Submitted:
25 November 2024
Posted:
26 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
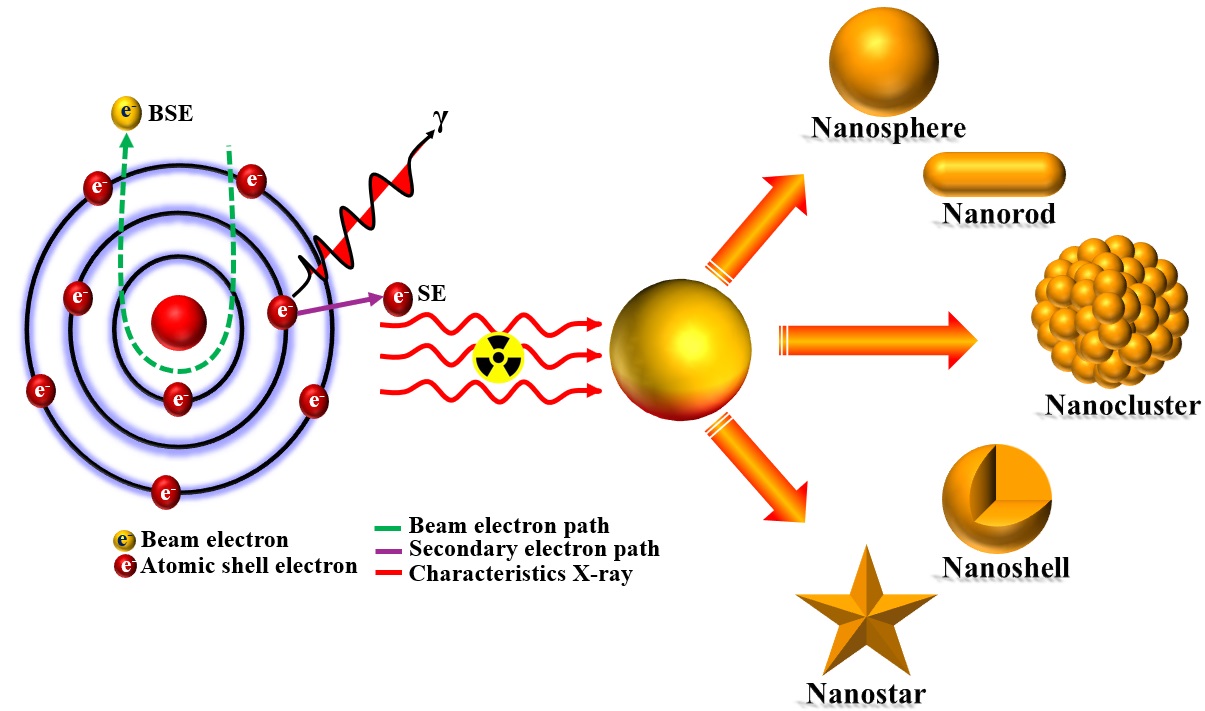
Keywords:
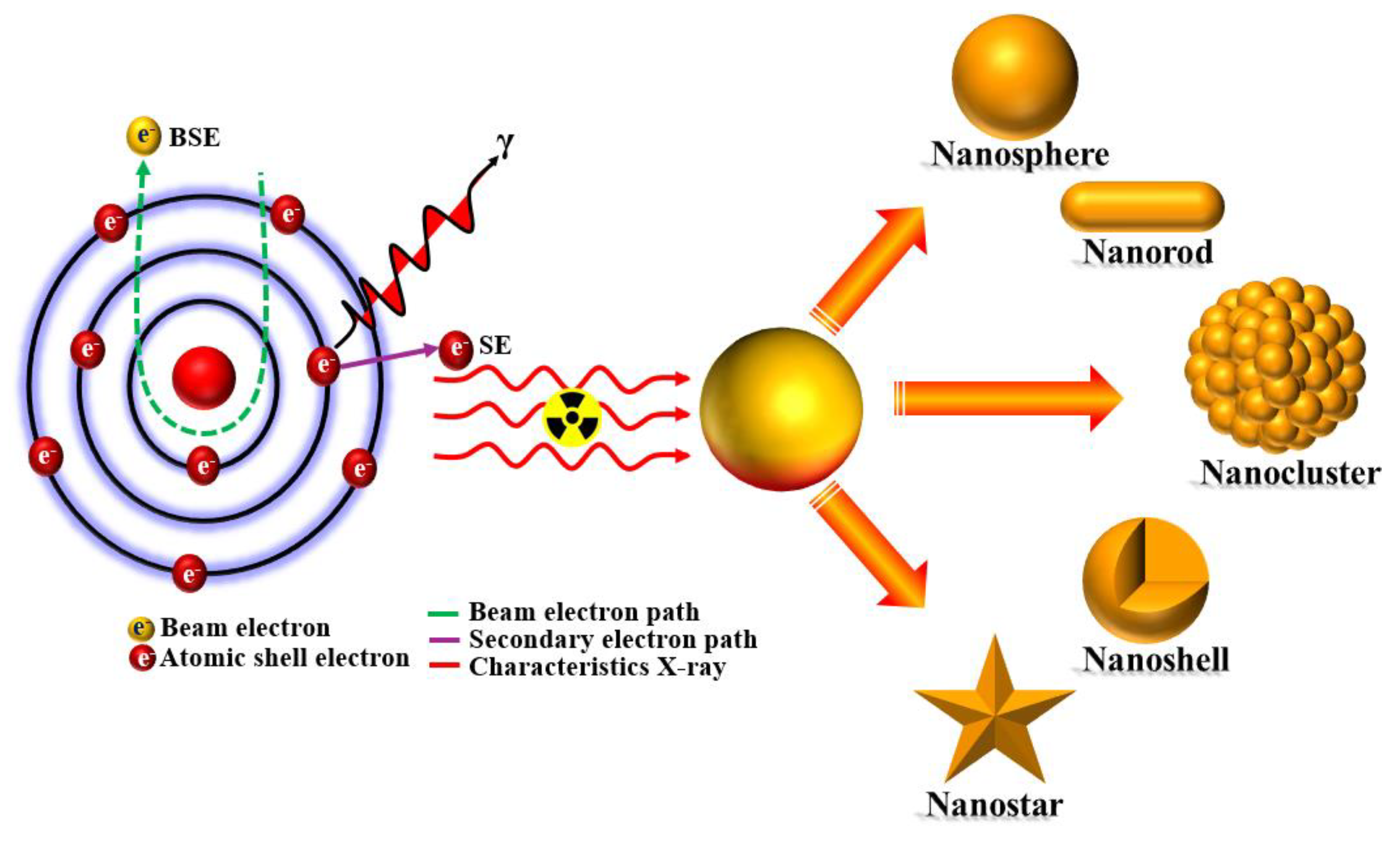
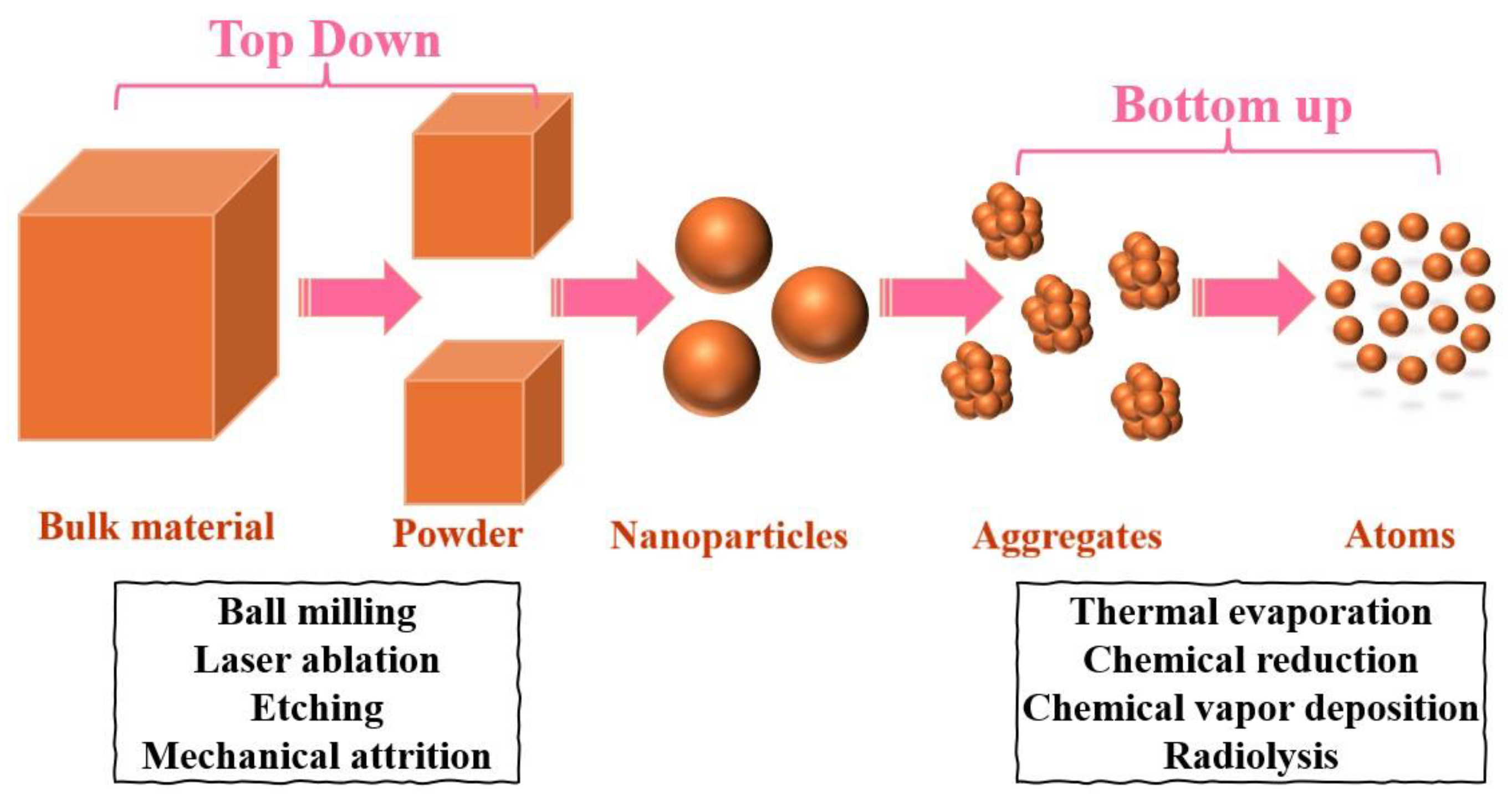
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Nanomaterials by Radiation Method and Application
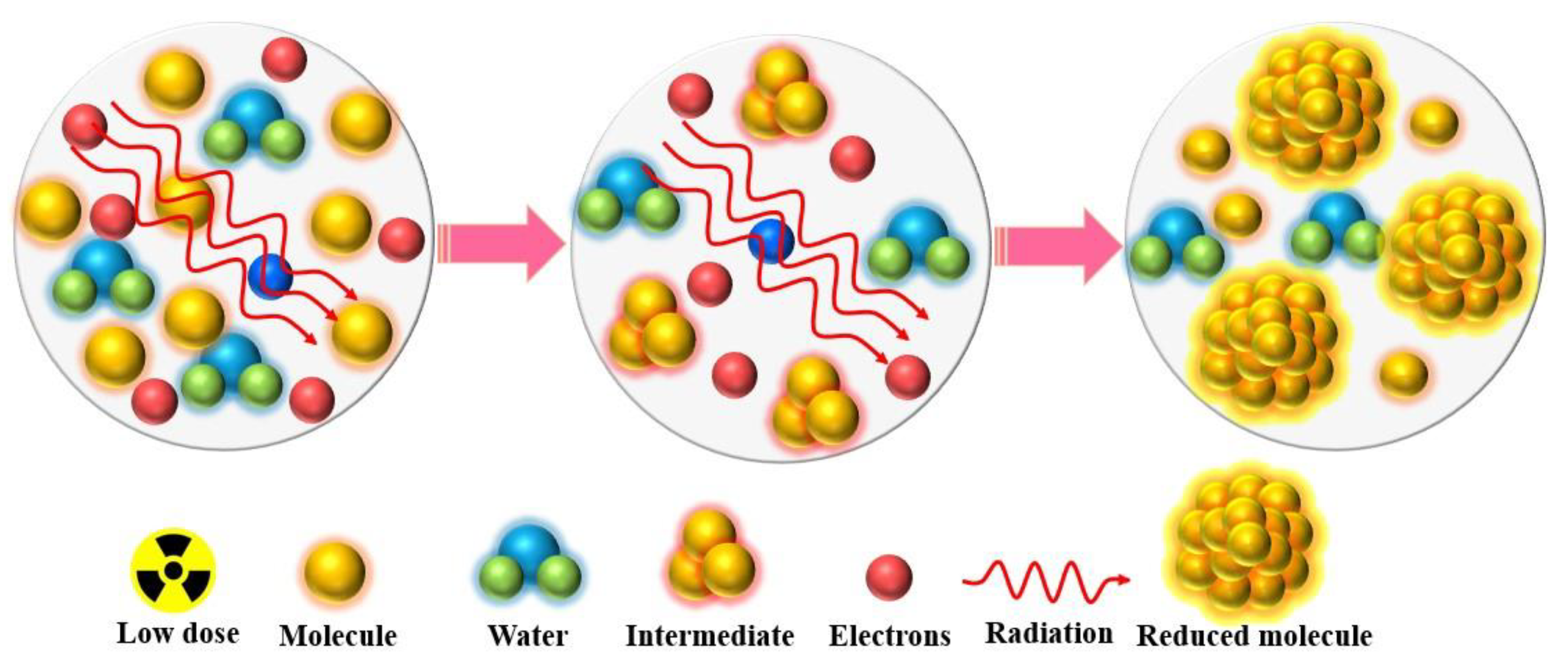
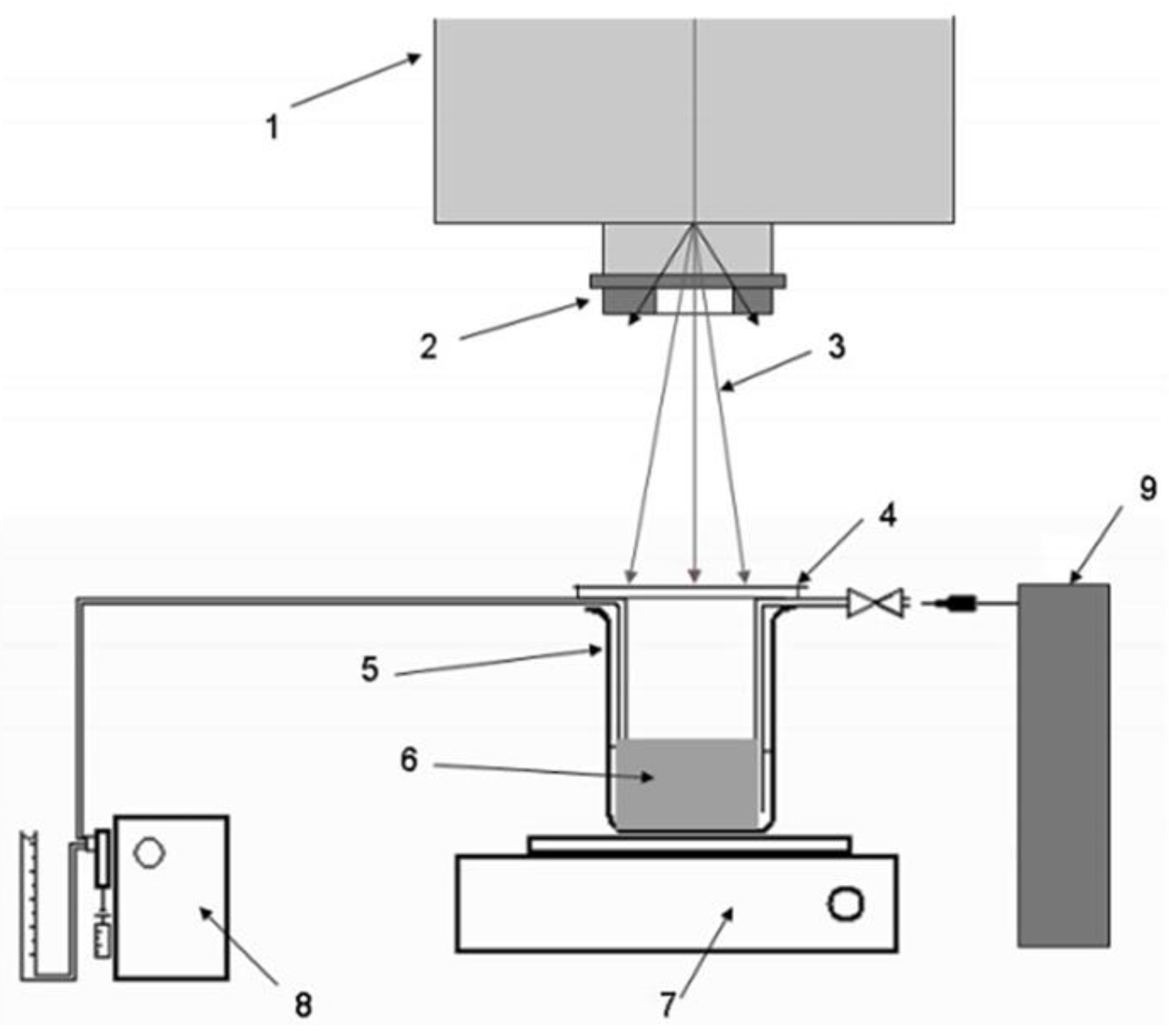
2.1. Electron Beam Synthesis
2.1.1. Electron-Matter Interactions
2.1.2. Transition Metal Nano Materials
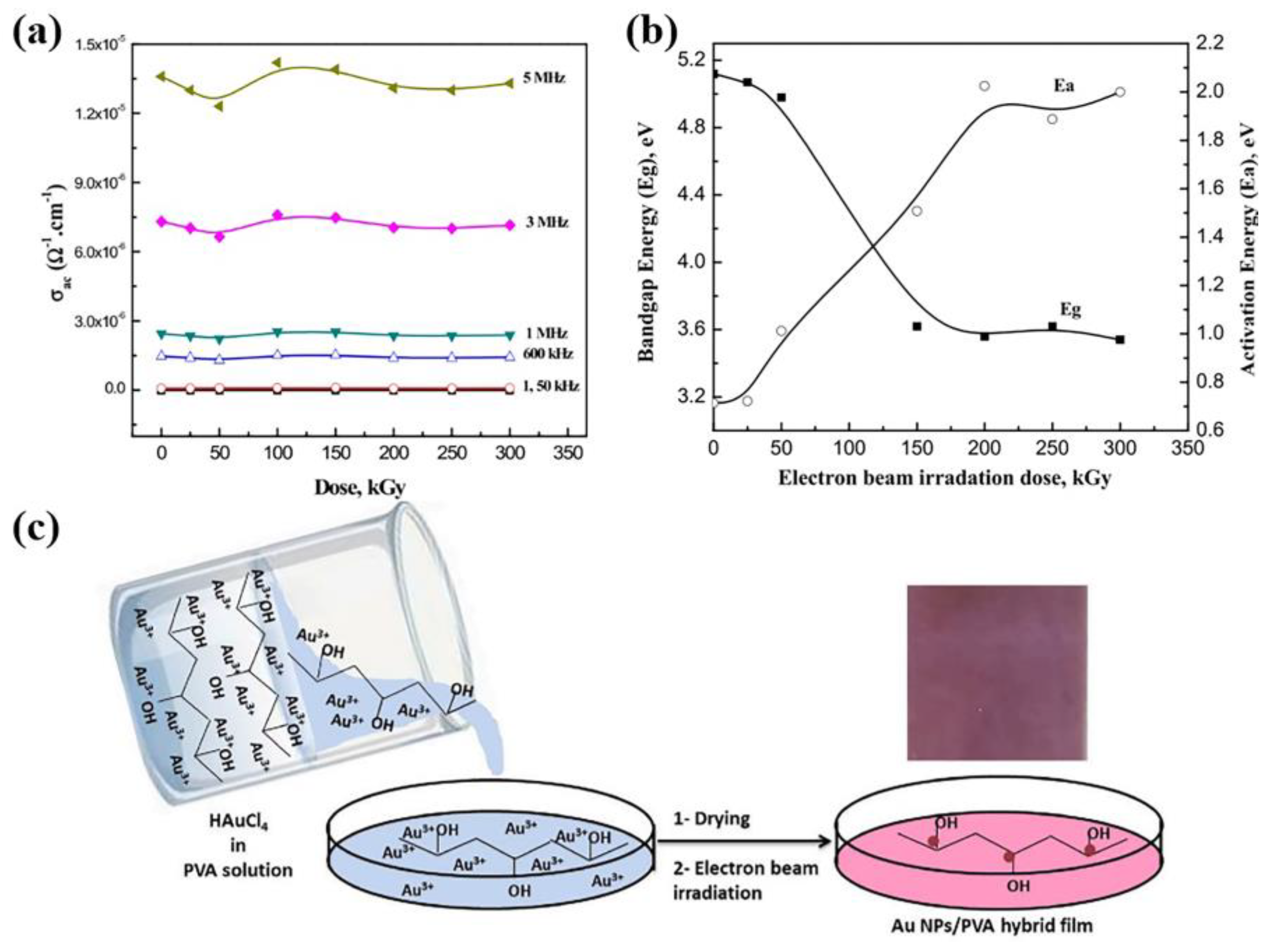
2.1.3. Gold Nanoparticles
2.1.4. Platinum Nanoparticles
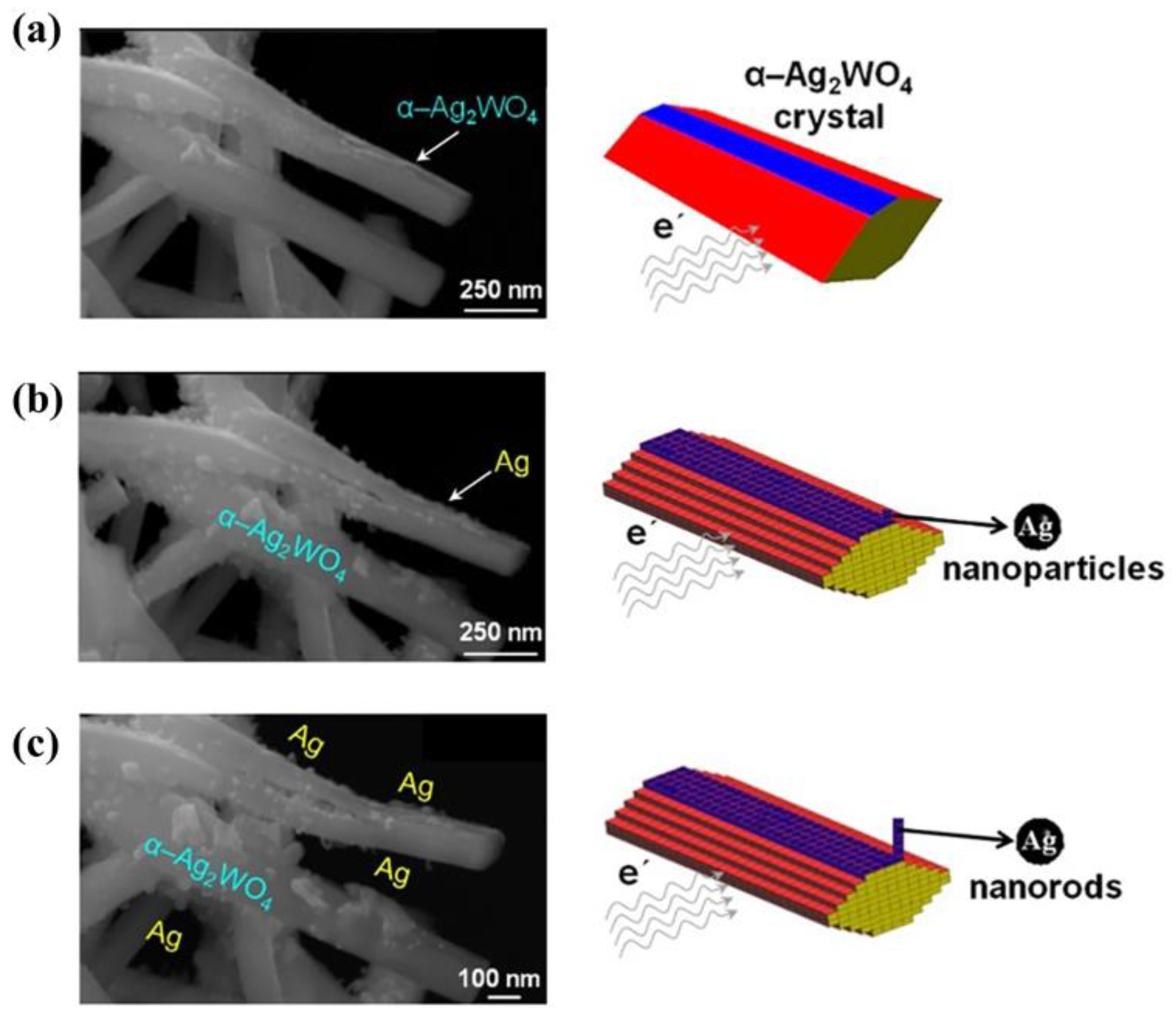
2.1.5. Silver Nanoparticles
2.1.6. Other Metal Nano Materials
2.1.7. Carbon-Based Nanocomposite
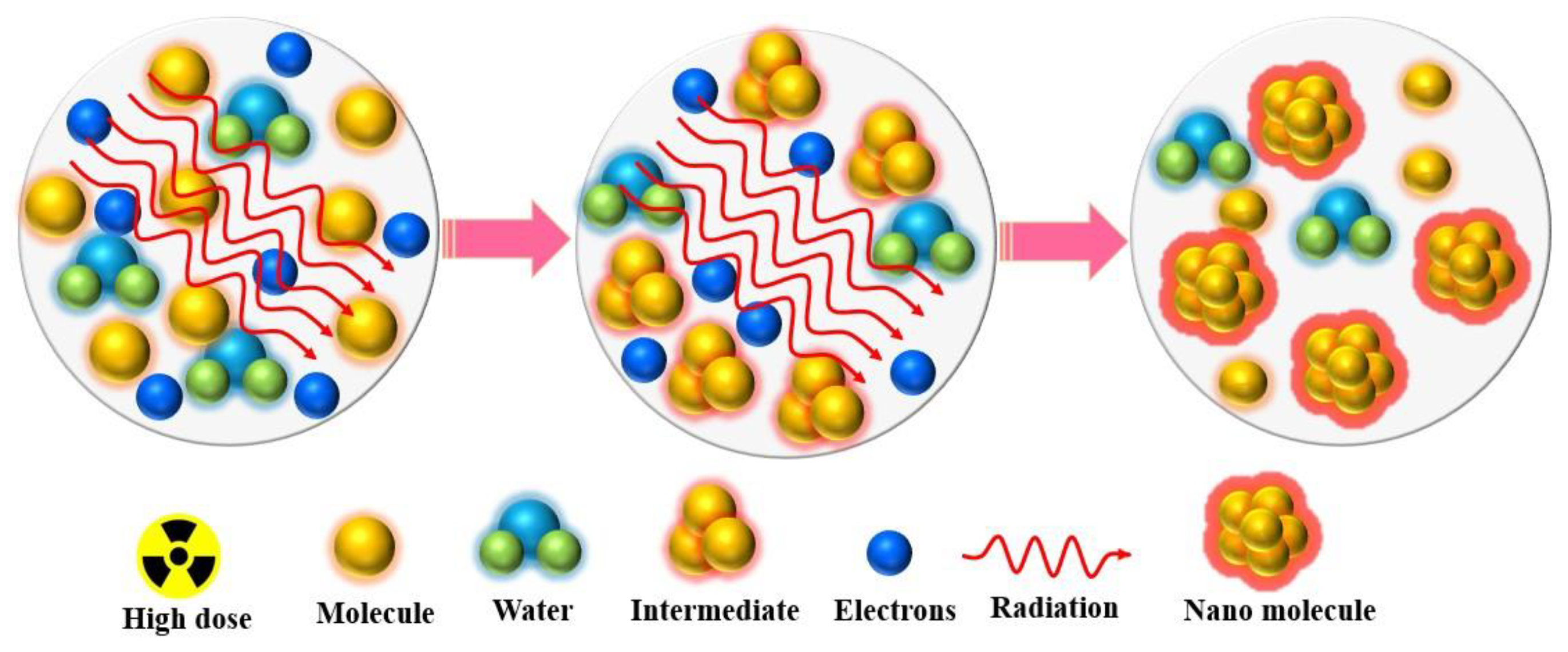
2.2. Gama Radiation Induced Synthesis
2.2.1. Metal Nano Particles and Nanocomposites
2.2.2. Metal Perovskites Nanocomposites
2.2.3. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials
3. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mekuye, B.; Abera, B. Nanomaterials: An overview of synthesis, classification, characterization, and applications. Nano Sel. 2023, 4, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, Z.; Habib, Z.; Chung, S.; Badshah, M. A. Exposure route of TiO2 NPs from industrial applications to wastewater treatment and their impacts on the agro-environment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, H. A Review on nanoparticles: their synthesis and types. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2014, 4, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mhlanga, N.; Mphuthi, N.; Van der Walt, H.; Nyembe, S.; Mokhena, T.; Sikhwivhilu, L. Nanostructures and nanoparticles as medical diagnostic imaging contrast agents: A review. Mater Today Chem. 2024, 40, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrajac, L.; Abbas, A.; Chrzanowski, W.; et al. Nanotechnology for a Sustainable Future: Addressing Global Challenges with the International Network4Sustainable Nanotechnology. ACS Nano. 2021, 15, 18608–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coelho Escobar, C.; Dos Santos, J.H.Z. Effect of the sol-gel route on the textural characteristics of silica imprinted with Rhodamine B. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Min, C.; Hu, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by reduction of HAuCl4 under UV irradiation. Solid State Sci. 2013, 15, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susi, T.; Meyer, J.C.; Kotakoski, J. Quantifying transmission electron microscopy irradiation effects using two-dimensional materials. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 1, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyaneh, M.K.; Paramanik, D.; Varma, S.; Gosavi, S.W.; Kulkarni, S.K. Formation of gold nanoparticles in polymethylmethacrylate by UV irradiation. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 3771–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.-L.; Cao, K.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.; He, L.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, M. Gamma irradiation-induced preparation of graphene–Ni nanocomposites with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Materials 2018, 11, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepi´c, D.P.; Kleut, D.N.; Markovi´c, Z.M.; Bajuk-Bogdanovi´c, D.V.; Pavlovi´c, V.B.; Krmpot, A.J.; Leki´c, M.M.; Jovanovi´c, D.J.; Todorovi´c-Markovi´c, B.M. One-step preparation of gold nanoparticles - exfoliated graphene composite by gamma irradiation at low doses for photothermal therapy applications. Mater. Char. 2021, 173, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Velamakanni, A.; Bozoklu, G.; Park, S.; Stoller, M.; Piner, R.D.; Stankovich, S.; Jung, I.; Field, D.A.; Ventrice, C.A.; Ruoff, R.S. Chemical analysis of graphene oxide films after heat and chemical treatments by X-ray photoelectron and micro-Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 2009, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shen, R.; Liu, S.; et al. Free radical evolution and decay of PAN nanofibers formed by irradiation and thermal stabilization. