Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus type 2 is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases globally, with significant impacts on the quality of life of affected individuals. [
1] Effective management of this condition requires a multidimensional approach, addressing biological, psychological, social, and spiritual aspects. [
2] One of the primary challenges in managing type 2 diabetes is ensuring patient adherence to treatment regimens and healthy lifestyle changes, which are often influenced by family support. [
3] Family-centered care has become a crucial component in managing type 2 diabetes. [
4]
The family-centered nursing approach is grounded in the philosophy that family is integral to a patient’s health and well-being. [
5] This perspective highlights the interconnectedness between patients and their family systems, emphasizing the need to consider familial dynamics, support structures, and cultural values in delivering holistic care. [
6] In the context of type 2 diabetes, involving families in care planning and interventions can enhance patients’ motivation, adherence, and long-term outcomes. [
7]
Despite the increasing recognition of family-centered care in chronic disease management, its application in type 2 diabetes care remains underexplored. [
8] Existing studies suggest incorporating family into nursing care can significantly improve patients’ glycemic control and psychological well-being. [
9] However, there needs to be a more comprehensive synthesis of evidence to substantiate the effectiveness and challenges of this approach, highlighting the need for systematic exploration and analysis. [
10]
A systematic literature review and meta-analysis provide an opportunity to bridge this gap by synthesizing evidence from various studies and offering a broader understanding of the philosophy and outcomes of family-centered nursing in type 2 diabetes care. [
11,
12] This method enables the identification of common themes, challenges, and best practices, contributing to the development of evidence-based guidelines for healthcare providers. [
13]
Given the increasing burden of type 2 diabetes and the critical role of the family in patient care, understanding and integrating the philosophy of family-centered nursing in clinical practice is imperative. [
13] By exploring the existing body of literature, this study aims to provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of this approach, paving the way for more holistic and patient-centered diabetes care strategies.
Materials and Methods
While existing research has explored various strategies for managing type 2 diabetes, including pharmacological and lifestyle interventions, there remains a significant gap in understanding the role of family-centered nursing in improving patient outcomes. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to address this gap by evaluating the impact of family-centered nursing on glycemic control, psychological well-being, treatment adherence, and diabetes-related complications. By examining how family involvement enhances self-care behaviors, such as diet adherence, physical activity, and medication compliance, compared to standard nursing approaches, this study seeks to elucidate the mechanisms and cultural factors that influence the success of such interventions. Additionally, it will assess the broader implications of family-centered care in improving patients’ quality of life and reducing complications through holistic, culturally sensitive approaches. By synthesizing available evidence, this research aspires to provide valuable insights into the philosophy of family-centered nursing, paving the way for more patient-centered strategies in managing chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes.
This study follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [
14] to enhance report quality for Systematic Literature Reviews (SLR). [
15,
16] We created keyword development, conducted a database search and cleaned and sorted data. This study used the Participants, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, and Study Design (PICOS) framework to formulate the research questions (
Table 1).
Keyword Development
Initial keyword development for this study focused on constructing comprehensive search terms related to family-centered nursing, type 2 diabetes, and patient outcomes. The keywords include terms such as “family-centered nursing AND type 2 diabetes AND glycemic control,” “family involvement AND diabetes management AND quality of life,” and “holistic nursing AND diabetes complications AND adherence.” This systematic approach ensures a robust search strategy to identify relevant studies.
After compiling the search keywords and obtaining relevant articles using tools like PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, the next step involves meticulously screening and analyzing the gathered literature. [
17] This process focuses on evaluating the effects of family-centered nursing on glycemic control, treatment adherence, self-care behaviors, psychological well-being, quality of life, and the incidence of diabetes-related complications. By systematically synthesizing evidence and comparing outcomes with standard nursing practices, this study aims to provide valuable insights into the efficacy of family-centered nursing and its potential to transform chronic disease management, particularly in type 2 diabetes.
Database Search
We searched databases such as PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Web of Science to collect literature relevant to the philosophy and effects of family-centered nursing in managing type 2 diabetes. Articles published between 2020 and 2024 were included to capture recent advancements and foundational studies. Initially, 4,504 articles were identified in English and other languages. The reduction and extraction process involved removing duplicate articles, assessing topic relevance, and applying predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Subsequently, the collected articles underwent a rigorous screening process to ensure the inclusion of only high-quality studies directly addressing the impact of family-centered nursing on glycemic control, treatment adherence, psychological well-being, and diabetes-related complications. This meticulous approach included evaluating experimental designs, study populations, and outcome measures such as HbA1c levels, quality of life, and self-care behaviors. The final selection of studies was systematically reviewed to identify patterns, trends, and key findings, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness and clinical implications of family-centered nursing in managing type 2 diabetes.
