Submitted:
13 November 2024
Posted:
15 November 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Cachexia is a complex multiorgan syndrome associated with various chronic diseases, characterized by anorexia and increased tissue wasting in the context of chronic inflammation. A specific form of this syndrome, known as cancer cachexia (CC), occurs alongside different types of tumors. The pathogenesis of CC is multifactorial, with inflammatory mediators and hormones released by either the tumor or the host identified as key drivers of the peripheral catabolic process through several direct mechanisms. Accumulating evidence indicates that the central nervous system (CNS) is also recognized as an integral component in the pathogenesis of CC. Hypothalamus has emerged as a critical brain area that senses and amplifies peripheral stimuli, generating an inappropriate neuronal signaling, leading to deregulation of feeding behavior and impaired control of energy homeostasis. Circulating cytokines may act in concert with hormones and neurotransmitters and perturbate the hypothalamic melanocortin system, shifting its activity towards the anorexigenic pathway and increase energy expenditure. The purpose of this review is to provide insights on the potential mechanisms mediating the hypothalamic inflammation in the context of anorexia and cachexia associated with cancer.
Keywords:
1. Methods
2. Introduction
3. Cytokines Signaling in the Brain
4. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1/Growth differentiation factor-15 (MIC-1, GDF-15)
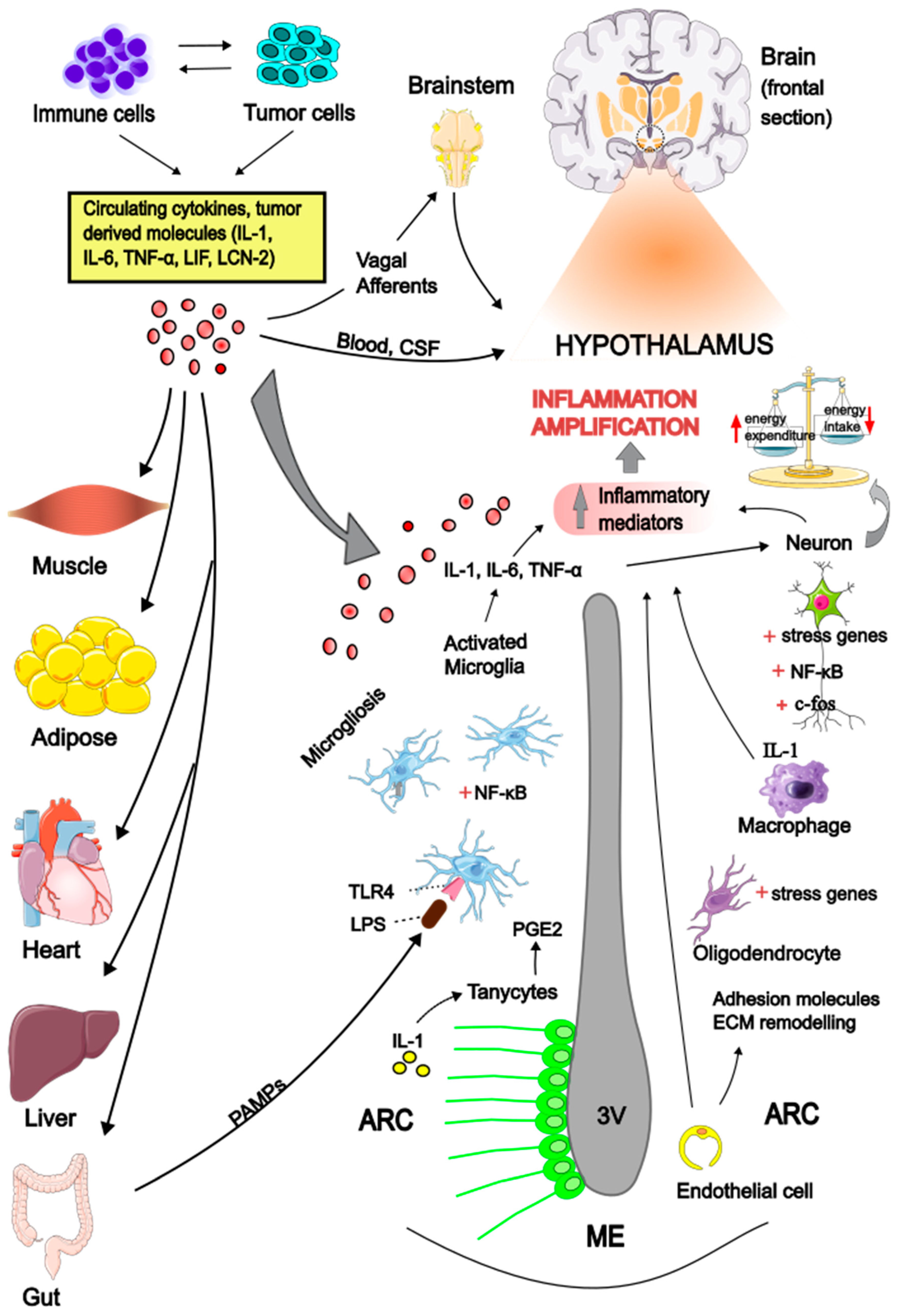
4.1. Hypothalamic Inflammation
4.2. Inflammatory Signals Across the Gut-Brain Axis
4.3. The Role of Hypothalamic Microglia
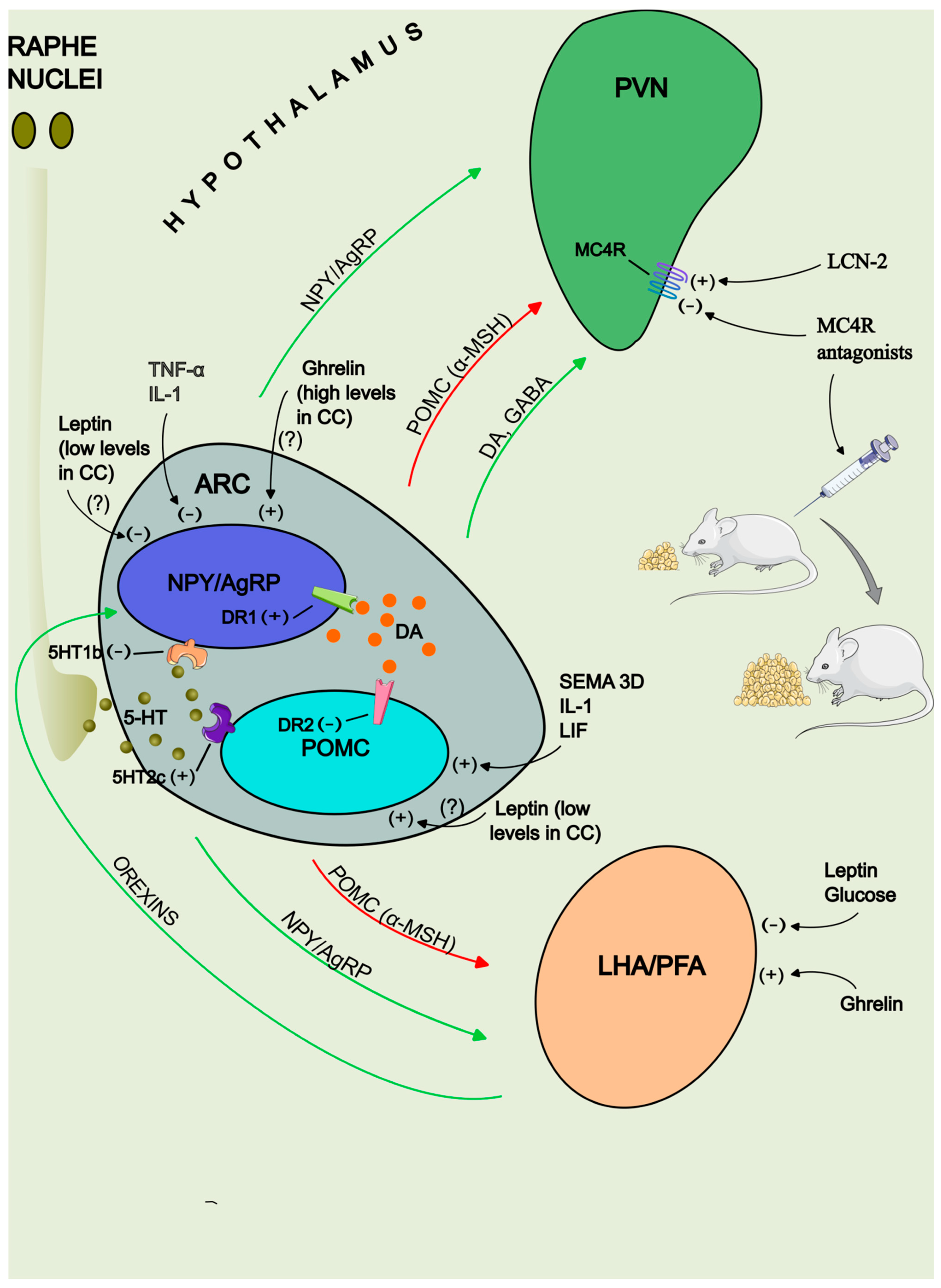
4.4. The Melanocortin System
5. Neurotransmitters Implicated in Energy Balance
5.1. NPY
5.2. 5-hydroxytryptamine
5.3. Dopamine
5.4. Orexins
5.5. Nesfatin-1
6. Peripheral Hormone Signals: Leptin and Ghrelin
Neuroendocrine and Autonomic Regulation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Declarations
Conflicts of Interest
References
- L. Koppe, D. Fouque, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, Kidney cachexia or protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease: facts and numbers. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 10, 479-484 (2019).
- S.D. Anker, A.J. Coats, Cachexia in heart failure is bad for you. Eur. Heart J. 19, 191e3 (1998).
- M.L.N. McDonald, E.F.M. Wouters, E. Rutten, R. Casaburi, S.I. Rennard, M. Bamman, B. Celli, A. Agusti, R. Tal-Singer, C.P. Hersh, M. Dransfield, E.K. Silverman, It’s more than low BMI: prevalence of cachexia and associated mortality in COPD. Respir. Res. 20, 100 (2019).
- K. Mulligan, V.W. Tai, M. Schambelan, Cross-sectional and longitudinal evaluation of body composition in men with HIV infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 15, 43e8 (1997).
- M.J. Tisdale, Biology of cachexia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 89, 1763-1773 (1997).
- M.J. Tisdale, Cachexia in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 862-871 (2002).
