Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
30 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- No need to establish the model structure of the actual system, as the neural network itself serves as a model for network identification.
- It is capable of identifying any linear or nonlinear model.
- The neural network not only serves as a model but is also an actual system achievable through physics.
- Local minimum problem.
- Lengthy training time and slow learning speed.
- Difficulty in extracting ideal training samples.
- Challenges in optimizing the network structure.
- Difficulty in completely solving the convergence problem theoretically for the neural network algorithm.
2. Mathematical Model of a Quadrotor
3. System Identification Methods
3.1. Extended Kalman Filter
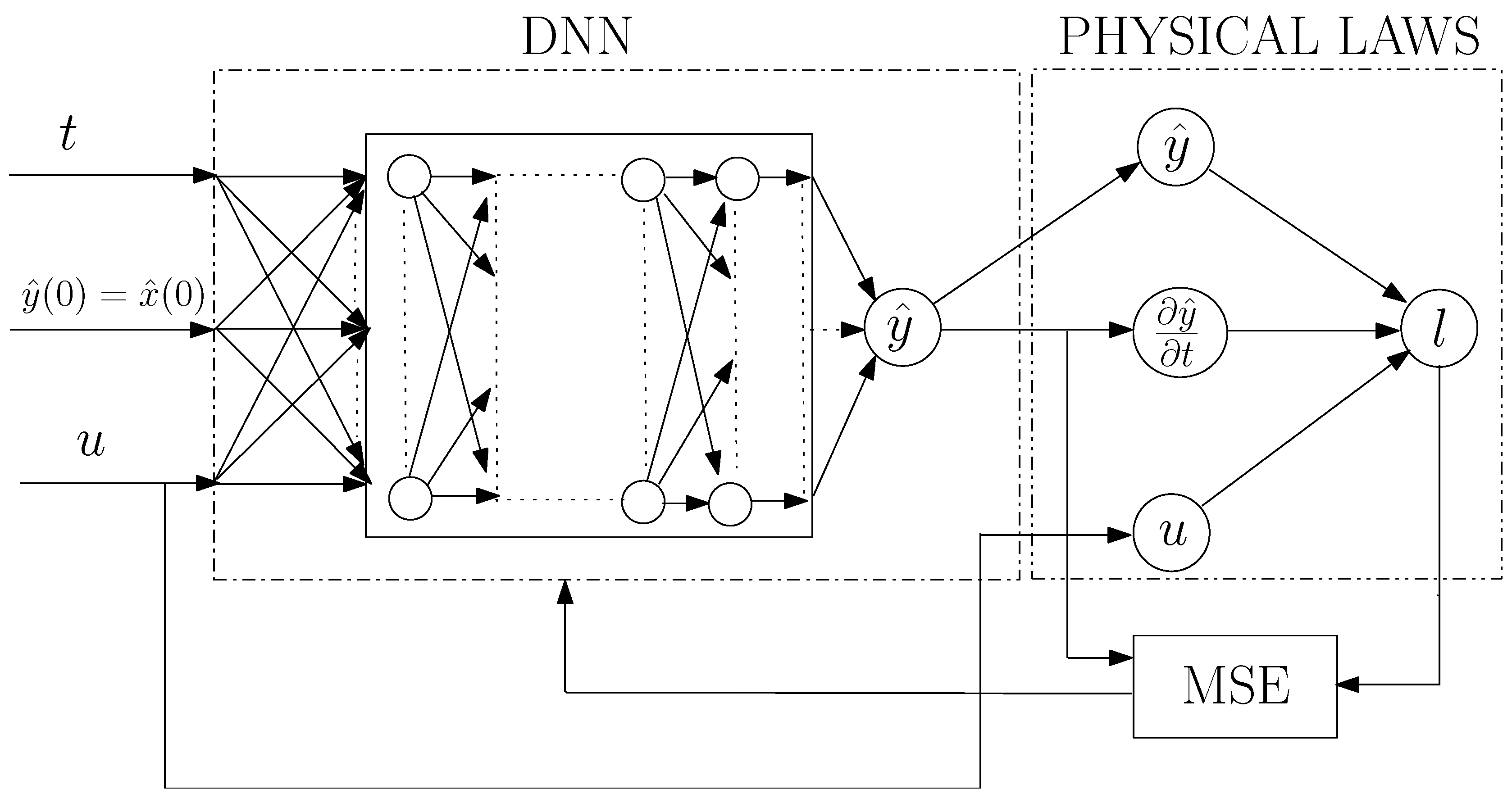
3.2. Physics-Informed Neural Networks
4. Simulation Results
4.1. PINNs Hyperparameters Tuning
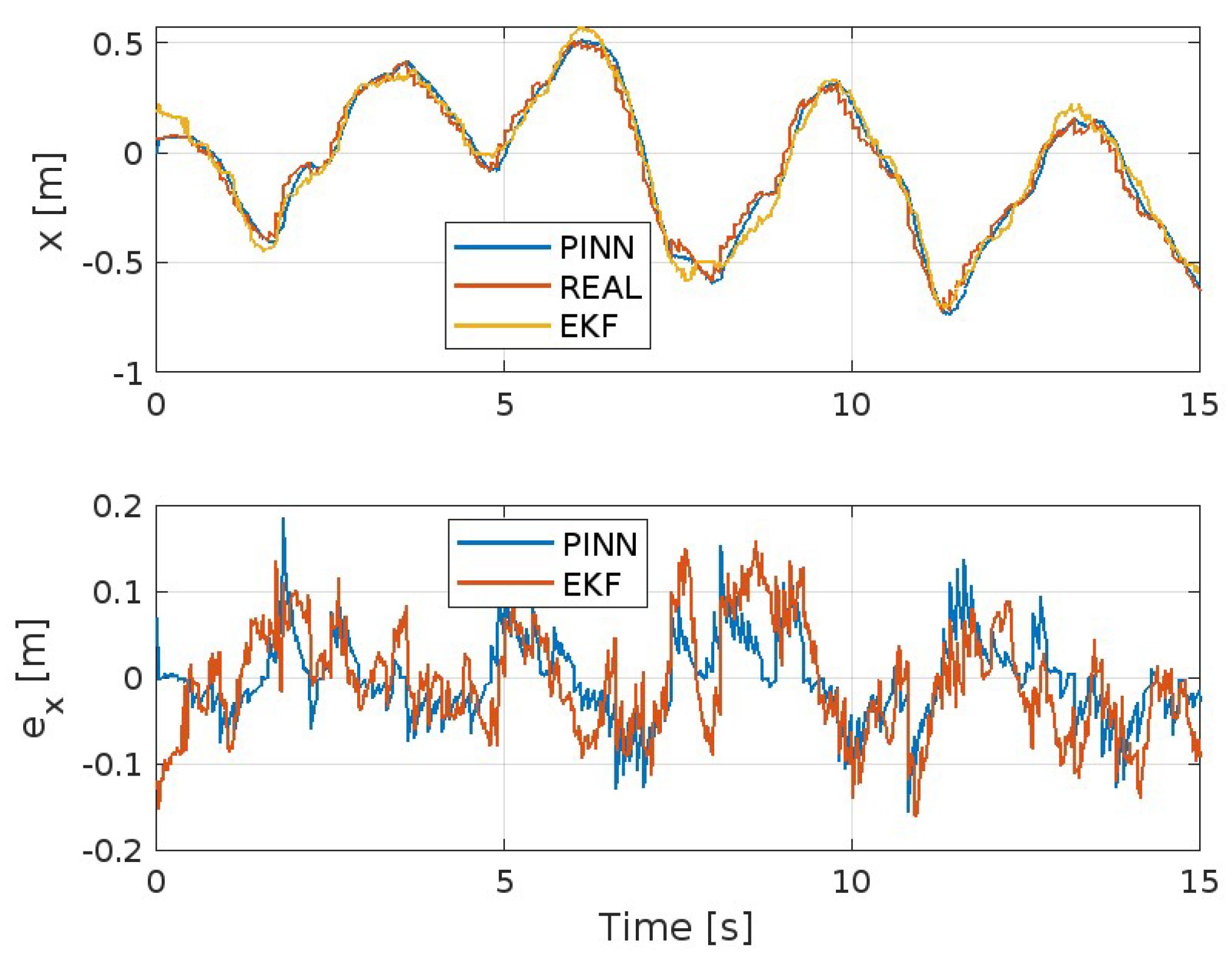
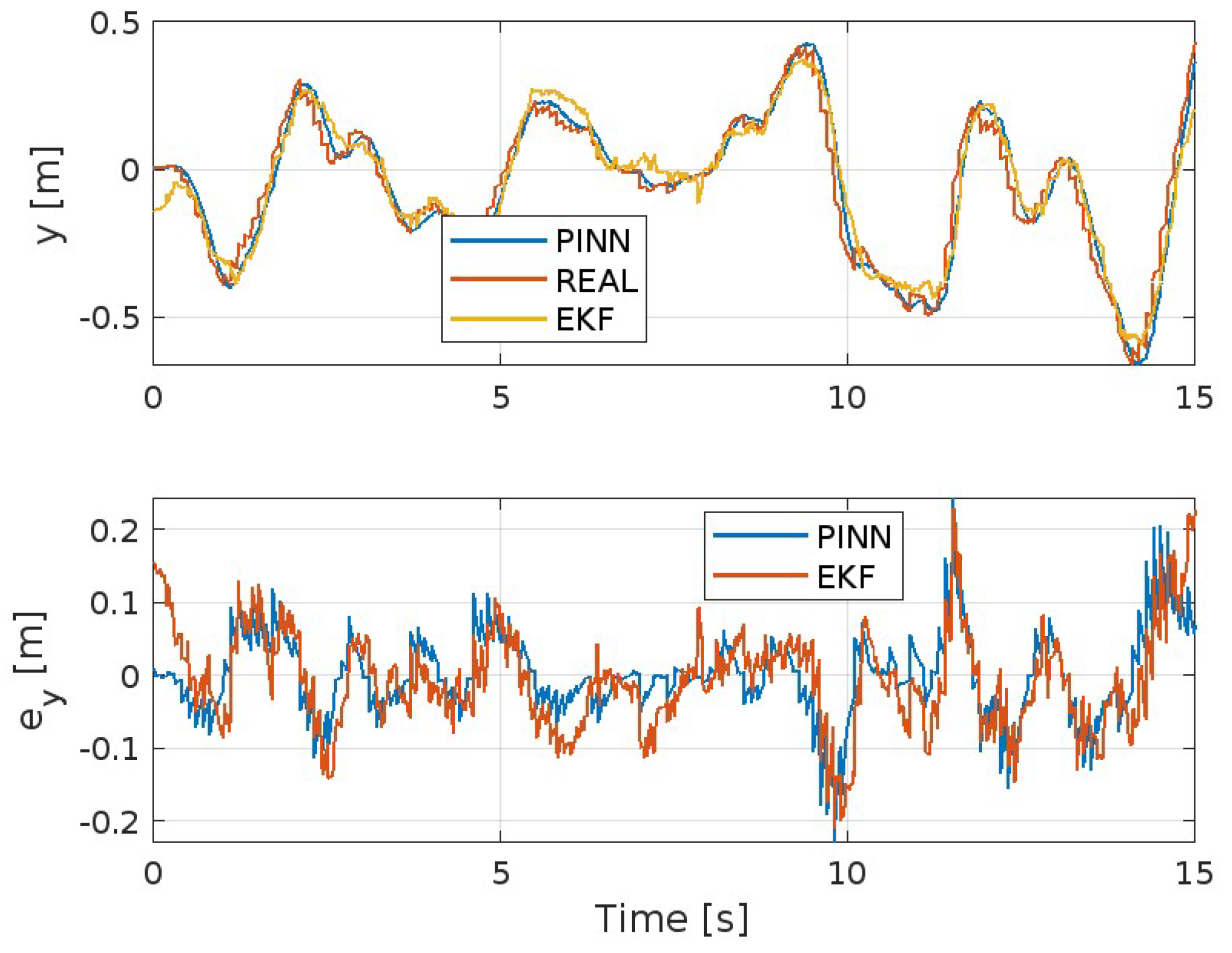
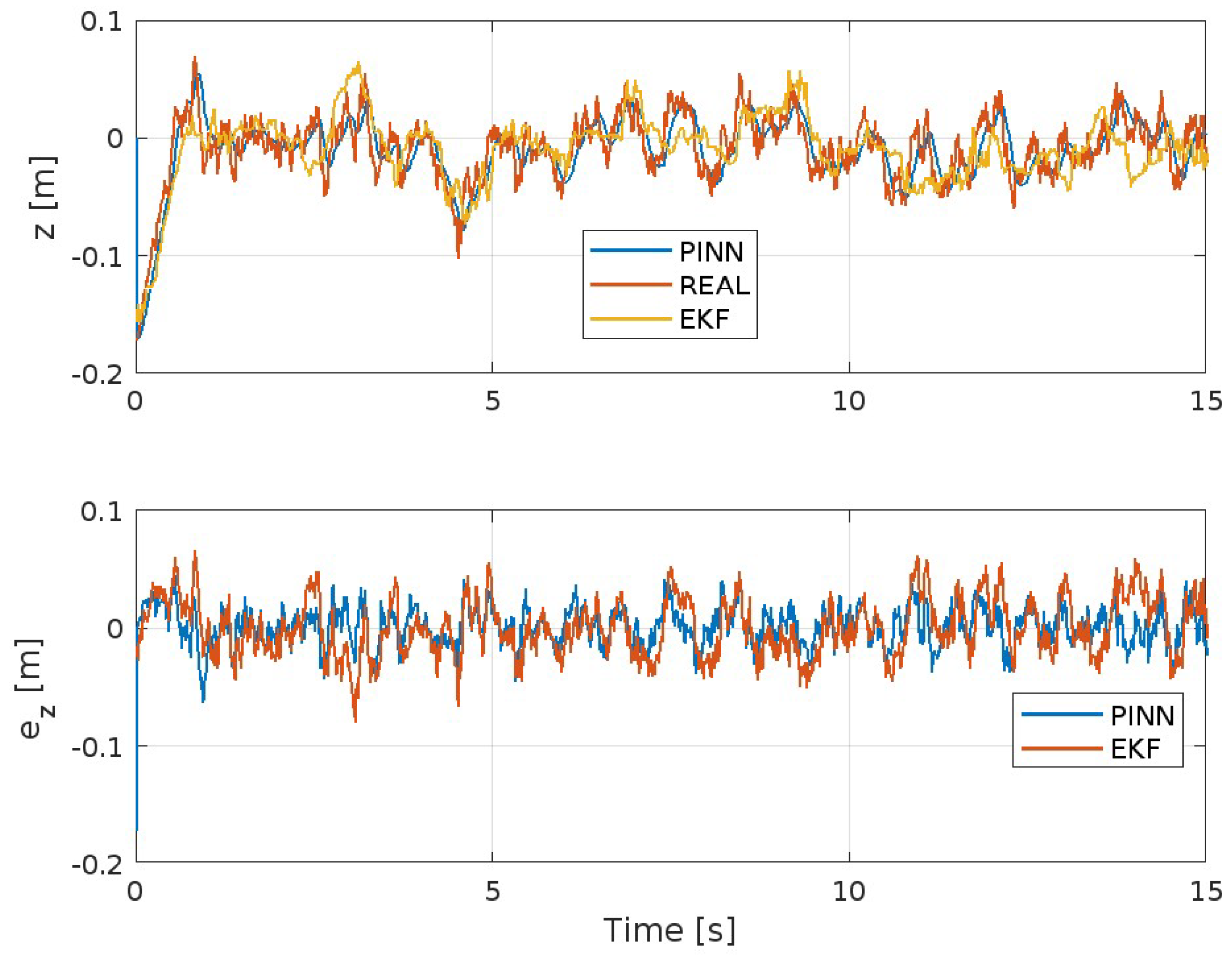
4.2. Model and Performance Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Ricardo, A. RM; Jorge, J. L.S.; Introducing system identification strategy into Model Predictive Control, Journal Systems Science Complexity, 2020, 33, pp. 1402–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssell, U.; Lindskog, P. ; Combining Semi-Physical and Neural Network modeling: An example of its usefulness, IFAC Proceedings, 1997, 30 (11), pp. [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Li, P. ; The Research Survey of System Identification Method, In Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, 2013, pp. 397-401. [CrossRef]