Data Cleaning and Sorting
The data obtained for this study was based on related keywords through a rigorous data cleaning and sorting process. Several stages were carried out, including removing duplicate articles, filtering articles based on abstracts and titles to determine their relevance, and applying inclusion and exclusion criteria specific to the topic. Articles that indirectly addressed the role of family-centered nursing in managing type 2 diabetes were excluded to maintain the study’s precision.
After the initial data cleaning and sorting stages, the remaining articles were scrutinized to ensure they met the specific inclusion criteria aligned with the study’s objectives. [
18] This process involved meticulously reviewing abstracts, titles, and keywords to confirm their relevance. Articles that did not directly address outcomes such as glycemic control, treatment adherence, self-care behaviors, psychological well-being, or diabetes-related complications were excluded. The refined dataset consisted of a focused collection of studies providing valuable insights into the philosophy and practical implications of family-centered nursing for type 2 diabetes management.
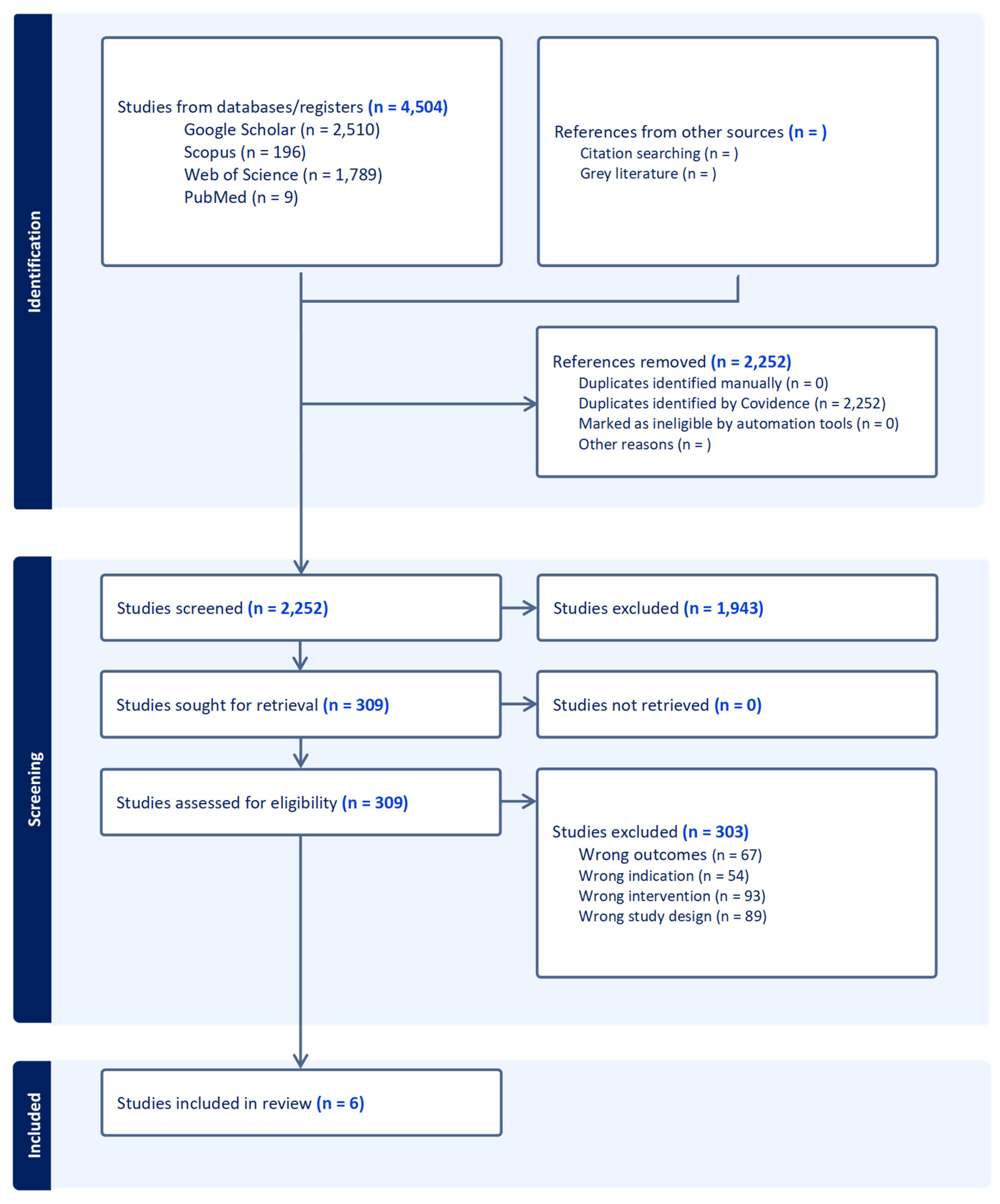
Citation data from 4,504 papers, downloaded in RIS format, were initially screened to remove duplicates, resulting in 2,252 articles. A systematic literature review was conducted to identify, assess, and interpret relevant research findings. After reviewing titles, abstracts, and keywords, 1,943 irrelevant papers and those with unclear methodologies or unsuitable theoretical frameworks were excluded, leaving six articles for in-depth analysis.
