Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Governing equations of the plate
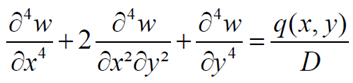
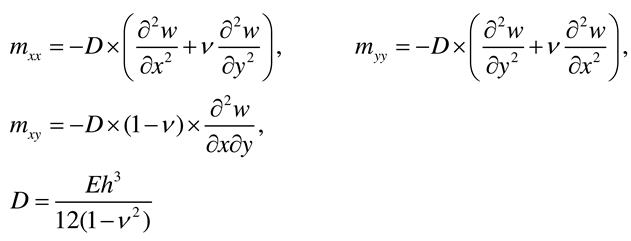


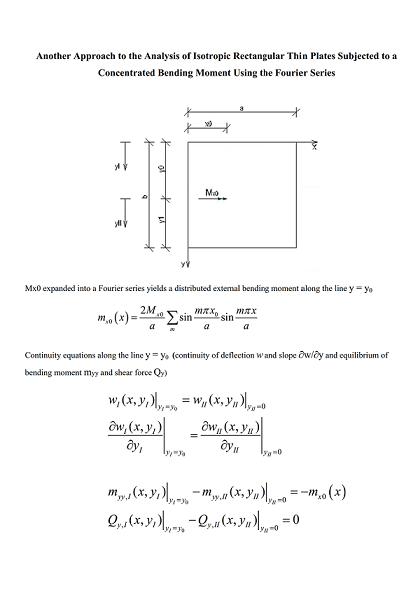
2.2. Rectangular plate supported along two opposite edges and subjected to external concentrated bending moments
2.2.1. Standard solution to the problem
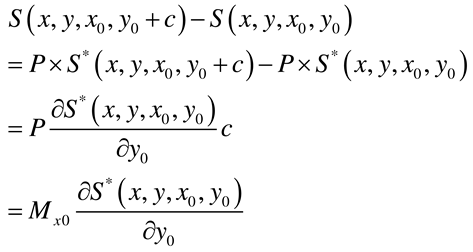
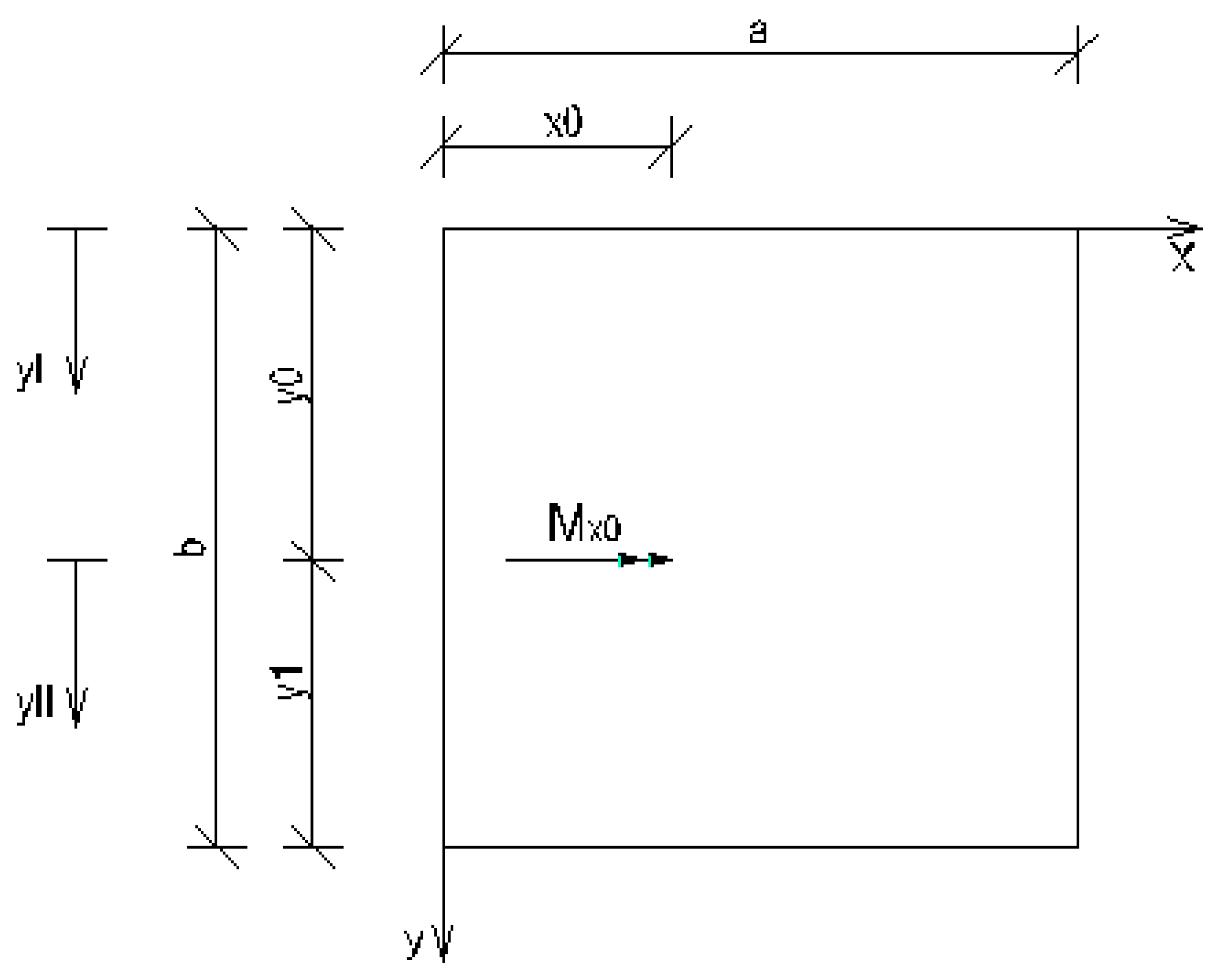
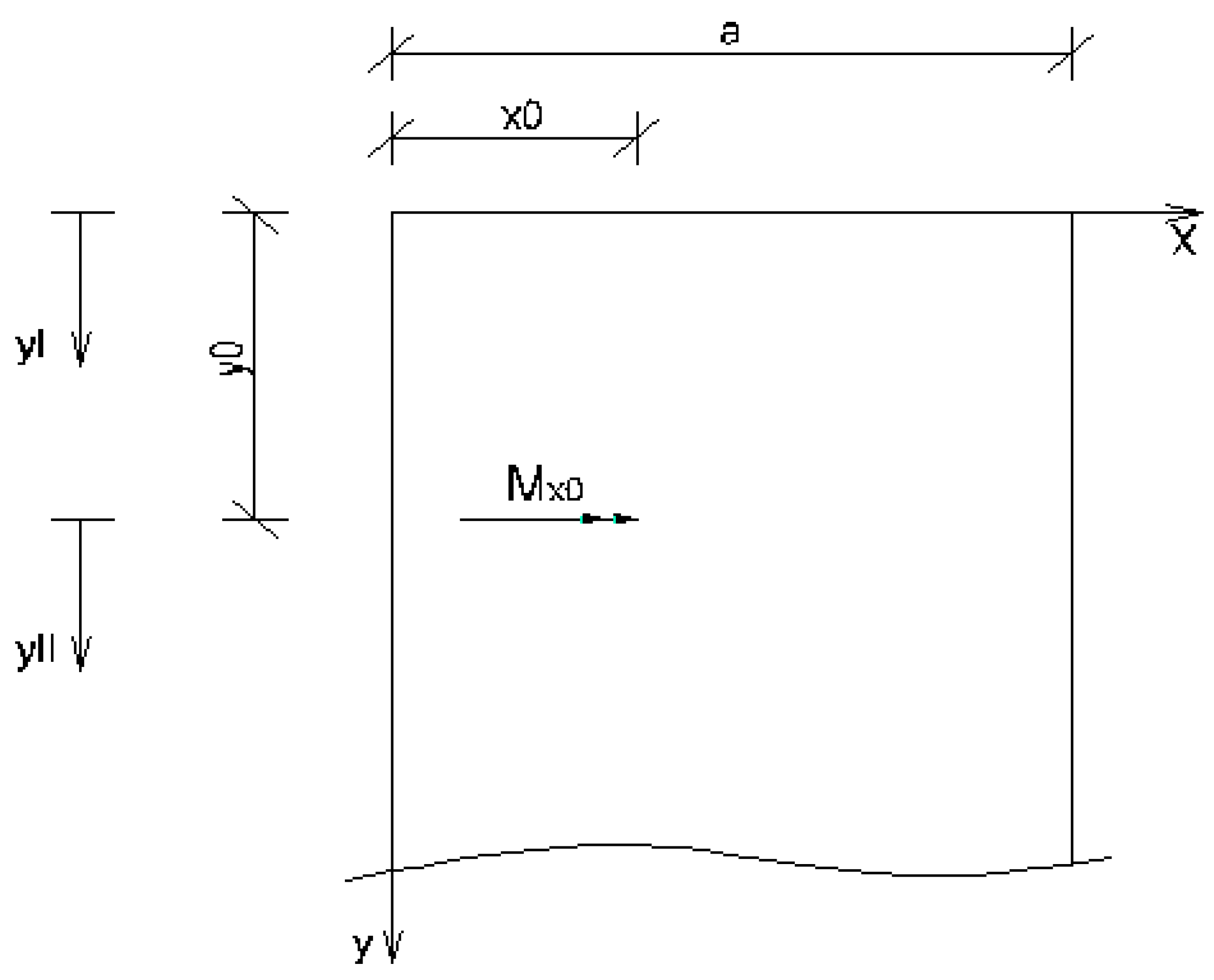
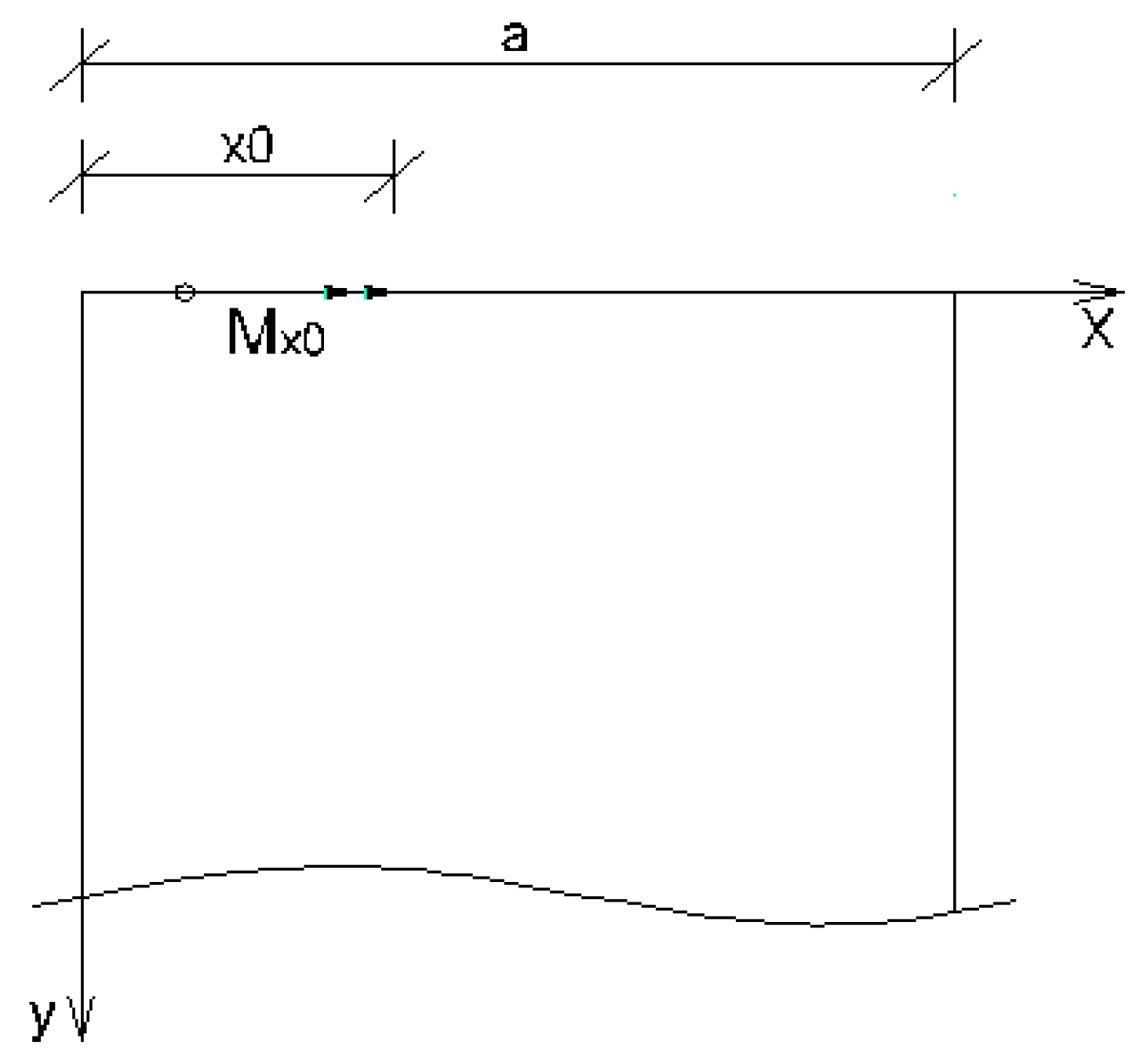
2.2.2. Rectangular plate with two opposite edges simply supported and subjected to an external concentrated bending moment Mx0
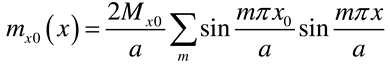
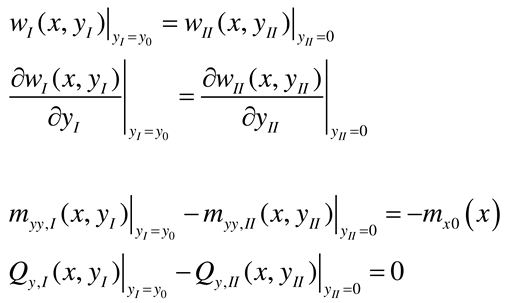
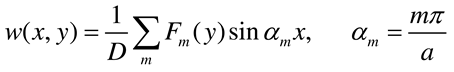
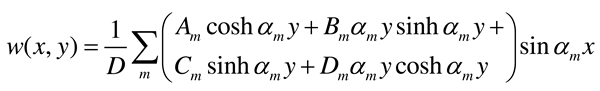
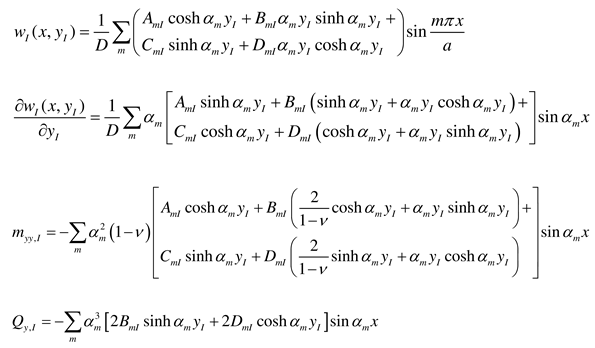
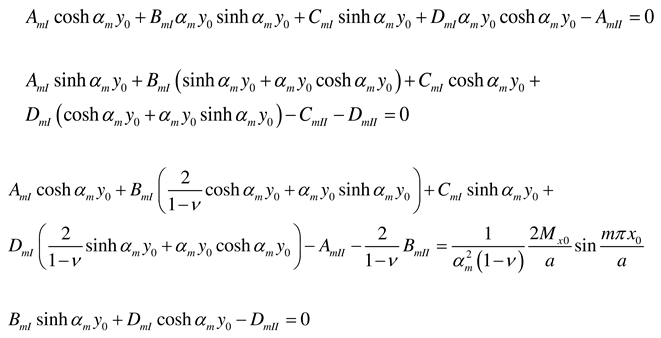
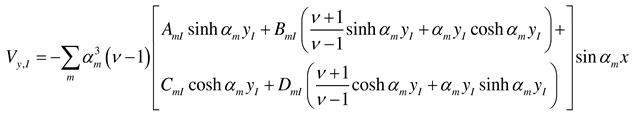
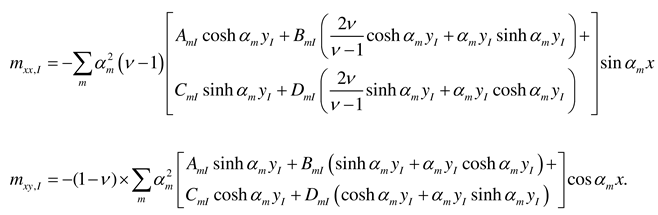
- Load case “Concentrated bending moment applied at the edge x = 0”
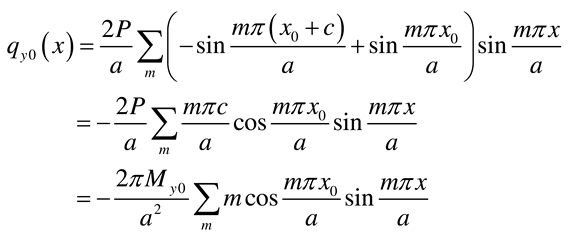
