Submitted:
29 October 2024
Posted:
30 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
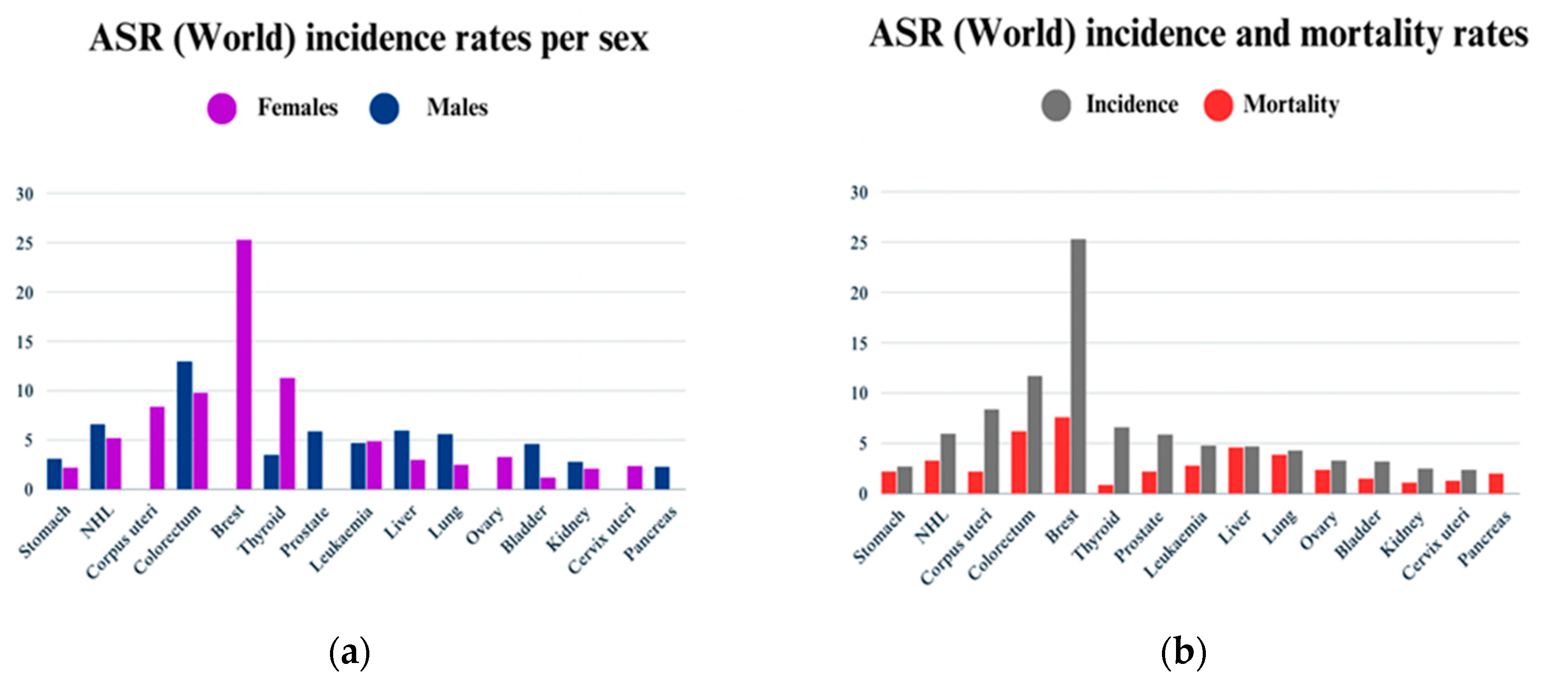
1.1. Cancer Statistics for Saudi Arabia
1.2. Challenges Associated with the Development of Anticancer Drugs
1.3. Drug Repurposing
2. Drug Repurposing Cases for Cancer Treatment
2.1. Repurposing with a Multi-Type Anticancer Activity
2.1.1. Repurposing Anti-Platelet Medication for Cancer Treatment
2.1.2. Repurposing Anti-Diabetic Medication for Cancer Treatment
2.1.3. Repurposing Anti-Helminthic Medication for Cancer Treatment
2.1.4. Repurposing Anti-Viral Medication for Cancer Treatment
2.1.5. Repurposing Cardiovascular Medications for Cancer Treatment
- Anti-Hypertension Medication
- Antihyperlipidemic
- Repurposing Ion Channels modulators for Cancer Treatment
2.1.6. Repurposing Antibiotic Medications for Cancer Treatment
2.1.7. Repurposing Anti-Malarial Medications for Cancer Treatment
2.1.8. Repurposing Anti-Psychotic Medications for Cancer Treatment
2.1.9. Repurposing NSAID Medications for Cancer Treatment
2.1.10. Repurposing Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug (DMARD) for Cancer Treatment
2.1.11. Repurposing Anti-Epileptic Medications for Cancer Treatment
2.1.12. Repurposing Anesthetic Medications for Cancer Treatment
2.2. Repurposing with Type-Specific Anticancer Activity
2.2.1. Repurposing Medications for Prostate Cancer (PC) Treatment
- Anti-Dyslipidemic Drugs
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs
- Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
- Antidepressant Drugs
- Beta-Blockers
- Miscellaneous
2.2.2. Repurposed Medications in the Treatment of Gastric Cancer (GC)
- Antidepressant
- Antiepileptic
- Antipsychotic
- Agents that chelate iron
2.2.3. Repurposed Medications in the Treatment of Blood Malignancies
2.2.4. Repurposed Medications in the Treatment of Breast Cancer
2.2.5. Repurposed Medications in the Treatment of Colon Cancer
- Antihypertensive and Antiarrhythmic Medications
- Anti-Helminthic
2.2.6. Repurposed Medications in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
2.3. Repurposing with a Mechanism-Directed Anticancer Activity
2.3.1. Repurposed Medications to Target Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism in Cancer
- Anti-diabetic
- Anti-microbe
2.3.2. Repurposed Drugs as a ROS Inducer in Cancer
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pina-Sanchez, Patricia, et al. "Cancer biology, epidemiology, and treatment in the 21st century: current status and future challenges from a biomedical perspective." Cancer Control 28 (2021). [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health. NIH curriculum supplement series. The Institutes, 2007. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK20362/.
- Cooper, Geoffrey M., and Robert E. Hausman. "The development and causes of cancer." The cell: A molecular approach 2 (2000): 725-766.
- Correia, Ana Salomé, Fátima Gärtner, and Nuno Vale. "Drug combination and repurposing for cancer therapy: the example of breast cancer." Heliyon 7.1 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Brown, Joel S., et al. "Updating the definition of cancer." Molecular Cancer Research 21.11 (2023): 1142-1147. [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health. NIH curriculum supplement series. The Institutes, 2007.
- Goodman, Emily N. "“What is the Environment Doing to Our Genes?”: A Pedigree Analysis of the Possible Genetic Basis of a Set of Familial Clinical Disorders." (2022).
- Cooper, Geoffrey M., and Robert E. Hausman. "The development and causes of cancer." The cell: A molecular approach 2 (2000): 725-766.
- Ramalingam, Satish, ed. Cancer Genes. Bentham Science Publishers, 2023.
- National Institutes of Health. NIH curriculum supplement series. The Institutes, 2007.
- Pelengaris, Stella, and Michael Khan, eds. "The molecular biology of cancer: A bridge from bench to bedside." (2013). https://library.iau.edu.sa/scholarly-journals/molecular-biology-cancer-bridge-bench-bedside-2nd/docview/1349242751/se-2.
- Hejmadi, Momna. Introduction to cancer biology. Bookboon, 2014.