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 188, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pei, X.; et al. Free radical scavenging behavior of multidimensional nanomaterials in γ-irradiated epoxy resin and mechanical and thermal performance of γ-irradiated composites. Compos Part C: Open Access 2021, 4, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čubová, K.; Čuba, V. Synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles by ionizing radiation – a review. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 169, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Baidak, A.; Yu, Z. Recent advances in green synthesis and modification of inorganic nanomaterials by ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020, 8, 23029–23058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Islam, M.; Hasan, M.K.; Nam, K.-W. A Comprehensive Review of Radiation-Induced Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Multidimensional Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, M.M.; Ansari, I.; Arora, C.; et al. Nanomaterials: A comprehensive review of applications, toxicity, impact, and fate to environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 121046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Islam, M.; Raut, B.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Nam, K.-W. A Comprehensive Review of Functional Gel Polymer Electrolytes and Applications in Lithium-Ion Battery. Gels 2024, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, I.G.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Bezugly, V.; et al. Electron-beam induced synthesis of nanostructures: A review. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11340–11362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Khan, A.M.; Shujait, S.; et al. Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: A review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, P.F.M.; Torresi, R.M.; Emmerling, F.; Camargo, P.H.C. Challenges and opportunities in the bottom-up mechanochemical synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020, 8, 16114–16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Bayer, I.S.; Biris, A.S.; Wang, T.; Dervishi, E.; Faupel, F. Advances in top-down and bottom-up surface nanofabrication: Techniques, applications & future prospects. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2012, 170, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Ghule, N.W.; Bamer, A.H.; Kalaskar, M.G. Metal nanoparticles synthesis: an overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci Technol. 2019, 53, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vu, K.L.; Tran, N.T.T.; Nguyen, D.N.; Nguyen, L.T.T.; Phan, T.D. Application of electron beam irradiation for selenium nanoparticles production using gum Arabic as stabilizer. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 211, 111061. [Google Scholar]
- Afify, T.A.; Ghazy, O.A.; Saleh, H.H.; Ali, Z.I. Efficient in situ synthetic routes of polyaniline/poly(vinyl alcohol)/TiO2 nanocomposites using gamma irradiation. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1153, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.I. Control and modification of nanostructured materials by electron beam irradiation. Quantum Beam Sci. 2021, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA, 2010. Use of Mathematical Modelling in Electron Beam Processing: A Guidebook. IAEA, Austria.
- Grand, J.; Ferreira, S.R.; De Waele, V.; Mintova, S.; Nenoff, T. M. Nanoparticle Alloy Formation by Radiolysis. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2018, 122, 12573–12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, S.; Shall, H.; Thabet Mliki, N. Towards sustainable Nanomaterials: Exploring green synthesis methods and their impact on electrical properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 168, 112872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobashy, M.M.; Sharshir, A.I.; Zaghlool, R.A.; Mohamed, F. Investigating the impact of electron beam irradiation on electrical, magnetic, and optical properties of XLPE/Co3O4 nanocomposites. Sci Rep. 2024, 14, 4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, V.; Ansari, M.M.; Tewari, D.; et al. Cutting-edge advances in tailoring size, shape, and functionality of nanoparticles and nanostructures: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 149, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, H.; Barhoum, A.