- W.J. Evans, J.E. Morley, J. Argiles, C. Bales, V. Baracos, D. Guttridge, A. Jatoi, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, H. Lochs, G. Mantovani, D. Marks, W.E. Mitch, M. Muscaritoli, A. Najand, P. Ponikowski, F. Rossi Fanelli, M. Schambelan, A. Schols, M. Schuster, D. Thomas, R. Wolfe, S.D. Anker, Cachexia: a new definition. Clin. Nutr. 27, 793–799 (2008).
- R.D. Cone, M.A. Cowley, A.A. Butler, W. Fan, D.L. Marks, M.J. Low, The arcuate nucleus as a conduit for diverse signals relevant to energy homeostasis. Int. J. Obesity 25, S63–S67 (2001).
- R.D. Cone, Anatomy and regulation of the central melanocortin system, Nat. Neurosci. 8, 571–578 (2005).
- A. Laviano, A. Inui, D.L. Marks, M.M. Meguid, C. Pichard, F. Rossi Fanelli, M. Seelander, Neural control of the anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 295, E1000-1008 (2008).
- M. Petruzzelli, M. Schweiger, R. Schreiber, R. Campos-Olivas, M. Tsoli, J. Allen, M. Swarbrick, S. Rose-John, M. Rincon, G. Robertson, R. Zechner, E.F. Wagner, A switch from white to brown fat increases energy expenditure in cancer-associated cachexia. Cell Metab. 20, 433–447 (2014).
- R. Suriben, M. Chen, J. Higbee, J. Oeffinger, R. Ventura, B. Li, K. Mondal, Z. Gao, D. Ayupova, P. Taskar, D. Li, S.R. Starck, H.H. Chen, M. McEntee, S.D. Katewa, V. Phung, M. Wang, A. Kekatpure, D. Lakshminarasimhan, A. White, A. Olland, R. Haldankar, M.J. Solloway, J.Y. Hsu, Y. Wang, J. Tang, D.A. Lindhout, B.B. Allan, Antibody-mediated inhibition of GDF15–GFRAL activity reverses cancer cachexia in mice. Nat. Med. 26, 1264-1270 (2020).
- N. Fujitsuka, A. Asakawa, Y. Uezono, K. Minami, T. Yamaguchi, A. Niijima, T. Yada, Y. Maejima, U. Sedbazar, T. Sakai, T. Hattori, Y. Kase, A. Inui, Potentiation of ghrelin signaling attenuates cancer anorexia-cachexia and prolongs survival. Transl. Psychiatry 1, e23 (2011).
- A. Martin, J. Castells, V. Allibert, A. Emerit, C. Zolotoff, V. Cardot-Ruffino, Y.S. Gallot, B. Vernus, V. Chauvet, L. Bartholin, L. Schaeffer, A.C. Durieux, C. Hourdé, F.B. Favier, L. Mazelin, D. Freyssenet, Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation and glucocorticoid-responsive gene expression in skeletal muscle and liver of Apc mice. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13, 1686-1703 (2022).
- Y. Suda, K. Nakamura, F. Matsuyama, Y. Hamada, H. Makabe, M. Narita, Y. Nagumo, T. Mori, N. Kuzumaki, M. Narita, Peripheral-central network analysis of cancer cachexia status accompanied by the polarization of hypothalamic microglia with low expression of inhibitory immune checkpoint receptors. Mol Brain 17, 20. (2024).
- N. Nunn, M. Womack, C. Dart, R. Barrett-Jolley, Function and pharmacology of spinally-projecting sympathetic pre-autonomic neurones in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 9, 262-277. (2011).
- A.G. Watts, S.E. Kanoski, G. Sanchez-Watts, W. Langhans, The physiological control of eating: signals, neurons, and networks. Physiol. Rev. 102, 689-813 (2022).
- G. Mantovani, A. Macciò, L. Mura, E. Massa, M.C. Mudu, C. Mulas, M.R. Lusso, C. Madeddu, A.J. Dessì, Serum levels of leptin and proinflammatory cytokines in patients with advanced –stage cancer at different sites, Mol. Med. 78, 554-561 (2000).
- J. Pfitzenmaier, R. Vessella, C.S. Higano, J.L. Noteboom, D. Wallace Jr, E. Corey, Elevation of cytokine levels in cachectic patients with prostate carcinoma. Cancer 97, 1211-1216 (2003).
- M. Krzystek-Korpacka, M. Matusiewicz, D. Diakowska, K. Grabowski, K. Blachut, I. Kustrzeba-Wojcicka, T. Banas, Impact of weight loss on circulating IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-alpha, VEGF-A, VEGF-C and midkine in gastroesophageal cancer patients. Clin. Biochem. 40, 1353-1360 (2007).
- C. Scheede-Bergdahl, H.L. Watt, B. Trutschnigg, R.D. Kilgour, A. Haggarty, E. Lucar, A. Vigano, Is IL-6 the best pro-inflammatory biomarker of clinical outcomes of cancer cachexia? Clin. Nutr. 31, 85-88 (2012).
- L. Lerner, T.G. Hayes, N. Tao, B. Krieger, B. Feng, Z. Wu, R. Nicoletti, M.I. Chiu, J. Gyuris, J.M. Garcia, Plasma growth differentiation factor 15 is associated with weight loss and mortality in cancer patients. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 6, 317-324 (2015).
- Y.C. Hou, C.J. Wang, Y.J. Chao, H.Y. Chen, H.C. Wang, H.L. Tung, J.T. Lin, Y.S. Shan, Elevated Serum Interleukin-8 Level Correlates with Cancer-Related Cachexia and Sarcopenia: An Indicator for Pancreatic Cancer Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 7, 502 (2018).
- W.A. Banks, J.L. Lynch, O. Tulin O. Price, in The Neuroimmunological Basis of Behavior and Mental Disorder, ed. by A. Siegel, S.S. Zalcman (Springer New York, 2009), p.3.
- V. Prevot, B. Dehouck, A. Sharif, P. Ciofi, P. Giacobini, J. Clasadonte, The versatile tanycyte: a hypothalamic integrator of reproduction and energy metabolism. Endocrine Reviews 39, 333–368 (2018).
- M. Böttcher, H. Müller-Fielitz, S.M. Sundaram, S. Gallet, V. Neve, K. Shionoya, A. Zager, N. Quan, X. Liu, R. Schmidt-Ullrich, R. Haenold, J. Wenzel, A. Blomqvist, D. Engblom, V. Prevot, M. Schwaninger, NF-κB signaling in tanycytes mediates inflammation-induced anorexia. Mol. Metab. 39, 101022 (2020).
- G.R. Johnston, N.R. Webster, Cytokines and the immunomodulatory function of the vagus nerve. Br. J. Anaesth. 102, 453-462 (2009).
- C.R. Plata-Salaman, Central nervous system mechanisms contributing to the cachexia–anorexia syndrome. Nutrition 16, 1009-1012 (2000).
- A.J. Grossberg, J.M. Scarlett, D.L. Marks, Hypothalamic mechanisms in cachexia Physiol. Behav. 100, 478-489 (2010).
- H. Johnen, S. Lin, T. Kuffner, D.A. Brown, V.W. Tsai, A.R. Bauskin, L. Wu, G. Pankhurst, L. Jiang, S. Junankar, M. Hunter, W.D. Fairlie, N.J. Lee, R.F. Enriquez, P.A. Baldock, E. Corey, F.S. Apple, M.M. Murakami, E.J. Lin, C. Wang, M.J. During, A. Sainsbury, H. Herzog, S.N. Breit, Tumor-induced anorexia and weight loss are mediated by the TGF-beta superfamily cytokine MIC-1. Nat. Med. 13, 1333-1340 (2007).
- C.R. Plata-Salamán, S.E. Ilyin, D. Gayle, Brain cytokine mRNAs in anorectic rats bearing prostate adenocarcinoma tumor cells. Am. J. Physiol. 275, R566-573 (1998).
- E.R. Ropelle, J.R. Pauli, K.G. Zecchin, M. Ueno, C.T. de Souza, J. Morari, M.C. Faria, L.A. Velloso, M.J. Saad, J.B. Carvalheira, A central role for neuronal adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase in cancer-induced anorexia. Endocrinology 148, 5220-5229 (2007).
- F.S. Lira, A.S. Yamashita, J.C. Rosa, F.L. Tavares, E. Caperuto, L.C. Carnevali Jr, G.D. Pimentel, R.V. Santos, M.L. Batista Jr, A. Laviano, F. Rossi-Fanelli, M. Seelaende, Hypothalamic inflammation is reversed by endurance training in anorectic-cachectic rats. Nutr. Metab. (Lond) 8, 60 (2011).
- K.A. Michaelis, X. Zhu, K.G. Burfeind, S.M. Krasnow, P.R. Levasseur, T.K. Morgan, D.L. Marks, Establishment and characterization of a novel murine model of pancreatic cancer cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 8, 824–838. (2017).
- K.G. Burfeind, X. Zhu, P.R. Levasseur, K.A. Michaelis, M.A. Norgard, D.L. Marks, TRIF is a key inflammatory mediator of acute sickness behavior and cancer cachexia. Brain Behav. Immun. 73, 364–374 (2018).
- X. Zhu, K.G. Burfeind, K.A. Michaelis, T.P. Braun, B. Olson, K.R. Pelz, T.K. Morgan, D.L. Marks, MyD88 signalling is critical in the development of pancreatic cancer cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 10, 378–390 (2019).
- B. Olson, M.A. Norgard, P.R. Levasseur, X. Zhu, D.L. Marks, Physiologic and molecular characterization of a novel murine model of metastatic head and neck cancer cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 12, 1312-1332 (2021).
- A. Cernackova, A. Tillinger, J. Bizik, B. Mravec, L. Horvathova, Dynamics of cachexia-associated inflammatory changes in the brain accompanying intra-abdominal fibrosarcoma growth in Wistar rats. J. Neuroimmunol. 15, 376 (2023).
- S. Layé, G. Gheusi, S. Cremona, C. Combe, K. Kelley, R. Dantzer, P. Parnet, Endogenous brain IL-1 mediates LPS-induced anorexia and hypothalamic cytokine expression. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 279, R93-98 (2000).
- R.M. Bluthé, S. Layé, B. Michaud, C. Combe, R. Dantzer, P. Parnet, Role of interleukin-1beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behaviour: a study with interleukin-1 type I receptor-deficient mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 4447-4456 (2000).
