Submitted:
27 November 2024
Posted:
28 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
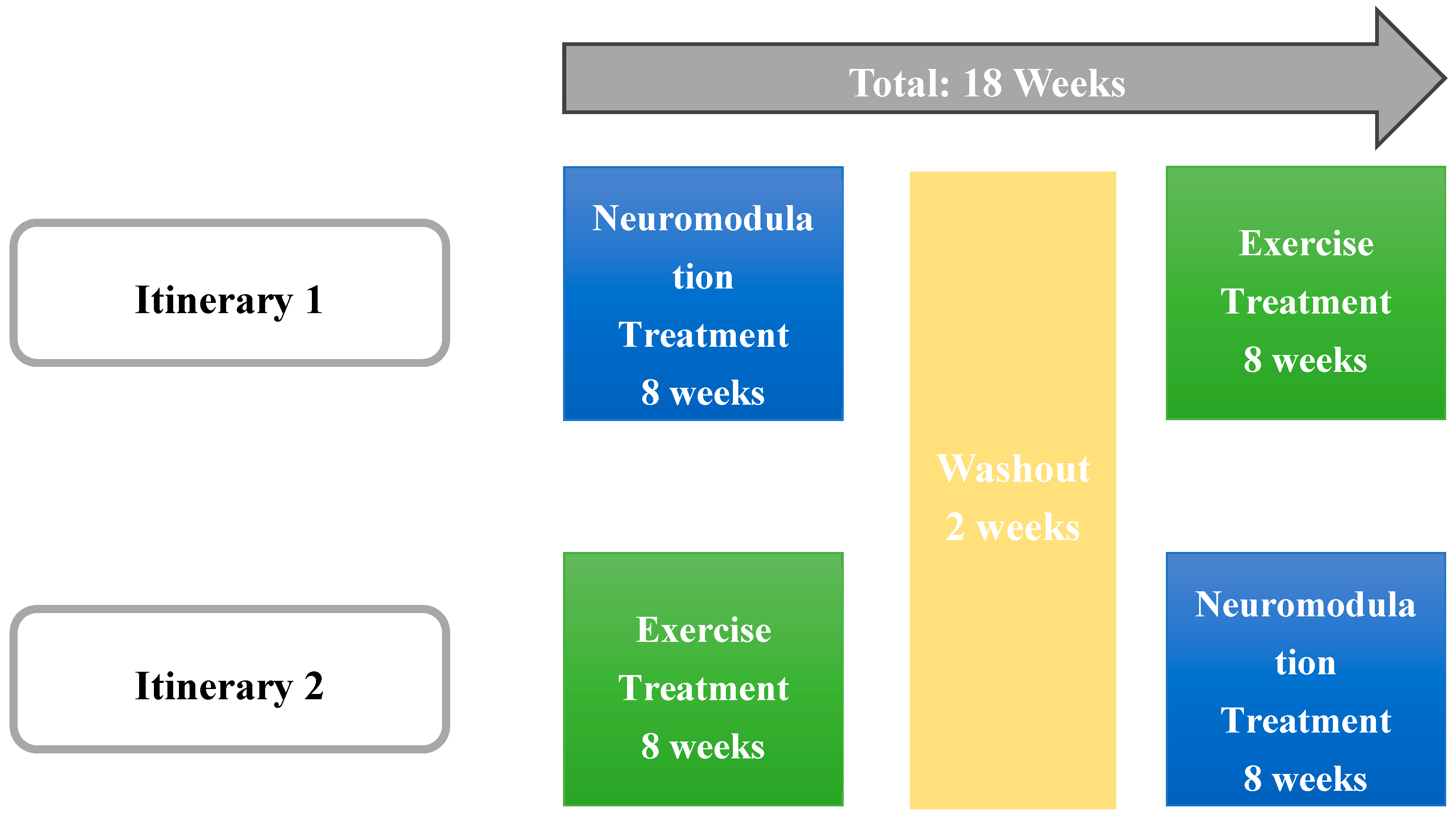
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Intervention
- Suit: Participants engaged in a 60-minute session with the EXOPULSE Mollii suit, which utilized all 58 electrodes set at an intensity of 2 milliamperes (mA) and a pulse width of 30 milliseconds (ms). This protocol adhered to the treatment procedures established in earlier research [17,18,35,38,43,44]. A certified professional ensured proper placement of the electrodes for each participant. Once the suit was properly fitted and the control unit connected, the participant was positioned lying down on a massage table, after which the session began with the activation of the suit.