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; et al. Magnetic nanofibers: unique properties, fabrication techniques, and emerging applications. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 9127–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Singh, P.; Haraz, F.A.; Barhoum, A. Chapter 19 - Biological synthesis of nanoparticles: an environmentally benign approach. In Barhoum A, Hamdy Makhlouf ASBT-F of N, editors. Micro Nano Technol; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 571–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Hammad, E.N.; Mohamed, A.A.; El-Dougdoug, W. A comprehensive review of nanomaterials: types, synthesis, characterization, and applications. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2023, 13, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Barhoum, A.; Rehan, M.; Rahier, H.; Bechelany, M.; Van Assche, G. Seed-mediated hot- injection synthesis of tiny Ag nanocrystals on nanoscale solid supports and reaction mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10551–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
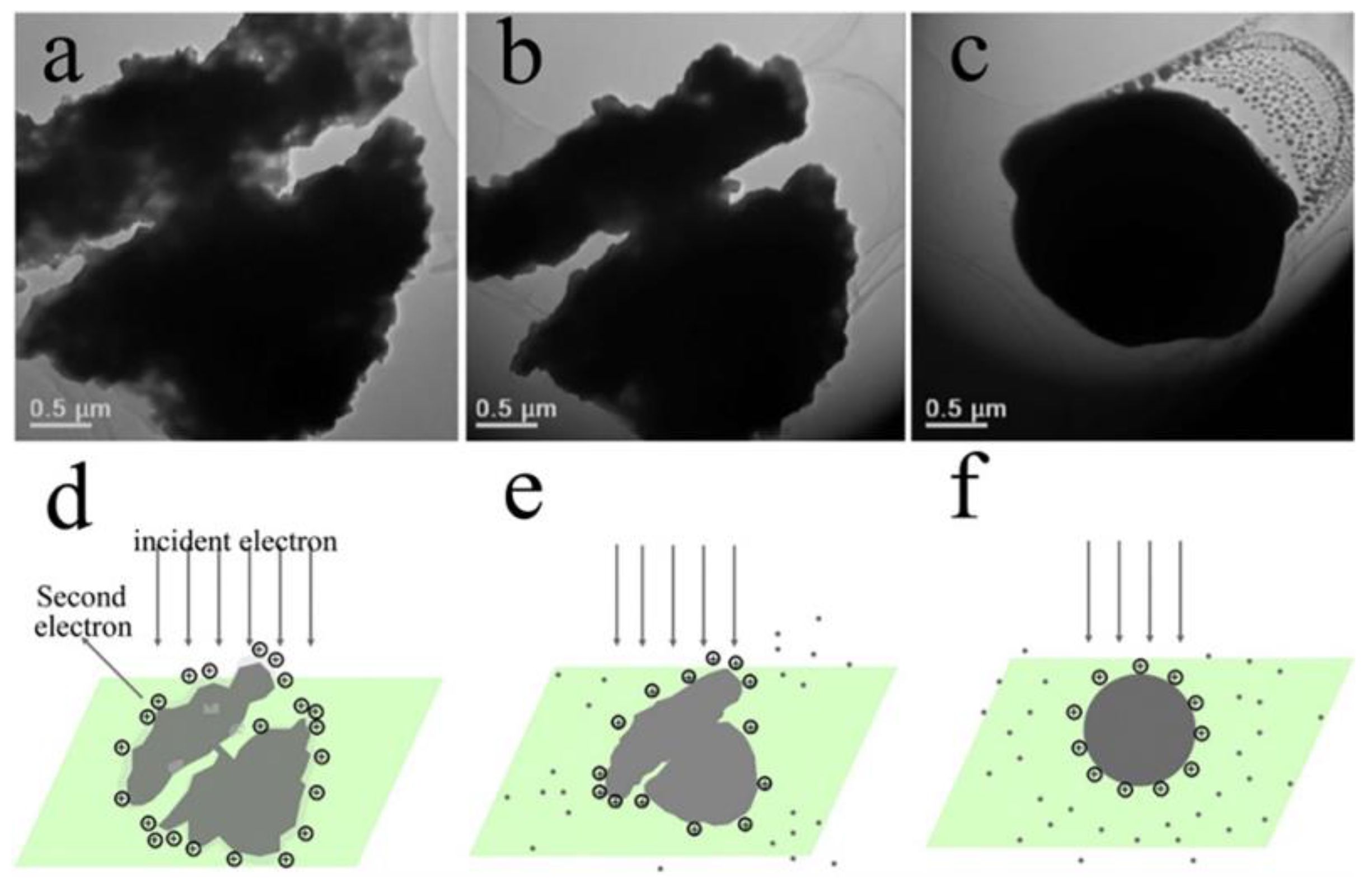
- Egerton, R.F.; Li, P.; Malac, M. Radiation damage in the TEM and SEM. Micron 2004, 35, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Ruckenstein, E. Nano-structured Li2O from LiOH by electronirradiation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 430, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N. Electron beam damage in oxides: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 016501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mel, A.A.; Bittencourt, C. In situ conversion of nanostructures from solid to hollow in transmission electron microscopes using electron beam. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 10876–10884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, I.G.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Bezugly, V.; Kunstmann, J.; Gemming, T.; et al. Electron-beam induced synthesis of nanostructures: A review. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11340–11362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesse, S.; Borisevich, A.Y.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Lupini, A.R.; Rack, P.D.; et al. Directing Matter: Towards Atomic Scale 3D Nanofabrication. ACS Nano 2016, 1, 5600–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazy, O.A.; Saleh, H.H.; Shehata, M.M.; Hosni, H.M.; Ali, Z.I. Electron beam radiation induced solid-state synthesis of gold nanoparticles in polyvinyl alcohol films and their physico-chemical properties. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 191, 109848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Reda, M.M.; Klingner, A. Preparation and characterization of green carboxymethylchitosan (CMCS) - Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) electrospun nanofibers containing gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and its potential use as biomaterials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamunya, Ye.P.; Davydenko, V.V.; Pissis, P.; Lebedev, E.V. Electrical and thermal conductivity of polymers filled with metal powders. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobashy, M. M.; Alkhursani Sh., A.; Alqahtani, H. A.; El-damhougy, T. K.; Madani, M. Gold nanoparticles in microelectronics advancements and biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Engineering: B 2024, 301, 117191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Meng, T.; Yang, X. Au and Au-Based nanomaterials: Synthesis and recent progress in electrochemical sensor applications. Talanta 2020, 206, 120210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.U.; Cha, S.H.; Shin, K.; Jho, J.Y.; Lee, J.C. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Gold(I)−Alkanethiolate Complexes with Supramolecular Structures through Electron Beam Irradiation in TEM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9962–9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jeon, H.C.; Yang, S.M. Unconventional methods for fabricating nanostructures toward high-fidelity sensors. J. Mater Chem. 2012, 22, 5900–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, H.A.; Polman, A. Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Duy, N.; Kim Lan, N.T.; Van Phu, D.; Thuan, N. C.; Quoc, L. A.; Chung, C. V.; Thang, P.P. Study on the preparation of bimetallic silver-copper nanoparticles by electron beam irradiation. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Marchelek, M.; Diak, M.; Grabowska, E. Noble metal-based bimetallic nanoparticles: the effect of the structure on the optical, catalytic and photocatalytic properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 80–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, Y.; Shibata, M.; Kageyama, S.; Seino, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Kugai, J.; Nitani, H.; Yamamoto, T. A. Carbon-supported AuPd bimetallic nanoparticles synthesized by high-energy electron beam irradiation for direct formic acid fuel cell. J Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 2142–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.A.; Nakagawa, T.; Seino, S.; Nitani, H. Bimetallic nanoparticles of PtM (M = Au, Cu, Ni) supported on iron oxide: Radiolytic synthesis and CO oxidation catalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 387, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, J. Nucleation, growth and properties of nanoclusters studied by radiation chemistry: Application to catalysis. Catal. Today. 2006, 113, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Towata, A.; Yasui, K.; et al. Fabrication of nanosized Pt on rutile TiO2 using a standing wave sonochemical reactor (SWSR) - observation of an enhanced catalytic oxidation of CO. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Tsukamoto, D.; Sugano, Y.; Shiro, A.; Ichikawa, S.; Tanaka, S.; Hirai, T. Platinum Nanoparticles Supported on Anatase Titanium Dioxide as Highly Active Catalysts for Aerobic Oxidation under Visible Light Irradiation. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, S.; Sugano, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; et al. Pt/TiO2 composite nanoparticles synthesized by electron beam irradiation for preferential CO oxidation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Călinescu, I.; Martin, D.; Ighigeanu, D.; et al. Nanoparticles synthesis by electron beam radiolysis. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2014, 12, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.; Biswal, J.; Dhamgaye, V.P.; Lodha, G.S.; Sabharwal, S. A comparative study of gamma, electron beam, and synchrotron X-ray irradiation method for synthesis of silver nanoparticles in PVP. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2013, 4, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, I.; Stancu, E.; Mitu, C.M.; Marinescu, V.; Lungulescu, E.M.; Nicula, N.O. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded in Micro-Hydrogel Particles by Electron Beam Irradiation. Chem. Proc. 2022, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, C.; Zou, Y.; Dong, H.; et al. Unveiling the Switching Riddle of Silver Tetracyanoquinodimethane Towards Novel Planar Single Crystalline Electrochemical Metallization Memories. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7094–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, H.; Tamura, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Hosaka, S. Nano-dots formation on silver sulphide surface using electron beam irradiation. Microelectron Eng. 2006, 83, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; O’Hayre, R.; Prinz, F.B.; Gür, T.M. Electrochemical nanopatterning of Ag on solid-state ionic conductor RbAg4I5 using atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3552–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Tsuruoka, T.; Terabe, K.; Gimzewski, J.K.; et al. (2011) Short-term plasticity and long-term potentiation mimicked in single inorganic synapses. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; Liu, Z.G. Electric switching and memory devices made from RbAg4I5 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 22508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
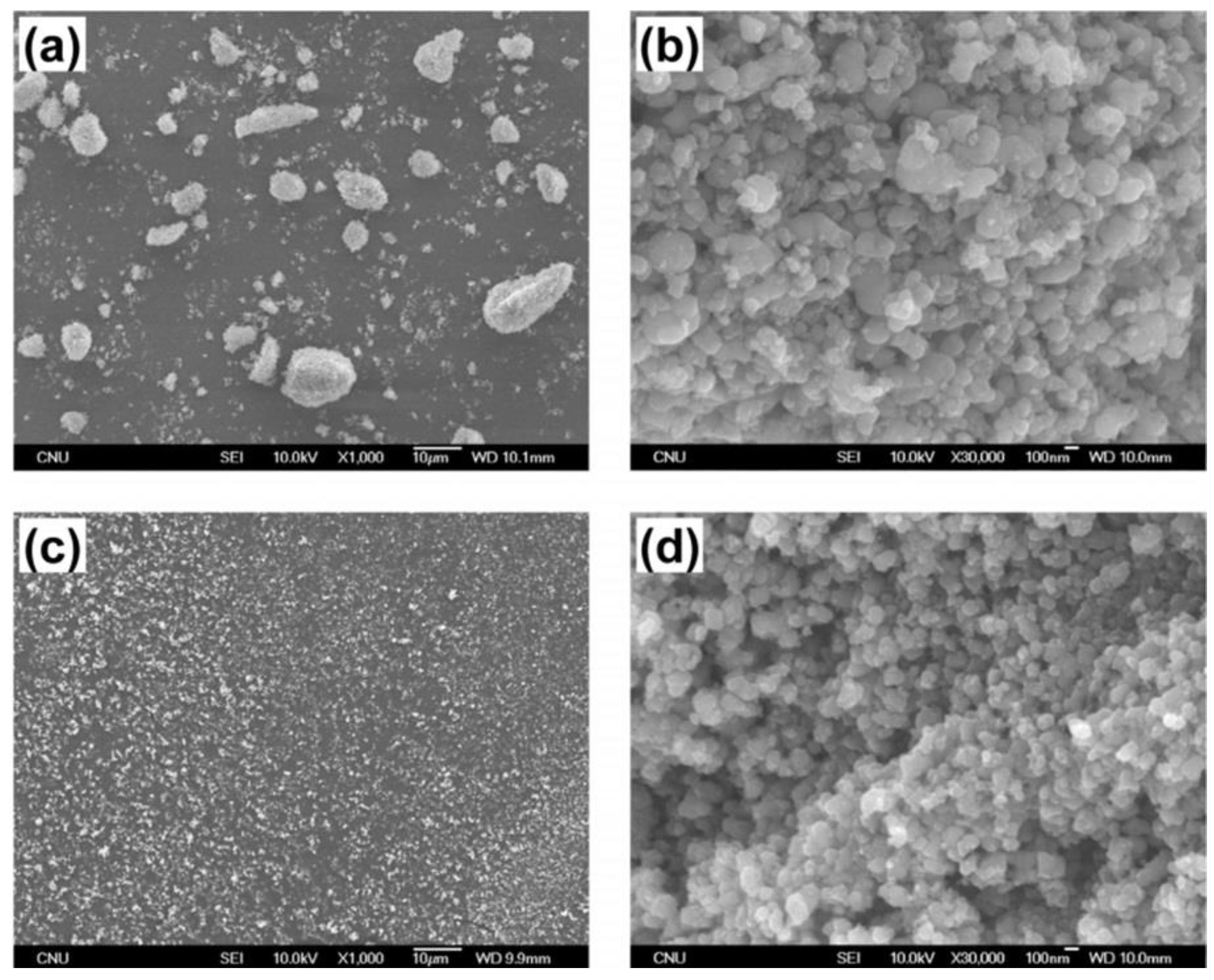