- E.I. Opara, A. Laviano, M.M. Meguid, Correlation between food intake and cerebrospinal fluid interleukin 1 alpha in anorectic tumor-bearing rats. Nutrition 11, 678-679 (1995).
- J.M. Scarlett, E.E. Jobst, P.J. Enriori, D.D. Bowe, A.K. Batra, W.F. Grant, M.A. Cowley, D.L. Marks, Regulation of central melanocortin signaling by interleukin-1 beta. Endocrinology 148, 4217-4225 (2007).
- J.M. Scarlett, X. Zhu, P.J. Enriori, D.D. Bowe, A.K. Batra, P.R. Levasseur, W.F. Grant, M.M. Meguid, M.A. Cowley, D.L. Marks, Regulation of agouti-related protein messenger ribonucleic acid transcription and peptide secretion by acute and chronic inflammation. Endocrinology 149, 4837-4845 (2008).
- A. Laviano, T. Renvyle, M.M. Meguid, Z.J. Yang, C. Cangiano, F. Rossi Fanelli, Relationship between interleukin-1 and cancer anorexia. Nutrition 11, 680-683 (1995).
- K.G. Burfeind, K.A. Michaelis, D.L. Marks, The central role of hypothalamic inflammation in the acute illness response and cachexia. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 54, 42-52 (2016).
- A.P. Arruda, M. Milanski, T. Romanatto, C. Solon, A. Coope, L.C. Alberici, W.T. Festuccia, S.M. Hirabara, E. Ropelle, R. Curi, J.B. Carvalheira, A.E. Vercesi, L.A. Velloso, Hypothalamic actions of tumor necrosis factor alpha provide the thermogenic core for the wastage syndrome in cachexia. Endocrinology 151, 683–694 (2010).
- G.F. Torelli, M.M. Meguid, L.L. Moldawer, C.K. Edwards 3rd, H.J. Kim, J.L. Carter, A. Laviano, F. Rossi Fanelli, Use of recombinant human soluble TNF receptor in anorectic tumor-bearing rats. Am. J. Physiol. 277, R850-855 (1999).
- C.R. Plata-Salamán, Y. Oomura, Y. Kai, Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 beta: suppression of food intake by direct action in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 448, 106-114 (1988).
- F.M. Chaves, N.S. Mansano, R. Frazão, J. Donato Jr, Tumor Necrosis Factor α and Interleukin-1β Acutely Inhibit AgRP Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 8928 (2020).
- A.P. Arruda, M. Milanski, T. Romanatto, C. Solon, A. Coope, L.C. Alberici, W.T. Festuccia, S.M. Hirabara, E. Ropelle, R. Curi, J.B. Carvalheira, A.E. Vercesi, L.A. Velloso, Hypothalamic actions of tumor necrosis factor alpha provide the thermogenic core for the wastage syndrome in cachexia. Endocrinology 151, 683-694 (2010).
- A. Jatoi, S.R. Dakhil, P.L. Nguyen, J.A. Sloan, J.W. Kugler, K.M. Rowland Jr, G.S. Soori, D.B. Wender, T.R. Fitch, P.J. Novotny, C.L. Loprinzi, A placebo-controlled double blind trial of etanercept for the cancer anorexia/weight loss syndrome: results from N00C1 from the North Central Cancer Treatment Group Cancer. 110, 1396-1403 (2007).
- A. Jatoi, H.L. Ritter, A. Dueck, P.L. Nguyen, D.A. Nikcevich, R.F. Luyun, B.I. Mattar, C.L. Loprinzi, A placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of infliximab for cancer-associated weight loss in elderly and/or poor performance non-small cell lung cancer patients (N01C9). Lung Cancer 68, 234-239 (2010).
- P.C. Heinrich, I. Behrmann, G. Müller-Newen, F. Schaper, L. Graeve, Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem. J. 334, 297-314 (1998).
- G. Arora, A. Gupta, T. Guo, A. Gandhi, A. Laine, D. Williams, C. Ahn, P. Iyengar, R. Infante, JAK Inhibitors Suppress Cancer Cachexia-Associated Anorexia and Adipose Wasting in Mice. JCSM Rapid Commun. 3, 115-128 (2020).
- W. Wang, E. Svanberg, D. Delbro, K. Lundholm, NOS isoenzyme content in brain nuclei as related to food intake in experimental cancer cachexia. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 134, 205-214 (2005).
- B. Yu, Y. Zhao, S. Teng, Y. Ni, S. Xu, X. Wu, J. Zhang, X. Xu, Y. Fang, J. Shi, B. Zhang, Atractylodin alleviates cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome by regulating NPY through hypothalamic Sirt1/AMPK axis-induced autophagy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 625, 154-160 (2022).
- Z. Qiu, D. Wo, X. Zhong, J. Chen, E. Ma, J. He, J. Peng, W. Zhu, D.N. Ren, Babao Dan Alleviates Cancer Cachexia in Mice Via Inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Integr. Cancer Ther. 22, 15347354231168369 (2023).
- R.G.F. Costa, P.L. Caro, E.M. de Matos-Neto, J.D.C.C. Lima, K. Radloff, M.J. Alves, R.G. Camargo, A.F.M. Pessoa, E. Simoes, P. Gama, D.C. Cara, A.S.F. da Silva, W.O Pereira, L.F. Maximiano, P.S.M. de Alcântara, J.P. Otoch, G. Trinchieri, A. Laviano, M. Muscaritoli, M. Seelaender, Cancer cachexia induces morphological and inflammatory changes in the intestinal mucosa. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 10, 1116-1127 (2019).
- J. Fujita, T. Tsujinaka, M. Yano, C. Ebisui, H. Saito, A. Katsume, K. Akamatsu, Y. Ohsugi, H. Shiozaki, M. Monden, Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody prevents muscle atrophy in colon-26 adenocarcinoma-bearing mice with modulation of lysosomal and ATP-ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic pathways. Int. J. Cancer 68, 637-643 (1996).
- Y. Du, X.Y. Liu, R.L. Pan, X.T. Zhang, X.Y. Si, M. Chen, M. Wang, L. Zhang, Tocilizumab for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with concomitant inflammatory cachexia: A single-centre study. J. Clin. Oncol. 42, 2647 (2024).
- Y.Y. Kwon, S. Hui, IL-6 promotes tumor growth through immune evasion but is dispensable for cachexia. EMBO Rep. 25, 2592-2609 (2024).
- M.D. Burton, N.L. Sparkman, R.W. Johnson, Inhibition of interleukin-6 trans-signaling in the brain facilitates recovery from lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behavior. J. Neuroinflammation 8, 54 (2011).
- K. Timper, J.L. Denson, S.M. Steculorum, C. Heilinger, L. Engström-Ruud, C.M. Wunderlich, S. Rose-John, F.T. Wunderlich, J.C. Brüning, IL-6 Improves Energy and Glucose Homeostasis in Obesity via Enhanced Central IL-6 trans-Signaling. Cell Rep. 19, 267-280 (2017).
- V.C. Bobbo, D.F. Engel, C.P. Jara, N.F. Mendes, R. Haddad-Tovolli, T.P. Prado, D. Sidarta-Oliveira, J. Morar, L.A. Velloso, E.P. Araujo, Interleukin-6 actions in the hypothalamus protects against obesity and is involved in the regulation of neurogenesis. J. Neuroinflammation 18, 192 (2021).
- K. Wallenius, V. Wallenius, D. Sunter, S.L. Dickson, J.Q. Jansson, Intracerebroventricular interleukin-6 treatment decreases body fat in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293, 560-565. (2022).
- A. Benrick, E. Schéle, S.B. Pinnock, I. Wernstedt-Asterholm, S.L. Dickson, L. Karlsson-Lindahl, J.O. Jansson, Interleukin-6 gene knockout influences energy balance regulating peptides in the hypothalamic paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. J. Neuroendocrinol. 21 620-628 (2009).
- C.K. Katashima, T. de Oliveira Micheletti, R.R. Braga, R.S. Gaspar, L.J.E. Goeminne, A. Moura-Assis, B.M. Crisol, R.S. Brícola, V.R.R. Silva, C. de Oliveira Ramos, A.L. da Rocha, M.R. Tavares, F.M. Simabuco, V.A. Matheus, L. Buscaratti, H. Marques-Souza, P. Pazos, D. Gonzalez-Touceda, S. Tovar, M. Del Carmen García, J.C.R. Neto, R. Curi, S.M. Hirabara, P.C. Brum, P.O. Prada, L.P. de Moura, J.R. Pauli, A.S.R. da Silva, D.E. Cintra, L.A. Velloso, E.R. Ropelle, Evidence for a neuromuscular circuit involving hypothalamic interleukin-6 in the control of skeletal muscle metabolism. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm7355 (2022).
- Q. Xu, Y. Cao, F. Kong, J. Liu, X. Chen, Y. Zhao, C.H. Lai, X. Zhou, H. Hu, W. Fu, J. Chen, J. Yang, Multiple cancer cell types release LIF and Gal3 to hijack neural signals. Cell Res. 34, 345-354 (2024).
- C. Di Giorgio, S. Marchianò, E. Marino, M. Biagioli, R. Roselli, M. Bordoni, R. Bellini, G. Urbani, A. Zampella, E. Distrutti, A. Donini, L. Graziosi, S. Fiorucci, Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis of Gastric Cancer Identifies the Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor as a Driving Factor in Gastric Cancer Progression and as a Predictor of Poor Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 12, 939969 (2022).
- F. Zhang, Y. Yan, X. Cao, C. Guo, K. Wang, S. Lv, TGF-β-driven LIF expression influences neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and contributes to peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 15, 218 (2024).
