Submitted:
19 December 2024
Posted:
19 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
METODS
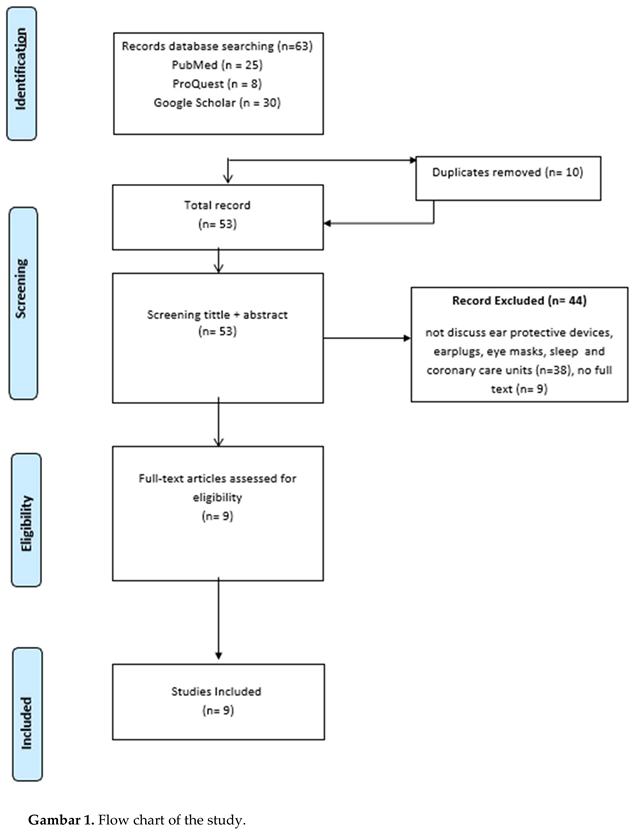
Article search
| Author/ Year | Article Title | Method | Results |
| (Molavynejad et al., 2022) | A randomized trial of comparing video telecare education vs. in-person education on dietary regimen compliance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a support for clinical telehealth Providers | RCT | The research results found that education via video was more significant than direct face-to-face education, but the researchers added that direct face-to-face education was just as good. |
| (Adam et al., 2018) | Evaluating the Impact of Diabetes Self-Management Education Methods on Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviours of Adult Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | RCT | The research conducted was to analyze the independence of diabetes patients by looking at the knowledge, attitudes and behavior of diabetes sufferers through direct face-to-face education and supervision at home. |
| (Hu et al., 2022) | Leveraging Social Media to Increase Access to an Evidence-Based Diabetes Intervention Among Low-Income Chinese Immigrants: Protocol for a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial | RCT | This study focuses on Chinese immigrants, where this study utilizes social media-based educational videos to improve the health status of Chinese immigrants, and finds that there is an increase in knowledge and an increase in the level of health of Chinese immigrants. |
| (Cha et al., 2017) | Community-based randomized controlled trial of diabetes prevention study for high-risk individuals of type 2 diabetes: Lifestyle intervention using web-based system | RCT | This study aims to prevent the increase in diabetes sufferers, where the results of the study said that there was an increase in knowledge about preventing diabetes and an increase in interest in sports. This study used the video method. |
| (Dyson et al., 2010) | An assessment of lifestyle video education for people newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes | RCT | This study aims to improve and maintain the health status of newly diagnosed diabetes patients (acute), where this study resulted in an increase in knowledge and interest in learning from patients who were given educational videos. |
| (Subramanian et al., 2020) | Effectiveness of nurse-led intervention on self-management, self-efficacy and blood glucose level among patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus | RCT | The results of the study prove that intervention in the form of providing educational videos can improve self-management in diabetes patient |
| (Leong et al., 2022) | Social Media-Delivered Patient Education to Enhance Self-management and Attitudes of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Randomized Controlled Trial | RCT | The results of the study prove that providing video-based education via social media can improve self-management in diabetes patients. |
| (Hidrus et al., 2020) | Effects of brain breaks videos on the motives for the physical activity of Malaysians with type-2 diabetes mellitus | RCT | The research results found that there was an increase in interest in learning from the intervention given, namely providing educational videos to diabetes patients. |
| (Hamidi et al., 2022) | The Effects of Self-Efficacy and Physical Activity Improving Methods on the Quality of Life in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review | SYSTEMATIC REVIEW | The research results found that there was an increase in self-efficacy in the intervention of providing education via video. |
Results and Discussion
Conclusions
References
- Abidin, Z. (2018). Health Education dengan Pendekatan Sosial Media Reminder dan Audiovisula terhadap Kepatuhan dan Kadar Glukosa Darah Pasien DM Tipe 2 di Rumah Sakit Universitas Airlangga Surabaya. Jurnal Perpustakaan Universitas Airlangga, 1–135.
