Submitted:
28 November 2024
Posted:
29 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
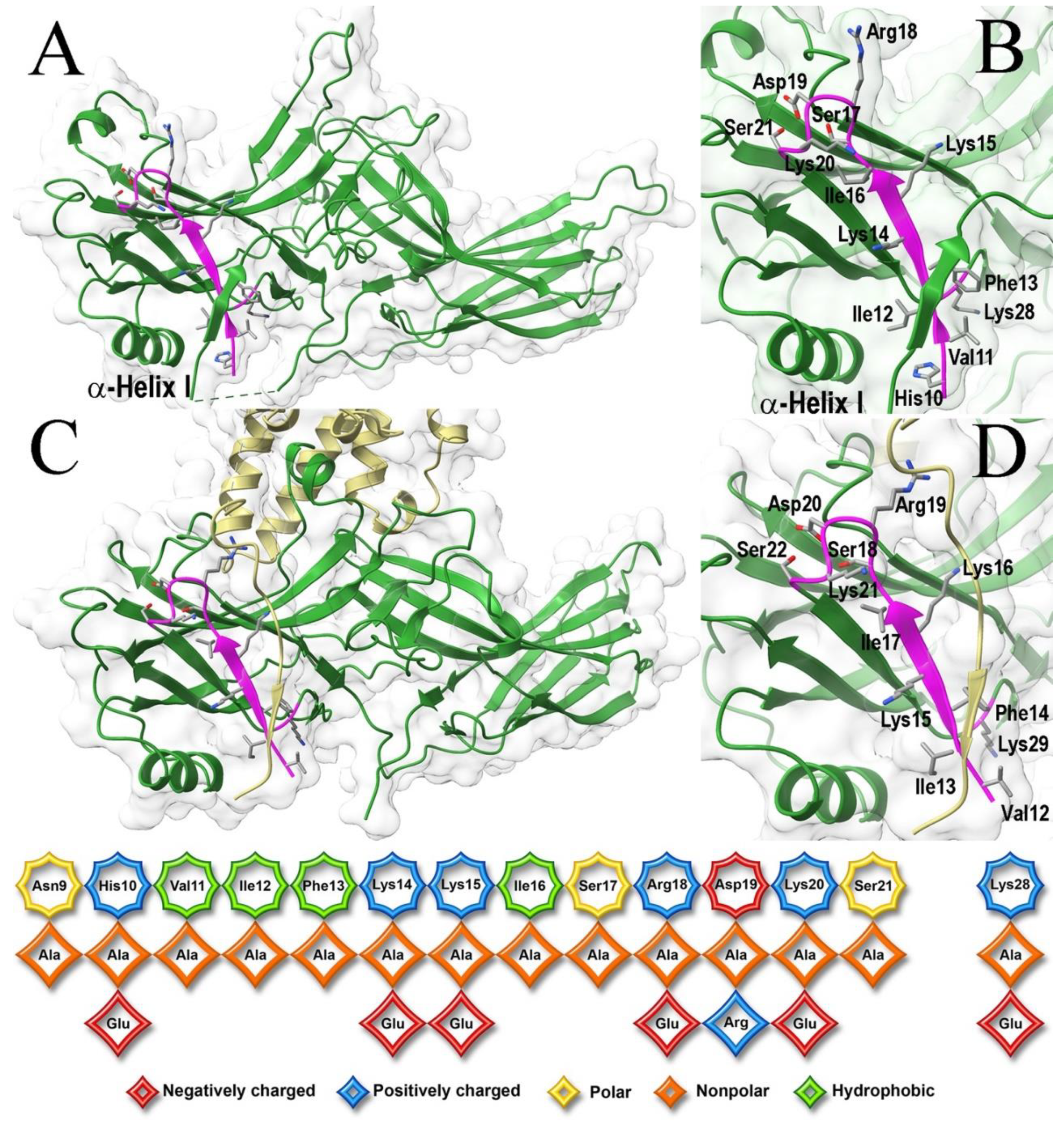
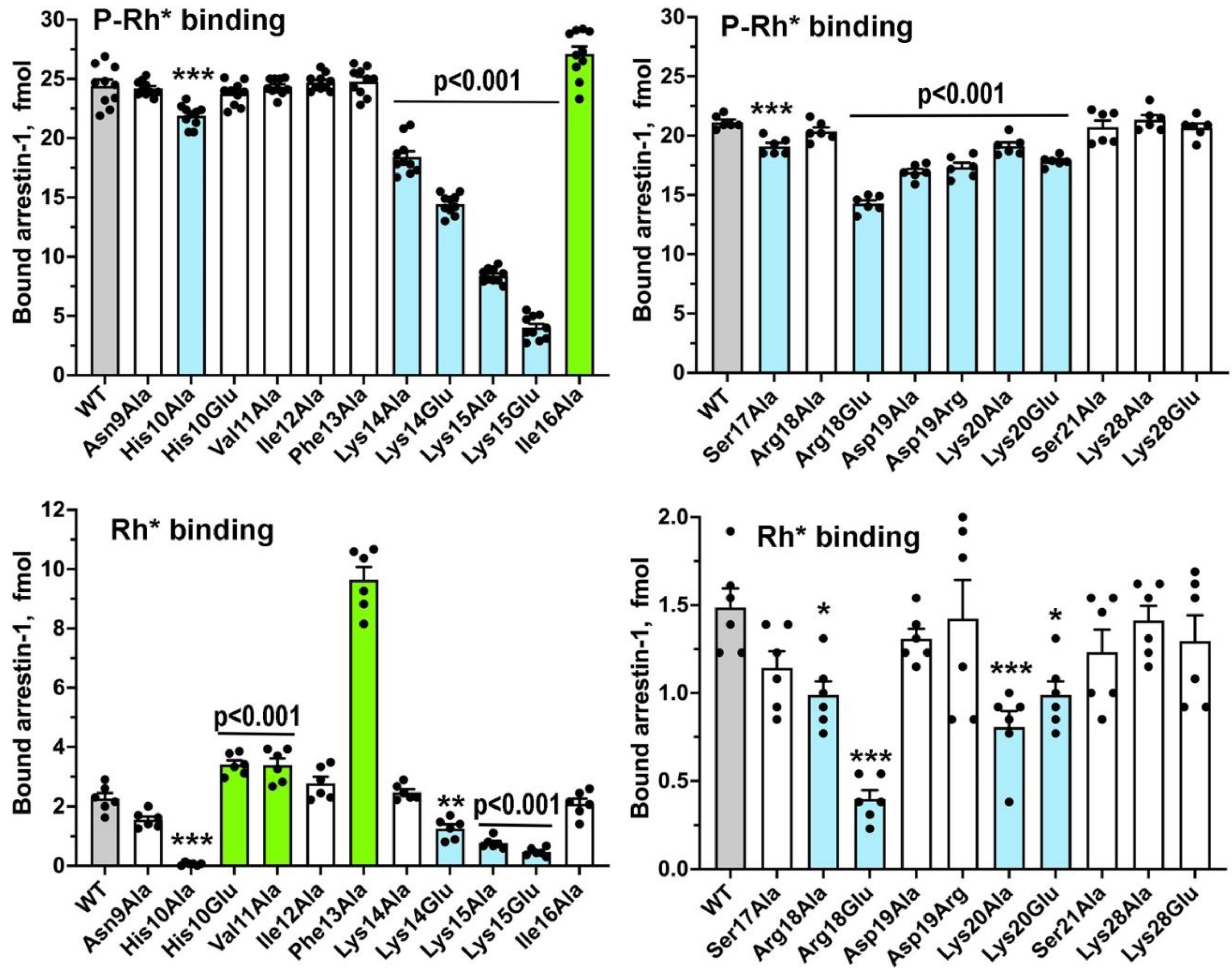
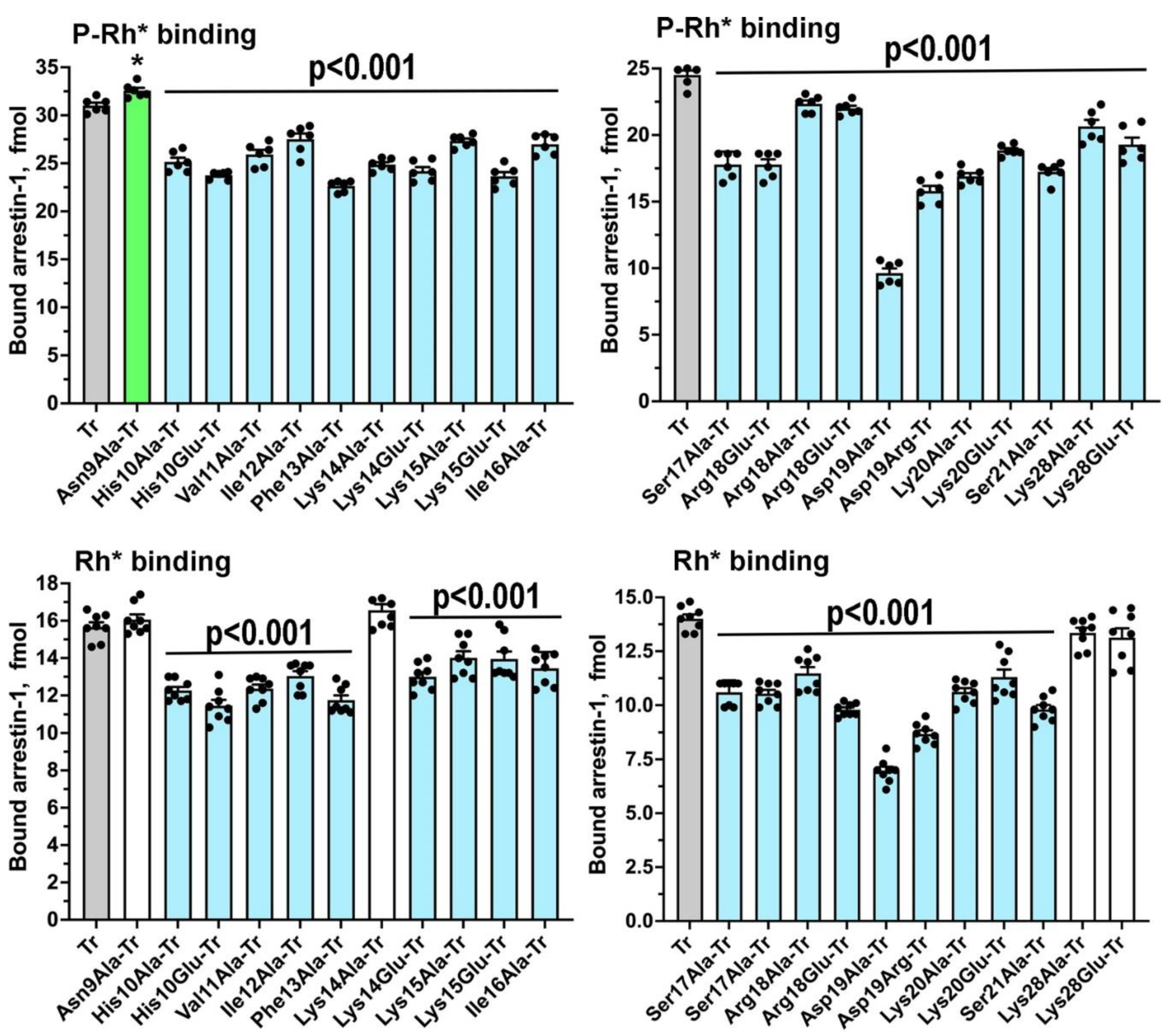
Sequences and three-dimensional structures of the four vertebrate arrestins are very similar, yet in sharp contrast to other subtypes arrestin-1 demonstrates exquisite selectivity for the active phosphorylated form of its cognate receptor, rhodopsin. The N-terminus participates in receptor binding and serves as the anchor of the C-terminus, the release of which facilitates arrestin transition into receptor-binding state. We tested the effects of substitutions of fourteen residues in the N-terminus of arrestin-1 on the binding to phosphorylated and unphosphorylated light-activated rhodopsin of wild type protein and its enhanced mutant with C-terminal deletion that demonstrates higher binding to both functional forms of rhodopsin. Profound effects of mutations identified lysine-15 as the main phosphate sensor and phenylalanine-13 as the key anchor of the C-terminus. These residues are conserved in all arrestin subtypes. Substitutions of five other residues reduced arrestin-1 selectivity, indicating that wild type residues participate in fine-tuning of arrestin- 1 binding to rhodopsin. Differential effects of numerous substitutions in wild type and an enhanced mutant arrestin-1 shows that these two proteins bind rhodopsin differently.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuhn, H. , Light-regulated binding of rhodopsin kinase and other proteins to cattle photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 4389–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, T.; Dietzschold, B.; Craft, C.M.; Wistow, G.; Early, J.J.; Donoso, L.A.; Horwitz, J.; Tao, R. , Primary and secondary structure of bovine retinal S antigen (48 kDa protein). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1987, 84, 6975–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilden, U. , Duration and amplitude of the light-induced cGMP hydrolysis in vertebrate photoreceptors are regulated by multiple phosphorylation of rhodopsin and by arrestin binding. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupnick, J.G.; Gurevich, V.V.; Benovic, J.L. , Mechanism of quenching of phototransduction. Binding competition between arrestin and transducin for phosphorhodopsin. J Biol Chem 1997, 272, 18125–18131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Dodd, R.L.; Makino, C.L.; Simon, M.I.; Baylor, D.A.; Chen, J. , Prolonged photoresponses in transgenic mouse rods lacking arrestin. Nature 1997, 389, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.K.; Burns, M.E.; Spencer, M.; Niemi, G.A.; Chen, J.; Hurley, J.B.; Baylor, D.A.; Simon, M.I. , Abnormal photoresponses and light-induced apoptosis in rods lacking rhodopsin kinase. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 1999, 96, 3718–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, A.; Burns, M.E.; Roca, A.; Lem, J.; Wu, L.W.; Simon, M.I.; Baylor, D.A.; Chen, J. , Rapid and reproducible deactivation of rhodopsin requires multiple phosphorylation sites. Neuron 2000, 28, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, T.D.; Kraft, T.W. , Quantitative modeling of the molecular steps underlying shut-off of rhodopsin activity in rod phototransduction. Mol Vis 2016, 22, 674–696. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, C.L.; Wen, X.H.; Lem, J. , Piecing together the timetable for visual transduction with transgenic animals. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2003, 13, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, G.D.; Rieke, F. , Mechanisms regulating variability of the single photon responses of mammalian rod photoreceptors. Neuron 2002, 35, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado Allina, G.; Fortenbach, C.; Naarendorp, F.; Gross, O.P.; Pugh, E.N. J.; Burns, M.E. , Bright flash response recovery of mammalian rods in vivo is rate limited by RGS9. J Gen Physiol 2017, 149, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.J.; Benovic, J.L.; Codina, J.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. , beta-Arrestin: A protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science 1990, 248, 1547–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.J.; Andexinger, S.; Pitcher, J.; Trukawinski, S.; Codina, J.; Faure, J.P.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. , Receptor-specific desensitization with purified proteins. Kinase dependence and receptor specificity of beta-arrestin and arrestin in the beta 2-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin systems. J Biol Chem 1992, 267, 8558–8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, C.V.; Benovic, J.L. , G-protein-coupled receptors: Turn-ons and turn-offs. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1998, 8, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. , The molecular acrobatics of arrestin activation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004, 25, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylor, D.A.; Lamb, T.D.; Yau, K.W. , Responses of retinal rods to single photons. J Physiol 1979, 288, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, T.M.; Chabre, M.; Stryer, L. , Millisecond activation of transducin in the cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Nature 1984, 311, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, J.F.; Falk, G. , The single-photon signal in rod bipolar cells of the dogfish retina. J Physiol 1980, 300, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.; Hall, S.W.; Wilden, U. , Light-induced binding of 48-kDa protein to photoreceptor membranes is highly enhanced by phosphorylation of rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1984, 176, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Benovic, J.L. , Visual arrestin interaction with rhodopsin: Sequential multisite binding ensures strict selectivity towards light-activated phosphorylated rhodopsin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11628–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V. , Arrestins: A Small Family of Multi-Functional Proteins. