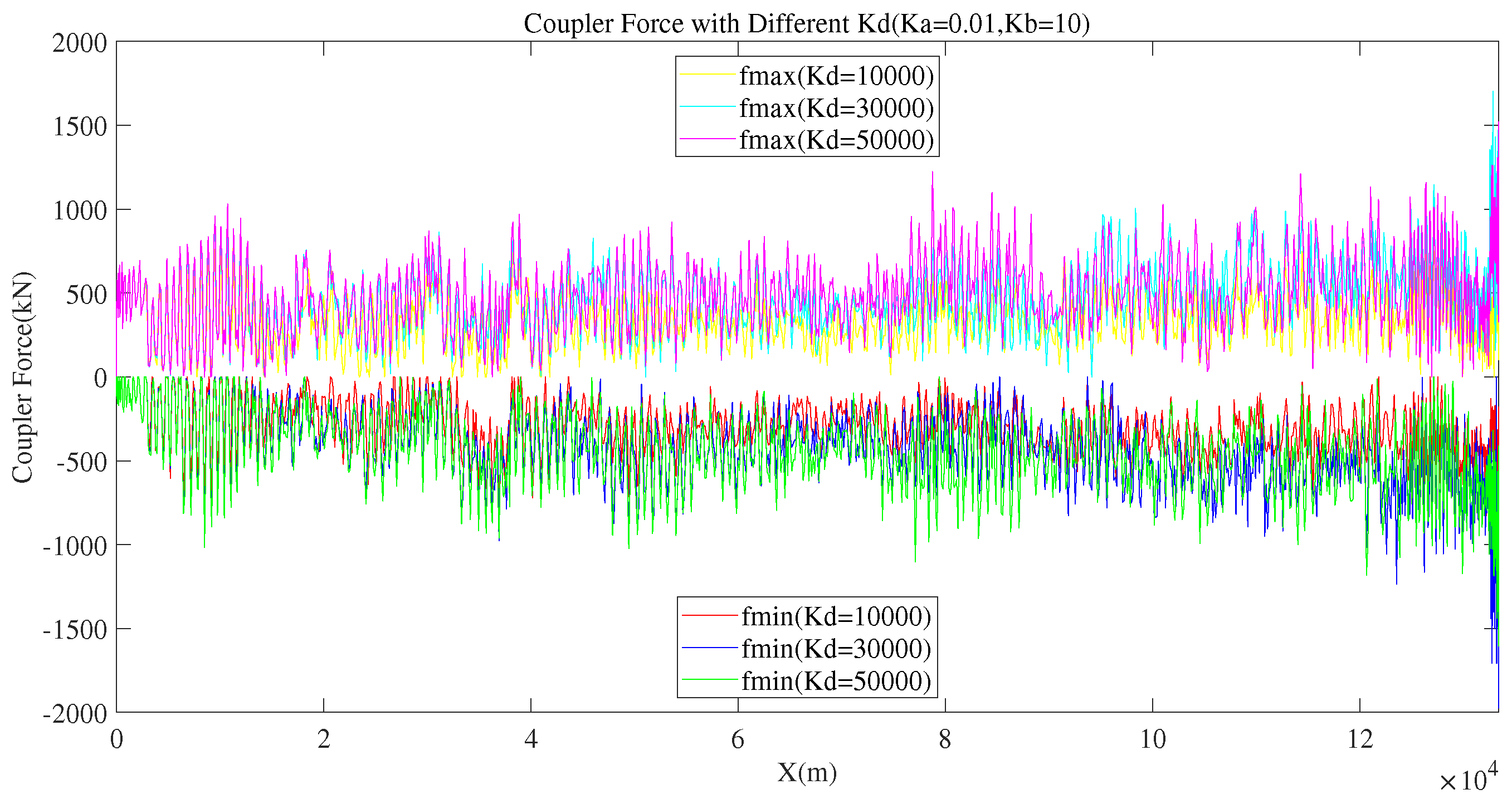
| 0.01 | 10 | 10000 | 1021.8 | -1034.6 | 15 |
| 0.01 | 10 | 30000 | 1701.7 | -1974.5 | 20 |
| 0.01 | 10 | 50000 | 1520.9 | -1604.7 | 25 |
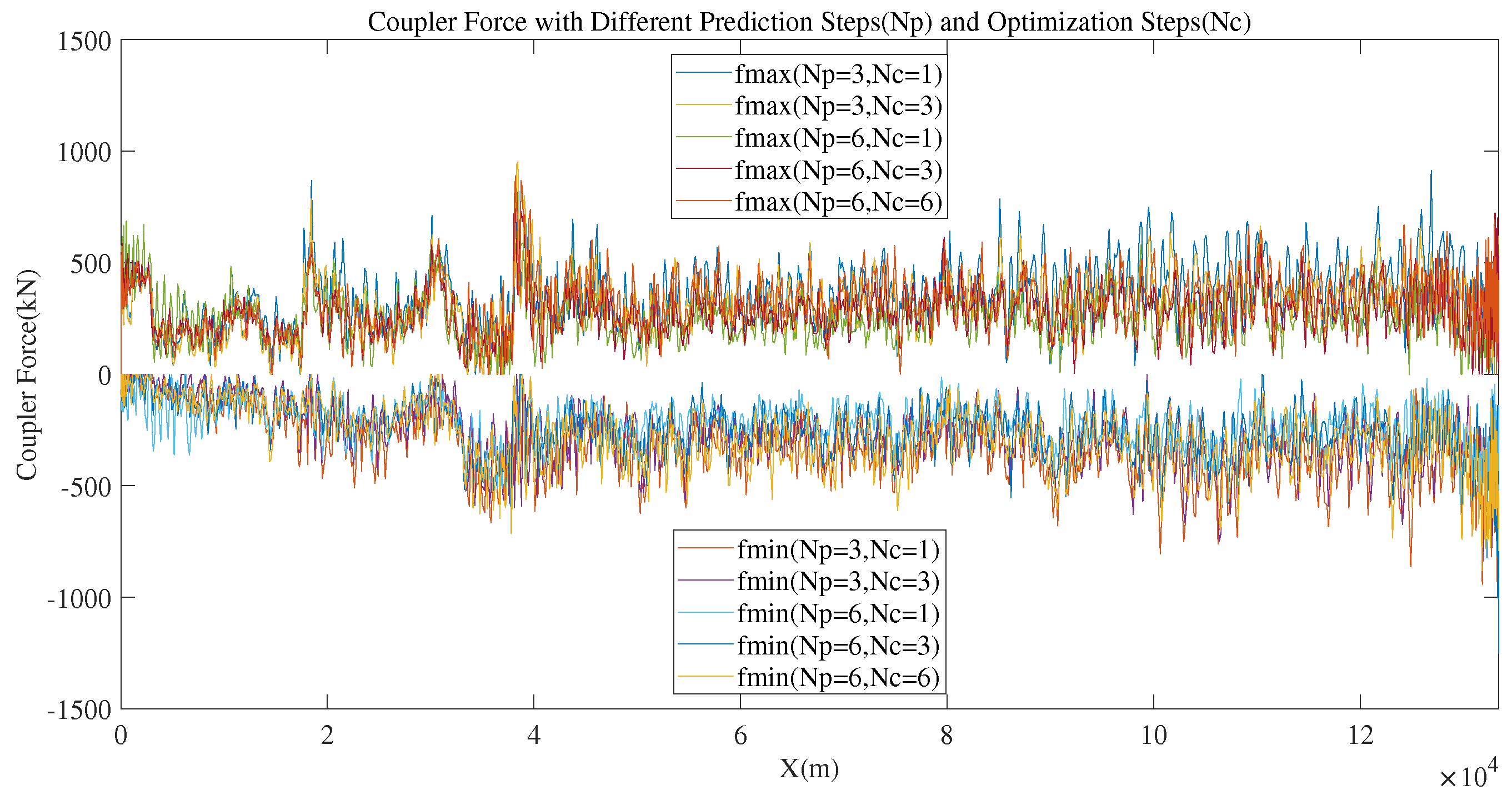
| 6 | 6 | 763.9 | -875.8 | 35 |
| 6 | 3 | 831.9 | -1005.4 | 35 |
| 6 | 1 | 687.2 | -804.2 | 20 |
| 3 | 3 | 785.7 | -706.5 | 160 |
| 3 | 1 | 868.4 | -851.1 | 150 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





