Submitted:
18 December 2024
Posted:
19 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
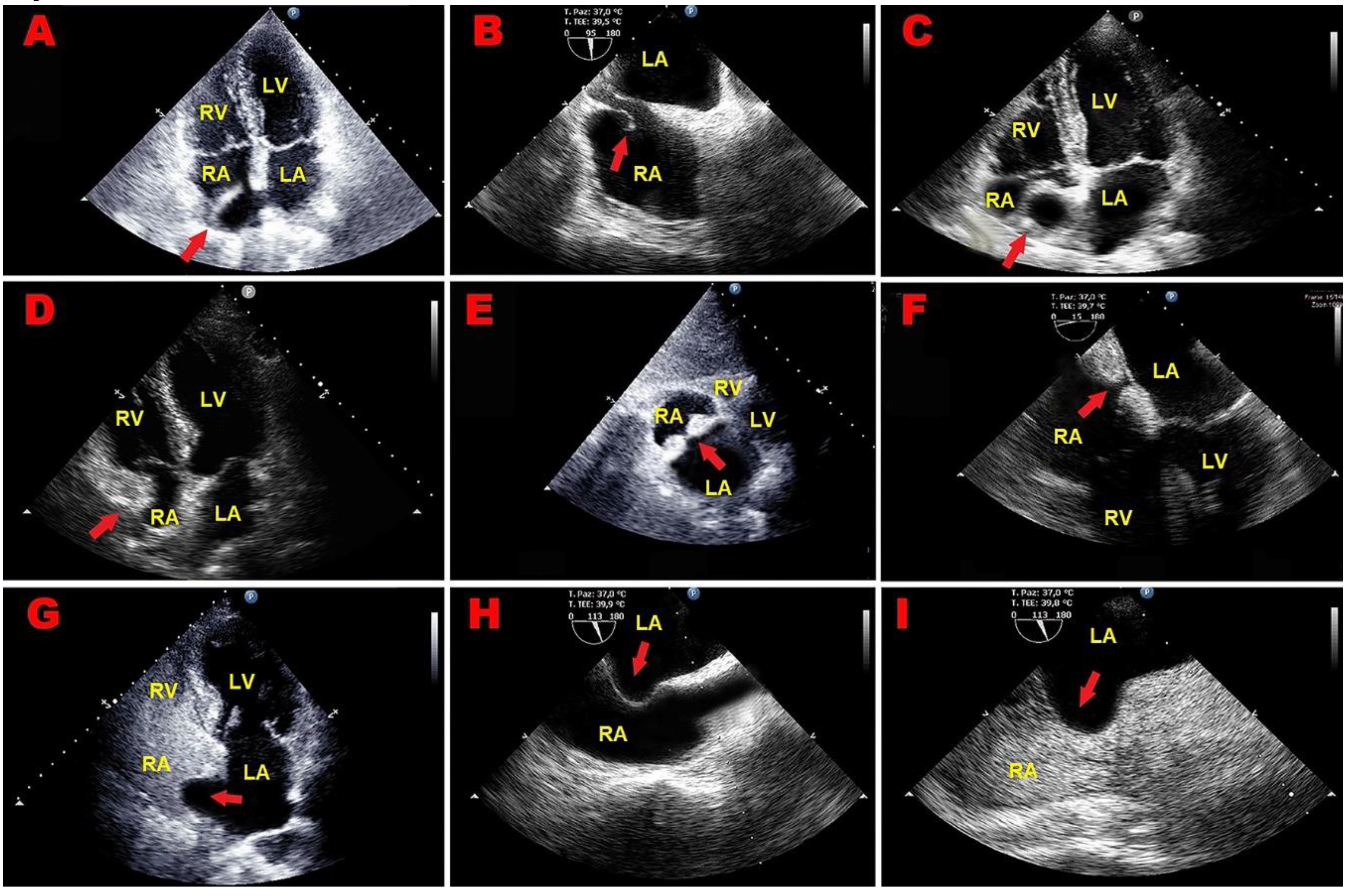
2. Case Series
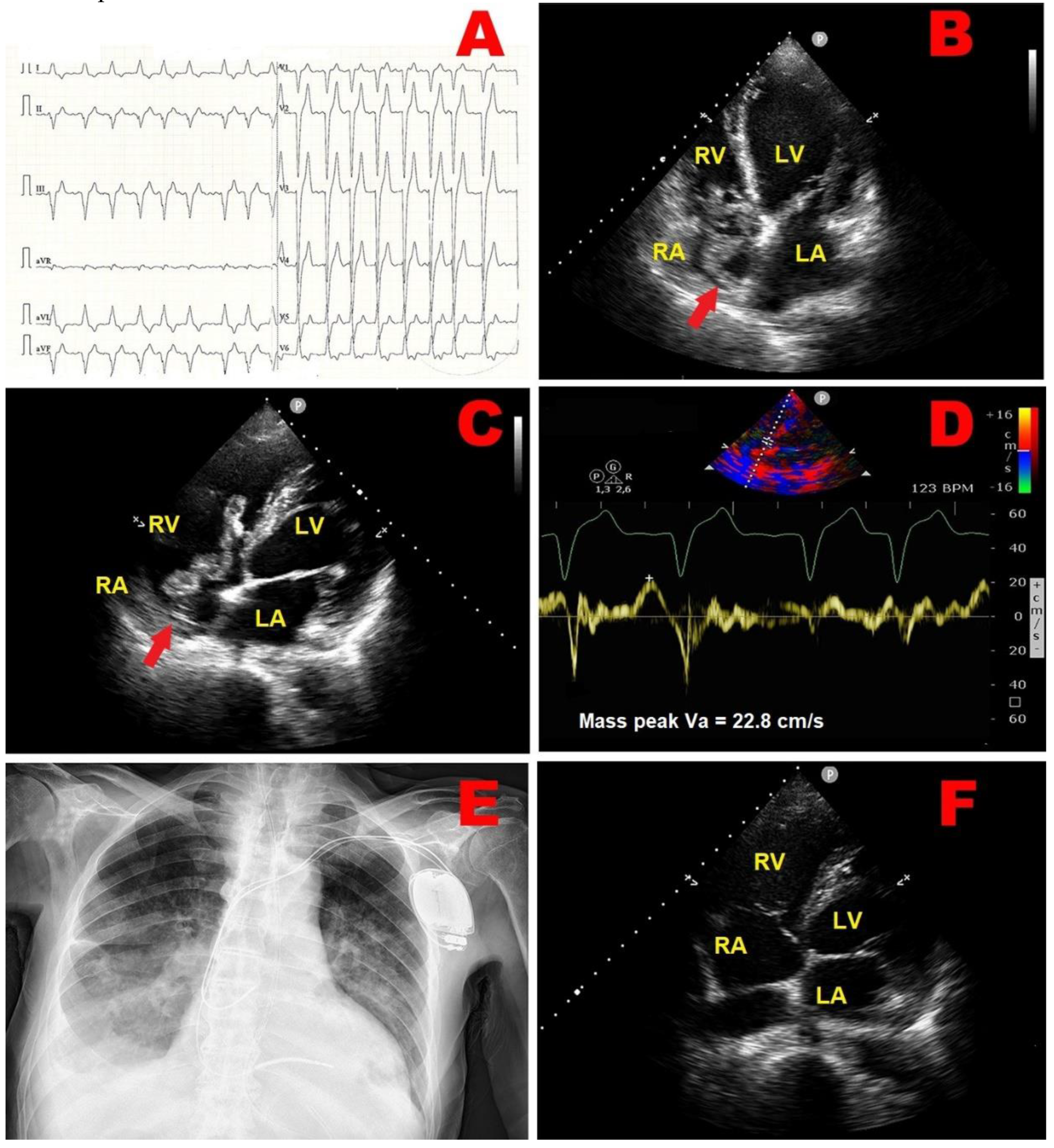
2.1. Clinical Case 1
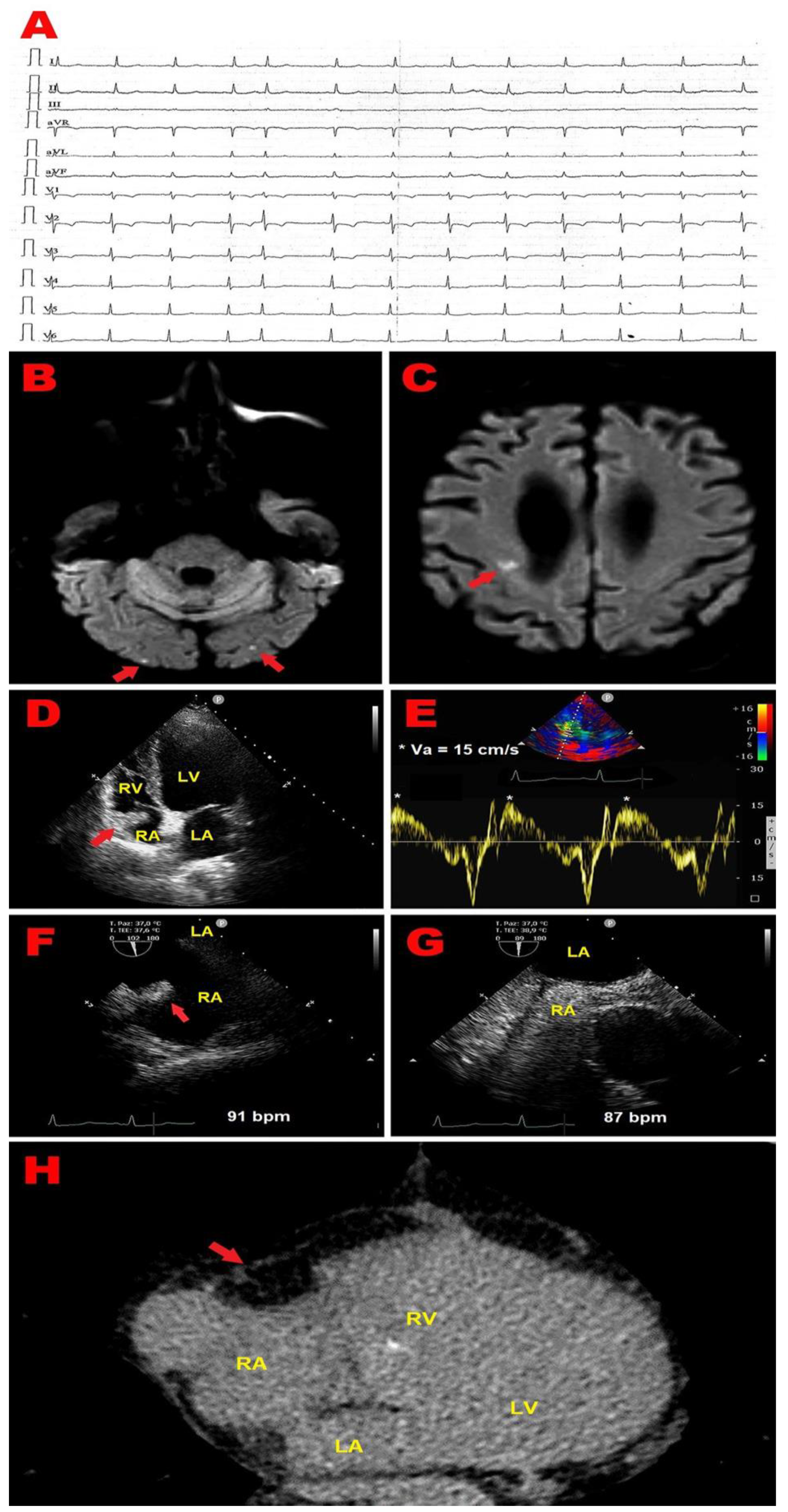
2.2. Clinical Case 2
3. Discussion
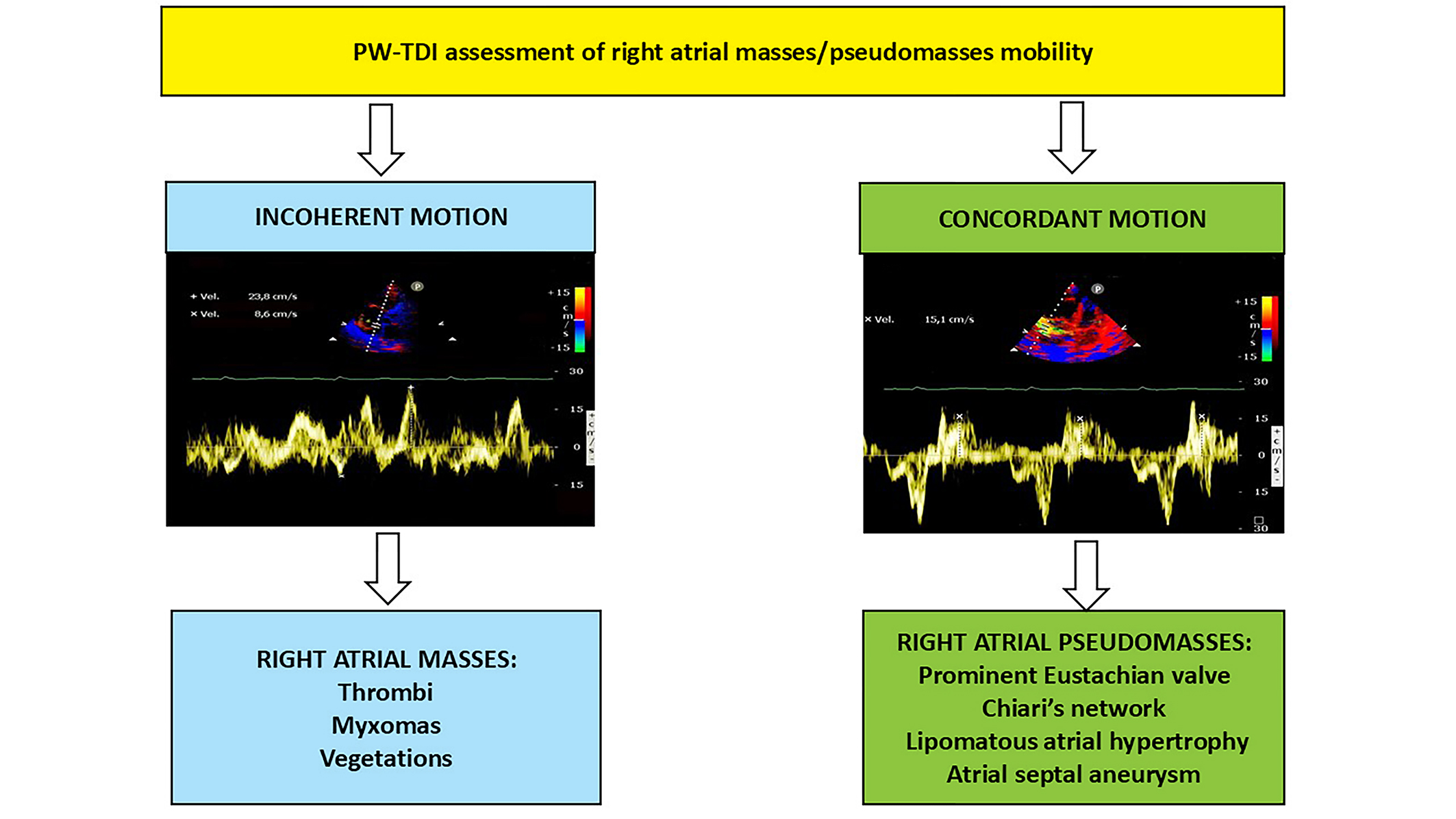
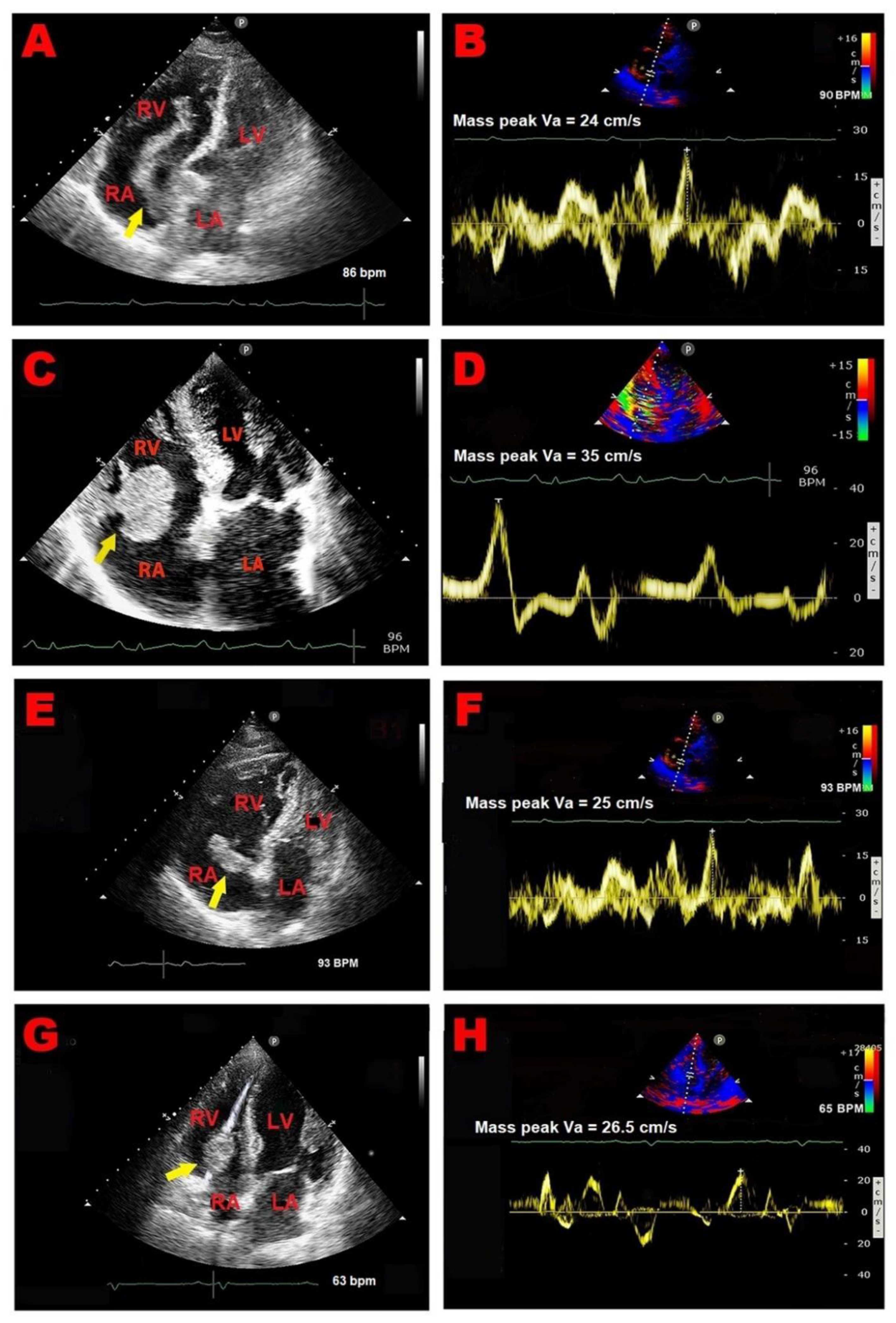
3.1. Right Atrial Masses
3.1.1. Right Atrial Thrombi
3.1.2. Right Atrial Myxomas
3.1.3. Right Atrial Vegetations
3.2. Right Atrial Pseudomasses
3.2.1. Prominent Eustachian Valve
3.2.2. Chiari’s Network
3.2.3. Lipomatous Atrial Hypertrophy
3.2.4. Atrial Septal Aneurysm
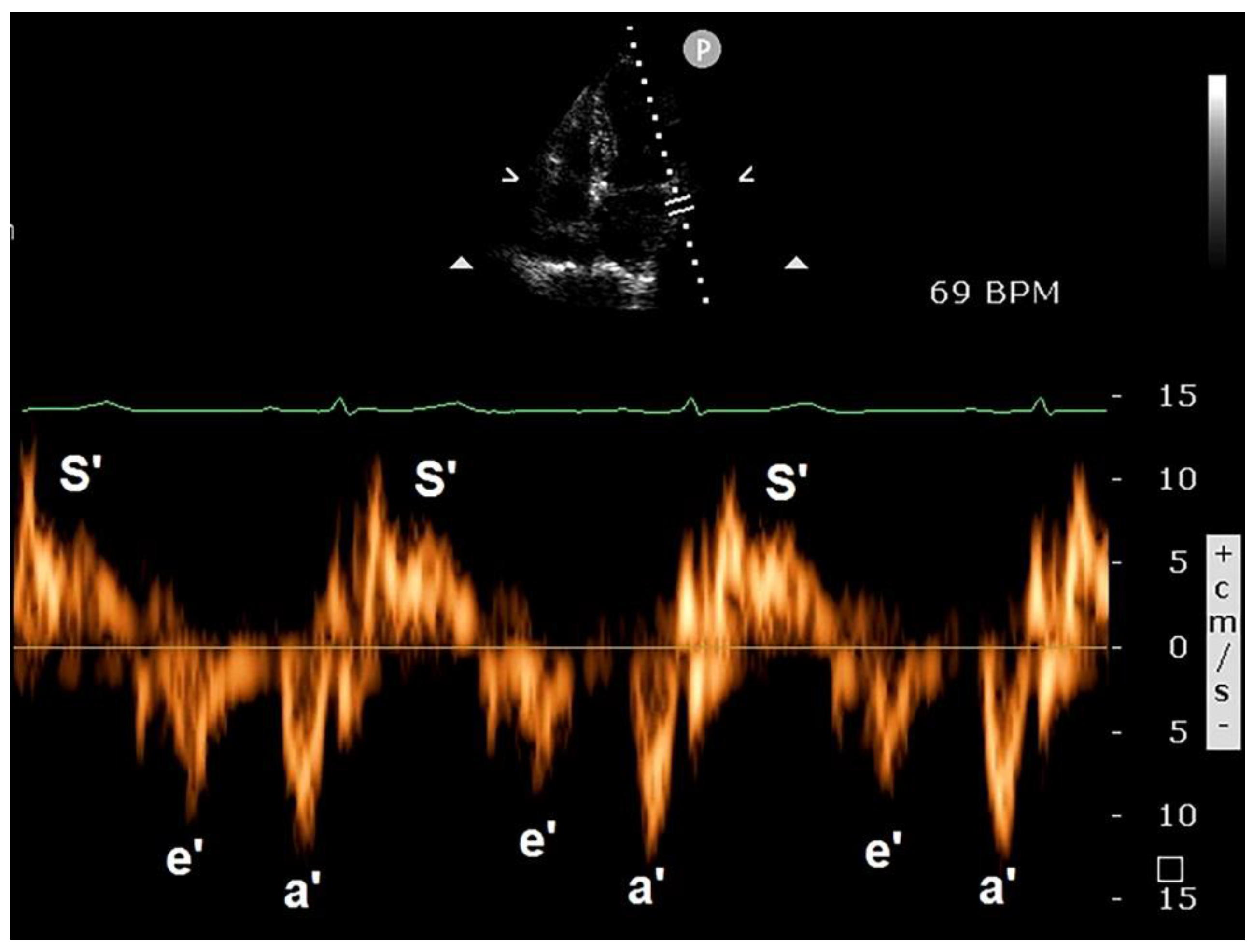
3.3. Clinical Applications of PW-TDI
3.4. Implications for Clinical Practice
3.5. Limitations of PW-TDI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poterucha, T.J.; Kochav, J.; O'Connor, D.S.; Rosner, G.F. Cardiac Tumors: Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Management. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2019, 20, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmidi, I.; Assoweh, C.D.; Haddiya, I.; Bentata, Y.; Ouafi, N.E.; Ismaili, N. Clinicopathological features of adult right-sided cardiac masses: Analysis of 19 cases. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2022, 77, 103613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradella, S.; Grazzini, G.; Letteriello, M.; De Amicis, C.; Grassi, R.; Maggialetti, N.; Carbone, M.; Palumbo, P.; Carotti, M.; Di Cesare, E.; et al. Masses in right side of the heart: spectrum of imaging findings. Acta Biomed 2020, 91, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casazza, F.; Becattini, C.; Guglielmelli, E.; Floriani, I.; Morrone, V.; Caponi, C.; Pizzorno, L.; Masotti, L.; Bongarzoni, A.; Pignataro, L. Prognostic significance of free-floating right heart thromboemboli in acute pulmonary embolism: results from the Italian Pulmonary Embolism Registry. Thromb Haemost 2014, 111, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Lombardo, M.; Anza, C. A Nonfatal Massive Pulmonary Embolism in a Very Old Patient: The Protective Filter-Effect of the Chiari Network. J Cardiovasc Echogr 2019, 29, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massoure, P.L.; Reuter, S.; Lafitte, S.; Laborderie, J.; Bordachard, P.; Clementy, J.; Roudaut, R. Pacemaker endocarditis: clinical features and management of 60 consecutive cases. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2007, 30, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Ogilby, J.D.; Segal, B. Tricuspid valve endocarditis. Am Heart J 1989, 117, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentata, Y.; Haddiya, I.; Ismailli, N.; El Ouafi, N.; Benzirar, A.; El Mahi, O.; Azzouzi, A. Infective endocarditis in chronic hemodialysis: A transition from left heart to right heart. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2016, 27, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, C.; Di Michele, S.; Cera, M.; Nguyen, B.L.; Pannarale, G.; Alessandri, N. Prominent crista terminalis mimicking a right atrial mixoma: cardiac magnetic resonance aspects. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2004, 8, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tagliati, C.; Fogante, M.; Palmisano, A.; Catapano, F.; Lisi, C.; Monti, L.; Lanni, G.; Cerimele, F.; Bernardini, A.; Procaccini, L.; et al. Cardiac Masses and Pseudomasses: An Overview about Diagnostic Imaging and Clinical Background. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, I.S.; Raiker, K. Atrial lipomatous hypertrophy: lipomatous atrial hypertrophy with significant involvement of the right atrial wall. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1993, 6, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Rispoli, G.A.; Lombardo, M. Incidental Finding of Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Right Atrial Free Wall in an Elderly Female With Severe Pulmonary Hypertension: Early Detection by Multimodality Imaging. Cureus 2023, 15, e50665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sušić, L.; Baraban, V.; Vincelj, J.; Maričić, L.; Ćatić, J.; Blažeković, R.; Manojlović, S. Dilemma in clinical diagnosis of right ventricular masses. J Clin Ultrasound 2017, 45, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazos-López, P.; Pozo, E.; Siqueira, M.E.; García-Lunar, I.; Cham, M.; Jacobi, A.; Macaluso, F.; Fuster, V.; Narula, J.; Sanz, J. Value of CMR for the differential diagnosis of cardiac masses. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2014, 7, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Angelo, E.C.; Paolisso, P.; Vitale, G.; Foà, A.; Bergamaschi, L.; Magnani, I.; Saturi, G.; Rinaldi, A.; Toniolo, S.; Renzulli, M.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cardiac Computed Tomography and 18-F Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Cardiac Masses. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2020, 13, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankad, R.; Herrmann, J. Cardiac tumors: echo assessment. Echo Res Pract 2016, 3, R65–r77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motwani, M.; Kidambi, A.; Herzog, B.A.; Uddin, A.; Greenwood, J.P.; Plein, S. MR imaging of cardiac tumors and masses: a review of methods and clinical applications. Radiology 2013, 268, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Gan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Tang, X.; Wen, L.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y. Use of transesophageal echocardiography and contrast echocardiography in the evaluation of cardiac masses. Int J Cardiol 2017, 236, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seward, J.B.; Khandheria, B.K.; Oh, J.K.; Freeman, W.K.; Tajik, A.J. Critical appraisal of transesophageal echocardiography: limitations, pitfalls, and complications. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1992, 5, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, T.; Müller, S.; Nesser, H.J.; Möhlenkamp, S.; Bruch, C.; Erbel, R. Usefulness of motion patterns indentified by tissue Doppler echocardiography for diagnosing various cardiac masses, particularly valvular vegetations. Am J Cardiol 1999, 84, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Lombardo, M.; Anzà, C.; Ambrosio, G. Prognostic Relevance of Left Ventricular Thrombus Motility: Assessment by Pulsed Wave Tissue Doppler Imaging. Angiology 2021, 72, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemetzberger, R.; Müller, S.; Bartel, T. Incremental use of