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Schubert, C.; Climaco, G.C.; Gurevich, Y.V.; Velez, M.-G.; Gurevich, V.V. , An additional phosphate-binding element in arrestin molecule: Implications for the mechanism of arrestin activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 41049–41057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Zheng, C.; May, M.B.; Karnam, P.C.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. , Lysine in the lariat loop of arrestins does not serve as phosphate sensor. J Neurochem 2021, 156, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, J.A.; Schubert, C.; Gurevich, V.V.; Sigler, P.B. , The 2.8 A crystal structure of visual arrestin: A model for arrestin’s regulation. Cell 1999, 97, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Gurevich, V.V.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Sigler, P.B.; Schubert, C. , Crystal structure of beta-arrestin at 1.9 A: Possible mechanism of receptor binding and membrane translocation. Structure 2001, 9, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, S.K.; Pace, H.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Brenner, C.; Benovic, J.L. , Scaffolding functions of arrestin-2 revealed by crystal structure and mutagenesis. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.B.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Robert, J.; Hanson, S.M.; Raman, D.; Knox, B.E.; Kono, M.; Navarro, J.; Gurevich, V.V. , Crystal Structure of Cone Arrestin at 2.3Å: Evolution of Receptor Specificity. J Mol Biol 2005, 354, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Gimenez, L.E.; Gurevich, V.V.; Spiller, B.W. , Crystal structure of arrestin-3 reveals the basis of the difference in receptor binding between two non-visual arrestins. J Mol Biol 2011, 406, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Ishchenko, A.; Barty, A.; White, T.A.; Yefanov, O.; Han, G.W.; et al. , Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin determined by femtosecond X-ray laser. Nature 2015, 523, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.E.; He, Y.; de Waal, P.W.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Van Eps, N.; Yin, Y.; Pal, K.; Goswami, D.; White, T.A.; Barty, A.; Latorraca, N.R.; Chapman, H.N.; Hubbell, W.L.; Dror, R.O.; Stevens, R.C.; Cherezov, V.; Gurevich, V.V.; Griffin, P.R.; Ernst, O.P.