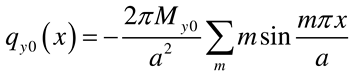
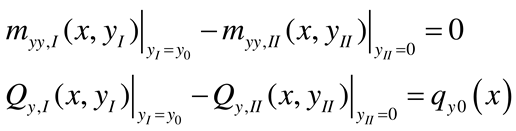
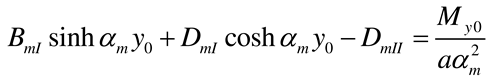
- Load case “Distributed bending moment applied along the edge x = 0”
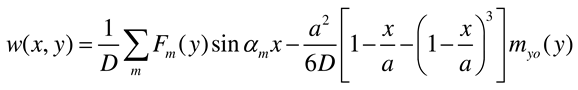
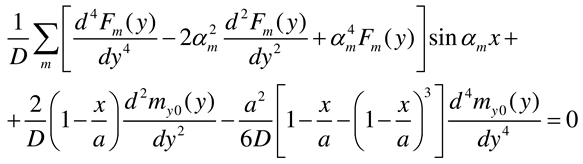
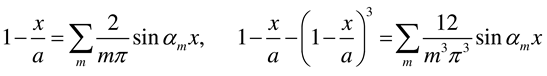
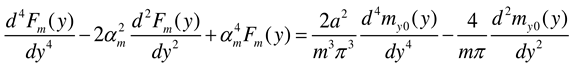
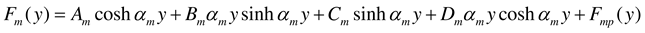
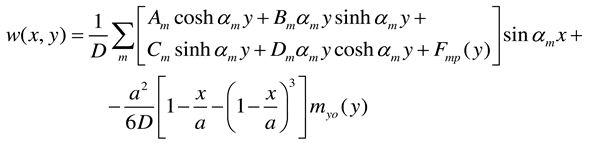
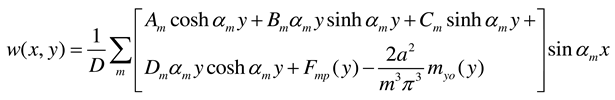
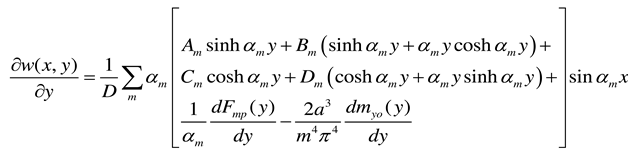
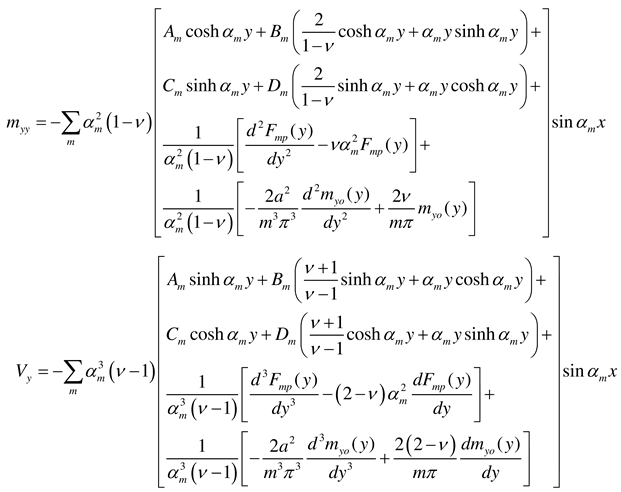
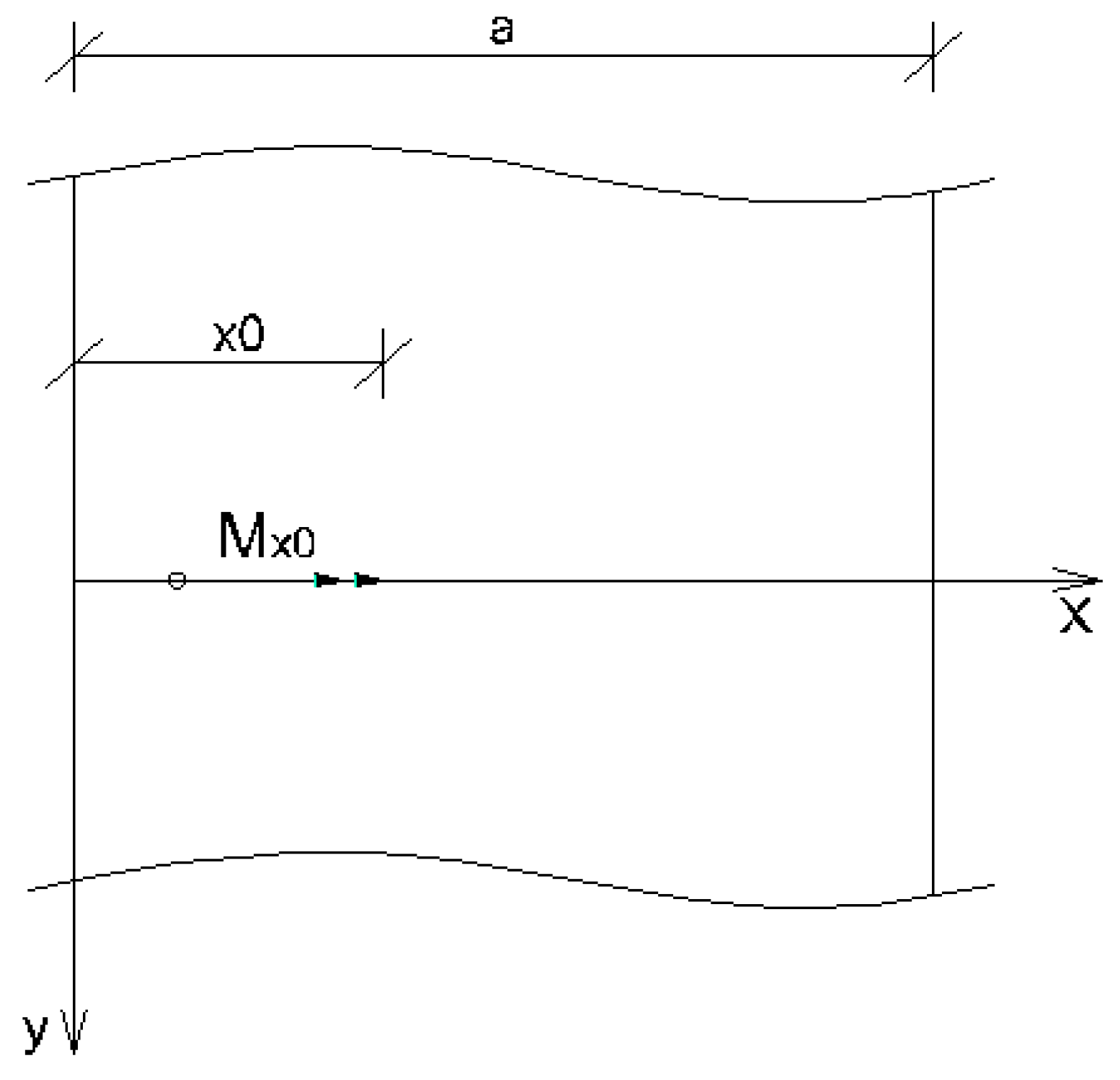
2.2.3. Rectangular plate of infinite length loaded near its end and having two opposite edges simply supported
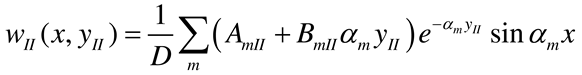
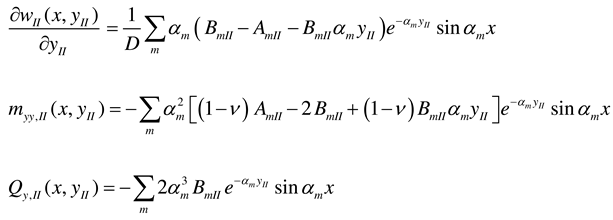
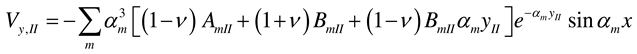
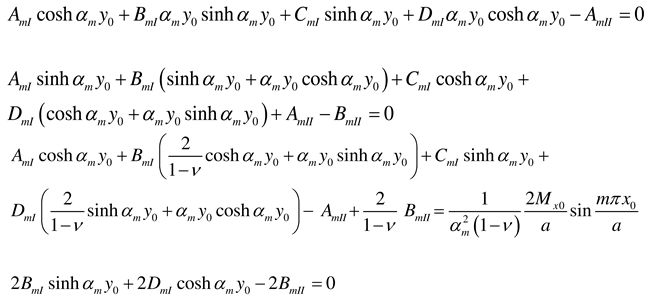
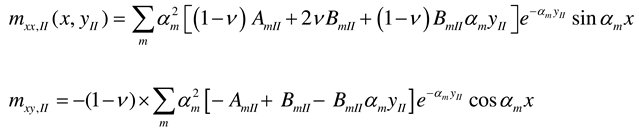
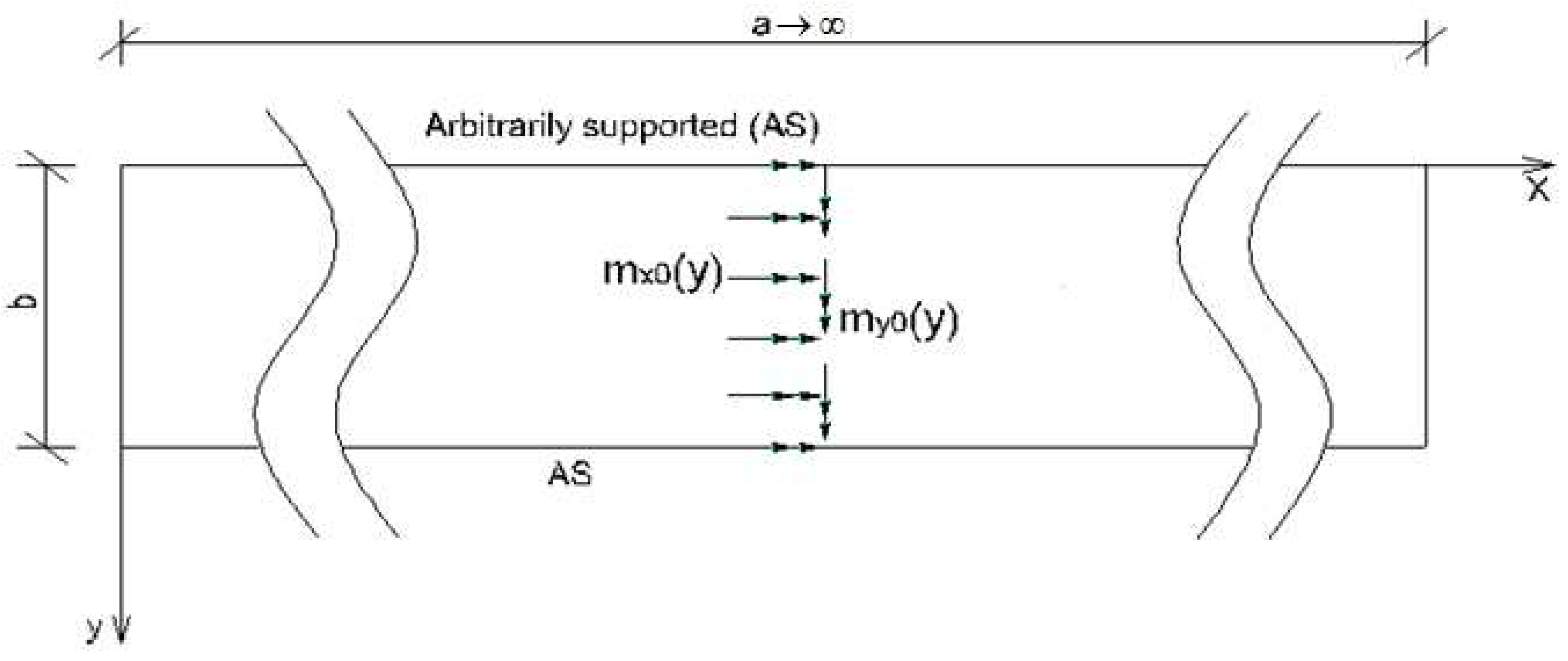
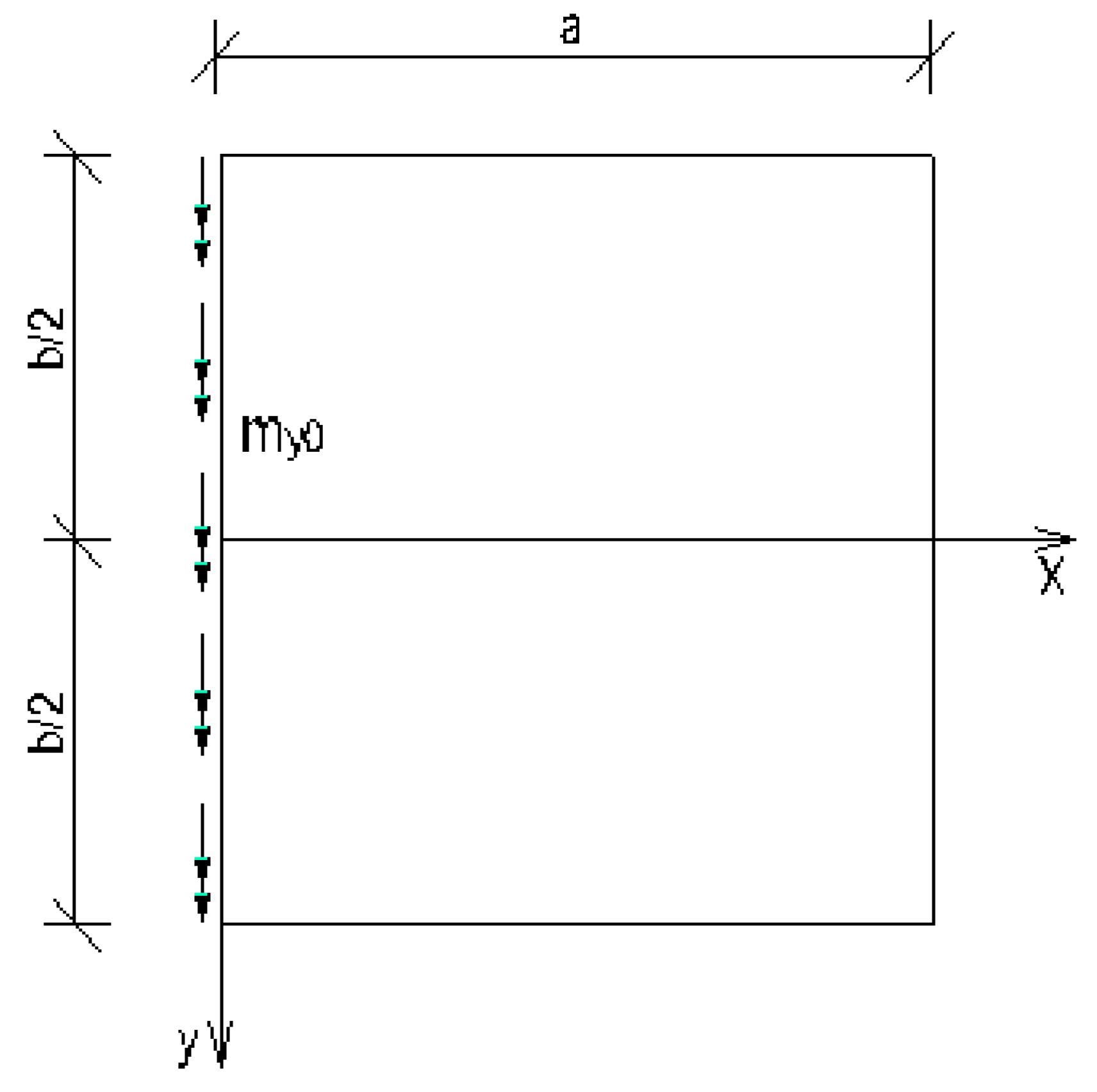
2.2.4. Rectangular plate of infinite length loaded around the plate middle and having two opposite edges arbitrarily supported
