Submitted:
17 December 2024
Posted:
19 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
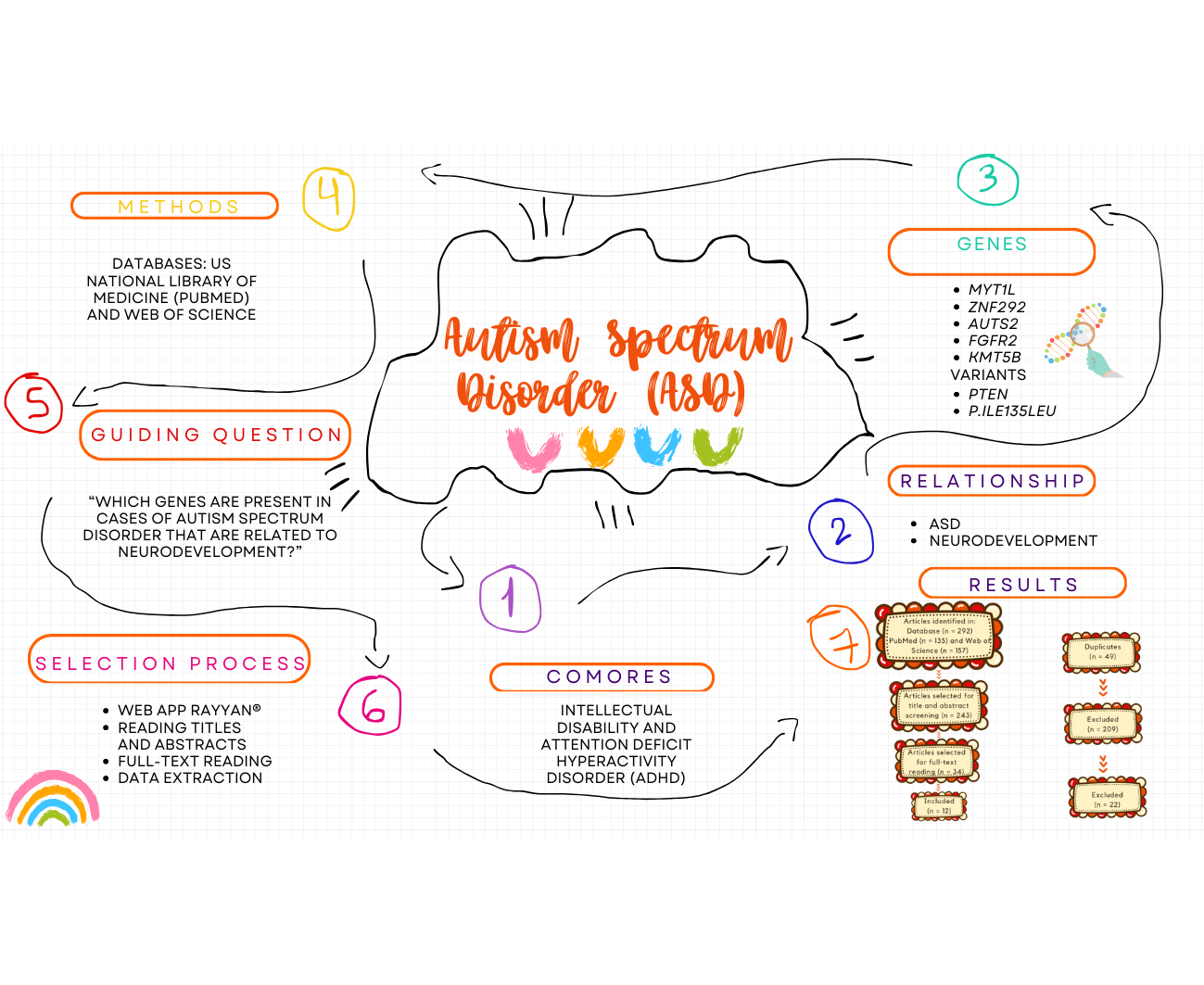
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition with a multifactorial origin and significant genetic contribution. It is characterized by difficulties in social interaction, communication, and the presence of repetitive behaviors, often associated with comorbidities such as intellectual disability and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). This integrative review analyzed articles published in the last five years to explore relevant genes related to ASD and neurodevelopment. Genes such as MYT1L, ZNF292, AUTS2, and regulatory genes involved in the production of microRNAs were highlighted, demonstrating their relationship with critical processes such as neurogenesis and synaptogenesis. Genes such as FGFR2 and KMT5B have been strongly associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism and ADHD, underscoring their importance in understanding the genetic basis of these conditions. Additionally, the identification of specific variants, such as PTEN p.Ile135Leu, and their relationship with changes in neurogenesis, neural maturation, and synaptic function highlights the need for more in-depth studies on the molecular pathways regulating these genes expression. The findings reinforce the genetic heterogeneity