- Bogle, K.A.; Dhole, S.D.; Bhoraskar, V.N. Silver nanoparticles: synthesis and size control by electron irradiation. Nanotechnol. 2006, 17, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, J. Nucleation, growth and properties of nanoclusters studied by radiation chemistry: Application to catalysis. Catal. Today 2006, 113, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, J.; Mostafavi, M.; Remita, H.; Marignier, J.L.; Marie, O.D. Radiationinduced synthesis of mono- and multi-metallic clusters and nanocolloids. New J. Chem. 1998, 22, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henglein, A. Physicochemical properties of small metal particles in solution: "microelectrode" reactions, chemisorption, composite metal particles, and the atom-to-metal transition. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 5457–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
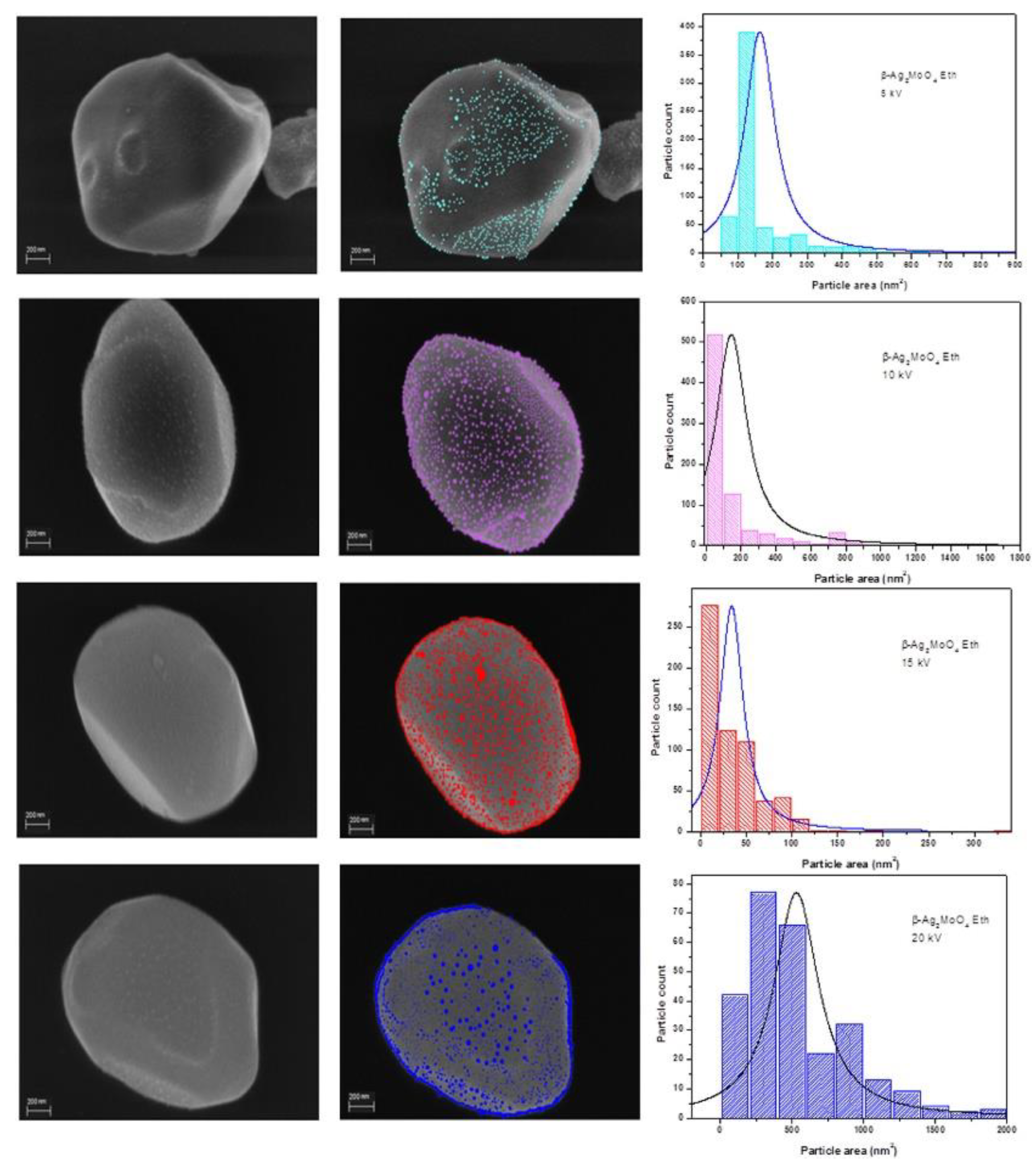
- Longo, E.; Cavalcante, L.S.; Volanti, D.P.; Gouveia, A.F.; Longo, V.M.; et al. Direct in situ observation of the electron-driven synthesis of Ag filaments on α-Ag2WO4 crystals. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, J.; Ferrer, M.M.; Gracia, L.; Beltran, A.; Longo, V.M.; et al. A combined experimental and theoretical study on the formation of Ag filaments on β-Ag2MoO4 induced by electron irradiation. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, M.T.; Saliby, C.; Rios, L.R.; La Porta, F.A.; Gracia, L.; et al. Identifying and rationalizing the morphological, structural, and optical properties of beta Ag2MoO4 microcrystals, and the formation process of Ag nanoparticles on their surfaces: combining experimental data and first-principles calculations. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, R.C.; Assis, M.; Teixeira, M.M.; da Silva, M.D.P.; Li, M.S.; et al. An Experimental and Computational Study of β-AgVO3: Optical Properties and Formation of Ag Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 12254–12264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, G.; Sczancoski, J.C.; Andres, J.; Gracia, L.; Longo, E. Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Structure, Optical Properties, and Growth of Metallic Silver Nanostructures in Ag3PO4. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 6293–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, M.T.; Gracia, L.; Silva, G.S.; Santos, L.P.S.; Andrés, J.; et al. Understanding the formation and growth of Ag nanoparticles on silver chromate induced by electron irradiation in electron microscope: A combined experimental and theoretical study. J Solid State Chem. 2016, 239, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, E.; Volanti, D.P.; Longo, V.M.; Gracia, L.; Nogueira, I.C.; et al. Toward an Understanding of the Growth of Ag Filaments on α-Ag2WO4 and Their Photoluminescent Properties: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, J.; Gracia, L.; Gonzalez-Navarrete, P.; Longo, V.M.; Avansi, W.; et al. Structural and electronic analysis of the atomic scale nucleation of Ag on α-Ag2WO4 induced by electron irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, P.; et al. Electronic Reconstruction of α-Ag2WO4 Nanorods for Visible-Light Photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7256–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; et al. Photocatalytic activity of Ag2MO4 (M = Cr, Mo, W) photocatalysts. J. Mater Chem. A 2015, 3, 20153–20166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Janáky, C.; Samu, G.F.; Huda, M.N.; Sarker, P.; et al. Time- and Energy-Efficient Solution Combustion Synthesis of Binary Metal Tungstate Nanoparticles with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2015, 8, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, A.; Priyanka, K.P.; Babitha, K.K.; Ganesh, S.; Vargheses, T. Influence of electron beam irradiation on structural and optical properties of α-Ag2WO4 nanoparticles. Micron 2016, 88, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dukes, K.D.; Christensen, K. A.; Chumanov, G. Core-shell silver nanoparticles for optical labeling of cells. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 458, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, F.; Loessl, M.; Baeumner, A.J. Signaling strategies of silver nanoparticles in optical and electrochemical biosensors: considering their potential for the point-of-care. Mikrochim. Acta. 2023, 190, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.