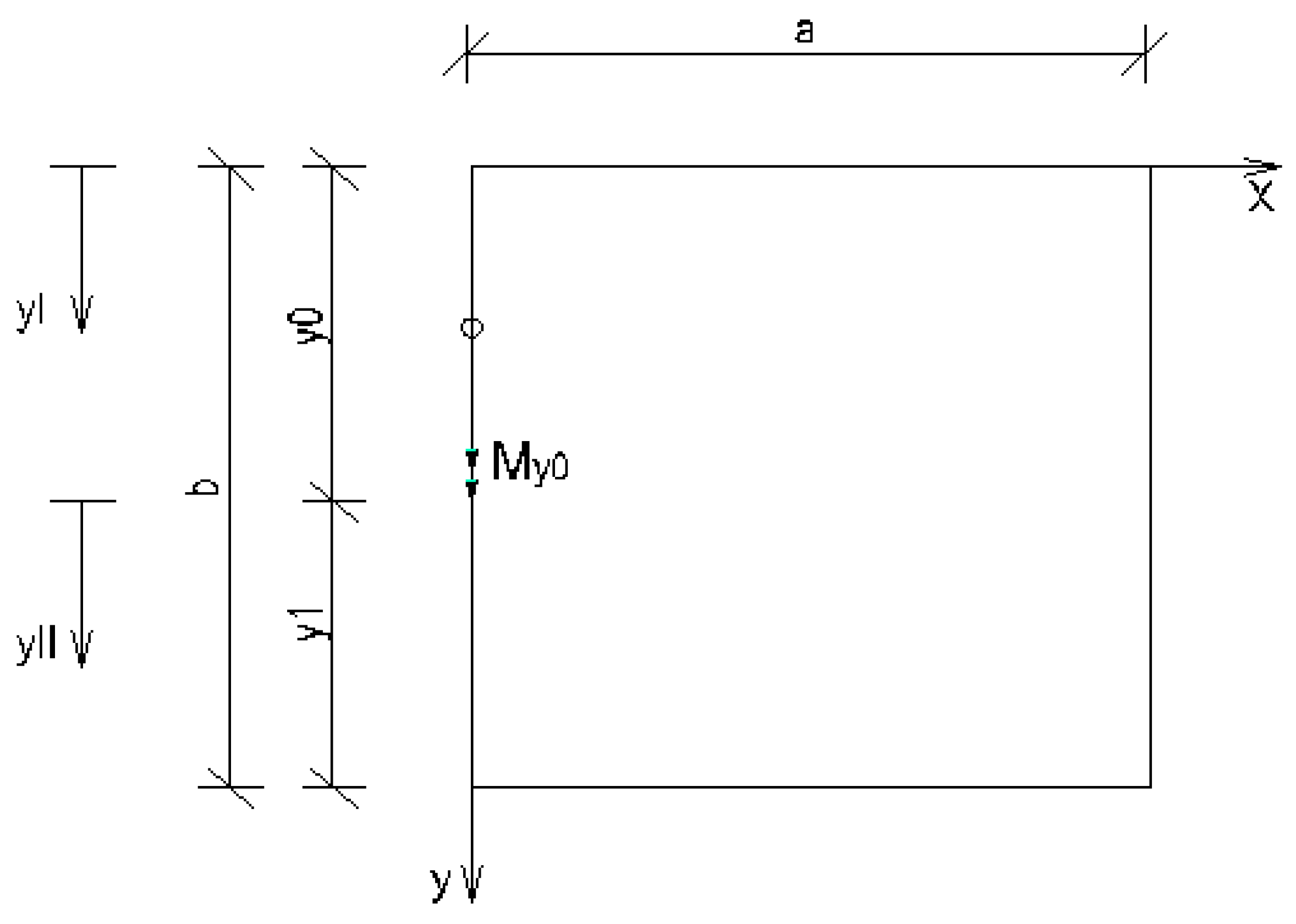
- Load case “Distributed bending moment mx0(y) applied along x = a/2”
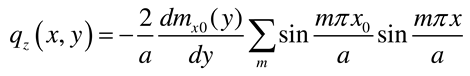
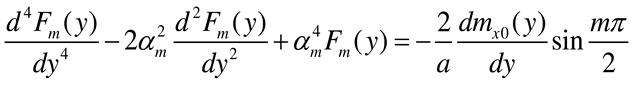
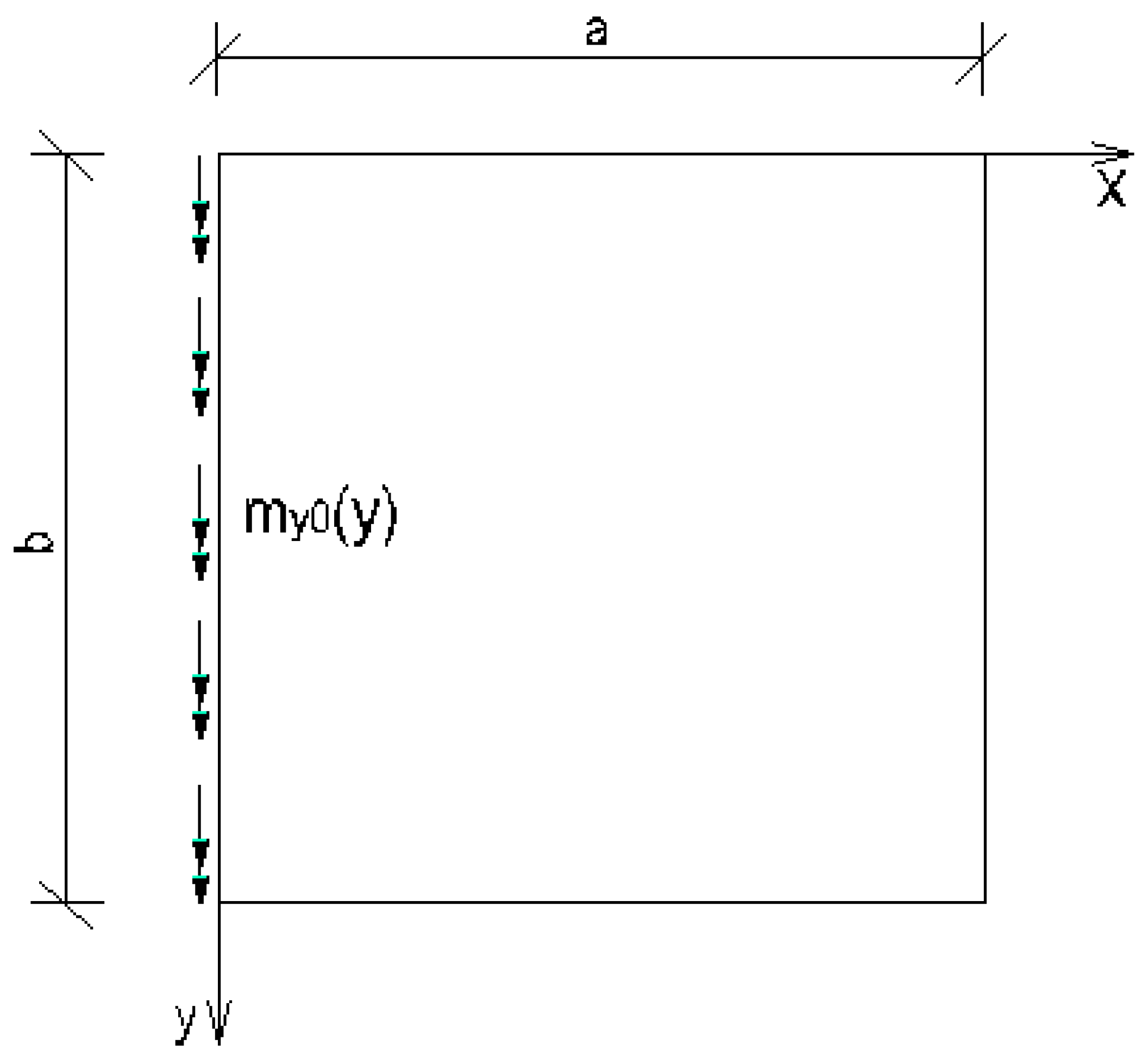
- Load case “Distributed bending moment my0(y) applied along x = a/2”
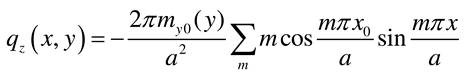
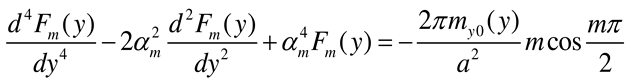
- Load case “External concentrated bending moments applied at (x = a/2, y = b)”
2.2.5. Solution of this study: Rectangular plate with one or two opposite edges clamped
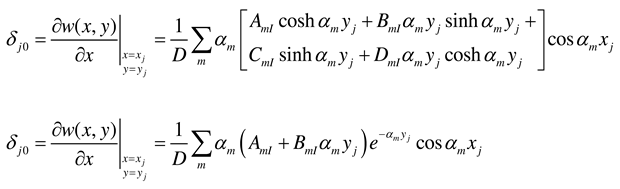
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Plate of infinite length subjected to an external concentrated moment at the middle
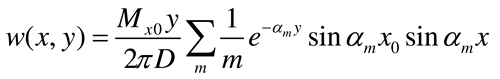
3.2. Plate of infinite length subjected to a concentrated moment at its end
- Case 1: Edge y = 0 simply supported
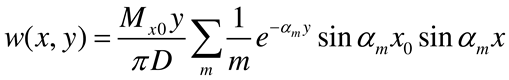
- Case 2: Edge y = 0 free
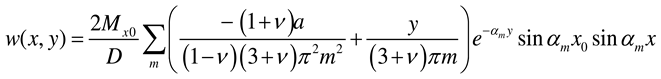
3.3. Rectangular plate with the edges x = 0 and x = a simply supported and subjected to a constant bending moment loading along x = 0