The six selected articles underwent comprehensive review and data extraction to uncover insights into the effects of family-centered nursing on managing type 2 diabetes. Key themes, patterns, and trends in the literature were identified, focusing on interventions, mechanisms of action, clinical outcomes, and cultural considerations. The findings offer a deeper understanding of the benefits of family-centered nursing, particularly its role in enhancing patient outcomes, adherence, and quality of life.
The results of this systematic review contribute to advancing the knowledge base regarding family-centered nursing as a transformative approach to managing type 2 diabetes. This research lays a robust foundation for developing evidence-based interventions and future studies by emphasizing its impact on patient and family dynamics. The detailed screening and analysis process, summarized in
Figure 1, ensures the inclusion of high-quality studies, reinforcing the validity and applicability of the findings in clinical practice.
Research Questions
This systematic literature review (SLR) and meta-analysis is conducted to answer the following questions:
- (1)
What is the impact of family-centered nursing on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes compared to standard nursing approaches?
- (2)
How does family-centered nursing influence treatment adherence, self-care behaviors, and psychological well-being in individuals with type 2 diabetes?
- (3)
What are the broader implications of family-centered nursing on reducing diabetes-related complications, enhancing quality of life, and supporting culturally sensitive care?
Results and Discussion
Results
This section presents the data analysis results in three sub-sections: classification by publication year, characteristics, and review of included studies.
Classification Based on the Publication Year
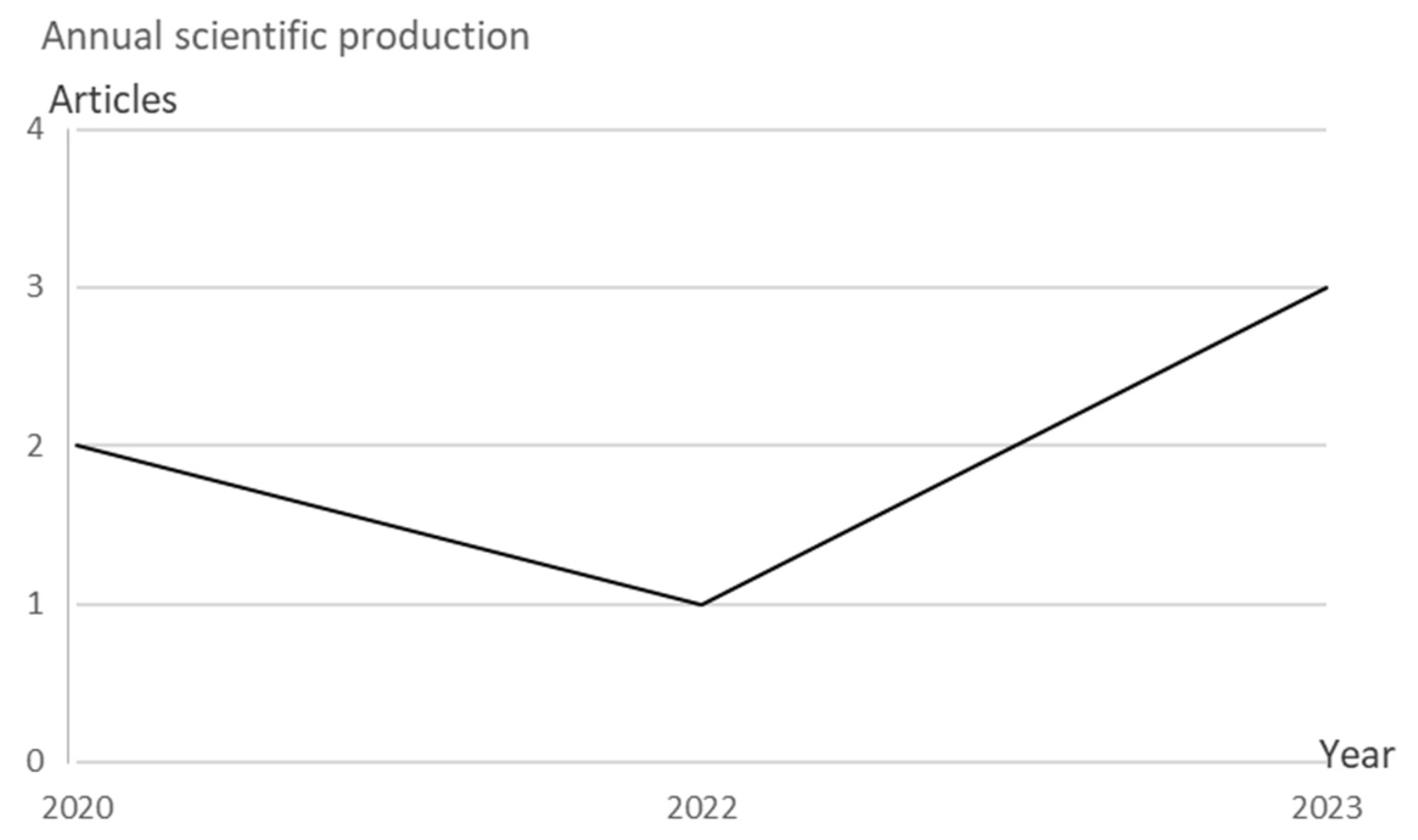
Figure 2.