- Gueho, D.; Singla, P.; Majji, M.; Juang, J.-N. ; Advances in System Identification: Theory and Applications, In Proceedings of 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2021, pp. 22-30. [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.L.; Kalman, R.E. ; Editorial: Effective construction of linear state-variable models from input/output functions: Die Konstruktion von linearen Modeilen in der Darstellung durch Zustandsvariable aus den Beziehungen für Ein-und Ausgangsgrößen" at - Automatisierungstechnik, 1966, 14 (1-12), pp. [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. ; Mathematical Description of Linear Dynamical Systems, Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Series A: Control, 1963, 1 (2), pp. 152-192. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Lee, G.; Juang, J.-N. ; Several recursive techniques for observer/Kalman filter system identification from data, 1992, 92-4386, Hilton Head Island, SC, U.S.A. [CrossRef]
- Germani, A.; Manes, C.; Palumbo, P. ; Polynomial extended Kalman filter, IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control, 2005, 50 (12), pp. 2059-2064. [CrossRef]
- Peyada, N.K.; Sen, A.; Ghosh, A.K. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, D.; Borri, A.; Di Benedetto, M.D.; Di Gennaro, S. ; Active Attitude Control of Ground Vehicles with Partially Unknown Model, IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53 (2), pp. 14420-14425, doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.1440.
