Submitted:
14 January 2025
Posted:
16 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
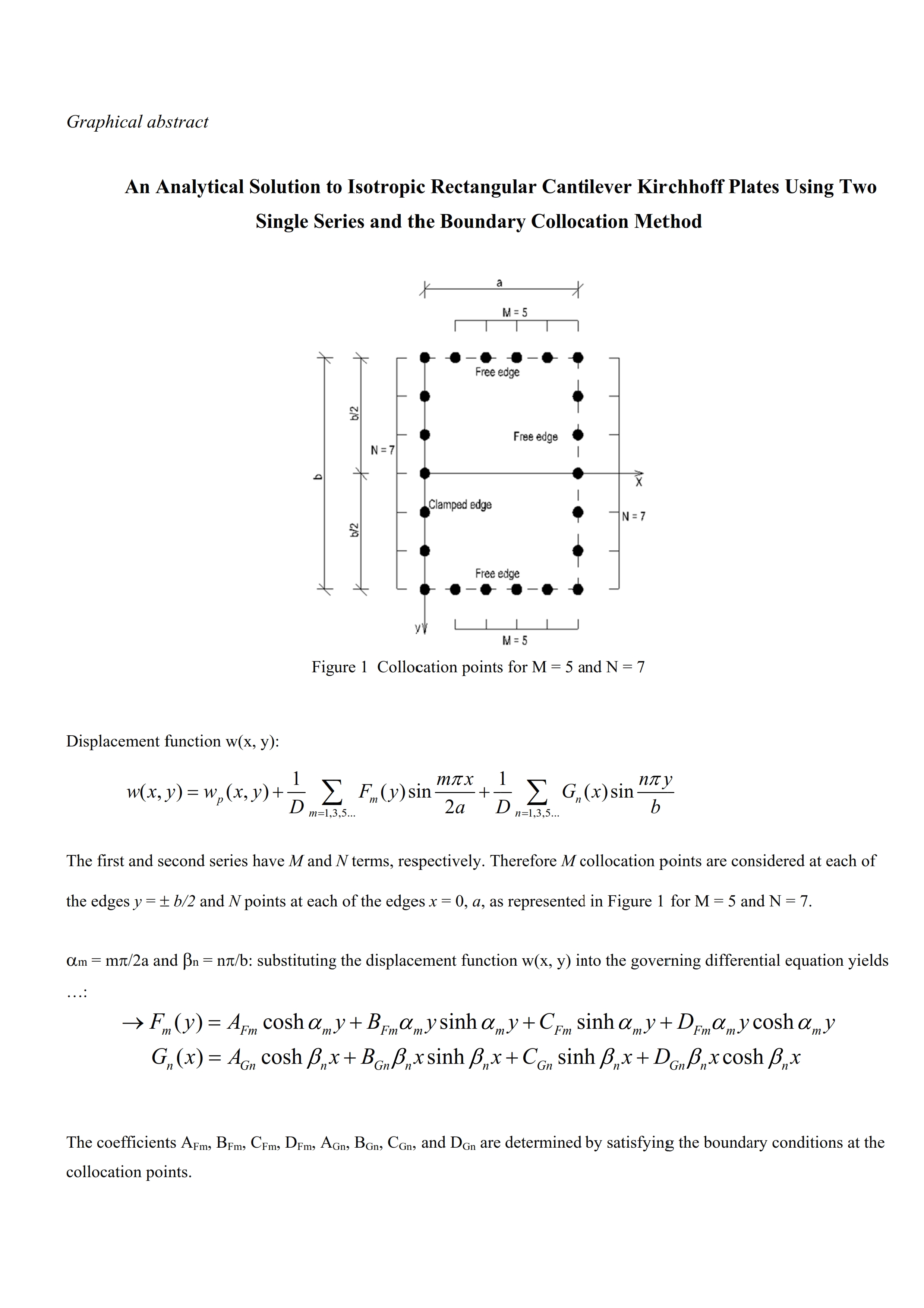
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.2. Governing Equations of the Plate
