Submitted:
30 October 2024
Posted:
31 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Culture
2.2. Genome Sequencing of A. oryzae XJ1
2.2.1. Extraction of Genomic DNA of A. oryzae XJ1
2.2.2. Library Construction of A. oryzae XJ1
2.2.3. Sequencing
2.2.4. Genome Assembly
2.2.4.1. Preliminary Assembly with SMRT Link
2.2.4.2. Correction of the Preliminary Assembly
2.2.5. Genome Component Prediction
2.2.6. Prediction of Gene Functions
2.3. Comparative Genomic Analysis
2.3.1. Gene Family Analysis
2.3.2. Phylogenomic tree Reconstruction Based on Genome Alignment
2.3.3. Core/Pan-Genome Analysis
2.3.4. Genomic Synteny Analysis
3. Results
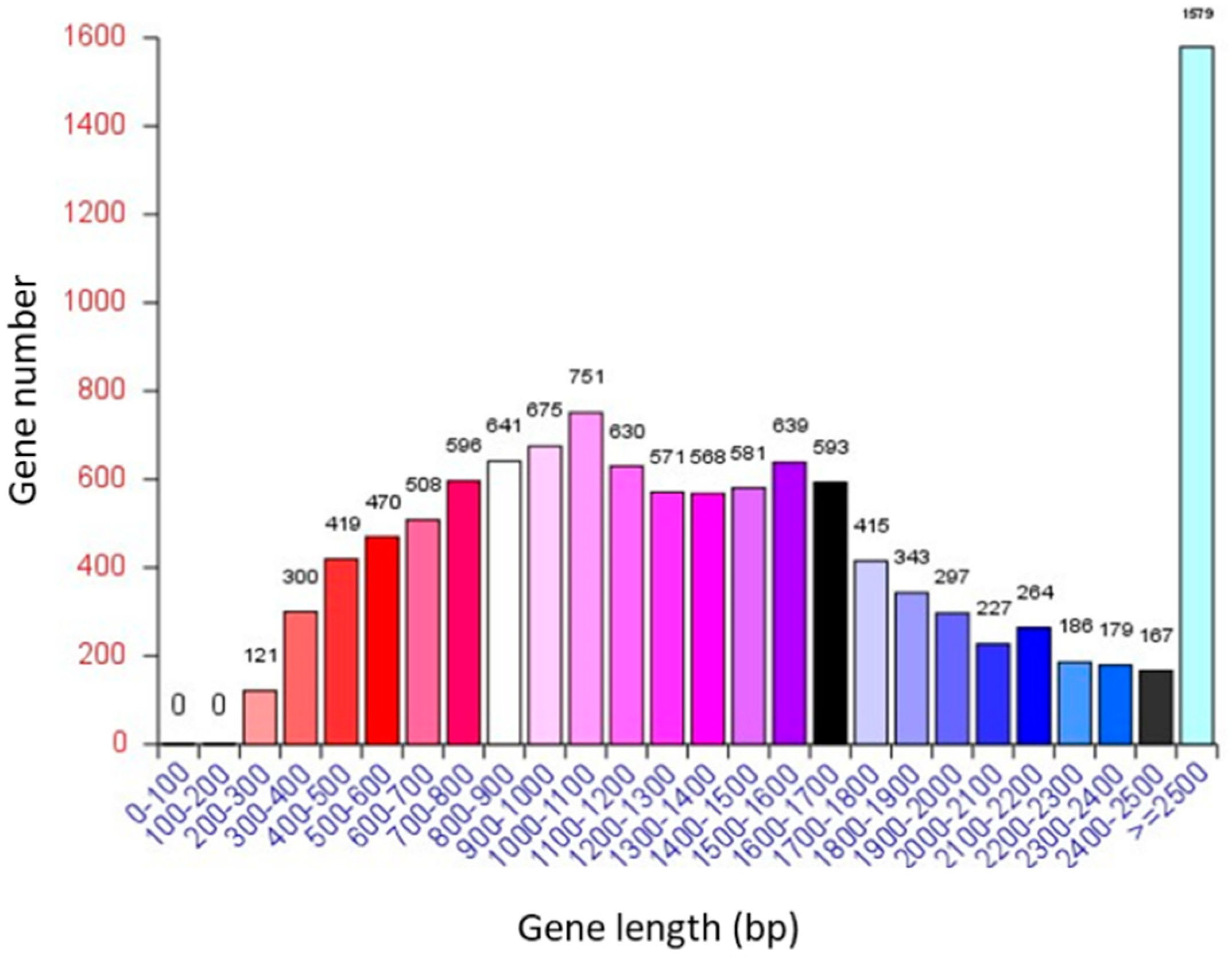
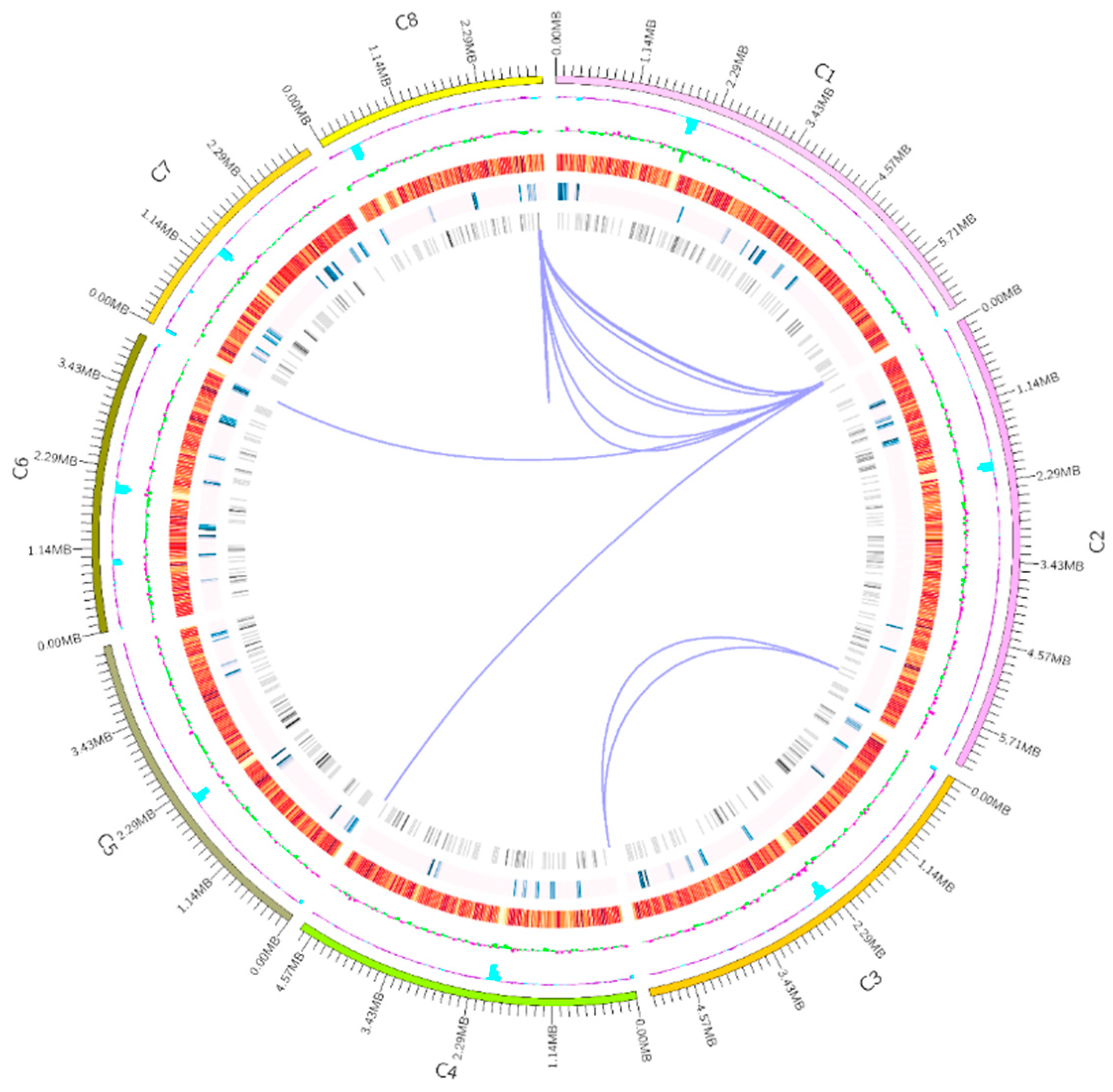
3.1. General Information on the A. oryzae XJ1 Genome
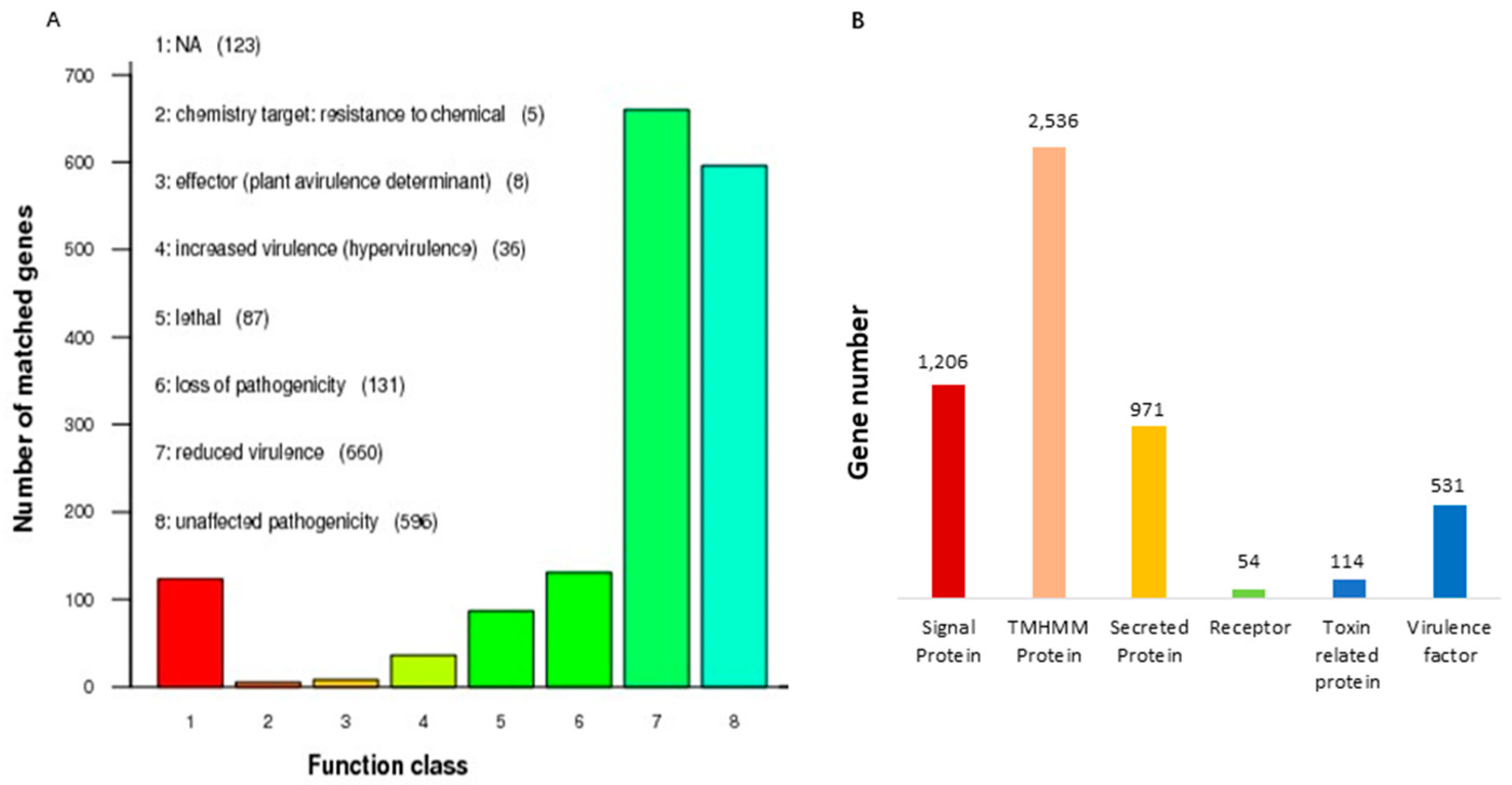
3.2. Analysis of Predicted Gene Functions in A. oryzae XJ1
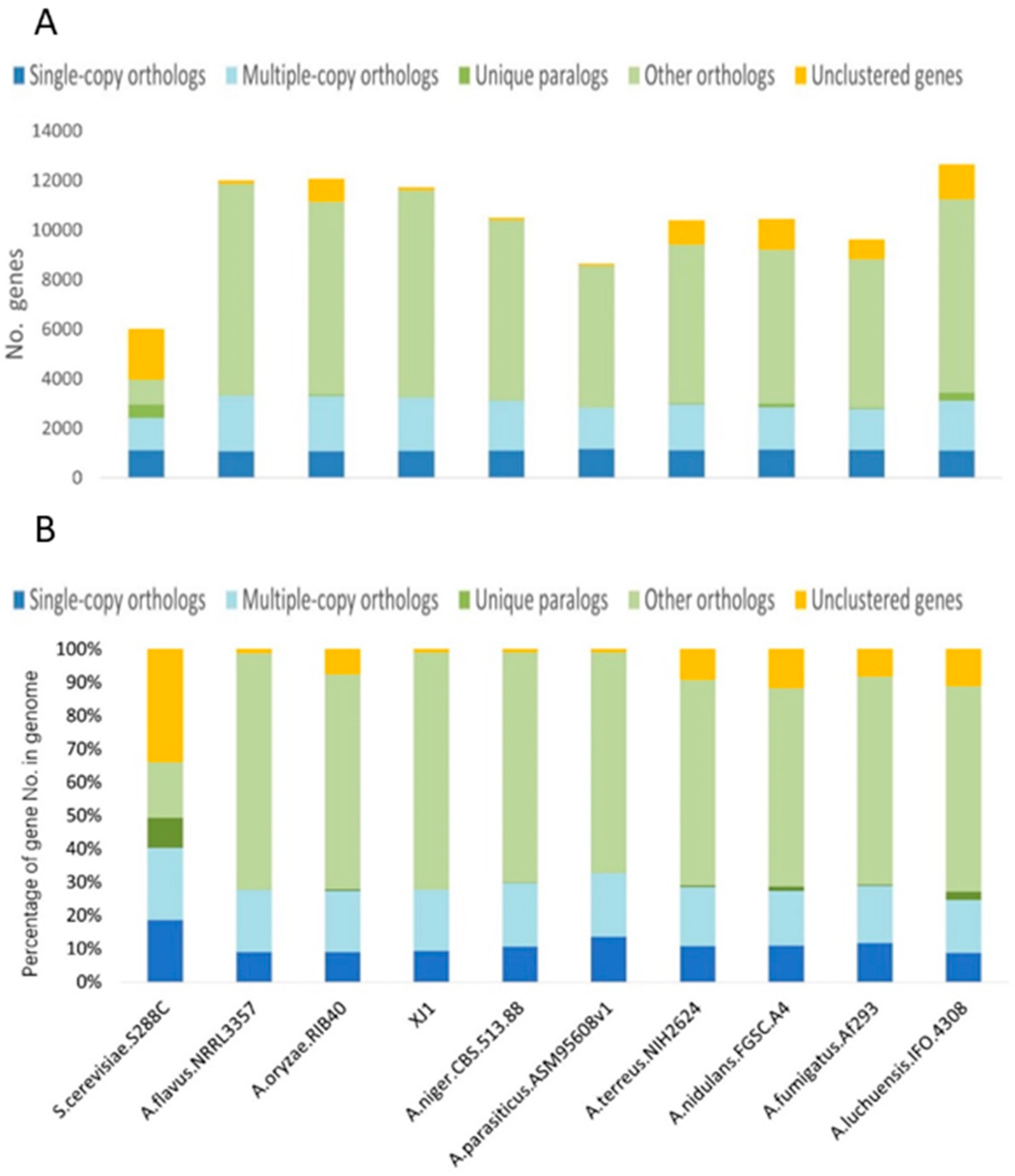
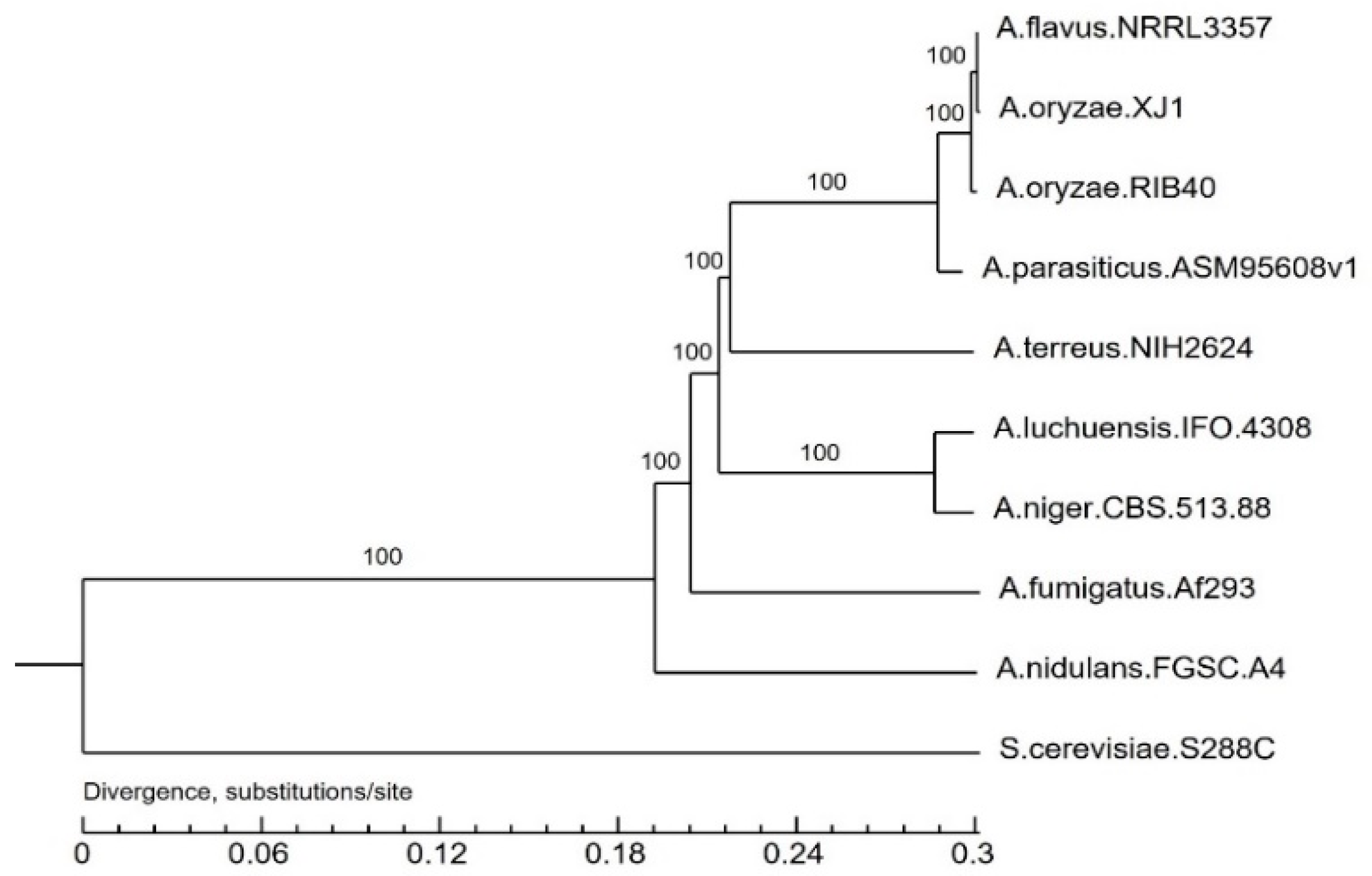
