Submitted:
06 December 2024
Posted:
09 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- The goal of this scientific research is to answer the explanation of the phenomenon of quantum leap and quantum entanglement and to add some modifications in the Bohr model.
2. Equations
3. These laws have been modified from the mix Planck laws
-
How quantum entanglement occurs?What happens is that the electron connects to the other electron through space-time, as space-time acts like a quantum tunnel that connects the two electrons. In this way, the electron does not penetrate the speed of light, But in relation to large objects, you see that it has crossed the speed of light.
-
This hypothesis was based on scientific foundations, the most important of which is:
- 1)
- the connection between relativity and quantum mechanics occurs via quantum entanglement and loop gravitational entanglement.
- 2)
- quantum entanglement occurs by the contraction of space-time.
- 3)
- space-time contraction occurs by space-time absorbing energy.
- 4)
- the quantum jump of the electron occurs as a result of the contraction of space-time.
4. Derivation of Equations
5. Method
- This part of the research will explain the spectrum of the hydrogen atom in a new way, as the results presented in these tables from previous research match the results extracted from the equation, and this is consistent with the validity of this equation. Because the new equation is consistent with the photon energy equation. We will discuss that part of the research in the results and discussion.
-
Table 5 shows the measurement results tested.[3] (Nanni, 2015)
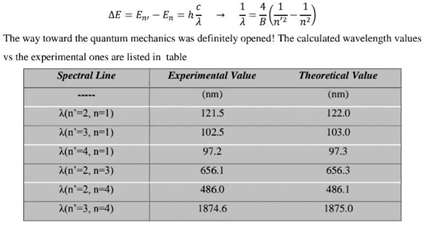
- Table 5 it represents the theoretical and experimental value of the hydrogen atom. Using the photon energy law mentioned above, this table.
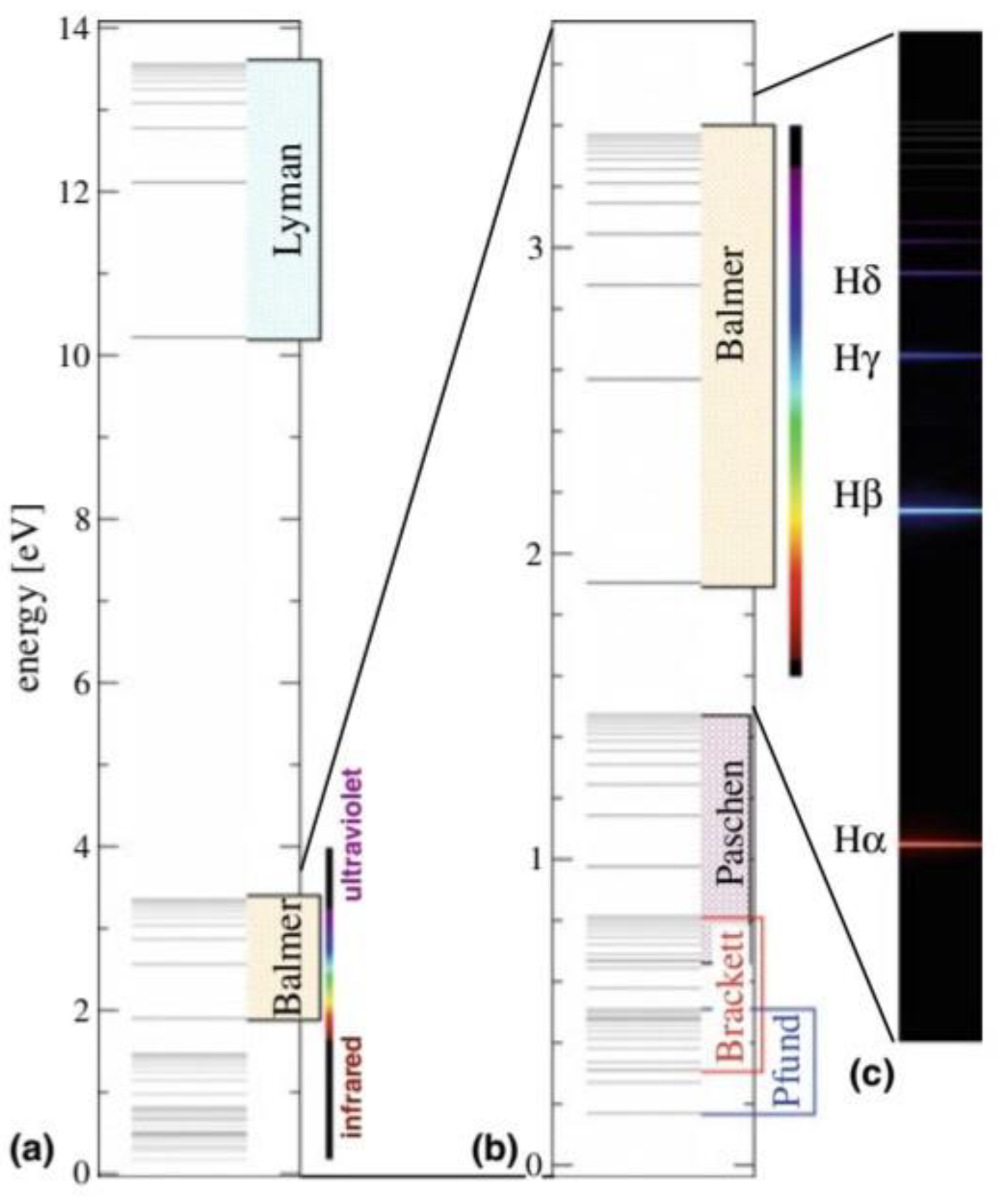
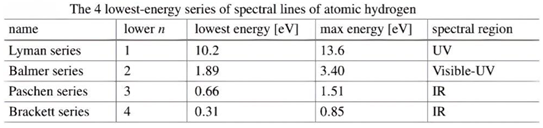
- Table 6 shows the measurement results of one of the previous researches related to the spectrum of the hydrogen atom in chapter 2 atoms.[5] (Manini, 2020)