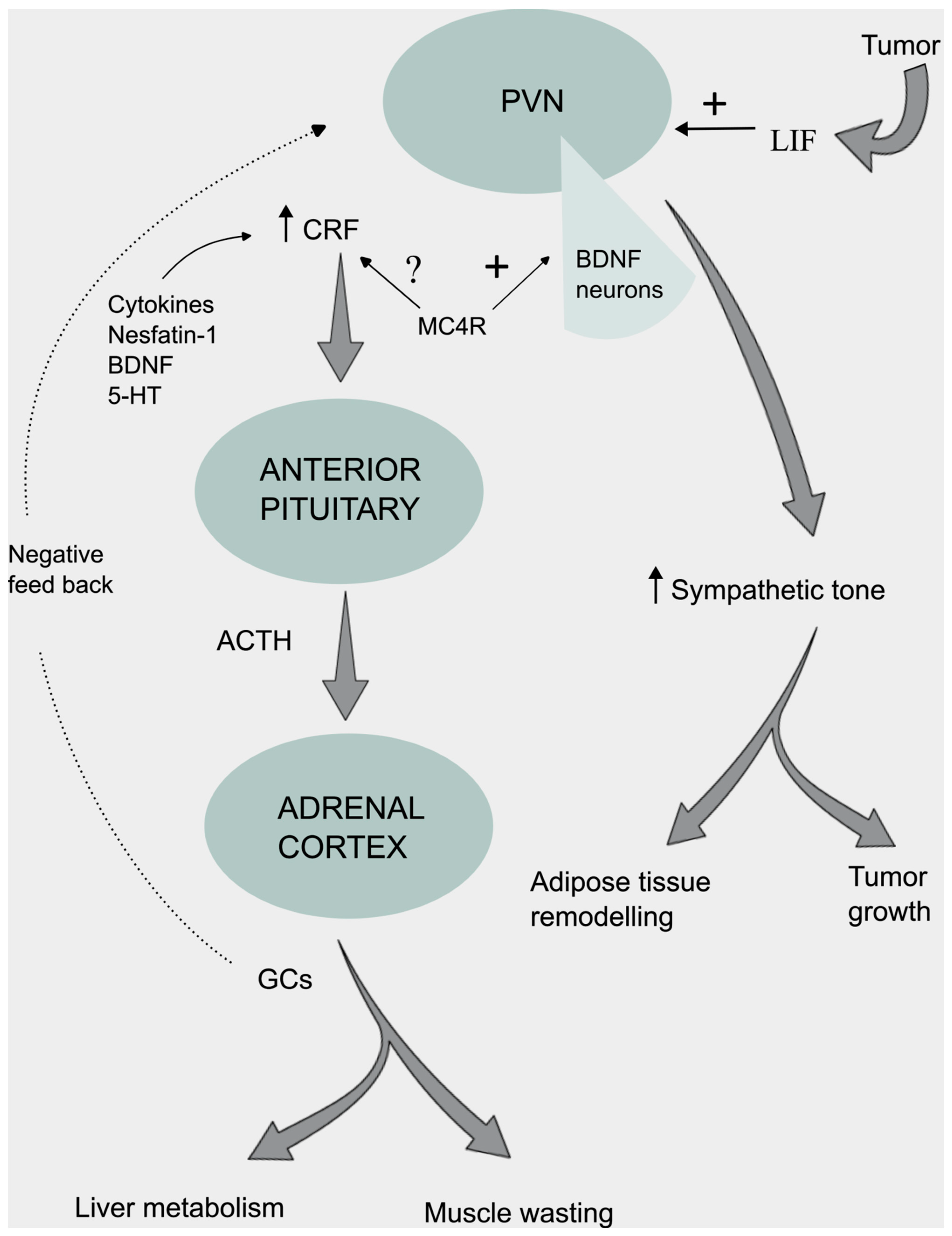
- S.C. Kandarian, R.L. Nosacka, A.E. Delitto, A.R. Judge, S.M. Judge, J.D. Ganey, J.D. Moreira, R.W. Jackman, Tumour-derived leukaemia inhibitory factor is a major driver of cancer cachexia and morbidity in C26 tumour-bearing mice. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 9, 1109-1120 (2018).
- X. Yang, J. Wang, C.Y. Chang, F. Zhou, J. Liu, H. Xu, M. Ibrahim, M. Gomez, G.L. Guo, H. Liu, W.X. Zong, F.E. Wondisford, X. Su, E. White, Z. Feng, W. Hu, Leukemia inhibitory factor suppresses hepatic de novo lipogenesis and induces cachexia in mice. Nat. Commun. 15, 627 (2024).
- G.K. Arora, A. Gupta, S. Narayanan, T. Guo, P. Iyengar, R.E. Infante, Cachexia-associated adipose loss induced by tumor-secreted leukemia inhibitory factor is counterbalanced by decreased leptin. JCI Insight 3, e121221 (2018).
- W. Pan, A.J. Kastin, J.M. Brennan, Saturable entry of leukemia inhibitory factor from blood to the central nervous system. J. Neuroimmunol. 106, 172-180 (2000).
- A.J. Grossberg, J.M. Scarlett, X. Zhu, D.D. Bowe, A.K. Batra, T.P. Braun, D.L. Marks, Arcuate nucleus proopiomelanocortin neurons mediate the acute anorectic actions of leukemia inhibitory factor via gp130. Endocrinology 151, 606-616 (2010).
- K. Terawaki, Y. Sawada, Y. Kashiwase, H. Hashimoto, M. Yoshimura, M. Suzuki, K. Miyano, Y. Sudo, S. Shiraishi, Y. Higami, K. Yanagihara, Y. Kase, Y. Ueta, Y. Uezono, New cancer cachexia rat model generated by implantation of a peritoneal dissemination-derived human stomach cancer cell line. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 306, E373-387 (2014).
- T. Ling, J. Zhang, F. Ding, L. Ma, Role of growth differentiation factor 15 in cancer cachexia (Review). Oncol. Lett. 26, 462 (2023).
- V.W. Tsai, R. Manandhar, S.B. Jørgensen, K.K. Lee-Ng, H.P. Zhang, C.P. Marquis, L. Jiang, Y. Husaini, S. Lin, A. Sainsbury, P.E. Sawchenko, D.A. Brown, S.N. Breit, The anorectic actions of the TGFβ cytokine MIC-1/GDF15 require an intact brainstem area postrema and nucleus of the solitary tract. PLoS One 9, e100370 (2014).
- A.A. Worth, R. Shoop, K. Tye, C.H. Feetham, G. D'Agostino, G.T. Dodd, F. Reimann, F.M. Gribble, E.C. Beebe, J.D. Dunbar, J.T. Alexander-Chacko, D.K. Sindelar, T. Coskun, P.J. Emmerson, S.M. Luckman, The cytokine GDF15 signals through a population of brainstem cholecystokinin neurons to mediate anorectic signaling. Elife 9, e55164 (2020).
- J.Y. Hsu, S. Crawley, M. Chen, D.A. Ayupova, D.A. Lindhout, J. Higbee, A. Kutach, W. Joo, Z. Gao, D. Fu, C. To, K. Mondal, B. Li, A. Kekatpure, M. Wang, T. Laird, G. Horner, J. Chan, M. McEntee, M. Lopez, D. Lakshminarasimhan, A. White, S.P. Wang, J. Yao, J. Yie, H. Matern, M. Solloway, R. Haldankar, T. Parsons, J. Tang, W.D. Shen, Y. Alice Chen, H. Tian, B.B. Allan, Non-homeostatic body weight regulation through a brainstem-restricted receptor for GDF15. Nature 550, 255–259 (2017).
- J.K. Elmquist, T.E. Scammell, C.D. Jacobsen, C.B. Saper, Distribution of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain following intravenous lipopolysaccharide administration. J. Comp. Neurol. 371, 85–103 (1996).
- S. Tolchard, A.S. Hare, D.J. Nutt, G. Clarke, TNF alpha mimics the endocrine but not the thermoregulatory responses of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): correlation with 83. FOS-expression in the brain. Neuropharmacology 35, 243–248 (1996).
- M. Herkenham, H.Y. Lee, R.A. Baker, Temporal and spatial patterns of c-fos mRNA induced by intravenous interleukin-1: a cascade of non-neuronal cellular activation at the blood-brain barrier. J. Comp. Neurol. 400, 175–196 (1998).
- A. Ericsson, C. Liu, R.P. Hart, P.E. Sawchenko, Type 1 interleukin-1 receptor in the rat brain: distribution, regulation, and relationship to sites of IL-1-induced cellular activation. J. Comp. Neurol. 361, 681–698 (1995).
- M. Utsuyama, K. Hirokawa, Differential expression of various cytokine receptors in the brain after stimulation with LPS in young and old mice. Exp. Gerontol. 37, 411–420 (2002).
- H. Yamakuni, M. Minami, M. Satoh, Localization of mRNA for leukemia inhibitory factor receptor in the adult rat brain. J. Neuroimmunol. 70, 45–53 (1996).
- S.K. Patra, S. Arora, Integrative role of neuropeptides and cytokines in cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Clin. Chim. Acta 413, 1025-1034 (2012).
- S.J. Hopkins, N.J. Rothwell, Cytokines and the nervous system I: expression and recognition. Trends Neurosci. 18, 83-88 (1995).
- W.L. Reis, C.X. Yi, Y. Gao, M.H. Tschöp, J.E. Stern, Brain innate immunity regulates hypothalamic arcuate neuronal activity and feeding behavior. Endocrinology 156, 1303–1315 (2015).
- P.G. Jang, C. Namkoong, G.M. Kang, M.W. Hur, S.W. Kim, G.H. Kim, Y. Kang, M.J. Jeon, E.H. Kim, M.S. Lee, M. Karin, J.H. Baik, J.Y. Park, K.U. Lee, Y.B Kim, M.S. Kim, NF-κB activation in hypothalamic pro-opiomelanocortin neurons is essential in illness- and leptin-induced anorexia. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 9706–9715 (2010).
- M. Valdearcos, J.D. Douglass, M.M. Robblee, M.D. Dorfman, D.R. Stifler, M.L. Bennett, I. Gerritse, R. Fasnacht, B.A. Barres, J.P. Thaler, S.K. Koliwad, Microglial inflammatory signaling orchestrates the hypothalamic immune response to dietary excess and mediates obesity susceptibility. Cell Metab. 26, 185-197 (2017).
- C.D. Breder, C.A. Dinarello, C.B. Saper, Interleukin- 1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science 240, 321-324 (1988).
- L. Acarin, B. Gonzalez, B. Castellano, Neuronal, astroglial and microglial cytokine expression after an excitotoxic lesion in the immature rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 3505–3520 (2000).
- J.T. Dwarkasing, R.F. Witkamp, M.V. Boekschoten, M.C. Ter Laak, M.S. Heins, K. van Norren, Increased hypothalamic serotonin turnover in inflammation-induced anorexia. BMC Neurosci. 17, 26 (2016).
- C. Huisman, M.A. Norgard, P.R. Levasseur, S.M. Krasnow, M.G.P. van der Wijst, B. Olson, D.L. Marks, Critical changes in hypothalamic gene networks in response to pancreatic cancer as found by single-cell RNA sequencing. Mol. Metab. 58, 101441 (2022).
