Introduction
The algorithm selects random variables and creates hundreds of trees..The real estate market plays a huge role in the economy of any country, as well as in Kyrgyzstan.Many developed countries have long used modern technologies such as machine learning to analyze the market and predict prices.
However, these technologies have only just begun to be implemented in Kyrgyzstan.
Forecasting real estate prices is an important task that helps people better understand the market and make informed decisions about buying a home or investing.
For example, if you know in advance how much a house or apartment will cost, you can more accurately plan your budget and organize housing. This is especially true for countries such as Kyrgyzstan, where there is insufficient information about the real estate market. In developed countries, such studies have been conducted for a long time and complex models are often created there to analyze many factors. However, in Kyrgyzstan, the situation is different: due to the smaller amount of data, simpler methods can be used that make it possible to interpret information and achieve changes much easier than, for example, in Turkey [
8].
Machine learning models have produced good results in our work.It can be used in completely different fields, such as computer engineering, ecology or even medicine.For example, significant progress has been made in the field of morphological classification of galaxies using SpinalNet [
11].] As mentioned earlier, machine learning methods are effectively used to predict ecological problems [
13] or some diseases [
14].
One of the most basic investment tools for Kyrgyz residents is real estate.The country has a very developed construction industry, which is why people buy housing not only for living, but also consider it a good investment.The valuation of the house might have a leading impact on the portfolio of the household [
15].This study examines the indicators of the Kyrgyz real estate market.
Why Random Forest Regression method?
1.High precision.A random forest makes accurate predictions because it uses many small models.These models work together to take into account different things that affect the price, such as the size of the house, the cost per square meter and the condition of the property.And in comparison with other algorithms it showed best accuracy.
2.Working with incomplete data.There is often a lack of information in the real estate market. For example, ads may not contain the exact year of construction or details about the condition of the house. Random forest is able to work with such incomplete data and it does not affect accuracy.
3.It is well protected from errors, even if there is not much data. It does not attach too much to the training data and gives stable results, which is especially important for this analysis of real estate in Kyrgyzstan, given their lack.