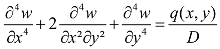
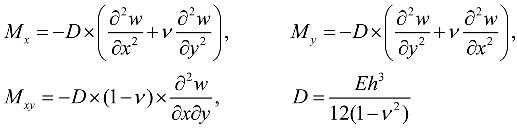
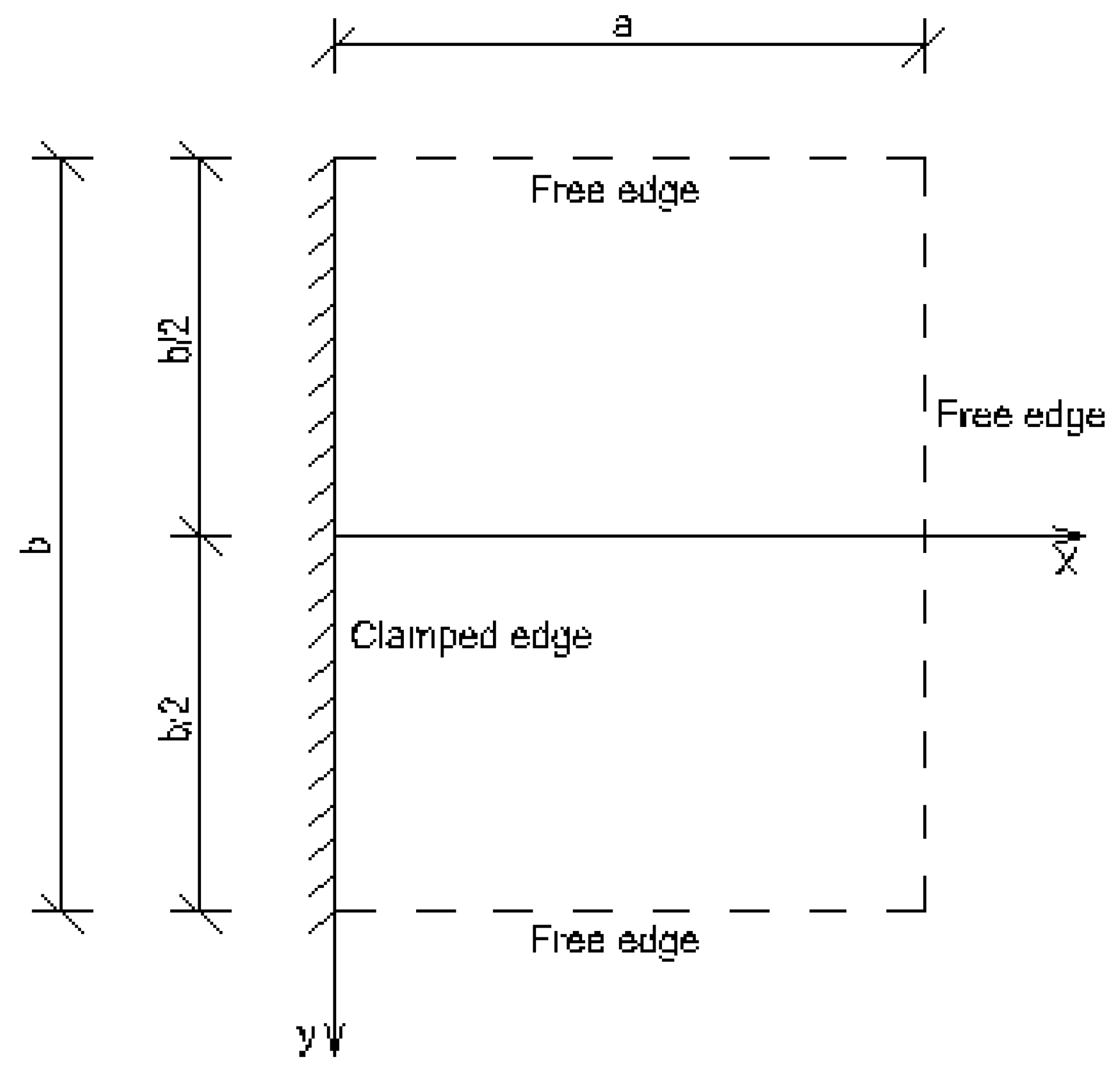
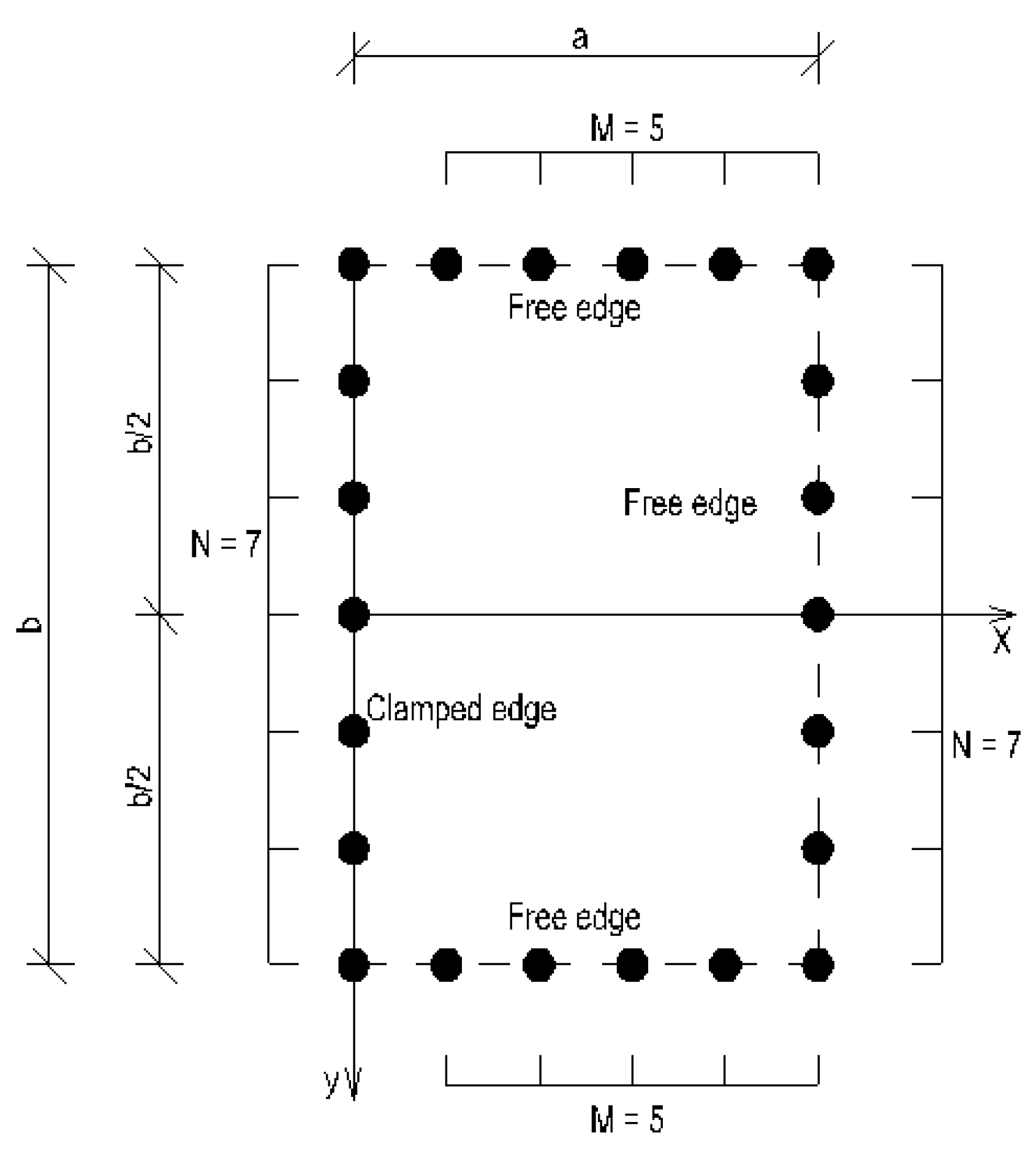