of ASD and suggest potential targets for personalized therapies within the context of precision medicine. However, the importance of incorporating epigenetic and environmental factors into analyses is emphasized to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of gene-environment interactions and their clinical implications.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
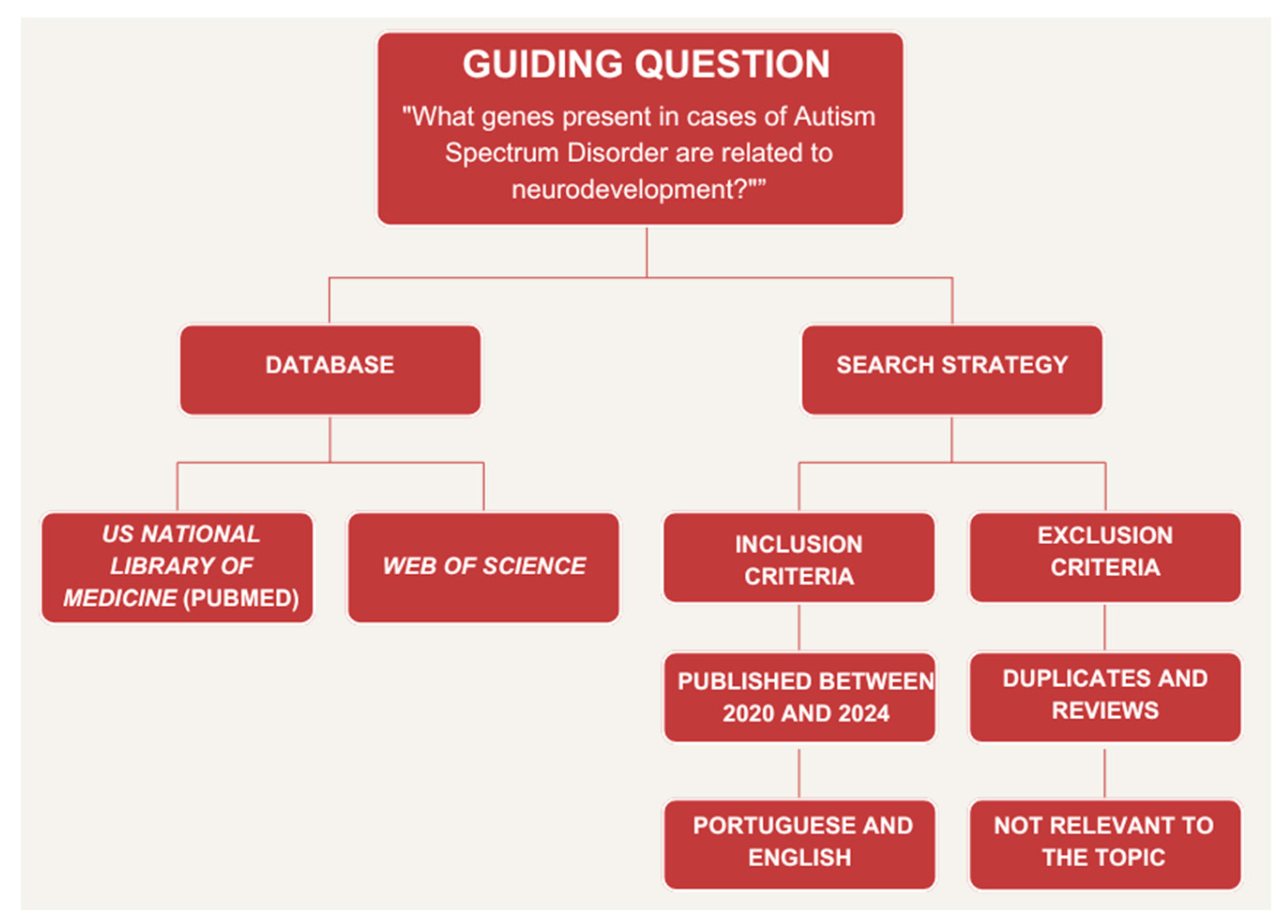
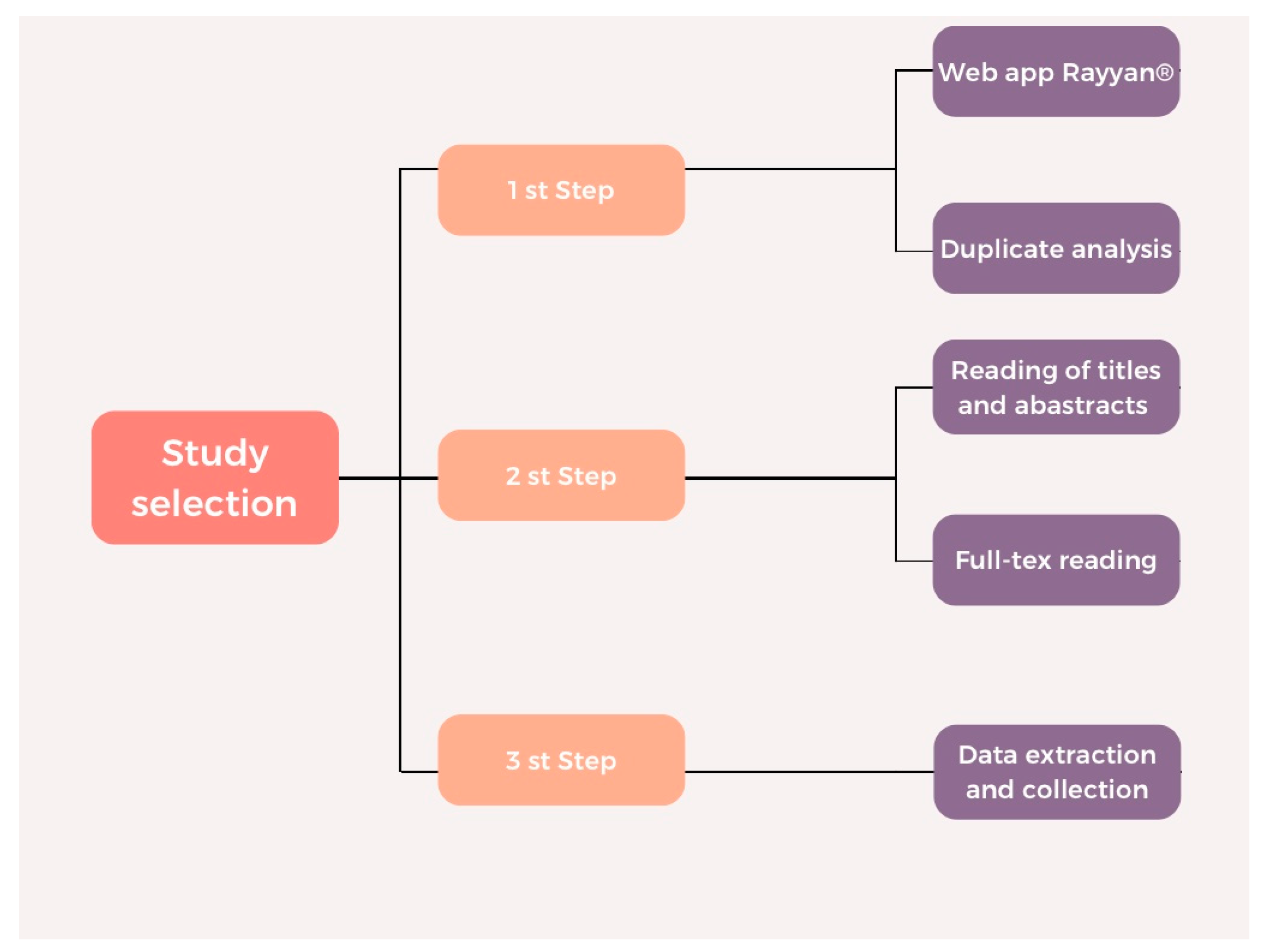
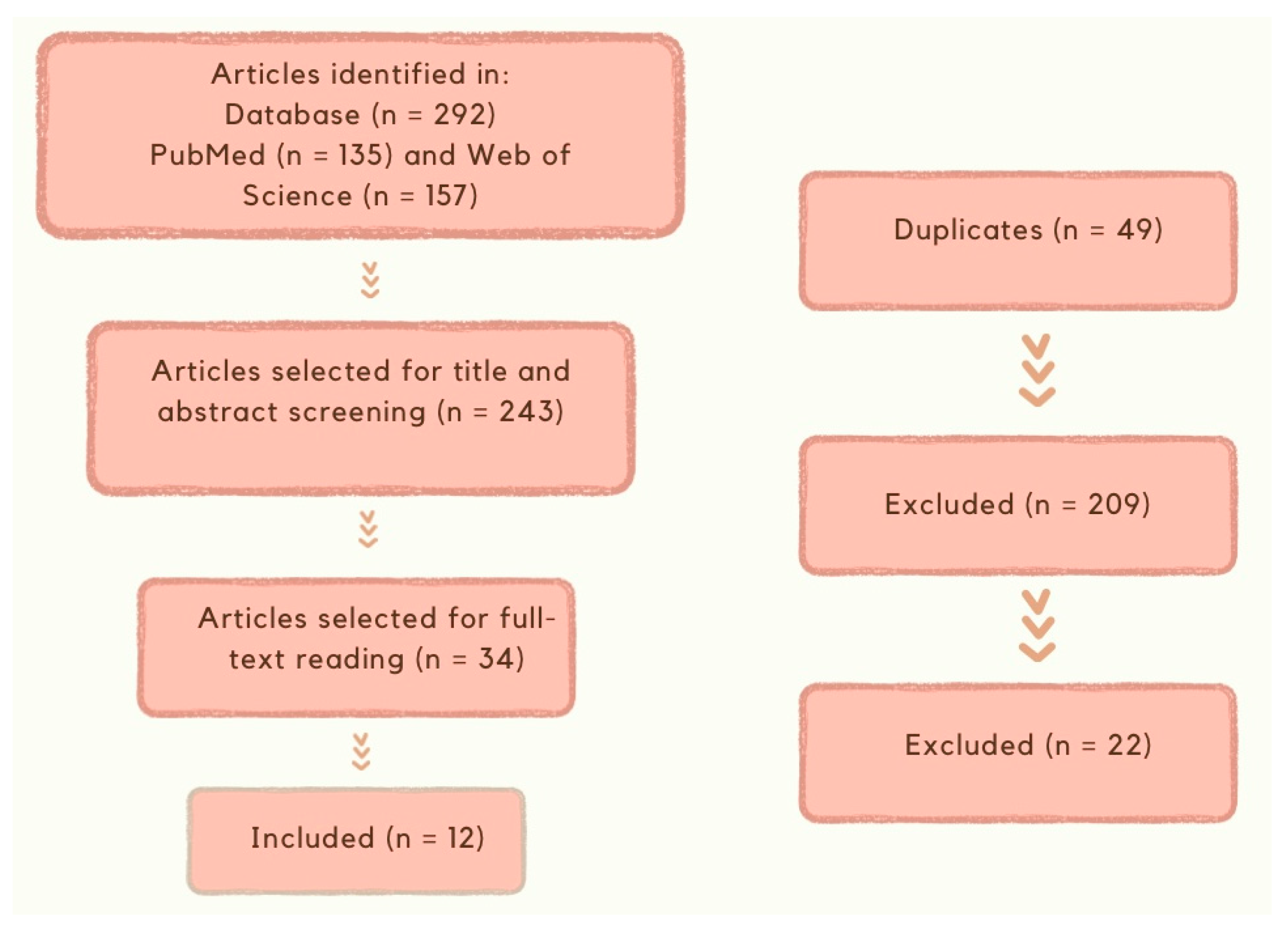
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pavinato, L.; Vedove, A.D.; Carli, D.; Ferrero, M.; Carestiato, S.; Howe, J.L.; Agolini, E.; Coviello, D.A.; Laar, I.V.D.; Au, P.Y.B.; et al. CAPRIN1 Haploinsufficiency Causes a Neurodevelopmental Disorder with Language Impairment, ADHD and ASD. Brain : A journal of neurology 2023, 146, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, R.; Zhou, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, C.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Tang, S. PLPPR4 Haploinsufficiency Causes Neurodevelopmental Disorders by Disrupting Synaptic Plasticity via mTOR Signalling. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2023, 27, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Harada, T.; Nishimura, T.; Okumura, A.; Choi, D.; Iwabuchi, T.; Kuwabara, H.; Takagai, S.; Nomura, Y.; Takei, N.; et