Let’s say you want to know how much a house will cost. The neural network studies all the data: the size of the house, location, condition, and even such small things as finishing materials. It finds the connection between these parameters and the price herself, and then makes an accurate forecast.
Dataset Description:
The dataset of this study was obtained from Kaggle, a popular opened source for data science challenges or free-to-use datasets. Kaggle is a great platform for aspiring to experienced data scientists since they provide high-quality datasets from the real world across myriad fields. The housing data in this project are suitable for scoring house price in the house price index and diverse in type and attributes. This structure, feature density, and access make it very suitable for supervised machine learning problems.
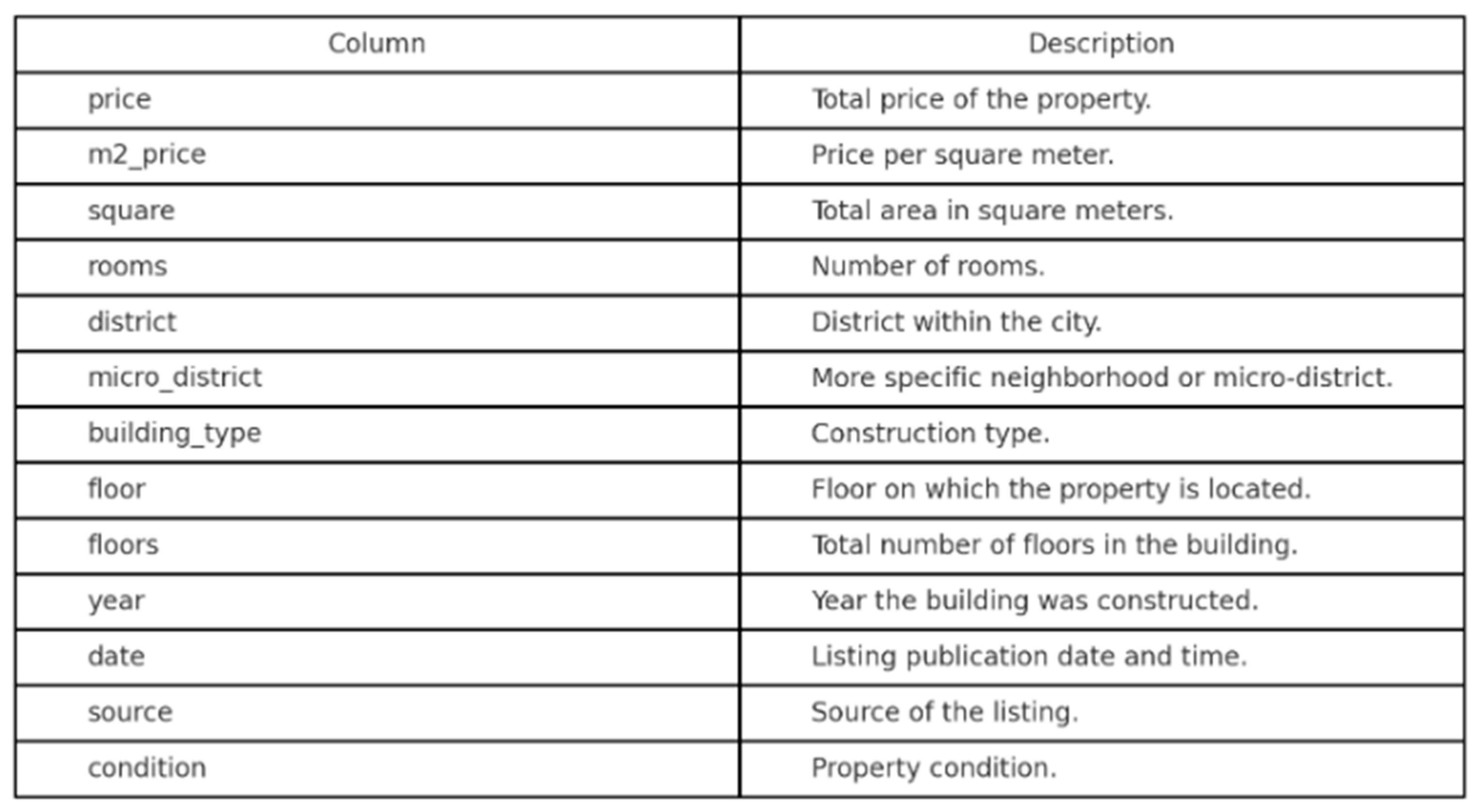
The data used in this study consists of many thousands of observations, each corresponding to a specific residential listing. Each listing offers comprehensive information on the physical features of the property and contextual aspects that can be used to estimate price. The response variable will be the price of the property, denominated dependent variable in regression models.The dataset includes 13 columns, covering both numerical and categorical variables:
The dataset has the following features and the description of each feature:
Table 1.
Features and their description.
Table 1.
Features and their description.
Comparison of Algorithms
The main method employed for prediction was Random Forest Regressor.
It was selected due to its capacity for large data and overfitting resistance. It operates by producing many decision trees from random sets of the data and combining their predictions to maximize prediction accuracy.
XGBoost is an optimized gradient boosting implementation that has been widely used due to its efficiency and performance in machine learning contests. XGBoost is a method that builds trees incrementally, where each additional tree attempts to correct the errors of the previous trees.
GexBoost is a robust gradient boosting library that excels at handling categorical features and missing data [21].
When working with machine learning, it deals with datasets that include categorical data. We use techniques like
One-Hot Encoding or
Label Encoding to convert these categorical features into numerical values. However One-Hot Encoding can lead to sparse matrix and cause overfitting. This is where CatBoost (categorical boosting) helps as it automatically handles everything hence improving model performance without the need for extra preprocessing.[
20]
Methodology
The methodology is based on doing fair comparison among models through careful data preprocessing and model tuning.