- This shape is a result of the fact that the electron, after a quantum leap occurred as a result of an interference between the orbital that it occupies and the energy level above it, was in an unstable state. Therefore, when the highest level of energy returns to its position, it releases energy in the form of spectral lines. These lines are determined according to the amount of energy, as shown in the picture.
6. Results Obtained
- Example of a hydrogen atom in the Balmer series.
- Example of a hydrogen atom in the Balmer series.
- Example of a hydrogen atom in the Balmer series.
| Theoretical value (My work) | Experimental value | ||||
| Spectral Line | Energy | λ | λ | ||
| λ(n’=2, n=1) | 10.204269824 | eV | 121.50227268 | nm | 121.5 nm |
| λ(n’=3, n=1) | 12.093949421 | eV | 102.51754257 | nm | 102.5 nm |
| λ(n’=4, n=1) | 12.75533728 | eV | 97.20181814 | nm | 97.20 nm |
| λ(n’=3, n=2) | 1.8896795971 | eV | 656.11227245 | nm | 656.1 nm |
| λ(n’=4, n=2) | 2.5510674561 | eV | 486.0090907 | nm | 486.0 nm |
| λ(n’=4, n=3) | 0.66138785898 eV | 1874.6064927 | nm | 1874.6 nm | |
- These are the results of a relationship between energy and wavelength. The observed results show that whenever the energy increases, the wavelength decreases, as shown by this equation in the hydrogen atom.
7. Conclusions
References
- Svidzinsky, A. Scully, M. Bohr's molecular model, a century later. Physics T. 2014, 67, 33-39. [CrossRef]
- Udema, I. I. Renaissance of Bohr's model via derived alternative equation. American J. Mod. Phys 2017, 6, 23-31. [CrossRef]
- Nanni, L. The hydrogen atom: A review on the birth of modern quantum mechanics. Physics 2015. [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R. B. Principles of Inorganic Chemistry. Springer N., 2024; pp. 1--18. [CrossRef]
- Manini, N. Introduction to the physics of matter: basic atomic, molecular, and solid-state physics. Springer N., 2020; pp. 11--16. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