- Greenwald, Peter, and Barbara K. Dunn. "Landmarks in the history of cancer epidemiology." Cancer research 69.6 (2009): 2151-2162. [CrossRef]
- Almatroudi, Ahmad. "The incidence rate of colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia: An observational descriptive epidemiological analysis." International Journal of General Medicine (2020): 977-990. [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, Wedad Saeed, et al. "Epidemiology of cancer in Saudi Arabia thru 2010–2019: a systematic review with constrained meta-analysis." AIMS public health 7.3 (2020): 679. [CrossRef]
- Basudan, Ahmed M. "Breast cancer incidence patterns in the Saudi female population: A 17-year retrospective analysis." Medicina 58.11 (2022): 1617. [CrossRef]
- Elwali, Nasr Eldin, et al. "Colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia: The way forward." Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP 24.1 (2023): 13. [CrossRef]
- Flemban, Arwa F., et al. "Patterns of thyroid cancer mortality and incidence in Saudi Arabia: a 30-year study." Diagnostics 12.11 (2022): 2716. [CrossRef]
- Youk, Tae Mi, et al. "Estimation of the Three Phases by Direct Cost of Care for Non-surviving Patients with Cancer: A National Population-based Patient-level Study." Journal of Cancer 15.1 (2024): 20. [CrossRef]
- Correia, Ana Salomé, Fátima Gärtner, and Nuno Vale. "Drug combination and repurposing for cancer therapy: the example of breast cancer." Heliyon 7.1 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Sleire, Linda, et al. "Drug repurposing in cancer." Pharmacological research 124 (2017): 74-91. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V. S., et al. "Drug repurposing: an effective tool in modern drug discovery." Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry 49.2 (2023): 157-166. [CrossRef]
- Song, Jae W., and Kevin C. Chung. "Observational studies: cohort and case-control studies." Plastic and reconstructive surgery 126.6 (2010): 2234-2242. [CrossRef]
- Weth, Freya R., et al. "Unlocking hidden potential: advancements, approaches, and obstacles in repurposing drugs for cancer therapy." British Journal of Cancer 130.5 (2024): 703-715. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Xi, et al. "Drug repurposing for cancer treatment through global propagation with a greedy algorithm in a multilayer network." Cancer Biology & Medicine 19.1 (2022): 74. [CrossRef]
- Sung, Hyuna, et al. "Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries." CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 71.3 (2021): 209-249. [CrossRef]
- Li, Mengyuan, et al. "An algorithm to quantify intratumor heterogeneity based on alterations of gene expression profiles." Communications biology 3.1 (2020): 505. [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, Arran K., et al. "Unlocking the transcriptomic potential of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded clinical tissues: comparison of gene expression profiling approaches." BMC bioinformatics 21 (2020): 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Rheinbay, Esther, et al. "Analyses of non-coding somatic drivers in 2,658 cancer whole genomes." Nature 578.7793 (2020): 102-111. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, Douglas, and Robert A. Weinberg. "Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation." cell 144.5 (2011): 646-674. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO report on cancer: setting priorities, investing wisely and providing care for all. World Health Organization, 2020. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330745.
- Creighton, Chad J. "Making use of cancer genomic databases." Current protocols in molecular biology 121.1 (2018): 19-14.
- Pushpakom, Sudeep et al. “Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations.” Nature reviews. Drug discovery vol. 18,1 (2019): 41-58. [CrossRef]
- Schcolnik-Cabrera, Alejandro et al. “Perspectives on Drug Repurposing.” Current medicinal chemistry vol. 28,11 (2021): 2085-2099. [CrossRef]
- Schein, Catherine H. "Repurposing approved drugs for cancer therapy." British Medical Bulletin 137.1 (2021): 13-27. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, Rafaela, Diana Duarte, and Nuno Vale. "Drug repurposing in cancer therapy: influence of patient’s genetic background in breast cancer treatment." International journal of molecular sciences 23.8 (2022): 4280. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, Sadhna, et al. "Drug repurposing for breast cancer therapy: Old weapon for new battle." Seminars in cancer biology. Vol. 68. Academic Press, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Elwood, Peter, et al. "Aspirin and cancer treatment: systematic reviews and meta-analyses of evidence: for and against." British Journal of Cancer 130.1 (2024): 3-8. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Xiaoyuan, et al. "Aspirin mediates histone methylation that inhibits inflammation-related stemness gene expression to diminish cancer stemness via COX-independent manner." Stem Cell Research & Therapy 11 (2020): 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Yue, et al. "The epigenetic effects of aspirin: the modification of histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation in the prevention of colon carcinogenesis in azoxymethane-and dextran sulfate sodium-treated CF-1 mice." Carcinogenesis 37.6 (2016): 616-624. [CrossRef]
- Elwood, Peter, et al. "Aspirin and cancer: biological mechanisms and clinical outcomes." Open Biology 12.9 (2022): 220124. [CrossRef]
- Motta, Rodrigo, et al. "Immunotherapy in microsatellite instability metastatic colorectal cancer: Current status and future perspectives." Journal of clinical and translational research 7.4 (2021): 511. PMCID: PMC8445628 PMID: 34541365.
- Nounu, Aayah, et al. "A combined proteomics and Mendelian randomization approach to investigate the effects of aspirin-targeted proteins on colorectal cancer." Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 30.3 (2021): 564-575. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, Rafaela, Diana Duarte, and Nuno Vale. "Drug repurposing in cancer therapy: influence of patient’s genetic background in breast cancer treatment." International journal of molecular sciences 23.8 (2022): 4280. [CrossRef]
- Malik, Jonaid Ahmad, et al. "Drugs repurposed: An advanced step towards the treatment of breast cancer and associated challenges." Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 145 (2022): 112375. [CrossRef]
- Lord, Simon R., and Adrian L. Harris. "Is it still worth pursuing the repurposing of metformin as a cancer therapeutic?." British Journal of Cancer 128.6 (2023): 958-966. [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, Jean-Pierre, et al. "Drug repositioning: a brief overview." Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 72.9 (2020): 1145-1151. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Shafina, et al. "Drug repurposing: re-inventing therapies for cancer without re-entering the development pipeline—a review." Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute 34.1 (2022): 33. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Lin et al. “Metformin as anticancer agent and adjuvant in cancer combination therapy: Current progress and future prospect.” Translational oncology vol. 44 (2024): 101945. [CrossRef]
- LaMoia, Traci E., and Gerald I. Shulman. "Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action." Endocrine reviews 42.1 (2021): 77-96. [CrossRef]
- Bose, Sminu, Cissy Zhang, and Anne Le. "Glucose metabolism in cancer: The Warburg effect and beyond." Adv Exp Med Biol 1311 (2021): 3-15. http://www.springercom/series/5584.
- Bailey, Clifford J. "Metformin: historical overview." Diabetologia 60.9 (2017): 1566-1576. [CrossRef]
- Hunter, Roger W., et al. "Metformin reduces liver glucose production by inhibition of fructose-1-6-bisphosphatase." Nature medicine 24.9 (2018): 1395-1406. [CrossRef]
- Qi, Jiying, et al. "Cancer risk among patients with type 2 diabetes: A real-world study in Shanghai, China." Journal of Diabetes 11.11 (2019): 878-883. [CrossRef]
- Olatunde, Ahmed, et al. "Cancer and diabetes: the interlinking metabolic pathways and repurposing actions of antidiabetic drugs." Cancer cell international 21 (2021): 1-27. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Yi-Chun, et al. "Does long-term use of antidiabetic drugs changes cancer risk?." Medicine 98.40 (2019): e17461. [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, Mohamad Ali, André Gessner, and Nahed El-Najjar. "Repurposing of chronically used drugs in cancer therapy: a chance to grasp." Cancers 15.12 (2023): 3199. [CrossRef]
- Schcolnik-Cabrera, Alejandro, Daniel Juárez-López, and Alfonso Duenas-Gonzalez. "Perspectives on drug repurposing." Current Medicinal Chemistry 28.11 (2021): 2085-2099. [CrossRef]
- Kirtonia, Anuradha, et al. "Repurposing of drugs: An attractive pharmacological strategy for cancer therapeutics." Seminars in cancer biology. Vol. 68. Academic Press, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, Mariusz. "Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and cancer risk in type 2 diabetes: focus on SGLT-2 inhibitors." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.4 (2021): 1680. [CrossRef]
- Kole, Labanyamoy et al. “Pioglitazone, an anti-diabetic drug requires sustained MAPK activation for its anti-tumor activity in MCF7 breast cancer cells, independent of PPAR-γ pathway.” Pharmacological reports: PR vol. 68,1 (2016): 144-54. [CrossRef]
- Chi, Tiange, et al. "PPAR-γ modulators as current and potential cancer treatments." Frontiers in oncology 11 (2021): 737776. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Yan, et al. "PPAR-α modulators as current and potential cancer treatments." Frontiers in oncology 11 (2021): 599995. [CrossRef]
- Mirza, Agha Zeeshan, Ismail I. Althagafi, and Hina Shamshad. "Role of PPAR receptor in different diseases and their ligands: Physiological importance and clinical implications." European journal of medicinal chemistry 166 (2019): 502-513. [CrossRef]
- Galal, Mariam Ahmed, et al. "Metformin: A Dual-Role Player in Cancer Treatment and Prevention." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.7 (2024): 4083. [CrossRef]