Removing duplicates and missing textual values.Some columns contained duplicate objects or missing values. To fix this, we either filled in the gaps with average values, or used the lowest possible values when it was justified.Some columns, such as the number of rooms, had text descriptions (for example, “6 or more”). We have converted them to numeric values to simplify our analysis.
In order to ensure that the models didn’t simply memorize data, we implemented a few strategies to prevent overfitting. We began by cleaning the data set — removing incomplete records, or obvious outlier – so the models could learn from clean and realistic examples. We also restricted the depth of the trees and included randomness during training in order to keep the models more general.
This helped us build models that didn’t just perform well on paper but could actually work well in practice too.We chose combinations by network search and forecast trends. This table summarizes the key hyperparameters used in the Random Forest model and their respective values and descriptions.
Table 2.
Hyperparameters used in model.
Table 2.
Hyperparameters used in model.
| Parameters |
Sum |
Description |
| n_estimators |
80 |
Number of trees in the forest |
| max_depth |
6 |
Maximum depth of each tree to avoid overfitting. |
| min_samples_split |
15 |
Minimum number of samples required to split an internal node. |
| min_samples_leaf |
8 |
Minimum number of samples that a leaf node must have. |
Feature Importance
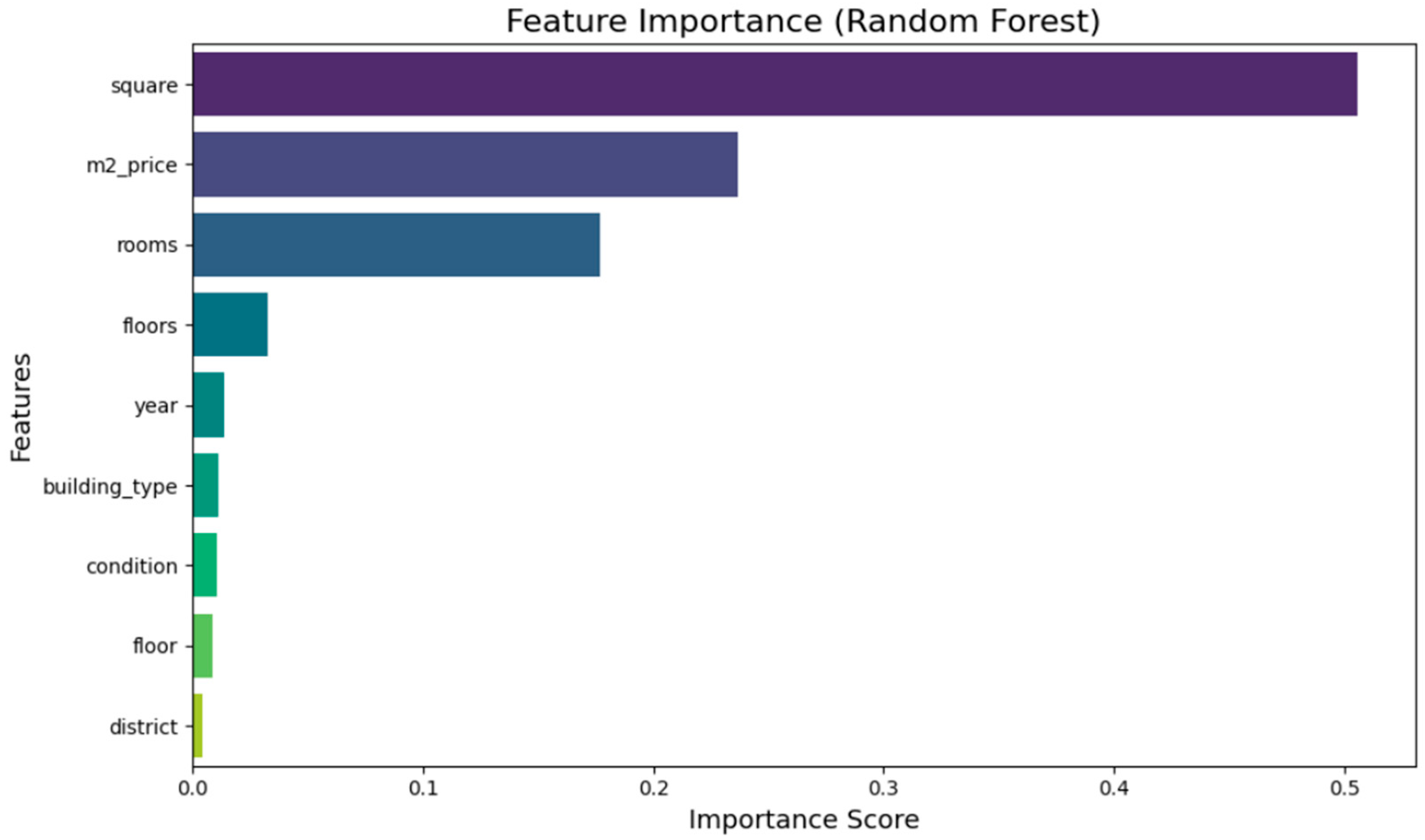
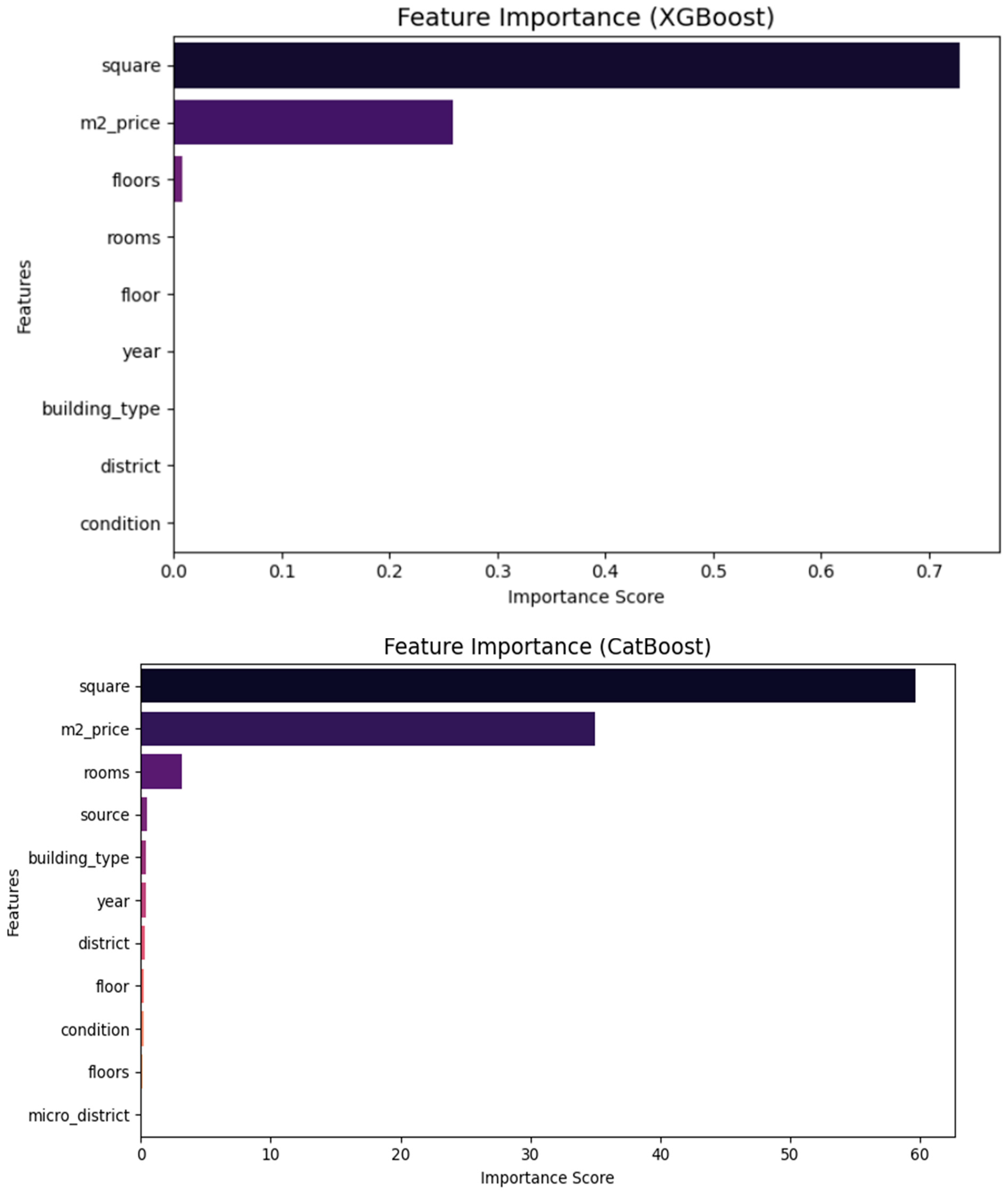
The key elements influencing the house price forecast were identified through feature importance analysis. Models based on trees compute importance scores. Each feature contributes toward lowering prediction error. District, property area, along with price per square meter, were actually the most important markers that the findings indicated. Elements including building type, construction year, and room count also provided a small impact. Because a person understands the importance of such characteristics, transparency is now improved and then the process of the making of well-informed judgments is now easier, according to data coming from housing market studies.We performed feature importance analysis for all three algorithms: Random Forest, XGBoost, and CatBoost.