Total publications from 2020-2024.
Figure 2.
Total publications from 2020-2024.
The data from the studies conducted on family-centered nursing in the care of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) patients indicate a growing recognition of the vital role families play in managing diabetes and its complications. The 2020 research focused on creating a nursing care plan for T2DM patients based on Faye Glenn Abdellah’s model, emphasizing individual care planning and assessment. It highlighted how a personalized approach, rooted in Abdellah’s theory, can enhance care outcomes, helping to address patients’ unique needs better. Another study from 2020 assessed the ability of families to care for T2DM patients in Tasikmalaya, identifying a significant need for health education to improve caregiving practices, particularly in recognizing health problems and making treatment decisions. [
19,
20]
In 2022, further exploration into the role of family support in diabetes care took center stage, with a study on the impact of family involvement on improving self-care agency among T2DM patients. This qualitative study underscored families’ diverse coping strategies, which can either enhance or hinder patient self-care practices. The findings highlighted that family understanding and participation in diabetes management lead to better self-care behaviors, improving the patient’s overall health. [
21] The year 2023 saw an interesting development in the application of family-centered care (FCC) in critical settings, such as intensive care units (ICU), where FCC interventions in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) led to reduced family anxiety and higher satisfaction with care, illustrating the psychological benefits of family involvement in acute diabetes management.
The most recent study from 2023 explored the impact of family-centered interventions (FCIS) on key indicators of diabetes management, confirming that such interventions led to significant improvements in clinical indicators like weight, HbA1c, and physical activity. This research reinforced the effectiveness of FCIS in managing T2DM compared to traditional patient-centered approaches, emphasizing the importance of family engagement in diabetes care. Together, these studies highlight the transformative potential of family-centered nursing in managing diabetes, offering valuable insights into both clinical outcomes and the emotional well-being of patients and their families. [
4,
5,
22]
Future research should continue to build on these findings by exploring the long-term effects of family-centered interventions, developing targeted health education programs for families, and further evaluating the psychological benefits of family involvement in chronic disease management. The integration of family-centered nursing practices into standard diabetes care models has the potential to improve both the quality of life and clinical outcomes for patients with T2DM.
Characteristics of Included Studies
Table 2 shows the characteristics of the included studies. The first study by Ernawati, Podo Yuwono, and Devie Tika Sari aimed to examine family attitudes and motivation in caring for patients with Diabetes Mellitus (DM) at Adimulyo Community Health Center. The research utilized a descriptive quantitative survey approach with family members of DM patients. The results showed that 73.8% of family members displayed positive attitudes, and 65% demonstrated strong motivation toward caring for their relatives with DM. The study concluded that positive attitudes and strong motivation are key factors in family care for DM patients, highlighting the importance of family support in managing diabetes. [
22]
The second study by Hakim Tobroni HR and Sonti Kogoya aimed to describe the role of family in improving self-care agency for type 2 diabetes patients at Amelia Pare Hospital. Using a qualitative phenomenological study, the research revealed that families of diabetes patients had diverse experiences and coping strategies, resulting in different understandings of self-care. The study concluded that family understanding and involvement are crucial for enhancing self-care agency, emphasizing that increased family support can lead to better self-care practices and improved health outcomes for diabetes patients. [
21]
In the third study, Bayu Brahmantia, Miftahul Falah, Lilis Lismayanti, and Vina Erviana assessed family ability in caring for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients, involving 31 family members of patients. The research used a descriptive quantitative approach and found that while the majority of families were effective in recognizing problems (51.6%), making positive decisions (61.3%), and managing treatment (80.6%), they had difficulty with environmental modifications (58.1%). The study concluded that family involvement is crucial for diabetes management, and health education is essential to improve the caregiving environment for diabetes patients. [
20]
The fourth study by Mokhtari et al. aimed to determine the effect of family-centered intervention (FCIS) on diabetes management indicators in 64 type 2 diabetes patients. The study found significant weight, HbA1c, FBS, energy intake, and physical activity improvements in the intervention group. The research concluded that FCIS is more effective than patient-centered care in managing type 2 diabetes, suggesting that family involvement should be prioritized in diabetes education programs. [
5]
The fifth study by Nurul Darmawulan and Etika Emaliyawati described family-centered care (FCC) for a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) in an ICU setting. The study found that FCC interventions helped reduce family anxiety and improved satisfaction with care. The conclusion emphasized that the FCC decreases anxiety in family members and enhances their satisfaction with healthcare services. It highlights the need for FCC programs in ICUs to involve all stakeholders effectively. [
4]
Finally, the study of Parisa Mehraeen et al. aimed to assess a 34-year-old female patient’s problems and develop a care plan based on Abdellah’s nursing model. The study used the nursing process and found that the intervention improved the patient’s awareness and care outcomes. The conclusion highlighted that Abdellah’s theory effectively identified nursing problems and enhanced care quality, suggesting that future studies with larger populations and longer evaluation periods are needed to assess its effectiveness further. [
19]
Philosophy of Family-Centered Nursing in Patient Diabetes Type 2
