Submitted:
10 December 2024
Posted:
11 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. ATPase1
2.2. ATPase3
2.3. Non-Plasmodium Orthologues
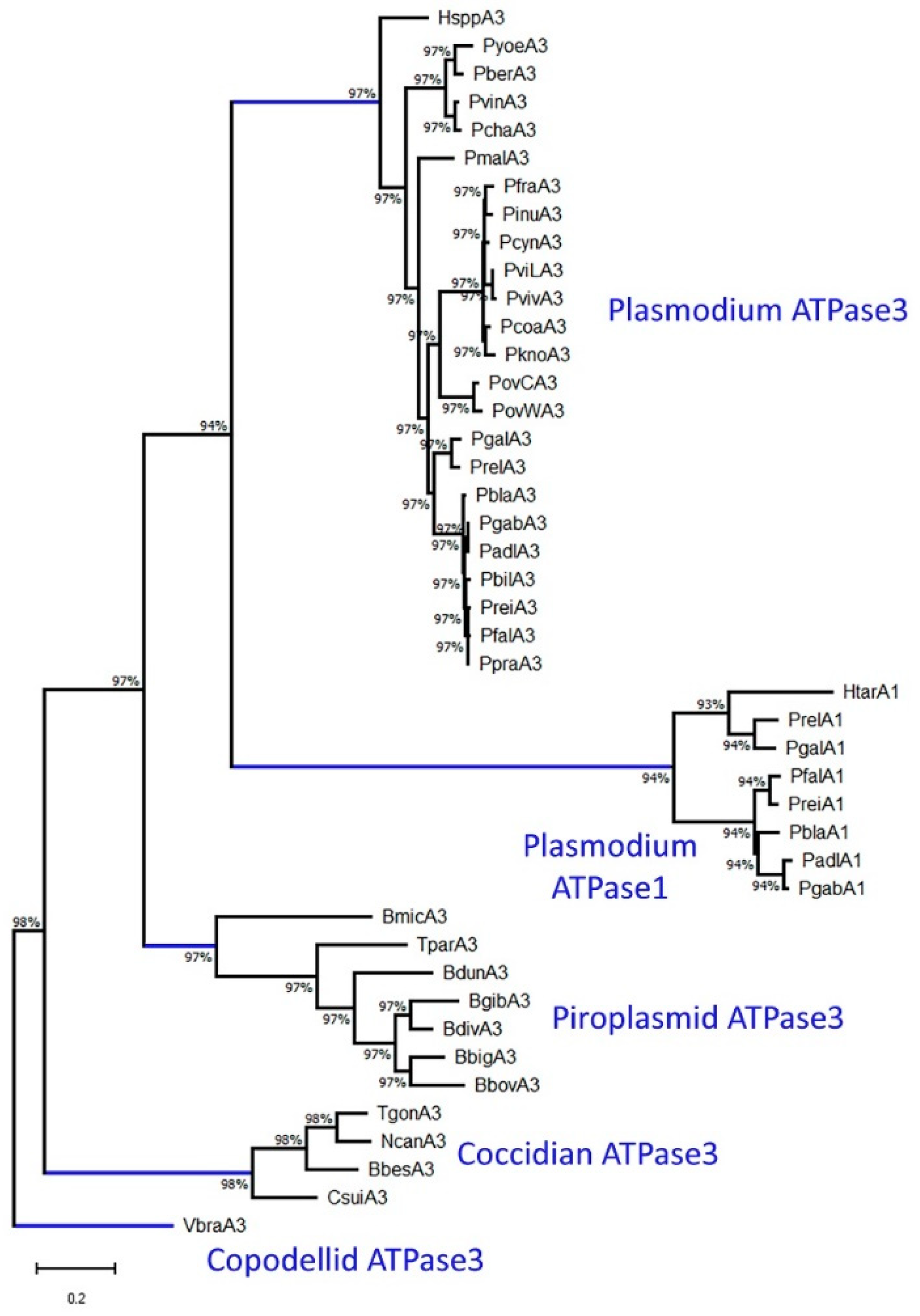
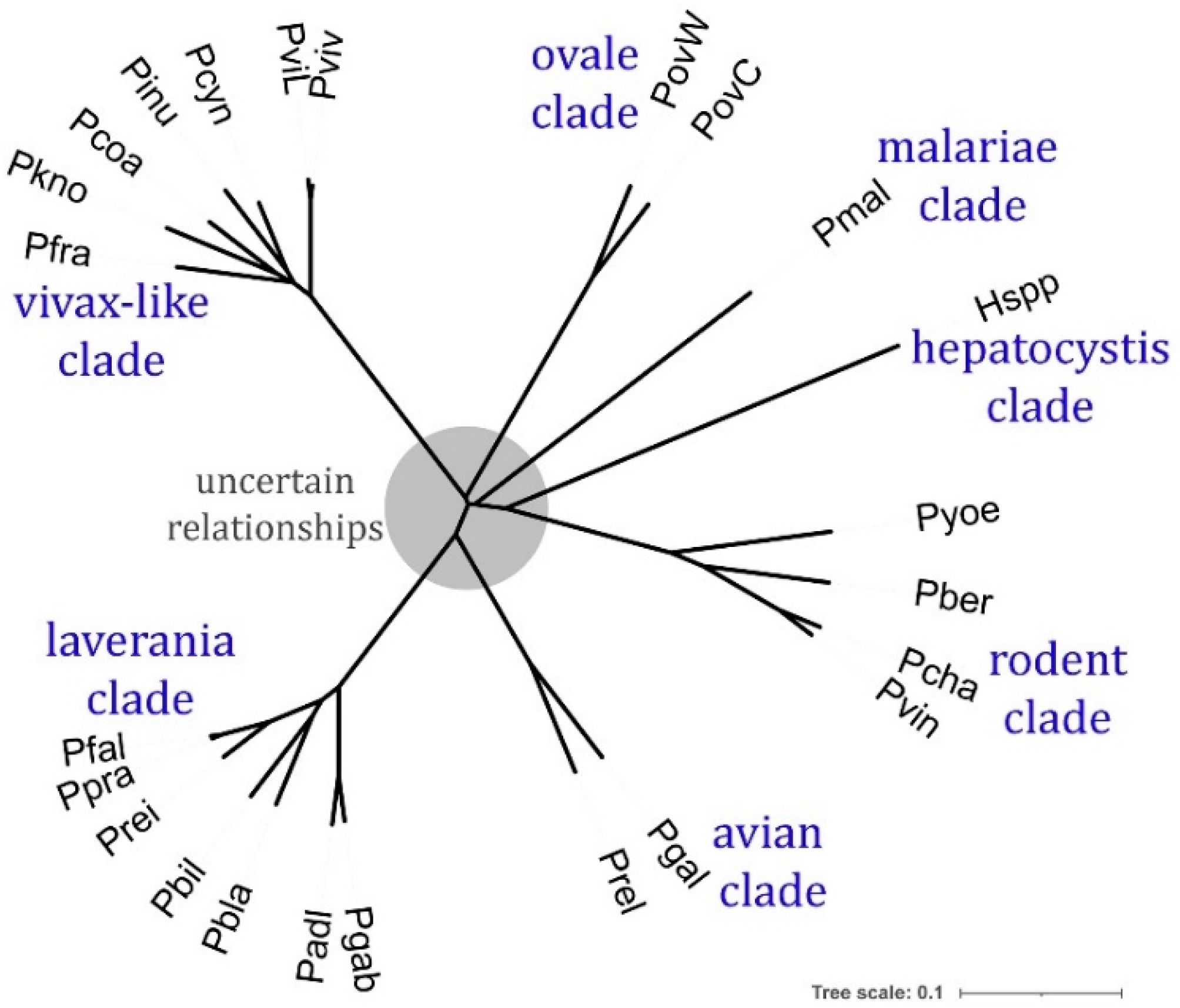
2.4. Phylogeny of ATPase1 and ATPase3
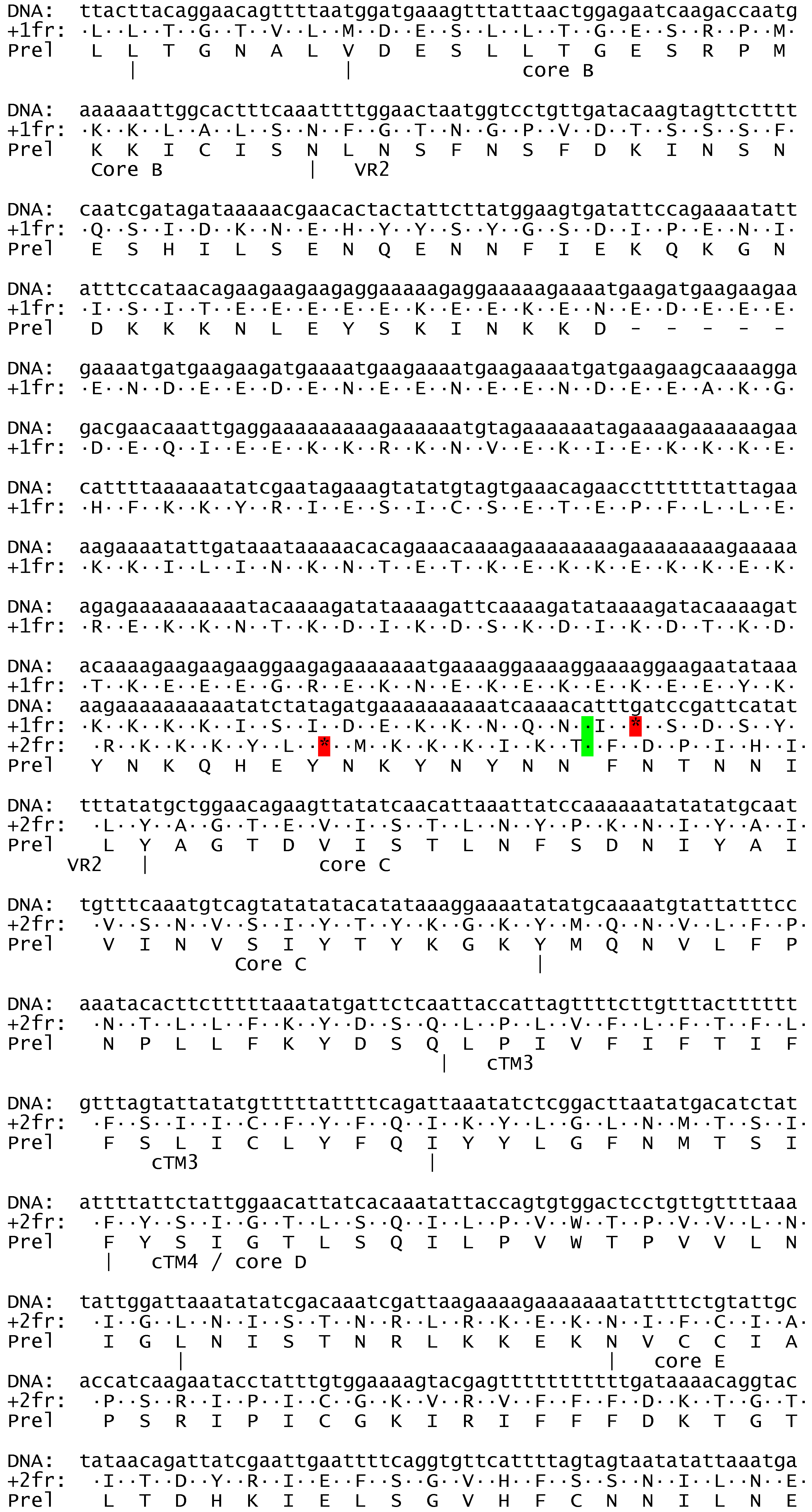