-W.; Zheng, Y.-S.; Sun, Y.-S.; Cheng, Y.-C. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectroscopy on localized silver nanoparticle-decorated porous silicon substrate. Analyst 2021, 146, 7645–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. In-situ synthesis of Ag nanoparticles by electron beam irradiation. Mater Charact. 2015, 110, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, N.; Su, J.; Li, L.; Gao, Y. Fabrication of nanoscale Ga balls via a Coulomb explosion of microscale silica-covered Ga balls by TEM electron-beam irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, C.; Quan, Z.; et al. One-step aqueous solvothermal synthesis of In2O3 nanocrystal. Cryst Growth Des. 2008, 8, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neng, W.; Sun, L.T.; Hu, X. H.; et al. Charge supported growth and super plasticity of sodium nanostructures. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 3899–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.I.; Zhao, Y.P.; Wang, G.C.; Lu, T.M. Novel growth mechanism of single crystalline Cu nanorods by electron beam irradiation. Nanotechnol. 2004, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, M.Y.; Chiu, C.W.; Chen, F.R.; Kai, J.J.; Lee, C.Y.; et al. Convergent Electron Beam Induced Growth of Copper Nanostructures: Evidence of the Importance of a Soft Template. Langmuir 2004, 20, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.A.; Edmondson, M.J.; Edwards, P.P.; Gameson, I.; Meadows, P.J.; et al. Production of Ultrafine Single-Crystal Copper Wires through Electron Beam Irradiation of Cu-containing Zeolite X. J. Inorg. General Che. 2005, 631, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, S.K.; Gottapu, S.N.; Krishna, M.G. Electron-beam irradiation induced transformation of Cu2(OH)3NO3 nanoflakes into nanocrystalline CuO. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11194–11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanavel, T.; Möbus, G. In-situ cobalt nanocrystal synthesis by intense electron beams in TEM. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2012, 371, 012047. [Google Scholar]
- Assis, M.; Macedo, N. G.; Machado, T. R.; Ferrer, M. M.; Gouveia, A. F.; et al. Laser/Electron Irradiation on Indium Phosphide (InP) Semiconductor: Promising Pathways to In Situ Formation of Indium Nanoparticles. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1800237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Angel, P.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.H.; Garcia-Borquez, A.; de la Fuente, J.A.M. Nucleation and growth of Ni0 nanoparticles and thin films by TEM electron irradiation. Catal. Today 2013, 212, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Feng, Y.; Dou, Y.; Tang, H.; Ding, D.; et al. Effect of electron irradiation on Ti3AlC2. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Eom, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, S.S. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles induced by electron beam irradiation and their electrochemical performance as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.I.G.; Gemming, T.; Mendes, R.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Bezugly, V.; et al. In-situ Quasi-Instantaneous e-beam Driven Catalyst-Free Formation of Crystalline Aluminum Borate Nanowires. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichert, J.A.; Tong, Y.; Mutz, N.; Vollmer, M.; Fischer, S.; et al. Quantum Size Effect in Organometal Halide Perovskite Nanoplatelets. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6521–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Men, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Bhattacharjee, U.; et al. Shape Evolution and Single Particle Luminescence of Organometal Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2948–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Wong, A.B.; Yu, Y.; Lai, M.; Kornienko, N.; et al. Atomically thin two dimensional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites. Sci. 2015, 349, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Di Stasio, F.; Dang, Z.; Canale, C.; Khan, A.H.; et al. Colloidal Synthesis of Strongly Fluorescent CsPbBr3 Nanowires with Width Tunable down to the Quantum Confinement Regime. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6450–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, J.; Dang, Z.; Bianchini, P.; Canale, C.; Di Stasio, F.; et al. Colloidal Synthesis of Quantum Confined Single Crystal CsPbBr3 Nanosheets with Lateral Size Control up to the Micrometer Range. J Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7240–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Kang, K.; Yang, S.I. Controlled growth of bismuth nanoparticles by electron beam irradiation in TEM. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, G.S.; Elizondo, V.N.; Ferrer, D.; Torres, C.A.; Gao, X.; et al. In situ formation of bismuth nanoparticles through electron-beam irradiation in a transmission electron microscope. Nanotechnol. 2007, 18, 335–604. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Qi, Q.; Gondal, M.A.; Rashid, S.G.; et al. Insights into the growth of bismuth nanoparticles on 2D structured BiOCl photocatalysts: an in-situ TEM investigation. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 15888–15896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
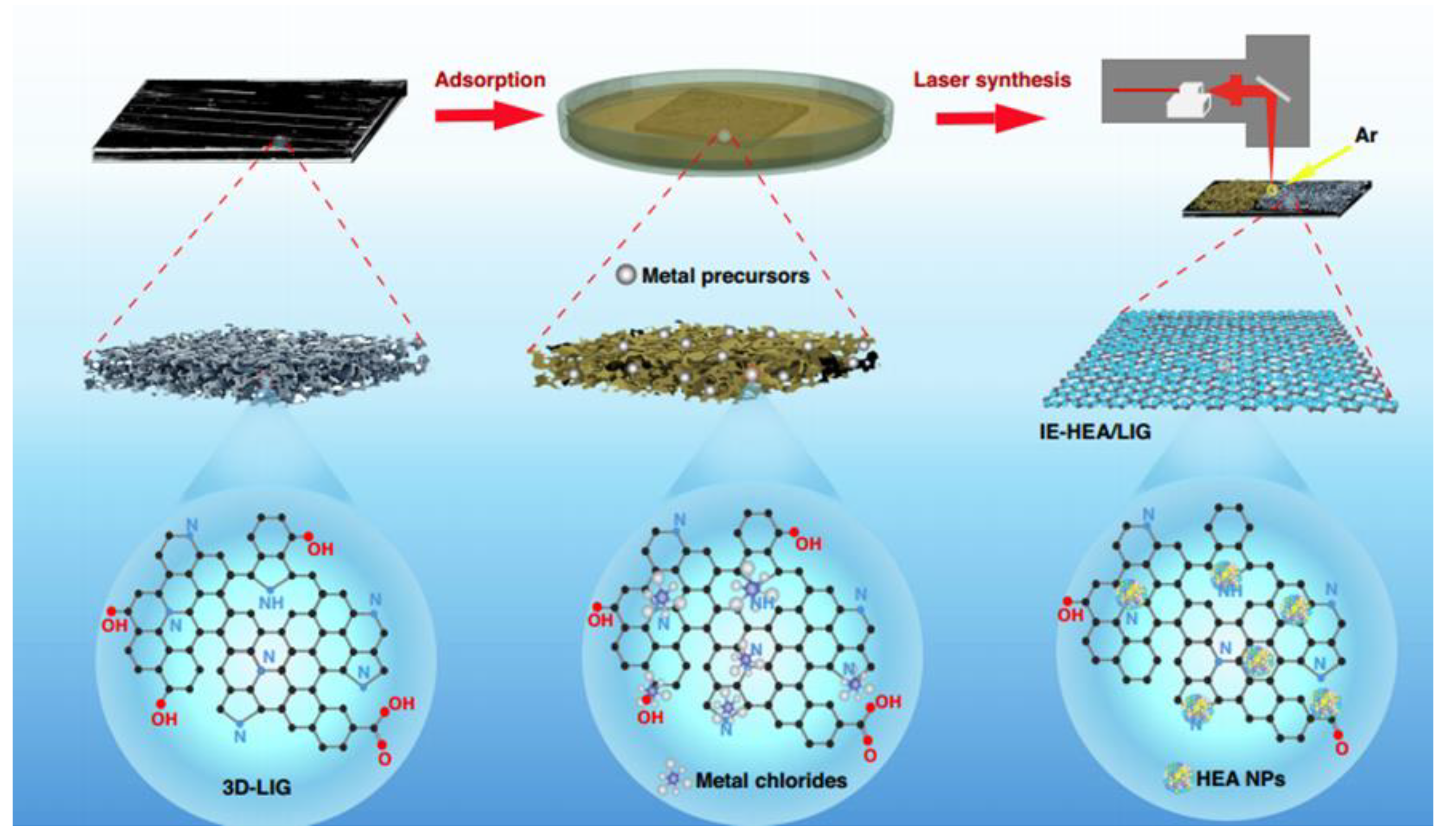
- Liu, Z. Laser solid-phase synthesis of graphene shell-encapsulated high-entropy alloy nanoparticles. Light Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boostani, A.F.; Yazdani, S.; Mousavian, R.T.; Tahamtan, S.; Khosroshahi, R.A.; Wei, D.; et al. Strengthening mechanisms of graphene sheets in aluminium matrix nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Liang, Y. Effects of atomic oxygen exposure on the tribological performance of ZrO2 reinforced polyimide nanocomposites for low earth orbit space applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 77, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.; Budholiya, S.; Raj, S.A.; et al. Review on nanocomposites based on aerospace applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Song, P.; Yu, B.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H. Flame retardant polymeric nanocomposites through the combination of nanomaterials and conventional flame retardants. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 114, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, M.; Fathy, E.S.; Sharaf, A. Effect of gamma irradiation on properties of the synthesized PANI-Cu nanoparticles assimilated into PS polymer for electromagnetic interference shielding application. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N.; Arora, S. Exploring the impact of gamma rays and electron beam irradiation on physico-mechanical properties of polymers & polymer composites: A comprehensive review. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact with Mater. Atoms, 2024, 549, 165297. [Google Scholar]
- Naikwadi, A.T.; Sharma, B.K.; Bhatt, K.D.; Mahanwar, P.A. Gamma Radiation Processed Polymeric Materials for High Performance Applications: A Review. Front Chem. 2022, 10, 837111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, E.; Taha, E.O.; Lotfy, S.; Anwar, A. Influence of Gamma irradiation on shape memory polymer nanocomposite for satellite deployment mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladjouzi, S.; Guerbous, L. Gamma–radiation synthesis and characterization of nanocomposite hydrogels based on poly(vinyl-alcohol)/zirconium NPs/ europium, Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2024, 215, 111349. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoreishian, S.M.; Kang, S.M.; Seeta Rama Raju, G.; et al. γ-Radiolysis as a highly efficient green approach to the synthesis of metal nanoclusters: A review of mechanisms and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1390–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhindawy, I.G.; Sayyed, M.I.; Almuqrin, A.H.; Mahmoud, K.A. Optimizing gamma radiation shielding with cobalt-titania hybrid nanomaterials. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsani, R.N.; Gareso, P.L.; Tahir, D. An overview of gamma radiation shielding: Enhancements through polymer-lead (Pb) composite materials. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2024, 218, 111619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.; Mackeyev, Y.; Krishnan, S. Radiolabeled nanomaterial for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics: principles and concepts. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taihua Li, H.; Gyu, P.; Seong-Ho, C. γ -Irradiation-induced preparation of Ag and Au nanoparticles and their characterizations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 105, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, J.; Tan, Y.; et al. Method for preparing silver nanopowder in aqueous solution by 60Co-γ -ray radiation reduction. Patent CN 101,612,670, 2009. p. 6.