The philosophy of family-centered nursing in managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is highlighted through various studies emphasizing the pivotal role of family involvement in improving patient outcomes. Ernawati, Podo Yuwono, and Devie Tika Sari’s study in Indonesia showed that family members’ positive attitudes and strong motivation significantly contribute to better diabetes care, demonstrating the importance of family support in managing T2DM. [
22] Similarly, Hakim Tobroni HR and Sonti Kogoya emphasized families’ diverse experiences and coping strategies, which directly affect the self-care agency of diabetes patients. [
21] Their findings underline that family understanding and active involvement in care can improve self-care behaviors and health outcomes, making family-centered care essential in managing T2DM.
Additionally, several studies further reinforced the significance of family support in diabetes management. Bayu Brahmantia et al. demonstrated that family members’ ability to recognize problems, make decisions, and manage treatments was crucial for diabetes care, although environmental modifications remained challenging. [
20] They emphasized the necessity of health education to improve the caregiving environment. In a randomized controlled trial, Mokhtari et al. found that family-centered interventions (FCIS) resulted in significant improvements in clinical indicators, such as weight, HbA1c, and physical activity, suggesting that family involvement is more effective than traditional patient-centered care in managing T2DM. [
5] These findings support the notion that involving families in diabetes care can yield better clinical outcomes.
Moreover, family-centered nursing extends beyond diabetes management to addressing care’s emotional and psychological aspects. In cases involving acute complications like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), studies like those by Nurul Darmawulan and Etika Emaliyawati demonstrated that family-centered care interventions helped reduce anxiety and improve family satisfaction with care. [
4] These outcomes highlight the emotional benefits of family involvement, not only for the patient but also for their loved ones. By reducing anxiety and fostering a supportive care environment, family-centered nursing enhances overall patient care, emphasizing its broader role in managing diabetes and improving the quality of life for patients and their families.
Discussion
This section is organized into three sub-sections of discussion: the impact of family-centered nursing on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes compared to standard nursing approaches, an analysis of how family-centered nursing influences treatment adherence, self-care behaviors, and psychological well-being, and an evaluation of the broader implications of family-centered care on reducing diabetes-related complications, improving quality of life, and promoting culturally sensitive care. Each sub-section aims to comprehensively understand the potential benefits and challenges of integrating family-centered nursing into diabetes management.
The Impact of Family-Centered Nursing on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Compared to Standard Nursing Approaches
Family-centered nursing has gained recognition as an essential approach to managing chronic conditions, including type 2 diabetes. [
23] It emphasizes the inclusion of family members in the care process, acknowledging the role of family dynamics in influencing patient behavior and outcomes. [
24] This approach is particularly relevant for patients with type 2 diabetes, where lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring are critical components of effective management. [
25,
26] Recent studies suggest that family-centered nursing can significantly improve glycemic control, as it fosters a supportive environment that enhances patient motivation and adherence to treatment plans. [
13]
Compared to standard nursing approaches, which typically focus solely on the patient, family-centered care involves educating and empowering family members to participate actively in diabetes management. [
27] Family members can assist with monitoring blood glucose levels, administering insulin, ensuring proper diet and exercise, and providing emotional support. [
28] This holistic approach encourages patients to view their health management as a shared responsibility, often resulting in better adherence to medication regimens and improved lifestyle choices. [
29] Studies have shown that patients with family involvement tend to exhibit better self-care behaviors, leading to more consistent glycemic control. [
23]
Additionally, family-centered nursing allows for personalized interventions that consider each family unit’s cultural, emotional, and practical aspects. [
30] For example, family members can help identify and address barriers to treatment, such as difficulties with transportation to medical appointments or challenges in understanding complex medical instructions. [
31] This tailored approach helps ensure that patients receive the support they need in a way sensitive to their circumstances, potentially leading to more effective glycemic control than one-size-fits-all standard nursing care. [
32]
In contrast, standard nursing care often lacks a focus on the family unit, primarily addressing the patient’s immediate medical needs. [
33] While these approaches are essential for managing type 2 diabetes, they may overlook the social and emotional factors that play a significant role in a patient’s ability to manage their condition. [
34] The absence of family support can lead to gaps in self-management, non-adherence to prescribed treatments, and suboptimal outcomes. [
35] Research has highlighted that patients who do not have family involvement may experience greater difficulty in managing the emotional burdens of the disease, resulting in poorer glycemic control over time. [
21]
Overall, integrating family-centered nursing into diabetes care can significantly enhance glycemic control. By recognizing the role of family in the patient’s health journey, this approach creates a more comprehensive and supportive care environment. The positive impact of family-centered nursing on glycemic control suggests that this model should be considered a key strategy for improving long-term health outcomes for patients with type 2 diabetes. Future studies are needed to explore further the specific mechanisms through which family-centered nursing influences glycemic control and to assess its broader applicability across diverse patient populations.