- Exercise: Participants attended 1-hour training sessions that began with a mobility warm-up, followed by a main workout consisting of strength exercises and High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT). The intervention followed a methodology previously described [35,38] being divided into three phases: the first block, comprising sessions 1 and 2, focused on strength training and served as a familiarization phase, essential for building a foundation for the more intense training that followed. This phase helped participants adjust to the exercise routine, ensuring they were comfortable and minimizing the risk of injury. The second block, covering sessions 3 through 8, concentrated on HIIT training; each session included 4 circuits that participants had to complete, with an increasing training volume throughout this phase. The final block focused on strength training using a circuit format, where participants completed all exercises within a circuit before resting and moving on to the next circuit, continuing this pattern until the session was completed.
2.4. Measurements
2.4.1. Respiratory Variables
2.4.2. Functional Test
- Chair stand test: The patient is instructed to stand beside a chair, and the test involves counting how many times they can move from a seated to a fully standing position within 30 seconds. During the assessment, the patient must keep their back straight, feet flat on the ground, and refrain from using their arms to assist in standing.
- Handgrip strength test: This assessment is carried out using a grip dynamometer (Kuptone, model EH101). The patient completes the test twice with their dominant hand while standing, ensuring the arm is fully extended and held at a 30° angle from the trunk.
- Ten meter up-and-go test: The test begins with the patient seated in a chair. Once given the start signal, the patient is required to stand up and walk 10 meters as fast as possible without breaking into a run.
- One-leg balance: The participant is instructed to balance on one leg for as long as possible with their eyes open. This test is conducted separately on each leg.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
| Variables | Suit | Exercise | ||||||||||
| 1st session | 8th session | 16th session | 1st session | 8th session | 16th session | |||||||
| pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | pre | post | |
| FEV 1, L | 2.34 ± 0.52 | 2.28 ± 0.44 | 2.35 ± 0.46 | 2.35 ± 0.55 | 2.36 ± 0.52 | 2.43 ± 0.50 | 2.37 ± 0.49 | 2.46 ± 0.56 | 2.38 ± 0.48 | 2.35 ± 0.46 | 2.36 ± 0.53 | 2.27 ± 0.49 |
| FEV 1, % | 93.33 ± 12.12 | 91.56 ± 9.98 | 96.30 ± 11.81 | 95.70 ± 15.66 | 96.60 ± 12.44 | 99.30 ± 10.91 | 96.70 ± 11.72 | 100.10 ± 13.78 | 97.00 ± 11.51 | 95.70 ± 10.81 | 97.00 ± 13.60 | 94.44 ± 10.96 |
| FEV 6, L | 2.77 ± 0.62 | 2.77 ± 0.65 | 2.77 ± 0.69 | 2.73 ± 0.69 | 2.76 ± 0.66 | 2.79 ± 0.61 | 2.75 ± 0.64 | 2.82 ± 0.67 | 2.71 ± 0.60 | 2.72 ± 0.59 | 2.75 ± 0.61 | 2.72 ± 0.57 |