- Rodrigues, L.; Givigi, S. ; System Identification and Control Using Quadratic Neural Networks, IEEE Control Systems Letters 2023, 7, pp. 2209-2214. [CrossRef]
- Cavone, G.; Epicoco, N.; Carli, R.; Del Zotti, A.; Ribeiro Pereira, J.P.; Dotoli, M. ; Parcel delivery with drones: Multi-criteria analysis of trendy system architectures, Proceedings of 29th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation 2021, pp. 693-698. [CrossRef]
- Carli, R. ; Cavone, G; Epicoco, N., Di Ferdinando, M., Scarabaggio, P., Dotoli, M., Eds.; Consensus-based algorithms for controlling swarms of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2020, 12338; pp. 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, D.; Borri, A.; Di Gennaro, S.; Preziuso, M. ; UAV trajectory control with rule-based minimum-energy reference generation, Proceedings of European Control Conference 2022, London, United Kingdom, pp. 1497-1502. [CrossRef]
- Stiasny, J.; Misyris, G.S.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. ; Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Non-linear System Identification for Power System Dynamics, 2021, IEEE Madrid PowerTech. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, W.; Xing, J. ; Physics-informed Neural Network for system identification of rotors, IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2024, 58 (15), pp. 307-312. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Meidani, H. ; Physics-Informed Neural Networks for System Identification of Structural Systems with a Multiphysics Damping Model, 2023, Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 149 (10), art. 04023079. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.W.X.; Lu, L.; Cao, Q. ; Motion estimation and system identification of a moored buoy via physics-informed neural network, Applied Ocean Research, 2023, 138, art. 10 3677. [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Primatesta, S.; Rizzo, A. ; Physics-informed Neural Network for Quadrotor Dynamical Modeling, Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2024, 171. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, D.; Borri, A.; Cappuzzo, F.; Di Gennaro, S. Quadrotor Trajectory Control Based on Energy-Optimal Reference Generator, Drones 2024, 8, 29. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, D.; Di Gennaro, S.; Di Ferdinando, M.; Lua, C.A. ; Robust Control of UAV with Disturbances and Uncertainty Estimation, Machines 2023, 11 (3): 352. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, P.C. ; Spacecraft Attitude Dynamics. Dover Publications, Inc.: Mineola, NY, USA, 1986.
- Nagaty, A.; Saeedi, S.; Thibault, C.; Seto, M.; Li, H. ; Control and Navigation Framework for Quadrotor Helicopters, Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems 2013, 70, pp. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K. ; Extended kalman filter, 2013, Refernce Manual.