- L.B. Bindels, A.M. Neyrinck, A. Loumaye, E. Catry, H. Walgrave, C. Cherbuy, S. Leclercq, M. Van Hul, H. Plovier, B. Pachikian, L.G. Bermúdez-Humarán, P. Langella, P.D. Cani, J.P. Thissen, N.M. Delzenne, Increased gut permeability in cancer cachexia: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Oncotarget 9, 18224-18238 (2018).
- H. Liu, Y. Cheng, Y. Qu, G. Wu, Unraveling the gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids characteristics and associations in a cancer cachexia mouse model. Microb. Pathog. 183, 106332 (2023).
- X. Li, T. Holtrop, F.A.C. Jansen, B. Olson, P. Levasseur, X. Zhu, M. Poland, W. Schalwijk, R.F. Witkamp, D.L. Marks, K. van Norren, Lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothalamic inflammation in cancer cachexia-anorexia is amplified by tumour-derived prostaglandin E2. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13, 3014-3027 (2022).
- P.A. Carpentier, D.S. Duncan, S.D. Miller, Glial toll-like receptor signaling in central nervous system infection and autoimmunity. Brain Behav. Immun. 22, 140–147 (2008).
- T. Kawai, S. Akira, The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 (2010).
- T. Kawai, S. Akira, Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 13, 460–469 (2007).
- M. Yamamoto, S. Sato, H. Hemmi, K. Hoshino, T. Kaisho, H. Sanjo, O. Takeuchi, M. Sugiyama, M. Okabe, K. Takeda, S. Akira, Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 301, 640–643 (2003).
- S. Jin, J.G. Kim, J.W. Park, M. Koch, T.L. Horvath, B.J. Lee, Hypothalamic TLR2 triggers sickness behavior via a microglia-neuronal axis. Sci. Rep. 6, 29424 (2016).
- Y.T. Kim, B.S. Park, H.R. Yang, S. Yi, I.S. Nam-Goong, J.G. Kim, Exploring the potential hypothalamic role in mediating cisplatin-induced negative energy balance. Chem. Biol. Interact. 385, 110733 (2023).
- S. Kashihara, K. Shinohara, S. Ikeda, H. Tsutsui, Microglia contribute to cancer cachexia through affecting PVN neurons and POMC neurons. FASEB J. 34, 1-1 Experimental Biology 2020 Meeting Abstracts.
- K.G. Burfeind, X. Zhu, M.A. Norgard, P.R. Levasseur, C. Huisman, K.A. Michaelis, B. Olson, D.L. Marks, Microglia in the hypothalamus respond to tumor-derived factors and are protective against cachexia during pancreatic cancer. Glia 68, 1479-1494 (2020).
- C.I. Chang, J.C. Liao, L. Kuo, Arginase modulates nitric oxide production in activated macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. 274, H342–H348 (1998).
- L. Ye, Y. Huang, L. Zhao, Y. Li, L. Sun, Y. Zhou, G. Qian, J.C. Zheng, IL-1β and TNF-α induce neurotoxicity through glutamate production: a potential role for neuronal glutaminase. J. Neurochem. 125, 897-908 (2013).
- M. Olah, K. Biber, J. Vinet, H.W.G.M. Boddeke, Microglia phenotype diversity. CNS & Neurological Disorders. Drug Targets 10, 108–118 (2011).
- A.D. Nguyen, N.F. Mitchell, S. Lin, L. Macia, E. Yulyaningsih, P.A. Baldock, R.F. Enriquez, L. Zhang, Y.C. Shi, S. Zolotukhin, H. Herzog, A. Sainsbury, Y1 and Y5 Receptors Are Both Required for the Regulation of Food Intake and Energy Homeostasis in Mice. PLoS One 7, e40191 (2012).
- B.E. Wisse, R.S. Frayo, M.W. Schwartz, D.E. Cummings, Reversal of cancer anorexia by blockade of central melanocortin receptors in rats. Endocrinology 142, 3292-301 (2001).
- D.L. Marks, N. Ling, R.D. Cone, Role of the central melanocortin system in cachexia. Cancer Res. 61, 1432-1438 (2001).
- M.A. Joppa, K.R. Gogas, A.C. Foster, S. Markison, Central infusion of the melanocortin receptor antagonist agouti-related peptide (AgRP(83-132)) prevents cachexia-related symptoms induced by radiation and colon-26 tumors in mice. Peptides 28, 636-642 (2007).
- B. Olson, X. Zhu, M.A. Norgard, P.R. Levasseur, J.T. Butler, A. Buenafe, K.G. Burfeind, K.A. Michaelis, K.R. Pelz, H. Mendez, J. Edwards, S.M. Krasnow, A.J. Grossberg, D.L. Marks, Lipocalin 2 mediates appetite suppression during pancreatic cancer cachexia. Nat. Commun. 12, 2057 (2021).
- X. Zhu, M.F. Callahan, K.A. Gruber, M. Szumowski, D.L. Marks, Melanocortin-4 receptor antagonist TCMCB07 ameliorates cancer- and chronic kidney disease-associated cachexia. J. Clin. Invest. 130, 4921-4934 (2020).
- S.M. Axiak-Bechtel, S.B. Leach, J.R. Newton-Northup, R.J. Milner, S.A. Fox-Alvarez, L.I. Fagman, K.A. Young, D.J. Tate, Z.M. Wright, J.D. Chretin, J.W. Allen, S.K. Yoshimoto, K.A. Selting, B.K. Flesner, C.R. White, T. Mills, M. Aherne, P.J. Bergman, L. Qi, K.A. Gruber, M.F. Callahan, Safety of TCMCB07, a melanocortin-4 antagonist peptide, in dogs with naturally occurring cachexia. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 37, 2344-2355 (2023).
- L.A.K. Qi, X. Zhu, K. Gruber, E.J. Roeland, R. Potterfield, D. Marks, Preliminary data from the phase I study of TCMCB07, a study to assess the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of the melanocortin antagonist TCMCB07 in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Oncol. 41, e15195 (2023).
- D. Huszar, C.A. Lynch, V. Fairchild-Huntress, J.H. Dunmore, Q. Fang, L.R. Berkemeier, W. Gu, R.A. Kesterson, B.A. Boston, R.D. Cone, F.J. Smith, L.A. Campfield, P. Burn, F. Lee, Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 88, 131–141 (1997).
- A.A. Butler, R A. Kesteson, K. Khong, M. Jane Cullen, M.A. Pelleymounter, J. Dekoning, M. Baetscher, R.D. Cone, A unique metabolic syndrome causes obesity in the melanocortin-3 receptor-deficient mouse. Endocrinology 141, 3518–3521 (2000).
- M. Ghamari-Langroudi, I. Cakir, R.N. Lippert, P. Sweeney, M.J. Litt, K.L.J. Ellacott, R.D. Cone, Regulation of energy rheostasis by the melanocortin-3 receptor. Sci. Adv. 4, eaat0866 (2018).
- Dahir, Y. Gui, Y. Wu, P.R. Sweeney, A.A. Rouault, S.Y. Williams, L.E. Gimenez, T.K. Sawyer, S.T. Joy, A.K. Mapp, R.D. Cone, Subthreshold activation of the melanocortin system causes generalized sensitization to anorectic agents in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 134, e178250 (2024).
- D.L. Marks, A.A. Butler, R. Turner, G. Brookhart, R.D. Cone, Differential Role of Melanocortin Receptor Subtypes in Cachexia. Endocrinology 144, 1513-1523 (2003).
- C. Bica, A. Tirpe, A. Nutu, C. Ciocan, S. Chira, E.S. Gurzau, C. Braicu, I. Berindan-Neagoe, Emerging roles and mechanisms of semaphorins activity in cancer.Life Sci. 318, 121499 (2023).
- A.A. van der Klaauw, S. Croizier, E. Mendes de Oliveira, L.K.J. Stadler, S. Park, Y. Kong, M.C. Banton, P. Tandon, A.E. Hendricks, J.M. Keogh, S.E. Riley, S. Papadia, E. Henning, R. Bounds, E.G. Bochukova, V. Mistry, S. O'Rahilly, R. Simerly, J.E.N. Minchin, I. Barroso, E.Y. Jones, S.G. Bouret, I.S. Farooqi, Human Semaphorin 3 Variants Link Melanocortin Circuit Development and Energy Balance. Cell 176, 729–742 (2019).
- Y. Zhang, Q. Xi, M. Zhong, Y. Jiang, Q. Zhuang, Z. Ding, S. Tan, J. Wang, H. Liu, Z. Zhang, B. Zhou, G. Wu, Tumor-derived semaphorin 3D promoting cancer cachexia via regulating hypothalamic pro-opiomelanocortin neurons. FASEB J. 37, e22980 (2023).
- B.E. Wisse, M.W. Schwartz, D.E. Cummings, Melanocortin Signaling and Anorexia in Chronic Disease States. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 994, 275-281 (2003).
- J.T. Dwarkasing, M. van Dijk, F.J. Dijk, M.V. Boekschoten, J. Faber, J.M. Argilès, A. Laviano, M. Müller, R.F. Witkamp, K. van Norren, Hypothalamic food intake regulation in a cancer-cachectic mouse model. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 5, 159-169 (2014).
- H. Suzuki, H. Hashimoto, M. Kawasaki, M. Watanabe, H. Otsubo, T. Ishikura, H. Fujihara, H. Ohnishi, E. Onuma, H. Yamada-Okabe, Y. Takuwa, E. Ogata, T. Nakamura, Y. Ueta, Similar changes of hypothalamic feeding-regulating peptides mRNAs and plasma leptin levels in PTHrP-, LIF-secreting tumors-induced cachectic rats and adjuvant arthritic rats. Int. J. Cancer 128, 2215-2223 (2011).
- M. Suzuki, M. Narita, M. Ashikawa, S. Furuta, M. Matoba, H. Sasaki, K. Yanagihara, K. Terawaki, T. Suzuki, Y. Uezono, Changes in the melanocortin receptors in the hypothalamus of a rat model of cancer cachexia. Synapse 66, 747-751 (2012).
- W.T. Chance, S. Sheriff, R. Dayal, A. Balasubramaniam, Refractory hypothalamic alpha-mSH satiety and AGRP feeding systems in rats bearing MCA sarcomas. Peptides 24, 1909-1919 (2003).
- V. Sergeyev, C. Broberger, T. Hökfel, Effect of LPS administration on the expression of POMC, NPY, galanin, CART and MCH mRNAs in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 90, 93-100 (2001).