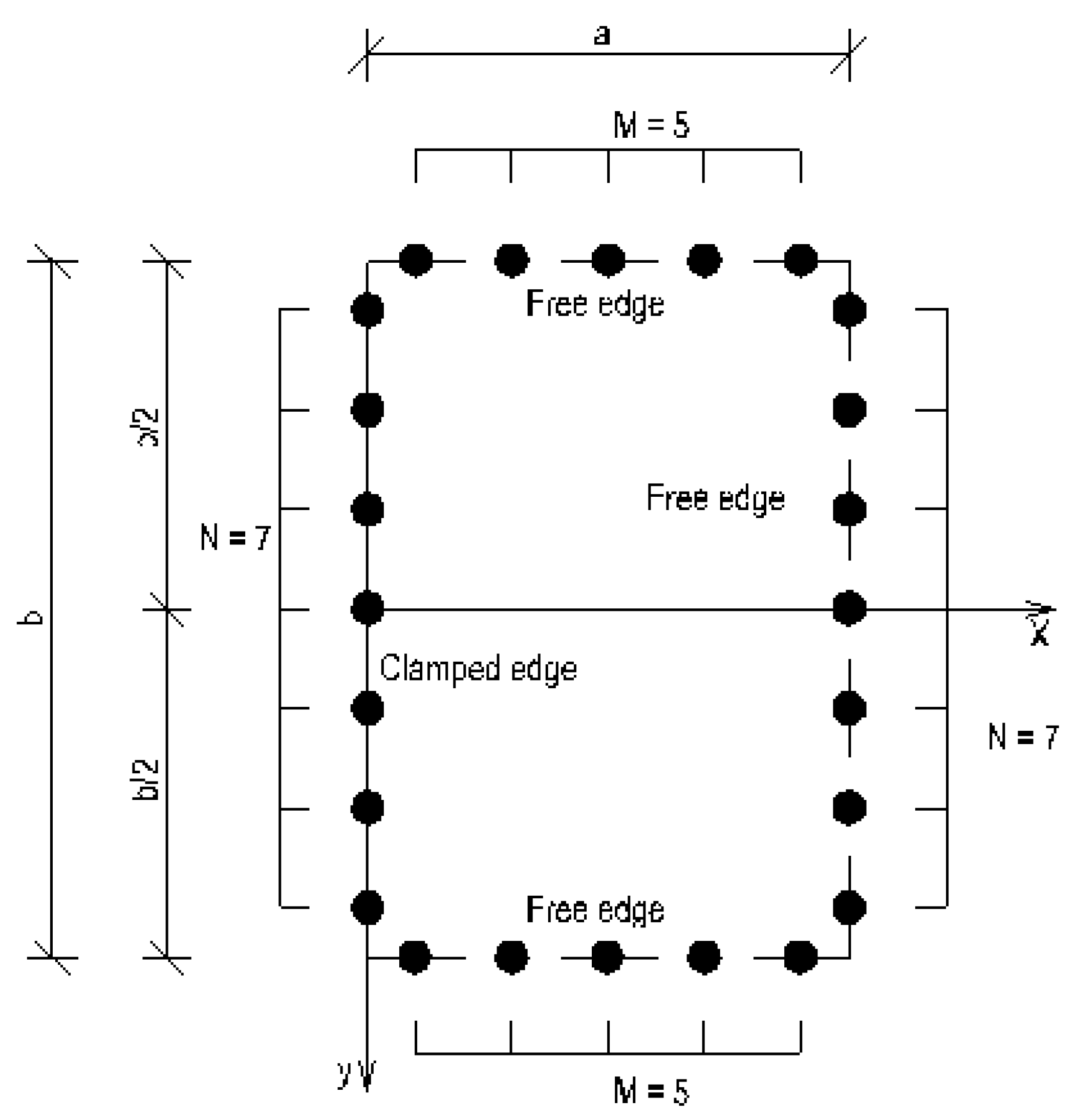
2.3. Plate Having Two Adjacent Edges Free and Supported at Three Corner Points
- Loading symmetrical about x axis, i.e., q(x, y) = q(x, -y): Equation (5b) is considered for the displacement whereby only the even parts of Fm(y) are considered, leading to CFm = Dfm = 0. The boundary conditions are then applied at only one half of the structure (e.g. y ≥ 0).