| FEV 6, % | 93.89 ± 13.12 | 93.11 ± 13.73 | 95.80 ± 17.81 | 84.88 ± 34.40 | 95.80 ± 15.65 | 97.00 ± 12.89 | 95.60 ± 15.01 | 97.80 ± 15.33 | 93.90 ± 13.58 | 94.30 ± 13.99 | 95.78 ± 13.65 | 94.67 ± 11.95 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, n | 0.85 ± 0.05 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 0.86 ± 0.06 | 0.86 ± 0.02 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | 0.87 ± 0.04 | 0.87 ± 0.04 | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.87 ± 0.05 | 0.86 ± 0.05 | 0.84 ± 0.07 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, % | 107.44 ± 6.84 | 106.11 ± 7.36 | 109.40 ± 8.67 | 109.30 ± 4.11 | 109.00 ± 5.10 | 110.20 ± 5.65 | 109.30 ± 6.38 | 110.30 ± 4.81 | 111.40 ± 4.86 | 109.40 ± 6.93 | 108.78 ± 7.79 | 106.00 ± 9.14 |
| Chest perimeter difference, cm | 7.62 ± 1.92 | 7.98 ± 1.79 | 7.60 ± 2.46 | 7.77 ± 2.52 | 8.80 ± 1.93 | 9.40 ± 2.33 | 7.20 ± 1.75 | 7.90 ± 1.91 | 8.70 ± 1.34 | 8.85 ± 1.49 | 7.68 ± 2.90 | 8.56 ± 2.65 |
| Handgrip strength test, kg | 24.07 ± 4.59 | 23.62 ± 4.64 | 24.28 ± 3.58 | 25.47 ± 3.99 | 23.38 ± 5.70 | 24.33 ± 5.28 | 23.64 ± 4.65 | 24.45 ± 2.95 | 23.55 ± 4.24 | 24.41 ± 3.75 | 24.24 ± 1.92 | 24.72 ± 2.29 |
| Chair stand test, n | 18.00 ± 8.46 | 19.90 ± 9.18 | 22.20 ± 9.08 | 23.45 ± 9.16 | 24.50 ± 9.35 | 26.60 ± 10.44 | 19.50 ± 8.87 | 20.70 ± 10.76 | 21.90 ± 8.36 | 23.30 ± 9.02 | 23.56 ± 8.97 | 24.56 ± 9.98 |
| 10 m up and go test, s | 6.06 ± 1.85 | 5.66 ± 1.41 | 5.45 ± 1.29 | 5.31 ± 1.27 | 5.43 ± 1.20 | 5.40 ± 0.97 | 5.45 ± 1.19 | 5.32 ± 1.32 | 5.15 ± 1.22 | 5.05 ± 1.07 | 5.20 ± 0.87 | 4.97 ± 0.85 |
| One leg balance right, s | 45.50 ± 37.85 | 42.46 ± 21.84 | 62.45 ± 36.31 | 72.52 ± 59.97 | 88.60 ± 72.19 | 94.63 ± 77.76 | 71.47 ± 51.97 | 78.54 ± 57.38 | 91.19 ± 92.53 | 71.69 ± 56.66 | 57.80 ± 48.26 | 64.26 ± 37.11 |
| One leg balance left, s | 43.94 ± 33.49 | 53.54 ± 47.97 | 59.09 ± 28.84 | 67.52 ± 55.92 | 63.37 ± 53.37 | 58.91 ± 48.58 | 63.51 ± 50.20 | 98.07 ± 91.49 | 56.84 ± 36.52 | 71.03 ± 45.05 | 74.74 ± 98.84 | 45.36 ± 27.95 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Future Research
4.2. Practical Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bair, M.J.; Krebs, E.E. Fibromyalgia. Ann Intern Med 2020, 172, ITC33–ITC48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Giorgi, V.; Marotto, D.; Atzeni, F. Fibromyalgia: An Update on Clinical Characteristics, Aetiopathogenesis and Treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2020, 16, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, J.C.; Bannwarth, B.; Failde, I.; Abello Carbonell, J.; Blotman, F.; Spaeth, M.; Saraiva, F.; Nacci, F.; Thomas, E.; Caubère, J.P.; Le Lay, K.; Taieb, C.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Prevalence of Fibromyalgia: A Survey in Five European Countries. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, L.P. Worldwide Epidemiology of Fibromyalgia Topical Collection on Fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2013, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Di Lollo, A.C.; Guzzo, M.P.; Giacomelli, C.; Atzeni, F.; Bazzichi, L.; Di Franco, M. Fibromyalgia and Nutrition: What News? Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lacasse, J.R.; Leo, J. Serotonin and Depression: A Disconnect between the Advertisements and the Scientific Literature. PLoS Med 2005, 2, e392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, C.L.; Kool, M.B.; Da Silva, J.A.P.; Geenen, R. The Prevalence of Severe Fatigue in Rheumatic Diseases: An International Study. Clin Rheumatol 2016, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, L.; Mannix, S.; Arnold, L.M.; Burbridge, C.; Howard, K.; McQuarrie, K.; Pitman, V.; Resnick, M.; Roth, T.; Symonds, T. Assessment of Sleep in Patients with Fibromyalgia: Qualitative Development of the Fibromyalgia Sleep Diary. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, L.S.; Leach, L.; Butterworth, P. Mental Health Problems and Internet Access: Results from an Australian National Household Survey. JMIR Mental Health. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepez, D.; Grandes, X.A.; Talanki Manjunatha, R.; Habib, S.; Sangaraju, S.L. Fibromyalgia and Depression: A Literature Review of Their Shared Aspects. Cureus 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whealy, M.; Nanda, S.; Vincent, A.; Mandrekar, J.; Cutrer, F.M. Fibromyalgia in Migraine: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Headache and Pain 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdrich, S.; Hawrelak, J.A.; Myers, S.P.; Harnett, J.E. A Systematic Review of the Association between Fibromyalgia and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.D.; Maxwell, C.; Mist, S.D.; King, V.; Denman, M.A.; Gregory, W.T. Pelvic Floor and Urinary Distress in Women with Fibromyalgia. Pain Management Nursing 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, L.M.; Bennett, R.M.; Crofford, L.J.; Dean, L.E.; Clauw, D.J.; Goldenberg, D.L.; Fitzcharles, M.-A.; Paiva, E.S.; Staud, R.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Buskila, D.; Macfarlane, G.J. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia. J Pain 2019, 20, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Farah, S.; Beci, G.; Schettino, M.; Carotti, M.; Di Carlo, M. Development and Validation of the Simple Fibromyalgia Screening Questionnaire for Improving the Recognition of Fibromyalgia in Daily Practice. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2020, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Villafaina, S.; Collado-Mateo, D.; Fuentes, J.P.; Rohlfs-Domínguez, P.; Gusi, N. Effects of Exergames on Brain Dynamics in Women with Fibromyalgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Med 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Zarapuz, A.; Apolo-Arenas, M.D.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Costa, A.R.; Pardo-Caballero, D.; Parraca, J.A. Acute Effects of a Session with The EXOPULSE Mollii Suit in a Fibromyalgia Patient: A Case Report. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Zarapuz, A.; Apolo-Arenas, M.D.; Tomas-Carus, P.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Parraca, J.A. Comparative Analysis of Psychophysiological Responses in Fibromyalgia Patients: Evaluating Neuromodulation Alone, Neuromodulation Combined with Virtual Reality, and Exercise Interventions. Medicina (B Aires) 2024, 60, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.E.; Denault, D.; Varacallo, M. Physiology, Oxygen Transport; 2023.