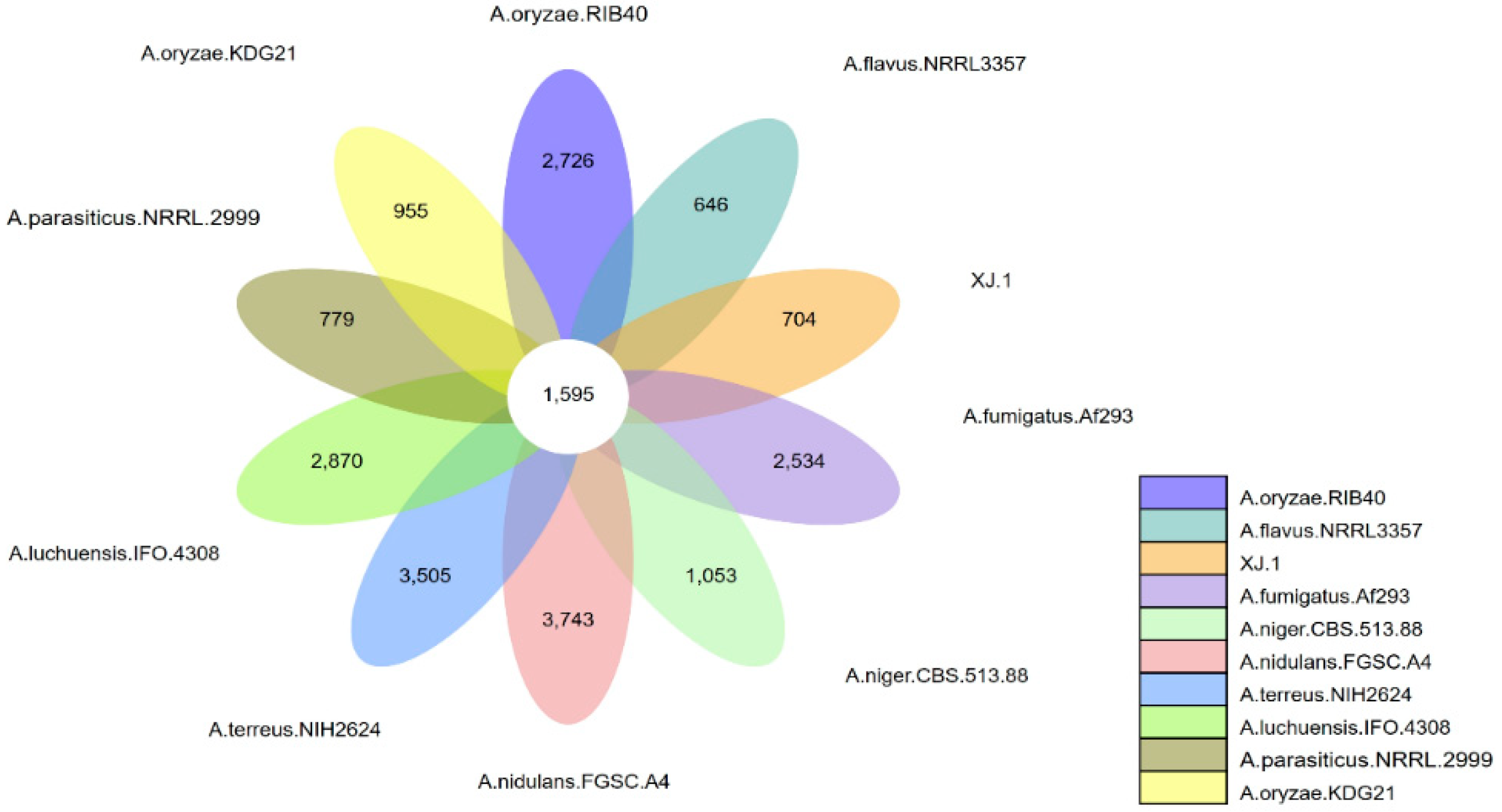
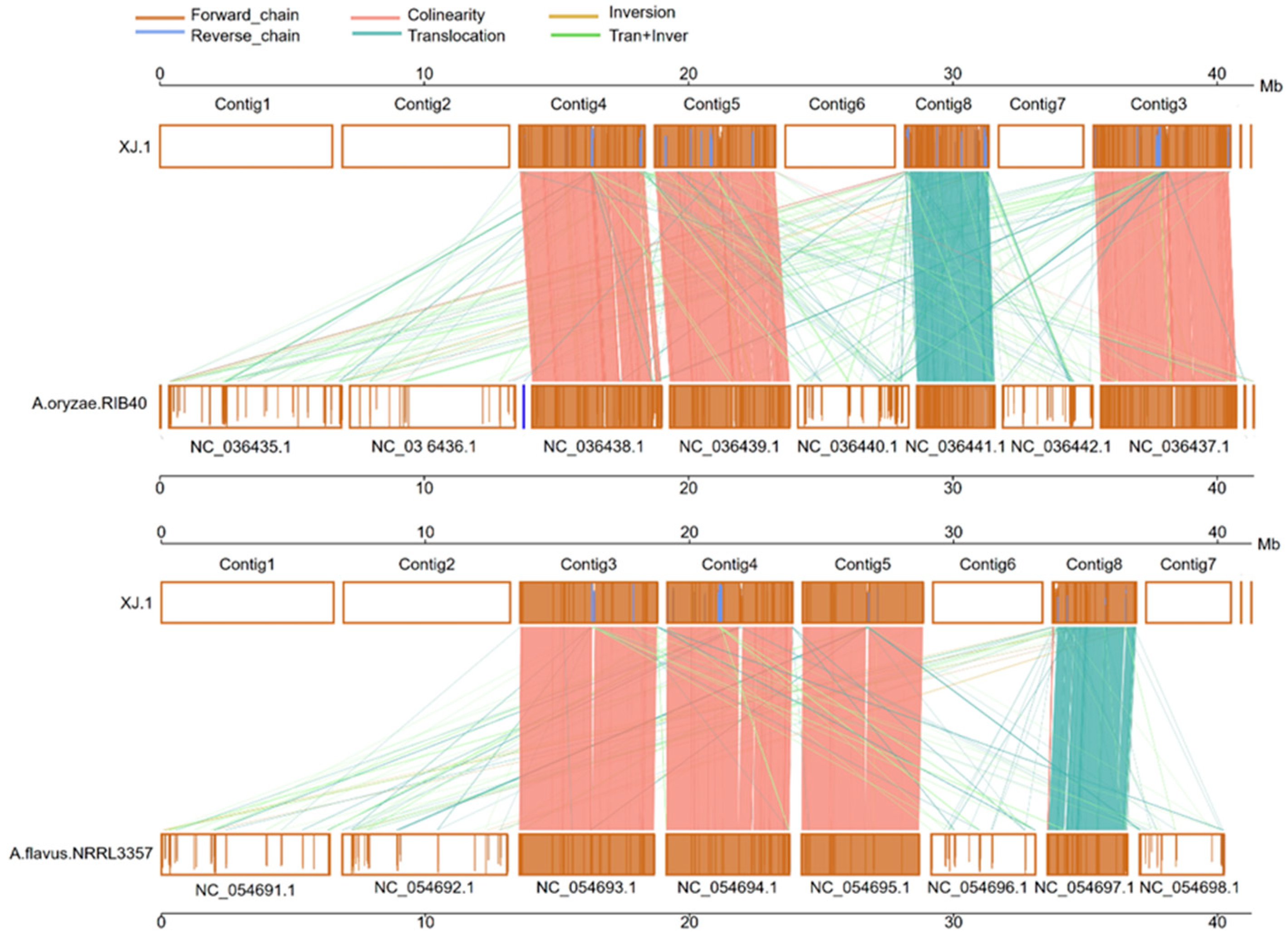
3.3. Evolutionary Analysis of the A. oryzae XJ1 Genome
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lomer, C.J., Bateman, R.P., Johnson, D.L., Langewald, J., Thomas, M. Biological control of locusts and grasshoppers. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 667–702. [CrossRef]
- de Faria, M.R., Wraight, S.P. Mycoinsecticides and Mycoacaricides: a comprehensive list with worldwide coverage and international classification of formulation types. Biol. Control. 2007, 43, 237–256. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P., You, Y., Song, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, L. First record of Aspergillus oryzae (Eurotiales: Trichocomaceae) as an entomopathogenic fungus of the locust, Locusta migratoria (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Biocontrol Sci. Techn. 2015, 25: 1285–1298. [CrossRef]
- You, Y., An, Z., Zhang, X., Liu, H., Yang, W., Yang, M., Wang, T., Xie, X., Zhang, L. Virulence of the fungal pathogen, Aspergillus oryzae XJ-1 to adult locusts (Orthoptera: Acrididae) in both laboratory and field trials. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 3767–3772. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y., Lu, X., Xing, L., Ho, S.W.A., Kwan, H.S. Genomic and transcriptomic comparison of Aspergillus oryzae strains: a case study in soy sauce koji fermentation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 839–853. [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, M.V., Joshi, K.R., Harjai, S.C., Ramdeo, I.N. Aspergillosis in desert locust (Schistocerka gregaria Forsk). Mycopathologia 1975, 57, 135–138. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., Slutana, R., Wagan, M.S. Pathogenic application of Aspergillus species for the control of agricultural important grasshoppers. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 223–229.