tissue Doppler imaging and three-dimensional echocardiography for optimal assessment of intracardiac masses. Echocardiography 2008, 25, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Rigamonti, E.; Trotta, G.; Lombardo, M. Is There a Role for Tissue Doppler Imaging in Infective Endocarditis? J Cardiovasc Echogr 2014, 24, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Grasso, E.; Lombardo, M. An unusual right atrial myxoma triggering presumed takotsubo syndrome in a 97-year-old female. Eur Heart J Case Rep 2023, 7, ytad256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.L.; Grimm, R.A.; Murray, R.D.; Apperson-Hansen, C.; Asinger, R.W.; Black, I.W.; Davidoff, R.; Erbel, R.; Halperin, J.L.; Orsinelli, D.A.; et al. Use of transesophageal echocardiography to guide cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2001, 344, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degiovanni, A.; Carassia, C.; De Vecchi, S.; Erbetta, R.; Patti, G. Atrial thrombosis: Not only left, think also about right! J Clin Ultrasound 2022, 50, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, K.E.; McLaren, A. Catheter-related right atrial thrombus and pulmonary embolism: a case report and systematic review of the literature. Can Respir J 2009, 16, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Gurlertop, Y.; Erdogan, F. Right atrial thrombus following closure of an atrial septal defect. Heart 2003, 89, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.M.; Afzal, A.; Chamogeorgakis, T.; Feghali, G.A. Right atrial thrombus and its causes, complications, and therapy. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2017, 30, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.S.; Punjabi, N.M.; Pearse, D.B. Treatment of right heart thromboemboli. Chest 2002, 121, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Cooperative Study on the clinical significance of right heart thrombi. European Working Group on Echocardiography. Eur Heart J 1989, 10, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmektzoglou, K.A.; Samelis, G.F.; Xanthos, T. Heart and tumors: location, metastasis, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches and therapeutic considerations. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2008, 9, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynen, K. Cardiac myxomas. N Engl J Med 1995, 333, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee Rad, M.; Ghasempour Dabaghi, G.; Darouei, B.; Amani-Beni, R.; Zare, M.M.; Shirin, F.; Jamalian, M. Clinical and laboratory manifestations, ECG findings, and outcomes of right atrial myxoma: a systematic review of cases reported worldwide. Egypt Heart J 2024, 76, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojji, D.B.; Ajiduku, S.S.; Omonua, O.O.; Abdulkareem, L.L.; Parsonage, W. A probable right atrial myxoma prolapsing through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle: a case report. Cases J 2008, 1, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Wang, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Ying, K. Pulmonary embolism as the initial manifestation of right atrial myxoma: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e18386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifkazemi, M.; Rezaian, G.; Abtahi, F. Right