al. Association of Genetic Risks With Autism Spectrum Disorder and Early Neurodevelopmental Delays Among Children Without Intellectual Disability. JAMA network open 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaa, G.M.; Chong, J.X.; Piton, A.; Popp, B.; Foss, K.; Guo, H.; Harripaul, R.; Xia, K.; Scheck, J.; Aldinger, K.A.; et al. De Novo and Inherited Variants in ZNF292 Underlie a Neurodevelopmental Disorder with Features of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Genetics in Medicine : Official Journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 2019, 22, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Lin, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Xu, X. Deleterious Variation in BR Serine/Threonine Kinase 2 Classified a Subtype of Autism. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 2022, 15, 904935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, A.G.; Amore, G.; Saia, M.C.; Vinci, M.; Musumeci, A.; Chiavetta, V.; Federico, C.; Spoto, G.; Saccone, S.; Rosa, G.D.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 (FGFR2), a New Gene Involved in the Genesis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neuromolecular medicine 2023, 25, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, S.; Calli, K.; Qiao, Y.; Trost, B.; Scherer, S.W.; Lewis, M.E.S. Complex Autism Spectrum Disorder in a Patient with a Novel De Novo Heterozygous MYT1L Variant. Genes 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Xue, K.; Gu, S.; Lv, L.; Huang, S.; Xie, W. Potential Role of Genomic Imprinted Genes and Brain Developmental Related Genes in Autism. BMC Medical Genomics 2020, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Zhou, A.; Cao, X.; Mahaganapathy, V.; Azaro, M.; Gwin, C.; Wilson, S.; Buyske, S.; Bartlett, C.W.; Flax, J.F.; et al. MicroRNA and MicroRNA-Target Variants Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Related Disorders. Genes 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odak, L.; Vulin, K.; Meašić, A.M.; Šamadan, L.; Batoš, A.T. Neurodevelopmental Disorder Caused by an Inherited Novel KMT5B Variant: Case Report. Croatian Medical Journal 2023, 64, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Bury, L.A.D.; Eum, J.; Wynshaw-Boris, A. Autism-Specific PTEN p.Ile135Leu Variant and an Autism Genetic Background Combine to Dysregulate Cortical Neurogenesis. American journal of human genetics 2023, 110, 826–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.R.; Azzara, D.; Cohen, E.D.; Boomhower, S.R.; Diwadkar, A.R.; Himes, B.E.; O’Reilly, M.A.; Lu, Q. Identification of Novel NRF2-Dependent Genes as Regulators of Lead and Arsenic Toxicity in Neural Progenitor Cells. Journal of hazardous materials 