- Hua, Yu, et al. "Metformin and cancer hallmarks: shedding new lights on therapeutic repurposing." Journal of Translational Medicine 21.1 (2023): 403. [CrossRef]
- Brown, Jason R., et al. "Phase II clinical trial of metformin as a cancer stem cell–targeting agent in ovarian cancer." JCI insight 5.11 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Pantziarka, Pan, et al. "Repurposing Drugs in Oncology (ReDO)—mebendazole as an anti-cancer agent." ecancermedicalscience 8 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Laudisi, Federica, et al. "Repositioning of anthelmintic drugs for the treatment of cancers of the digestive system." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.14 (2020): 4957. [CrossRef]
- Younis, Nancy S., Amal MH Ghanim, and Sameh Saber. "Mebendazole augments sensitivity to sorafenib by targeting MAPK and BCL-2 signalling in n-nitrosodiethylamine-induced murine hepatocellular carcinoma." Scientific reports 9.1 (2019): 19095. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Haifeng, Zhen Weng, and Chunfang Xu. "Albendazole suppresses cell proliferation and migration and induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells." Anti-Cancer Drugs 31.5 (2020): 431-439. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Ming Cheng, et al. "Niclosamide inhibits the cell proliferation and enhances the responsiveness of esophageal cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents." Oncology reports 43.2 (2020): 549-561. [CrossRef]
- Xing, Xing, et al. "Anticancer role of flubendazole: Effects and molecular mechanisms." Oncology Letters 28.6 (2024): 558. [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, Sneha, et al. "Recent advances of benzimidazole as anticancer agents." Chemical Biology & Drug Design 102.2 (2023): 357-376. [CrossRef]
- Mohi-Ud-Din, Roohi, et al. "Repurposing approved non-oncology drugs for cancer therapy: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, efficacy, and clinical prospects." European journal of medical research 28.1 (2023): 345. [CrossRef]
- Guerini, Andrea Emanuele, et al. "Mebendazole as a candidate for drug repurposing in oncology: An extensive review of current literature." Cancers 11.9 (2019): 1284. [CrossRef]
- Rushworth, Linda K., et al. "Repurposing screen identifies mebendazole as a clinical candidate to synergise with docetaxel for prostate cancer treatment." British journal of cancer 122.4 (2020): 517-527. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Zhenzhan, Jianguang Ji, and Hao Liu. "Drug repurposing in oncology: Current evidence and future direction." Current Medicinal Chemistry 28.11 (2021): 2175-2194. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Zhe, et al. "Overcoming cancer therapeutic bottleneck by drug repurposing." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 5.1 (2020): 113. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Lu, et al. "Activation of STAT3 and Bcl-2 and reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) promote radioresistance in breast cancer and overcome of radioresistance with niclosamide." Oncogene 37.39 (2018): 5292-5304. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Biyin, et al. "The antiparasitic clioquinol induces apoptosis in leukemia and myeloma cells by inhibiting histone deacetylase activity." Journal of Biological Chemistry 288.47 (2013): 34181-34189. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Biyin, et al. "The Proteasomal Inhibitor Clioquinol Induces Apoptosis in Leukemia and Myeloma Cells by Inhibiting Histone Deacetylase Activity." Blood 120.21 (2012): 2449. [CrossRef]
- Borcherding, Nicholas, Yogesh Jethava, and Praveen Vikas. "Repurposing anti-cancer drugs for COVID-19 treatment." Drug design, development and therapy (2020): 5045-5058. [CrossRef]
- Pfab, Christina, et al. "Repurposing of antimicrobial agents for cancer therapy: what do we know?." Cancers 13.13 (2021): 3193. [CrossRef]
- Aldea, Mihaela, et al. "Repurposing of anticancer drugs expands possibilities for antiviral and anti-inflammatory discovery in COVID-19." Cancer Discovery 11.6 (2021): 1336-1344. [CrossRef]
- Pal, Dilipkumar, et al. "Indazole-based microtubule-targeting agents as potential candidates for anticancer drugs discovery." Bioorganic Chemistry 122 (2022): 105735. [CrossRef]
- De Lellis, Laura, et al. "Drug repurposing, an attractive strategy in pancreatic cancer treatment: preclinical and clinical updates." Cancers 13.16 (2021): 3946. [CrossRef]
- Sung, Hyuna, et al. "Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries." CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 71.3 (2021): 209-249. [CrossRef]
- Regulska, Katarzyna, et al. "Can cardiovascular drugs support cancer treatment? The rationale for drug repurposing." Drug discovery today 24.4 (2019): 1059-1065. [CrossRef]
- Hashemzehi, Milad, et al. "Angiotensin receptor blocker Losartan inhibits tumor growth of colorectal cancer." Excli Journal 20 (2021): 506. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Xin, Shu Guo, and Chenchao Wang. "Propranolol in the treatment of infantile hemangiomas." Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology (2021): 1155-1163. [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Ji Hee, et al. "Cardiac Evaluation before and after Oral Propranolol Treatment for Infantile Hemangiomas." Journal of Clinical Medicine 13.11 (2024): 3332. [CrossRef]
- Benish, Marganit, et al. "Perioperative use of β-blockers and COX-2 inhibitors may improve immune competence and reduce the risk of tumor metastasis." Annals of surgical oncology 15 (2008): 2042-2052. [CrossRef]
- De Lellis, Laura, et al. "Drug repurposing, an attractive strategy in pancreatic cancer treatment: preclinical and clinical updates." Cancers 13.16 (2021): 3946. [CrossRef]
- Li, Zhe, et al. "Artemisinin and its derivatives as a repurposing anticancer agent: what else do we need to do?." Molecules 21.10 (2016): 1331. [CrossRef]
- Chae, Young Kwang, et al. "Reduced risk of breast cancer recurrence in patients using ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and/or statins." Cancer investigation 29.9 (2011): 585-593. [CrossRef]
- Coulson, Rhiannon et al. “The angiotensin receptor blocker, Losartan, inhibits mammary tumor development and progression to invasive carcinoma.” Oncotarget vol. 8,12 (2017): 18640-18656. [CrossRef]
- Vinson, Gavin P. "Why isn’t the angiotensin type 1 receptor a target in cancer?." Oncotarget 8.12 (2017): 18618. [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, Ehsan, et al. "Inhibition of angiotensin II type 1 receptor by candesartan reduces tumor growth and ameliorates fibrosis in colorectal cancer." Excli Journal 20 (2021): 863. [CrossRef]
- Asgharzadeh, Fereshteh, et al. "Inhibition of angiotensin pathway via valsartan reduces tumor growth in models of colorectal cancer." Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 440 (2022): 115951. [CrossRef]
- Hashemzehi, Milad, et al. "Angiotensin receptor blocker Losartan inhibits tumor growth of colorectal cancer." Excli Journal 20 (2021): 506. [CrossRef]
- Pantziarka, Pan, et al. "ReDO_DB: the repurposing drugs in oncology database." ecancermedicalscience 12 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Carnet Le Provost, Killian, et al. "Trial watch: beta-blockers in cancer therapy." (2023): 2284486. [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Calderón, Diego Mauricio, et al. "Beta adrenergic receptor activation inhibits oral cancer migration and invasiveness." Archives of Oral Biology 118 (2020): 104865. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Soon Young, et al. "β2 adrenergic receptor expression and the effects of norepinephrine and propranolol on various head and neck cancer subtypes." Oncology Letters 22.5 (2021): 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Shebl, Rania Ibrahim. "Anti-cancer potential of captopril and botulinum toxin type-A and associated p53 gene apototic stimulating activity." Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: IJPR 18.4 (2019): 1967. [CrossRef]
- Hassani, Bahareh, Zeinab Attar, and Negar Firouzabadi. "The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) signaling pathways and cancer: foes versus allies." Cancer Cell International 23.1 (2023): 254. [CrossRef]
- Fukushiro-Lopes, Daniela, et al. "Repurposing Kir6/SUR2 channel activator minoxidil to arrests growth of gynecologic cancers." Frontiers in Pharmacology 11 (2020): 577. [CrossRef]
- Salanci, Šimon, et al. "The Induction of G2/M Phase Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by the Chalcone Derivative 1C in Sensitive and Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cells Is Associated with ROS Generation." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.14 (2024): 7541. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Shiwen, et al. "Anti-invasive effects of minoxidil on human breast cancer cells: Combination with ranolazine." Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 39.4 (2022): 679-689. [CrossRef]
- Carlos-Escalante, José A., et al. "The use of antihypertensive drugs as coadjuvant therapy in cancer." Frontiers in oncology 11 (2021): 660943. [CrossRef]
- Ioakeim-Skoufa, Ignatios, et al. "Drug repurposing in oncology: a systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials." Cancers 15.11 (2023): 2972. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, Eduarda, and Nuno Vale. "Repurposing of the Drug Tezosentan for Cancer Therapy." Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45.6 (2023): 5118-5131. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Rong, and Roderick H. Dashwood. "Endothelins and their receptors in cancer: identification of therapeutic targets." Pharmacological research 63.6 (2011): 519-524. [CrossRef]
- Lian, Xin, et al. "Anticancer properties of fenofibrate: a repurposing use." Journal of Cancer 9.9 (2018): 1527. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Lulu, et al. "Fenofibrate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic reprogramming reversal: the anti-tumor effects in gastric carcinoma cells mediated by the PPAR pathway." American Journal of Translational Research 12.2 (2020): 428. PMCID: PMC7061836 PMID: 32194894.
