Submitted:
03 February 2025
Posted:
06 February 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Customer churn is a critical challenge for subscription-based businesses, especially in telecommunications, where retaining customers is essential to maintaining profitability. This study investigates the efficacy of two ML models, XGBoost and Random Forest, for predicting customer churn using a publicly available telecommunications dataset. The dataset, characterized by imbalanced classes, presents a crucial challenge addressed by incorporating the Gaussian Noise Upsampling (GNUS) sampling technique. The study evaluates and compares the two models using essential performance indicators, including precision, recall, accuracy, F1-score, and ROC-AUC, both with and without GNUS sampling. The results indicate that while XGBoost initially outperforms Random Forest across most metrics, both models show improved recall after the GNUS application, particularly in identifying churn cases. However, this improvement in recall comes with a trade-off in precision and overall accuracy. The findings highlight the relevance of using appropriate sampling techniques to tackle class imbalance in churn prediction and provide valuable insights for developing proactive customer retention strategies.
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Purpose of the Study
IIII. Related Work
A. Data Preparation Techniques
B. Addressing Class Imbalance
C. ML Techniques for Churn Prediction
D. Ensemble Learning Techniques
E. Hybrid Learning Approaches
F. Rule-Based and Social Network Analysis Approaches
G. Applications in Various Sectors
IV. Method
A. Training and Validation Process
B. Evaluation Metrics
V. Results
A. Setup
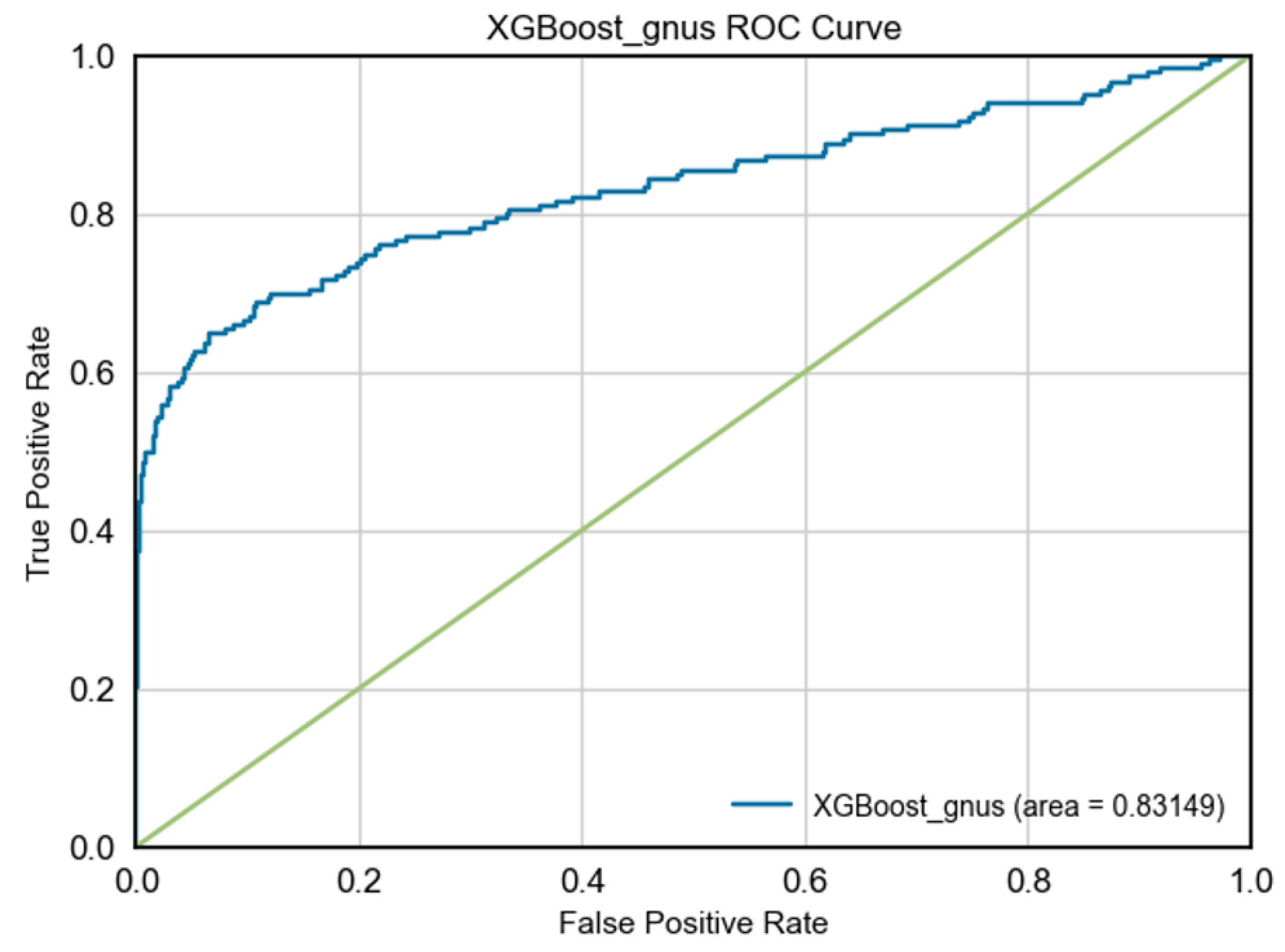
B. Results
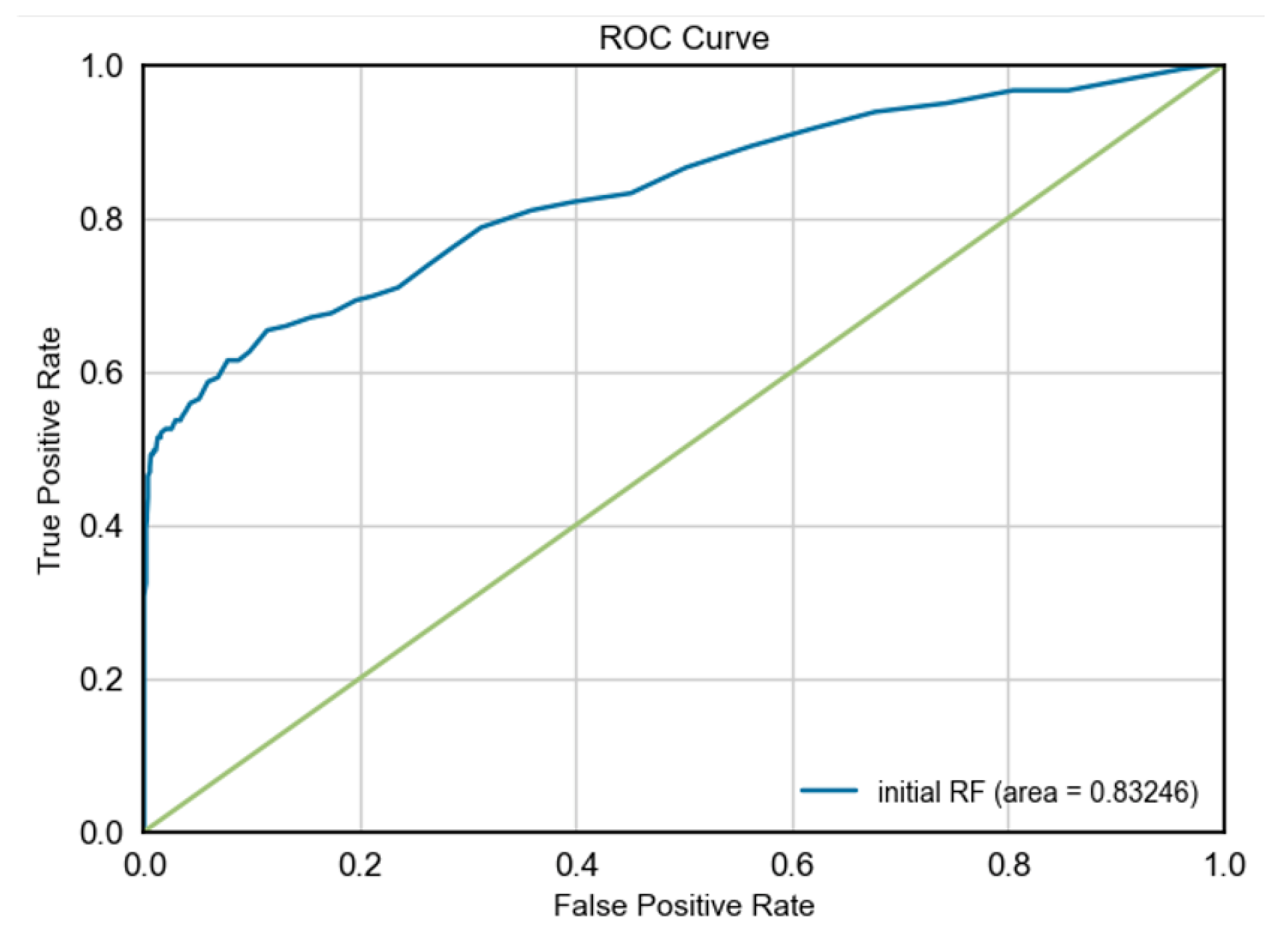
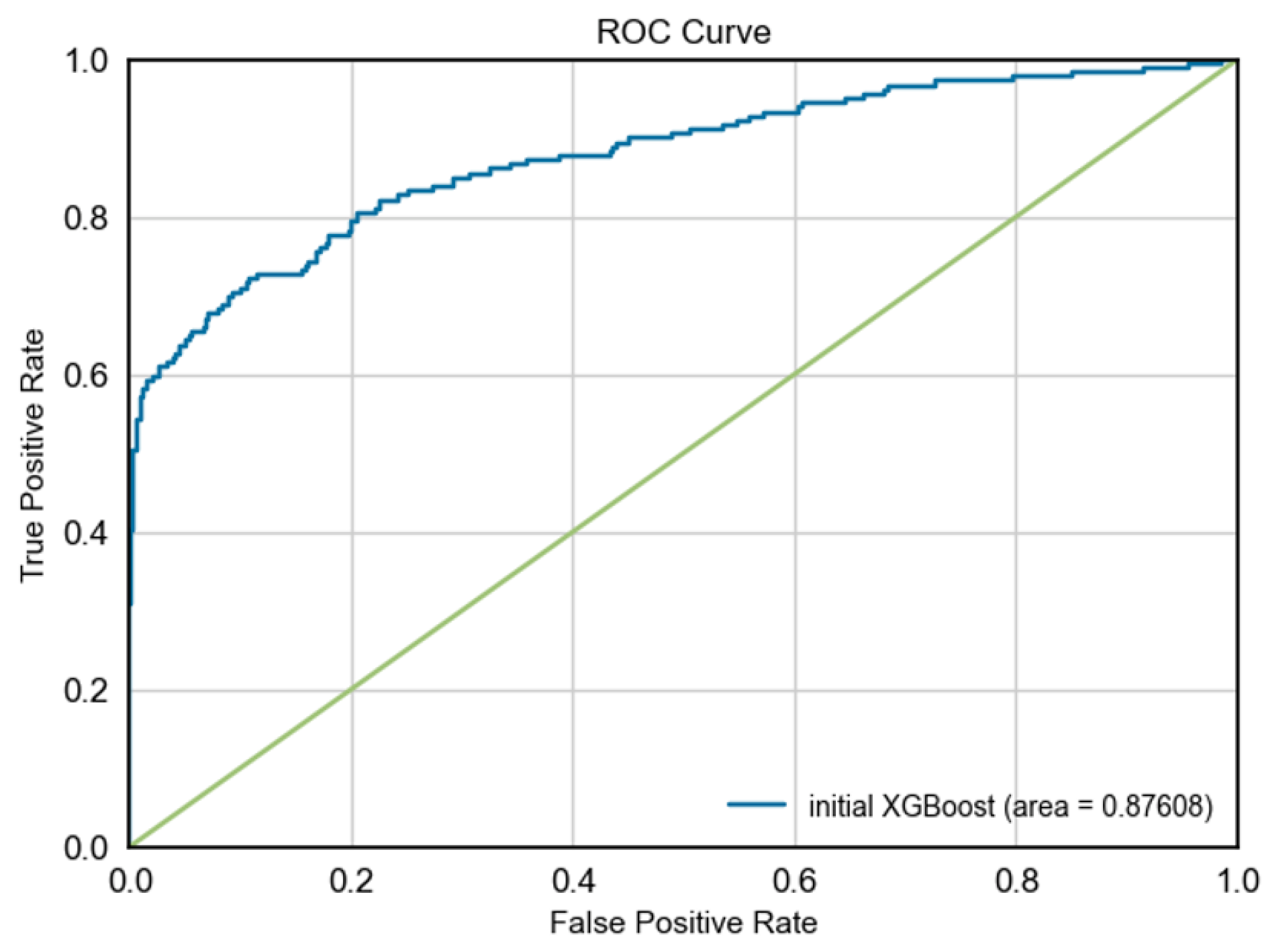
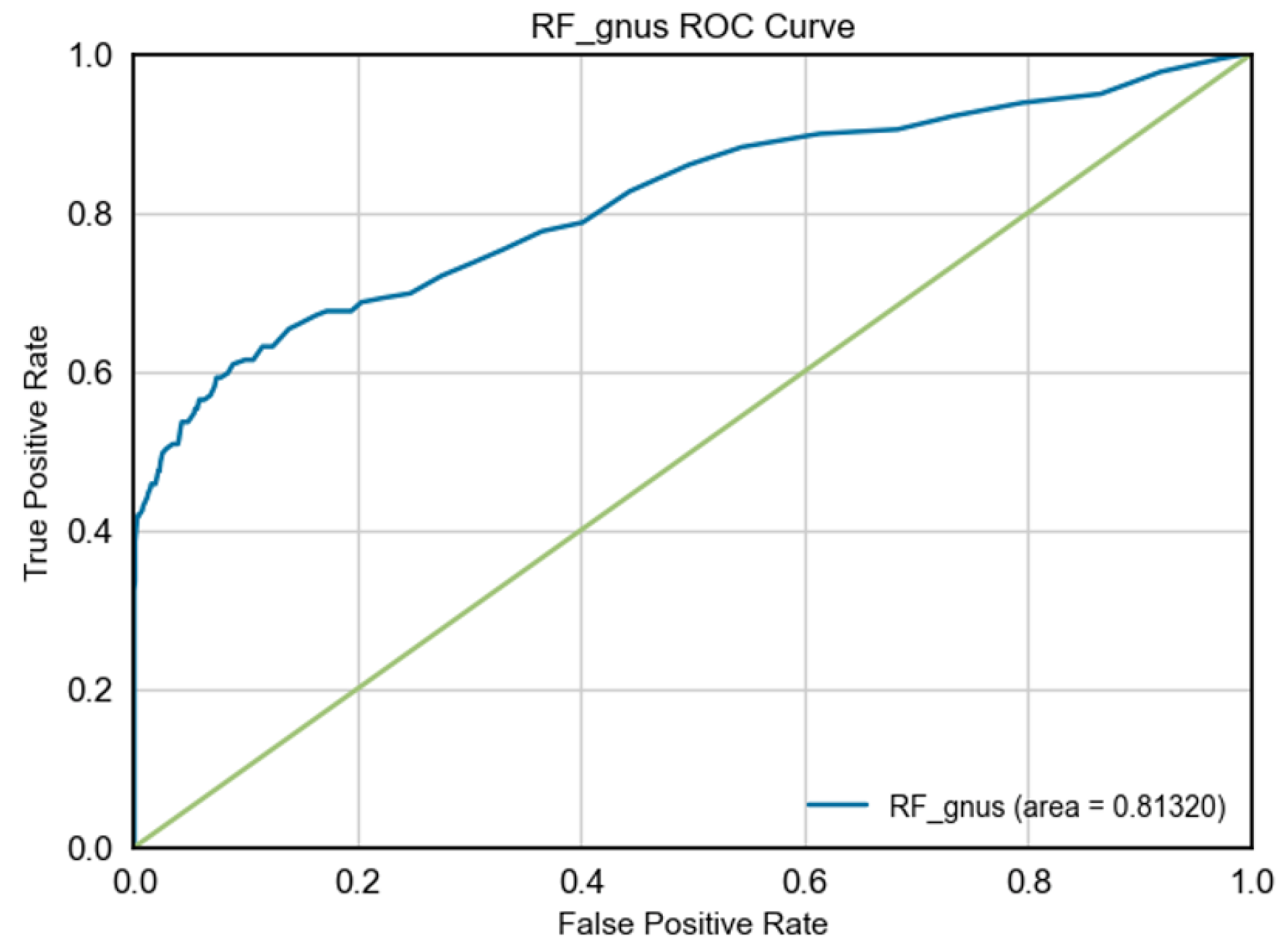
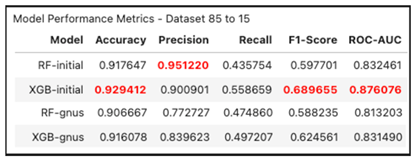 |
- Accuracy:
- Precision:
- Recall:
- F1-Score:
- ROC-AUC:
VI. Conclusions
References
- Vafeiadis, Thanasis & Diamantaras, Kostas & Sarigiannidis, G. & Chatzisavvas, Konstantinos. (2015). A Comparison of Machine Learning Techniques for Customer Churn Prediction. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory. 55. 10.1016/j.simpat.2015.03.003.