Family-Centered Nursing Influence Treatment Adherence, Self-Care Behaviors, and Psychological Well-Being in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Family-centered nursing has been increasingly recognized as a key factor in improving treatment adherence, self-care behaviors, and psychological well-being in patients with type 2 diabetes. [
36] One of the primary ways this approach influences treatment adherence is by involving family members in the decision-making and support processes. Family members can help patients remember medication schedules, provide reminders for blood glucose monitoring, and assist with meal planning and preparation. [
37] This active involvement ensures that patients are more likely to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen, as they are supported by a network that reinforces positive behaviors and encourages consistency. [
38]
In addition to enhancing treatment adherence, family-centered nursing plays a significant role in improving self-care behaviors. [
39] Diabetes management requires a combination of lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress, all of which can be challenging for patients to maintain independently. [
40] When family members are actively involved, they can provide emotional support, help with practical tasks, and create a positive environment that encourages the patient to make healthier choices. [
41] Studies have shown that when family members are educated about diabetes and its management, they can better assist their loved ones in adopting healthier behaviors, resulting in improved self-care practices such as regular exercise and better dietary choices. [
42]
Psychological well-being is another critical aspect of diabetes management that family-centered nursing directly addresses. Type 2 diabetes often comes with emotional challenges, including anxiety about the future, stress related to disease management, and feelings of isolation. Family members can offer emotional support by providing encouragement, empathy, and reassurance. A strong family support system can help alleviate the mental and emotional strain associated with managing a chronic condition, contributing to a more positive outlook and a reduction in psychological distress. By fostering an emotionally supportive environment, family-centered nursing helps patients better cope with the psychological challenges of living with diabetes. [
43]
Research has demonstrated that patients with strong family involvement in their care report higher satisfaction with their treatment and experience greater improvements in mental health. Family-centered care can reduce feelings of depression, anxiety, and frustration, which are common in individuals with chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes. By improving psychological well-being, this approach not only enhances the quality of life for patients but also has the potential to improve overall health outcomes. Psychological well-being is strongly linked to better adherence to treatment regimens and self-care behaviors, making it a crucial component of successful diabetes management. [
32]
In conclusion, family-centered nursing plays a pivotal role in influencing treatment adherence, self-care behaviors, and psychological well-being in individuals with type 2 diabetes. By actively involving family members in care, this approach creates a supportive, collaborative environment that encourages patients to take responsibility for their health while receiving the emotional and practical support they need. This holistic approach has been shown to improve patients’ physical and mental health with type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of incorporating family dynamics into diabetes care. Future research should continue to explore how family-centered nursing can be optimized to enhance these outcomes further.
Conclusions
Based on the reviewed literature, family-centered nursing is a transformative approach to managing type 2 diabetes, offering significant benefits in treatment adherence, self-care behaviors, and psychological well-being. By involving family members in the care process, this model ensures that patients receive continuous support, motivation, and education, which enhances their ability to manage their condition effectively. The active participation of family members helps improve glycemic control, prevent diabetes-related complications, and foster better self-management practices. Additionally, the emotional and psychological support provided by families contributes to a more positive outlook, reducing stress and anxiety often associated with living with a chronic condition.
Furthermore, family-centered nursing holds broader implications for enhancing the overall quality of life for patients with type 2 diabetes and supporting culturally sensitive care. This approach reduces complications and strengthens family dynamics by fostering open communication and shared responsibility for care. By addressing the cultural and socioeconomic factors that impact diabetes management, family-centered nursing ensures that care is personalized and relevant to the patient’s unique context. As healthcare systems evolve toward patient-centered care, integrating family-centered nursing into diabetes care can significantly improve patient outcomes, making it a crucial strategy for managing type 2 diabetes in diverse patient populations.
Funding
This work was supported by.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support from.