Figure 2.
Feature Importance for Random Forest Regressor, XGBoost, CatBoost.
Figure 2.
Feature Importance for Random Forest Regressor, XGBoost, CatBoost.
And also for visual analysis, we plotted scatter diagrams that compared actual house prices to predicted values for each model. In an ideal case, points must align along that diagonal line, and this represents a prediction that is perfect. Our results showed a high degree of accuracy in the models. Predictions came closely behind the expected trend line.Both plot size and prediction model form affects the accuracy [
12].These plots confirmed the algorithms had consistency coupled with reliability as training occurred was created a scatter plot to show how model works on Actual vs Predicted prices:
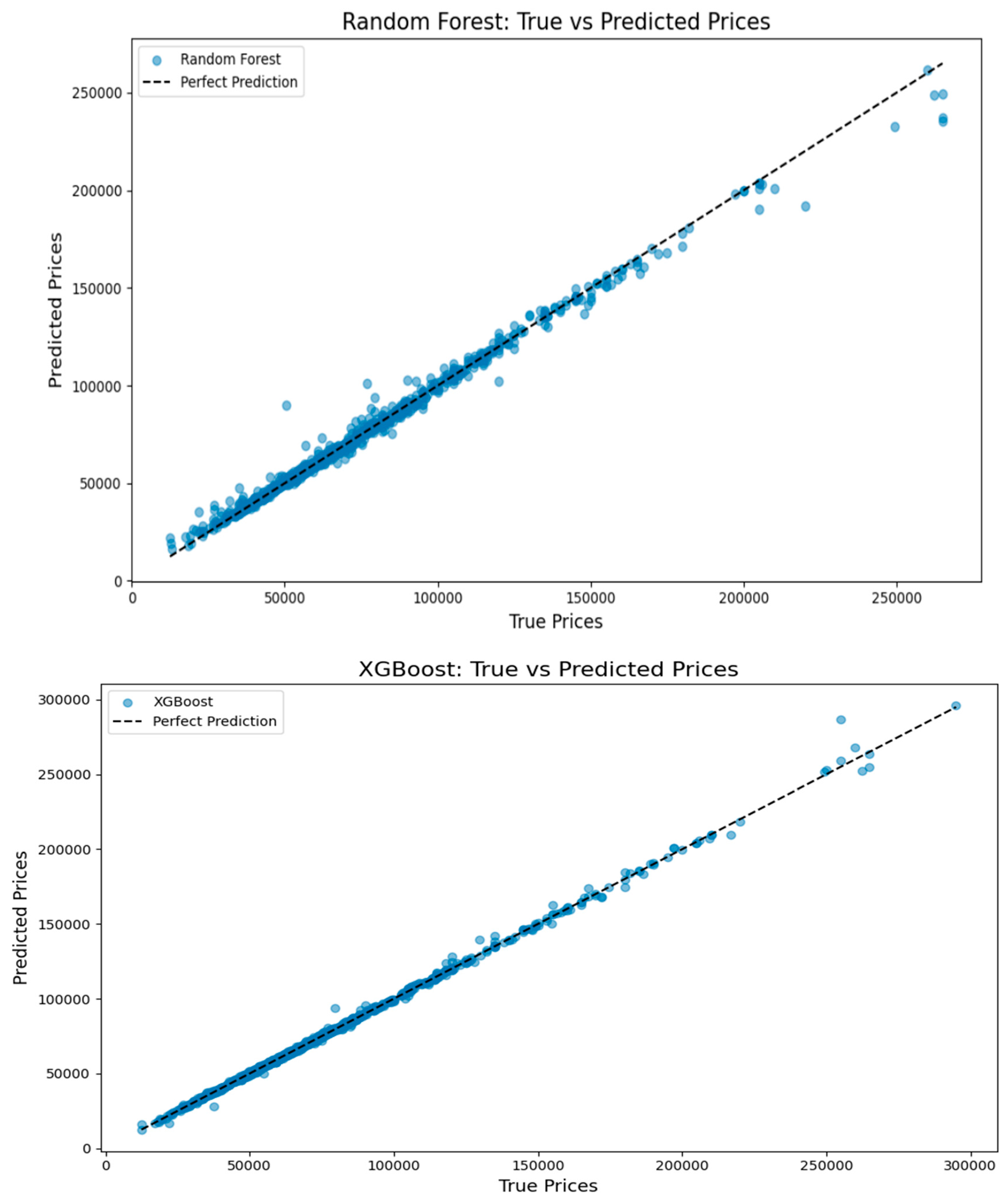
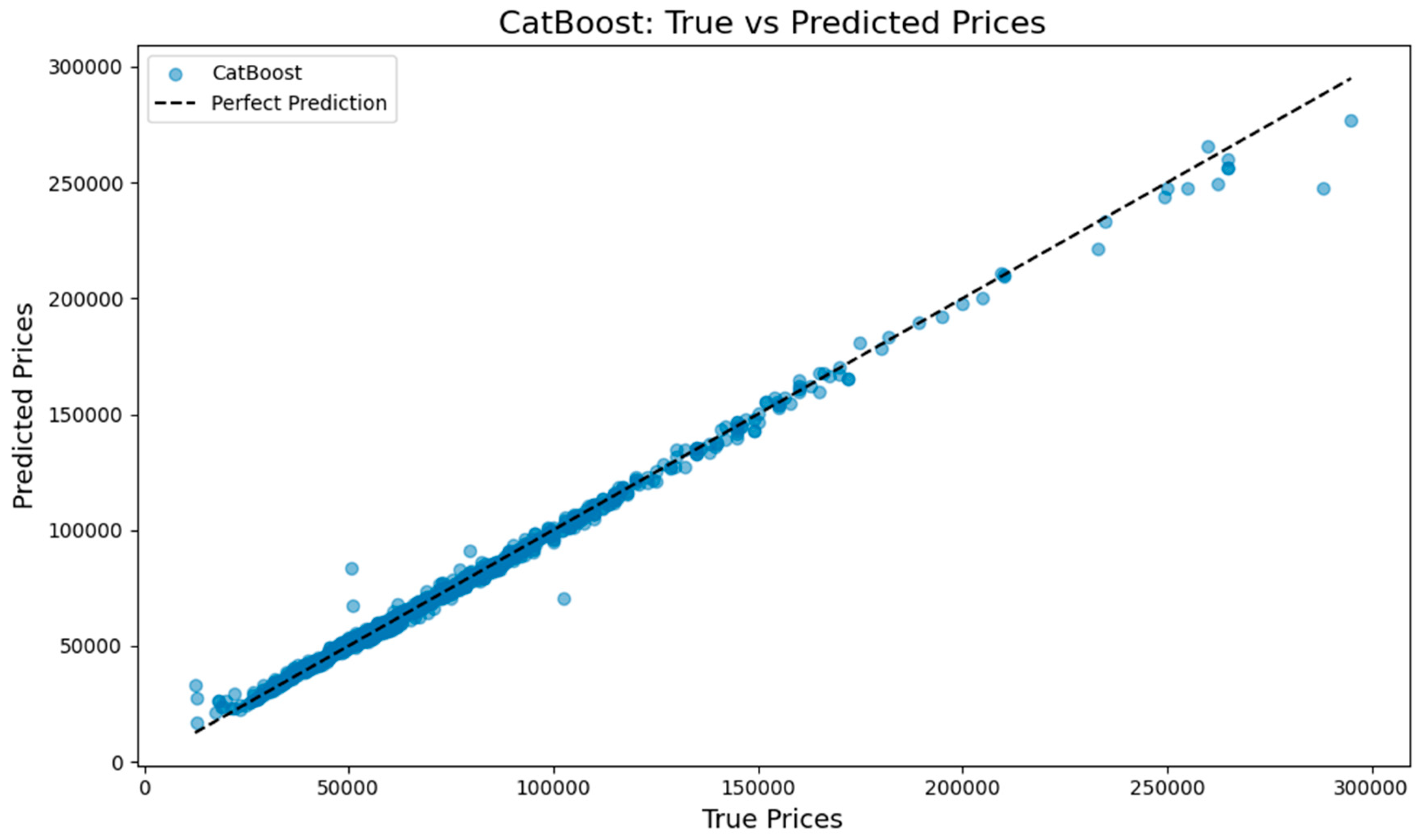
Since all three models have good P2 accuracy, here also shows good results in all models.
Result
Among the three models, Random Forest showed the best performance, achieving the highest R² score of 0.95.
| `MODEL |
R2 |
| Random Forest |
0.9545 |
| XGBoost |
0.9151 |
| CatBoost |
0.9409 |
Literature Review