- X. Shi, X. Wang, Q. Li, M. Su, E. Chew, E.T. Wong, Z. Lacza, G.K. Radda, V. Tergaonkar, W. Han, Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) suppresses food intake and energy expenditure in mice by directly activating the Pomc promoter. Diabetologia 56, 925-936 (2013).
- I. Mosialou, S. Shikhel, J.M. Liu, A. Maurizi, N. Luo, Z. He, Y. Huang, H. Zong, R.A. Friedman, J. Barasch, P. Lanzano, L. Deng, R.L. Leibel, M. Rubin, T. Nickolas, W. Chung, L.M. Zeltser, K.W. Williams, J.E. Pessin, S. Kousteni, Corrigendum: MC4R-dependent suppression of appetite by bone-derived lipocalin 2. Nature 546, 440 (2017).
- J.T. Dwarkasing, D.L. Marks, R.F. Witkamp, K. van Norren, Hypothalamic inflammation and food intake regulation during chronic illness. Peptides 77, 60-66 (2016).
- N. Nara-ashizawa, T. Tsukada, K. Maruyama, Y. Akiyama, N. Kajimura, K. Yamaguchi, Response of hypothalamic NPY mRNAs to a negative energy balance is less sensitive in cachectic mice bearing human tumor cells. Nutr. Cancer 41, 111-118 (2001).
- W.T. Chance, A. Balasubramaniam, H. Thompson, B. Mohapatra, J. Ramo, J.E. Fischer, Assessment of feeding response of tumor-bearing rats to hypothalamic injection and infusion of neuropeptide Y. Peptides 17, 797-801 (1996).
- N. Nara-ashizawa, T. Tsukada, K. Maruyama, Y. Akiyama, N. Kajimura, K. Nagasaki, T. Iwanaga, K. Yamaguchi, Hypothalamic appetite-regulating neuropeptide mRNA levels in cachectic nude mice bearing human tumor cells. 50, 1213–1219 (2001).
- W.T. Chance, C. Xiao, R. Dayal, S. Sheriff, Alteration of NPY and Y1 receptor in dorsomedial and ventromedial areas of hypothalamus in anorectic tumor-bearing rats. Peptides 28, 295–301 (2007).
- J.T. Dwarkasing, M.V. Boekschoten, J.M. Argilès, M. van Dijk, S. Busquets, F. Penna, M. Toledo, A. Laviano, R.F. Witkamp, K. van Norren, Differences in food intake of tumour-bearing cachectic mice are associated with hypothalamic serotonin signalling. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 6, 84-94 (2015).
- S.S. Dhillon, S.A. McFadden, J.A. Chalmers, M.L. Centeno, G.L. Kim, D.D. Belsham, Cellular Leptin Resistance Impairs the Leptin-Mediated Suppression of Neuropeptide Y Secretion in Hypothalamic Neurons. Endocrinology 152, 4138-4147 (2011).
- S.H. Cha, M.D. Lane, Central lactate metabolism suppresses food intake via the hypothalamic AMP kinase/malonyl-CoA signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys Res Commun. 386, 212-216 (2009).
- S.H. Lockie, R. Stark, M. Mequinion, S. Ch'ng, D. Kong, D.C. Spanswick, A.J. Lawrence, Z.B. Andrews, Glucose Availability Predicts the Feeding Response to Ghrelin in Male Mice, an Effect Dependent on AMPK in AgRP Neurons Endocrinology 159, 3605-3614 (2018).
- H. Shimizu, H. Arima, M. Watanabe, M. Goto, R. Banno, I. Sato, N. Ozaki, H. Nagasaki, Y. Oiso, Glucocorticoids increase neuropeptide Y and agouti-related peptide gene expression via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling in the arcuate nucleus of rats. Endocrinology 149, 4544-4553 (2008).
- H.D. McCarthy, P.E. McKibbin, A.V. Perkins, E.A. Linton, G. Williams, Alterations in hypothalamic NPY and CRF in anorexic tumor-bearing rats. Am. J. Physiol. 264, E638–E643 (1993).
- M.M. Meguid, E.J. Ramos, A. Laviano, M. Varma, T. Sato, C. Chen, Y. Qi, U.N. Das, Tumor anorexia: effects on neuropeptide Y and monoamines in paraventricular nucleus. Peptides 25, 261–266 (2004).
- J.P. Voigt, H. Fink, Serotonin controlling feeding and satiety. Behav. Brain Res. 277, 14-31 (2015).
- M.A. Geyer, A. Puerto, D.B. Menkes, D.S. Segal, A.J. Mandell, Behavioral studies following lesions of the mesolimbic and mesostriatal serotonergic pathways. Brain Res. 106, 257–269 (1976).
- L.K. Heisler, E.E. Jobst, G.M. Sutton, L. Zhou, E. Borok, Z. Thornton-Jones, H.Y. Liu, J.M. Zigman, N. Balthasar, T. Kishi, C.E. Lee, C.J. Aschkenasi, C.Y. Zhang, J. Yu, O. Boss, K.G. Mountjoy, P.G. Clifton, B.B. Lowell, J.M. Friedman, T. Horvath, A.A. Butler, J.K. Elmquist, M.A. Cowley, Serotonin reciprocally regulates melanocortin neurons to modulate food intake. Neuron 51, 239–249 (2006).
- Y. Xu, J.E. Jones, D. Kohno, K.W. Williams, C.E. Lee, M.J. Choi, J.G. Anderson, L.K. Heisler, J.M. Zigman, B.B. Lowell, J.K. Elmquist, HT2CRs Expressed by Pro-Opiomelanocortin Neurons Regulate Energy Homeostasis. Neuron 60, 582-589 (2008).
- V. Bláha, Z.J. Yang, M.M. Meguid, J.K. Chai, A. Oler, Z. Zadák, Ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus is related to the development of cancer-induced anorexia: in vivo microdialysis study. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) 41, 3-11 (1998).
- E.J. Ramos, S. Suzuki, M.M. Meguid, A. Laviano, T. Sato, C. Chen, U. Das, Changes in hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and monoaminergic system in tumor-bearing rats: pre- and post-tumor resection and at death. Surgery 136, 270-276 (2004).
- I.G. Makarenko, M.M. Meguid, L. Gatto, C. Chen, E.J. Ramos, C.G. Goncalves, M.V. Ugrumov, Normalization of hypothalamic serotonin (5-HT 1B) receptor and NPY in cancer anorexia after tumor resection: an immunocytochemical study. Neurosci. Lett. 383, 322-327 (2005).
- I.G. Makarenko, M.M. Meguid, L. Gatto, C.G. Goncalves, E.J. Ramos, C. Chen, M.V. Ugrumov, Hypothalamic 5-HT1B-receptor changes in anorectic tumor bearing rats. Neurosci Lett. 376, 71-75 (2005).
- A. Laviano, J.R. Gleason, M.M. Meguid, Z.J. Yang, C. Cangiano, F. Rossi Fanelli, Effects of intra-VMN mianserin and IL-1ra on meal number in anorectic tumor-bearing rats. J. Investig. Med. 48, 40-48 (2000).
- M. Sato, A. Laviano, M.M. Meguid, C. Chen, F. Rossi-Fanelli, K. Hatakeyama, Involvement of plasma leptin, insulin and free tryptophan in cytokine-induced anorexia. Clin. Nutr. 22, 139–146 (2003).
- W.T. Chance, M.F. von Meyenfeldt, J.E. Fischer, Changes in brain amines associated with cancer anorexia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 7, 471-479 (1983).
- C. Cangiano, A. Cascino, F. Ceci, A. Laviano, M. Mulieri, M. Muscaritoli, F. Rossi-Fanelli, Plasma and CSF tryptophan in cancer anorexia. J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 81, 225-233 (1990).
- C. Cangiano, A. Laviano, M.M. Meguid, M. Mulieri, L. Conversano, I. Preziosa, F. Rossi-Fanelli, Effects of administration of oral branched-chain amino acids on anorexia and caloric intake in cancer patients. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 88, 550-552 (1996).
- D.M. Kuhn, R. Arthur Jr, Molecular Mechanism of the Inactivation of Tryptophan Hydroxylase by Nitric Oxide: Attack on Critical Sulfhydryls that Spare the Enzyme Iron Center. J. Neurosci. 17, 7245-7251 (1997).
- F. Squadrito, G. Calapai, D. Altavilla, D. Cucinotta, B. Zingarelli, G.M. Campo, V. Arcoraci, L. Sautebin, G. Mazzaglia, A.P. Caputi, Food deprivation increases brain nitric oxide synthase and depresses brain serotonin levels in rats, Neuropharmacology 33, 83 – 86 (1994).
- A. Aguilera, J.A. Sanchez-Tomero, R. Selgas, NOS isoenzyme content in brain nuclei as related to food intake in experimental cancer cachexia. Brain activation in uremic anorexia. J. Ren Nutr. 17, 57-61 (2007).
- M.S. Szczypka, M.A. Rainey, D.S. Kim, W.A. Alaynick, B.T. Marck, A.M. Matsumoto, R.D. Palmiter, Feeding behavior in dopamine-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 96, 12138-12143 (1999).
- M.M. Meguid, Z.J. Yang, M. Koseki, Eating induced rise in LHA-dopamine correlates with meal size in normal and bulbectomized rats. Brain Res. Bull. 36, 487-490 (1995).
- Q. Zhang, Q. Tang, N.M. Purohit, J.B. Davenport, C. Brennan, R.K. Patel, E. Godschall, L.S. Zwiefel, A. Spano, J.N. Campbell, A.D. Güler, Food-induced dopamine signaling in AgRP neurons promotes feeding. Cell Rep. 41, 111718 (2022).
- M. Perez de la Mora, C. Hernandez-Mondragon, M. Crespo-Ramirez, J. Rejon-Orantes, D.O. Borroto-Escuela, K. Fuxe, Conventional and Novel Pharmacological Approaches to Treat Dopamine-Related Disorders: Focus on Parkinson’s Disease and Schizophrenia. Neuroscience 439, 301-318 (2020).
- T. Sato, M.M. Meguid, S.O. Fetissov, C. Chen, L. Zhang, Hypothalamic dopaminergic receptor expressions in anorexia of tumor-bearing rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 281, R1907-1916 (2001).