- Kale, Vijay Pralhad, Shantu G. Amin, and Manoj K. Pandey. "Targeting ion channels for cancer therapy by repurposing the approved drugs." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 1848.10 (2015): 2747-2755. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Jiayu, et al. "The modulation of ion channels in cancer chemo-resistance." Frontiers in Oncology 12 (2022): 945896. [CrossRef]
- Altamura, Concetta, et al. "Ion channel involvement in tumor drug resistance." Journal of personalized medicine 12.2 (2022): 210. PMCID: PMC8878471 PMID: 35207698.
- Leanza, Luigi, et al. "Pharmacological targeting of ion channels for cancer therapy: in vivo evidences." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 1863.6 (2016): 1385-1397. [CrossRef]
- Bell, Damian C., et al. "News and views on ion channels in cancer: is cancer a channelopathy?." Frontiers in Pharmacology 14 (2023): 1258933. [CrossRef]
- Li, Meizeng, et al. "Potassium channels: Novel targets for tumor diagnosis and chemoresistance." Frontiers in Oncology 12 (2023): 1074469. [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, Maryne, et al. "SKCa-and Kv1-type potassium channels and cancer: Promising therapeutic targets?." Biochemical Pharmacology 216 (2023): 115774. [CrossRef]
- Luis, Enoch, et al. "The Kv10. 1 channel: a promising target in cancer." International journal of molecular sciences 23.15 (2022): 8458. [CrossRef]
- Sakellakis, Minas, et al. "Novel insights into voltage-gated ion channels: Translational breakthroughs in medical oncology." Channels 18.1 (2024): 2297605. [CrossRef]
- Pasello, Giulia, et al. "Effects of sulfonylureas on tumor growth: a review of the literature." The oncologist 18.10 (2013): 1118-1125. [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, Leandro, et al. "Potassium channels as a target for cancer therapy: Current perspectives." OncoTargets and therapy 15 (2022): 783. PMCID: PMC9309325 PMID: 35899081.
- Wong, Bing-Sang, et al. "Anticancer effects of antihypertensive L-type calcium channel blockers on chemoresistant lung cancer cells via autophagy and apoptosis." Cancer Management and Research (2020): 1913-1927. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Ting, Jingyi Zhou, and Jianliu Wang. "Calcium and calcium-related proteins in endometrial cancer: opportunities for pharmacological intervention." International Journal of Biological Sciences 18.3 (2022): 1065. PMCID: PMC8771838 PMID: 35173539.
- Correia, Ana Salomé, Fátima Gärtner, and Nuno Vale. "Drug combination and repurposing for cancer therapy: the example of breast cancer." Heliyon 7.1 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xiyue, et al. "A pathology foundation model for cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction." Nature (2024): 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Parvathaneni, Vineela, et al. "Repurposing bedaquiline for effective non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) therapy as inhalable cyclodextrin-based molecular inclusion complexes." International journal of molecular sciences 22.9 (2021): 4783. [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, Marco, et al. "Bedaquiline, an FDA-approved antibiotic, inhibits mitochondrial function and potently blocks the proliferative expansion of stem-like cancer cells (CSCs)." Aging (Albany NY) 8.8 (2016): 1593. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Leilei, et al. "Repurposing non-oncology small-molecule drugs to improve cancer therapy: Current situation and future directions." Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 12.2 (2022): 532-557. [CrossRef]
- Li, Jiayu, et al. "Tetracycline antibiotics: Potential anticancer drugs." European journal of pharmacology (2023): 175949. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Zhen, et al. "Biological functions and molecular mechanisms of antibiotic tigecycline in the treatment of cancers." International journal of molecular sciences 20.14 (2019): 3577. [CrossRef]
- Bailly, Christian, and Gérard Vergoten. "A new horizon for the old antibacterial drug clofoctol." Drug Discovery Today 26.5 (2021): 1302-1310. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Minghua, et al. "Identification of an old antibiotic clofoctol as a novel activator of unfolded protein response pathways and an inhibitor of prostate cancer." British journal of pharmacology 171.19 (2014): 4478-4489. [CrossRef]
- van der Zanden, Sabina Y., Xiaohang Qiao, and Jacques Neefjes. "New insights into the activities and toxicities of the old anticancer drug doxorubicin." The FEBS journal 288.21 (2021): 6095-6111. [CrossRef]
- Shandilya, Manish, et al. "Molecular-level understanding of the anticancer action mechanism of anthracyclines." Advances in precision medicine oncology (2020). [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Hirofumi, et al. "A first-in-human Phase 1 study of epirubicin-conjugated polymer micelles (K-912/NC-6300) in patients with advanced or recurrent solid tumors." Investigational new drugs 35 (2017): 307-314. [CrossRef]
- Pourgholami, Mohammad H., et al. "Minocycline inhibits growth of epithelial ovarian cancer." Gynecologic oncology 125.2 (2012): 433-440. [CrossRef]
- Afshari, Amir R., Hamid Mollazadeh, and Amirhossein Sahebkar. "Minocycline in treating glioblastoma multiforme: far beyond a conventional antibiotic." Journal of oncology 2020.1 (2020): 8659802. [CrossRef]
- Reed, Gregory A., et al. "A Phase 1 study of intravenous infusions of tigecycline in patients with acute myeloid leukemia." Cancer medicine 5.11 (2016): 3031-3040. [CrossRef]
- Novella, Pugliese, et al. "Tigecycline-Based Front-Line Antibiotic Therapy Significantly Decreases Mortality Among Patients with Neutropenic Enterocolitis Following Cytarabine-Containing Chemotherapy for the Remission Induction of Acute Myeloid Leukemia." Blood 128.22 (2016): 3550. [CrossRef]
- Nowakowska, Justyna, et al. "Recent Development of Fluoroquinolone Derivatives as Anticancer Agents." Molecules 29.15 (2024). PMCID: PMC11314068 PMID: 39124943.
- AbuBaih, Rania Hamdy, Michael Atef Fawzy, and Maiiada Hassan Nazmy. "The prospective potential of fluoroquinolones as anticancer agents." Journal of Modern Research 5.1 (2023): 4-10. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Wenmin, et al. "Chloroquine against malaria, cancers and viral diseases." Drug Discovery Today 25.11 (2020): 2012-2022. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Yanqing, et al. "Pharmacology Progresses and Applications of Chloroquine in Cancer Therapy." International Journal of Nanomedicine (2024): 6777-6809. [CrossRef]
- Mauthe, Mario, et al. "Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing autophagosome-lysosome fusion." Autophagy 14.8 (2018): 1435-1455. [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, Nikolaos, et al. "Repurposing antipsychotics for cancer treatment." Biomedicines 9.12 (2021): 1785. [CrossRef]
- Lianos, Georgios D., et al. "Repurposing antipsychotic drugs for cancer treatment: current evidence and future perspectives." Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy 22.2 (2022): 131-134. [CrossRef]
- Moura, Catarina, and Nuno Vale. "The role of dopamine in repurposing drugs for oncology." Biomedicines 11.7 (2023): 1917. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, Sofia M., et al. "Repurposing some of the Well-known Non-steroid Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) for Cancer Treatment." Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 23.13 (2023): 1171-1195. [CrossRef]
- Ozleyen, Adem, et al. "Looking at NSAIDs from a historical perspective and their current status in drug repurposing for cancer treatment and prevention." Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 149.5 (2023): 2095-2113. [CrossRef]
- Joo, Young Bin, et al. "Use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs after cancer diagnosis in rheumatoid arthritis patients." Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 29.3 (2022): 162-170. [CrossRef]
- Calip, Gregory S., et al. "Targets of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and risk of multiple myeloma." International journal of cancer 147.5 (2020): 1300-1305. [CrossRef]
- Aroosa, Mir, et al. "The evidence for repurposing anti-epileptic drugs to target cancer." Molecular Biology Reports 50.9 (2023): 7667-7680. [CrossRef]
- Sulsenti, Roberta, et al. "Repurposing of the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam to restrain neuroendocrine prostate cancer and inhibit mast cell support to adenocarcinoma." Frontiers in immunology 12 (2021): 622001. [CrossRef]
- Malla, RamaRao, et al. "Revitalizing Cancer Treatment: Exploring the Role of Drug Repurposing." Cancers 16.8 (2024): 1463. [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, Ambra, et al. "In vitro antineoplastic effects of brivaracetam and lacosamide on human glioma cells." Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 36 (2017): 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Moutal, Aubin, et al. "CRMP2 phosphorylation drives glioblastoma cell proliferation." Molecular neurobiology 55 (2018): 4403-4416. [CrossRef]
- Morales-Urteaga, Xabier, et al. "CRMP2 as a candidate target to interfere with lung cancer cell migration." (2021). [CrossRef]