Atrial Myxoma and Chronic Transudative Ascites: A Rare and Challenging Clinical Presentation. CASE (Phila) 2018, 2, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, S.; Sahin, A.T.; Işık, M.; Görmüş, N. Confounding giant right atrial mass. Egypt Heart J 2024, 76, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, H.; Thomas, F.; Flint, N.; Setia, G.; Janjic, A.; Siegel, R.J. Right-Sided Infective Endocarditis 2020: Challenges and Updates in Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Heart Assoc 2020, 9, e017293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.M. Right-sided infective endocarditis: recent epidemiologic changes. Int J Clin Exp Med 2014, 7, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vilacosta, I.; Olmos, C.; de Agustín, A.; López, J.; Islas, F.; Sarriá, C.; Ferrera, C.; Ortiz-Bautista, C.; Sánchez-Enrique, C.; Vivas, D.; et al. The diagnostic ability of echocardiography for infective endocarditis and its associated complications. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2015, 13, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, Y.; Lytle, M.; Carlan, S.; Madruga, M. Bilateral Pneumothoraces: A Rare Complication of Septic Pulmonary Emboli in Intravenous Drug Abusers. Am J Case Rep 2018, 19, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiati, C.; Pollice, P.; Lepera, M.E.; Favale, S. Pacemaker Lead Endocarditis Investigated with Intracardiac Echocardiography: Factors Modulating the Size of Vegetations and Larger Vegetation Embolic Risk during Lead Extraction. Antibiotics (Basel) 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, N.E.; Habib, G.; Thuny, F.; Sogaard, P. Cardiac imaging in infectious endocarditis. Eur Heart J 2014, 35, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, V.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; de Waha, S.; Bonaros, N.; Brida, M.; Burri, H.; Caselli, S.; Doenst, T.; Ederhy, S.; Erba, P.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of endocarditis. Eur Heart J 2023, 44, 3948–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuz, T.; Nazli, C.; Kinay, O.; Kutsal, A. Giant eustachian valve with echocardiographic appearance of divided right atrium. Tex Heart Inst J 2002, 29, 336–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carson, W.; Chiu, S.S. Image in cardiovascular medicine. Eustachian valve mimicking intracardiac mass. Circulation 1998, 97, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onorato, E.M. Large eustachian valve fostering paradoxical thromboembolism: passive bystander or serial partner in crime? World J Cardiol 2021, 13, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, J.M.; Voelker, W.; Schanzenbaecher, P. Persistence of the eustachian valve in secundum atrial septal defects: possible implications for cerebral embolism and transcatheter closure procedures. Heart 2001, 86, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, Y.; Yamashita, M.; Yamada, K.; Arikawa, K.; Taira, A. Cyanosis in atrial septal defect due to persistent eustachian valve. Ann Thorac Surg 1985, 40, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashour, T.; Kabbani, S.; Saalouke, M.; Cheng, T.O. Persistent Eustachian valve causing severe cyanosis in atrial septal defect with normal right heart pressures. Angiology 1983, 34, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernizan, D.; Kharouf, R.; Robinson, B.; Radtke, W. Prominent Eustachian Valve and Atrial Septal Defect Presenting With Chronic Hypoxemia in a Teenager. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg 2020, 11, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriales, V.; Tamargo, J.A.; Aguado, M.G.; Martín, M.; Rondán, J.; Segovia, E.; Morís, C. Floating thrombi on the Eustachian valve as a complication of venous thromboembolic disease. Int J Cardiol 2004, 93, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.C.; Teo, S.G.; Yeo, T.C. An unusual right-sided endocarditis: a case report of eustachian valve endocarditis. Int J Cardiol 2006, 109, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannoli, E.D. The use of transesophageal echocardiography for differential diagnosis of poor venous return during cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth Analg 2007, 105, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.J.; Joyce, T.R.; Ferns, S.J. Prominent prolapsing Chiari network: presentation and prognosis in paediatric patients. Cardiol Young 2022, 32, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.; Hofmann, T.; Justen, M.H.; Meinertz, T. Chiari's network: normal anatomic variant or risk factor for arterial embolic events? J Am Coll Cardiol 1995, 26, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, K.P.; Nettleton, G.S.; Campbell, F.R.; Wagner, C.E.; Kuwabara, N.; Muresian, H. Chiari anomalies in the human right atrium. Clin Anat 2006, 19, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, P.; Wozniak, M.; Corretti, M.; Price, T.R. Cardiac chiari network as an etiology for embolic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 1994, 4, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, N.; Bhagirath, K.; Ariyarajah, V.; Fang, T.; Ahmadie, R.; Lytwyn, M.; Jassal, D.S.; Seifer, C. Chiari network endocarditis: not just an innocent bystander. Echocardiography 2008, 25, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwimmer-Okike, N.; Niebuhr, J.; Schramek, G.G.; Frantz, S.; Kielstein, H. The Presence of a Large Chiari Network in a Patient with Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke. Case Rep Cardiol 2016, 2016, 4839315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedde, T.A.; Conetta, D.; Rumisek, J.D. Chiari network entrapment of thromboemboli: congenital inferior vena cava filter. Ann Thorac Surg 1990, 49, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzello, V.; Lombardo, A.; Colizzi, C.; Pennestrì, F. Entrapment of a floating thrombus in the right atrium by persistent Chiari's network: a barrier to massive pulmonary embolism. Int J Cardiol 2009, 132, e40–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S.B.; Akansel, S.; Sargın, M.; Mete, M.E.T.; Arslanhan, G.; Aka, S.A. A case of a large Chiari network mimicking a right atrial thrombus. North Clin Istanb 2017, 4, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, C.M.; Kagel, T.; Lemburg, S.P.; Bauer, T.T.; Nicolas, V. Lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum: a prospective study of incidence, imaging findings, and clinical symptoms. Chest 2003, 124, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xanthos, T.; Giannakopoulos, N.; Papadimitriou, L. Lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum: a pathological and clinical approach. Int J Cardiol 2007, 121, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura, D.M.; Donnino, R.; Kim, E.E.; Benenstein, R.; Freedberg, R.S.; Saric, M. Lipomatous Atrial Septal Hypertrophy: A Review of Its Anatomy, Pathophysiology, Multimodality Imaging, and Relevance to Percutaneous Interventions. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2016, 29, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Du, Z. An asymptomatic right atrial intramyocardial lipoma: a management dilemma. World J Surg Oncol 2015, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Kusama, J.; Kunimasa, T.; Yoda, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Tani, S.; Saito, S. Lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum presenting as sick sinus syndrome. Int J Cardiol 2007, 119, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tugcu, A.; Yildirimturk, O.; Rizaoglu, E.; Sagbas, E.; Akpinar, B.; Aytekin, S. Lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum presenting as an obstructive right atrial mass in a patient with exertional dyspnea. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2007, 20, 1319.e1313–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampatzidou, F.; Koutsogiannidis, C.P.; Cheva, A.; Vasiliadis, K.; Drossos, G. Surgical treatment of atrial septum lipomatous hypertrophy associated with syncopal attacks. Ann Card Anaesth 2018, 21, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassop, D.; Donovan, M.S.; Cheezum, M.K.; Nguyen, B.T.; Gambill, N.B.; Blankstein, R.; Villines, T.C. Cardiac Masses on Cardiac CT: A Review. Curr Cardiovasc Imaging Rep 2014, 7, 9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imburgio, S.; Wiseman, K.; Udongwo, N.; Gor, D.; Desai, D.; Apolito, R. Atrial Septal Aneurysm: An Incidental Finding or a Clinically Significant Anomaly? Cureus 2022, 14, e29557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, A.; Gavras, C.; Sarioglou, S.; Agathagelou, F.; Kassapoglou, I.; Athanassiadou, F. Atrial septal aneurysms in childhood: prevalence, classification, and concurrent abnormalities. Cardiol Young 2014, 24, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares-Reyes, A.; Chan, S.; Lazar, E.J.; Bandlamudi, K.; Narla, V.; Ong, K. Atrial septal aneurysm: a new classification in two hundred five adults. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1997, 10, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaterre, H.R.; Cohen, F.; Kallee, K.; Deharo, J.C.; Djiane, P. Giant interatrial septal aneurysm mimicking a right atrial tumor. Int J Card Imaging 1998, 14, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, J.K.; Appelbe, A.F.; Martin, R.P. Atrial septal aneurysm mimicking a right atrial mass on transesophageal echocardiography. Am J Cardiol 1991, 68, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, K.D.; Arnaoutoglou, E.; Papadopoulos, G. Giant atrial septal aneurysm simulating a right atrial tumour. Heart 2004, 90, 493–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaaz, K.; Thompson, A.; Ethevenot, G.; Cloez, J.L.; Brembilla, B.; Pernot, C. Doppler echocardiographic