- I. Gaziano, S. Corneliussen, N. Biglari, R. Neuhaus, L. Shen, T. Sotelo-Hitschfeld, P. Klemm, L. Steuernagel, A.J. De Solis, W. Chen, F.T. Wunderlich, P. Kloppenburg, J.C. Brüning, Dopamine-inhibited POMCDrd2+ neurons in the ARC acutely regulate feeding and body temperature JCI Insight. 7, e162753 (2022).
- X. Zhang, A.N. van den Pol, Hypothalamic arcuate nucleus tyrosine hydroxylase neurons play orexigenic role in energy homeostasis. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1341-1347 (2016).
- J. Gatfield, C. Brisbare-Roch, F. Jenck, C. Boss, Orexin receptor antagonists: a new concept in CNS disorders? Chem. Med.Chem. 5, 1197-1214 (2010).
- C.F. Elias, C.B. Saper, E. Maratos-Flier, N.A. Tritos, C. Lee, J. Kelly, J.B. Tatro, G.E. Hoffman, M.M. Ollmann, G.S. Barsh, T. Sakurai, M. Yanagisawa, J.K. Elmquist, Chemically defined projections linking the mediobasal hypothalamus and the lateral hypothalamic area. J. Comp. Neurol. 402, 442–459 (1998).
- T. Sakurai, A. Amemiya, M. Ishii, I. Matsuzaki, R.M. Chemelli, H. Tanaka, S.C. Williams, J.A. Richardson, G.P. Kozlowski, S. Wilson, J.R. Arch, R.E. Buckingham, A.C. Haynes, S.A. Carr, R.S. Annan, D.E. McNulty, W.S. Liu, J.A. Terrett, N.A. Elshourbagy, D.J. Bergsma, M. Yanagisawa, Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92, 573-585 (1998).
- A. Yamanaka, T. Sakurai, T. Katsumoto, M. Yanagisawa, K. Goto, Chronic intracerebroventricular administration of orexin-A to rats increases food intake in daytime, but has no effect on body weight. Brain Res. 849, 248-252 (1999).
- X.J. Cai, P.S. Widdowson, J. Harrold, S. Wilson, R.E. Buckingham, J.R. Arch, M. Tadayyon, J.C. Clapham, J. Wilding, G. Williams, Hypothalamic orexin expression: modulation by blood glucose and feeding. Diabetes. 48, 2132-2137 (1999).
- A.J. Grossberg, X. Zhu, G.M. Leinninger, P.R. Levasseur, T.P. Braun, M.G. Myers Jr, D.L. Marks, Inflammation-induced lethargy is mediated by suppression of orexin neuron activity. J. Neurosci. 31, 11376–11386 (2011).
- F. Guo, L. Xu, S. Gao, X. Sun, N. Zhang, Y. Gong, Effect of orexin-A in the arcuate nucleus on cisplatin-induced gastric side effects in rats. Neurosci. Res. 143, 53-60 (2019).
- H. Tsuneki, E. Tokai, Y. Nakamura, K. Takahashi, M. Fujita, T. Asaoka, K. Kon, Y. Anzawa, T. Wada, I. Takasaki, K. Kimura, H. Inoue, M. Yanagisawa, T. Sakurai, T. Sasaoka, Hypothalamic orexin prevents hepatic insulin resistance via daily bidirectional regulation of autonomic nervous system in mice. Diabetes. 64, 459-470 (2015).
- 177. S. Oh-I, H. Shimizu, T. Satoh, S. Okada, S. Adachi S, K. Inoue, H. Eguchi, M. Yamamoto, T. Imaki, K. Hashimoto, T. Tsuchiya, T. Monden, K. Horiguchi, M. Yamada, M. Mori, Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature 443, 709-712 (2006).
- S.K. Rupp, A. Stengel, Interactions between nesfatin-1 and the autonomic nervous system-an overview. Peptides 149, 170719 (2022).
- D. Stephan, N. Taege, R. Dore, J. Folberth, O. Jöhren, M. Schwaninger, H. Lehnert, C. Schulz, Knockdown of Endogenous Nucb2/Nesfatin-1 in the PVN Leads to Obese-Like Phenotype and Abolishes the Metformin- and Stress-Induced Thermogenic Response in Rats. Horm. Metab. Res. 54, 768-779 (2022).
- L. Ren, D. Bao, L. Wang, Q. Xu, Y. Xu, Z. Shi, Nucleobindin-2/nesfatin-1 enhances the cell proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 26, 4986-4994 (2022).
- S. Ning, C. Liu, K. Wang, Y. Cai, Z. Ning, M. Li, L. Zeng, NUCB2/Nesfatin-1 drives breast cancer metastasis through the up-regulation of cholesterol synthesis via the mTORC1 pathway. J. Transl. Med. 21, 362 (2023).
- J.R. Burgos, B.M. Iresjö, U. Smedh, MCG101-induced cancer anorexia-cachexia features altered expression of hypothalamic Nucb2 and Cartpt and increased plasma levels of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptides. Oncol. Rep. 35, 2425-2430 (2016).
- G.L.C. Yosten, W.K. Samson, Nesfatin-1 exerts cardiovascular effects in brain: possible interaction with the central melanocortin system. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 297, R330–R336 (2009).
- Y. Maejima, U. Sedbazar, S. Suyama, D. Kohno, E. Takano, N. Yoshida, M. Koike, Y. Uchiyama, K. Fujiwara, T. Yashiro, T.L. Horvath, M.O. Dietrich, S. Tanaka, K. Dezaki, S. Oh -I, K. Hashimoto, H. Shimizu, M. Nakata, M. Mori, T. Yada, Nesfatin-1-regulated oxytocinergic signaling in the paraventricular nucleus causes anorexia through a leptin-independent melanocortin pathway. Cell Metab 10, 355–365 (2009).
- A. Stengel, M. Goebel, L. Wang, J. Rivier, P. Kobelt, H. Moennikes, N.W.G. Lambrecht, Y. Tache, Central nesfatin-1 reduces dark-phase food intake and gastric emptying: differential role of corticotropin-releasing-factor 2 receptor. Endocrinology 150, 4911–4919 (2009).
- C.J. Price, W.K. Samson, A.V. Ferguson, Nesfatin-1 inhibits NPY neurons in the arcuate nucleus. Brain Res. 1230, 99-106 (2008).
- M. Tanida, H. Gotoh, N. Yamamoto, M. Wang, Y. Kuda, Y. Kurata, M. Mori, T. Shibamoto, Hypothalamic Nesfatin-1 Stimulates Sympathetic Nerve Activity via Hypothalamic ERK Signaling Diabetes 64, 3725-3736 (2015).
- Y. Liu, X. Chen, Y. Qu, L. Song, Q. Lin, M. Li, K. Su, Y. Li, J. Dong, Central nesfatin-1 activates lipid mobilization in adipose tissue and fatty acid oxidation in muscle via the sympathetic nervous system. Biofactors 46, 454-464 (2020).
- J.M. Friedman, Modern science versus the stigma of obesity. Nature Medicine 10, 563–569 (2004).
- H. Baumann, K.K. Morella, D.W. White, M. Dembski, P.S. Bailon, H. Kim, C.F. Lai, L.A. Tartaglia, The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 93, 8374-8378 (1996).
- M.A. Cowley, J.L. Smart, M. Rubinstein, M.G Cerdán, S. Diano, T.L. Horvath, R.D. Cone, M.J. Low, Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 411, 480-484 (2001).
- M. Ghamari-Langroudi, D. Srisai, R.D. Cone, Multinodal regulation of the arcuate/paraventricular nucleus circuit by leptin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 108, 355-360 (2011).
- J.P. Simons, A.M. Schols, L.A. Campfield, E.F. Wouters, W.H. Saris, Plasma concentration of total leptin and human lung-cancer-associated cachexia. Clin Sci (Lond) 93, 273-277 (1997).
- J. Smiechowska, A. Utech, G. Taffet, T. Hayes, M. Marcelli, J.M. Garcia, Adipokines in patients with cancer anorexia and cachexia. J. Investig Med. 58, 554–559 (2010).
- C. Bing, S. Taylor, M.J. Tisdale, G. Williams, Cachexia in MAC16 adenocarcinoma: suppression of hunger despite normal regulation of leptin, insulin and hypothalamic neuropeptide Y. J. Neurochem. 79, 1004-1112 (2001).
- P.D. Lambert, K.D. Anderson, M.W. Sleeman, V. Wong, J. Tan, A. Hijarunguru, T.L. Corcoran, J.D. Murray, K.E. Thabet, G.D. Yancopoulos, S.J. Wiegand, Ciliary neurotrophic factor activates leptin-like pathways and reduces body fat, without cachexia or rebound weight gain, even in leptin-resistant obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 98, 4652-4657 (2001).
- M. Kojima, H. Hosoda, Y. Date, M. Nakazato, H. Matsuo, K. Kangawa, Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402, 656-660 (1999).
- M. Nakazato, N. Murakami, Y. Date, M. Kojima, H. Matsuo, K. Kangawa, S. Matsukura, A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 409, 194-198 (2001).
- M.G. Willesen, P. Kristensen, J. Romer, Co-localization of growth hormone secretagogue receptor and NPY mRNA in the arcuate nucleus of the rat. Neuroendocrinology 70, 306-316 (1999).
- J. Kamegai, H. Tamura, T. Shimizu T, S. Ishii, H. Sugihara I. Wakabayashi, Chronic central infusion of ghrelin increases hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and Agouti-related protein mRNA levels and body weight in rats. Diabetes 50, 2438-2443 (2001).
- M.A. Cowley, R.G. Smith, S. Diano S. M. Tschöp, N. Pronchuk, K.L. Grove, C.J. Strasburger, M. Bidlingmaier, M. Esterman, M.L. Heiman, L.M. Garcia-Segura, E.A. Nillni, P. Mendez, M.J. Low, P. Sotonyi, J.M. Friedman, H. Liu, S. Pinto, W.F. Colmers, R.D. Cone, T.L. Horvath, The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron 37, 649–661 (2003).
- S.R. Chen, H. Chen, J.J. Zhou, G. Pradhan, Y. Sun, H.L. Pan, D.P. Li, Ghrelin receptors mediate ghrelin-induced excitation of agouti-related protein/neuropeptide Y but not pro-opiomelanocortin neurons. J. Neurochem. 142, 512-520 (2017).
- Y. Date, N. Murakami, K. Toshinai, S. Matsukura, A. Niijima, H. Matsuo, K. Kangawa, M. Nakazato, The role of the gastric afferent vagal nerve in ghrelin-induced feeding and growth hormone secretion in rats. Gastroenterology 123, 1120-1128 (2002).