- Sultana, R., Wagan, Y.S., Naeem, M., Wagan, M.S., Khatri, I. Susceptibility of three Hieroglyphus species (Hemiacridinae: Acrididae: Orthoptera) to some strains of the entomopathogenic fungi from Pakistan. Can. J. Pure & Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 2325–2332.
- He, B., Tu, Y., Jiang, C., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Zeng, B. Functional genomics of Aspergillus oryzae: strategies and progress. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 103. [CrossRef]
- Watarai, N., Yamamoto, N., Sawada, K., Yamada, T., Watarai, N., Yamamoto, N., Sawada, K., Yamada, T. Evolution of Aspergillus oryzae before and after domestication inferred by large-scale comparative genomic analysis. DNA Res. 2019, 26, 465–472. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J., Kim, J.A., Park, S.Y., Kim, G.W., Park, C.S., Kim, C., Park, H.Y., Yeo, J.H., Lee, Y.H., Kim, S. Draft genome sequence of Aspergillus oryzae BP2-1, isolated from traditional malted rice in South Korea. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e01405–19. [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Vargas, K., McCarthy, C.O., Choi, D., Wang, L., Yu, J.H., Gibbons, J.G. Comparison of two Aspergillus oryzae genomes from different clades reveals independent evolution of alpha-amylase duplication, variation in secondary metabolism genes, and differences in primary metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12: 691296. [CrossRef]
- Umemura, M., Koike, H., Yamane, N., Koyama, Y., Satou, Y., Kikuzato, I., Teruya, M., Tsukahara, M., Imada, Y., Wachi, Y., Miwa, Y., Yano, S., Tamano, K., Kawarabayasi, Y., Fujimori, K.E., Machida, M., Hirano, T. Comparative genome analysis between Aspergillus oryzae strains reveals close relationship between sites of mutation localization and regions of highly divergent genes among Aspergillus species. DNA Res. 2012, 19, 375–382. [CrossRef]
- Kjærbølling, I., Vesth, T., Frisvad, J.C., Nybo, J.L., Theobald, S., Kildgaard, S., Petersen, T.I., Kuo, A., Sato, A., Lyhne, E.K., Kogle, M.E., Wiebenga, A., Kun, R.S., Lubbers, R.J.M., Mäkelä, M.R., Barry, K., Chovatia, M., Clum, A., Daum, C., Haridas, S., He, G., LaButti, K., Lipzen, A., Mondo, S., Pangilinan, J., Riley, R., Salamov, A., Simmons, B.A., Magnuson, J.K., Henrissat, B., Mortensen, U.H., Larsen, T.O., de Vries, R.P., Grigoriev, I.V., Machida, M., Baker, S.E., Andersen, M.R. A comparative genomics study of 23 Aspergillus species from section Flavi. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1106. [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J, Lee, E.-H, Yoon Y, Chua B., Son, A. Portable lysis apparatus for rapid single-step DNA extraction of Bacillus subtilis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 379–387. [CrossRef]
- Machida, M., Asai, K., Sano, M., Tanaka, T., Kumagai, T., Terai, G., Kusumoto, K., Arima, T., Akita, O., Kashiwagi, Y., Abe, K., Gomi, K., Horiuchi, H., Kitamoto, K., Kobayashi, T., Takeuchi, M., Denning, D.W., Galagan, J.E., Nierman, W.C., Yu, J., Archer, D.B., Bennett, J.W., Bhatnagar, D., Cleveland, T.E., Fedorova, N.D., Gotoh, O., Horikawa, H., Hosoyama, A., Ichinomiya, M., Igarashi, R., Iwashita, K., Juvvadi, P.R., Kato, M., Kato, Y., Kin, T., Kokubun, A., Maeda, H., Maeyama, N., Maruyama, J., Nagasaki, H., Nakajima, T., Oda, K., Okada, K., Paulsen, I., Sakamoto, K., Sawano, T., Takahashi, M., Takase, K., Terabayashi, Y., Wortman, J.R., Yamada, O., Yamagata, Y., Anazawa, H., Hata, Y., Koide, Y., Komori, T., Koyama, Y., Minetoki, T., Suharnan, S., Tanaka, A., Isono, K., Kuhara, S., Ogasawara, N., Kikuchi, H. Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature 2005, 438, 1157–1161. [CrossRef]