Machine learning has become an effective method to predict prices for homes as real estate data becomes more accessible to everyone. To find which are most reliable and affordable methods for capturing market dynamics, researchers tested several types of algorithms.
Machine learning techniques have been employed in numerous studies for house price prediction. Artificial neural networks were identified as being superior to multiple regression models by Nghiep and Al (2001) through empirical proof from the Tennessee single-family home market. Annamoradnejad and Annamoradnejad (2022) developed stable and robust house price prediction models with implications for better consistency under different market conditions. Likewise, Vathana et al. (2022) employed various machine learning algorithms for automating real estate price prediction and compared prediction performance. Rawool et al. employed various models in “House Price Prediction Using Machine Learning,” with a comparative analysis of algorithm performance.Alsulamy (2025) also carried out a comparative study of XGBoost, CatBoost, and ridge regression to predict real estate prices in Saudi Arabia. Using data gathered through the Aqar website, the results showed that XGBoost performed better than the others, recording an R² of 0.82 for the test data and 0.98 for the trained data. The study highlights the role of machine learning algorithms in achieving higher prediction accuracy and enabling sustainable urban planning. Yılmazel, S., Afşar, A., & Yılmazel, O. (2018) gathered information on over 5000 real properties for sale, including their varied features. In their study, they created 19 different neural network models.Adetunji et al. (2022) is using the employment of k-fold cross-validation and the analysis of features highlighted the effectiveness of the Random Forest algorithm in handling the complexity in the case of housing data. More so, the authors suggested that there was scope for conducting more work in the domain of alternate models which use deep learning.Obagbuwa and Danster have contrasted the use of several machine learning algorithms—Linear Regression, Random Forest, Gradient Boost Machine, MLP, and LSTM—to predict house prices using a Kaggle data. Among the models tested, Linear Regression reported the highest value of R² as 0.91 followed by GBM and Random Forest.