- Case y = 0 and y = b simply supported
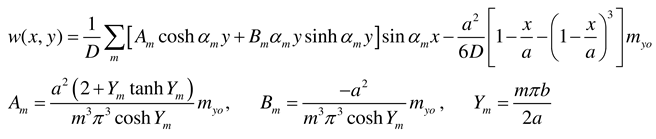
- Case y = 0 and y = b clamped
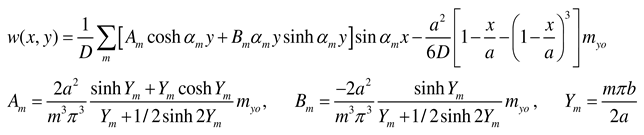
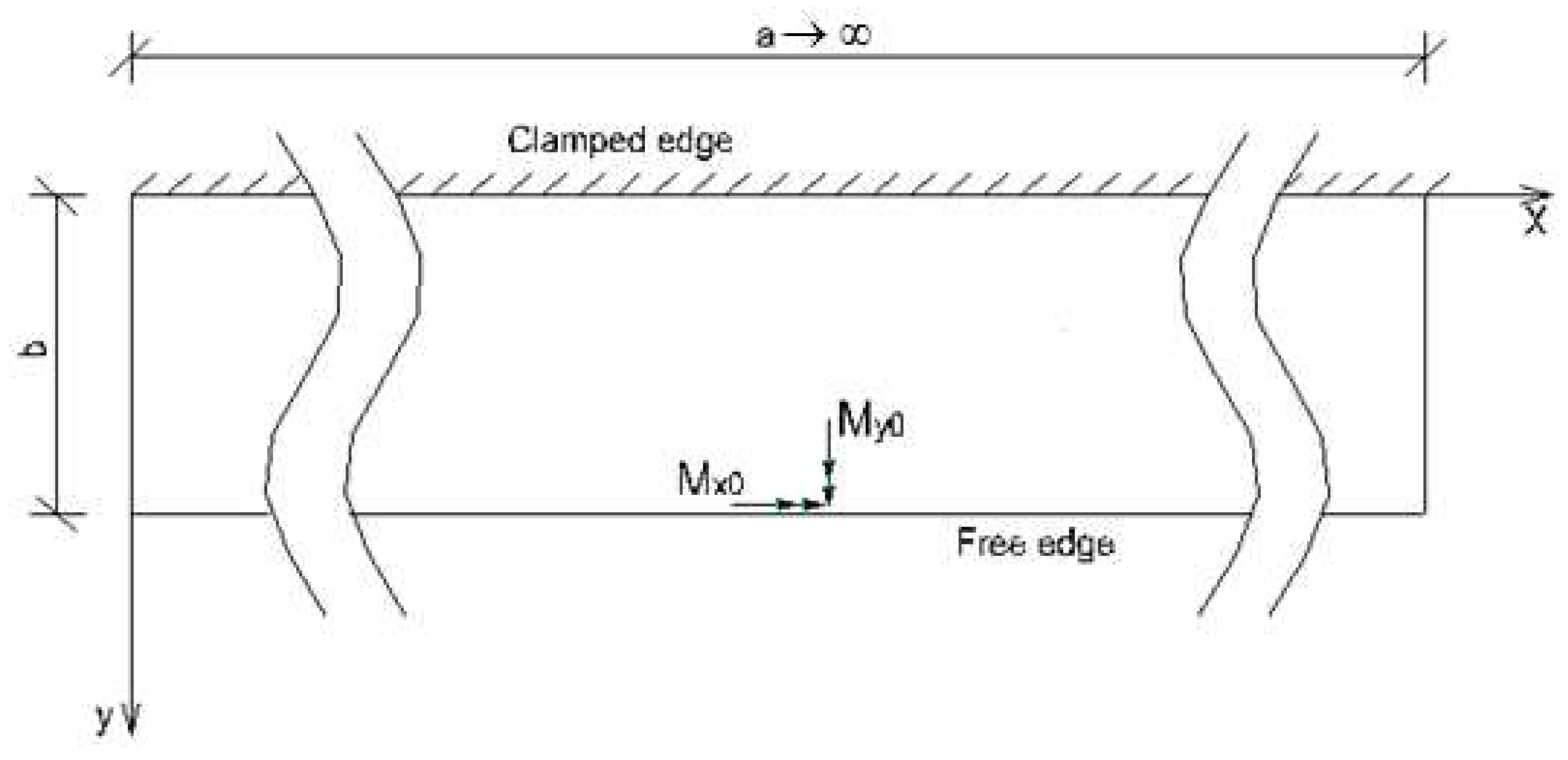
3.4. Cantilever plate of infinite length subjected to external concentrated moments at the middle
- Load case “Concentrated bending moment Mx0 applied at (x = a/2, y = b)”
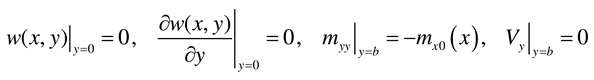
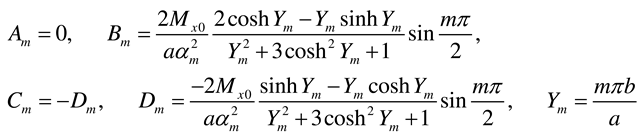
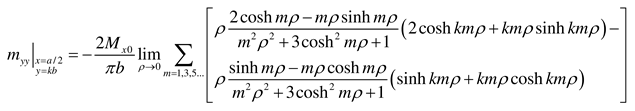
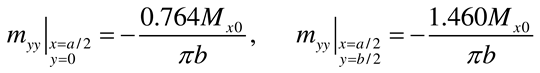
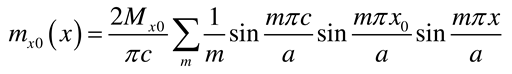
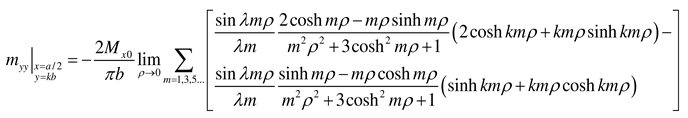
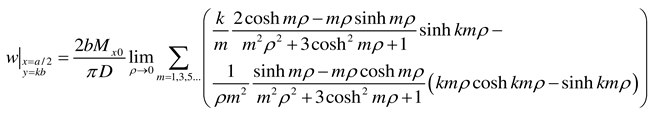
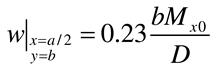
- Load case “Concentrated bending moment My0 applied at (x = a/2, y = b)”
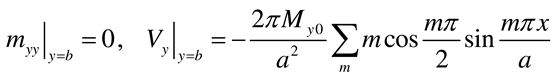
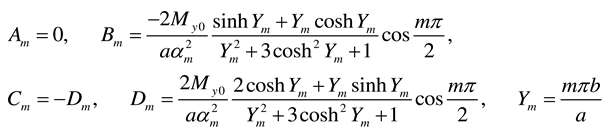
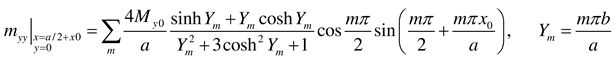
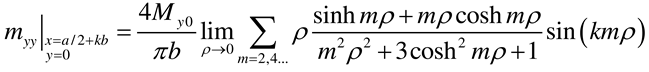
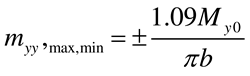
3.5. Plate of infinite length subjected to a concentrated moment Mx0 at (x = a/2, y = b)
- Case y = 0 clamped and y = b simply supported