- Ahmad, A.K. , Jafar, A. & Aljoumaa, K. Customer churn prediction in telecom using machine learning in the big data platform. J Big Data 2019, 6, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Kristof Coussement, Stefan Lessmann, Geert Verstraeten, A comparative analysis of data preparation algorithms for customer churn prediction: A case study in the telecommunication industry. Decision Support Systems 2017, 95, 27–36. [CrossRef]
- Adnan Amin, Babar Shah, Asad Masood Khattak, Fernando Joaquim Lopes Moreira, Gohar Ali, Alvaro Rocha, Sajid Anwar, Cross-company customer churn prediction in telecommunication: A comparison of data transformation methods. International Journal of Information Management 2019, 46, 304–319. [CrossRef]
- D. Do, P. D. Do, P. Huynh, P. Vo, and T. Vu, "Customer churn prediction in an internet service provider," 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Boston, MA, USA, 2017, pp. 3928–3933.
- J. Burez, D. Van den Poel, Handling class imbalance in customer churn prediction. Expert Systems with Applications 2009, 36, 4626–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaya Xie, Xiu Li, E. W.T. Ngai, Weiyun Ying, Customer churn prediction using improved balanced random forests. Expert Systems with Applications 2009, 36, 5445–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, Rahul & Pawar, Usharani. (2011). Churn Prediction in Telecommunication Using Data Mining Technology. International Journal of Advanced Computer Sciences and Applications. 2. 10.14569/IJACSA.2011.020204.