- Nakazawa, M.S.; Keith, B.; Simon, M.C. Oxygen Availability and Metabolic Adaptations. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, N.R.; Semenza, G.L. Oxygen Sensing and Homeostasis. Physiology. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlejohn, G.O.; Guymer, E.K.; Ngian, G.S. Is There a Role for Opioids in the Treatment of Fibromyalgia? Pain Manag 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, G.J.; Kronisch, C.; Dean, L.E.; Atzeni, F.; Häuser, W.; Fluß, E.; Choy, E.; Kosek, E.; Amris, K.; Branco, J.; Dincer, F.; Leino-Arjas, P.; Longley, K.; McCarthy, G.M.; Makri, S.; Perrot, S.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Taylor, A.; Jones, G.T. EULAR Revised Recommendations for the Management of Fibromyalgia. Ann Rheum Dis 2017, 76, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walitt, B.; Klose, P.; Üçeyler, N.; Phillips, T.; Häuser, W. Antipsychotics for Fibromyalgia in Adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya, H.J.M.; Ortiz, M.P.T.; Valencia, D.H.F.; Ribero, O.F.G. Efficacy of Cannabinoids in Fibromyalgia: A Literature Review. Colombian Journal of Anesthesiology. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomershine, C.S.; Crofford, L.J. A Symptom-Based Approach to Pharmacologic Management of Fibromyalgia. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardy, K.; Klose, P.; Welsch, P.; Häuser, W. Efficacy, Acceptability and Safety of Cognitive Behavioural Therapies in Fibromyalgia Syndrome – A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. European Journal of Pain (United Kingdom) 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ríos, M.C.; Navarro-Ledesma, S.; Tapia-Haro, R.M.; Toledano-Moreno, S.; Casas-Barragán, A.; Correa-Rodríguez, M.; Aguilar-Ferrándiz, M.E. Effectiveness of Health Education in Patients with Fibromyalgia: A Systematic Review. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, S.; Russell, I.J. More Ubiquitous Effects from Non-Pharmacologic than from Pharmacologic Treatments for Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis Examining Six Core Symptoms. Eur J Pain 2014, 18, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Su, M.I.; Chiu, C.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, W.L. Treating Fibromyalgia with Electrical Neuromodulation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clinical Neurophysiology 2023, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riachi, N.; Chalah, M.A.; Ahdab, R.; Arshad, F.; Ayache, S.S. Effects of the TENS Device, Exopulse Mollii Suit, on Pain Related to Fibromyalgia: An Open-Label Study. Neurophysiologie Clinique 2023, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Mansilla, J.; Mejías-Gil, A.; Garrido-Ardila, E.M.; Jiménez-Palomares, M.; Montanero-Fernández, J.; González-López-Arza, M.V. Effects of an Exercise for Well-Being and Physical Training Programme on Muscle Strength, Range of Movement, Respiratory Capacity and Quality of Life in Women with Fibromyalgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Med 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnier, F.; Labrunée, M.; Pathak, A.; Pavy-Le Traon, A.; Galès, C.; Sénard, J.M.; Guiraud, T. Exercise Training-Induced Modification in Autonomic Nervous System: An Update for Cardiac Patients. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesta-García, I.; Martínez-González-moro, I.; Rubio-Arias, J.; Carrasco-Poyatos, M. High-Intensity Interval Circuit Training versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training on Functional Ability and Body Mass Index in Middle-Aged and Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Zarapuz, A.; Apolo-Arenas, M.D.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F.; Parraca, J.A.