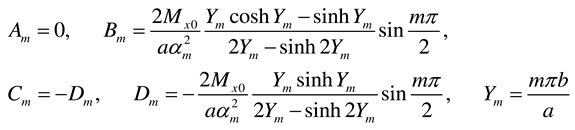
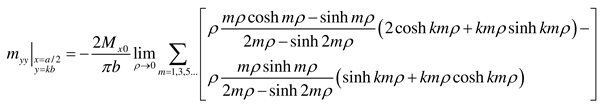
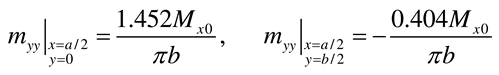
- Case y = 0 and y = b simply supported
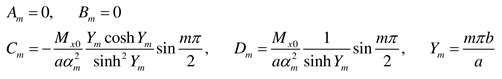
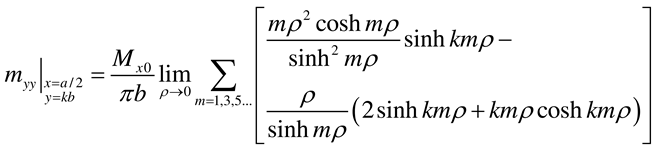
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Coefficients AmI, BmI, CmI, and DmI and AmII, BmII, CmII, and DmII for various support conditions at y = 0 and y = b
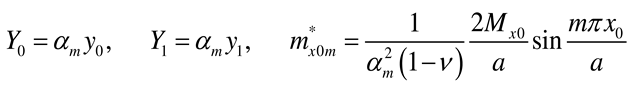


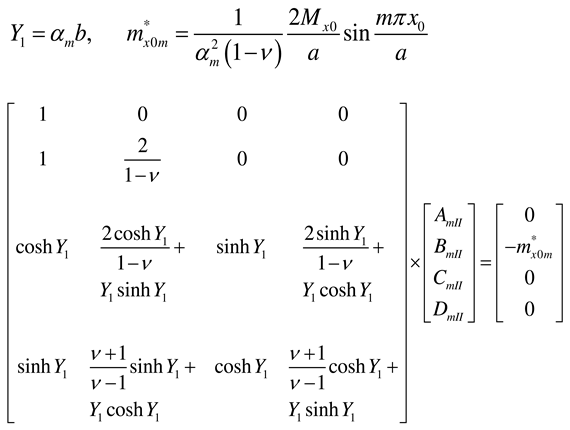
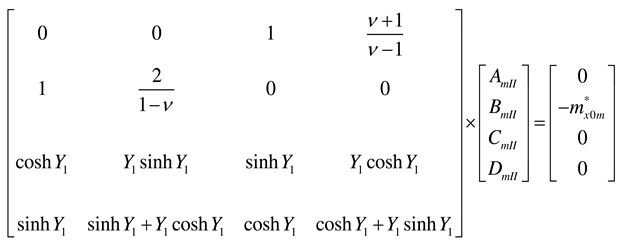
Appendix B. Plate of infinite length: coefficients AmI, BmI, CmI, DmI, AmII, and BmII for various support conditions at y = 0
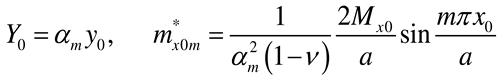
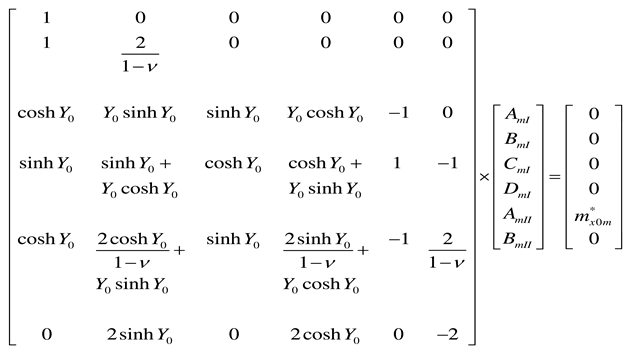
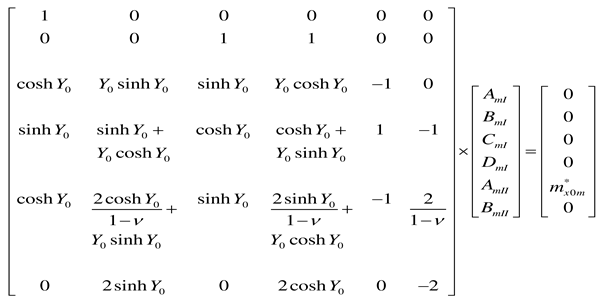
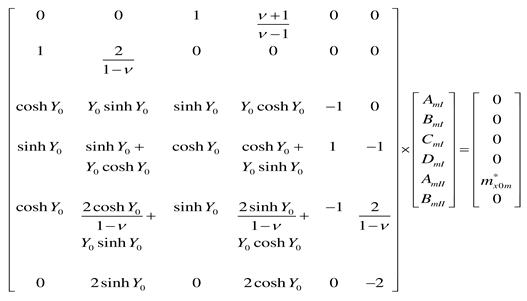
References
- Kirchhoff, G. Über das Gleichgewicht und die Bewegung einer elastischen Scheibe. J. für die Reine und Angew. Math. 1850, 18, 51–88. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, S. Remarques sur la nature, les bornes et l’étendue de la question des surfaces élastiques et équation générale de ces surfaces. impr. de Huzard-Courcier, paris, 1826.