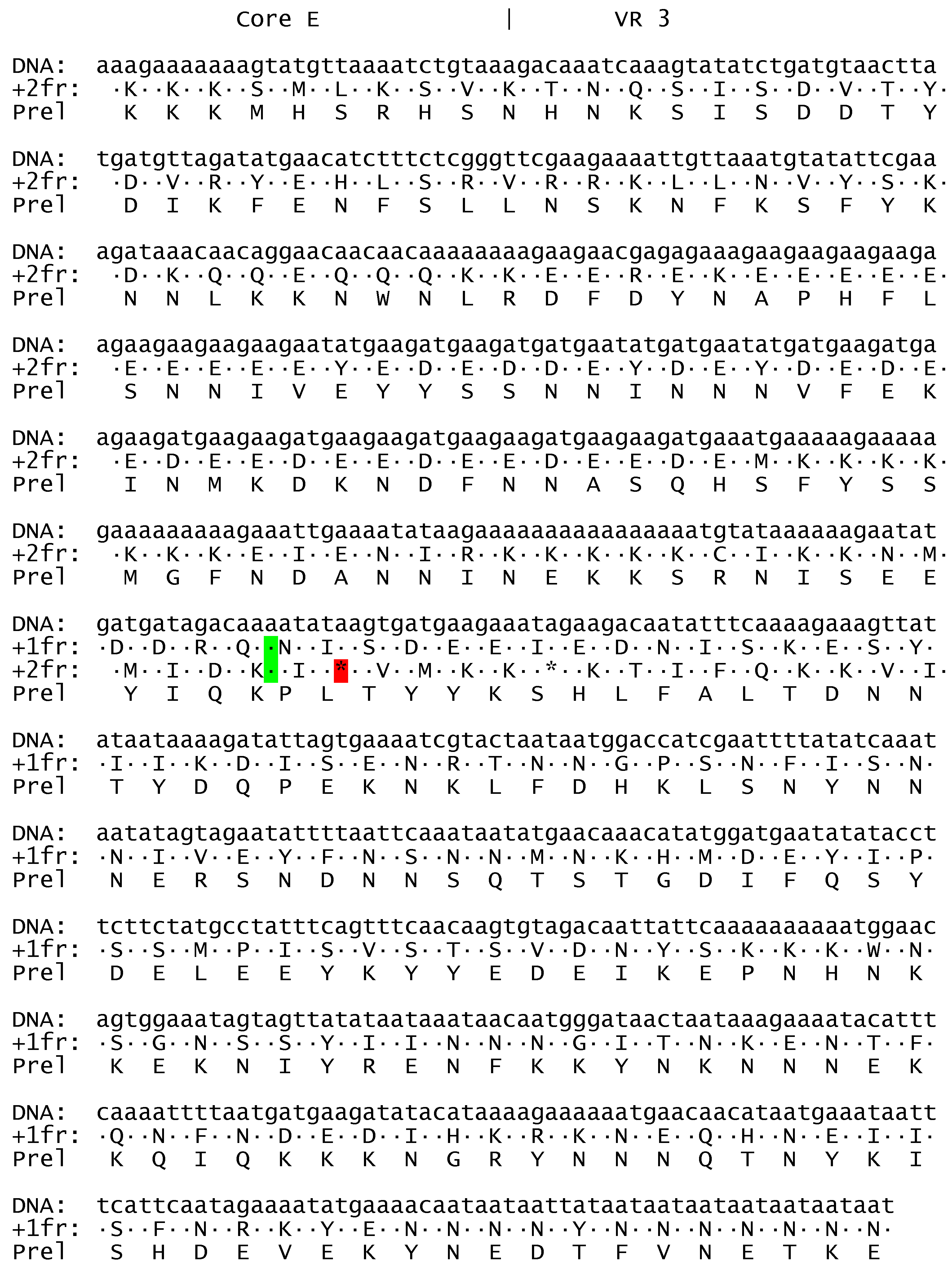
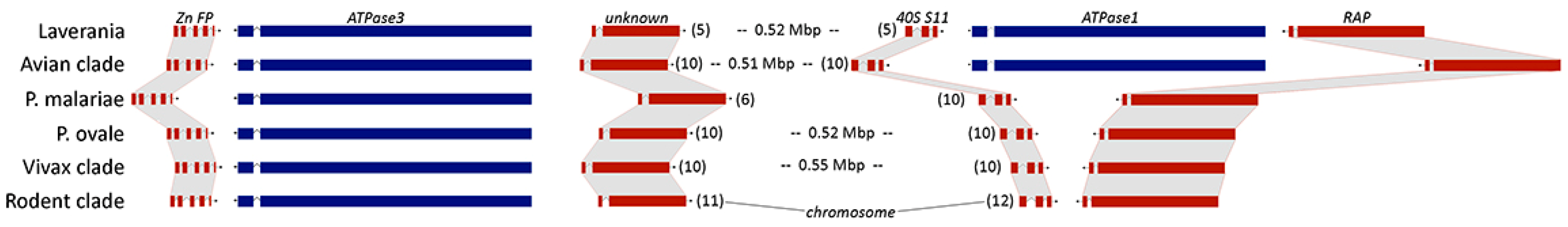
2.5. Synteny of ATPase1 and ATPase3
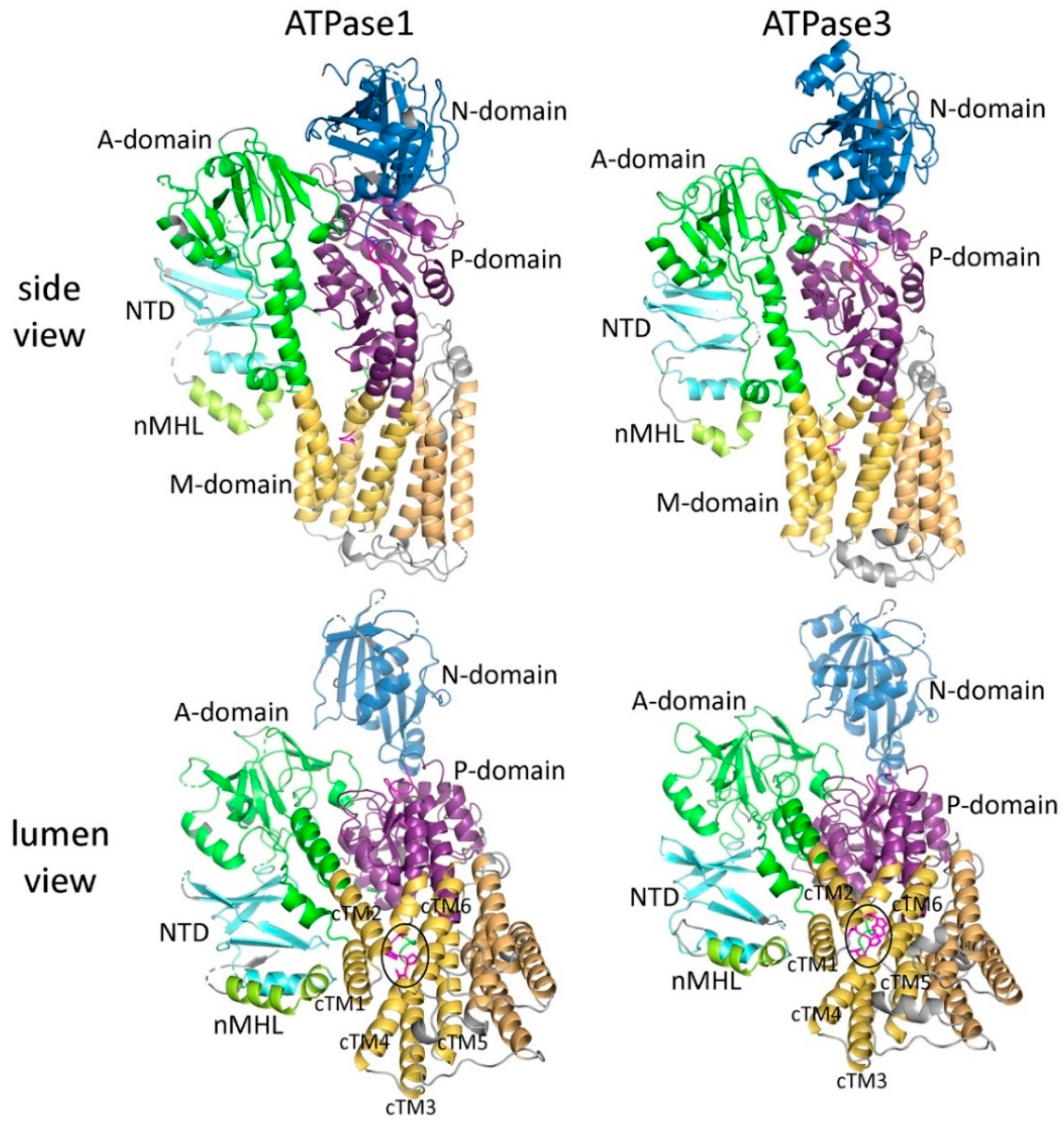