- T. Vafeiadis, K.I. Diamantaras, G. Sarigiannidis, K.Ch. Chatzisavvas, A comparison of machine learning techniques for customer churn prediction. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory 2015, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouter Verbeke, David Martens, Christophe Mues, Bart Baesens, Building comprehensible customer churn prediction models with advanced rule induction techniques. Expert Systems with Applications 2011, 38, 2354–2364. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Mahreen & Afzal, Hammad & Siddiqi, Imran & Amjad, Muhammad & Khurshid, Khawar. (2020). Exploring nested ensemble learners using overproduction and choosing an approach for churn prediction in the telecom industry. Neural Computing and Applications. 32. 10.1007/s00521-018-3678-8.
- Kimura, Takuma. (2022). Customer Churn Prediction with Hybrid Resampling and Ensemble Learning.. 1-23.
- Arno De Caigny, Kristof Coussement, Koen W. De Bock, A new hybrid classification algorithm for customer churn prediction based on logistic regression and decision trees. European Journal of Operational Research 2018, 269, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan Amin, Feras Al-Obeidat, Babar Shah, Awais Adnan, Jonathan Loo, Sajid Anwar, Customer churn prediction in telecommunication industry using data certainty. Journal of Business Research 2019, 94, 290–301. [CrossRef]
- Xiaohang Zhang, Ji Zhu, Shuhua Xu, Yan Wan, Predicting customer churn through interpersonal influence. Knowledge-Based Systems 2012, 28, 97–104. [CrossRef]
- Wouter Verbeke, David Martens, Bart Baesens, Social network analysis for customer churn prediction. Applied Soft Computing 2014, 14, 431–446. [CrossRef]
- L. Bin, S. L. Bin, S. Peiji, and L. Juan, "Customer Churn Prediction Based on the Decision Tree in Personal Handyphone System Service," 2007 International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, Chengdu, China, 2007, pp. 1–5.
- Jennifer Karlberg, Maja Axén. (2020). Binary Classification for Predicting Customer Churn. Department of Mathematics and Mathematical Statistics at Umeå University.
- Shaaban, Essam; Helmy, Yehia; Khedr, Ayman; Nasr, Mona. A Proposed Churn Prediction Model. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications IJERA 2012, 2, 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Imani, Mehdi, et al. "The Impact of SMOTE and ADASYN on Random Forest and Advanced Gradient Boosting Techniques in Telecom Customer Churn Prediction." 2024 10th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR). IEEE, 2024.
- Imani, Mehdi, and Hamid Reza Arabnia. Hyperparameter optimization and combined data sampling techniques in machine learning for customer churn prediction: a comparative analysis. Technologies 2023, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinichristy, “Customer Churn Prediction 2020,” Kaggle, Dec. 12, 2022.https://www.kaggle. 2020.
- Litjens, Geert, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Medical image analysis 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, James B. , Nick G. Polson, and Jan Hendrik Witte. Deep learning for finance: deep portfolios. Applied Stochastic Models in Business and Industry 2017, 33, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudaki, Majid, et al. "Presenting a New Approach for Predicting and Preventing Active/Deliberate Customer Churn in Telecommunication Industry." Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Management (SAM). The Steering Committee of the World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering and Applied Computing (WorldComp), 2011.
- Mazhari, N. , et al. "An overview of the classification and its algorithm." 3rd Data Mining Conference (IDMC'09): Tehran. 2009.
- Joudaki, Majid, Mehdi Imani, and Hamid R. Arabnia. A New Efficient Hybrid Technique for Human Action Recognition Using 2D Conv-RBM and LSTM with Optimized Frame Selection. Technologies 2025, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, M.; Beikmohammadi, A.; Arabnia, H. R. Comprehensive Analysis of Random Forest and XGBoost Performance with SMOTE, ADASYN, and GNUS Upsampling Under Varying Imbalance Levels. Preprints 2025, 2025012274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