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J. Comparative Efficacy of Neuromodulation and Structured Exercise Program on Pain and Muscle Oxygenation in Fibromyalgia Patients: A Randomized Crossover Study. Front Physiol 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haß, U.; Herpich, C.; Norman, K. Anti-Inflammatory Diets and Fatigue. Nutrients. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, P.; Estévez, A.F.; Miras, A.; Sánchez-Labraca, N.; Cañadas, F.; Vivas, A.B.; Cardona, D. A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial to Explore Cognitive and Emotional Effects of Probiotics in Fibromyalgia. Sci Rep 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Zarapuz, A.; Apolo-Arenas, M.D.; Fernandes, O.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Parraca, J.A. Comparative Efficacy of Neuromodulation and Structured Exercise Program on Autonomic Modulation in Fibromyalgia Patients: Pilot Study. J Clin Med 2024, 13, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, R.N.; Edwards, R.R.; Curran, S.; Wan, L.; Ross, E.L.; Gilligan, C.J.; Gozani, S.N. Effects of Wearable Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Fibromyalgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Pain Res 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Alventosa, R.; Inglés, M.; Cortés-Amador, S.; Gimeno-Mallench, L.; Sempere-Rubio, N.; Serra-Añó, P. Effectiveness of High-Frequency Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Physical Exercise in Women with Fibromyalgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys Ther 2021, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeken, C.; Vanderhasselt, M.A.; Remue, J.; Herremans, S.; Vanderbruggen, N.; Zeeuws, D.; Santermans, L.; De Raedt, R. Intensive HF-RTMS Treatment in Refractory Medication-Resistant Unipolar Depressed Patients. J Affect Disord 2013, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthulingam, J.A.; Hansen, T.M.; Olesen, S.S.; Drewes, A.M.; Frøkjær, J.B. Two-Week Cervical Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Chronic Pancreatitis Patients Induces Functional Connectivity Changes of Limbic Structures. Neuromodulation 2022, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennati, G.V.; Bergling, H.; Carment, L.; Borg, J.; Lindberg, P.G.; Palmcrantz, S. Effects of 60 Min Electrostimulation With the EXOPULSE Mollii Suit on Objective Signs of Spasticity. Front Neurol 2021, 12, 706610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffalt, P.C.; Bencke, J.; Mortensen, K.; Torabi, T.P.; Wong, C.; Speedtsberg, M.B. Electro-Suit Treatment of Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy Alters Nonlinear Dynamics of Walking. Clinical Biomechanics 2022, 98, 105714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, T.; Rummey, C.; Leinonen, M.; Voit, T.; Schara, U.; Straathof, C.; D’Angelo, M.; Bernert, G.; Cuisset, J.-M.; Finkel, R.; Goemans, N.; McDonald, C.; Buyse, G. The Use of a Hand-Held Device (ASMA-1) for Home-Based Monitoring of Respiratory Function Changes in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Neuromuscular Disorders 2015, 25, S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, U.; Ucok, K.; Ulasli, A.M.; Genc, A.; Karabacak, H.; Coban, N.F.; Simsek, H.; Cevik, H. Evaluation of Health-Related Physical Fitness Parameters and Association Analysis with Depression, Anxiety, and Quality of Life in Patients with Fibromyalgia. Int J Rheum Dis 2016, 19, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, M.; Zamunér, A.R.; Andrade, C.P.; Silva, E. Lung Function, Respiratory Muscle Strength, and Thoracoabdominal Mobility in Women With Fibromyalgia Syndrome. Respir Care 2016, 61, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, K.; Peterson, M. Peak Expiratory Flow Rate and Thoracic Mobility in People with Fibromyalgia. A Cross Sectional Study. Scand J Pain 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padkao, T.; Boonla, O. Relationships between Respiratory Muscle Strength, Chest Wall Expansion, and Functional Capacity in Healthy Nonsmokers. J Exerc Rehabil 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Baeza, A.; Álvarez-Gallardo, I.C.; Segura-Jiménez, V.