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. , Identification of Phosphorylation Codes for Arrestin Recruitment by G protein-Coupled Receptors. Cell 2017, 170, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bous, J.; Fouillen, A.; Orcel, H.; Trapani, S.; Cong, X.; Fontanel, S.; Saint-Paul, J.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Urbach, S.; Sibille, N.; Sounier, R.; Granier, S.; Mouillac, B.; Bron, P. , Structure of the vasopressin hormone-V2 receptor-β-arrestin1 ternary complex. Sci Adv 2022, 8, eabo7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Barros-Álvarez, X.; Zhang, S.; Kim, K.; Dämgen, M.A.; Panova, O.; Suomivuori, C.M.; Fay, J.F.; Zhong, X.; Krumm, B.E.; Gumpper, R.H.; Seven, A.B.; Robertson, M.J.; Krogan, N.J.; Hüttenhain, R.; Nichols, D.E.; Dror, R.O.; Skiniotis, G.; Roth, B.L. , Signaling snapshots of a serotonin receptor activated by the prototypical psychedelic LSD. Neuron 2022, 110, 3154–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Masureel, M.; Qianhui, Q.; Janetzko, J.; Inoue, A.; Kato, H.E.; Robertson, M.J.; Nguyen, K.C.; Glenn, J.S.; Skiniotis, G.; Kobilka, B.K. , Structure of the neurotensin receptor 1 in complex with β-arrestin 1. Nature 2020, 579, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Q.; Cai, C.; Ding, Y.; Shen, D.D.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.M. , Snapshot of the cannabinoid receptor 1-arrestin complex unravels the biased signaling mechanism. Cell 2023, 186, 5784–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Warne, T.; Nehmé, R.; Pandey, S.; Dwivedi-Agnihotri, H.; Chaturvedi, M.; Edwards, P.C.; García-Nafría, J.; Leslie, A.G. W.; Shukla, A.K.; Tate, C.G. , Molecular basis of β-arrestin coupling to formoterol-bound β(1)-adrenoceptor. Nature 2020, 583, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staus, D.P.; Hu, H.; Robertson, M.J.; Kleinhenz, A.L. W.; Wingler, L.M.; Capel, W.D.; Latorraca, N.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Skiniotis, G. , Structure of the M2 muscarinic receptor-β-arrestin complex in a lipid nanodisc. Nature 2020, 579, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Li, Z.; Jin, M.; Yin, Y.L.; de Waal, P.W.; Pal, K.; Yin, Y.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Melcher, K.; Jiang, Y.; Cong, Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Yu, X.; Xu, H.E. , A complex structure of arrestin-2 bound to a G protein-coupled receptor. Cell Res 2019, 29, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.H.; Thomsen, A.R. B.; Cahill, T.J., 3rd; Huang, R.; Huang, L.Y.; Marcink, T.; Clarke, O.B.; Heissel, S.; Masoudi, A.; Ben-Hail, D.; Samaan, F.; Dandey, V.P.; Tan, Y.Z.; Hong, C.; Mahoney, J.P.; Triest, S.; Little, J., 4th; Chen, X.; Sunahara, R.; Steyaert, J.; Molina, H.; Yu, Z.; des Georges, A.; Lefkowitz, R.J. , Structure of an endosomal signaling GPCR-G protein-β-arrestin megacomplex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2019, 26, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.C. , A splice variant of