- Y. Shimizu, N. Nagaya, T. Isobe, M. Imazu, H. Okumura, H. Hosoda, M. Kojima, K. Kangawa, N. Kohno, Increased plasma ghrelin level in lung cancer cachexia. Clin. Cancer Res. 9, 774-778 (2003).
- J.M. Garcia, M. Garcia-Touza, R.A. Hijazi, G. Taffet, D. Epner, D. Mann, R.G. Smith, G.R. Cunningham, M. Marcelli, Active ghrelin levels and active to total ghrelin ratio in cancer-induced cachexia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 2920–2926 (2005).
- D. Murata, K. Azuma, N. Matsuo, K. Murotani, G. Matama, A. Kawahara, T. Sasada, T. Tokito, T. Hoshino, Survival and biomarkers for cachexia in non-small cell lung cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Med. 12, 19471-19479 (2023).
- W. Wang, M. Andersson, B.M. Iresjo, C. Lonnroth, K. Lundholm, Effects of ghrelin on anorexia in tumor-bearing mice with eicosanoid-related cachexia. Int. J. Oncol. 28, 1393–1400 (2006).
- K. Terawaki, Y. Kashiwase, Y. Sawada, H. Hashimoto, M. Yoshimura, K. Ohbuchi, Y. Sudo, M. Suzuki, K. Miyano, S. Shiraishi, Y. Higami, K. Yanagihara, T. Hattori, Y Kase, Y. Ueta, Y Uezono, Development of ghrelin resistance in a cancer cachexia rat model using human gastric cancer-derived 85As2 cells and the palliative effects of the Kampo medicine rikkunshito on the model. PLoS One 12, e0173113 (2017).
- K. Yakabi, S. Kurosawa, M. Tamai, M. Yuzurihara, M. Nahata, S. Ohno, S. Ro, S. Kato, T. Aoyama, T. Sakurada, H. Takabayashi, T. Hattori, Rikkunshito and 5-HT2C receptor antagonist improve cisplatin-induced anorexia via hypothalamic ghrelin interaction. Regul Pept. 161, 97–105 (2010).
- N.M. Neary, C.J. Small, A.M. Wren, J.L. Lee, M.R. Druce, C. Palmieri C, G.S. Frost, M.A. Ghatei, R.C. Coombes, S.R. Bloom, Ghrelin increases energy intake in cancer patients with impaired appetite: acute, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 2832–2836 (2004).
- T. Hanada, K. Toshinai, N. Kajimura, N. Nara-Ashizawa, T. Tsukada, Y. Hayashi, K. Osuye, K. Kangawa, S. Matsukura, M. Nakazato, Anti-cachectic effect of ghrelin in nude mice bearing human melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 301, 275-279 (2003).
- H. Tsubouchi, S. Yanagi, A. Miura, N. Matsumoto, K. Kangawa, M. Nakazato, Ghrelin relieves cancer cachexia associated with the development of lung adenocarcinoma in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 743, 1-10 (2014).
- M.D. DeBoer, X.X. Zhu, P. Levasseur, M.M. Meguid, S. Suzuki, A. Inui, J.E. Taylor, H.A. Halem, J.Z. Dong, R. Datta, M.D. Culler, D.L. Marks, Ghrelin treatment causes increased food intake and retention of lean body mass in a rat model of cancer cachexia. Endocrinology 148, 3004-3012 (2007).
- Y. Ishioka, H. Tanaka, T. Makiguchi, S. Fujishima, Y. Nunomura, H. Sakamoto, T. Shiratori, K. Taima, S. Tasaka, Predictors of efficacy of anamorelin in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and cachexia: A retrospective study. Oncol. Lett. 27, 22 (2023).
- L.J. Rohrbasser, H. Alsaffar, J. Blair, in Principles of Endocrinology and Hormone Action, ed. by A. Belfiore, D. LeRoith (Springer, Cham, Switzerland, 2018) P.287.
- A.L. Goldberg, Protein turnover in skeletal muscle. II. Effects of denervation and cortisone on protein catabolism in skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 244, 3223–3229 (1969).
- M.P. Cala, M.T. Agullo-Ortuno, E. Prieto-Garcia, C. Gonzalez-Riano, L. Parrilla-Rubio, C. Barbas, C.V. Díaz-García, A. García, C. Pernaut, J. Adeva, M.C. Riesco, F.J. Rupérez, J.A. Lopez-Martin, Multiplatform plasma fingerprinting in cancer cachexia: a pilot observational and translational study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 9, 348-357 (2018).
- S. Lundström, C.J. Fürst, Symptoms in advanced cancer: Relationship to endogenous cortisol levels. Palliat. Med. 17, 503-508 (2003).
- M.L. Knapp, S. al-Sheibani, P.G. Riches, I.W. Hanham, R.H. Phillips, Hormonal factors associated with weight loss in patients with advanced breast cancer. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 28, 480-486 (1991).
- D.E. Rivadeneira, H.A. Naama, M.D. McCarter, J. Fujita, D. Evoy, P. Mackrell J.M. Daly, Glucocorticoid blockade does not abrogate tumor-induced cachexia. Nutr. Cancer 35, 202-206 (1999).
- S.T. Russell, M.J. Tisdale, The role of glucocorticoids in the induction of zinc-alpha2 glycoprotein expression in adipose tissue in cancer cachexia. Br. J. Cancer 92, 876-881 (2005).
- Y. Tanaka, H. Eda, T. Tanaka, T. Udagawa, T. Ishikawa, I. Horii, H. Ishitsuka, T. Kataoka, T. Taguchi, Experimental cancer cachexia induced by transplantable colon 26 adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Res. 50, 2290-2295 (1990).
- P. Costelli, N. Carbo, L. Tessitore, G.J. Bagby, F.J. Lopez-Soriano, J.M. Argiles, F.M. Baccino, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates changes in tissue protein turnover in a rat cancer cachexia model. J. Clin. Invest. 92, 2783–2789 (1993).
- N.J. Rothwell, Central effects of CRF on metabolism and energy balance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 14, 263–271 (1990).
- K. Kageyama, S. Kagaya, S. Takayasu, K. Hanada, Y. Iwasaki, T. Suda, Cytokines induce NF-κB, Nurr1 and corticotropin-releasing factor gene transcription in hypothalamic 4B cells. Neuroimmunomodulation 17, 305-313 (2010).
- M. Tasso, K. Kageyama, Y. Iwasaki, Y. Watanuki, K. Niioka, S. Takayasu, M. Daimon, Growth differentiation factor-15 stimulates the synthesis of corticotropin-releasing factor in hypothalamic 4B cells. Peptides 170, 171112 (2023).
- A. Uehara, C. Sekiya, Y. Takasugi, M. Namiki, A. Arimura, Anorexia induced by interleukin 1: involvement of corticotropin-releasing factor. Am. J. Physiol. 257, R613-617 (1989).
- K. Gotoh, T. Masaki, S. Chiba, H. Ando, K. Fujiwara, T. Shimasaki, K. Mitsutomi, I. Katsuragi, T. Kakuma, T. Sakata, H. Yoshimatsu, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, corticotropin-releasing factor, and hypothalamic neuronal histamine interact to regulate feeding behavior. J. Neurochem. 125, 588-598 (2013).
- Z. Liposits, C. Phelix, W.K. Paull, Synaptic interaction of serotonergic axons and corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) synthesizing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of the rat. A light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. Histochemistry 86, 541-549 (1987).
- L.D. Van de Kar, A. Javed, Y. Zhang, F. Serres, D.K. Raap, T.S. Gray, 5-HT2A receptors stimulate ACTH, corticosterone, oxytocin, renin, and prolactin release and activate hypothalamic CRF and oxytocin-expressing cells. J. Neurosci. 21, 3572-3579 (2001).
- X.Y. Lu, G.S. Barsh, H. Akil, S.J. Watson, Interaction between α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone in the regulation of feeding and hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal responses. J. Neurosci. 23, 7863–7872 (2003).
- A.V. Vergoni, A. Bertolini, J.E. Wikberg, H.B. Schioth Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) induced anorexia is not influenced by a melanocortin 4 receptor blockage. Peptides 20, 509–513 (1999).
- S. Kawashima, S. Sakihara, K. Kageyama, T. Nigawara, T. Suda, Corti cotropin-releasing factor (CRF) is involved in the acute anorexic effect of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone: A study using CRF-deficient mice. Peptides 29, 2169-2174 (2008).
- J. Wang, L. Sun, J. You, H. Peng, H. Yan, J. Wang, F. Sun, M. Cui, S. Wang, Z. Zhang, X. Fan, D. Liu, C. Liu, C. Qiu, C. Chen, Z. Xu, J. Chen, W. Li, B. Liu, Role and mechanism of PVN-sympathetic-adipose circuit in depression and insulin resistance induced by chronic stress. EMBO Rep. 24, e57176 (2023).
- M. Erdem, D. Möckel, S. Jumpertz, C. John, A. Fragoulis, I. Rudolph, J. Wulfmeier, J. Springer, H. Horn, M. Koch, G. Lurje, T. Lammers, S. Olde Damink, G. van der Kroft, F. Gremse, T. Cramer, Macrophages protect against loss of adipose tissue during cancer cachexia J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 10, 1128-1142 (2019).
- B. Xu, E.H. Goulding, K. Zang, D. Cepoi, R.D. Cone, K.R. Jones, L.H. Tecott, L.F. Reichardt, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 736-742 (2003).
- C. Wang, E. Bomberg, C.J. Billington, A.S. Levine, C.M. Kotz, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus increases energy expenditure. Brain Res. 1336, 66-77 (2010).
- P. Wang, K.H. Loh, M. Wu, D.A. Morgan, M. Schneeberger, X. Yu, J. Chi, C. Kosse, D. Kim, K. Rahmouni, P. Cohen, J. Friedman, A leptin-BDNF pathway regulating sympathetic innervation of adipose tissue. Nature 583, 839-844 (2020).
- J.J. An, G.Y. Liao, C.E. Kinney, N. Sahibzada, B. Xu, Discrete BDNF neurons in the paraventricular hypothalamus control feeding and energy expenditure. Cell Metab. 22, 175–188 (2015).
- Y. Zhang, L. Zhou, H. Lian, Y. Zhang, S. Tong, Z. Wang, Dopamine receptor 2 downregulation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor upregulation in the paraventricular nucleus are correlated with brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in rats with bilateral substantia nigra lesions. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 117, 102016 (2021).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