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
References
- He, K.J.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Gong, G.; Liu, X.; Guan, H. Global burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2044: a systematic analysis across SDI levels for the global burden of disease study 2021. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2024, 15, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Trisnadewi, N.W.; Suniyadewi, N.W. Family Support with Diabetes Management in Type 2 DM: Correlation Study. Nurs. Heal. Sci. J. 2022, 2, 345–348. [CrossRef]
- Safaruddin, S.; Permatasari, H. Dukungan Keluarga Dengan Manajemen Diri Diabetes Pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2: Tinjauan Sistematik. J. Kesehat. Komunitas 2022, 8, 195–204. [CrossRef]
- Darmawulan, N.; Emaliyawati, E.; Lin, C.L. Family-centered care for a patient with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in the intensive care unit: A case report. J. Palembang Nurs. Stud. 2023, 293–301. [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, Z.; Mokhtari, S.; Afrasiabifar, A.; Hosseini, N. Alloimmunization in thalassemia patients: New insight for healthcare. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
- Matrook, K.A.; Cowman, S.; Pertl, M.; Whitford, D. Nurse-led family-based approach in primary health care for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a qualitative study. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-being 2024, 19. [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, F.; Shamsaei, F. The Effect of Family-centered Care on Management of Blood Glucose Levels in Adolescents with Diabetes. Endocr. Abstr. 2016, 3, 177–186. [CrossRef]
- Pamungkas, R.A.; Chamroonsawasdi, K.; Vatanasomboon, P. A systematic review: Family support integrated with diabetes self-management among uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus patients. Behav. Sci. (Basel). 2017, 7, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Chesla, C.A.; Chun, K.M.; Kwan, C.M.L. Cultural and family challenges to managing type 2 diabetes in immigrant Chinese Americans. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1812–1816. [CrossRef]
- Sinawang, G.W.; Kusnanto, K.; Pratiwi, I.N. Systematic Review of Family Members in Improving the Quality of Life of People with T2DM. J. Ners 2020, 15, 107–112. [CrossRef]
- Ee, C.C.; Armour, M.; Piya, M.K.; McMorrow, R.; Al-Kanini, I.; Sabag, A. Mindfulness-based interventions for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Nadatien, I.; Puspita, U.N.; Kartini, Y.; Setiyowati, E.; Hidayah, N. Does Education Influence Self Care Management in Diabetes Mellitus Patients? : Systematic Review. J. Appl. Nurs. Heal. 2024, 6, 102–112. [CrossRef]
- Pramita, R.; Nasution, S.S.; Marlindawani, J. Effect of family empowerment on self care of patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 224–233. [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Antes, G.; Atkins, D.; Barbour, V.; Barrowman, N.; Berlin, J.A.; Clark, J.; et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6. [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, n71. [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, N.M.; Paraoan, L.; Khaliddin, N.; Kamalden, T.A. Thymoquinone in Ocular Neurodegeneration: Modulation of Pathological Mechanisms via Multiple Pathways. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Rezac, S.J.; Salkind, N.J.; McTavish, D.; Loether, H. Exploring Research. Teach. Sociol. 2001, 29, 257. [CrossRef]
- Parisa Mehraeen; Parivash Nazarpour; Atefeh Ghanbari Designing a Nursing Care Plan Based on Faye Glenn Abdellah Model in Patients with Diabetes Type 2: A Case Study. Int. J. Caring Sci. 2020, 13, 2250–2262.
- Brahmantia, B.; Falah, M.; Lismayanti, L.; Erviana, V. Family’s Ability to Take Care The Patient of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Tasikmalaya. Media Keperawatan Indones. 2020, 3, 150. [CrossRef]
- Hakim tobroni HR; Kogoya, S. Peran Keluarga dalam Meningkatkan Self Care Agency Pada Klien DM Tipe II. Arter. J. Ilmu Kesehat. 2022, 3, 37–44. [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, P.; Tika Sari, D.; Ilmu Kesehatan, F.; Muhammadiyah Gombong, U. Sikap dan Motivasi Keluarga dalam Perawatan Penderita Diabetes Melitus di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Adimulyo. Devie Tika Sari J. Holistics Heal. Sci. 2023, 5, 349–356.
- Maimuna, S. Family-centered interventions for children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: an integrative review. Child Heal. Nurs. Res. 2023, 29, 7–23. [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, A. Family Support and Diabetes Self-Management Program for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review. Healthc. Nurs. J. 2022, 4, 278–290. [CrossRef]
- Mphasha, M.H.; Mothiba, T.M.; Skaal, L. Family support in the management of diabetes patients’ perspectives from Limpopo province in South Africa. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Baig, A.A.; Benitez, A.; Quinn, M.T.; Burnet, D.L. Baig A, Benitez A, Quinn M. Family interventions to improve diabetes outcomes for adults. Ann N Y Acad Sci. Author manuscript [revista en Internet] 2015 [acceso 13 de mayo de 2022]; 1353(1): 89-112. 2016, 1353, 89–112. [CrossRef]
- Hendrawati, S.; Nurhidayah, I.; Adistie, F. Kebutuhan perawatan berpusat keluarga dalam manajemen diabetes pada anak dengan diabetes melitus. J. Keperawatan Muhammadiyah 2019, 4, 302–308. [CrossRef]
- Maimuna, S. MODEL FAMILY CENTERED CARE IN CHILDREN WITH DIABETES MELITUS : A PHILOSOPHICAL PERSPECTIVE. Doctoral Student of Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Airlangga (2022).