arrestin from human retina. Exp Eye Res 1996, 62, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Syed, M.; Bugra, K.; Whelan, J.P.; McGinnis, J.F.; Shinohara, T. , Structural analysis of mouse S-antigen. Gene 1988, 73, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne-Marr, R.; Gurevich, V.V.; Goldsmith, P.; Bodine, R.C.; Sanders, C.; Donoso, L.A.; Benovic, J.L. , Polypeptide variants of beta-arrestin and arrestin3. J Biol Chem 1993, 268, 15640–15648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parruti, G.; Peracchia, F.; Sallese, M.; Ambrosini, G.; Masini, M.; Rotilio, D.; De Blasi, A. , Molecular analysis of human beta-arrestin-1: Cloning, tissue distribution, and regulation of expression. Identification of two isoforms generated by alternative splicing. J Biol Chem 1993, 268, 9753–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsmore, S.F.; Peppel, K.; Suh, D.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Seldin, M.F. , Genetic mapping of the beta-arrestin 1 and 2 genes on mouse chromosomes 7 and 11 respectively. Mamm Genome 1995, 6, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, B.; Kaufman, K.D.; Chazenbalk, G.D. , Cloning of a member of the arrestin family from a human thyroid cDNA library. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1992, 84, R39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Ohguro, H.; Sohma, H.; Kuroki, Y.; Wada, H.; Okisaka, S.; Murakami, A. , Purification and characterization of bovine cone arrestin (cArr). FEBS Lett. 2000, 470, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.; Yajima, T.; Sakuma, H.; McLaren, M.J.; Inana, G. , X-arrestin: A new retinal arrestin mapping to the X chromosome. FEBS Lett. 1993, 334, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, D.R.; Mecklenburg, K.L.; Pollock, J.A.; Vihtelic, T.S.; Benzer, S. , Twenty Drosophila visual system cDNA clones: One is a homolog of human arrestin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1990, 87, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Komori, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Sakai, Y.; Hotta, Y.; Matsumoto, H. , A 49-kilodalton phosphoprotein in the Drosophila photoreceptor is an arrestin homolog. Science 1990, 246, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.C.; Tift, F.W.; McCauley, A.; Liu, L.; Roman, G. , Functional characterization of kurtz, a Drosophila non-visual arrestin, reveals conservation of GPCR desensitization mechanisms. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2008, 38, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M.; Orii, H.; Yoshida, N.; Jojima, E.; Horie, T.; Yoshida, R.; Haga, T.; Tsuda, M. , Ascidian arrestin (Ci-arr), the origin of the visual and nonvisual arrestins of vertebrate. Eur J Biochem 2002, 269, 5112–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmitessa, A.; Hess, H.A.; Bany, I.A.; Kim, Y.M.; Koelle, M.R.; Benovic, J.L. , Caenorhabditus elegans arrestin regulates neural G protein signaling and olfactory adaptation and recovery. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 24649–24662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, C.L.; Luu, J.; Kim, K.; Furkert, D.; Jang, K.; Reichenwallner, J.; Kang, M.; Lee, H.J.; Eger, B.T.; Choe, H.W.; Fiedler, D.; Ernst, O.P.; Kim, Y.J.; Palczewski, K.; Kiser, P.D. , Structural evidence for visual arrestin priming via complexation of phosphoinositols. Structure 2022, 30, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Weinstein, L.D.; Nguen, K.K.; Grewal, A.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. , GPCR binding and JNK activation by arrestin-3 have different structural requirements. Cells 2023, 12, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrischek, H.; Prohaska, S.J.; Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V.; Stadler, P.F. , Uncovering missing pieces: Duplication and deletion history of arrestins in deuterostomes. BMC Evol Biol 2017, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, O.P.; Burns, M.E. , Control of rhodopsin’s active lifetime by arrestin-1 expression in mammalian rods. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 3450–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.E.; Baylor, D.A. , Activation, deactivation, and adaptation in vertebrate photoreceptor cells. Annu Rev Neurosci 2001, 24, 779–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, K.P.; Lamb, T.D. , Rhodopsin, light-sensor of vision. Prog Retin Eye Res 2023, 93, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, G.D.; Uzzell, V.; Chichilnisky, E.J.; Rieke, F. , Temporal resolution of single-photon responses in primate rod photoreceptors and limits imposed by cellular noise. J Neurophysiol 2019, 121, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.E. , Deactivation mechanisms of rod phototransduction: The Cogan lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010, 51, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichilnisky, E.J.; Rieke, F. , Detection sensitivity and temporal resolution of visual signals near absolute threshold in the salamander retina. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonov, S.S.; Brown, B.M.; Davis, J.A.; Zuniga, F.I.; Bragin, A.; Pugh, E.N., Jr; Craft, C.M. , Mouse cones require an arrestin for normal inactivation of phototransduction. Neuron 2008, 59, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, Y.K.; Luttrell, L.M. , The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling. Pharmacol Rev 2017, 69, 256–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerstrom, M.C.; Lundin, L.G.; Schioth, H.B. , The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol 2003, 63, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockaert, J.; Pin, J.P. , Molecular tinkering of G protein-coupled receptors: An evolutionary success. EMBO J 1999, 18, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. , Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2017, 16, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Scharf, M.M.; Bermudez, M.; Egyed, A.; Franco, R.; Hansen, O.K.; Jagerovic, N.; Jakubík, J.; Keserű, G.M.; Kiss, D.J.; Kozielewicz, P.; Larsen, O.; Majellaro, M.; Mallo-Abreu, A.; Navarro, G.; Prieto-Díaz, R.