- Costa, Bárbara, and Nuno Vale. "Understanding Lamotrigine’s role in the CNS and possible future evolution." International journal of molecular sciences 24.7 (2023): 6050. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Ki Jung, Seung Hyun Jeun, and Ki-Wug Sung. "Lamotrigine, an antiepileptic drug, inhibits 5-HT3 receptor currents in NCB-20 neuroblastoma cells." The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology: Official Journal of the Korean Physiological Society and the Korean Society of Pharmacology 21.2 (2017): 169. [CrossRef]
- Wu, King-Chuen, et al. "Drug repurposing: the mechanisms and signaling pathways of anti-cancer effects of anesthetics." Biomedicines 10.7 (2022): 1589. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Daipeng, et al. "Repositioning lidocaine as an anticancer drug: the role beyond anesthesia." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 8 (2020): 565. [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, Tânia, and Nuno Vale. "Pharmacological efficacy of repurposing drugs in the treatment of prostate cancer." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.4 (2023): 4154. [CrossRef]
- Alfaqih, Mahmoud A., et al. "CYP27A1 loss dysregulates cholesterol homeostasis in prostate cancer." Cancer research 77.7 (2017): 1662-1673. [CrossRef]
- Geng, Xinran, et al. "Cardiac glycosides inhibit cancer through Na/K-ATPase-dependent cell death induction." Biochemical pharmacology 182 (2020): 114226. [CrossRef]
- Kumavath, Ranjith, et al. "Emergence of cardiac glycosides as potential drugs: Current and future scope for cancer therapeutics." Biomolecules 11.9 (2021): 1275. [CrossRef]
- Thiruchenthooran, Vaikunthavasan, Elena Sánchez-López, and Anna Gliszczyńska. "Perspectives of the application of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer therapy: Attempts to overcome their unfavorable side effects." Cancers 15.2 (2023): 475. [CrossRef]
- Duarte, Diana, and Nuno Vale. "Antidepressant drug sertraline against human cancer cells." Biomolecules 12.10 (2022): 1513. [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, Rita, Maria de Lourdes Pereira, and Miguel Oliveira. "Beta-blockers and cancer: where are we?." Pharmaceuticals 13.6 (2020): 105. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Sai-Nan, et al. "The anti-cancer properties of heparin and its derivatives: A review and prospect." Cell adhesion & migration 14.1 (2020): 118-128. [CrossRef]
- Rawla, Prashanth. "Epidemiology of prostate cancer." World journal of oncology 10.2 (2019): 63. [CrossRef]
- Bahmad, Hisham F., et al. "Overcoming drug resistance in advanced prostate cancer by drug repurposing." Medical Sciences 10.1 (2022): 15. [CrossRef]
- Araújo, Diana, et al. "Repurposed drugs in gastric cancer." Molecules 28.1 (2022): 319. [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, Nayeralsadat, et al. "Current trends and future prospects of drug repositioning in gastrointestinal oncology." Frontiers in Pharmacology 14 (2024): 1329244. [CrossRef]
- Mu, Jiasheng, et al. "Thioridazine, an antipsychotic drug, elicits potent antitumor effects in gastric cancer." Oncology reports 31.5 (2014): 2107-2114. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Zheng-Yan, et al. "Thioridazine reverses trastuzumab resistance in gastric cancer by inhibiting S-phase kinase associated protein 2-mediated aerobic glycolysis." World Journal of Gastroenterology 29.45 (2023): 5974. [CrossRef]
- Bedford, Matthew R., et al. "Iron chelation in the treatment of cancer: a new role for deferasirox?." The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 53.9 (2013): 885-891. [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A. Keith. "How thalidomide works against cancer." Science 343.6168 (2014): 256-257. [CrossRef]
- Kale, Vijay P., et al. "Old drugs, new uses: Drug repurposing in hematological malignancies." Seminars in cancer biology. Vol. 68. Academic Press, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Licht, Jonathan D., Jake Shortt, and Ricky Johnstone. "From anecdote to targeted therapy: the curious case of thalidomide in multiple myeloma." Cancer cell 25.1 (2014): 9-11. [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, Vishruti, Lokesh Kumar Vyas, and Dileep Kumar Bharati. "Rebirth of thalidomide." World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 11.7 (2022): 842-854.
- Iqbal, Nida, and Naveed Iqbal. "Imatinib: a breakthrough of targeted therapy in cancer." Chemotherapy research and practice 2014.1 (2014): 357027. [CrossRef]
- Phuar, Hsiao Ling, et al. "Tyrosine kinase inhibitors initiation, cost sharing, and health care utilization in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia: A retrospective claims-based study." Journal of Managed Care & Specialty Pharmacy 25.10 (2019): 1140-1150.
- Jabbour, Elias, and Hagop Kantarjian. "Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring." American journal of hematology 93.3 (2018): 442-459. [CrossRef]
- Senapati, Jayastu, et al. "Pathogenesis and management of accelerated and blast phases of chronic myeloid leukemia." Leukemia 37.1 (2023): 5-17. [CrossRef]
- Anjum, Sadia, et al. "Enhancing therapeutic efficacy: sustained delivery of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) via thiolated chitosan nanoparticles targeting CD44 in triple-negative breast cancer." Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 11431. [CrossRef]
- Shivani, Dave, et al. "Drug repurposing: a retrospective revolution in breast cancer medicine." Discover Medicine 1.1 (2024): 11. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. I., et al. "Preclinical pharmacodynamic evaluation of antibiotic nitroxoline for anticancer drug repurposing." Oncology Letters 11.5 (2016): 3265-3272. [CrossRef]
- El Zarif, Talal, et al. "Overcoming therapy resistance in colon cancer by drug repurposing." Cancers 14.9 (2022): 2105. [CrossRef]
- Qi, Jia, et al. "Antihypertensive medications and risk of colorectal cancer in British Columbia." Frontiers in Pharmacology 14 (2023): 1301423. [CrossRef]
- Kedika, Ramalinga, et al. "Long-term use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors is associated with decreased incidence of advanced adenomatous colon polyps." Journal of clinical gastroenterology 45.2 (2011): e12-e16. [CrossRef]
- Massalee, Rachel, and Xuefang Cao. "Repurposing beta-blockers for combinatory cancer treatment: effects on conventional and immune therapies." Frontiers in Pharmacology 14 (2024): 1325050. [CrossRef]
- El Zarif, Talal, et al. "Overcoming therapy resistance in colon cancer by drug repurposing." Cancers 14.9 (2022): 2105.
- Schein, Catherine H. "Repurposing approved drugs for cancer therapy." British Medical Bulletin 137.1 (2021): 13-27. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, Laine Celestino, et al. "Mebendazole induces apoptosis via C-MYC inactivation in malignant ascites cell line (AGP01)." Toxicology in Vitro 60 (2019): 305-312. [CrossRef]
- Arend, Rebecca C., et al. "Niclosamide and its analogs are potent inhibitors of Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR and STAT3 signaling in ovarian cancer." Oncotarget 7.52 (2016): 86803. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Jiangbo, et al. "Niclosamide-induced Wnt signaling inhibition in colorectal cancer is mediated by autophagy." Biochemical Journal 476.3 (2019): 535-546. [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, Gerhard, and Barbara Rath. "Repurposing of anthelminthics as anticancer drugs." Oncomedicine 3 (2018): 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Mussin, Nadiar, et al. "Sirolimus and metformin synergistically inhibits colon cancer in vitro and in vivo." Journal of Korean Medical Science 32.9 (2017): 1385-1395. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Plumed, J. A. , et al. "Sirolimus, the first mTOR inhibitor." Nefrología (English Edition) 26 (2006): 21-32.
- Granata, Simona, et al. "mTOR-inhibitors and post-transplant diabetes mellitus: a link still debated in kidney transplantation." Frontiers in Medicine 10 (2023): 1168967. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Ge, et al. "The antipsychotic drug pimozide promotes apoptosis through the RAF/ERK pathway and enhances autophagy in breast cancer cells." Cancer Biology & Therapy 25.1 (2024): 2302413. [CrossRef]
- Lianos, Georgios D., et al. "Repurposing antipsychotic drugs for cancer treatment: current evidence and future perspectives." Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy 22.2 (2022): 131-134. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Jia-Jie, et al. "Antipsychotic agent pimozide promotes reversible proliferative suppression by inducing cellular quiescence in liver cancer." Oncology reports 42.3 (2019): 1101-1109. [CrossRef]
- Attia, Yasmeen M., Heba Ewida, and Mahmoud Salama Ahmed. "Successful stories of drug repurposing for cancer therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma." Drug Repurposing in Cancer Therapy. Academic Press, 2020. 213-229. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Sheng-Teng, et al. "Improved survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with cardiac arrhythmia by amiodarone treatment through autophagy." International journal of molecular sciences 20.16 (2019): 3978. [CrossRef]
- Attia, Yasmeen M., Heba Ewida, and Mahmoud Ahmed. "Successful Stories of Drug Repurposing for Cancer Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, To and Cho_Drug Repurposing in Cancer Therapy." (2020). https://buescholar.bue.edu.