References
- Nguyen, Nghiep & Cripps, Al. (2001). Predicting Housing Value: A Comparison of Multiple Regression Analysis and Artificial Neural Networks. Journal of Real Estate Research. 22. 313-336. [CrossRef]
- Annamoradnejad, R., & Annamoradnejad, I. (2022). Machine learning for housing price prediction. [CrossRef]
- Vathana, D., Patel, R., & Bargoti, M. (2022). Real estate price prediction using machine learning algorithm. In Proceedings of ICRTCSE 2021.
- Rawool, A. G., Rogue, D. V., Rane, S. G., & Bharadi, V. A. (2017). House price prediction using machine learning. Iconic Research and Engineering Journals, 4(11).
- Sharma, A., Kashyap, I., & Rana, S. (2020). House price prediction using linear regression.
- Abigail Bola Adetunji, Oluwatobi Noah Akande, Funmilola Alaba Ajala, Ololade Oyewo, Yetunde Faith Akande, Gbenle Oluwadara,.
- House Price Prediction using Random Forest Machine Learning Technique.
- Yılmazel, S., Afşar, A., & Yılmazel, O. (2018). Real estate market price prediction model of Istanbul. [CrossRef]
- Tekin, Mert & Uçal Sarı, İrem. (2022). Real Estate Market Price Prediction Model of Istanbul. Real Estate Management and Valuation. 30. 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Obagbuwa, I. C., & Danster, S. (2024). Housing price prediction using machine learning techniques. [CrossRef]
- Agha, K., Alzoubi, H. M., & Alshurideh, M. T. (2021). Measuring reliability and validity instruments of technologically driven cognitive intrusion towards work-life balance. In The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision (pp. 601–614). Springer. [CrossRef]
- 11.D. Shaiakhmetov, R. R. Mekuria, R. Isaev and F. Unsal, “Morphological Classification of Galaxies Using SpinalNet,” 2021 16th International Conference on Electronics Computer and Computation (ICECCO), Kaskelen, Kazakhstan, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Bankston, J. B., Sabatia, C. O., & Poudel, K. P. (2021). Effects of sample plot size and prediction models on diameter distribution recovery. Forest Science, 67(3), 245-255. [CrossRef]
- Jaqaman, K., Danuser, G. Linking data to models: data regression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7, 813–819 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Ying, X. (2019, February). An overview of overfitting and its solutions. In Journal of physics: Conference series (Vol. 1168, p. 022022). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Case, Karl. (2000). Real Estate and Macroeconomy. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity.
- Sadriddin, Z., Mekuria, R. R., & Gaso, M. S. (2024, June). Machine Learning Models for Advanced Air Quality Prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies 2024 (pp. 51-56). [CrossRef]
- Gaso, M. S., Mekuria, R. R., Khan, A., Gulbarga, M. I., Tologonov, I., & Sadriddin, Z. (2024, June). Utilizing Machine and Deep Learning Techniques for Predicting Re-admission Cases in Diabetes Patients. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies 2024 (pp. 76-81). [CrossRef]
- Alsulamy, S. (2025). Artificial intelligence models in real estate forecasting: A machine learning approach for sustainable urban construction in Saudi Arabia. [CrossRef]
- GeeksforGeeks. (2025, February 10). CatBoost in Machine learning. GeeksforGeeks.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).