- Lévy, M. Sur l’équilibre élastique d’une plaque rectangulaire. Comptes rendus l’Académie des Sci. Paris 1899, 129, 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S.; Woinowsky-Krieger, S. Theory of plates and shells, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Girkmann, K. Flächentragwerke; Springer-Verlag: Wien, New York, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L. Trends in Developing Critical Elastic Buckling Formula for Fixed Rectangular Plate Subjected To a Concentrated Load. Trends Civ. Eng. its Arch. 2018, 1, 001–003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Z. Exact solutions for rectangular anisotropic plates with four clamped edges. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyia, M.E.; Rowland-Lato, E.O.; Ike, C.C. Elastic Buckling Analysis of SSCF and SSSS Rectangular Thin Plates using the Single Finite Fourier Sine Integral Transform Method. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imrak, C.E.; Gerdemeli, I. An Exact Solution for the Deflection of a Clamped Rectangular Plate under Uniform Load. Applied Mathematical Sciences 2007, 1, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar]
- Fogang, V. Analysis of Arbitrarily Loaded Rectangular Thin Plates with Two Opposite Edges Supported, One or Both of them Clamped, Using the Flexibility Method and a Modified Lévy Solution. Preprints.org 2023, 2023052121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, B.O.; Oguaghamba, O.A.; Ike, C.C. Single Finite Fourier Sine Integral Transform Method for the Flexural Analysis of Rectangular Kirchhoff Plate with Opposite Edges Simply Supported, Other Edges Clamped for the Case of Triangular Load Distribution. IJERT 2020, 13, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.-K. Finite Fourier transform for solving potential and steady-state temperature problems. Advances in Difference Equations 2018, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courbon, J.; Theillout, J.N. Formulaire de résistance des matériaux. Techniques de l’Ingénieur, Traité Construction 1987, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| k = | 0,00 | 0,20 | 0,40 | 0,50 | 0,60 | 0,70 | 0,80 | 0,90 |