- Chao, Min-Wu, et al. "Lanatoside C, a cardiac glycoside, acts through protein kinase Cδ to cause apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells." Scientific reports 7.1 (2017): 46134. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Xiaoge, et al. "Anti-malarial atovaquone exhibits anti-tumor effects by inducing DNA damage in hepatocellular carcinoma." American Journal of Cancer Research 8.9 (2018): 1697. PMCID: PMC6176191 PMID: 30323964.
- Stevens, Alexandra McLean, et al. "Repurposing atovaquone as a therapeutic against acute myeloid leukemia (AML): combination with conventional chemotherapy is feasible and well tolerated." Cancers 15.4 (2023): 1344. [CrossRef]
- Hua, Yu, et al. "Metformin and cancer hallmarks: shedding new lights on therapeutic repurposing." Journal of Translational Medicine 21.1 (2023): 403. [CrossRef]
- Kalyanaraman, Balaraman, et al. "Modified metformin as a more potent anticancer drug: mitochondrial inhibition, redox signaling, antiproliferative effects and future EPR studies." Cell biochemistry and biophysics 75 (2017): 311-317. [CrossRef]
- Hua, Yu, et al. "Metformin and cancer hallmarks: shedding new lights on therapeutic repurposing." Journal of Translational Medicine 21.1 (2023): 403. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Gang, et al. "Mitochondria-targeted analogues of metformin exhibit enhanced antiproliferative and radiosensitizing effects in pancreatic cancer cells." Cancer research 76.13 (2016): 3904-3915. [CrossRef]
- Amengual-Cladera, Emilia, et al. "Metformin: From Diabetes to Cancer—Unveiling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies." Biology 13.5 (2024): 302. [CrossRef]
- Basak, Debasish, David Gamez, and Subrata Deb. "SGLT2 inhibitors as potential anticancer agents." Biomedicines 11.7 (2023): 1867. [CrossRef]
- Aminzadeh-Gohari, Sepideh, et al. "From old to new—Repurposing drugs to target mitochondrial energy metabolism in cancer." Seminars in cell & developmental biology. Vol. 98. Academic Press, 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.025.
- Papadopoli, David, et al. "Perturbations of cancer cell metabolism by the antidiabetic drug canagliflozin." Neoplasia 23.4 (2021): 391-399. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Ping, et al. "Mitochondrial adaptation in cancer drug resistance: prevalence, mechanisms, and management." Journal of Hematology & Oncology 15.1 (2022): 97. [CrossRef]
- Raafat, Shereen Nader, et al. "Enhancing the anticancer potential of metformin: fabrication of efficient nanospanlastics, in vitro cytotoxic studies on HEP-2 cells and reactome enhanced pathway analysis." International Journal of Pharmaceutics: X 6 (2023): 100215. [CrossRef]
- Aminzadeh-Gohari, Sepideh, et al. "From old to new—Repurposing drugs to target mitochondrial energy metabolism in cancer." Seminars in cell & developmental biology. Vol. 98. Academic Press, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Sheng-Fan, Ling-Ming Tseng, and Hsin-Chen Lee. "Role of mitochondrial alterations in human cancer progression and cancer immunity." Journal of biomedical science 30.1 (2023): 61. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Yi, et al. "The mechanisms of action of mitochondrial targeting agents in cancer: inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation and inducing apoptosis." Frontiers in Pharmacology 14 (2023): 1243613. [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, Marco, et al. "Bedaquiline, an FDA-approved antibiotic, inhibits mitochondrial function and potently blocks the proliferative expansion of stem-like cancer cells (CSCs)." Aging (Albany NY) 8.8 (2016): 1593. [CrossRef]
- Greene, John, Ashvina Segaran, and Simon Lord. "Targeting OXPHOS and the electron transport chain in cancer; Molecular and therapeutic implications." Seminars in Cancer Biology. Vol. 86. Academic Press, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, Marco, et al. "Repurposing atovaquone: targeting mitochondrial complex III and OXPHOS to eradicate cancer stem cells." Oncotarget 7.23 (2016): 34084. [CrossRef]
- Schultz, Christopher W., and Avinoam Nevler. "Pyrvinium pamoate: Past, present, and future as an anti-cancer drug." Biomedicines 10.12 (2022): 3249. [CrossRef]
- Tomitsuka, Eriko, Kiyoshi Kita, and Hiroyasu Esumi. "An anticancer agent, pyrvinium pamoate inhibits the NADH–fumarate reductase system—a unique mitochondrial energy metabolism in tumour microenvironments." The journal of biochemistry 152.2 (2012): 171-183. [CrossRef]
- Weng, Ningna, et al. "Repurposing antifungal drugs for cancer therapy." Journal of Advanced Research 48 (2023): 259-273. [CrossRef]
- Tsubamoto, Hiroshi, et al. "Repurposing itraconazole as an anticancer agent." Oncology letters 14.2 (2017): 1240-1246. [CrossRef]
- Head, Sarah A., et al. "Antifungal drug itraconazole targets VDAC1 to modulate the AMPK/mTOR signaling axis in endothelial cells." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112.52 (2015): E7276-E7285. [CrossRef]
- Pancu, Daniel Florin, et al. "Antibiotics: conventional therapy and natural compounds with antibacterial activity—a pharmaco-toxicological screening." Antibiotics 10.4 (2021): 401. [CrossRef]
- Stokes, Jonathan M., et al. "A deep learning approach to antibiotic discovery." Cell 180.4 (2020): 688-702. [CrossRef]
- Bano, Nilofer, et al. "Drug Repurposing of Selected Antibiotics: An Emerging Approach in Cancer Drug Discovery." ACS omega 9.25 (2024): 26762-26779. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Jiabing, et al. "Targeting reactive oxygen species capacity of tumor cells with repurposed drug as an anticancer therapy." Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2021.1 (2021): 8532940. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, Vikas, and Puneet Talwar. "Repositioning of fluoroquinolones from antibiotic to anti-cancer agents: An underestimated truth." Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 111 (2019): 934-946. [CrossRef]
- Bano, Nilofer, et al. "Drug Repurposing of Selected Antibiotics: An Emerging Approach in Cancer Drug Discovery." ACS omega 9.25 (2024): 26762-26779. [CrossRef]
- Chai, Jong-Yil, Bong-Kwang Jung, and Sung-Jong Hong. "Albendazole and mebendazole as anti-parasitic and anti-cancer agents: an update." The Korean Journal of Parasitology 59.3 (2021): 189. PMCID: PMC8255490 PMID: 34218593.