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. ; Physics-Informed Neural Networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations, Journal of Computational Physics 2019, 378, pp. 686-707. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. ; Batra, S; Raman, B. ; Deep neural network hyper-parameter tuning through twofold genetic approach, Soft Computing 2021, 25, pp. 8747–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

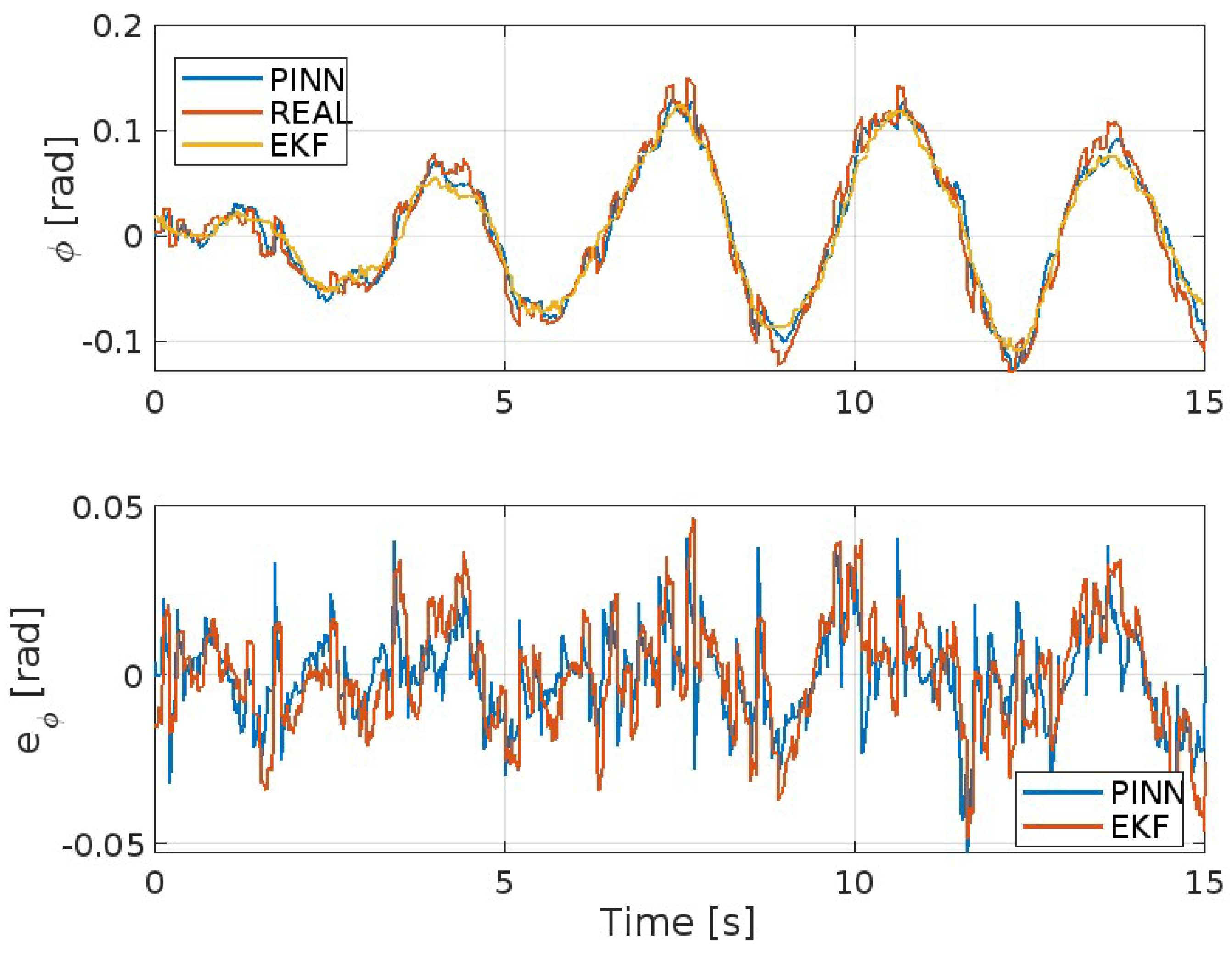
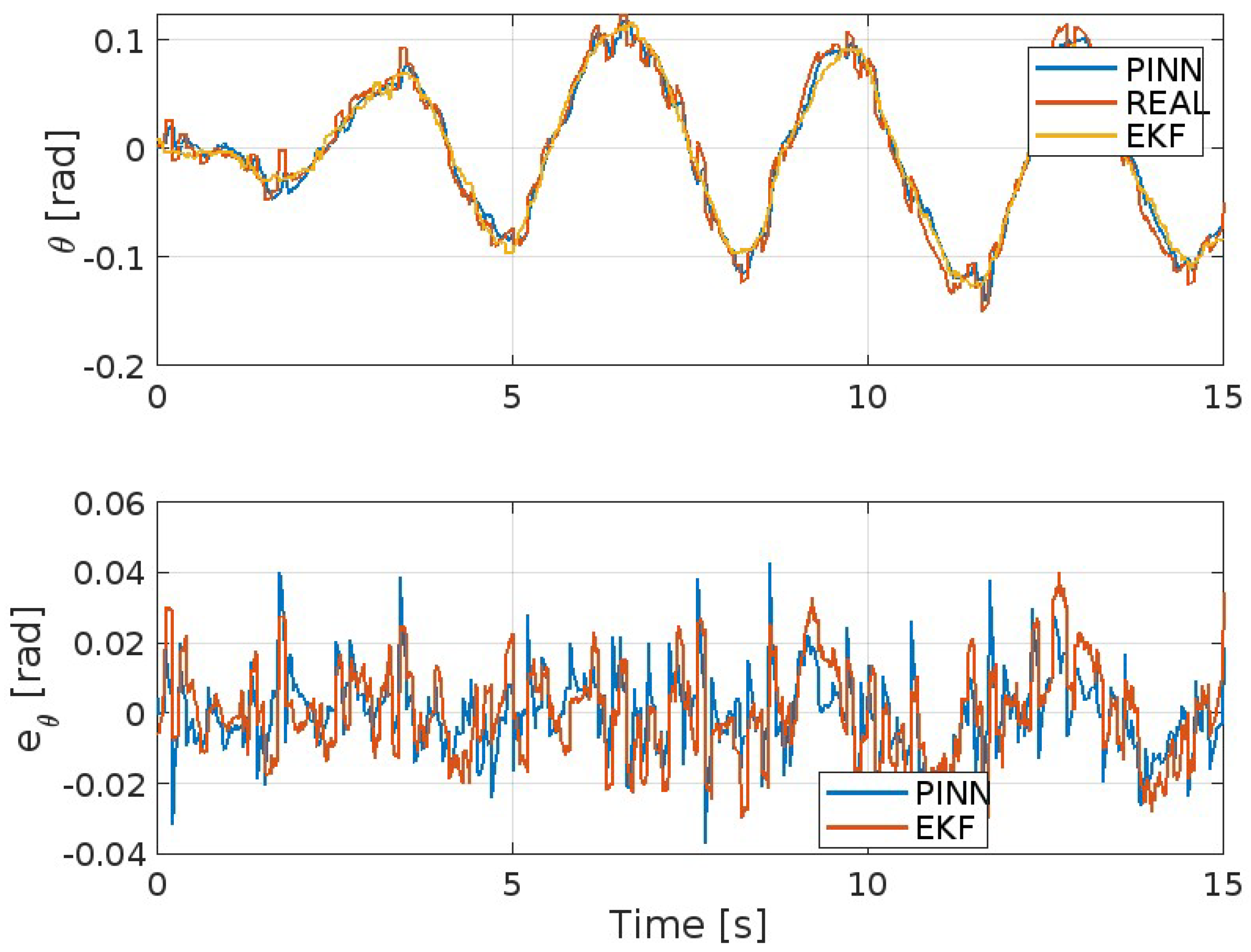
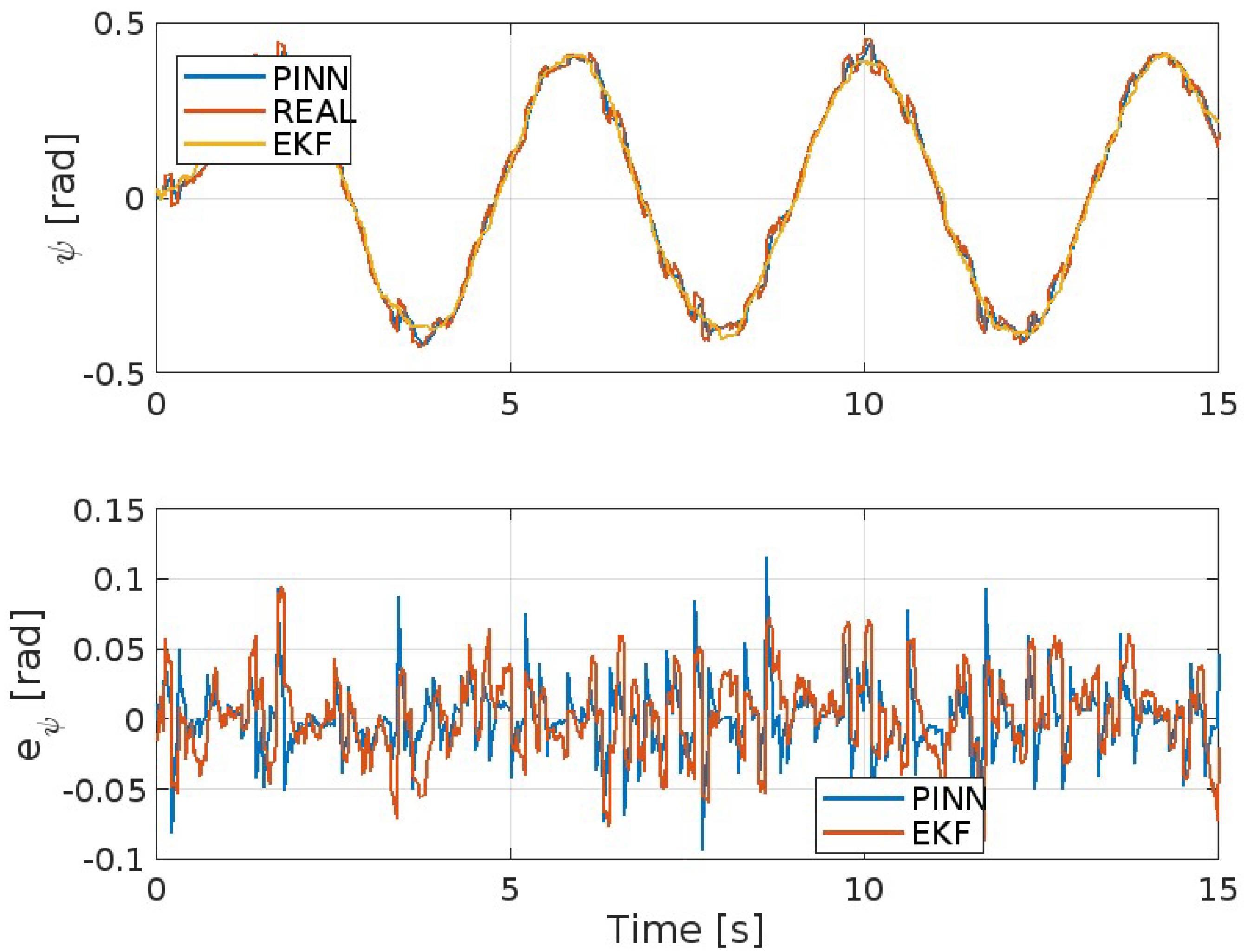