- Damayanti, S.; N, N.; Kurniawan, T. Dukungan Keluarga pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 dalam Menjalankan Self-Management Diabetes. J. Keperawatan Padjadjaran 2014, v2, 43–50. [CrossRef]
- Yuliana, S.; Junaidin Efektifitas Family Based Diabetes Self-Management Education terhadap Self-Care dan Kualitas Hidup Pasien Diabetes Mellitus. J. Keperawatan Jiwa 2021, 9, 879–886.
- Husada, I.; Ilmiah, J.; Juli, V.N. PENDERITA DIABETES MELLITUS DENGAN KETOASIDOSIS DIABETIKUM DI FAMILY BASED EDUCATION ON THE FIRST TREATMENT FOR DIABETES MELLITUS PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC CETOASIDOSIS IN THE GONDANGREJO Pendahuluan Salah satu tantangan terbesar dalam dunia adalah penyakit . 2024, 12, 342–352. [CrossRef]
- Sari, C.W.M.; Haroen, H.; Nursiswati, N. Pengaruh Program Edukasi Perawatan Kaki Berbasis Keluarga terhadap Perilaku Perawatan Kaki pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2. J. Keperawatan Padjadjaran 2017, 4. [CrossRef]
- Rahmi, H.; Malini, H.; Huriani, E. Peran Dukungan Keluarga Dalam Menurunkan Diabetes Distress Pada Pasien Diabetes Mellitus Tipe II. J. Kesehat. Andalas 2020, 8, 127–133. [CrossRef]
- Arini, H.N.; Anggorowati, A.; Pujiastuti, R.S.E. Dukungan keluarga pada lansia dengan Diabetes Melitus Tipe II: Literature review. NURSCOPE J. Penelit. dan Pemikir. Ilm. Keperawatan 2022, 7, 172. [CrossRef]
- Marlinda, N.W.Y.; Nuryanto, I.K.; Noriani, N.K. Hubungan Dukungan Keluarga Dengan Perawatan Diri (Self Care Activity) Pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2. J. Ris. Kesehat. Nas. 2019, 3, 82–86. [CrossRef]
- Olagbemide, O.J.; Omosanya, O.E.; Ayodapo, A.O.; Agboola, S.M.; Adeagbo, A.O.; Olukokun, T.A. Family support and medication adherence among adult type 2 diabetes: Any meeting point? Ann. Afr. Med. 2021, 20, 282–287. [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.A.; DiMatteo, M.R. Importance of family/social support and impact on adherence to diabetic therapy. Diabetes, Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2013, 6, 421–426. [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, Febtian Cendradevi, B.E.F.T. Penerapan Family Intervention Model Berbasis Pendidikan Kesehatan terhadap Self-Care Pasien Diabetes Mellitus Tipe II. 2023, 6, 388–398.
- Karingga, D.D.; Indah Jayani; Idola Perdana Sulistyoning Suharto; Moh Alimansur; Eva Dwi Ramayanti Pengaruh Dukungan Keluarga dan Sosial Pada Peningkatan Status Kesehatan dan Self-Care Managemen Diabetes Melitus: Tinjauan Sistematis. J. Keperawatan Florence Nightingale 2024, 7, 262–271. [CrossRef]
- Joeliantina, A.; Agil, M.; Qomaruddin, M.B.; Kusnanto; Soedirham, O. Family support for diabetes self-care behavior in t2dm patients who use herbs as a complementary treatment. Medico-Legal Updat. 2019, 19, 238–243. [CrossRef]
- Rahmah, G.N.; Sukartini, T.; Utami, S. “Family is My Diabetes Savior”: A Case Study of Family Support in Reaching Goals of Self Care Adherence in Diabetic Patient. Int. J. Nurs. Heal. Serv. 2023, 6, 88–95. [CrossRef]
- Pramita, R.; Nasution, S.S.; Purba, J.M. INTERVENSI PEMBERDAYAAN BERBASIS KELUARGA TERHADAP PENINGKATAN PERILAKU PERAWATAN DIRI PASIEN DENGAN DIABETES MELLITUS TIPE 2. J. Telenursing 2021, 3, 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Alkhusari; Safitri, S.W.; Alfiyanti, R.D. Pengaruh Home Care Terhadap Tingkat Kemandirian Keluarga Dalam Merawat Penyakit Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2. J. Ilm. Multidisiplin 2022, 179, 179–184. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).