measurement of low velocity motion of the left ventricular posterior wall. Am J Cardiol 1989, 64, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggoner, A.D.; Bierig, S.M. Tissue Doppler imaging: a useful echocardiographic method for the cardiac sonographer to assess systolic and diastolic ventricular function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2001, 14, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Smiseth, O.A.; Appleton, C.P.; Byrd, B.F., 3rd; Dokainish, H.; Edvardsen, T.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Gillebert, T.C.; Klein, A.L.; Lancellotti, P.; et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2016, 29, 277–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Wardell, J.; Andersson, E.; Samad, B.A.; Nordlander, R. Effects of first myocardial infarction on left ventricular systolic and diastolic function with the use of mitral annular velocity determined by pulsed wave doppler tissue imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2000, 13, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, L.; Kou, S.; Dulgheru, R.; Gonjilashvili, N.; Athanassopoulos, G.D.; Barone, D.; Baroni, M.; Cardim, N.; Gomez de Diego, J.J.; Oliva, M.J.; et al. Echocardiographic reference ranges for normal cardiac Doppler data: results from the NORRE Study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2015, 16, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Rimington, H.; Smeeton, N.; Chambers, J. Long axis excursion in aortic stenosis. Heart 2001, 86, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, F.L.; Galderisi, M.; Nistri, S.; Buralli, S.; Ballo, P.; Mele, D.; Badano, L.P.; Faggiano, P.; de Gregorio, C.; Rosa, G.M.; et al. Abnormal left ventricular longitudinal function assessed by echocardiographic and tissue Doppler imaging is a powerful predictor of diastolic dysfunction in hypertensive patients: the SPHERE study. Int J Cardiol 2013, 168, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correale, M.; Totaro, A.; Ieva, R.; Ferraretti, A.; Musaico, F.; Di Biase, M. Tissue Doppler imaging in coronary artery diseases and heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rev 2012, 8, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Rad, N.; Walker, J.R.; Wassef, A.; Lytwyn, M.; Bohonis, S.; Fang, T.; Tian, G.; Kirkpatrick, I.D.; Singal, P.K.; Krahn, M.; et al. The utility of cardiac biomarkers, tissue velocity and strain imaging, and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in predicting early left ventricular dysfunction in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor II-positive breast cancer treated with adjuvant trastuzumab therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011, 57, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Jensen, J.S.; Iversen, A.Z.; Sogaard, P.; Galatius, S.; Olsen, N.T.; Bech, J.; Fritz-Hansen, T.; Biering-Sorensen, T.; Badskjaer, J.; et al. Tissue Doppler echocardiography improves the diagnosis of coronary artery stenosis in stable angina pectoris. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2012, 13, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadappu, K.K.; Thomas, L. Tissue Doppler imaging in echocardiography: value and limitations. Heart Lung Circ 2015, 24, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Tabata, T.; Yamada, H.; Wakatsuki, T.; Shinohara, H.; Nishikado, A.; Iuchi, A.; Fukuda, N.; Ito, S. Clinical application of pulsed Doppler tissue imaging for assessing abnormal left ventricular relaxation. Am J Cardiol 1997, 79, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Pellerin, D.; Gaze, D.C.; Mehta, R.L.; Gregson, H.; Streather, C.P.; Collinson, P.O.; Brecker, S.J. Mitral peak Doppler E-wave to peak mitral annulus velocity ratio is an accurate estimate of left ventricular filling pressure and predicts mortality in end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2006, 19, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.; Ring, L.; Oxborough, D.; Harkness, A.; Bennett, S.; Rana, B.; Sutaria, N.; Lo Giudice, F.; Shun-Shin, M.; Paton, M.; et al. The assessment of left ventricular diastolic function: guidance and recommendations from the British Society of Echocardiography. Echo Res Pract 2024, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.S.; Tapp, R.J.; Thom, S.A.; Francis, D.P.; Hughes, A.D.; Stanton, A.V.; Zambanini, A.; O'Brien, E.; Chaturvedi, N.; Lyons, S.; et al. Tissue Doppler E/E' ratio is a powerful predictor of primary cardiac events in a hypertensive population: an ASCOT substudy. Eur Heart J 2010, 31, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arques, S. Clinical Relevance of the Spectral Tissue Doppler E/e' Ratio in the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: a Comprehensive Review of the Literature. J Atr Fibrillation 2018, 11, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.B. Prognostic impact of the E/e' ratio in patients with chronic severe aortic regurgitation undergoing aortic valve replacement. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2024, 167, 116–126.e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, J.J.; Bleeker, G.B.; Marwick, T.H.; Molhoek, S.G.; Boersma, E.; Steendijk, P.; van der Wall, E.E.; Schalij, M.J. Left ventricular dyssynchrony predicts response and prognosis after cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004, 44, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.M.; Fung, W.H.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Sanderson, J.E.; Lau, C.P. Predictors of left ventricular reverse remodeling after cardiac resynchronization therapy for heart failure secondary to idiopathic dilated or ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol 2003, 91, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dénes, M.; Farkas, K.; Erdei, T.; Lengyel, M. Comparison of tissue Doppler velocities obtained by different types of echocardiography systems: are they compatible? Echocardiography 2010, 27, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storaa, C.; Aberg, P.; Lind, B.; Brodin, L.A. Effect of angular error on tissue Doppler velocities and strain. Echocardiography 2003, 20, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.Y.; Solomon, S.D. A clinician's guide to tissue Doppler imaging. Circulation 2006, 113, e396–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T.P.; Dimaano, V.L.; Liang, H.Y. Role of tissue Doppler and strain echocardiography in current clinical practice. Circulation 2007, 116, 2597–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