- Castro, L. S. E. P. W., et al. "Albendazole as a promising molecule for tumor control." Redox biology 10 (2016): 90-99. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Ge, et al. "The antipsychotic drug pimozide promotes apoptosis through the RAF/ERK pathway and enhances autophagy in breast cancer cells." Cancer Biology & Therapy 25.1 (2024): 2302413. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Ukjin, et al. "Pimozide inhibits the human prostate cancer cells through the generation of reactive oxygen species." Frontiers in Pharmacology 10 (2020): 1517. [CrossRef]
- El-Habib, Dakir, et al. "The anti-psychotic drug pimozide is a novel chemotherapeutic for breast cancer." Oncotarget 9.79 (2018): 34889-34910. [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, Nikolaos, et al. "Repurposing antipsychotics for cancer treatment." Biomedicines 9.12 (2021): 1785. [CrossRef]
| Pharmacological class | Drug name | Chemical structure | New therapeutic indication | New target | Original target | Development status | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
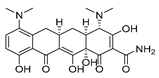
| Anti-Platelet | Aspirin | 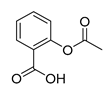 |
gastric, esophageal, colorectal, pancreatic, ovarian, endometrial, breast, and prostate cancers | PIK3CA, mTORC1 and AMPK. | COXs | Phase II and III clinical trials, meta-analysis | 37-45 |
| Anti-Diabetic | Metformin (biguanides) |
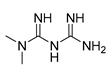 |
Colorectal, breast, pancreatic, prostate, lung, and cervical malignancies. | cell cycle/pSTAT3, S6 kinase, and mTOR/AMPK/ | Mitochondrial respiration | Phase II and III clinical trials. | 46-54,65-67, 201-206, 216-220, 225 |
| Pioglitazone (TZDs) |
|
Breast, prostate, and colon cancer |
PPAR γ | PPAR γ | Phase II trials. | 61-67 | |
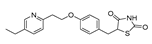
| Desmopressin |  |
Colon cancer | COX-2 and CD1 | AVPR2 | Preclinical | 57-60 | |
| Anti-Helminthic | Flubendazole (benzimidazole) |
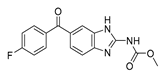 |
Neuroblastoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, lung, liver, colorectal, and breast cancer. | Apoptosis (caspase 3 and 7) | Tubulin polymerization | Preclinical | 70-74 |
| Parbendazole | 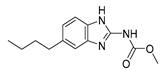 |
pancreatic cancer | Apoptosis, cell cycle, and DNA damage. | Tubulin polymerization | Preclinical | 57 | |
| Mebendazole (MZ) | 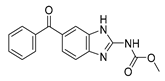 |
Glioblastoma, melanoma, prostate, breast, brain, ovarian, colon, lung, colorectal and endocrine cancers. | Cell cycle, apoptosis (caspase-3 pathway), ABL and BRAF. | Tubulin polymerization | Preclinical | 68-70,75-78, 200,243 | |
| Niclosamide |
 |
Colon, prostate, liver, ovarian, and breast cancers. | Wnt/β-catenin, NF-KB, mTOR, and JAK/STAT3 pathways. | uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation | Preclinical | 72,79-80,201-203 | |
| Clioquinol |  |
leukemia and malignant myeloma. |
HDAC | DNA replication | Preclinical | 81-82 | |
| Anti-Viral | Ritonavir | 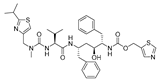 |
Ovarian, pancreatic, and breast cancer, lymphocytic leukemia | Apoptosis | Protease inhibitors target HIV | Preclinical | 84-86 |
| Ribavirin | 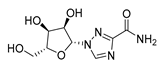 |
acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | Induces VEGF mRNA translation | RNA replicating | phase II clinical trial | 87 | |
| Cidofovir | 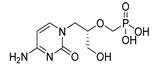 |
Glioblastomas | Apoptosis | viral DNA polymerase | Preclinical | 87 | |
|
Cardiovascular Anti-Hypertension Medication | |||||||
| Angiotensin receptor blocker | Losartan | 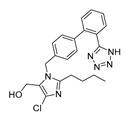 |
Pancreatic cancer | depleting the matrix and reducing collagen I levels | Angiotensin receptor | phase II clinical trials. | 88-90,97,101 |
| Candesartan | 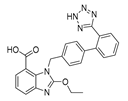 |
Colon cancer, prostate cancer, liver and kidney cancer | VEGF expression | Angiotensin receptor | Preclinical | 99-101,106-107,111 | |
| Irbesartan | 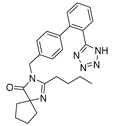 |
Colon cancer, liver and kidney cancer | AP-1 DNA binding, pErbB3, and p38/MAPK | Angiotensin receptor | Preclinical | 88-90,99-101,111 | |
| Telmisartan | 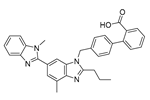 |
Colon cancer, liver and kidney cancer | pErbB3, p38/MAPK caspase-3, Bcl-2, PI3/AKT pathway |
Angiotensin receptor | Preclinical | 88-90,111-112 | |
| ACE inhibitors | Captopril | 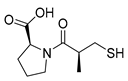 |
Colorectal liver metastases prostate cancer liver and kidney cancer |
p53 expression | ACE | Preclinical | 88-90,99-101,106-107,111-112 |
| Enalapril | 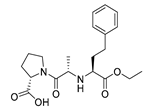 |
Colorectal cancer (CRC) | IGF-IR 1 | ACE | Preclinical | 99-101 | |
| Beta-blockers | Carvedilol | 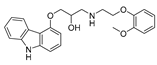 |
Breast cancer | Growth factor receptors and mitochondrial function | Beta receptors | Phase II trials for prostate cancer. | 88-90,104-105 |
| Propranolol |
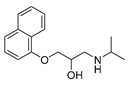 |
Ovarian, colorectal, lung, prostate, breast cancer, multiple myeloma. pancreatic, neuroblastoma, angiosarcoma, melanoma, and leukemia. |
p-AKT/p-ERK/p-MEK and CD8+ T cells JNK signaling pathway and ROS. |
Beta receptors | Phase I trials for ovarian cancer Phase II trials for prostate cancer. | 91-92,93-95,96-98,104-105 | |
| Direct vasodilator | Minoxidil | 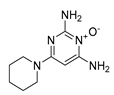 |
Ovarian cancer | caspase-3 |
ATP-sensitive potassium channels | Phase II trial | 108-110 |
| Hydralazine |
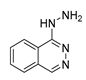 |
Prostate cancer |
Induces demethylation, re-expressing suppressed genes | Direct vasodilator | Preclinical | 106-107 | |
| Tezosentan | 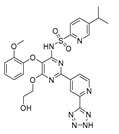 |
Various cancer types especially with high expression of endothelin receptor type A | Endothelin receptor A | Endothelin receptor A/B | Preclinical | 113-114 | |
|
Cardiovascular Antihyperlipidemic |
Fenofibrate |
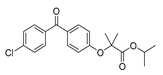 |
Breast cancer lung cancer |
AMPK, NF-κB and ERK signaling | PPARα | Preclinical | 115-116 |
| Ion Channels modulators | |||||||
|
Potassium K+ Channel Inhibitors |
Glipalamide |
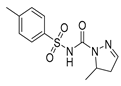 |
Melanoma, lung, stomach, and breast cancers |
Kv10.1, Kv10.2 (EAG2), and Kv11.1 channels | K channel (SUR). | Preclinical | 126-27 |
| Verapamil |
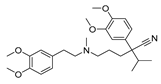 |
Neuroblastoma and prostate cancer | K and Ca channels | T- and L-type Ca2+ channel antagonist | Preclinical | 126-127 | |
| Astemizole |  |
Various cancer cell lines | Kv10.1 | H1-antagonist | Preclinical | 126-127 | |
|
Calcium (Cav) Channel Blockers |
Mibefradil | 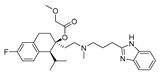 |
High-grade glioma tumors |
T-type Ca2+ channel | T and L-type Ca2+ channel | Phase 1b clinical trials | 130-131 |
| Nifedipine | 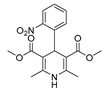 |
Colon cancer | PDL-1 | Calcium Channel | Preclinical | 99-101 | |
| Antibiotic | Bedaquiline | 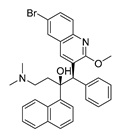 |
Breast | Mitochondrial ATP-synthase | ATP synthase | Preclinical | 132-134,229 |
| Doxycycline (Tetracycline) | 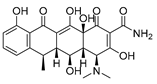 |
Various cancer cell lines | AMPK-mediated mTOR, WNT/b-catenin, and PI3K/AKT | 30S ribosomal subunit | Preclinical | 84,135-136,142-145,226-228 | |
| Clofoctol |
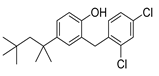 |
Various cancer cell lines | UPR pathway | bacterial protein synthesis | Preclinical | 137-138 | |
| Doxorubicin (Anthracyclines) | 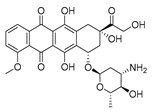 |
Breast cancer | DNA intercalator | DNA intercalator | Approved | 139-141 | |
| Minocycline (Tetracycline) |
 |
Ovarian, breast cancer, glioblastoma | Cell cycle arrest, cyclins A, B, and E | Inhibit the 30S ribosomal subunit | Clinical trials | 142-142 | |
| Tigecycline (Tetracycline) | 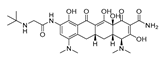 |
Gliomas, myeloid leukemia, non-small cell lung cancer. |
Cell cycle arrest | Inhibit the 30S ribosomal subunit | Phase I trials for acute myeloid leukemia | 135-136,144-145,239-240 | |
| Ciprofloxacin (Fluoroquinolones) |
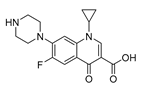 |
leukemia, osteoblastoma, osteosarcoma, colon, bladder, and prostate cancers. | miRNA production | Inhibit bacterial gyrase | Preclinical | 146-147 | |
| Anti-Malarial | Chloroquine |
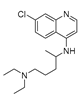 |
Glioblastoma | Autophagy | Inhibits heme polymerase | Preclinical | 68-69,148-150 |
| Artesunate |
