Submitted:
08 December 2024
Posted:
10 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
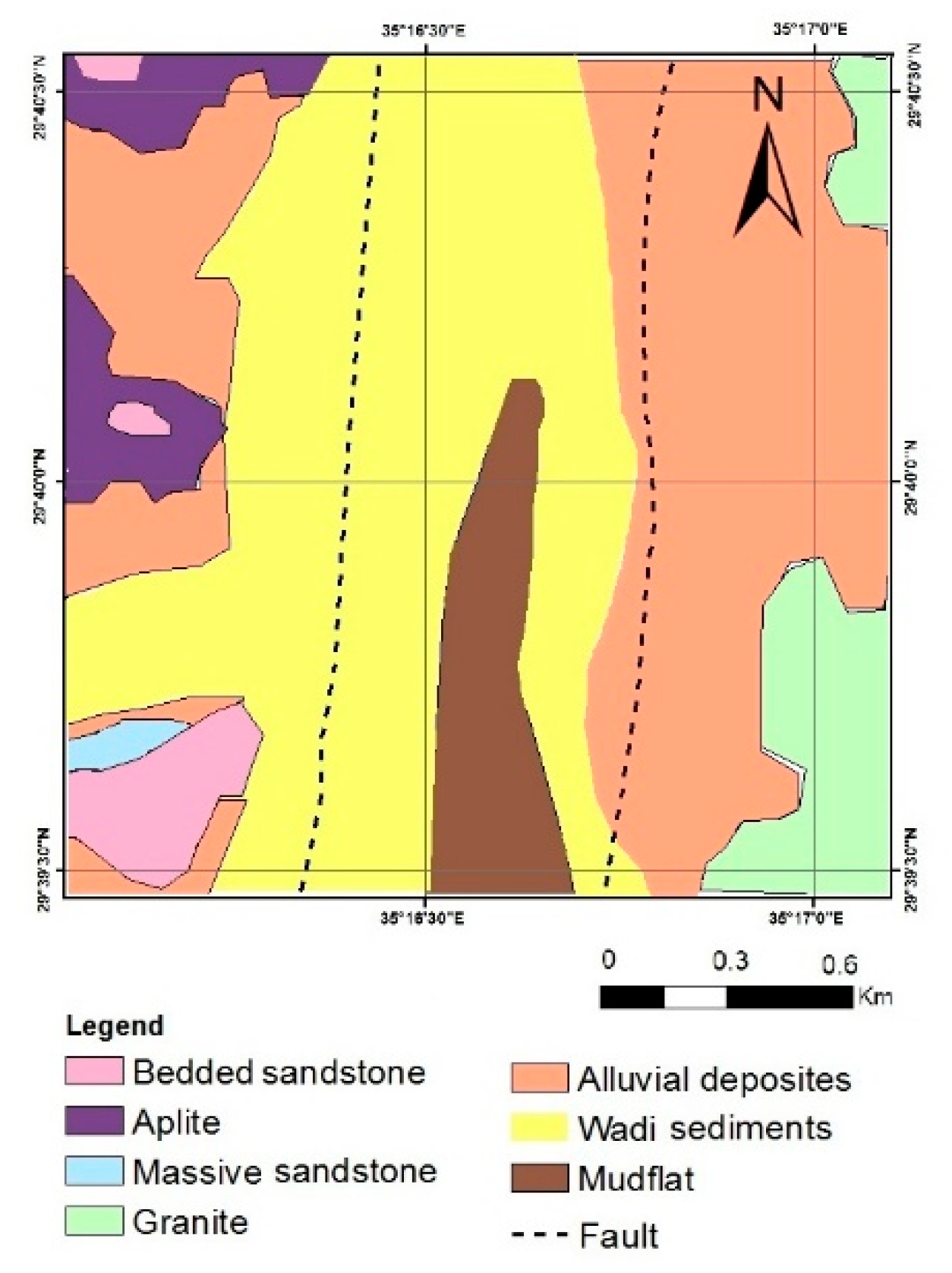
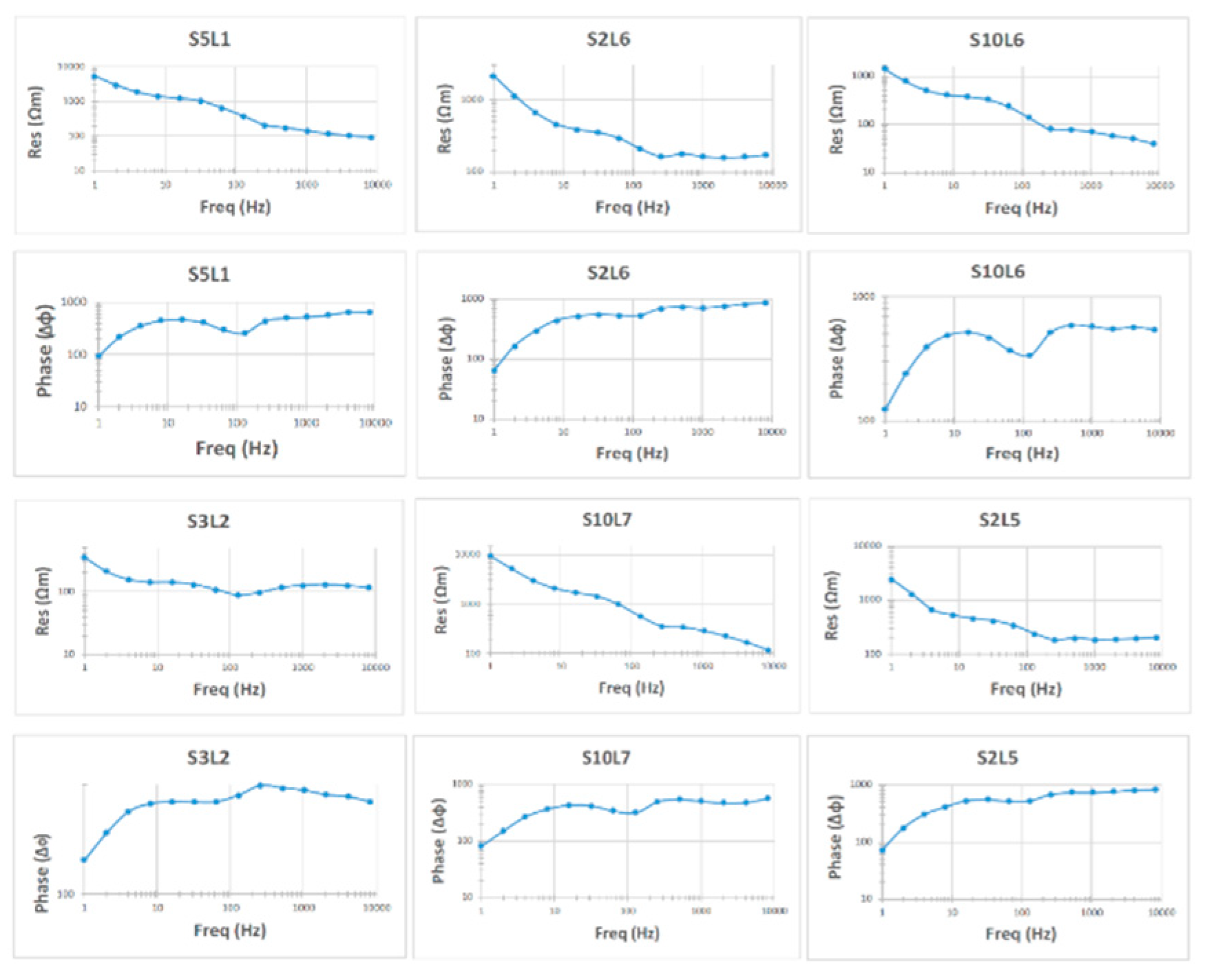
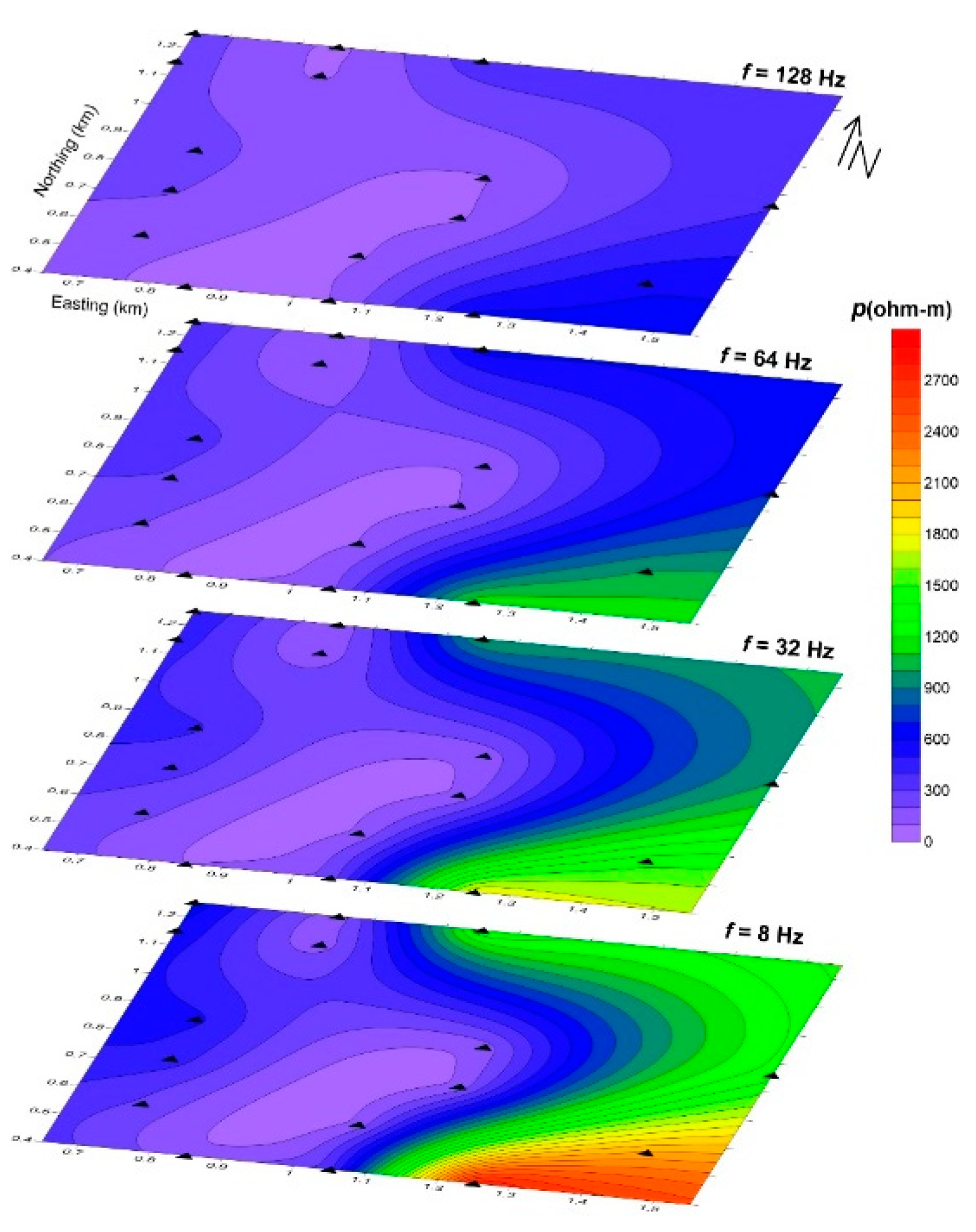
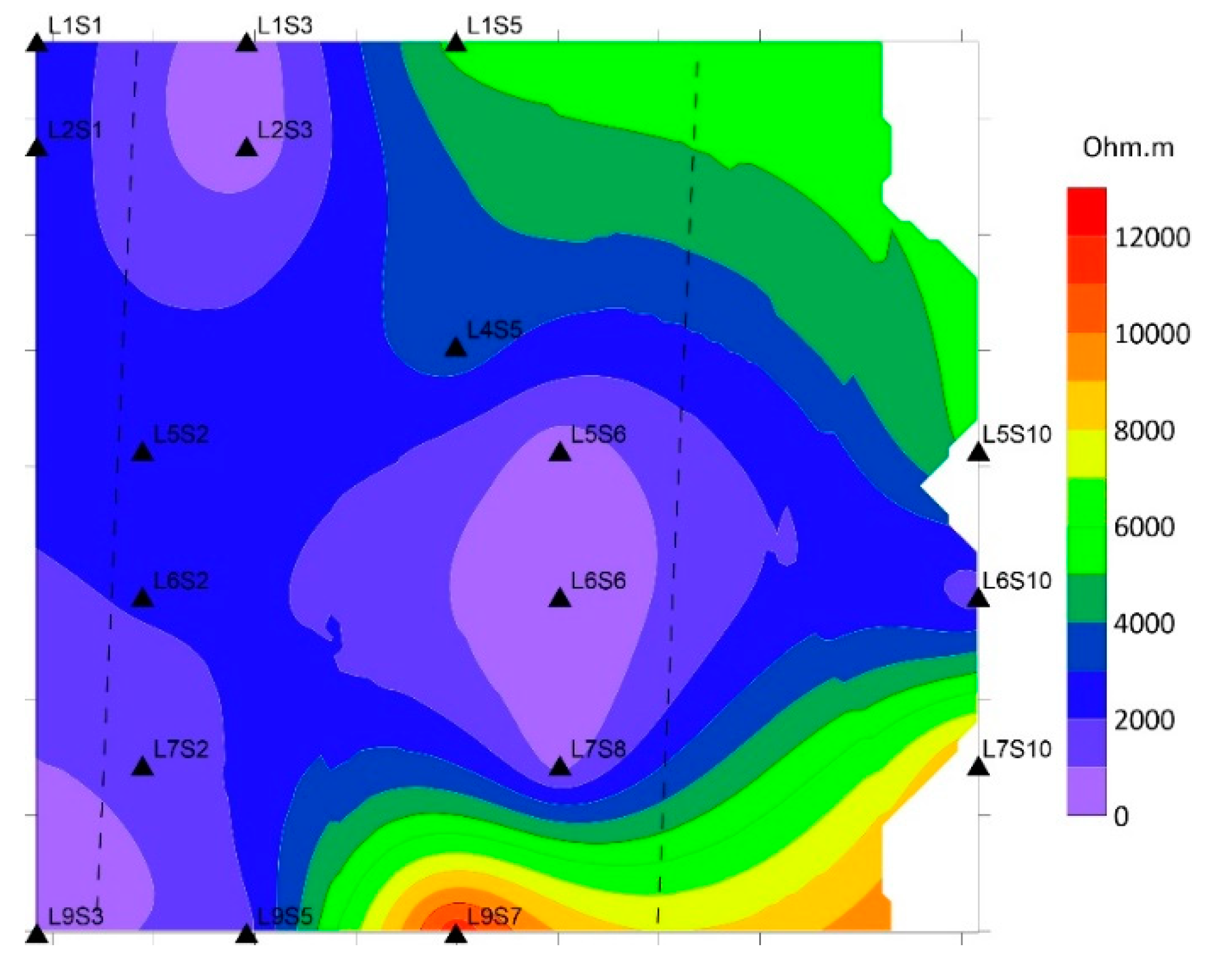
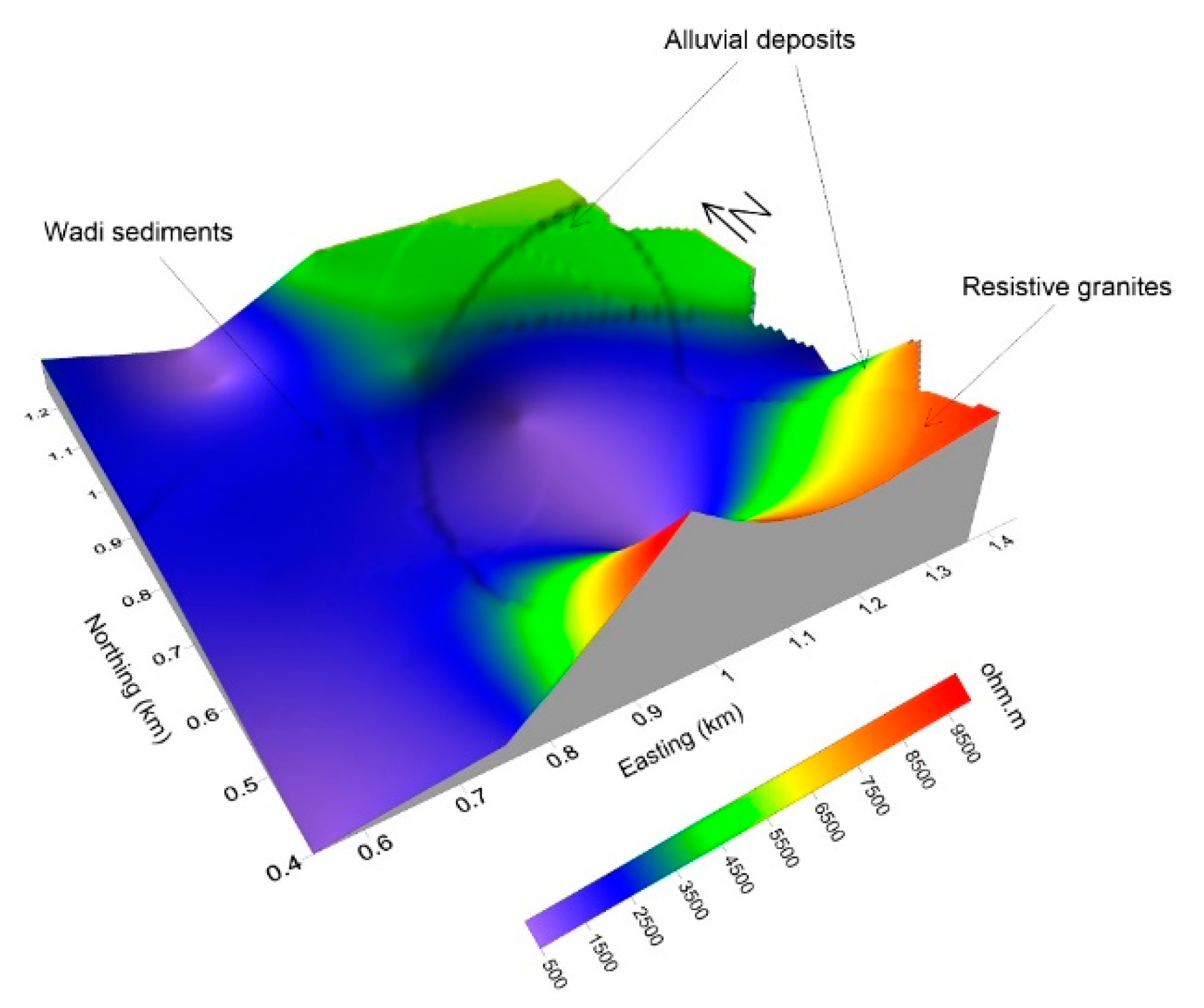
The UNISCO World Heritage Center announced in 2011 that the Wadi Rum Protected Area (WRPA) is a global landmark for natural and cultural attraction, which represents an emerging industrial suburban and a critical socio-economic significance to the country of Jordan. The study area in