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Ruiz, J.R.; Delgado-Fernández, M.; Aparicio, V.A. Reliability and Feasibility of Physical Fitness Tests in Female Fibromyalgia Patients. Int J Sports Med 2015, 36, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Suit | Exercise | ||
| Pre (p) | Post (p) | Pre (p) | Post (p) | |
| FEV 1, L | 0.926 | 0.082 | 0.895 | 0.347 |
| FEV 1, % | 0.969 | 0.124 | 0.895 | 0.562 |
| FEV 6, L | 0.926 | 0.584 | 0.49 | 1 |
| FEV 6, % | 0.971 | 0.391 | 0.625 | 0.889 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, n | 0.905 | 0.045* | 0.717 | 0.121 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, % | 0.581 | 0.1 | 0.405 | 0.093 |
| Chest perimeter difference, cm | 0.402 | 0.318 | 0.035* | 0.326 |
| Handgrip strength test, kg | 0.767 | 0.202 | 0.641 | 0.459 |
| Chair stand test, n | 0.005* | <.001* | 0.002* | 0.006* |
| 10 m up and go test, s | 0.007* | 0.273 | 0.117 | 0.045* |
| One leg balance right, s | 0.301 | 0.273 | 0.459 | 0.895 |
| One leg balance left, s | 0.264 | 0.0025* | 0.882 | 0.135 |
| Variables | Pre 1st session | Post 1st session | Pre 8th session | Post 8th session | Pre 16th session | Post 16th session | ||||||
| p | ε² | p | ε² | p | ε² | p | ε² | p | ε² | p | ε² | |
| FEV 1, L | 0.762 | 0.005 | 0.545 | 0.019 | 0.88 | 0.001 | 0.821 | 0.003 | 0.775 | 0.005 | 0.235 | 0.078 |
| FEV 1, % | 0.513 | 0.024 | 0.19 | 0.095 | 0.85 | 0.002 | 0.91 | 0.001 | 0.838 | 0.002 | 0.165 | 0.107 |
| FEV 6, L | 1 | 0.000 | 0.88 | 0.001 | 0.791 | 0.004 | 0.88 | 0.001 | 0.838 | 0.002 | 0.713 | 0.008 |
| FEV 6, % | 0.683 | 0.009 | 0.513 | 0.024 | 0.734 | 0.006 | 0.545 | 0.019 | 0.902 | 0.001 | 0.623 | 0.013 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, n | 0.406 | 0.036 | 0.034* | 0.236 | 0.151 | 0.109 | 0.199 | 0.087 | 0.683 | 0.009 | 0.288 | 0.063 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, % | 0.437 | 0.034 | 0.083 | 0.167 | 0.363 | 0.043 | 0.79 | 0.004 | 0.902 | 0.001 | 0.461 | 0.030 |
| Chest perimeter difference, cm | 0.591 | 0.015 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.117 | 0.129 | 0.393 | 0.038 | 0.385 | 0.042 | 0.385 | 0.042 |
| Handgrip strength test, kg | 0.88 | 0.001 | 0.406 | 0.036 | 0.762 | 0.005 | 0.82 | 0.003 | 0.93 | 0.000 | 0.967 | 0.000 |
| Chair stand test, n | 0.733 | 0.006 | 0.939 | 0.000 | 0.88 | 0.001 | 0.82 | 0.003 | 0.87 | 0.001 | 0.713 | 0.008 |
| 10 m up and go test, s | 0.597 | 0.015 | 0.597 | 0.015 | 0.406 | 0.036 | 0.597 | 0.015 | 0.744 | 0.006 | 0.165 | 0.107 |
| One leg balance right, s | 0.326 | 0.051 | 0.199 | 0.087 | 0.65 | 0.011 | 0.762 | 0.005 | 0.624 | 0.013 | 0.744 | 0.006 |
| One leg balance left, s | 0.597 | 0.015 | 0.226 | 0.077 | 0.757 | 0.006 | 0.683 | 0.009 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.935 | 0.000 |
| Variables | Suit | Exercise | ||||
| 1st session | 8th session | 16th session | 1st session | 8th session | 16th session | |
| Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | |
| FEV 1, L | -0.365 | -0.024 | 0.570 | 0.798* | -0.376 | -0.6608 |
| FEV 1, % | -0.280 | -0.074 | 0.614 | 0.755* | -0.337 | -0.489 |
| FEV 6, L | -0.032 | -0.145 | 0.281 | 0.596 | 0.097 | -0.319 |
| FEV 6, % | -0.257 | -0.164 | 0.273 | 0.5546 | 0.087 | -0.298 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, n | -0.241 | 0.046 | 1.021* | 0.217 | -0.501 | -0.919* |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, % | -0.175 | -0.017 | 0.813* | 0.139 | -0.500 | -0.970* |