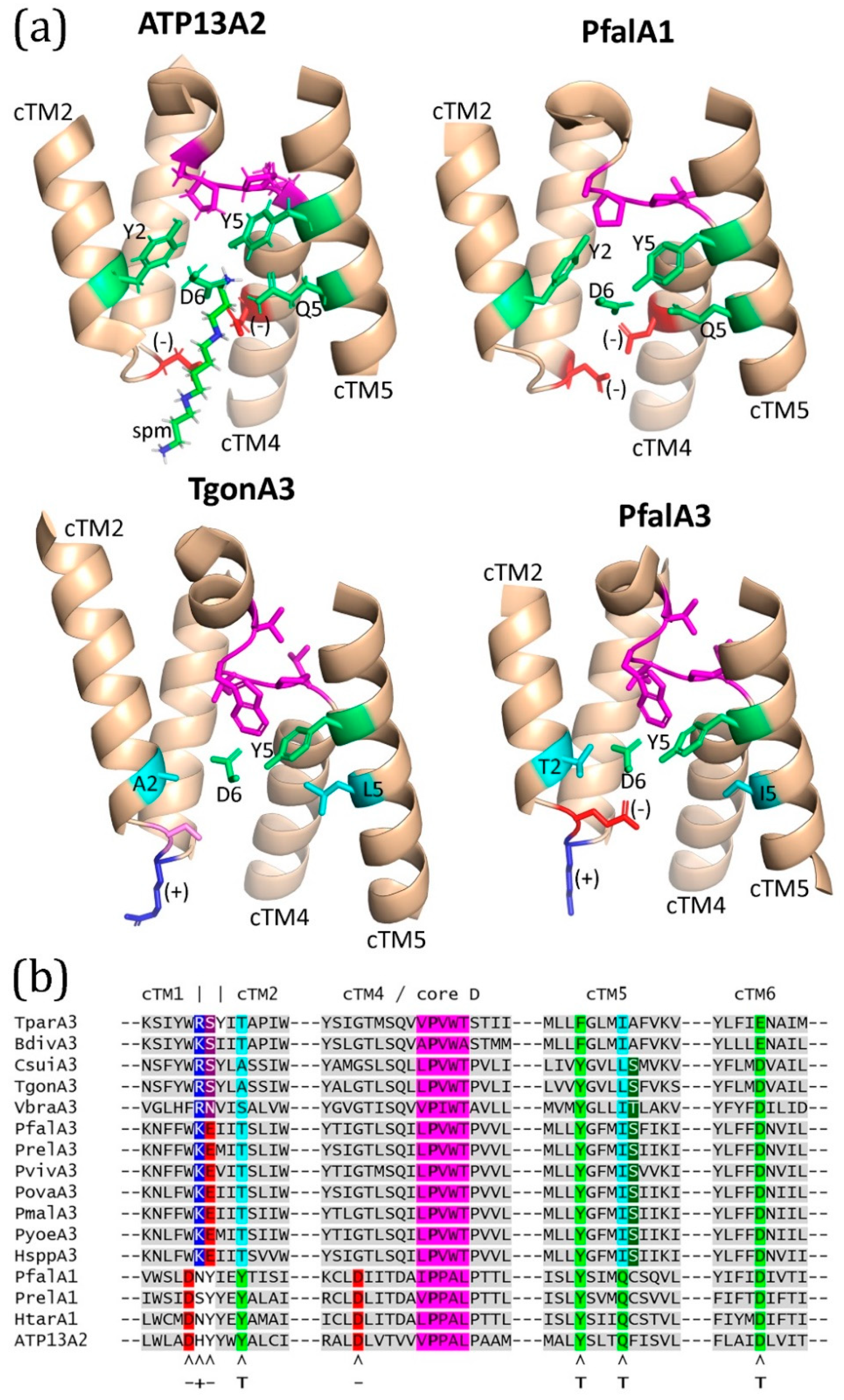
2.6. Predicted Three-Dimensional Structures of ATPase1 and ATPase3
3. Discussion
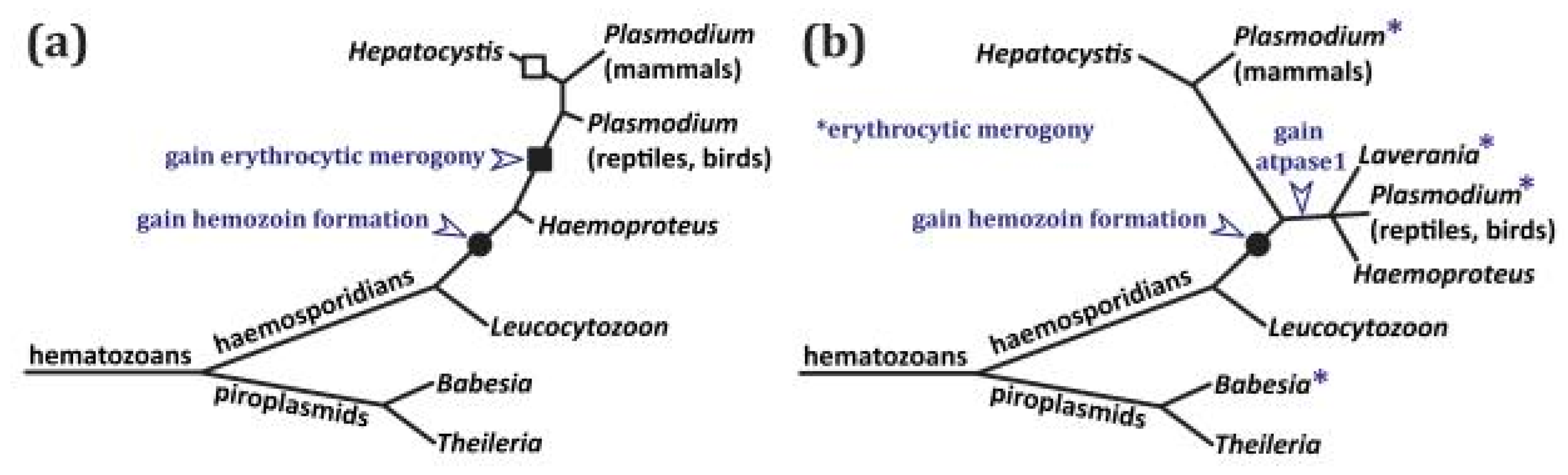
3.1. Phylogenetic Implications of ATPase1
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. BLAST Searches
4.2. Alignments and Tree Building
4.3. Three-Dimensional Structure Predictions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Description of ATPase1 and ATPase3 from Haemoproteus tartakovskyi.