- Kepić, D.P.; Stefanović, A.M.; Budimir, M.D.; et al. Gamma rays induced synthesis of graphene oxide/gold nanoparticle composites: structural and photothermal study. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 202, 110545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, I.L.; Tarakina, N.V.; Hermansson, A.; Bigum, L.; Widerberg, R.; Andersson, M.S.; Mathieu, R.; Paulraj, A.R.; Kiros, Y. Radiation-induced synthesis of nanoscale Co- and Ni-based electro-catalysts on carbon for the oxygen reduction reaction. Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 9995–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Johansson, M.; Wiorek, A.; et al. Gamma-radiation induced synthesis of freestanding nickel nanoparticles. Dalt. Trans. 2021, 50, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
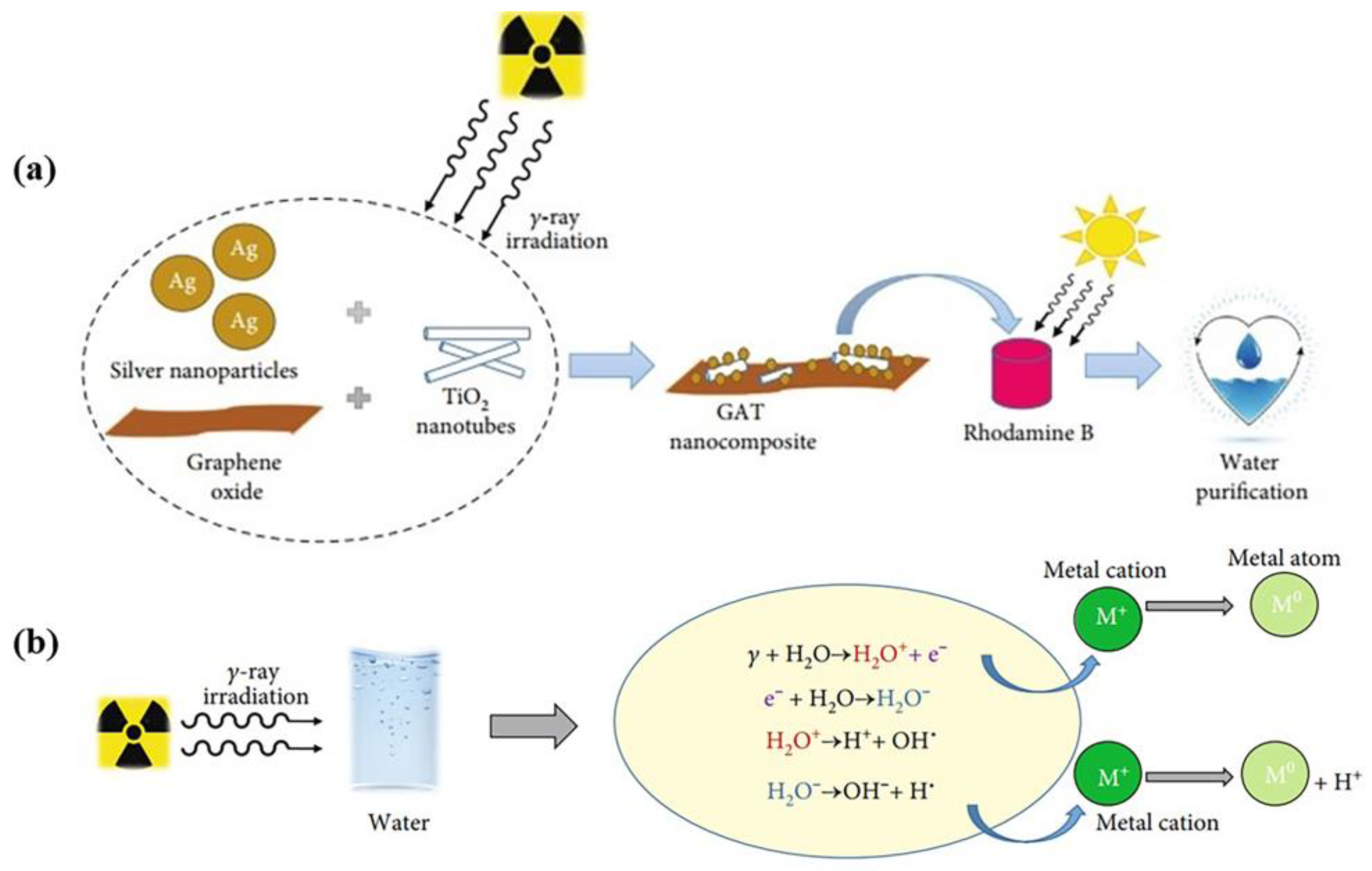
- Vu, D.K.N.; Nguyen, D.K.V. Gamma Irradiation-Assisted Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticle-Embedded Graphene Oxide-TiO2 Nanotube Nanocomposite for Organic Dye Photodegradation. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 679637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
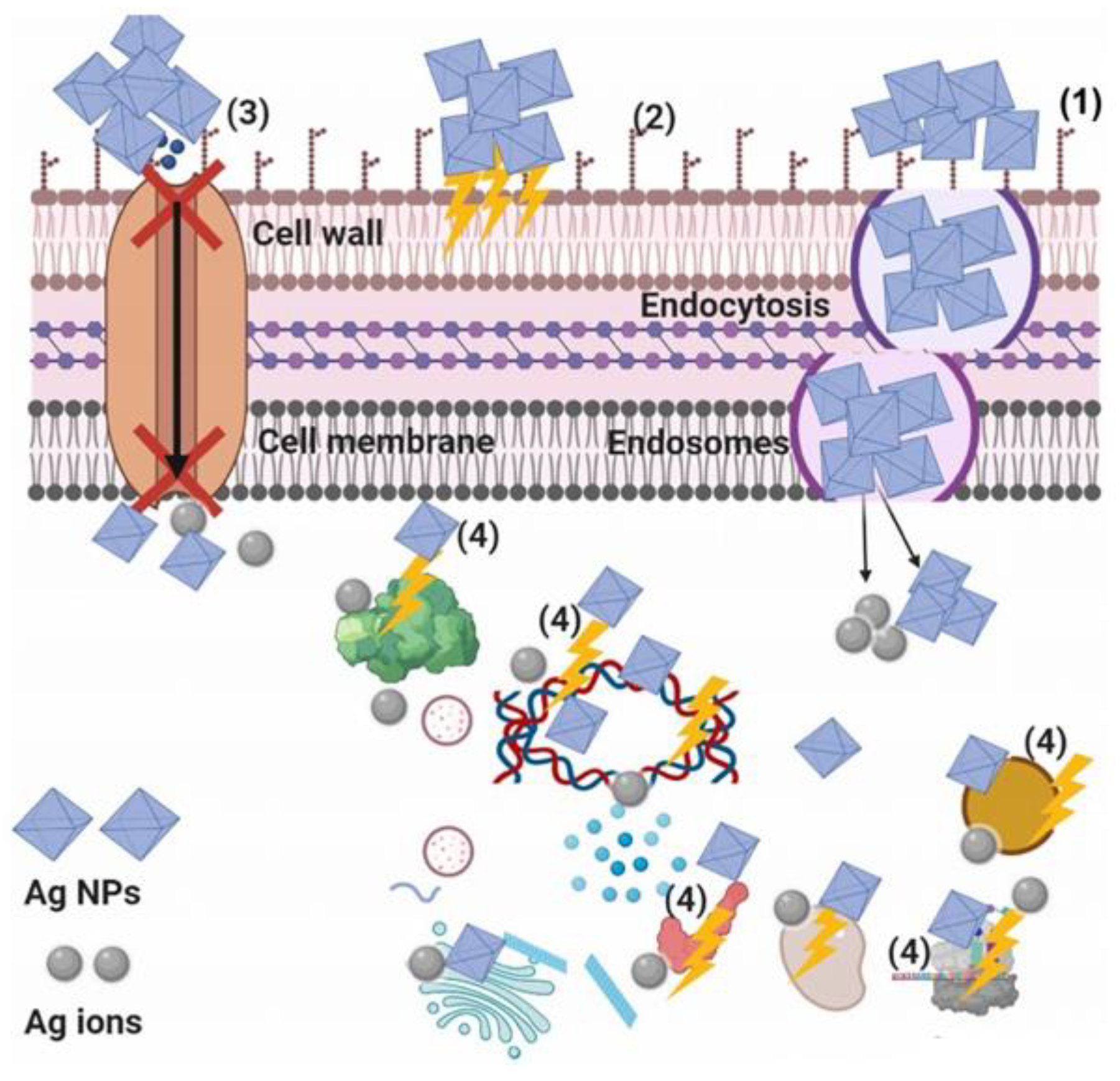
- Bekhit, M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Sokary, R. Gamma Radiation-Induced Synthesis and Characterization of Decahedron-Like Silver Nanostructure and Their Antimicrobial Application. J Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023, 33, 2906–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M. B.; Abdel-Kader, M.H. Effect of annealed ZnS nanoparticles on the structural and optical properties of PVA polymer nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 241, 122285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugumaran, S.; Bellan, C.S.; Nadimuthu, M. Characterization of composite PVA–Al2O3 thin films prepared by dip coating method. Iran. Polym. J. 2015, 24, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, H.; Yi, Z.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; et al. Enhanced photocatalytic performance and mechanism of Au@CaTiO3 composites with Au nanoparticles assembled on CaTiO3 nanocuboids. Micromachines 2019, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
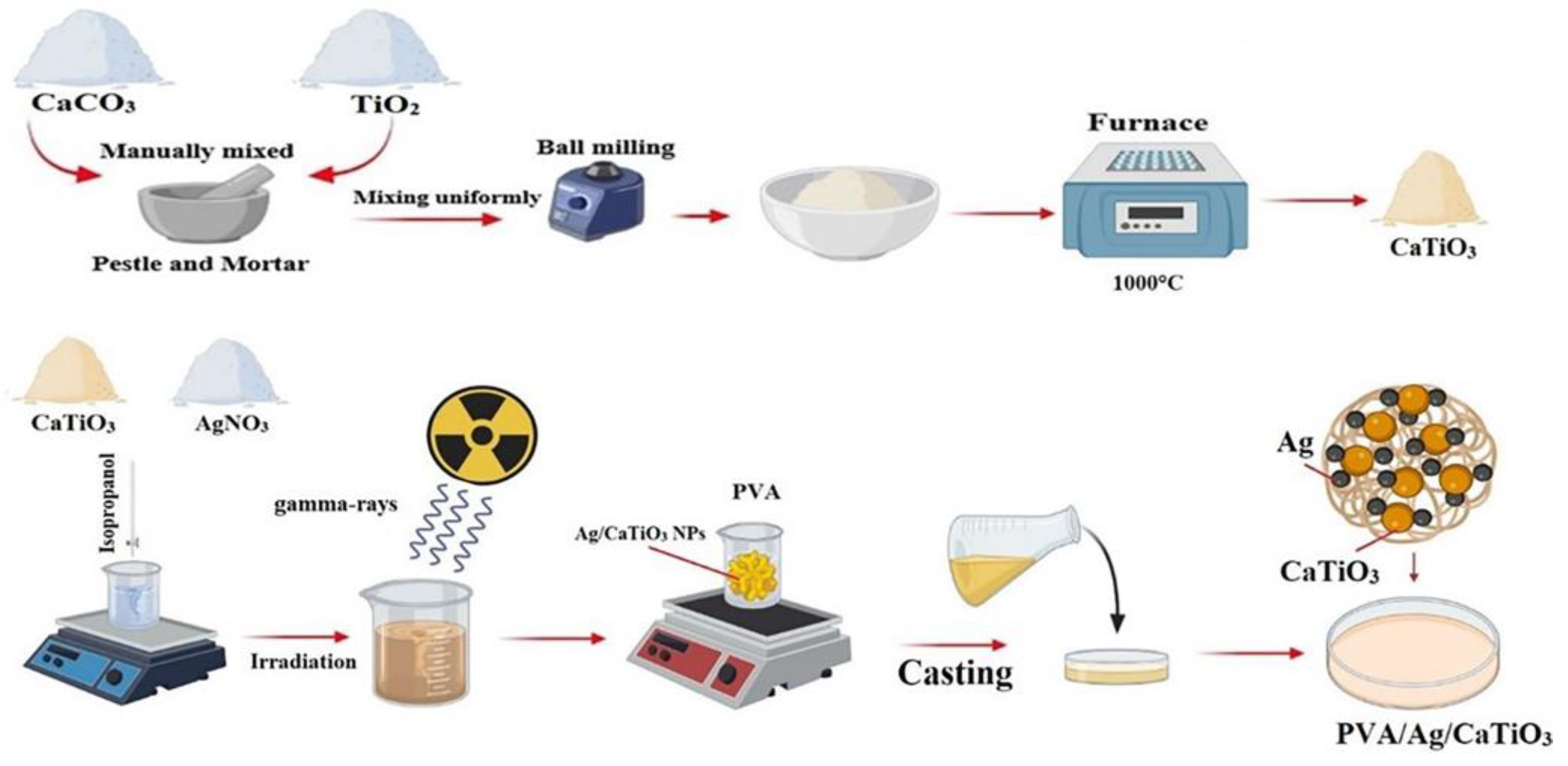
- Abdel Maksoud, M.I.A.; Abdelhaleem, S.; Tawfik, E.K.; Awed, A.S. Gamma radiation-induced synthesis of novel PVA/Ag/CaTiO3 nanocomposite film for flexible optoelectronics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meera, K.; Ramesan, M.T. Performance of boehmite nanoparticles reinforced carboxymethyl chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol blend nanocomposites tailored through green synthesis. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesan, M.T.; Anjitha, T.; Parvathi, K.; et al. Nano zinc ferrite fller incorporated polyindole/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend: Preparation, characterization, and investigation of electrical properties. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M. J.; et al. XCOM: Photon cross section database (Version 1.5). National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD http://physics.nist.gov/xcom.
- Hubbell, J.H. Review of photon interaction cross section data in the medical and biological context. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, R1–R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbell, J.H. Review and history of photon cross section calculations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, R245–R262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filak-Mędoń, K.; Fornalski, K.W.; Bonczyk, M.; et al. Graphene-based nanocomposites as gamma- and X-ray radiation shield. Sci Rep. 2024, 14, 18998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