Wadi Rum is located northeast of the Gulf of Aqaba between the African and Arabian plates. The region is historically characterized by significant tectonic activity and seismic events. This study focuses on characterizing the subsurface structural features of Wadi Rum through the application of the geophysical method Controlled Source Audio-frequency Magnetotellurics (CSAMT). CSAMT data were collected from 16 sounding stations, processed, and qualitatively interpreted. The qualitative interpretation involved two main approaches: constructing sounding curves for each station and generating apparent resistivity maps at fixed depths (frequencies). The results revealed the presence of at least four distinct subsurface layers. The surface layer exhibited relatively low resistivity values (<200 Ω·m), corresponding to alluvial and wadi sediments, as well as mud flats. Two intermediate layers were identified: the first showed very low resistivity values (80–100 Ω·m), likely due to medium-grained bedded sandstone, while the second displayed intermediate resistivity values (100–800 Ω·m), representing coarse basal conglomerates and coarse sandstone formations. The deepest layer demonstrated very high resistivity values (>1000 Ω·m), which are likely attributed to basement rocks. Analysis of resistivity maps, combined with prior geological information, indicates that the subsurface in the study area features a graben-like structure, characterized by two detected faults trending in the northeast (NE) and southwest (SW) directions. The findings of this study, by providing critical insights into the subsurface structure, make a considerable contribution to the technical and scientific outlook that is necessary for the careful assessment