| Parameter | Value | Units | Known | Known |
| for EKF | for PINNs | |||
| m | 0.65 | kg | YES | NO |
| d | 0.165 | m | YES | NO |
| 0.03 | NO | NO | ||
| 0.025 | NO | NO | ||
| 0.045 | NO | NO | ||
| b | 3.50 | NO | NO | |
| k | 0.06 | NO | NO |
| MAE | MSE | ISE | IAE | ITAE | |
| EKF | 0.0514 | 0.0039 | 5.8711 | 77.17 | 599.94 |
| PINNs | 0.0367 | 0.0022 | 3.3427 | 55.07 | 432.52 |
| MAE | MSE | ISE | IAE | ITAE | |
| EKF | 0.0533 | 0.0047 | 7.0927 | 79.96 | 638.23 |
| PINNs | 0.0426 | 0.0033 | 4.8822 | 64 | 543.46 |
| MAE | MSE | ISE | IAE | ITAE | |
| EKF | 0.0198 | 5.85e-04 | 0.8786 | 29.71 | 229.05 |
| PINNs | 0.0135 | 2.99e-04 | 0.4491 | 20.3 | 147.99 |
| MAE | MSE | ISE | IAE | ITAE | |
| EKF | 0.0133 | 4.4527e-04 | 0.4204 | 20.02 | 163.38 |
| PINNs | 0.0103 | 2.801e-04 | 0.2656 | 15.44 | 128.97 |
| MAE | MSE | ISE | IAE | ITAE | |
| EKF | 0.0107 | 1.81e-04 | 0.2718 | 16.11 | 130.64 |
| PINNs | 0.0085 | 1.27e-04 | 0.1838 | 12.78 | 102.45 |
| MAE | MSE | ISE | IAE | ITAE | |
| EKF | 0.0234 | 8.92e-04 | 0.7541 | 35.07 | 269.87 |
| PINNs | 0.0149 | 5.53e-04 | 0.5828 | 22.39 | 170.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