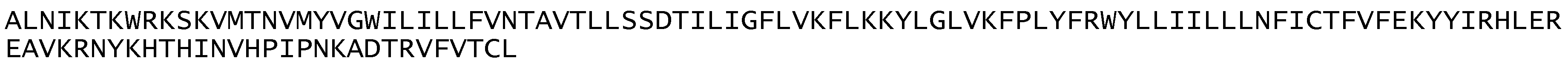


References
- Palmgren, M. P-type ATPases: many more enigmas left to solve. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsen, K.B.; Palmgren, M.G. Evolution of substrate specificities in the P-type ATPase superfamily. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 46, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, A.B.; Asp, T.; Holm, P.B.; Palmgren, M.G. Phylogenetic analysis of P5 P-type ATPases, a eukaryotic lineage of secretory pathway pumps. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 46, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.; Cowan, G.; Meade, J.C.; Wells, R.A.; Stringer, J.R.; Robson, K.J. A family of cation ATPase-like molecules from Plasmodium falciparum. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 120, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozmajzl, P.J.; Kimura, M.; Woodrow, C.J.; Krishna, S.; Meade, J.C. Characterization of P-type ATPase 3 in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 116, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Tanabe, K.; Krishna, S.; Tsuboi, T.; Saito-Ito, A.; Otani, S.; Ogura, H. Gametocyte-dominant expression of a novel P-type ATPase in Plasmodium yoelii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1999, 104, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.; Cowan, G.M.; Robson, K.J.; Meade, J.C. Plasmodium falciparum: further characterization of putative cation ATPases. Exp. Parasitol. 1994, 78, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, T.D.; Gilabert, A.; Crellen, T.; Böhme, U.; Arnathau, C.; Sanders, M.; Oyola, S.O.; Okouga, A.P.; Boundenga, L.; Willaume, E.; et al. Genomes of all known members of a Plasmodium subgenus reveal paths to virulent human malaria. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagner, S.C.; Misof, B.; Maier, W.A.; Kampen, H. Bayesian analysis of new and old malaria parasite DNA sequence data demonstrates the need for more phylogenetic signal to clarify the descent of Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, G.T.; Beltran, M.M.G.; Gómez-Alegría, C.J.; Wiser, M.F. Identification of a protein unique to the genus Plasmodium that contains a WD40 repeat domain and extensive low-complexity sequence. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 2617–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePristo, M.A.; Zilversmit, M.M.; Hartl, D.L. On the abundance, amino acid composition, and evolutionary dynamics of low-complexity regions in proteins. Gene 2006, 378, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, S.R.; Lwin, N.; Phelan, D.; Escalante, A.A.; Battistuzzi, F.U. Comparative analysis of low complexity regions in Plasmodia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, gkae268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votýpka, J.; Modrý, D.; Oborník, M.; Šlapeta, J.; Lukeš, J. Apicomplexa. In Handbook of the Protists; Archibald, J.M., Simpson, A.G.B., Slamovits, C.H., Margulis, L., Melkonian, M., Chapman, D.J., Corliss, J.O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 1–58. ISBN 978-3-319-32669-6. [Google Scholar]
- Martinsen, E.S.; Perkins, S.L.; Schall, J.J. A three-genome phylogeny of malaria parasites (Plasmodium and closely related genera): evolution of life-history traits and host switches. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 47, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, F.; Roger, A.J.; Brown, M.W.; Simpson, A.G.B. The new tree of eukaryotes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiser, M.F. Protozoa. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity (Volume 2); Scheiner, S.M.B.T., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2024; pp. 802–817. ISBN 978-0-323-98434-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancio, A.; Scippa, S.; Finetti-Sialer, M.; De Candia, A.; Avallone, B.; De Vincentiis, M. Redescription of Cardiosporidium cionae (Van Gaver and Stephan, 1907) (Apicomplexa: Piroplasmida), a plasmodial parasite of ascidian haemocytes. Eur. J. Protistol. 2008, 44, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethke, L.L.; Zilversmit, M.; Nielsen, K.; Daily, J.; Volkman, S.K.; Ndiaye, D.; Lozovsky, E.R.; Hartl, D.L.; Wirth, D.F. Duplication, gene conversion, and genetic diversity in the species-specific acyl-CoA synthetase gene family of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 150B, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, A.S.; Mello, B.; Pacheco, M.A.; Luo, Z.; Sullivan, S.A.; Carlton, J.M.; Escalante, A.A. The genome of Plasmodium gonderi: insights into the evolution of human malaria parasites. Genome Biol. Evol. Evol. 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brayton, K.A.; Lau, A.O.T.; Herndon, D.R.; Hannick, L.; Kappmeyer, L.S.; Berens, S.J.; Bidwell, S.L.; Brown, W.C.; Crabtree, J.; Fadrosh, D.; et al. Genome sequence of Babesia bovis and comparative analysis of apicomplexan hemoprotozoa. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesh, C.; Stevens, G.J.; Xie, P.; De Jesus Martinez, T.; Hershberg, E.A.; Leung, A.; Guo, E.; Dider, S.; Zhang, J.; Bridge, C.; et al. JBrowse 2: a modular genome browser with views of synteny and structural variation. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurrecoechea, C.; Brestelli, J.; Brunk, B.P.; Dommer, J.; Fischer, S.; Gajria, B.; Gao, X.; Gingle, A.; Grant, G.; Harb, O.S.; et al. PlasmoDB: A functional genomic database for malaria parasites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillinghast, J.; Drury, S.; Bowser, D.; Benn, A.; Lee, K.P.K. Structural mechanisms for gating and ion selectivity of the human polyamine transporter ATP13A2. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 4650–4662.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, K.; Salustros, N.; Grønberg, C.; Gourdon, P. Structure and transport mechanism of P5B-ATPases. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Wolfe, D.M.; Stiller, B.; Pearce, D.A. Cd2+, Mn2+, Ni2+ and Se2+ toxicity to Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacking YPK9p the orthologue of human ATP13A2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 383, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiser, M.F. The digestive vacuole of the malaria parasite: a specialized lysosome. Pathogens 2024, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarque, M.; Tastet, C.; Poncet, J.; Demettre, E.; Jouin, P.; Vial, H.; Dubremetz, J.-F. Food vacuole proteome of the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Proteomics. Clin. Appl. 2008, 2, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.A. Polyamines in protozoan pathogens. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 18746–18756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemand, J.; Louw, A.I.; Birkholtz, L.; Kirk, K. Polyamine uptake by the intraerythrocytic malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, S.; Canbäck, B.; DeBarry, J.D.; Johansson, T.; Hellgren, O.; Kissinger, J.C.; Palinauskas, V.; Videvall, E.; Valkiūnas, G. The genome of Haemoproteus tartakovskyi and its relationship to human malaria parasites. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, U.; Otto, T.D.; Cotton, J.A.; Steinbiss, S.; Sanders, M.; Oyola, S.O.; Nicot, A.; Gandon, S.; Patra, K.P.; Herd, C.; et al. Complete avian malaria parasite genomes reveal features associated with lineage-specific evolution in birds and mammals. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borner, J.; Pick, C.; Thiede, J.; Kolawole, O.M.; Kingsley, M.T.; Schulze, J.; Cottontail, V.M.; Wellinghausen, N.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Bruchhaus, I.; et al. Phylogeny of haemosporidian blood parasites revealed by a multi-gene approach. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 94, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pick, C.; Ebersberger, I.; Spielmann, T.; Bruchhaus, I.; Burmester, T. Phylogenomic analyses of malaria parasites and evolution of their exported proteins. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, M.A.; Escalante, A.A. Origin and diversity of malaria parasites and other Haemosporida. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, J.; Stoklasa, M.; Nayak, S.; En Low, K.; Qian Hui Lee, E.; Duong Tien, Q.H.; Rénia, L.; Malleret, B.; Bozdech, Z. The artemisinin-induced dormant stages of Plasmodium falciparum exhibit hallmarks of cellular quiescence/senescence and drug resilience. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCrue, A.N.; Scheel, M.; Kennedy, K.; Kumar, N.; Kyle, D.E. Effects of artesunate on parasite recrudescence and dormancy in the rodent malaria model Plasmodium vinckei. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, L.; Reményi, I.; Tusnády, G.E. CCTOP: a consensus constrained TOPology prediction web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W408–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Taxonomic Group | PfATPase3 | PfATPase1 |
|---|---|---|
| Piroplasmids | 5E-70 – 2E-101 | 9E-39 |
| Coccidians | 8E-62 – 6E-64 | 5E-33 |
| Vitrella brassicaformis (colpodellid) | 1E-87 | 5E-40 |
| Cryptosporidia | 4E-48 | 2E-30 – 1E-30 |
| Ciliates | ND | 6E-31 – 3E-34 |
| Oomycetes (stramenopile) | 3E-48 – 1E-53 | ND |
| Fungi | 4E-48 – 2E-52 | 3E-30 – 8E-35 |
| Bee (insect) | ND | 2E-42 |
| Anaeramoeba ignava (metamonad) | ND | 4E-32 – 7E-34 |
| The range of E-values from a BLAST search using PfATPase3 or PfATPase1 as queries is shown for the indicated group or species. A single E-value means that there was a single hit for that taxonomic group. ND = none detected in the top 100 hits for PfATPase3 nor the top 50 hits for PfATPase1. No common subjects (i.e., hits) were identified between the top 100 hits using PfATPase3 as a query and the top 50 hits using PfATPase1 as a query. | ||
| Species (queries) | 7op1 | 6xms | 8ier | 7m5x | 7n78 | 7fjp | 3b8c |
| Plasmodium falciparum (A1) | 1 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 2 |
| Plasmodium relictum (A1) | 1 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 31 |
| Haemoproteus tartakovskyi (A1) | 1 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 40 |
| Plasmodium falciparum (A3) | 2 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 1 |
| Plasmodium relictum (A3) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| Plasmodium vivax (A3) | 5 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 26 |
| Plasmodium malariae (A3) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 18 |
| Plasmodium ovale (A3) | 2 | 6 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 32 |
| Plasmodium yoelii (A3) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Hepatocystis spp (A3) | 3 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 1 |
| Vitrella brassicaformis (A3) | 5 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 13 |
| Theileria parvum (A3) | 1 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 19 |
| Babesia divergens (A3) | 2 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 33 |
| Toxoplasma gondii (A3) | 1 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| Cystoisospora suis (A3) | 3 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 24 |
| Sequences from the indicated species were analyzed by Phyre® and shown are the ranks of common templates (denoted with PDB IDs in column headers) for each of the species. These templates are Ypk9 from Chaetomium thermophilum (7op1), ATP13A2 of Homo sapiens (8ier, 7m5x, 7n78, or 7fjp), a P5A-ATPase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (6xms), and a sodium-potassium pump from Sus scrofa (3b8c). | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