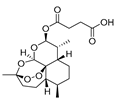 |
Leukemia Kaposi’s sarcoma |
ROS production and apoptosis | Free radicals generation | Preclinical | 148 | |
| Mefloquine |
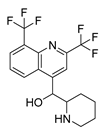 |
Breast, leukemia, gastric, cervical, and colon cancers. | P-gp expression, production of ROS | Inhibits 80S ribosome | Preclinical | 148-150 | |
| Anti-Psychotic | Haloperidol |
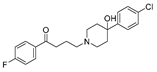 |
Pancreatic cancer | DRD2 | DRD2 | Preclinical | 151-153 |
| Penfluridol | 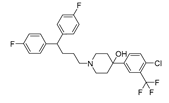 |
Pancreatic cancer | DRD2, autophagy, JAK2–STAT3 and ERK/AKT signaling pathways | DRD2 | Preclinical | 151-153 | |
| nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) | Diclofenac |
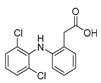 |
Pancreatic cancer | Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | COXs | Preclinical | 154-155,172 |
| Celecoxib (selective COX-2 inhibitor) |
 |
Breast cancer | Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | COX-2 | Clinical trials | 142-143 | |
| disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) | Auranofin |
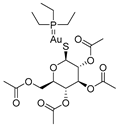 |
Various cancer types | TrxR, UPS system | redox enzymes | Phase I, and phase II | 156-157 |
| anti-epileptic | Oxcarbazepine |
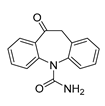 |
Various cancer types | cell cycle arrest, HDAC, PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway | Na channel inhibitor | Preclinical | 158-159 |
| lacosamide | 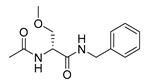 |
Glioblastoma | CRMP2 | Na channel | Preclinical | 160-165 | |
| Lamotrigine | 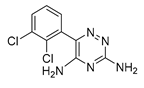 |
brain tumors | N-, L-, and P-type Ca channels, 5-HT3 receptors. | Na+ channels | Preclinical | 164-165 | |
| anesthetic medications | ketamine |
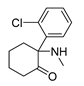 |
lung cancer ovarian cancer breast cancer hepatocellular carcinomas |
CD69, P57, glutathione peroxidase 4 | NMDA receptor | Preclinical | 57 |
| Propofol | 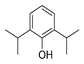 |
Squamous cell carcinoma | caspase and MAPK pathways | GABA receptors | Preclinical | 166-167 | |
| New Therapeutic Indication | Pharmacological Class | Drug Name | Chemical Structure | New Target | Original Target | Status | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostate Cancer | Anti-Dyslipidemic Drugs | Atorvastatin (Statins) |
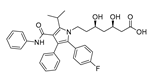 |
Block cholesterol synthesis and androgen production | HMG-CoA reductase | Clinical trials | 52-54,168-169 |
| Antiarrhythmic Drugs | Digoxin |  |
Cell cycle topoisomerase II |
Na/K pump inhibition | Preclinical | 65-67,170-171 | |
| Ouabain | 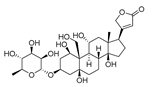 |
Apoptosis by blocking the production of survivin and STAT3 | Na/K pump inhibition | Preclinical | 170-171 | ||
| Anti-Inflammatory Drugs | Indomethacin | 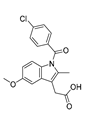 |
MYC gene family expression | Cyclooxygenases (COXs) | Preclinical | 172 | |
| Antidepressant Drugs | Sertraline | 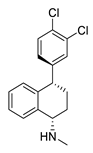 |
Angiogenesis, metastasis, and autophagy | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor | Preclinical | 173 | |
|
Beta-Blockers |
Propranolol |  |
CREB1-EZH2-TSP1 pathway | Beta receptors | phase II trial | 174 | |
| Miscellaneous | Heparin | 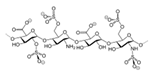 |
Cytokine, adhesion molecule, and angiogenic factor expression | Antithrombin | Preclinical | 175 | |
| zoledronic acid | 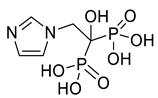 |
G1 arrest, metastasis | osteoclast proliferation | Preclinical | 176-177 | ||
| Mifepristone | 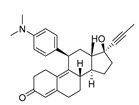 |
suppressing over-expressed cell surface receptors in CRPC cells | Anti-progesterone | Preclinical | 176-177 | ||
| Rapamycin | 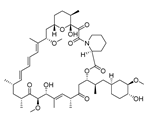 |
Binding to the FRB domain of mTOR, inhibiting mTORC1 | cytokine signaling | Preclinical | 55-56, 176-177, 204-206 | ||
| Gastric cancer (GC) | Antidepressant | Fluoxetine |  |
Inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum stress marker (CHOP) | Serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) |
Preclinical | 178 |
| Paroxetine | 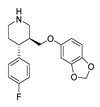 |
Enhanced DNA damage and reduced DNA repair | Preclinical | 178 | |||
| Antiepileptic | Valproic acid (VPA) | 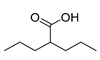 |
HDAC1/PTEN/Akt signaling pathway | Na channel | phase II trial | 164-165,178-179 | |
| Antipsychotic | Risperidone | 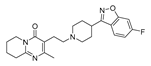 |
Caspase 3, 8,9, ROS | Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition | Preclinical | 180-181 | |
| Agents that chelate iron | Deferasirox |  |
NDRG1, mTOR and c-myc expression | Iron chelator/iron toxicity | Preclinical | 178,182 | |
|
Blood malignancies |
Antiemetic | Thalidomide |
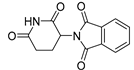 |
TNF-α | Immunomodulation | Approved | 183-186 |
| Tyrosine kinase inhibitor | Imatinib |  |
suppression of KIT kinase gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) | chronic myelogenous leukemia | approved | 187-190 | |
| Dasatinib | 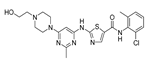 |
Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) | chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) | Approved | 189-190 | ||
| Breast cancer | Antibiotic | Nitroxoline (NTX) | 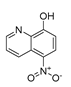 |
anti-angiogenic activity, cathepsin B | chelation of divalent cations | Preclinical | 166,193 |
| Colon cancer | Antibiotic | Rapamycin | 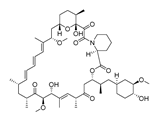 |
mTOR pathway | mTOR pathway | Preclinical | 55-56,176-177,204-206 |
| Anti-Helminthic | Mebendazole (benzimidazole) |
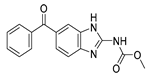 |
MYC pathway | Tubulin polymerization | Phase I and II clinical trials. | 68,76,200 | |
| Niclosamide | 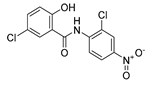 |
Wnt/β-catenin cascade | Phase I clinical trials. | 201-203 | |||
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | Antipsychotic | Pimozide |  |
Apoptosis expression of STAT3 |
DRD2 | Preclinical | 207-209,245-248 |
| Antiarrhythmic | Amiodarone | 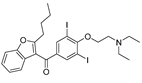 |
mTOR inhibitor | Na and K channels | Preclinical, meta-analysis | 210-211 | |
| Lanatoside C | 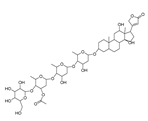 |
mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), AKT/mTOR, PKCd | Na channel | Preclinical | 212-213 | ||
| Anti-microbe | Atovaquone | 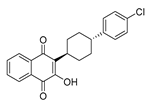 |
p53 and p21, kinase-2 and H2AX | ETC at the bc1 complex | Preclinical | 214-214,230-231 |
| Targeted Mechanism |
Pharmacological Class | Drug Name | Chemical Structure | New Therapeutic Indication | Development Status | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitochondrial energy metabolism | Anti-diabetic | Metformin (biguanides) |
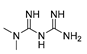 |
Colorectal, breast, pancreatic, prostate, lung, and cervical malignancies. | Phase II and III clinical trials. | 216-218 |
| Phenformin | 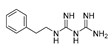 |
colorectal cancer | phase I | 219-220 | ||
| Canagliflozin | 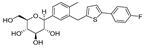 |
prostate and lung cancer | Preclinical | 222-224 | ||
| Pioglitazone | 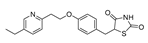 |
Breast, prostate, and colon cancer | Phase II trials. | 61-67, 222 & 224 |
||
| Anti-microbe | Bedaquiline | 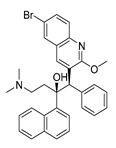 |
Breast | Preclinical | 229 | |
| Ivermectin | 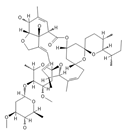 |
pancreatic and colorectal cancers. | Preclinical | 230-231 | ||
| Pyrvinium |  |
Pancreatic, colorectal, and breast cancers | phase I | 232-233 | ||
| Itraconazole | 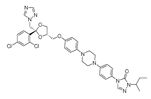 |
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate cancer, and basal cell carcinoma (BCC) | Phase II | 234-236 | ||
| ROS inducer | Antibiotic | Tigecycline | 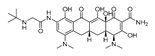 |
hepatocellular carcinoma and acute myeloid leukemia |
phase I clinical trial for acute myeloid leukemia | 239-240 |
| Levofloxacin | 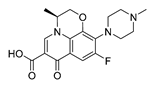 |
lung and breast cancer | Preclinical | 241-242 | ||
| Antiparasitic | Albendazole | 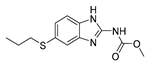 |
Ovarian, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers | phase I | 243-244 | |
| Antipsychotic | Pimozide | 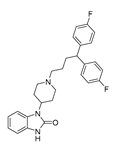 |
Hepatocellular carcinoma | Preclinical | 245-248 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