of potential hazards and the strategic planning of future urban development within the protected area.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
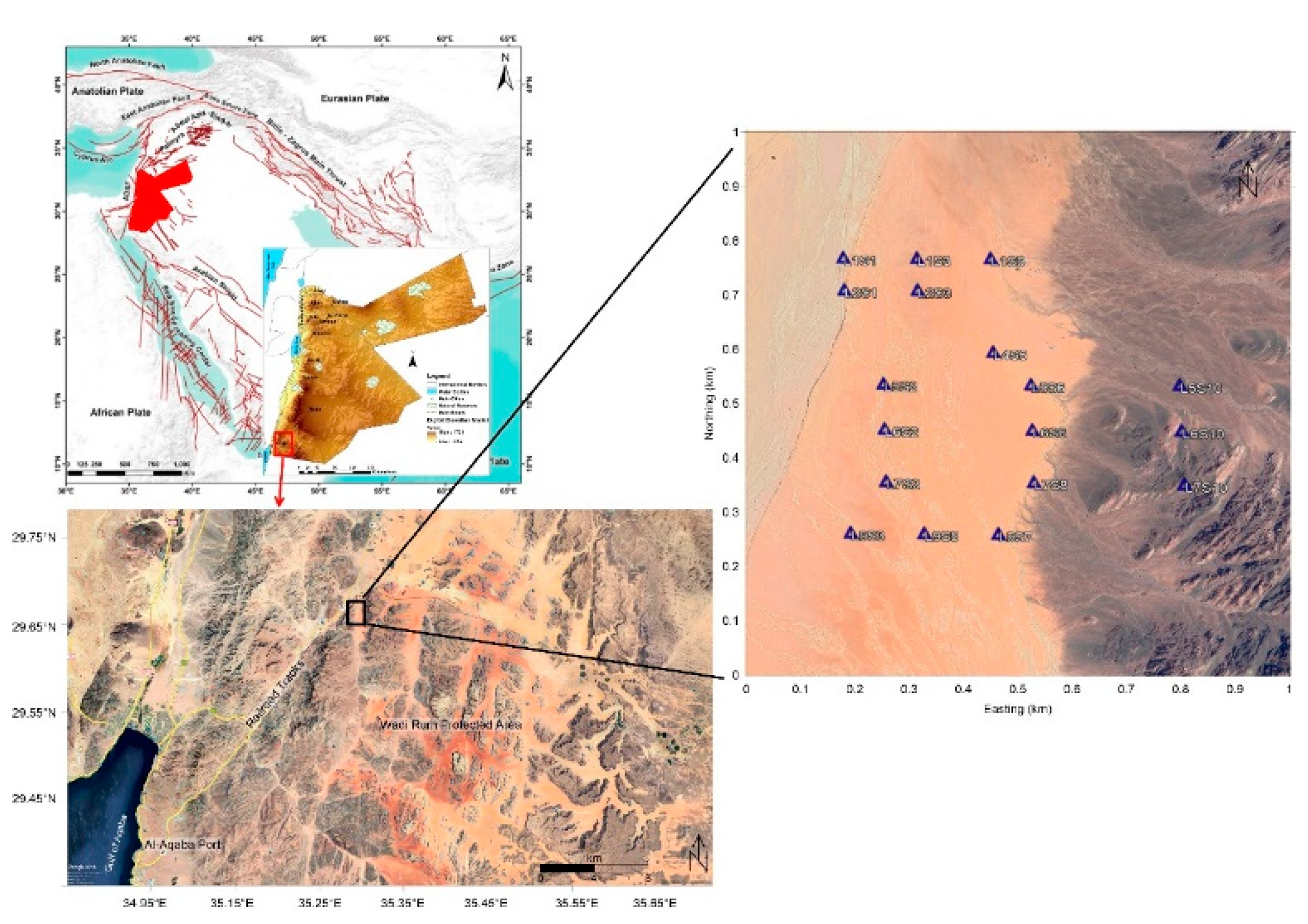
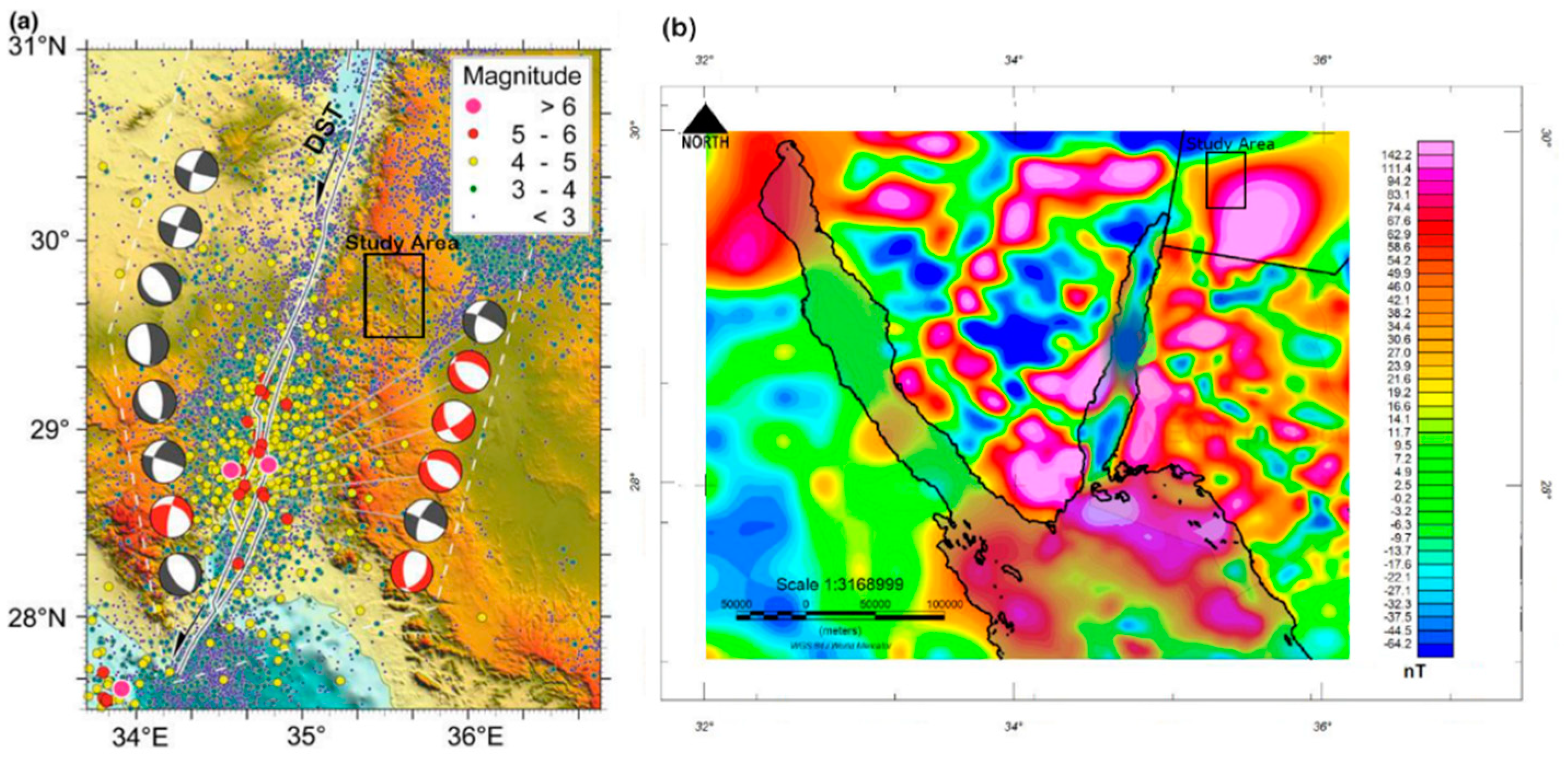
2. Geological Setting
| Geological age | Lithology | Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Quaternary deposits (youngest) |
alluvial and wadi sediments, alluvium sand and mud flats | few meters (~10 m) |
| Rum formation | Medium-grained bedded sandstone | 60 - 100 m |
| Continental sandstone | Coarse basal conglomerate Coarse-grained sandstone Coarse-grained massive sandstone |
100 - 300 m 300 - 650 m |
| Precambrian Basement rocks |
Granites with some granodiorite, and metamorphic rocks with some intrusive dikes |
3. Data and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UISCO World Heritage Center (Report on June 2011). https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1377/#:~:text=The%2074%2C000%2Dhectare%20property%2C%20inscribed,the%20region.&text=a%20varied%20desert%20landscape,the%20region.&text=in%20the%20site%20testify,the%20region.&text=trace%20the%20evolution%20of,the%20region.