| Chest perimeter difference, cm | 0.184 | 0.111 | 0.444 | 0.559 | 0.106 | 0.467 |
| Handgrip strength test, kg | -0.152 | 0.858* | 0.402 | 0.234 | 0.473 | 0.342 |
| Chair stand test, n | 0.650 | 0.628 | 0.917* | 0.425 | 0.515 | 0.577 |
| 10 m up and go test, s | -0.746* | -0.527 | -0.055 | -0.400 | -0.182 | -0.556 |
| One leg balance right, s | -0.127 | 0.127 | 0.200 | 0.309 | -0.127 | 0.200 |
| One leg balance left, s | 0.442 | 0.200 | -0.200 | 0.673 | 0.883* | -0.600 |
| Variables | 1st vs 8th pre session | 8th vs 16th pre session | 1st vs 16th pre session | 1st vs 8th post session | 8th vs 16th post session | 1st vs 16th post session | 1st pre vs 8th post session | 1st pre vs 16th post session | 8th pre vs 16th post session |
| Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | |
| FEV 1, L | -0.0361 | -0.0717 | -0.126 | -0.388 | -0.413 | -0.851* | -0.00798 | -0.471 | -0.361 |
| FEV 1, % | -0.203 | -0.0534 | -0.124 | -0.198 | -0.442 | -0.902* | -0.0673 | -0.462 | -0.407 |
| FEV 6, L | 0.0103 | 0.0797 | 0.0743 | -0.00512 | -0.344 | -0.248 | 0.165 | -0.233 | -0.147 |
| FEV 6, % | 0.0759 | 0 | 0.121 | 0.393 | -0.4 | -0.343 | 0.356 | -0.177 | -0.191 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, n | -0.208 | -0.0195 | -0.257 | -0.834* | -0.273 | -1.01* | -0.255 | -0.458 | -0.268 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, % | -0.417 | 0.0831 | -0.272 | -0.816* | -0.22 | -0.934* | -0.342 | -0.419 | -0.146 |
| Chest perimeter difference, cm | 0.139 | -0.75 | -0.422 | -0.111 | -0.778 | -0.529 | -0.0556 | -0.522 | -0.86* |
| Handgrip strength test, kg | -0.0689 | 0.246 | 0.147 | -0.848* | 0.286 | -0.229 | -0.54 | -0.0486 | -0.012 |
| Chair stand test, n | -0.973* | -0.889* | -0.945* | -0.863* | -1.48* | -1.28* | -1.1* | -1.38* | -1.47* |
| 10 m up and go test, s | 1* | 0.236 | 0.6 | 0.673 | -0.164 | 0.345 | 1* | 0.573 | 0.145 |
| One leg balance right, s | -0.402 | -0.6 | -0.636 | -0.273 | -0.345 | -0.747* | -0.564 | -0.745* | -0.66 |
| One leg balance left, s | -0.364 | -0.0222 | -0.527 | -0.636 | 0.455 | -0.0182 | -0.481 | -0.127 | -0.093 |
| 1st vs 8th pre session | 8th vs 16th pre session | 1st vs 16th pre session | 1st vs 8th post session | 8th vs 16th post session | 1st vs 16th post session | 1st pre vs 8th post session | 1st pre vs 16th post session | 8th pre vs 16th post session | |
| Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | Effect Size | |
| FEV 1, L | -0.0765 | -0.107 | -0.128 | 0.537 | 0.17 | 0.582 | 0.111 | 0.266 | 0.299 |
| FEV 1, % | -0.031 | -0.172 | -0.172 | 0.499 | -0.111 | 0.5 | 0.121 | 0.156 | 0.056 |
| FEV 6, L | 0.211 | -0.554 | -0.213 | 0.415 | -0.211 | 0.302 | 0.148 | -0.005 | -0.35 |
| FEV 6, % | 0.198 | -0.537 | -0.252 | 0.414 | -0.309 | 0.211 | 0.16 | -0.071 | -0.395 |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, n | -0.839* | 0.732 | 0.223 | 0.0899 | 0.689 | 0.662 | -0.135 | 0.709 | 1* |
| FEV 1/FEV 6, % | -0.738* | 0.698 | 0.295 | -0.127 | 0.678 | 0.786 | -0.035 | 0.776* | 0.998* |
| Chest perimeter difference, cm | -0.789* | 0.395 | -0.434 | -0.65* | 0.077 | -0.36 | -1,28* | -1.03* | 0.095 |
| Handgrip strength test, kg | 0.0505 | -0.145 | -0.037 | 0.0208 | -0.08 | -0.091 | -0.267 | -0.186 | -0.368 |
| Chair stand test, n | -0.692 | -0.62 | -1.35* | -0.683* | -0.84* | -1.06* | -1.28* | -1.36* | -0.664 |
| 10 m up and go test, s | 0.673 | -0.0556 | 0.583 | 0.6 | 0.378 | 0.733 | 0.673 | 0.867* | 0.378 |
| One leg balance right, s | -0.345 | 0.6 | -0.111 | -0.018 | -0.067 | 0.216 | -0.091 | -0.2 | 0.022 |
| One leg balance left, s | 0.609 | -0.333 | -0.378 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.511 | -0.1 | 0.333 | 0.167 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