- Adam, L. , O’Connor, C., & Garcia, A. C. (2018). Evaluating the Impact of Diabetes Self-Management Education Methods on Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviours of Adult Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Canadian Journal of Diabetes, 42(5), 470-477.e2. [CrossRef]
- Astuti, W. (2018). Kuesioner Penelitian Pengaruh Pemberan Konseling Melalui Vidio, Pengetahuan, Sikap, Kepatuhan Diet Dan Kadar ula Darah Sewaktu Pasien DM Tipe 2 Di RSUD Cibinong Tahun 2018. July, 1–4. https://digilib.esaunggul.ac.id/public/UEU-Undergraduate-11691-KUESIONER PENELITIAN.Image.Marked.pdf.
- Cha, S. A. , Lim, S. Y., Kim, K. R., Lee, E. Y., Kang, B., Choi, Y. H., Yoon, K. H., Ahn, Y. B., Lee, J. H., & Ko, S. H. (2017). Community-based randomized controlled trial of diabetes prevention study for high-risk individuals of type 2 diabetes: Lifestyle intervention using web-based system. BMC Public Health, 17(1), 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Dyson, P. A. , Beatty, S., & Matthews, D. R. (2010). An assessment of lifestyle video education for people newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics, 23(4), 353–359. [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, S. , Gholamnezhad, Z., Kasraie, N., & Sahebkar, A. (2022). The Effects of Self-Efficacy and Physical Activity Improving Methods on the Quality of Life in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Journal of Diabetes Research, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidrus, A. , Kueh, Y. C., Norsaádah, B., Chang, Y. K., Hung, T. M., Naing, N. N., & Kuan, G. (2020). Effects of brain breaks videos on the motives for the physical activity of Malaysians with type-2 diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(7), 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Hu, L. , Islam, N., Zhang, Y., Shi, Y., Li, H., Wang, C., & Sevick, M. A. (2022). Leveraging Social Media to Increase Access to an Evidence-Based Diabetes Intervention Among Low-Income Chinese Immigrants: Protocol for a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Research Protocols, 11(10), e42554. [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Kesehatan, RI. (2020). Infodatin tetap produktif, cegah, dan atasi Diabetes Melitus 2020. In Pusat Data dan Informasi Kementerian Kesehatan RI (pp. 1–10).
- Leong, C. M. , Lee, T. I., Chien, Y. M., Kuo, L. N., Kuo, Y. F., & Chen, H. Y. (2022). Social Media-Delivered Patient Education to Enhance Self-management and Attitudes of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 24(3), 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Massi, G. , Kallo, V., Studi, P., Keperawatan, I., Kedokteran, F., & Ratulangi, U. S. (2018). Efektifitas Pemberian Edukasi Dengan Metode Video Dan Focus Group Discussion (Fgd) Terhadap Tingkat Pengetahuan Pasien Dm Tipe 2 Di Klinikdiabetes Kimia Farma Husada Manado. Jurnal Keperawatan, 6(1), 1–6.
- Molavynejad, S. , Miladinia, M., & Jahangiri, M. (2022). A randomized trial of comparing video telecare education vs. in-person education on dietary regimen compliance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a support for clinical telehealth Providers. BMC Endocrine Disorders, 22(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, P. S. , & Sari, Y. (2020). HubunganTingkat Pendidikandan Usiadengan Kejadian HipertensidiWilayah Kerja Puskesmas Palaran Tahun 2019. Jurnal Dunia Kesmas, 8(4), 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Pangestika, H. , Ekawati, D., & Murni, N. S. (2022). FAKTOR-FAKTOR YANG BERHUBUNGAN DENGAN KEJADIAN DIABETES MELLITUS TIPE 2 PENDAHULUAN Saat ini penyakit Diabetes Melitus ( DM ) merupakan masalah kesehatan yang sering dikeluhkan oleh masyarakat di dunia karena pola kejadiannya Organisasi mengalami Internat. 7, 132–150.
- Sayekti, I. L. (2019). Pengaruh Pendidikan Kesehatan dengan Media Video Terhadap Pengetahuan, Sikap, dan Perilaku Pencegahan Diabetes Mellitus di Desa Mangunsoko Kecamatan Dukun Kabupaten Magelang. 64.
- Subramanian, S. C. , Porkodi, A., & Akila, P. (2020). Effectiveness of nurse-led intervention on self-management, self-efficacy and blood glucose level among patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, 17(3), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, S. , & Alkaff, R. N. (2013). Diabetes Melitus Pada Perempuan Usia Reproduksi Di Indonesia. Jurnal Kesehatan Reproduksi, 3(1), 46–51. https://media.neliti.com/media/publications/107315-ID-diabetes- mellitus-pada-perempuan-usia-re.pdf.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