- Izzeldin, A. Y. (1987). Seismic, gravity and magnetic surveys in the central part of the Red Sea: their interpretation and implications for the structure and evolution of the Red Sea. Tectonophysics, 143(4), 269-306. [CrossRef]
- El-Waheidi, M. M. , Merlanti, F., & Pavan, M. (1992). Geoelectrical Resistivity Survey of the Central Part of Azraq Basin (Jordan) for Identifying Saltwater/Freshwater Interface. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 29, 125-133. [CrossRef]
- Al-Amri, A. M. S. , Punsalan, B. T., & Uy, E. A. (1998). Spatial distribution of the seismicity parameters in the Red Sea regions. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 16(5-6), 557-563. [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, H. A., Fnais, M. S., Al-Amri, A. M., & Abdel-Rahman, K. (2012). Tectonic framework of Lunayyir area, northwest Saudi Arabia through aftershock sequence analysis of 19 May 2009 earthquake and aeromagnetic data. Int. J. Phys. Sci, 7(44), 5821-5833.
- Bender, F. (1975). Geology of the Arabian Peninsula, Jordan (No. 560-I).
- Barberi, F. , Capaldi, G., GA SPARINI, P., Marinelli, G., Santacroce, R., Scandone, R.,... & Varet, J. (1980). Recent basaltic volcanism of Jordan and its implications on the geodynamic hi-story of the Dead Sea shear zone. In Geodynamic evolution of the Afro-Arabian rift system (pp. 667-683). https://hdl.handle.net/11568/208804.
- Basaloom, A. , & Geri, M. B. (2019, June). Contribution of Rifting Activities to Spatial and Temporal Variations of Seismic B-Values Along the Gulf of Aden Area, Case Study. In ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium (pp. ARMA-2019). ARMA.
- Aboud, E. , Alqahtani, F., Abdulfarraj, M., Abraham, E., El-Masry, N., & Osman, H. (2023). Geothermal imaging of the Saudi cross-border city of NEOM deduced from magnetic data. Sustainability, 15(5), 4549. [CrossRef]
- Al-shijbi, Y. , El-Hussain, I., Deif, A. et al. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment for the Arabian Peninsula. Pure Appl. Geophys. 176, 1503–1530 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W., Montagna, P., Pons-Branchu, E., Rasul, N., & Taviani, M. (2017). Seismic hazards implications of uplifted Pleistocene coral terraces in the Gulf of Aqaba. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Meqbel, N. M. , Ritter, O., & Group, D. E. S. I. R. E. (2013). A magnetotelluric transect across the Dead Sea Basin: electrical properties of geological and hydrological units of the upper crust. Geophysical Journal International, 193(3), 1415-1431. [CrossRef]
- Kahal, A.Y. Geological assessment of the Neom mega-project area, northwestern Saudi Arabia: an integrated approach. Arab J Geosci 13, 345 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Freund, R., Garfunkel, Z., Zak, I., Goldberg, M., Weissbrod, T., Derin, B., ... & Girdler, R. W. (1970). The shear along the Dead Sea rift. Philosophical Transactions for the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 107-130.
- Eyal, M. , Bartov, Y., Shimron, A., Bentor, Y.K. (1980). Si-nai—geological map (1:500,000). Survey of Israel.
- Aboud, E., Alotaibi, A. M., & Saud, R. (2016). Relationship between Curie isotherm surface and Moho discontinuity in the Arabian shield, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 128, 42-53. [CrossRef]
- Aboulela, H. A., Aboud, E., & Bantan, R. A. (2017). Seismicity and major geologic structures of Tiran and Sanafir islands and their surroundings in the Red Sea. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Hamimi, Z. , El-Barkooky, A., Frías, J. M., Fritz, H., & Abd El-Rahman, Y. (Eds.). (2020). The geology of Egypt (p. 711). Cham: Springer. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Avraham, Z. , & Von Herzen, R. P. (1987). Heat flow and continental breakup: the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba). Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 92(B2), 1407-1416. [CrossRef]
- Hassouneh, M. H. (2003). Interpretation of potential fields by modern data processing and 3-dimensional gravity modeling of the Dead Sea pull-apart basin/Jordan Rift Valley (JRV) (Doctoral dissertation, Universität Würzburg).
- Khalil, S. M. , & McClay, K. R. (2009). Structural control on syn-rift sedimentation, northwestern Red Sea margin, Egypt. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 26(6), 1018-1034. [CrossRef]
- Folkman, Y. (1980). Magnetic and gravity investigations of the Dead Sea rift and adjacent areas in northern Israel.
- Blakely, R. J. (1996). Potential theory in gravity and magnetic applications. Cambridge university press.
- Maus, S. , Barckhausen, U., Berkenbosch, H., Bournas, N., Brozena, J., Childers, V.,... & Caratori Tontini, F. (2009). EMAG2: A 2–arc min resolution Earth Magnetic Anomaly Grid compiled from satellite, airborne, and marine magnetic measurements. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(8). [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, N. , Shirav, M., & Freund, R. (1974). Structure of the Western Margin of the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba) in the Wadi EI Quseib-Wadi Haimur Area, Sinai. Isr. J. Earth Sci, 23, 117-130.