- Loading anti-symmetrical about x axis, i.e., q(x, y) = -q(x, -y): Equation (5a) is considered for the displacement whereby only the odd parts of Fm(y) are considered, leading to AFm = Bfm = 0. The boundary conditions are also applied at only one half of the structure (e.g. y ≥ 0).
Analysis of Special Cases
- a)
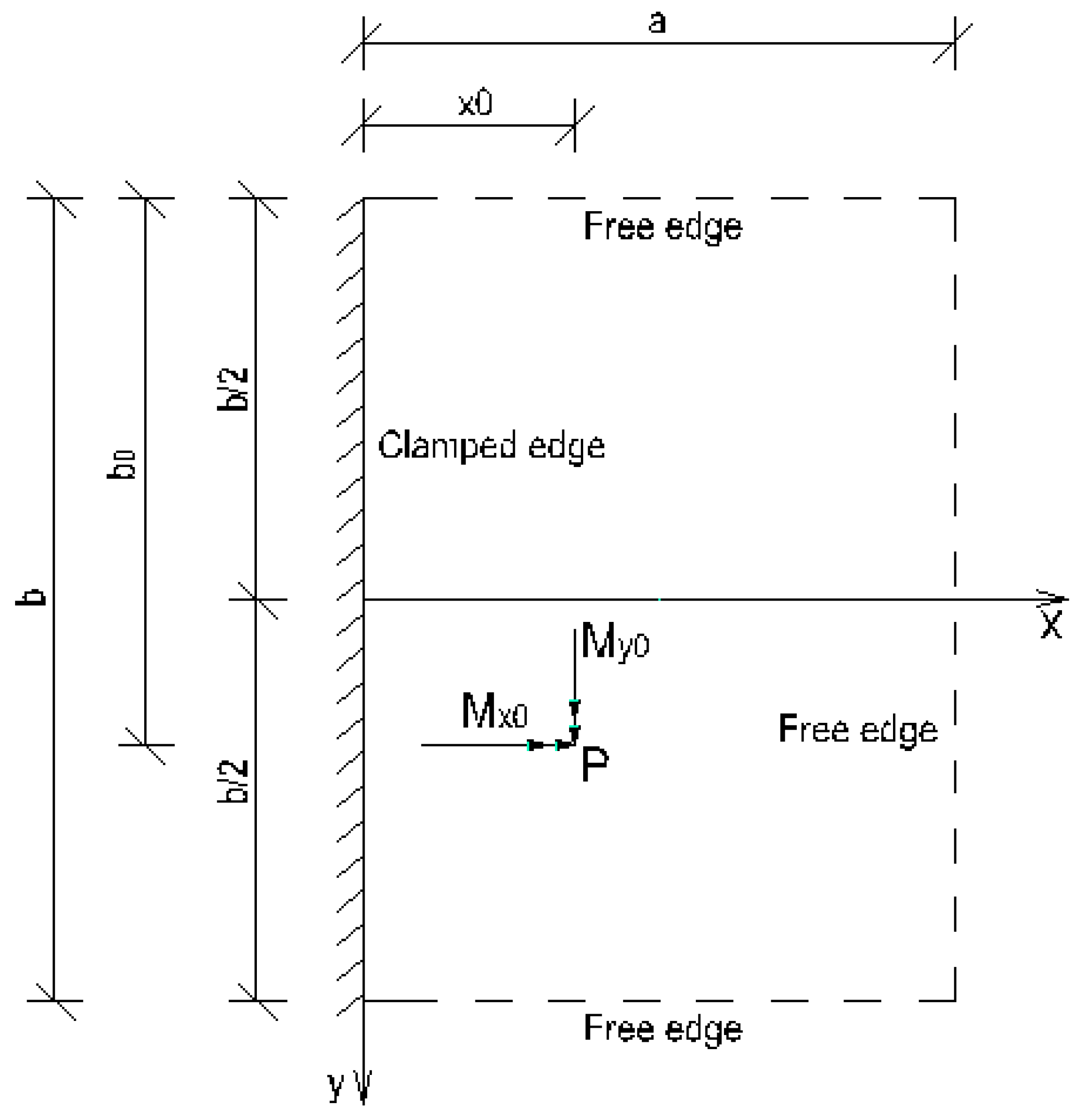
- Concentrated load acting at unsupported angles
- b)
- Concentrated force and moment applied at the interior of the plate
- If the force P or moment Mx0 is applied at a node the corresponding distributed load p or moment mx0 is obtained by dividing it with the node spacing; otherwise the force or moment is first distributed to the two neighboring nodes and then divided with the grid spacing to obtain the corresponding distributed loads or moments at the nodes.
- Plate zone I: 2NI equations at each of the edges x = 0, a and 2M equations at y = -b/2
- Plate zone II: 2NII equations at each of the edges x = 0, a and 2M equations at y = b/2
- 4M continuity equations at y = -b/2 + b0.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cantilever Plate Subjected to an Anti-Symmetrical Surface Loading p(x, y) = 2py/b
3.2. Cantilever Plate Subjected to an Anti-Symmetrical Line Loading p(y) = 2py/b Along x = a
3.3. Cantilever Plate Subjected to a Uniform Surface Loading p
3.4. Cantilever Plate Subjected to a Uniform Line Loading p Along the x-Axis
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A: Efforts and Deformations for the Formulation of Equation (5b)
References