2024, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, K.; Shimaoka, K.; Hoshino, M. AUTS2 Gene: Keys to Understanding the Pathogenesis of Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cells 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruel, A.L.; Vitobello, A.; Thiffault, I.; Manwaring, L.; Willing, M.; Agrawal, P.B.; Bayat, A.; Kitzler, T.M.; Brownstein, C.A.; Genetti, C.A.; et al. ITSN1: A Novel Candidate Gene Involved in Autosomal Dominant Neurodevelopmental Disorder Spectrum. European journal of human genetics: EJHG 2022, 30, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaarsveld, R.H. van; Reilly, J.; Cornips, M.C.; Hadders, M.A.; Agolini, E.; Ahimaz, P.; Anyane-Yeboa, K.; Bellanger, S.A.; Binsbergen, E. van; Boogaard, M.J. van den; et al. Delineation of a KDM2B-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder and Its Associated DNA Methylation Signature. Genetics in medicine : Official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 2023, 25, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Tai, Y.T.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Z. AUTS2 Disruption Causes Neuronal Differentiation Defects in Human Cerebral Organoids through Hyperactivation of the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | OMIM Code | Genomic Coordinates | Clinical Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| MYT1L | 613084 | 2:1,789,113-2,331,275 | DI (Developmental Delay) |