- Abdelhamid, G. , 1990. The Geology of Jabal Um Ishrin Area (Wadi Rum), Map sheet No. 3049 II. Bulletin 14, National Resources Authority, Amman.
- Korhonen, J. V. , Faihead, J. D., Hamoudi, M., Lesur, V., Mandea, M., Maus, S.,... & Thebault, E. (2007). Magnetic anomaly map of the world= Carte des anomalies magnétiques du monde. https://wdmam.org/.
- Smith, J. T. , & Booker, J. R. (1991). Rapid inversion of two-and three-dimensional magnetotelluric data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 96(B3), 3905-3922. [CrossRef]
- Vozoff, K. (1991). The Magnetotelluric Method. In M. N. Nabighian (Ed.), Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics (Vol. 22, pp. 1943-1961). [CrossRef]
- Heinson, G. , Direen, N. and Gill, R.M., 2006. Magnetotelluric evidence for a deep-crustal mineralizing system beneath the Olympic Dam iron oxide copper-gold deposit, southern Australia. Geology, 34, 573–576. [CrossRef]
- El-Waheidi, M. M. , Ghrefat, H. A., Batayneh, A., Nazzal, Y. H., & Zumlot, T. (2016). Integrated application of geoelectrical techniques for structural investigations: case study of Wadi Marsad Graben, Jordan. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Cagniard, L. (1953). Basic theory of the magneto-telluric method of geophysical prospecting. Geophysics, 18(3), 605-635. [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, S. K. , & Hohmann, G. W. (1982). Controlled-source audiomagnetotellurics in geothermal exploration. Geophysics, 47(1), 100-116. [CrossRef]
- Adepelumi, A.A. , Yi, M.J., Kim, J.H. et al. Integration of surface geophysical methods for fracture detection in crystalline bedrocks of southwestern Nigeria. Hydrogeol J 14, 1284–1306 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Mariita, N. O. , & Keller, G. R. (2007). An integrated geophysical study of the northern Kenya rift. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 48(2-3), 80-94. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. , Hu, X., Huo, G., & Zhou, X. (2012). Geophysical exploration for geothermal resources: an application of MT and CSAMT in Jiangxia, Wuhan, China. Journal of Earth Science, 23(5), 757-767. [CrossRef]
- Basaloom, A. (2020, November). 3D Seismic Interpretation in Salt Basins: Analytic Review of Case Studies. In ARMA/DGS/SEG International Geomechanics Symposium (pp. ARMA-IGS). ARMA.
- Jones, C. J. , Robinson, M. J., & Macy, J. P. (2022). Characterization of the Sevier/Toroweap Fault Zone in Kane County, Utah, using controlled-source audio-frequency magnetotelluric (CSAMT) surveys (No. 2022-5071). US Geological Survey. [CrossRef]
- Zonge, K. L. "Introduction to CSAMT." Practical Geophysics II for the Exploration Geologist. Northwest Mining Association Spokane, WA, (1992). 439-523. http://zonge.com/geophysical-methods/electrical-em/csamt (last visited, 14/11/2024).
- Goldstein, M. A. , & Strangway, D. W. (1975). Audio-frequency magnetotellurics with a grounded electric dipole source. Geophysics, 40(4), 669-683. [CrossRef]
- Bai, D., Meju, M. A., & Liao, Z. (2001). Magnetotelluric images of deep crustal structure of the Rehai geothermal field near Tengchong, southern China. Geophysical Journal International, 147(3), 677-687. [CrossRef]
- Routh, P. S. , & Oldenburg, D. W. (1999). Inversion of controlled source audio-frequency magnetotellurics data for a horizontally layered earth. Geophysics, 64(6), 1689-1697. [CrossRef]
- Streich, R. (2016). Controlled-source electromagnetic approaches for hydrocarbon exploration and monitoring on land. Surveys in geophysics, 37, 47-80. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. , & Nie, F. (2024). Advancing Sustainable Geothermal Energy: A Case Study of Controlled Source Audio-Frequency Magnetotellurics Applications in Qihe, Shandong. Sustainability (2071-1050), 16(15). [CrossRef]
- Staelin, D. H. (2011). Electromagnetics and applications (pp. 1-442). Cambridge, MA, USA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- Zonge, K. L. , & Hughes, L. J. (1991). Controlled source audio-frequency magnetotellurics. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, Larry J., and Norman R. Carlson. "Structure mapping at Trap Spring Oilfield, Nevada, using controlled-source magnetotellurics." First Break 5.11 (1987).
- Lajaunie, M. , Sailhac, P., & Malet, J. P. (2018, April). Controlled-Source Audio-frequency MagnetoTelluric methods from the near-to the far-field: theory and applications. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts (p. 13744).
- David Tilley, Exploration using telluric currents – MT and CSAMT (2013). Geology for Investors, last visited 1/12/2024). https://www.geologyforinvestors.com/exploration-using-telluric-currents-mt-and-csamt/.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