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Sotelo, E.; Stark, H.; Werner, T.; Wingler, L.M. , Progress on the development of Class A GPCR-biased ligands. Br J Pharmacol 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, T.; Lu, X.; Lan, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S. , G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): Advances in structures, mechanisms, and drug discovery. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.D. , Information Transmission in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Chiu, Y.T.; Pickett, J.E.; Roth, B.L. , Illuminating the understudied GPCR-ome. Drug Discov Today 2024, 29, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manglik, A.; Kim, T.H.; Masureel, M.; Altenbach, C.; Yang, Z.; Hilger, D.; Lerch, M.T.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Hubbell, W.L.; Prosser, R.S.; Kobilka, B.K. , Structural Insights into the Dynamic Process of β2-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling. Cell 2015, 161, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Kaindl, J.; Risel, P.; Hübner, H.; Maeda, S.; Niu, X.; Li, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Jin, C.; Kobilka, B.K. , Conformational Complexity and Dynamics in a Muscarinic Receptor Revealed by NMR Spectroscopy. Mol Cell 2019, 75, 53–65.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eps, N.; Caro, L.N.; Morizumi, T.; Kusnetzow, A.K.; Szczepek, M.; Hofmann, K.P.; Bayburt, T.H.; Sligar, S.G.; Ernst, O.P.; Hubbell, W.L. , Conformational equilibria of light-activated rhodopsin in nanodiscs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, E3268–E3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granzin, J.; Stadler, A.; Cousin, A.; Schlesinger, R.; Batra-Safferling, R. , Structural evidence for the role of polar core residue Arg175 in arrestin activation. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sente, A.; Peer, R.; Srivastava, A.; Baidya, M.; Lesk, A.M.; Balaji, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Babu, M.M.; Flock, T. , Molecular mechanism of modulating arrestin conformation by GPCR phosphorylation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2018, 25, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Schafer, C.T.; Mukherjee, S.; Gustavsson, M.; Agrawal, P.; Yao, X.Q.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Handel, T.M.; Tesmer, J.J. G. , ACKR3-arrestin2/3 complexes reveal molecular consequences of GRK-dependent barcoding. bioRxiv, 2023; bioRxiv:2023.07.18.549504. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermaier, M.K.; Peterhans, C.; Jaussi, R.; Deupi, X.; Standfuss, J. , Functional map of arrestin-1 at single amino acid resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterhans, C.; Lally, C.C.; Ostermaier, M.K.; Sommer, M.E.; Standfuss, J. , Functional map of arrestin binding to phosphorylated opsin, with and without agonist. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 28686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Weinstein, L.D.; Zheng, C.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. , Functional Role of Arrestin-1 Residues Interacting with Unphosphorylated Rhodopsin Elements. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Huh, E.K.; Karnam, P.C.; Oviedo, S.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. , The Role of Arrestin-1 Middle Loop in Rhodopsin Binding. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Francis, D.J.; Van Eps, N.; Kim, M.; Hanson, S.M.; Klug, C.S.; Hubbell, W.L.; Gurevich, V.V. , The role of arrestin alpha-helix I in receptor binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Huh, E.K.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. , The finger loop as an activation sensor in arrestin. J Neurochem 2021, 157, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, Y.; Böttke, T.; Lam, J.H.; Ernicke, S.; Fortmann, A.; Tretbar, M.; Zarzycka, B.; Gurevich, V.V.; Katritch, V.; Coin, I. , Structural details of a class B GPCR-arrestin complex revealed by genetically encoded crosslinkers in living cells. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Ohta, T. , On some principles governing molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1974, 71, 2848–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolph, P.J.; Ranganathan, R.; Colley, N.J.; Hardy, R.W.; Socolich, M.; Zuker, C.S. , Arrestin function in inactivation of G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin in vivo. Science 1993, 260, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloway, P.G.; Dolph, P.J. , A role for the light-dependent phosphorylation of visual arrestin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96, 6072–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentrop, J.; Paulsen, R. , Light-modulated ADP-ribosylation, protein phosphorylation and protein binding in isolated fly photoreceptor membranes. Eur J Biochem 1986, 161, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.K.; Xia, H.; Yan, L.; Liu, C.H.; Hardie, R.C.; Ready, D.F. , Arrestin translocation is stoichiometric to rhodopsin isomerization and accelerated by phototransduction in Drosophila photoreceptors. Neuron 2010, 67, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V. , Use of bacteriophage RNA polymerase in RNA synthesis. Methods Enzymol 1996, 275, 382–397. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