| ZNF292 | 616213 | 6:87,155,565-87,265,943 | DI (Developmental Delay) |
| GABRG5 | 137190 | 15:26,994,573-27,074,973 | Epilepsy |
| GABRG3 | 137192 | 15:26,971,181-27,541,984 | Epilepsy |
| NTM | 607938 | 11:131,370,615-132,336,822 | Congenital Malformations |
| SNRPN | 182279 | 15:25,799,840-25,807,303 | Prader-Willi Syndrome |
| OTX1 | 600372 | 2:63,049,735-63,057,831 | Microcephaly |
| FOXG1 | 164874 | 14:28,766,787-28,770,277 | Microcephaly |
| TSHZ3 | 614427 | 19:31,149,876-31,350,877 | Anxiety |
| CDH18 | 603019 | 5:19,471,296-20,575,713 | ADNPM (Developmental Disorder) |
| GABRB3 | 137192 | 15:26,514,275-26,986,768 | Epilepsy |
| GATM | 602360 | 15:45,361,124-45,402,227 | Neuro-muscular Disorder |
| HTR2A | 182135 | 13:46,831,546-46,898,082 | Schizophrenia, Depression, OCD |
| DHCR7 | 602858 | 11:71,427,287-71,449,043 | Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome |
| NLRP2 | 609364 | 19:54,965,284-55,001,138 | Neuroinflammation |
| Gene | Location | Neurodevelopmental Consequences | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|
| TUB | 11p15.4 | WLI | Dominant |
| SCP2 | 1p32.3 | WLI, ADHD | Dominant |
| ONECUT2 | 18q21.31 | SRI | Dominant |
| OSBP | 11q12.1 | WLI | Dominant |
| RBM24 | 6q22.3 | ADHD, OLI | De novo |
| UGCG | 9q31.3 | WLI, OLI | Dominant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