- Fogang, V. An Analytical Solution to Rectangular Kirchhoff Plates Supported at All Corner Points Using Two Single Series and the Boundary Collocation Method. Preprints 2024, 2024102244. [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, G. Über das Gleichgewicht und die Bewegung einer elastischen Scheibe. J. für die Reine und Angew. Math.; vol. 18, no. 40, pp. 51-88, 1850.
- Trefftz, E. Ein Gegenstück zum Ritzschen Verfahren (An alternative to the Ritz method). Proceedings, 2nd International Congress of Applied Mechanics, Zurich, pp. 131-137, 1926.
- B. Tian, Y. Zhong, R. Li. Analytic bending solutions of rectangular cantilever thin plates. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, Volume 11, Issue 4, 2011, Pages 1043-1052. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, S. Cui, H. Jing, W. Zhang. Analysis and modeling of a flexible rectangular cantilever plate. Applied Mathematical Modelling, Volume 78, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Hase. AA, Chang, J. "Multiple Point Loading on Thin Cantilever Rectangular Plate Subjected to Pure Bending." Proceedings of the ASME 2021 30th Conference on Information Storage and Processing Systems. ASME 2021 30th Conference on Information Storage and Processing Systems. Virtual, Online. June 2–3, 2021. V001T02A004. ASME. [CrossRef]
- Q. Xu, Z. Yang, S. Ullah, Z. Jinghui, Y. Gao. Analytical Bending Solutions of Orthotropic Rectangular Thin Plates with Two Adjacent Edges Free and the Others Clamped or Simply Supported Using Finite Integral Transform Method. Advances in Civil Engineering. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Zia Tohidi, R., Babai, H., & Sadeghi, A. (2023). Analysis of Clamped Circular Plates with Large Deflections under Uniform Loading using Point Collocation Method. Advance Researches in Civil Engineering, 5(1), 70-85. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