| F(k) = | 0,3820 | 0,4992 | 0,6289 | 0,7302 | 0,8853 | 1,1514 | 1,7021 | 3,4303 |
| k = | 0,00 | 0,20 | 0,40 | 0,50 | 0,60 | 0,70 | 0,80 | 0,90 |
| F(k, λ = 0.05) = | 0,3826 | 0,4992 | 0,6288 | 0,7300 | 0,8853 | 1,1510 | 1,6970 | 3,3397 |
| F(k, λ = 0.10) = | 0,3842 | 0,4994 | 0,6287 | 0,7297 | 0,8846 | 1,1484 | 1,6779 | 3,0979 |
| k = | 0,20 | 0,40 | 0,50 | 0,60 | 0,70 | 0,80 | 0,90 | 1,00 |
| F(k) = | 0,0085 | 0,0370 | 0,0603 | 0,0910 | 0,1307 | 0,1821 | 0,2513 | 0,3610 |
| k = | 0,00 | 0,25 | 0,50 | 0,75 | 1,00 | 1,50 | 2,50 |
| F(k) = | 0,000 | 0,1846 | 0,2686 | 0,2577 | 0,2070 | 0,1081 | 0,0264 |
| k = | 0,45 | 0,5 | 0,6 | ||||
| F(k) = | 0,2610 | 0,2686 | 0,2725 | ||||
| k = | 0,00 | 0,30 | 0,40 | 0,50 | 0,60 | 0,70 | 0,80 | 0,90 |
| F (k) = | -0,7258 | -0,1205 | 0,0369 | 0,2018 | 0,3984 | 0,6782 | 1,1577 | 2,6953 |
| k = | 0,00 | 0,30 | 0,40 | 0,50 | 0,60 | 0,70 | 0,80 | 0,90 |
| F (k) = | 0,0000 | -0,4002 | -0,5707 | -0,7858 | -1,0839 | -1,5619 | -2,5538 | -5,4557 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