- Nierman, W.C., Yu, J., Fedorova-Abrams, N.D., Losada, L., Cleveland, T.E., Bhatnagar, D., Bennett, J.W., Dean, R., Payne, G.A. Genome sequence of Aspergillus flavus NRRL 3357, a strain that causes aflatoxin contamination of food and feed. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00168–15. [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, T.R. Identification and toxigenic potential of the industrially important fungi, Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus sojae. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2916–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montiel, D., Dickinson, M.J., Lee, H.A., Dyer, P.S., Jeenes, D.J., Roberts, I.N., James, S., Fuller, L.J., Matsuchima, K., Archer, D.B. Genetic differentiation of the Aspergillus section Flavi complex using AFLP fingerprints. Mycol. Res. 2003, 107(Pt 12), 1427–1434. [CrossRef]
- Abastabar, M., Shabanzadeh, S., Valadan, R., Mayahi, S., Haghani, I., Khojasteh, S., Nargesi, S., Seyedmousavi, S., Hedayati, M.T. Development of RFLP method for rapid differentiation of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus oryzae, two species with high importance in clinical and food microbiology. J. Mycol. Med. 2022, 32, 101274. [CrossRef]
- Kumeda, Y., Asao, T. Heteroduplex panel analysis, a novel method for genetic identification of Aspergillus Section Flavi strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4084–4090. [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.K., Ehrlich, K.C., Hua, S.S. Cladal relatedness among Aspergillus oryzae isolates and Aspergillus flavus S and L morphotype isolates. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 108, 172–177. [CrossRef]
- Nargesi, S., Abastabar, M., Valadan, R., Mayahi, S., Youn, J.H., Hedayati, M.T., Seyedmousavi, S. Differentiation of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae targeting the cyp51A gene. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1279. [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, M.T., Taghizadeh-Armaki, M., Zarrinfar, H., Hoseinnejad, A., Ansari, S., Abastabar, M., Er, H., Özhak, B., Öğünç, D., Ilkit, M., Seyedmousavi, S. Discrimination of Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. Mycoses 2019, 62, 1182–1188. [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, W.B. A multi-aspect analysis of two analogous aspergillus spp. belonging to section Flavi: aspergillus flavus and aspergillus oryzae. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 71. [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M., Baek, J.H., Choi, D.G., Jeon, M.S., Eyun, S.I., Jeon, C.O. Comparative pangenome analysis of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus oryzae reveals their phylogenetic, genomic, and metabolic homogeneity. Food Microbiol. 2024, 119, 104435. [CrossRef]
- Barbesgaard, P., Heldt-Hansen, H.P., Diderichsen, B. On the safety of Aspergillus oryzae: a review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 36, 569–572. [CrossRef]
- Geiser, D.M., Pitt, J.I., Taylor, J.W. Cryptic speciation and recombination in the aflatoxin–producing fungus Aspergillus flavus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 388–393. [CrossRef]
- Tailor, M.J., Richardson, T. Applications of microbial enzymes in food systems and in biotechnology. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1979, 25, 7–35. [CrossRef]
- FAO_WHO. Committee on Food Additives 31. World Health Organization Technical Report Series: Geneva, 1987.
- Abe, K., Gomi, K., Hasegawa, F., Machida, M. Impact of Aspergillus oryzae genomics on industrial production of metabolites. Mycopathologia 2006, 162, 143–153. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver, F., Milner, R.J., Trueman, J.W..H. A taxonomic revision of Metarhizium based on a phylogenetic analysis of rDNA sequence data. Mycol. Res. 2000, 104, 134–150. [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.F., Rehner, S.A., Humber, R.A. A multilocus phylogeny of the Metarhizium anisopliae lineage. Mycologia 2009, 101, 512–530. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genome information summary | |
|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 37,874,054 |
| GC content of genome (%) | 47.31 |
| Gene number | 11,720 |
| Gene total length (bp) | 18,250,593 |
| GC content of gene (%) | 52.09 |
| Gene length/genome (%) | 48.19 |
| Gene average length (bp) | 1,557 |
| Gene internal length (bp) | 19,623,461 |
| Gene internal GC content (%) | 42.88 |
| Gene internal length/genome (%) | 51.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




